利用分子标记辅助选择改良闽恢3301稻瘟病抗性
田大刚 杨小双 陈子强 陈在杰 林艳 王锋



摘要:【目的】改良三系杂交籼稻强势恢复系闽恢3301的稻瘟病抗性,以提高其在生产中的应用价值。【方法】以75-1-127和C101A51为稻瘟病主效基因Pi9和Pi2的供体亲本,以闽恢3301为受体亲本,通过杂交、多代回交和自交,结合分子标记辅助选择和田间选择的方法,将供体亲本的Pi9和Pi2基因导入闽恢3301中,改良其稻瘟病抗性。利用21个福建近年流行的稻瘟菌菌株及其混合菌液对闽恢3301改良系进行人工接种抗性鉴定,并连续两年在上杭茶地病圃进行田间自然诱发抗性鉴定。将闽恢3301改良系和闽恢3301分别与三系不育系荟丰A和广8A及两系不育系GRD-7S进行测配,考察其农艺性状,以闽恢3301为父本的杂交组合为对照。【结果】通过利用Pi2/9分子标记对抗病基因进行跟踪选择,最终获得含Pi9和Pi2的闽恢3301改良系(闽恢3301-Pi9和闽恢3301-Pi2)各20份。除闽恢3301-Pi9对SH17004菌株表现为中感外,闽恢3301-Pi9对其他20个稻瘟病菌株及于2016和2017年在田间自然诱发鉴定中均表现出抗病,且闽恢3301-Pi2对21个稻瘟病菌株及于2016和2017年在田间自然诱发鉴定中均表现出抗病或高抗,二者抗性达到甚至超过两供体亲本75-1-127和C101A51的抗性水平,但闽恢3301对7个稻瘟病菌株表现感病,对1个菌株表现中感,对其他菌株则表现中抗或抗病,且田间自然诱发鉴定中均表现高感,说明闽恢3301-Pi9和闽恢3301-Pi2抗性水平得到有效提高。除RGD-7S×闽恢3301-Pi9和RGD-7S×闽恢3301-Pi2组合的单株产量分别极显著(P<0.01)高于相应的对照组合外,其他以闽恢3301改良株系为父本的杂交组合在株高、穗长、分蘖数、千粒重、单株产量和结实率上无显著差异(P>0.05),表明闽恢3301-Pi2和闽恢3301-Pi9在培育稻瘟病抗性杂交水稻组合上具有广阔的应用前景。【结论】闽恢3301-Pi9和閩恢3301-Pi2抗性得到有效提高的同时在农艺性状和配合力等方面保持了闽恢3301及其组合的主要特性,说明利用Pi9和Pi2基因可有效改良闽恢3301的稻瘟病抗性,不仅拓宽了稻瘟病抗谱,还不影响闽恢3301的配合力,二者可作为新的水稻材料进行推广应用。
关键词: 闽恢3301;稻瘟病;抗性;分子标记辅助选择;Pi9;Pi2;农艺性状
中图分类号: S511.203.51 文献标志码: A 文章编号:2095-1191(2019)08-1665-06
Improving resistance of Minhui 3301 to rice blast
by molecular marker-assisted selection
TIAN Da-gang1, YANG Xiao-shuang1,2, CHEN Zi-qiang1, CHEN Zai-jie1,
LIN Yan, WANG Feng 1*
(1Biotechnology Research Institute, Fujian Academy of Agricultural Sciences/Fujian Key Laboratory of Genetic Engineering for Agriculture, Fuzhou 350003, China; 2College of Plant Protection, Fujian Agriculture
and Forestry University, Fuzhou 350002, China)
Abstract:【Objective】This study aimed to improve the blast resistance of the hybrid indica rice strong restorer line,Minhui 3301,and increase its application value in production. 