蛴螬提取物对实验性兔视网膜静脉阻塞不同时间窗MMP-9表达的影响
蒋鹏飞 马俊旭 彭俊 彭清华


[摘要] 目的 評价蛴螬提取物对实验性兔视网膜静脉阻塞(RVO)不同时间窗的治疗作用及其机制。 方法 将40只兔随机分为四组:A组、B组、C组、D组,每组10只兔20只眼。除A组外,其余三组均用光化学动力法建立RVO动物模型,A、B组以生理盐水5 mL/kg灌胃,C组以复方血栓通混悬剂5 mL/kg灌胃,D组以蛴螬提取物1.5 mL/kg灌胃。给药后1、3周行荧光素眼底血管造影(FFA)计算无灌注区面积和视盘面积的比值,行HE染色观察视网膜形态学,采用免疫组化法检测基质金属蛋白酶(MMP)-9的表达量。 结果 FFA检测结果显示:造模后1、3周,C、D组无灌注区面积和视盘面积的比值均明显低于B组,差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05或P < 0.01)。视网膜切片光镜观察结果显示:B组在造模后1周,视网膜组织水肿,细胞排列较乱,尚无新生血管索,在造模后3周,出现大量的新生血管索;C组在造模后1周,视网膜组织水肿,细胞排列紊乱,在造模后3周,视网膜组织水肿减轻,无新生血管索;D组在造模后1周,视网膜组织细胞排列大致清晰,在造模后3周,视网膜组织水肿减轻,无新生血管索。MMP-9免疫组化结果示:各组MMP-9表达均上调,D组表达最弱,C组次之,B组表达最强,其中B、C、D组MMP-9表达均明显高于A组,但C、D组MMP-9表达均明显低于B组,差异均有统计学意义(P < 0.05)。结论 蛴螬提取物能改善视网膜缺血缺氧的状态,抑制实验性RVO模型中MMP-9的表达。
[关键词] 视网膜静脉阻塞;蛴螬提取物;基质金属蛋白酶9;新生血管
[中图分类号] R774.1 [文献标识码] A [文章编号] 1673-7210(2019)05(c)-0008-04
[Abstract] Objective To evaluate the therapeutic effect and mechanism of white grub extract on experimental rabbits with retinal vein occlusion (RVO) in different time windows. Methods Forty rabbits were randomly divided into 4 groups: group A, group B, group C, group D, with 10 rabbits and 20 eyes in each group. Except for group A, photochemical kinetic method was used to establish RVO animal model in the other three groups. Group A and B were intragastrically administered with 5 mL/kg of normal saline. Group C was intragastrically administered with 5 mL/kg of Compound Xueshuantong Suspension, and group D was intragastrically administered with 1.5 mL/kg of white grub extract. After administration for 1 and 3 weeks, fluorescein fundus angiography (FFA) was examined to calculate to the ratio of area of non-perfusion area and area of optic disk, HE staining was used to observe the retinal morphology, immunohistochemistry was used to detect the expression of matrix metalloproteinase (MMP)-9. Results The results of FFA test showed that the ratio of area of non-perfusion area and area of optic disk in group C and D was significantly lower than that of group B after modeling for 1 week and 3 weeks, the differences were statistically significant (P < 0.05 or P < 0.01). The results of light microscopy of retinal sections showed that in group B, 1 week after modeling, the retinal tissue was edematous, the cells were arranged in disorder, and there was no new vascular cord, after 3 weeks of modeling, a large number of neovascular cords appeared; in group C, 1 week after modeling, the retinal tissue was edematous, the cells were arranged in disorder, 3 weeks after modeling, the edema of retinal tissue was reduced, there was no neovascular cord; in group D, 1 week after modeling, the retinal tissue cells were roughly arranged, 3 weeks after modeling, the edema of retinal tissue was reduced, there was no neovascular cord. The results of MMP-9 immunohistochemistry showed that the expression of MMP-9 was up-regulated in each group, group D was the weakest, followed by group C, and group B was the strongest, the expression of MMP-9 in group B, C and D was higher than that of group A, while the expression of MMP-9 in group C and D was lower than that of group B, the differences were all statistically significant (P < 0.05). Conclusion White grub extract can improve the state of retinal ischemia and hypoxia and inhibit the expression of MMP-9 in the experimental RVO model.
