基于能耗感知的包簇资源分配算法研究
徐雨婷 陈世平
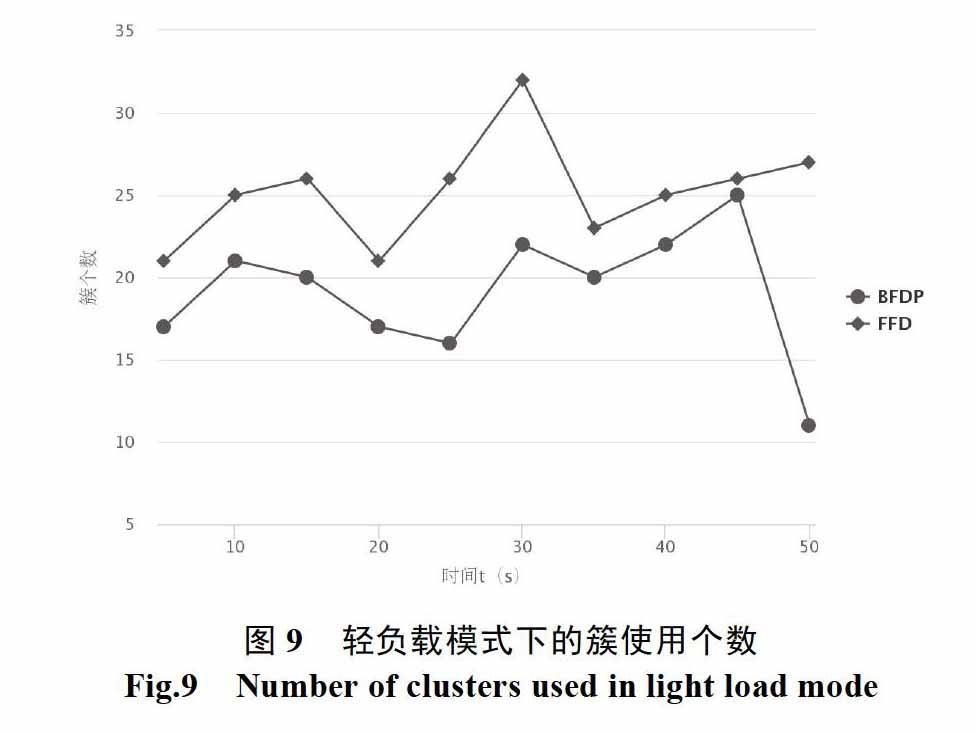


摘 要: 随着数据中心的扩大,现有的云计算资源的分配与调度机制,带来了许多庞大的工作调度问题,针对该问题,本文采用基于包簇框架的资源调度分配方式,并在此框架上,通过提出非线性能耗模型,在最大限度地不违背服务级别协议(SLAS)的情况下,并且同时以降低能耗为目标,提出基于BFDP(Best-Fit-Decreasing-Power)算法进行包簇资源的分配。通过实验表明,基于本文提出的包簇框架的能耗感知算法比较其他的适应算法,簇的使用个数降低,能耗根据系统各组件的利用率增高而降低。
关键词: 云计算;能耗;BFDP
【Abstract】: With the expansion of the data center, the existing cloud computing resource allocation and scheduling mechanism brings a huge redundant work problem. For this problem, this paper adopts the resource scheduling method of the clustering framework, and proposes energy consumption in this framework. The perceptual model proposes a BFDP (Best-Fit-Decreasing-Power) algorithm to allocate cluster resources without violating the Service Level Agreement (SLAS), and at the same time can reduce energy consumption. Experiments show that compared with other adaptive algorithms based on the energy-aware algorithm of the clustering framework, the number of clusters used is reduced, and the energy consumption is reduced according to the utilization of all aspects of the system.