【Method】75-1-127 and C101A51 were donor parents for rice blast major genes Pi9 and Pi2, and Minhui 3301 was as receptor parent. The genes Pi9 and Pi2 from donor lines 75-1-127 and C101A51 were respectively introduced into Minhui 3301 to improve its resistance to blast by crossbreeding, backcrossing, self-breeding assisted by molecular marker and field selection method. The artificial inoculation resistance assay was conducted using 21 rice blast strains epidemic in Fujian in recent years and their mixed strain liquid on Minhui 3301 improved line, and naturally induction resistance in field was also investigated in diseased fields in Chadi, Shanghang for two consecutive years. Minhui 3301 improved line and Minhui 3301 were crossed with two three-line sterile lines (Huifeng A and Guang 8A) and a two-line sterile line(GRD-7S) respectively to investigate the main agronomic traits. The hybrid combinations with Minhui 3301 as male parent were as control. 【Result】In the present study,with Pi2/9 molecular marker trace selection for disease resistance genes, 20 improved lines harboring Pi9 and 20 improved lines harboring Pi2 were respectively generated by marker-assisted selection,named Minhui 3301-Pi9 and Minhui 3301-Pi2. Apart from Minhui 3301-Pi9 presented moderate susceptibility to SH17004 strain, it presented resistance to all the other 20 tested blast strains as well as the field natural induction identification in 2016 and 2017. Minhui 3301-Pi2 displayed resistant or highly resistant to 21 strains in the field natural induction identification in 2016 and 2017. The resistance of the two was even higher than the two donor parents 75-1-127 and C101A51. However,Minhui 3301 were susceptible to seven strains and moderately susceptible to one strain,and were moderately resistant or resistant to other strains and were highly susceptible to natural induction identitfcation in field. It indicated that Minhui 3301-Pi2 and Minhui 3301-Pi9 improved resistance to blast. Investigation of agronomic characteristics showed that there were no significant differences