[Key words] Retinal vein occlusion; White grub extract; Matrix metalloproteinase-9; Neovascular
视网膜静脉阻塞(retinal vein occlusion,RVO)病程冗长,治疗困难,尚无特效疗法,新生血管(RNV)是RVO的常见并发症。蛴螬可治疗目疾,并有破血、行瘀、散结、明目之功效,前期研究发现蛴螬提取物可促进RVO出血的吸收,抑制RNV[1-2],为明确其机制,本研究通过建立RVO的动物模型,探讨蛴螬对RNV的作用机制。
1 材料与方法
1.1 实验材料
1.1.1 实验动物 选用40只健康实验性兔,SPF级,雌雄兼用,体重1.8~2.3 kg(湖南中医药大学动物实验室提供,合格证号:湘医动字第30-015号),饲养在湖南中医药大学实验楼动物实验中心SPF级实验房,湿度50%~55%,室温(23±2)℃,自由进食进水。
1.1.2 主要实验药品和试剂 蛴螬提取物,制备参考阳长明等[3]的方法;复方血栓通片(湖南中医药大学第一附属医院,批号:Z19990022);水合氯醛(湖南中医药大学病理实验室,批号:H37022673);Bradford蛋白浓度测定试剂盒(江苏碧云天生物技术研究所,批号:P0006);羊抗兔二抗(武汉赛维尔生物科技有限公司,批号:GB23303)。
1.1.3 主要实验仪器 电子秤(上海天平仪器厂,JY0001);眼科手术显微镜(苏州医疗器械设备厂,YZZOT);凝胶成像系统[美国,Bio-Rad(Gel Doc XR+)];台式高速冷冻离心机(Thermo);水平摇床(北京六一仪器厂,WD-9405B);扫描仪(日本Canon,9000F MarkⅡ)。
1.2 实验方法
1.2.1 动物分组 将40只实验性兔依次编为1~40号,通过随机数字表法分为A组、B组、C组、D组,每组10只动物、20只眼。
1.2.2 造模方法 应用光化学动力法[4]制作实验性RVO模型,B、C、D组双眼散瞳后,麻醉动物,固定兔于裂隙灯前,安置三面镜。激光器指示光斑定位于视盘边缘的静脉后,自耳缘静脉缓慢推入20%荧光素钠注射液(0.3 mL/kg),用倍频Nd:YAG激光对双侧视网膜静脉进行照射,同时避开伴行的动脉,看到有明显的远端静脉扩张时停止。
1.2.3 动物给药方法 A、B组:生理盐水5 mL/kg灌胃;C组:复方血栓通0.1 g/kg溶于生理盐水中制成混悬剂,5 mL/kg灌胃;D组:蛴螬提取物1.5 mL/kg灌胃。各组均为每日1次,持续至造模后3周,于造模后1、3周每组各随机处死5只动物。
1.2.4 取材方法 动物耳缘静脉注射空气处死后,立即摘除眼球(包括球后视神经2 mm),于角膜缘后0.5 mm处剪开眼球壁,将眼球壁在手术显微镜下剥离激光斑部位视网膜,逐级酒精脱水,常规石蜡包埋,经视乳头颜侧旁开1 mm纵向做4 μm厚的切片,烘干备用。
1.3 荧光素眼底血管造影(FFA)
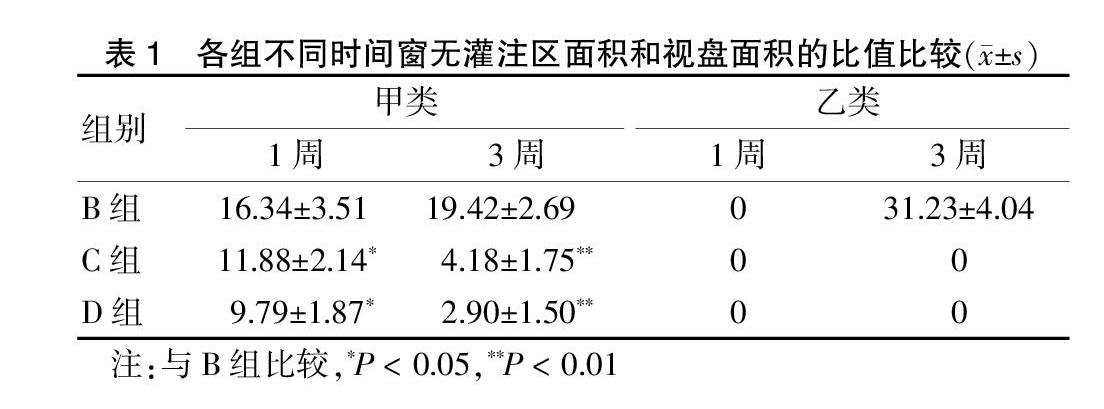
造模后1、3周对兔行FFA检查,将1周和3周的FFA结果应用Mias-2000型显微图象分析系统自动测量无灌注区(non perfusion area,NPA)和视盘(optic disk,OD)的面积,并求出比值(S=N/D)[5],分为有无灌注区、无新生血管(甲类)和有无灌注区、有新生血管(乙类)。
1.4 HE染色观察视网膜形态学
所取兔视网膜组织经脱水浸蜡、二甲苯溶液脱蜡、无水乙醇洗蜡、乙醇浸泡、自来水洗、苏木精染色、乙醇盐酸分色、伊红染色、乙醇分色脱水、二甲苯溶液透明、中性树胶封片等步骤,在光学显微镜下观察并拍照。