【Key words】: Digital watermark; Wavelet packet; Adaptive; Feature of texture
0 引言
云计算是新兴的计算模式,是一种新兴的服务模式和商业计算模型[1]。云计算数据中心是提供各种资源的平台,并且能够处理和托管各类复杂的任务和服务,有效地分配云计算资源是决定整个云计算系统的工作效率和性能的关键点所在。
随着云计算数据中心规模的扩大,服务器在提供资源的过程中需要消耗大量的能源,能耗过大,会导致大量电费和温室气体的排放[2]。对于云服务商来说,成本最小和利润最大是他们一直追求的目标,所以降低服务器产生的能耗显得十分重要[3]。
对数据中心的能耗研究一直从未停下脚步,现有对服务器的节能技术大致可以分为两个方面,其一是降低服务器CPU的频率和电压,其二是降低服务器的使用个数[4],包括其他各种方式,这些技术都可以降低数据中心的能耗。
1 相关工作
能耗感知算法,顾名思义,需要兼顧能耗和服务质量的多方面的要求,目标是在不违背SLA协议的情况下,实现物理资源利用的最优化。文献[5]提
出了一种新框架,能提供可扩展的、高效的绿色增强云计算架构,该框架采用能量感知的调度技术、实时迁移和最小的虚拟机设计,以最小的能耗获得整个系统的性能的提高。文献[6]侧重于多层虚拟化系统的资源分配问题,既获得了SLAS的最大收益目标,也最大限度地减少能源成本。文献[7]基于需求预测提出一种进化优化虚拟机放置算法,算法利用需求预测来分配虚拟机以及进行作业处理。文献[8]提出了利用约束满足问题对异构云数据中心的能耗优化问题资源调度问题建模,通过求解建立的约束模型可以获得最优的资源分配方式,并提出了能耗优化的资源分配算法。
文献[9]通过分别建立CPU以及内存和磁盘能耗优化线性模型,提出一种资源配置的虚拟机部署方案,找出合适的资源分配。文献[14]提出了一种基于虚拟机布局的遗传算法。该算法最大限度地减少了功耗、资源损耗和热耗散成本。在文献[15]中,作者提出了一种基于资源感知的虚拟机分配算法,并设计了资源利用率和多维资源使用模型,以最大限度地提高资源利用率和资源利用率为目标,提高资源利用率。
有作者[16]提出了适用于同构云数据中心的连续虚拟机请求的虚拟机放置算法。另外在文献[17]中,作者提出了一种改进的最佳拟合递减算法(MBFD),在这些计算机上,虚拟机的CPU利用率按递减顺序排序,并将这些VM放在这些主机上,从而将云数据中心的功耗降到最低。作者[18]提出了一种想法,使资源以平衡的方式被利用,这种方式减少了资源利用的碎片化,同时也能减少运行的物理机器的数量和整体的能源消耗。
本文通过一种将虚拟机到服务器的映射问题转换成包簇映射问题,通过采用文献[10]的基本框架,当包簇抽象层级增加时,简化相关映射问题。现有的大多数能耗模型考虑到能量的消耗与cpu和内存的利用率之间为线性关系,而线性模型适用于的模型参数是互相独立的情况下使用,但是在参数是相互依赖的情况下,线性模型的建立可能不会产生准确的结果,所以本文采用一个非线性模型来研究他们之间的关系。通过最佳适应下降(Best-Fit- Decreasing-Power BFDP)算法以降低能耗和最小化簇的个数为目标,在很好的保证SLA协议的水平的基础上,合理实现相应的资源分配。
2 包簇框架概念
2.1 包簇定义
现将包和簇来将虚拟机-服务器映射问题细化成一系列小问题。我们递归定义包为一系列子包的集合,而这些子包是一系列资源共享的虚拟机的结合。相似地,簇是数据中心拓扑位置中位置相近的服务器或者更低级别簇的集合,簇拥有的资源是其组成部分的资源之和。所以传统的以虚拟机为中心的资源分配就转换成簇资源被合理利用到包中的问题,云资源管理优化被转换为一个层次化,递归的,分而治之的问题。
参考文献
[1] 赵震, 任永昌. 大数据时代基于云计算的电子政务平台研究[J]. 计算机技术与发展, 2015(10): 145-148.