in plant height,panicle length,tiller number, weight of 1000-grain, yield per plant and seed setting rate in various hybrid combinations(P>0.05), except for yield per plant of GD-7S×Minhui 3301-Pi2 and RGD-7S×Minhui 3301-Pi9 were extremely higher than the corresponding control combinations(P<0.01), indicating Minhui 3301-Pi2 and Minhui 3301-Pi9 had broad prospect in breeding hybrid rice combination with rice blast resistance. 【Conclusion】Minhui 3301-Pi9 and Minhui 3301-Pi2 obtained in the present study have similar characteristics as Minhui 3301 and its combinations in agronomic traits and combining ability,but confer higher level and broader-spectrum resistance against blast. It indicates that Pi9 and Pi2 genes can improve the blast resistance of Minhui 3301. They broaden the resistant spectrum of rice blast, and do not affect the combining ability of Minhui 3301, therefore the two can be promoted as new rice materials.
Key words: Minhui 3301; rice blast; resistance; molecular marker-assisted selection; Pi9; Pi2; agronomic traits
0 引言
【研究意义】稻瘟病是世界上对水稻危害最严重的真菌性病害,一般导致水稻减产10%~30%,严重时甚至造成绝收(Skamnioti and Gurr,2009;Helliwell et al.,2013)。近年来,随着杂交稻亲本的遗传基础变窄及栽培中氮肥的不合理施用,稻瘟病害呈逐年递增趋势,给水稻生产带来了极大威胁(宋成艳等,2014),利用抗病基因改良品种抗性是水稻抗病防治最经济、有效的方法(Ashkani et al.,2015,2016;Tanweer et al.,2015)。由于稻瘟病菌无毒效应因子的高度变异,使含单一抗性基因的品种在短时间内丧失抗性(Zhu et al.,2000)。因此,改良現有水稻品种对稻瘟病的抗性,对水稻生产具有重要意义。【前人研究进展】前人研究发现,抗稻瘟病基因Pi9和Pi2是位于水稻第6号染色体短臂Pi2/9基因座上的广谱抗性基因(Zhou et al.,2006;Deng et al.,2017),其中,Pi9基因来自于小粒野生稻(Oryza minuta),对13个国家的43个稻瘟病菌株均表现出高抗性(Liu et al.,2002a);Pi2基因来自于Co39近等系,对从菲律宾不同地区和我国13个水稻主产区收集的792个稻瘟病菌株均表现出较高的抗性(Liu et al.,2002b)。因此,Pi2和Pi9基因用于改良品种抗性方面具有良好的应用前景。如陈志伟等(2004)将Pi2基因导入珍汕97B后获得的改良品系对稻瘟病抗性显著提高;倪大虎等(2005)、陈建民等(2009)分别将Pi9基因导入水稻恢复系M12和闽恢3139后也获得了稻瘟病抗性显著提高的改良品系。此外,还有部分学者利用分子标记辅助选择将Pi2或Pi9基因与其他抗病基因同时聚合到一个品种中,极大提高了水稻品种对稻瘟病的抗性及持久性(陈红旗等,2008;柳武革等,2008;Luo and Yin,2013;田大刚等,2014)。