代谢综合征与基因多态性研究进展
楼雪勇 刘艳芬
【摘要】 代谢综合征是一类以高血压、肥胖、高脂血症、胰岛素抵抗等多种危险因素集合的临床代谢异常综合征,是由遗传与环境因素共同作用的结果,随着发病率逐渐增加已成为当前研究的热点,目前研究发现许多基因多态性与代谢综合征发病有关,但其发病机制还需进一步深入研究,本文就代谢综合征危险因素与基因多态性进行系统的综述。
【关键词】 代谢综合征; 基因; 多态性
doi:10.14033/j.cnki.cfmr.2019.03.084 文献标识码 A 文章编号 1674-6805(2019)03-0-03
Research Progress of Metabolic Syndrome and Genetic Polymorphism/LOU Xueyong,LIU Yanfen.//Chinese and Foreign Medical Research,2019,17(3):-177
【Abstract】 Metabolic syndrome is a clinical metabolic syndrome contains hypertension,obesity,hyperlipidemia,insulin resistance and other risk factors.It is the result of the combination of genetic and environmental factors,it has become a hotspot of current research with the increasing incidence,many genetic polymorphisms are found to be associated with the pathogenesis of metabolic syndrome,but the mechanism needs further study,this paper reviews the metabolic syndrome risk factors and gene polymorphism.
【Key words】 Metabolic syndrome; Gene; Polymorphism,
First-authors address:Central Hospital of Jinhua,Jinhua 321000,China
代謝综合征是一类以高血压、肥胖、高脂血症、胰岛素抵抗等多种危险因素集合的临床代谢异常综合征[1],是导致心脑血管疾病等慢性病发病的“源泉”,是遗传因素和环境因素共同作用的结果[2-3],随着社会经济的发展,人们生活习惯的改变,饮食不规律,代谢综合征发病率日益增高,成为严重威胁公共健康、增加医疗负担、致残率和致死率的主要危险因素[4]。近些年来,各地对代谢综合征的各相关研究因素展开了广泛的研究,鉴于本综合征与多种代谢相关疾病有密切的联系,2005年4月,
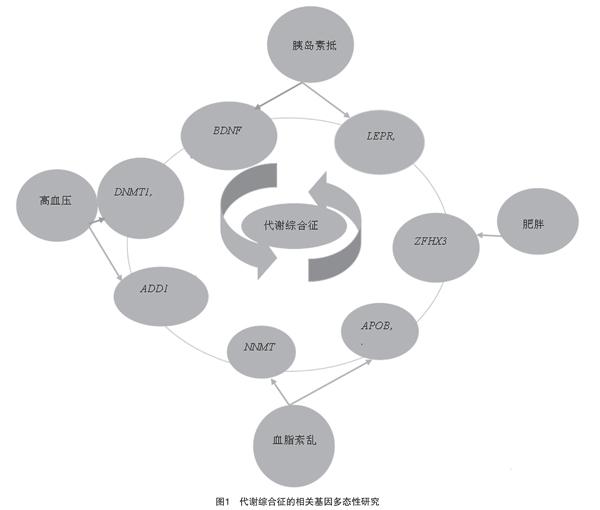
国际糖尿病联盟(IDF)就代谢综合征的诊断及防治提出了全球统一的诊断标准[5]。随着科学技术的发展和分子生物学水平的提升,代谢和相关基因的研究得到重视,目前已有研究证实基因多态性和代谢综合征相关,基因多态性是一种遗传变异方式,是指在一个生物群体中,同时和经常存在两种或多种不连续的变异型或基因型(genotype)或等位基因(allele),基因水平上的变异导致多态性的产生,一般发生在基因序列中非编码区域和无显著调节功能区。本文对代谢综合征各相关危险因素与基因多态性研究进行系统的综述,见图1。
1 代谢综合征相关基因多态性的研究
1.1 高血压相关基因多态性的研究
高血压对心脑血管疾病的影响地位使之成为重大的公共卫生问题[6],遗传因素对高血压有一定的影响[7]。
DNA甲基化转移酶1(DNA methyltransferase 1,DNMT1)位于染色体19p13.2,含有40个外显子和39个内含子,约有1620个氨基酸长度[8],DNMT1等位基因A位点rs2228611多态性会增加高血压风险,进一步调整性别后比较,发现只在男性中有统计学意义[9]。肿瘤坏死因子(tumor necrosis factor-a-308G/A,TNF-α-308G/A) 刺激细胞因子的产生,从而提高黏附分子的表达和增加中性粒细胞的活化,肿瘤坏死因子基因位于第6号染色体上,属于第三类区域人类白细胞抗原,促红细胞生成素人肝细胞受体A6基因(Erythropoietin-producing human hepatocellular receptor A6 gene,EPHA6)在韩国人群中研究发现,EPHA6 rs4857055 C>T位点TT基因型有更高的高血压风险[10]。
