茶叶高氯酸盐污染及分析技术
邓家军,潘华,张富生,张莉,曹芳,张志芳,陈俊松
茶叶高氯酸盐污染及分析技术
邓家军1,2,潘华1,2,张富生1,2,张莉1,2,曹芳1,2,张志芳1,2,陈俊松3
1. 江西省农产品质量安全检测中心,江西 南昌 330046;2. 农业部农产品质量安全风险评估实验室(南昌),江西 南昌 330046;3. 九江市农产品质量安全监测中心,江西 九江 332000
高氯酸盐是茶叶中的一种新型污染物,对茶叶产品质量安全、人体健康和对外贸易构成了潜在风险,已引起了国内外越来越多的关注。本文综述了茶叶中高氯酸盐的来源及污染现状,介绍了茶叶中高氯酸盐的分析技术,以期为开展高氯酸盐环境化学行为、农产品质量安全、人体健康风险及其相关安全标准等方面的研制提供借鉴。
茶叶;高氯酸盐;污染;分析技术
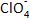
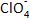
1.1 环境中污染来源
1.1.1 自然来源
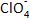
1.1.2 人为生产
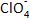
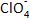
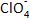
1.2 环境中污染状况
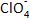
2 茶叶中的污染
2.1 茶叶中污染现状
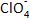
2.2 茶叶中污染来源
3.1 IC法
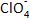
3.2 IC-MS/MS法
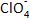
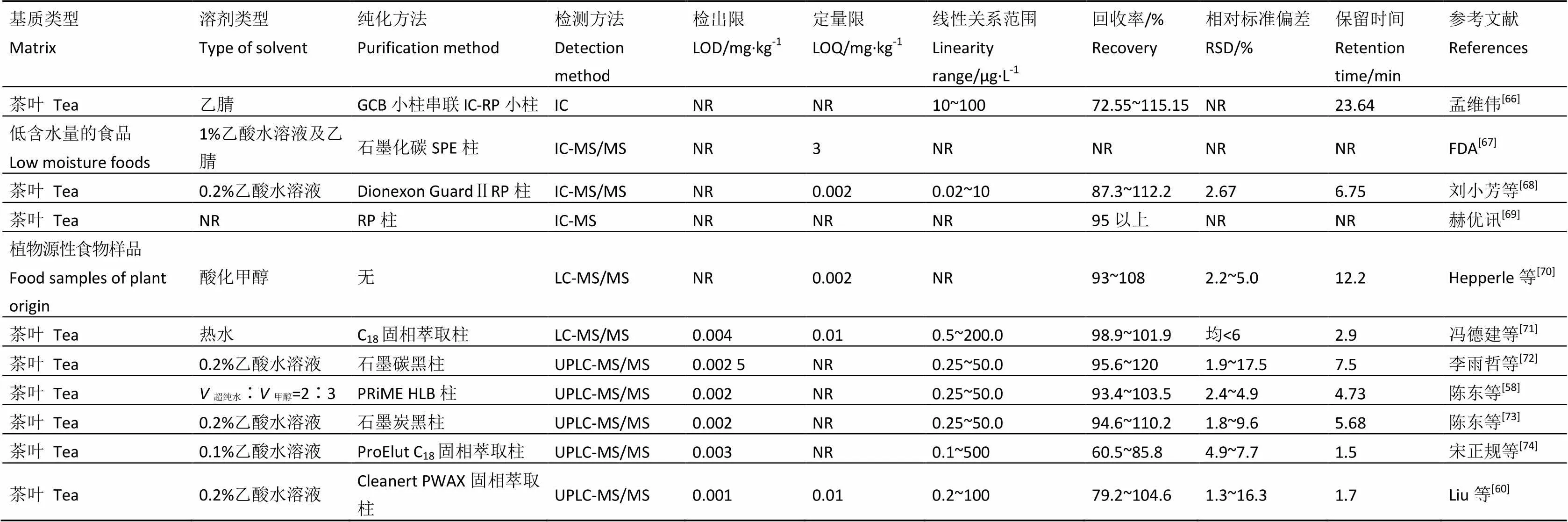
表1 文献报道过的方法比较
注:NR:未见报道
Note: NR: not reported
3.3 LC-MS/MS法
4 结语
[1] 梅宇. 2014年中国茶叶产销报告及2015年形势预测[J]. 茶世界, 2015(6): 50-59.