但Tian等(2016)利用Pi2和Pi9基因的功能标记分析我国434份水稻种质及育种材料,发现这两个抗病基因并未在我国种植品种中大规模应用,表明二者对改良水稻抗性具有较大的应用潜力。【本研究切入点】闽恢3301是福建省农业科学院生物技术研究所育成的三系杂交籼稻强势恢复系,以其配制的20个优势组合如天优3301、II优3301、谷优3301和花2优3301等均通过了国家或省级审定,但近年来闽恢3301的稻瘟病抗性呈逐年下降趋势。经本课题组前期研究发现,闽恢3301不含有Pi2和Pi9基因(Tian et al.,2016),利用这两个广谱高抗的基因改良闽恢3301的稻瘟病抗性具有较大的生产应用价值,但目前未见相关研究报道。【拟解决的关键问题】以75-1-127和C101A51为稻瘟病主效基因Pi9和Pi2的供体亲本,以闽恢3301为受体亲本,通过杂交、多代回交和自交,结合分子标记辅助选择和田间选择的方法,将供体亲本的Pi9和Pi2基因导入闽恢3301中,改良其稻瘟病抗性,采用人工接种法和田间自然诱发法对改良的闽恢330进行稻瘟病抗病性评价,筛选出对稻瘟病具有广谱抗性的改良株系,并分别与3个不育系配制杂交组合,考察各组合的相关农艺性状,最终筛选出具有闽恢3301遗传背景且可用于水稻生产的优良株系,为利用分子标记辅助选择改良现有水稻品种的稻瘟病抗性提供理论依据。
1 材料与方法
1. 1 试验材料
供试水稻品种为Pi9基因供体亲本75-1-127、Pi2基因供体亲本C101A51和受体亲本闽恢3301,其中,75-1-127的抗性基因Pi9来源于野生稻(O. minuta),C101A51的抗性基因Pi2来源于Co39近等系。以上材料均由福建省农业科学院生物技术研究所提供。三氯甲烷(分析纯)、异戊醇(分析纯)、75%(v/v)乙醇溶液和10 g/L琼脂糖溶液等均由福建省农业科学院生物技术研究所提供,双组分简单型PCR反应系统购自天根生化科技(北京)有限公司。主要仪器设备:PCR扩增仪(美国Bio-Rad公司)、凝胶成像系统(美国Bio-Rad公司)和电泳仪(美国Bio-Rad公司)等。
1. 2 Pi2/9分子标记检测
用于检测Pi2/9分子标记的引物为Pi2/9-F:5'-T TTGTTACTAGAATCGCTCCAT-3'和Pi2/9-R:5'-GA TTAGTGAGATCCATTGTTCC-3'(Tian et al.,2019)。所有引物均由福州铂尚生物有限公司合成。PCR反应体系和扩增程序参照Qu等(2006)、郑家团等(2009)的方法。
1. 3 构建分子标记辅助选择群体
于2013年4月在海南省三亚市藤桥育种基地分别以75-1-127和C101A51为供体亲本,闽恢3301为受体亲本杂交获得F1代杂交种。利用Pi2/9分子标记从中筛选出含抗病基因的单株,并与受体亲本闽恢3301连续多代回交获得BC5F1种子。2015年冬季于海南省三亚市藤桥育种基地种植BC5F1,选择基因型纯合且农艺性状和稻瘟病抗性与受体亲本一致的株系,自交两次,获得BC5F3株系(图1)。
1. 4 抗性鉴定
人工接种鉴定:于2016年从福建稻瘟病发病严重区(上杭县茶地乡、南靖县、厦门市、德化县、清流县、将乐县、宁化县、宁德市、武夷山和建阳市)分离获得21个稻瘟病菌株。于水稻苗期采用人工喷雾的方法接种21个稻瘟病菌株及其混合菌株。稻瘟病菌株的培养、产孢、接种及抗性调查等均参考Tian等(2019)的方法。
田间自然诱发鉴定:于2016─2017年在福建上杭茶地病圃进行田间抗性鉴定,分别于分苗期、分蘖盛期和抽穗结实期3个时期进行,种植期间通过重施氮肥,增加田间湿度创造发病条件。采用GB/T 15790—2009国家标准进行调查和分级,得出综合抗性水平,最终筛选出抗稻瘟病的改良株系。
1. 5 农艺性状考察
以三系不育系荟丰A、广8A和两系不育系RGD-7S作母本,分别与闽恢3301改良株系和闽恢3301配制杂交组合,以闽恢3301为父本的杂交组合为对照。该试验在福州寿山育种基地进行。按水稻正常种植季节播种插秧,株行距21 cm×21 cm,每小区种植100株,设3次重复。正常防治病虫害,常规水肥管理。考种时取每小区中间地段整齐一致的5个单株,测量自然不发病条件下各杂交组合的株高及考察穗数、穗长、分蘖数、结实率、千粒重和单株产量等农艺性状。
1. 6 统计分析
采用SPSS 19.0对农艺性状数据进行统计分析。
2 结果与分析
2. 1 Pi2/9标记在供受体间的多态性分析及基因纯合株系筛选结果
