线粒体DNA D-LOOP区点突变和长期慢性肝炎、肝癌的相关性分析
柳云 刘道洁 乔录新 陈德喜
[摘要] 目的 通过收集乙型肝炎病毒(HBV)相关的肝癌患者的标本,分析各组织线粒体DNA D-LOOP区碱基的变化,探究HBV相关的肝癌线粒体DNA D-LOOP区的相关性。 方法 选取2008年10月~2019年12月首都医科大学附属北京佑安医院就诊的慢性乙肝相关肝细胞癌(HCC)患者44例,其中31例患者的癌组织和对应的癌旁组织及外周血,7例患者的癌旁组织和相对应的外周血,5例患者有癌组织和对应的外周血,11例癌组织和对应的癌旁组织。同时选取了11例来自肝移植患者供体者的肝组织及对应的外周血作为对照。提取标本的线粒体DNA,设计引物和PCR反应获得线粒体D-LOOP区,对PCR产物进行一代测序。 结果 一代测序数据结果显示长期慢性HBV肝炎可引起炎症肝组织和肝癌线粒体DNA D-LOOP区大量单碱基突变,肝癌组织和肝组织之间差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05)。 结论 长期慢性HBV肝炎可引起肝炎组织大量线粒体DNA D-LOOP区碱基突变,肝癌组织不同于正常肝组织的突变模式,对于肝癌的早期诊断具有提示意义。
[关键词] 线粒体DNA D-LOOP区;乙型肝炎病毒;肝细胞癌
[中图分类号] R512.62 [文献标识码] A [文章編号] 1673-7210(2019)09(b)-0121-04
Correlation analysis between mitochondrial DNA D-LOOP point mutation and long-term chronic hepatitis and hepatocellular carcinoma
LIU Yun1 LIU Daojie2 QIAO Luxin1 CHEN Dexi1▲
1.Beijing Youan Hospital, Capital Medical University, Beijing Institute of Hepatology, Beijing 100069, China; 2.Laboratory Medicine, Haidian Maternal & Child Health Hospital of Beijing City, Beijing 100080, China
[Abstract] Objective To analyze the changes in bases of mitochondrial DNA D-LOOP in various tissues by collecting specimens of hepatitis B virus (HBV)-associated liver cancer patients, and to explore the correlation between HBV-associated liver cancer and mitochondrial DNA D-LOOP. Methods Forty-six patients with chronic hepatitis B-related hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) who were admitted to Beijing Youan Hospital, Capital Medical University from October 2008 to December 2019 were enrolled in the study. Thirty-one cases of cancerous tissues and corresponding adjacent tissues and peripheral blood, and 7 cases of adjacent tissues and corresponding peripheral blood, 5 cases of cancerous tissues and corresponding peripheral blood, 11 cases of cancer tissues and corresponding adjacent tissues. At the same time, 11 liver tissues from donors of liver transplantation patients and corresponding peripheral blood were selected as controls. The mitochondrial DNA of the specimen was extracted, primers and PCR reactions were designed to obtain the mitochondrial D-LOOP region, and the PCR product was sequenced for one generation. Results The results of one-generation sequencing data showed that long-term chronic HBV hepatitis caused a large number of single-base mutations in mitochondrial DNA D-LOOP region of inflammatory liver tissue and liver cancer, and the difference between liver cancer tissues and liver tissues was statistically significant (P < 0.05). Conclusion Long-term chronic HBV hepatitis can cause a large number of mitochondrial DNA D-LOOP region mutations in hepatitis tissues. Hepatoma tissue is different from normal liver tissue mutation mode, which has implications for the early diagnosis of liver cancer.