[2] 梅宇, 王智超. 2016全国春茶产销形势分析报告[J]. 茶世界, 2016(6): 40-49.
[3] 梅宇. 2016年中国茶业经济形势简报[J]. 茶世界, 2017(2): 14-18.
[4] 梅宇, 王智超, 林璇. 2017年全国春茶产销形势分析报告[J]. 茶世界, 2017(5): 14-22.
[5] 陈宗懋. 我国茶产业质量安全和环境安全问题研究[J]. 农产品质量与安全, 2011(3): 5-7.
[6] 韩文炎, 鲁成银, 刘新. 我国茶叶在种植环节的质量安全问题及对策[J]. 食品科学技术学报, 2014, 32(2): 12-15.
[7] 刘新, 张颖彬, 潘蓉, 等. 我国茶叶加工过程的质量安全问题及对策[J]. 食品科学技术学报, 2014, 32(2): 16-19.
[8] European Commission. Statement as regards the presence ofperchlorate in food endorsed by the Standing Committee on Plants, Animals, Food and Feed on 10 March 2015, updated on 23 June 2015 [EB/OL]. (2015-06-23)[2018-09-10]. https://ec.europa.eu/food/sites/food/files/safety/docs/cs_con taminants_catalogue_perchlorate_statement_food_update_en.pdf .
[9] Leung A M, Pearce E N, Braverman L E. Perchlorate, iodine and the thyroid [J]. Best Practice & Research Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism, 2010, 24(1): 133-141.
[10] Blount B C, Pirkle J L, Osterloh J D, et al.Urinary perchlorate and thyroid hormone levels in adolescent and adult men and women living in the United States [J]. Environmental Health Perspectives, 2006, 114(12): 1865-1871.
[11] EFSA Panel on Contaminants in the Food Chain (CONTAM). Scientific opinion on the risks to public health related to the presence of perchlorate in food, in particular fruits and vegetables [J]. EFSA Journal, 2014, 12(10), 3869. https://doi.org/10.2903/j.efsa.2014.3869.
[12] Acevedo-Barrios R, Sabater-Marco C, Olivero-Verbel J. Ecotoxicological assessment of perchlorate usingandassays [J]. Environmental Science & Pollution Research International, 2018, 25(14): 13697-13708.
[13] USEPA. Announcement of the Drinking Water Contaminant Candidate List. Notice [J]. Federal Regist, 1998, 63(40): 10273-10287.
[14] Kannan K, Praamsma M L, Oldi J F, et al. Occurrence of perchlorate in drinking water, groundwater, surface water and human saliva from India [J]. Chemosphere, 2009, 76(1): 22-26.
[15] Kumarathilaka P, Oze C, Vithanage M. Perchlorate mobilization of metals in serpentine soils [J]. Applied Geochemistry, 2016, 74: 203-209
[16] Kumarathilaka P, Oze C, Indraratne S P, et al. Perchlorate as an emerging contaminant in soil, water and food[J]. Chemosphere, 2016, 150: 667-677.
[17] Calderón R, Godoy F, Escudey M, et al. A review of perchlorate (ClO4-) occurrence in fruits and vegetables [J]. Environmental Monitoring & Assessment, 2017, 189(2): 82. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-017-5793-x.
[18] Lee S Y, Mccarthy A M, Stohl H E, et al. Urinary iodine, perchlorate, and thiocyanate concentrations in U.S. lactating women [J]. Thyroid, 2017, 27(12): 1574-1581.
[19] Zhang T, Wu Q, Sun H W, et al. Perchlorate and iodide in whole blood samples from infants, children, and adults in Nanchang, China [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2010, 44(18): 6947-6953.
[20] Qin X, Zhang T, Gan Z, et al. Spatial distribution of perchlorate, iodide and thiocyanate in the aquatic environment of Tianjin, China [J]. Environmental source analysis, Chemosphere, 2014, 111: 201-208.