[2] 陈真勇, 唐龙, 唐泽圣, 熊璋. 以鲁棒性为目标的数字多水印研究[J]. 计算机学报, 2006, 29(11).
[3] Mustafa S, Bilal K, Madani S A, et al. Performance Evaluation of Energy-Aware Best Fit Decreasing Algorithms for Cloud Environments[C]. IEEE International Conference on Data Science and Data Intensive Systems. IEEE, 2016: 464-469.
[4] Beloglazov A, Buyya R, Lee Y C, et al. A Taxonomy and Survey of Energy-Efficient Data Centers and Cloud Computing Systems[C]. Advances in Computers. Elsevier, Amsterdam. 2010: 47-111.
[5] Duy T V T, Sato Y, Inoguchi Y. Performance evaluation of a Green Scheduling Algorithm for energy savings in Cloud computing[C]. IEEE International Symposium on Parallel & Distributed Processing, Workshops and Phd Forum. IEEE, 2010:1-8.
[6] Mark C C T, Niyato D, Chen-Khong T. Evolutionary Optimal Virtual Machine Placement and Demand Forecaster for Cloud Computing[C]. IEEE International Conference on Advanced Information NETWORKING and Applications. IEEE Computer Society, 2011: 348-355.
[7] Mark C C T, Niyato D, Chen-Khong T. Evolutionary Optimal Virtual Machine Placement and Demand Forecaster for Cloud Computing[C]. IEEE International Conference on Advanced Information NETWORKING and Applications. IEEE Computer Society, 2011: 348-355.
Usman M J, Samad A, Ismail, et al. Energy-Efficient virtualmachine allocation technique using interior search algorithm for cloud datacenter[C]. Student Project Conference. IEEE, 2017: 1-4.
Ruiz M, Asensio A, Velasco L. Minimizing energy costs in federated datacenters under uncertain green energy availability [C]. International Conference on Transparent Optical Networks. IEEE, 2014: 1-4.
Pang C, Hindle A, Hassan A E, et al. What Do Programmers Know about Software Energy Consumption?[J]. IEEE Software, 2016, 33(3): 83-89.
盧浩洋, 陈世平. 基于包簇映射的云计算资源分配框架[J]. 计算机应用, 2016, 36(10): 2704-2709.
Atiewi S, Yussof S. Comparison between Cloud Sim and Green Cloud in Measuring Energy Consumption in a Cloud Environment[C]. International Conference on Advanced Computer Science Applications and Technologies. IEEE Computer Society, 2014: 9-14.
Li X, Garraghan P, Jiang X, et al. Holistic Virtual Machine Scheduling in Cloud Datacenters towards Minimizing Total Energy[J]. IEEE Transactions on Parallel & Distributed Systems, 2018, 29(6): 1-1.
陳小娇, 陈世平. 基于DEA的能耗感知虚拟机资源分配算法[J]. 小型微型计算机系统, 2015, 36(1): 167-171.
J. Xu, J.A.B. Fortes Multi-Objective Virtual Machine Placement in Virtualized Data Center Environments.In Proc. of IEEE ACM International Conference on Cyber, Physical and Social Computing, Green Computing and Communications, pp. 179-188, 2010.
Gupta M K , Amgoth T. Resource-aware virtual machine placement algorithm for IaaS cloud[J]. The Journal of Supercomputing, 2017.
Li X, Qian Z, Chi R, et al. Balancing Resource Utilization for Continuous Virtual Machine Requests in Clouds[C]// Sixth International Conference on Innovative Mobile & Internet Services in Ubiquitous Computing. IEEE Computer Society, 2012.
Beloglazov A, Abawajy J, Buyya R. Energy-aware resource allocation heuristics for efficient management of data centers for Cloud computing[J]. Future Generation Computer Systems, 2012, 28(5): 755-768.
Huang W, Li X, Qian Z. An Energy Efficient Virtual Machine Placement Algorithm with Balanced Resource Utilization[C]// Seventh International Conference on Innovative Mobile & Internet Services in Ubiquitous Computing. IEEE, 2013.