[Key words] Mitochondrial DNA D-LOOP region; Hepatitis B virus; Hepatocellular carcinoma
肝癌是世界上最常见的恶性肿瘤之一,其发病率位居男性第五位,女性位居第九位,死亡率在人群中居第二位[1]。肝细胞癌(HCC)是肝癌中最常见的组织学类型[2]。HBV感染和慢性肝病是HCC发生的主要危险因素[3]。
肝脏的功能依赖于线粒体的代谢稳态[4-6]。线粒体DNA(mtDNA)是一个16.6 kb的双链环状DNA[7-8]。由于线粒体内富含ROS且mtDNA缺乏组蛋白的保护,缺少有效、完整的修复系统[11]。mtDNA序列微小的变化可以导致功能上的严重损害[9]。mtDNA突变的累积有助于肿瘤的起始和进展[10-11]。mtDNA“D环”的非编码区,控制mtDNA的复制和转录[12]。线粒体的转录和翻译功能的改变与肝癌相关[13],在人类癌症中发现的大多mtDNA突变位于D-环区域,且报道与肝癌发生密切相关[14-15]。
线粒体DNA突变与肝癌的关系,已有很多横断面的研究[16-20],但是长期HBV慢性炎症引起的细胞ROS升高如何引起线粒体DNA的损伤累集,至今仍鲜见报道。本研究中以患者外周血PBMC的mtDNA序列为线粒体遗传对照,分析长期慢性肝炎及相关肝癌mtDNA突变积累特征,并以肝移植供体的肝脏组织及PBMC的线粒体DNA作为对照进行对比分析,阐明HBV慢性肝炎引起肝组织及肝癌mtDNA D-LOOP的突变深度和特征,对了解慢性肝炎进展程度和肝癌发生有一定提示意义。
1 资料与方法
1.1 一般资料
收集首都医科大学附属北京佑安医院(以下简称“我院”)就诊的初诊HCC患者43例,其中31例患者同时具有癌组织和对应的癌旁组织及外周血,7例患者有癌旁组织和相对应的外周血,5例患者有癌组织和对应的外周血,11例对照来自肝移植患者供体者的肝组织及对应的外周血。本研究标本为国家“十二五”项目收集的标本,项目所需人源组织标本已获我院医学伦理学委员会批准。肝穿组织获取后立即置于液氮中储存。NAA提取使用凯杰DNA提取试剂盒,根据制造商的说明书提取总基因組DNA。提取的DNA存储在-20℃备用。
1.2 方法
扩增所用引物见表1,使用Mt-D-LOOP S1、AS1扩增产物为1332 bp mtDNA D-LOOP片段。聚合酶链式反应(PCR)在50 μL的体系中进行,包括mix 25 μL,H2O 18 μL,前后引物各1 μL,mtDNA 1 μL。整个实验过程于冰上操作。PCR反应条件:94℃ 2 min,35个循环;94℃ 15 s,52℃ 30 s,72℃ 1 min 30 s,最终72℃下延伸5 min。通过1% TAE琼脂糖凝胶电泳分析PCR产物。PCR产物进行一代测序,测序引物为Mt-D-LOOP S1、AS1、S2、AS2、S3、AS3,由北京博迈德公司进行PCR产物测序。
表1 扩增和测序引物列表
1.3 统计学方法
mtDNA标准序列为mtDNA修订剑桥序列,将患者中序列的变异视为突变,供体的变异视为多态性。序列分析使用SanpGene。进化树作图使用MEGA6软件,使用Prism统计学软件进行数据统计分析,使用Two-way ANOVA分析组间差异,以P < 0.05为差异有统计学意义。
2 结果
2.1 PCR实验获得稳定特异的目的条带
PCR实验得到了稳定特异行mtDNA D-LOOP区片段,经1%的TAE琼脂糖胶进行电泳分析。见图1。
2.2 所有样本的进化树分析结果