[21] Wan Y, Wu Q, Abualnaja K O, et al. Occurrence of perchlorate in indoor dust from the United States and eleven other countries: Implications for human exposure [J]. Environment International, 2015, 75: 166-171.
[22] Jackson W A, Böhlke J K, Gu B, et al. Isotopic composition and origin of indigenous natural perchlorate an co-occurring nitrate in the Southwestern United States [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2010, 44(13): 4869-4876.
[23] Rao B, Anderson T A, Redder A, et al. Perchlorate formation by ozone oxidation of aqueous chlorine/oxy-chlorine species: Role of ClxOyradicals [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2010, 44(8): 2961-2967.
[24] Rao B, Estrada N, McGee S, et al. Perchlorate production by photodecomposition of aqueous chlorine solutions [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2012, 46(21): 11635-11643
[25] Kang N, Jackson W A, Dasgupta P K, et al. Perchlorate production by ozone oxidation of chloride in aqueous and dry systems [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2008, 405(1/3): 301-309.
[26] Jiang S, Li, Y S, Sun B. Determination of trace level of perchlorate in Antarctic snow and ice by ion chromatography coupled with tandem mass spectrometry using an automated sample on-line preconcentration method [J]. Chinese Chemical Letters, 2013, 24(4): 311-314.
[27] Duncan P B, Morrison R D, Vavricka E. Forensic identification of anthropogenic and naturally occurring sources of perchlorate [J]. Environmental Forensics, 2005, 6(2): 205-215.
[28] Michalski J, Böhlke J K, Thiemens M. Long-term atmospheric deposition as the source of nitrate and other salts in the Atacama Desert, Chile: New evidence from mass-independent oxygen isotopic compositions [J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2004, 68(20): 4023-4038.
[29] Wu C, Sullivan K, Chowdhury S, et al. Encapsulation of perchlorate salts within metal oxides for application as nanoenergetic oxidizers [J]. Advanced Functional Materials, 2012, 22(1): 78-85.
[30] Wilkin R T, Fine D D, Burnett N G. Perchlorate behavior in a municipal lake following fireworks displays [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2007, 41(11): 3966-3971.
[31] Shi Y L, Zhang N, Gao J M, et al. Effect of fireworks display on perchlorate in air aerosols during the Spring Festival [J]. Atmospheric Environment, 2011, 45(6): 1323-1327.
[32] Isobe T, Ogawa S P, Sugimoto R, et al. Perchlorate contamination of groundwater from fireworks manufacturing area in South India [J]. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 2013, 185(7): 5627-5637.
[33] Urbansky E T, Brown S K, Magnuson M L, et al. Perchlorate levels in samples of sodium nitrate fertilizer derived from Chilean caliche [J]. Environ Pollut, 2001, 112(3): 299-302
[34] Susarla S, Collette T W, Garrison A W, et al. Perchlorate identification in fertilizers [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 1999, 33(19): 3469-3472.
[35] Massachusetts Department of Environmental Protection. The occurrence and sources of perchlorate in Massachusetts—Draft report [EB/OL]. (2006-04)[2018-09-10].http://www.mass.gov/eea/docs/dep/cleanup/sites/percsour.pdf.
[36] Barron L, Nesterenko P N, Paull B. Rapid on-line preconcentration and suppressed micro-bore ion chromatography of part per trillion levels of perchlorate in rainwater [J]. Anal Chim Acta, 2006, 567(1): 127-134.
[37] Furdui V, Tomassini F. Trends and sources of perchlorate in Arctic snow [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2010, 44(2): 588-592.
[38] Parker D R, Seyfferth A L, Reese B K. Perchlorate in groundwater: a synoptic survey of “pristine” sites in the coterminous United States [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2008, 42(5): 1465-1471.
[39] Ji G L, Kong X L. Adsorption of chloride, nitrate and perchlorate by variable charge soils [J]. Pedosphere. 1992, 2(4): 317-326.
[40] Urbansky E T, Brown S K. Perchlorate retention and mobility in soils [J]. Journal of Environmental Monitoring, 2003, 5(3): 455-462.