1.5 免疫组化法检测基质金属蛋白酶(MMP)-9的表达量
①制备蛋白样品:所取兔视网膜组织块称量后剪碎、裂解,离心后取上清液,-20℃保存;②Bradford 法测定蛋白质含量;③SDS-PAGE凝胶电泳;④转膜:垫滤纸,铺凝胶,去气泡,加电转移缓冲液;⑤抗体孵育和显色;⑥图像分析软件IPP 6.0对图像进行灰度分析。
1.6 统计学方法
采用SPSS 21.0软件进行分析。计量资料以均数±标准差(x±s)表示。多组比较用单因素方差分析,组间两两比较用q检验(S-N-K法),相关性分析用Bivariate分析。以P < 0.05为差异有统计学意义。
2 结果
2.1 FFA检查结果
A組未出现无灌注区与新生血管;造模后1周,B、C、D组均出现无灌注区,但C、D组渗漏、出血较B组少,无灌注区面积和视盘面积的比值明显低于B组,差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05);造模后3周,B组渗漏、出血的静脉周围无灌注区面积增大,并出现新生血管,C组渗漏、出血明显减小,D组渗漏、出血基本吸收,C、D两组无灌注区面积和视盘面积的比值明显低于B组,差异有高度统计学意义(P < 0.01)。见表1。
2.2 HE染色结果
A组:视网膜各层结构清晰,排列正常(图1A)。B组:造模后1周,视网膜组织水肿,细胞排列较乱,尚无新生血管索(图1B);造模后3周,出现大量的新生血管索(图1C)。C组:造模后1周,视网膜组织水肿,细胞排列紊乱(图1D);造模后3周,视网膜组织水肿减轻,无新生血管索(图1E)。D组:造模后1周,视网膜组织细胞排列大致清晰(图1F);造模后3周,视网膜组织水肿减轻,无新生血管索(图1G)。
2.3 MMP-9免疫组化结果
造模后1、3周,A组MMP-9表达量很少,B、C、D三组中B组MMP-9表达最强,C组次之,D组MMP-9表达最弱,其中B、C、D组MMP-9表达均明显高于A组,但C、D组MMP-9表达均明显低于B组,差异均有统计学意义(P < 0.05)。A、B、C组造模后1、3周组内MMP-9表达比较差异无统计学意义(P > 0.05),D组造模后3周MMP-9表达明显低于造模后1周,差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05)。见表2、图2(封三)。
3 讨论
RVO发病率高,是仅次于糖尿病视网膜病变的第二大致盲性视网膜血管病[6-8],其发生机制目前尚不明了[9-12]。现代药理研究认为,蛴螬对RVO的缺血视网膜组织有保护作用[1-2],能够治疗RVO所致的视网膜病理损伤。
MMPs家族包括多个结构相似、能够消化基质和基膜的酶[13-17],RVO患者视网膜组织中MMP-9高度表达[18-20],视网膜缺血后,促分裂原活化蛋白激酶(MAPKs)会刺激MMP-9上调,导致新生血管的发生。視网膜缺血后,再灌注损伤会引起视网膜炎症,而MMP-9又是重要的炎性因子[21],MMP-9贯穿着RVO的发生发展。
本研究结果显示:在正常视网膜组织中,MMP-9蛋白表达微弱。当视网膜组织缺血缺氧时,MMP-9蛋白显著表达。而蛴螬提取物可明显抑制MMP-9的表达,降低其并发RNV的风险,同时在其后的再灌注损伤中,又可通过抑制MMP-9蛋白表达达到抑制炎症的目的,提示蛴螬提取物在视网膜静脉阻塞的治疗中作用显著,但其是否还可通过其他因子途径达到治疗RVO的作用还需要进一步研究。
[参考文献]
[1] 邱晓星,彭清华,陈梅,等.蛴螬提取物对兔脉络膜新生血管中Ang1和PEDF表达的影响[J].国际眼科杂志,2012,12(11):2053-2058.