1.2 肥胖相关基因多态性的研究
肥胖是一种由遗传因素、饮食习惯因素、环境因素等多种因素引起的严重危害人类健康的慢性疾病,是导致多种慢性病如糖尿病、心血管疾病发生的危险因素。
根据全基因组关联研究(GWAS)确定,有97个基因位点与肥胖有关[11],锌指同源盒3(zinc finger homeobox 3,ZFHX3)基因作为增强人甲胎蛋白(AFP)基因的被编码蛋白基因,在朝鲜人群中研究发现,分析由7个位点(rs4788480,rs8055870,rs1010852,rs16971447,rs9930445,rs4788489,rs879324)多态性与肥胖密切相关[12]。
1.3 血脂紊乱相关基因多态性的研究
血脂是血液中游离或与其他分子结合的脂质,血脂紊乱主要表现为高胆固醇、高甘油三酯、低密度脂蛋白胆固醇升高及高密度脂蛋白胆固醇(HDL-c)水平降低,随着生活水平的提高及饮食习惯的改变,我国人群血脂紊乱人群日益增高,血脂紊乱是导致心脑血管疾病的重要危险因素[13-14]。
载脂蛋白B(Apolipoprotein B,APOB)是一个主要的乳糜微粒的结构蛋白,位于人类染色体2p23-24,包含28个内含子和29个外显子,全长43 kb,APOB rs1042034和rs676210多态性与高脂血症相关,其中rs1042034AG基因型 、rs1042034 AG+AA基因型、rs676210AG基因型及rs676210AG+GG 基因型增加高血压的风险因素分别是1.67倍、1.63倍、1.72倍及1.67倍[15]。尼克酰胺N-甲基转移酶(Nicotinamide N-methyltransferase,NNMT)rs694539多态性与高血脂显著相关,可能与rs1941404多态性对静息能量消耗的影响有关[16]。
1.4 胰岛素抵抗相关基因多态性的研究
胰岛素抵抗(Insulin resistance,IR)是导致代谢综合征的土壤,是指机体对胰岛素敏感性下降的一种表现形式,全球范圍内胰岛素抵抗患病率由于肥胖流行而增加[17]。对胰岛素敏感性遗传基础的进一步了解可能会带来更好的诊断和治疗选择,已有研究表明相关基因多态性与胰岛素抵抗密切相关。
在人类研究中,肥胖和BDNF基因多态性呈正相关。BDNF基因多态性Val66Met rs6265位点的66Met杂合子人群的BMI指数比Val66Met纯合子+66Val杂合子的人群低,全基因组关联研究也发现Val66Met等位基因变异与BMI相关[18],瘦素(Leptin)是一种内分泌激素,通过瘦素受体(Leptinreceptor,LEPR)的介导调节体内稳态起关键作用,编码瘦素基因多态性与代谢异常有关,LEPR rs11804091基因多态性影响胰岛素抵抗[19]。
2 结语与展望
随着分子生物学的不断发展,代谢综合征与基因多态性之间的关系不断被揭示,以往的相关综述主要侧重于某些随机的基因多态性与代谢综合征的研究,而本文是从代谢综合征的危险因素出发,总结各危险因素相关基因多态性与代谢综合征的关系。在代谢综合征的危险因素高血压、肥胖、脂代谢紊乱及胰岛素抵抗中均发现大量基因多态性影响导致代谢综合征的发生及发展,表明这些基因多态性在代谢综合征发生发展中发挥重要作用,提示相关危险因素可能通过影响基因多态性进一步导致代谢综合征的发生。
虽然代谢综合征与基因多态性已取得了一定的进展,但是还有很多方面未曾了解,比如基因多态性发生的时间及机制,基因多态性在代谢综合征发病过程中的重要程度,基因筛选的特异性,是否从代谢综合征进展终末期心脑血管疾病着手筛选基因特异性会更强,如心脑血管疾病的重要影响因素高同型半胱氨酸血症相关基因入手,研究其基因多态性与代谢综合征的关系[20]。虽然基因多态性与代谢综合征发病影响关系的具体机制并不十分明确,某些基因多态性对代谢综合征的诊断仍存在争议,但是随着分子生物学技术的不断进步和研究的不断发展,它们之间的关系会逐渐明了,人类将在代谢综合征的早期预防及治疗中取得重大进展。
参考文献
[1] Samson S L,Garber A J.Metabolic syndrome[J].Endocrinology and Metabolism Clinics of North America,2014,43(1):1-23.
[2] Yamaoka K,Tango T.Effects of lifestyle modification on metabolic syndrome:a systematic review and meta-analysis[J].BMC Medicine,2012,10(1):138.