进化树分析,Bootstrap的值>70%,来自同一患者的标本分布于同一支,提示PCR产物无交叉污染,见图2。与外周PBMC比较,同一患者的肝癌和肝组织距离标准序列更远,而10例正常肝脏与PBMC的距离非常接近,提示长期慢性肝病可以影响肝组织的mtDNA D-LOOP的突变水平。完整的进化树图见图2。
2.3 来自肝移植供体肝脏和对应外周血之间mtDNA D-LOOP测序比较
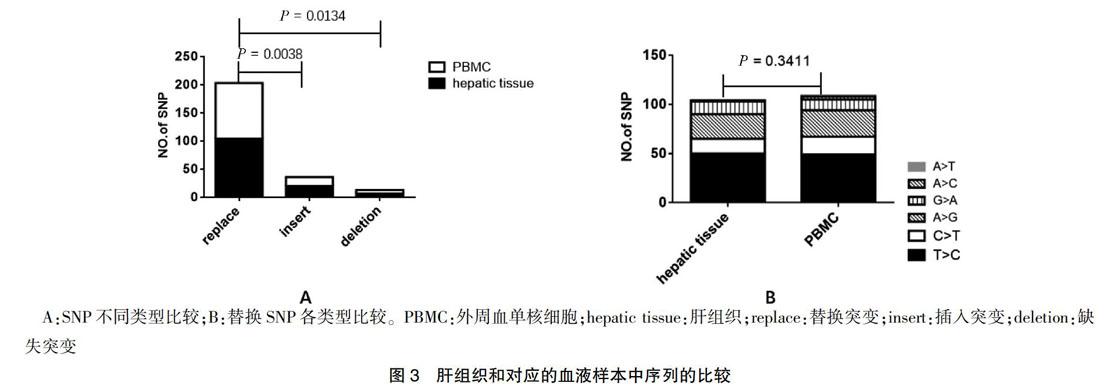
11个供体者的肝脏组织和对应的外周血中共观察到66个SNP位点,262个SNP。替换突变数量多于其他两种类型,差异有统计学意义(P = 0.0038、0.0134);供体的肝脏和对应的外周血替换SNP各类型比较差异无统计学意义(P = 0.3411)。见图3。
2.4 对31对完全配对HCC患者标本碱基序列比较
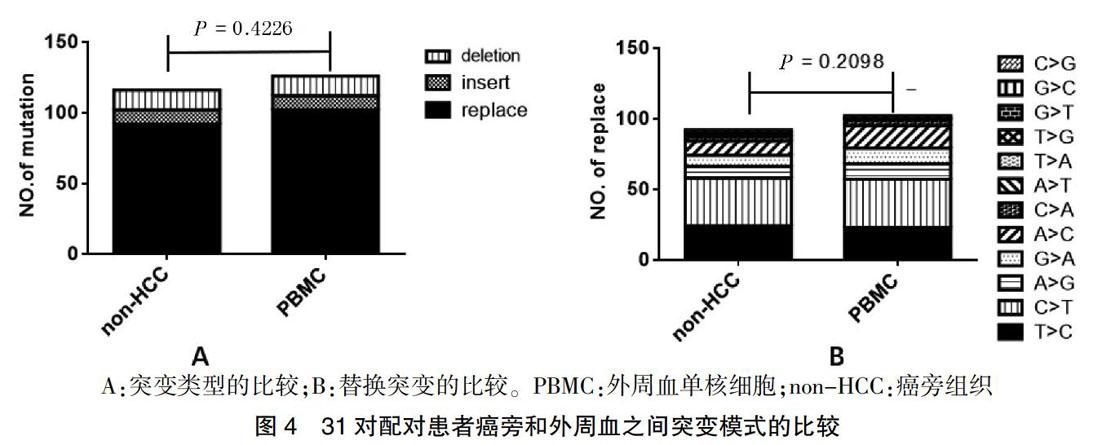
31个配对患者的HCC组织、癌旁组织和外周血中的突变类型和替换突变之间的差异分析,发现在同一患者中,不管是突变的类型还是替换突变的各类型之间,癌旁组织和对应的外周血之间差异无统计学意义(P = 0.4226、0.2098)。见图4。
2.5 所有患者标本碱基序列比较情况
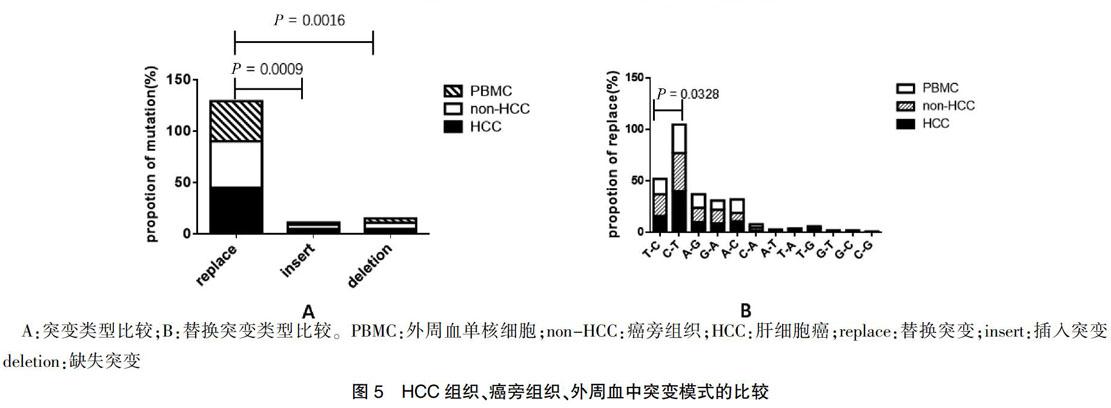
本研究分析了患者癌组织、非癌组织、外周血液组织,3种组织中替代突变明显高于插入突变和缺失突变,差异有统计学意义(P = 0.0009、0.0016),见图5A,且C 3 讨论 线粒体是体内唯一具有独立DNA的供能细胞器,与肝癌的发生发展具有密切关系。细胞mtDNA可能导致缺陷性线粒体的积累。目前研究表明,mtDNA可用于重症肝炎患者肝细胞的损伤评估。有研究证实肝癌患者血浆mtDNA表达量亦发生改变。由于mtDNA具有长度短、分子结构简单和拷贝数高等特点,使得监控早期肿瘤患者mtDNA的异常变化成为可能。相邻的癌旁组织的mtDNA并不能认为是正常的mtDNA。与以往的研究比较,本研究首次系统全面地收集组织的类型,系统多层次地比较不同组织类型的突变模式的差异,并且首次收集并使用了供体的肝脏和对应的外周血,为正常肝脏mtD-LOOP区,提供了宝贵且真实的线粒体正常肝脏序列。 本研究進一步证明了mtDNA D-LOOP区突变在HBV相关的慢性肝炎和肝硬化的过程,观察到癌组织和相邻的癌旁组织之间存在突变模式的差异,而癌旁组织和外周血之间没有显著的差异。本研究提示HCC和炎性肝组织中mtDNA的不同诱变机制以及肝癌发生过程中可能存在进化选择,在癌症的进化过程中存在着对于这些突变的阳性选择,突变模式的不同对肝癌的诊断有一定提示意义。 [参考文献] [1] Torre LA,Bray F,Siegel RL,et al. Global cancer statistics,2012 [J]. CA Cancer J Clin,2015,65(2):87-108. [2] Perz JF,Armstrong GL,Farrington,LA,et al. The contributions of hepatitis B virus and hepatitis C virus infections to cirrhosis and primary liver cancer worldwide [J]. J Hepatol,2006,45(4):529-538. [3] Yuan K,Lei Y,Chen HN,et al. HBV-induced ROS accumulation promotes hepatocarcinogenesis through Snail-mediated