利用Pi2/9-F和Pi2/9-R引物对75-1-127、C101A51和闽恢3301进行多态性分析,结果显示,从75-1-127、C101A51和闽恢3301扩增的片段大小为164、147和174 bp(图2-A和图2-B),表明Pi2/9标记在供受体亲本间具有明显的多态性,可应用于相应抗性基因的辅助筛选。在连续多代回交、自交过程中,利用该标记对抗病基因进行跟踪选择,最终获得含Pi9和Pi2基因的纯合BC5F3代株系各20份,分别将其命名为含Pi9闽恢3301改良系(闽恢3301-Pi9)和含Pi2闽恢3301改良系(闽恢3301-Pi2)(图2-A和图2-B)。
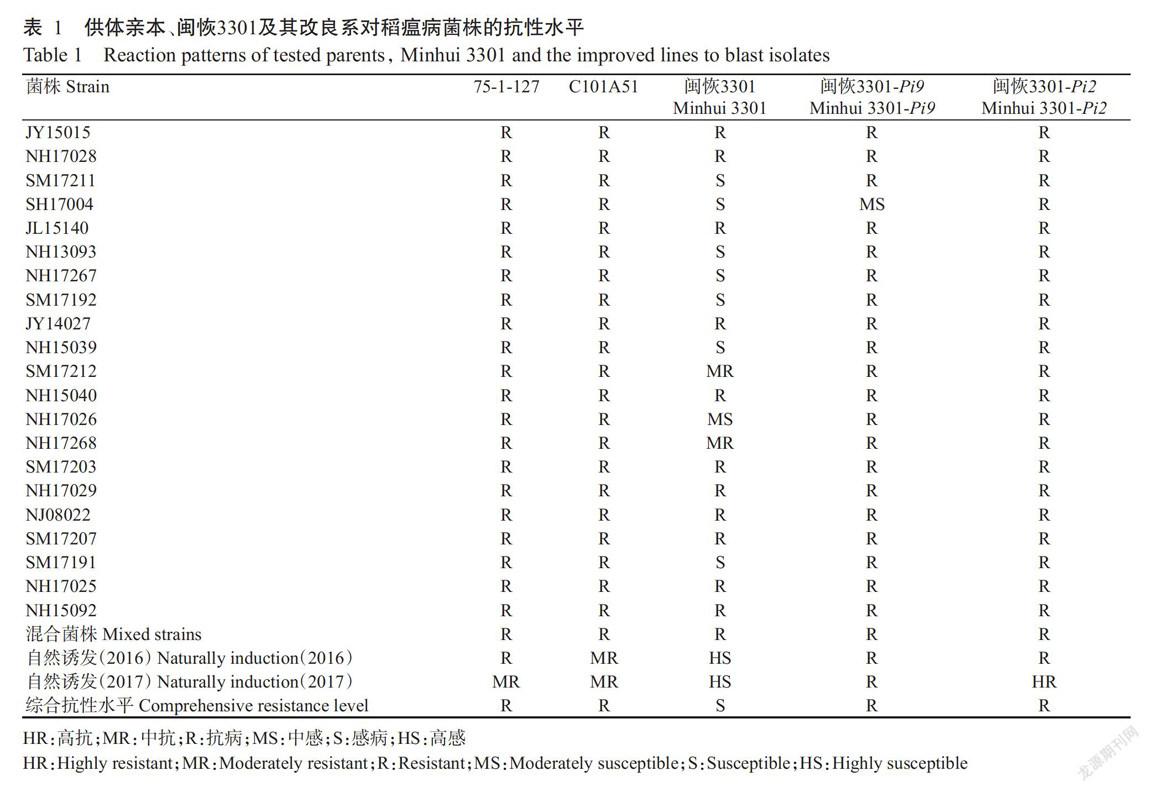
2. 2 闽恢3301改良系的稻瘟病抗性鉴定结果
由表1可知,人工接种后,75-1-127和C101A51對21个稻瘟病菌株及其混合菌株均表现为抗病,但二者于2016和2017年在福建上杭茶地病圃的田间自然诱发鉴定中抗性表现略有不同,其中,75-1-127在2016和2017年分别表现为抗病和中抗,而C101A51均表现为中抗,二者综合抗性水平均为抗病,表明Pi9和Pi2基因可用于上杭地区的稻瘟病抗性改良。
由表1还可知,闽恢3301对7个稻瘟病菌株(SM17211、SH17004、NH13093、NH17267、SM17192、NH15039和SM17191)表现感病,对NH17026菌株表现中感,对其他菌株则表现中抗或抗病,但闽恢3301于2016和2017年连续两年的田间自然诱发鉴定中均表现高感;除闽恢3301-Pi9对SH17004表现为中感外,闽恢3301-Pi9对其他稻瘟病菌株及于2016和2017年在田间自然诱发鉴定中均表现抗病,且闽恢3301-Pi2对21个稻瘟病菌株及于2016和2017年在田间自然诱发鉴定中均表现抗病或高抗。可见,与闽恢3301相比,闽恢3301-Pi9和闽恢3301-Pi2抗性得到有效提高,其抗性达到甚至超过供体亲本75-1-127和C101A51的抗性水平。通过比较闽恢3301-Pi9和闽恢3301-Pi2抗性发现,虽然Pi9和Pi2基因均能明显提高闽恢3301的抗性水平,但Pi2基因的提高效果更明显。
2. 3 闽恢3301改良系与不育系所配杂交组合的农艺性状表现
用三系不育系荟丰A、广8A和两系不育系RGD-7S作母本,分别与闽恢3301-Pi2、闽恢3301-Pi9和闽恢3301配制9个杂交组合,测定自然不发病条件下各组合的株高、穗长、分蘖数、千粒重、单株产量和结实率等农艺性状,结果如表2所示。除RGD-7S×闽恢3301-Pi9和RGD-7S×闽恢3301-Pi2组合的单株产量分别极显著(P<0.01)高于相应的对照组合(CK3)外,其他以闽恢3301改良系为父本的杂交组合在株高、穗长、分蘖数、千粒重、单株产量和结实率上与相应的对照组合(CK1和CK2)均无显著差异(P>0.05),说明稻瘟病抗性改良并未影响闽恢3301的配合力,闽恢3301-Pi2和闽恢3301-Pi9在培育稻瘟病抗性杂交水稻上具有广阔的应用前景。
3 讨论
Pi2/9基因座上的Pi2和Pi9基因是我国东北各地区抗性最好、抗谱最广的抗源基因(王倩等,2011),但目前这两个基因尚未在生产中广泛应用,具有很好的应用前景(Tian et al.,2016)。本研究利用稻瘟病菌株抗性较好的Pi2和Pi9供体亲本C101A51和75-1-127对闽恢3301进行抗性改良,获得了这两种抗性基因的改良系,即闽恢3301-Pi9和闽恢3301-Pi2,二者对稻瘟病菌株抗性水平得到有效提高,其抗性达到甚至超过供体亲本75-1-127和C101A51的抗性水平。此外,本研究以这两种抗性基因改良系为父本,分别与三系不育系荟丰A、广8A和两系不育系RGD-7S杂交,结果发现,除RGD-7S×闽恢3301-Pi9和RGD-7S×闽恢3301-Pi2组合的单株产量分别极显著高于相应的对照组合(CK3)外,其余以闽恢3301改良系父本的杂交组合的株高、穗长、分蘖数、千粒重、单株产量和结实率与以闽恢3301为父本的对照杂交组合间无显著差异,说明稻瘟病抗性改良并未影响闽恢3301的配合力。因此,这两份改良系可在实际生产中混合使用以提高改良系的生产应用范围。前人研究也发现,通过混合种植携带不同抗性基因的近等系可对稻瘟病产生高抗效果(Zhu et al.,2000;Abe,2004;Thakur et al.,2013),其原因在于利用不同品种在抗病性上的异质性或多样化以减弱单一品种对病原物小种群体的选择压力,有利于品种与菌群间形成平衡,以限制病原菌暴发(Tack et al.,2012),进一步明确了抗性基因型不同的品种与病原菌互作可产生抗性反应(Gallet et al.,2014)。