[41] Tipton D K, Rolston D E, Scow K M. Transport and biodegradation of perchlorate in soils [J]. Journal of Environmental Quality 2003, 32(1): 40-46.
[42] Gan Z, Sun H, Wang R, et al. Occurrence and exposure evaluation of perchlorate in outdoor dust and soil in mainland China [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2014, 470/471: 99-106.
[43] Ye L, You H, Yao J, et al. Seasonal variation and factors influencing perchlorate in water, snow, soil and corns in Northeastern China [J]. Chemosphere, 2013, 90(10): 2493-2498.
[44] Qin X, Zhang T, Gan Z, et al. Spatial distribution of perchlorate, iodide and thiocyanate in the aquatic environment of Tianjin, China: Environmental source analysis [J]. Chemosphere, 2014, 111: 201-208.
[45] Wu Q, Zhang T, Sun H, et al. Perchlorate in tap water, groundwater, surface waters, and bottled water from China and its association with other inorganic anions and with disinfection byproducts [J]. Archives of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 2010, 58(3): 543-550.
[46] Smith P N, Yu L, McMurry S T et al. Perchlorate in water, soil, vegetation, and rodents collected from the Las Vegas Wash, Nevada, USA [J]. Environmental Pollution, 2004, 132(1): 121-127.
[47] Kim D H, Yoon Y, Baek K, et al. Occurrence of perchlorate in rice from different areas in the Republic of Korea [J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 2014, 21(2): 1251-1257.
[48] Seyfferth A L, Sturchio N C, Parker D R. Is perchlorate metabolized or re-translocated within lettuce leaves? A stable isotope approach [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2008, 42(24): 9437-9442.
[49] Seyfferth A L, Henderson M K, Parker D R. Effects of common soil anions and pH on the uptake and accumulation of perchlorate in lettuce [J]. Plant Soil, 2008, 302(1/2): 139-148.
[50] Yu L, Canas J E, Cobb G P, et al. Uptake of perchlorate in terrestrial plants [J]. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 2004, 58(1): 44-49.
[51] Yifru D D, Nzengung V A. Uptake of perchlorate by vegetation growing at field sites in arid and subhumid climates [J]. Remediation Journal, 2007, 17(4): 53-68.
[52] Sanchez C A, Crump K S, Krieger R I, et al. Perchlorate and nitrate in leafy vegetables of North America [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2005, 39(24): 9391-9397.
[53] Yang M, Her N. Perchlorate in soybean sprouts (L. Merr.), water dropwort (DC), and lotus (Gaertn.) root in South Korea [J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 2011, 59(13): 7490-7495.
[54] 陈桂葵, 骆世明, 杜宁宁, 等. 高氯酸盐对水稻生理生态的影响及其在稻田系统中的分布规律[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 2011, 30(11): 2137-2144.
[55] Jackson W A, Joseph P, Laxman P, et al. Perchlorate accumulation in forage and edible vegetation [J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 2005, 53(2): 369-373.
[56] Seyfferth A L, Parker D R. Effects of genotype and transpiration rate on the uptake and accumulation of perchlorate (ClO4-) in lettuce [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2007, 41(9): 3361-3367.
[57] Seyfferth A L, Sturchio N C, Parker D R. Is perchlorate metabolized or re-translocated within lettuce leaves? A stable isotope approach [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2008, 42(24): 9437-9442.
[58] 陈东, 范赛, 沙博郁, 等. 同位素标记-超高效液相色谱-串联质谱法测定茶叶中的高氯酸盐[J]. 中国卫生检验杂, 2017, 27(16): 2298-2300.
[59] 华永有, 李宇翔, 林宏琳, 等. 茶叶中高氯酸盐检测与污染情况分析[J]. 海峡预防医学杂志, 2018, 24(1): 4-6, 12.
[60] Liu Y, Sun H Z, Zhou L, et al. Quantitative determination and contamination pattern of perchlorate in tea by ultra performance liquid chromatography and tandem mass spectrometry [J]. Food Chemistry. 2019, 274: 180-186.