epigenetic silencing of SOCS3 [J]. Cell Death Differ,2016,23(4):616-627. [4] Zhao Y,Liu S,Zhou L,et al. Aberrant shuttling of long noncoding RNAs during the mitochondria-nuclear crosstalk in hepatocellular carcinoma cells [J]. Am J Cancer Res,2019,9(5):999-1008. [5] Qiao L,Nie Z,Li Q,et al. Mitochondrial DNA depletion,mitochondrial mutations and high TFAM expression in hepatocellular carcinoma [J]. Oncotarget,2017,8(48):84 373-84 383. [6] Hikita H,Kodama T,Tanaka S,et al. Activation of the Mitochondrial Apoptotic Pathway Produces Reactive Oxygen Species and Oxidative Damage in Hepatocytes That Contribute to Liver Tumorigenesis [J]. Cancer Prev Res (Phila),2015,8(8):693-701. [7] Attardi G,Schatz G. Biogenesis of mitochondria [J]. Annu Rev Cell Biol,1988,4:289-333. [8] Anderson S,Bankier AT,Barrell BG,et al. Sequence and organization of the human mitochondrial genome [J]. Nature,1981,290(5806):457-465. [9] Nishikawa M,Nishiguchi S,Kioka K,et al. Interferon reduces somatic mutation of mitochondrial DNA in liver tissues from chronic viral hepatitis patients [J]. J Viral Hepat,2005,12(5):494-498. [10] Li X,Guo X,Li D,et al. Multi-regional sequencing reveals intratumor heterogeneity and positive selection of somatic mtDNA mutations in hepatocellular carcinoma and colorectal cancer [J]. Int J Cancer,2018,143(5):1143-1152. [11] Yu C,Wang X,Huang L,et al. Deciphering the Spectrum of Mitochondrial DNA Mutations in Hepatocellular Carcinoma Using High-Throughput Sequencing [J]. Gene Expr,2018,18(2):125-134. [12] Attardi G,Schatz G. Biogenesis