分子标记辅助育种应考虑目的基因和遗传背景的分子标记检测(Hittalmani et al.,2000;Gouda et al.,2013)。本研究在抗病基因回交转移时,通过Pi2/9标记检测结合对回交后代农艺性状的比较选择,在农艺性状与受体亲本一致时再自交2次,得到目的基因和遗传背景纯合的株系,结果表明本研究的试验方案具有很好的可行性,且本研究供受体亲本间均为籼型常规品种,遗传距离相对较小,经过5 次定向回交后和两次自交获得的纯合株系,其农艺性状已与轮回亲本基本一致。此外,虽然本研究证实稻瘟病抗性改良未影响闽恢3301的配合力,但是否影响其他重要病虫害抗性,尚有待研究。因此,在今后进行抗稻瘟病品种选育时,还应兼顾重要病虫害抗性及稻米品质,注重分子标记选择与常规育种手段的结合,力争使抗性、产量与品质达到同步改良。
4 结论
闽恢3301-Pi9和闽恢3301-Pi2抗性得到有效提高的同时在农艺性状和配合力等方面保持了闽恢3301及其组合的主要特性,说明利用Pi9和Pi2基因可有效改良闽恢3301的稻瘟病抗性,不仅拓宽了稻瘟病抗谱,还不影响闽恢3301的配合力,二者可作为新的水稻材料进行推广应用。
参考文献:
陈红旗,陈宗祥,倪深,左示敏,潘学彪,朱旭东. 2008. 利用分子标记技术聚合3个稻瘟病基因改良金23B的稻瘟病抗性[J]. 中国水稻科学,22(1):23-27. [Chen H Q,Chen Z X,Ni S,Zuo S M,Pan X B,Zhu X D. 2008. Pyramiding three genes with resistance to blast by marker-assisted selection to improve rice blast resistance of Jin 23B[J]. Chinese Journal of Rice Science,22(1):23-27.]
陈建民,付志英,权宝权,田大刚,李刚,王锋. 2009. 分子标记辅助培育双抗稻瘟病和白叶枯病杂交稻恢復系[J]. 分子植物育种,7(3):465-470. [Chen J M,Fu Z Y,Quan B Q,Tian D G,Li G,Wang F. 2009. Breeding hybrid rice restoring line with double resistance to rice blast and bacterial blight by marker-assisted selection[J]. Molecular Plant Breeding,7(3):465-470.]
陈志伟,郑燕,吴为人,赵长江. 2004. 抗稻瘟病基因Pi-2(t)紧密连锁的SSR标记的筛选与应用[J]. 分子植物育种,2(3):321-325. [Chen Z W,Zheng Y,Wu W R,Zhao C J. 2004. Screening and application of an SSR markers closely linked to Pi-2(t),a gene resistant to rice blast[J]. Molecular Plant Breeding,2(3):321-325.]
柳武革,王丰,金素娟,朱小源,李金华,刘振荣,廖亦龙,朱满山,黄慧君,符福鸿,刘宜柏. 2008. 利用分子标记辅助选择聚合Pi-1和Pi-2基因改良两系不育系的稻瘟病抗性[J]. 作物学报,34(7):1128-1136. [Liu W G,Wang F,Jin S J,Zhu X Y,Li J H,Liu Z R,Liao Y L,Zhu M S,Huang H J,Fu F H,Liu Y B. 2008. Improvement of rice blast resistance in TGMS line by pyramiding of Pi-1 and Pi-2 through molecular marker-assisted selection[J]. Acta Agronomica Sinica,34(7):1128-1136.]