[61] 邓家军, 张莉, 廖健, 等. 茶叶中高氯酸盐健康风险研究[J]. 乡村科技, 2016(36): 42.
[62] Sæbø A, Popek R , Nawrot B, et al. Plant species differences in particulate matter accumulation on leaf surfaces [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2012, 427/428: 347-354.
[63] 郭梦媚, 郭胜利, 周佳雯, 等. 江西省植被NDVI变化及其对气候变化的响应[J]. 江苏农业科学, 2015, 43(11): 421-426.
[64] Collette T W, Williams T L, Urbansky E T., et al. Analysis of hydroponic fertilizer matrixes for perchlorate: comparison of analytical techniques [J]. Analyst, 2003, 128(1): 88-97.
[65] 中华人民共和国国家质量监督检验检疫总局. SN/T 4089—2015出口食品中高氯酸盐的测定[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2015.
[66] 孟维伟. 茶叶中高氯酸盐的检测——离子色谱法[J]. 轻工科技, 2016, 32(11): 12-13.
[67] U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA). Rapid determination of perchlorate anion in foods by ion chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. Version 2[EB/OL]. (2005-04-12)[2018-09-10]. https://www.fda.gov/Food/FoodborneIllnessContaminants/ChemicalContaminants/ucm077793.html.
[68] 刘小芳, 方从容, 刘慧, 等. 离子色谱-串联质谱法检测茶叶中的高氯酸盐[J]. 色谱, 2016, 34(10): 986-988.
[69] 赫优讯. 赛默飞发布茶叶中高氯酸盐的检测方案[J]. 中国仪器仪表, 2016(2): 18.
[70] Hepperle J, Wolheim A, Kohlberg D, et al. Analysis of perchlorate in food samples of plant origin applying the QuPPe-method and LC-MS/MS [J]. Aspects of Food Control and Animal Health, 2013(2): 1-16.
[71] 冯德建, 邹燕, 史谢飞, 等. 茶叶中高氯酸盐的液相色谱-串联质谱测定方法研究[J]. 中国测试, 2016, 42(4): 1-4.
[72] 李雨哲, 杨杰, 王雨昕, 等. 同位素稀释-超高效液相色谱-串联质谱法测定茶叶中的高氯酸盐[J]. 中国食品卫生杂志, 2016, 28(5): 616-619.
[73] 陈东, 范赛, 沙博郁, 等. 超高效液相色谱-串联质谱法测定茶叶中高氯酸盐[J]. 食品安全质量检测学报, 2018, 9(4): 925-929.
[74] 宋正规, 张书芬, 周子焱, 等. 超高效液相色谱-串联质谱同时测定茶叶中高氯酸盐和氯酸盐[J]. 茶叶科学, 2017, 37(6): 597-604.
Perchlorate Contamination in Tea andIts Analytical Techniques
DENG Jiajun1,2, PAN Hua1,2, ZHANG Fusheng1,2, ZHANG Li1,2,CAO Fang1,2, ZHANG Zhifang1,2, CHEN Junsong3
1.Testing Center of Agro-Product Quality and Safety of Jiangxi Province, Nanchang 330046, China;2. Laboratory of Quality and Safety Risk Assessment for Agro-products (Nanchang), Ministry of Agriculture, Nanchang 330046, China;3. Monitoring Center of Agro-Product Quality and Safety of Jiujiang City, Jiujiang 332000, China
Perchlorate in tea, as an emerging contaminant, poses a potential risk for food safety, human health and foreign trade, which has raised increasing concerns over the contamination of tea with perchlorate. In this paper, pollution sources, status and the main causes of pollution in tea of perchlorate were described. The analytical techniques of perchloratein tea samples were also summarized. These data would provide references for studies of environmental transport behaviors, agri-food safety, human health risk and relevant standards of security in China.
tea, perchlorate, contamination, analytical techniques
S571.1;TS201.6
A
1000-369X(2019)04-372-10
2018-09-10
2018-12-12
农业部农产品质量安全风险评估项目(GJFP201700503、GJFP201800503)
邓家军,男,博士,主要从事农产品质量安全风险评价、污染生态修复等方面的研究,E-mail: dengjj2118@163.com