of mitochondria [J]. Annu Rev Cell Biol,1988,4:289-333. [13] Baechler SA,Factor VM,Dalla Rosa I,et al. The mitochondrial type IB topoisomerase drives mitochondrial translation and carcinogenesis [J]. Nat Commun,2019,10(1):83. [14] Li S,Wan P,Peng T,et al. Associations between sequence variations in the mitochondrial DNA D-loop region and outcome of hepatocellular carcinoma [J]. Oncol Lett,2016,11(6):3723-3728. [15] Yin C,Cao HY,Chen YB,et al. NGS-based profiling reveals a critical contributing role of somatic D-loop mtDNA mutations in HBV-related hepatocarcinogenesis [J]. Ann Oncol,2019,30(6):953-962. [16] Chen T,Xun Z,Lin J,et al. Association between mitochondrial DNA content and baseline serum levels of HBsAg in chronic hepatitis B infection [J]. J Med Virol,2017,89(11):1958-1962. [17] Li L,Hann HW,Wan S,et al. Cell-free circulating mitochondrial DNA content and risk of hepatocellular carcinoma in patients with chronic HBV infection [J]. Sci Rep,2016,6(1):23 992. [18] Campo DS,Nayak V,Srinivasamoorthy G,et al. Entropy of mitochondrial DNA circulating in blood is associated with hepatocellular carcinoma [J]. BMC Med Genomics,2019,12(4):74. [19] Guo ZS,Jin CL,Yao ZJ,et al. Analysis of the Mitochondrial 4977 Bp Deletion in Patients with Hepatocellular Carcinoma [J]. Balkan J Med Genet,2017,20(1):81-86. [20] Gao Y,Nie HJ,Yang D,et al. Changes of the mitochondrial DNA copy number and the antioxidant system in the PBMC of hepatocellular carcinoma [J]. Zhongguo Ying Yong Sheng Li Xue Za Zhi,2016,32(1):1-5. (收稿日期:2018-06-05 本文編辑:任 念)