[2] 张波涛,彭清华,叶群如,等.蛴螬提取物对兔视网膜静脉阻塞模型视网膜组织ET-1表达的影响[J].湖南中医药大学学报,2012,32(9):8-11.
[3] 阳长明,侯世祥,罗英杰,等.蛴螬滴眼液中氨基酸成分的测定[J].湖南中医杂志,2001,32(1):57-59.
[4] 陈立军,王雨生.“二步法”激光诱导脉络膜视网膜静脉吻合术治疗兔视网膜中央静脉阻塞的视觉电生理变化[J].眼科新进展,2006,26(4):253.
[5] 唐坤,李素芬.视网膜分支静脉阻塞无灌注区范围、视野阈值与新生血管关系的研究[J].国际眼科杂志,2009,9(6):15-16.
[6] Wolf-Schnurrbusch U E K. Retinal Vein Occlusion[M]//Spectral Domain Optical Coherence Tomography in Macular Diseases. New Delhi:Springer,2017:147-150.
[7] Goldenberg D,Loewenstein A. Retinal Vein Occlusion[M]//Medical Retina. Karger Publishers,2017:32-41.
[8] Jonas JB,Monés J,Glacet-Bernard A,et al. Retinal vein occlusions [M]// Macular Edema. Karger Publishers,2017:139-167.
[9] Starr MR,Norby SM,Scott JP,et al. Acute retinal vein occlusion and cystic fibrosis [J]. Int J of Ret,2018,4(1):26.
[10] Prajapati VA,Vasavada D,Patel SM,et al. A study of evaluation of various risk factors of retinal vein occlusion [J]. Int J Res Med Sci,2017,2(3):1054-1057.
[11] Bucciarelli P,Passamonti SM,Gianniello F,et al. Thrombophilic and cardiovascular risk factors for retinal vein occlusion [J]. Eur J Intern Med,2017,44:44-48.
[12] Winegarner A,Wakabayashi T,Hara-Ueno C,et al. Retinal microvasculature and visual acuity after intravitreal aflibercept in eyes with central retinal vein occlusion:an optical coherence tomography angiography study [J]. Retina,2018,38(10):2067-2072.
[13] 倪素娜,刘静.基质金属蛋白酶及组织抑制物与Toll样受体在胎膜早破患者胎膜组织中的表达[J].河北医药,2018,40(1):28-31.
[14] Carpio LR,Bradley EW,Westendorf JJ. Histone deacetylase 3 suppresses Erk phosphorylation and matrix metalloproteinase(Mmp)-13 activity in chondrocytes [J]. Connect Tissue Res,2017,58(1):27-36.
[15] Manicone AM,Gharib SA,Gong KQ,et al. Matrix Metalloproteinase-28 is a key contributor to emphysema pathogenesis [J]. Am J Path,2017,187(6):1288-1300.
[16] Lebre MC,Vieira PL,Tang MW,et al. Synovial IL-21/TNF- producing CD4+ T cells induce joint destruction in rheumatoid arthritis by inducing matrix metalloproteinase production by fibroblast-like synoviocytes [J]. J Leukocyte Biol,2017,101(3):775-783.
[17] Naveed S,Clements D,Jackson DJ,et al. Matrix metalloproteinase-1 activation contributes to airway smooth muscle growth and asthma severity [J]. Am J Resp and Crit Care,2017,195(8):1000-1009.
[18] Chao HM,Chao WJ,Chen L. Retinal Ischemia:MMP-9;Its Relation to Resveratrol,Baicalein,S-allyl L-cysteine and Chi Ju Di Huang Wan [M]// The Role of Matrix Metalloproteinase in Human Body Pathologies. InTech,2017.
[19] Zhu SH,Liu BQ,Hao MJ,et al. Paeoniflorin suppressed high glucose-induced retinal microglia MMP-9 expression and inflammatory response via inhibition of TLR4/NF-κB pathway through upregulation of SOCS3 in diabetic retinopathy [J]. Inflammation,2017,40(5):1475-1486.
[20] Halder K,Banerjee S,Ghosh S,et al. Mycobacterium indicus pranii(Mw)inhibits invasion by reducing matrix metalloproteinase(MMP-9)via AKT/ERK-1/2 and PKCα signaling:A potential candidate in melanoma cancer therapy [J]. Cancer Biol Ther,2017,18(11):850-862.
[21] Li W,Suwanwela NC,Patumraj S. Curcumin prevents reperfusion injury following ischemic stroke in rats via inhibition of NF-κB,ICAM-1,MMP-9 and caspase-3 expression [J]. Mol Med Rep,2017,16(4):4710-4720.
(收稿日期:2018-10-09 本文編辑:张瑜杰)