倪大虎,易成新,李莉,汪秀峰,王文相,杨剑波. 2005. 利用分子标记辅助选择聚合水稻基因Xa21和Pi9(t)[J]. 分子植物育种,3(3):329-334. [Ni D H,Yi C X,Li L,Wang X F,Wang W X,Yang J B. 2005. Pyramiding Xa21 and Pi9(t) in rice by marker-assisted selection[J]. Molecular Plant Breeding,3(3):329-334.]
宋成艳,王桂玲,刘乃生,周雪松,陈书强,陆文静. 2014. 不同施氮方式对黑龙江省水稻主栽品种稻瘟病发生的影响[J]. 北方水稻,44(4):19-22. [Song C Y,Wang G L,Liu N S,Zhou X S,Chen S Q,Lu W J. 2014. The effects of different nitrogen applications on the occurrence of rice blast on main cultivar rice in Heilongjiang Province[J]. North Rice,44(4):19-22.]
田大刚,陈在杰,陈子强,林艳,周元昌,陈松彪,王锋. 2014. 分子标记辅助选育聚合抗稻瘟病基因和抗白叶枯病基因的水稻改良新恢复系[J]. 分子植物育种,12(5):843-852. [Tian D G,Chen Z J,Chen Z Q,Lin Y,Zhou Y C,Chen S B,Wang F. 2014. Developing improved lines of three rice restorers pyramided resistant gene to blast and bacterial blight by marker-assisted selection[J]. Molecular Plant Breeding,12(5):843-852.]
王倩,李祥曉,王疏,周永力,徐建龙,黎志康. 2011. 水稻分子育种亲本材料在东北地区的稻瘟病抗性评价[J]. 分子植物育种,9(4):432-437. [Wang Q,Li X X,Wang S,Zhou Y L,Xu J L,Li Z K. 2011. Screening and evaluation of rice germplasm resources resistant to rice blast pathogen derived from north-eastern region[J]. Molecular Plant Breeding,9(4):432-437.]
郑家团,涂诗航,张建福,郑轶,赵开军,张水金,谢华安. 2009. 含白叶枯病抗性基因Xa23水稻恢复系的分子标记辅助选育[J]. 中国水稻科学,23(4):437-439. [Zheng J T,Tu S H,Zhang J F,Zheng Y,Zhao K J,Zhang S J,Xie H A. 2009. Breeding of restorer lines of hybrid rice with bacterial blight resistance gene Xa23 by using mar-ker-assisted selection[J]. Rice Science,23(4):437-439.]
Abe S. 2004. Breeding of a blast resistant multiline variety of rice,Sasanishiki BL[J]. Japan Agricultural Research Quarterly,38(3):149-154.
Ashkani S,Rafii M Y,Shabanimofrad M,Ghasemzadeh A,Ravanfar S A,Latif M A. 2016. Molecular progress on the mapping and cloning of functional genes for blast di-sease in rice(Oryza sativa L.):Current status and future considerations[J]. Critical Reviews in Biotechnology,36(2):353-367.
Ashkani S,Yusop M R,Shabanimofrad M,Azadi A,Latif M A. 2015. Allele mining strategies:Principles and utilisation for blast resistance genes in rice(Oryza sativa L.)[J]. Current Issues in Molecular Biology,17(1):57-74.
Deng Y,Zhai K,Xie Z,Yang D,Zhu X,Liu J,Wang X,Qin P,Yang Y,Zhang G,Li Q,Zhang J,Wu S,Milazzo J,Mao B,Wang E,Xie H,Tharreau D,He Z. 2017. Epige-netic regulation of antagonistic receptors confers rice blast resistance with yield balance[J]. Science,355(6328):962-965.
Gallet R,Bonnot F,Milazzo J,Tertois C,Adreit H,Ravigné V,Tharreau D,Fournier E. 2014. The variety mixture strategy assessed in a G×G experiment with rice and the blast fungus Magnaporthe oryzae[J]. Front Genet,4:312.
Gouda P K,Saikumar S,Varma C M K,Nagesh K,Thippeswamy S,Shenoy V,Ramesha M S,Shashidhar H E,Ahn S N. 2013. Marker-assisted breeding of Pi-1 and Piz-5 genes imparting resistance to rice blast in PRR78,restorer line of Pusa RH-10 Basmati rice hybrid[J]. Plant Breeding,132(1):61-69.
Helliwell E E,Wang Q,Yang Y. 2013. Transgenic rice with inducible ethylene production exhibits broad-spectrum disease resistance to the fungal pathogens Magnaporthe oryzae and Rhizoctonia solani[J]. Plant Biotechnology Journal,11(1):33-42.
Hittalmani S,Parco A,Mew T V,Zeigler R S,Huang N. 2000. Fine mapping and DNA marker-assisted pyrami-ding of the three major genes for blast resistance in rice[J]. Theoretical and Applied Genetics,100(7):1121-1128.
Liu G,Lu G,Zheng L,Wang G L. 2002a. Two broad-spectrum blast resistance genes,Pi9(t) and Pi2(t),are physically linked on rice chromosome 6[J]. Molecular Genetics and Genomics,267(4):472-480.
Liu S P,Li X,Wang C Y,Li X H,He Y Q. 2002b. Improvement of resistance to rice blast in Zhenshan 97 by mole-cular marker-aided selection[J]. Acta Botanica Sinica,45(11):1346-1350.
Luo Y C,Yin Z C. 2013. Marker-assisted breeding of Thai fragrance rice for semi-dwarf phenotype,submergence tolerance and disease resistance to rice blast and bacterial blight[J]. Molecular Breeding,32(3):709-721.
Qu S H,Liu G F,Zhou B,Bellizzi M,Zeng L R,Dai L Y,Han B,Wang G L. 2006. The broad-spectrum blast resistance gene Pi9 encodes a nucleotide-binding site-leucine-rich repeat protein and is a member of a multigene family in rice[J]. Genetics,172(3):1901-1914.
Skamnioti P,Gurr S J. 2009. Against the grain:safeguarding rice from rice blast disease[J]. Trends in Biotechnology,27(3):141-150.
Tack A J M,Thrall P H,Barrett L G,Burdon J J,Laine A L. 2012. Variation in infectivity and aggressiveness in space and time in wild host-pathogen systems:Causes and consequences[J]. Journal of Evolutionary Biology,25(10):1918-1936.
Tanweer F A,Rafii M Y,Sijam K,Rahim H A,Ahmed F,Latif M A. 2015. Current advance methods for the identification of blast resistance genes in rice[J]. Comptes Rendus Biologies,338(5):321-334.
Thakur S,Gupta Y K,Singh P K,Rathour R,Variar M,Prashanthi S K,Singh A K,Singh U D,Chand D,Rana J C,Singh N K,Sharma T R. 2013. Molecular diversity in rice blast resistance gene Pi-ta makes it highly effective against dynamic population of Magnaporthe oryzae[J]. Functional & Integrative Genomics,13(3):309-322.
Tian D G,Chen Z J,Chen Z Q,Zhou Y C,Wang Z H,Wang F,Chen S B. 2016. Allele-specific marker-based assessment revealed that the rice blast resistance genes Pi2 and Pi9 have not been widely deployed in Chinese indica rice cultivars[J]. Rice,9(1):19.
Tian D G,Guo X R,Zhang Z J,Wang M,Wang F. 2019. Improving blast resistance of the rice restorer line,Hui 316,by introducing Pi9 or Pi2 with marker-assisted selection[J]. Biotechnology & Biotechnological Equipment,33(1):1195-1203.
Zhou B,Qu S,Liu G,2006. The eight amino acid differences within three leucine-rich repeats between Pi2 and Piz-t resistance proteins determine the resistance specificity to Magnaporthe grisea[J]. Molecular Plant-microbe Interactions,19(11):1216-1228.
Zhu Y Y,Chen H R,Fan J H,Wang Y Y,Li Y,Chen J B,Fan J X,Yang S S,Hu L P,Leung H,Mew T W,Teng P S,Wang Z H,Mundt C C. 2000. Genetic diversity and disease control in rice[J]. Nature,406:718-722.
(責任编辑 陈 燕)