[3] Povel C M,Boer J M,Reiling E,et al.Genetic variants and the metabolic syndrome:a systematic review[J].Obesity Reviews:an Official Hournal of the International Association for the Study of Obesity,2011,12(11):952-967.
[4] Appels C W,Vandenbroucke J P.Overweight,obesity,and mortality[J].The New England Journal of Medicine,2006,355(25):2699.
[5] Holt R I.International Diabetes Federation re-defines the metabolic syndrome[J].Diabetes,Obesity & Metabolism,2005,7(5):618-620.
[6] International Consortium for Blood Pressure Genome-Wide Association S,Ehret G B,Munroe P B,et al.Genetic variants in novel pathways influence blood pressure and cardiovascular disease risk[J].Nature 2011,478(11):103-109.
[7] Botzer A,Grossman E,Moult J,et al.A system view and analysis of essential hypertension[J].Journal of Hypertension,2018,36(5):1094.
[8] Subramaniam D,Thombre R,Dhar A,et al.DNA methyltransferases:a novel target for prevention and therapy[J].Frontiers in Oncology,2014,4(4):80.
[9] Chen H L,Li Z M,Liu J F,et al.Polymorphism of the DNA methyltransferase 1 gene is associated with the susceptibility to essential hypertension in male[J].Clinical and Experimental Hypertension 2018,40(3):1-7.
[10] Kim M,Yoo H J,Kim M,et al.EPHA6 rs4857055 C > T polymorphism associates with hypertension through triglyceride and LDL particle size in the Korean population[J].Lipids in Health and Disease,2017,16(1):230.
[11] Locke A E,Kahali B,Berndt S I,et al.Genetic studies of body mass index yield new insights for obesity biology[J].Nature,2015,518(7538):197-206.
[12] Yang S A.Association study between ZFHX3 gene polymorphisms and obesity in Korean population[J].Journal of Exercise Rehabilitation,2017,13(4):491-494.
[13] Williams P T,Franklin B A.Incident diabetes mellitus,hypertension,and cardiovascular disease risk in exercising hypercholesterolemic patients[J].The American Journal of Cardiology,2015,116(10):1516-1520.
[14] Contel N R.Perches for primate squeeze cages[J].Laboratory Animal Science,1989,39(6):537.
[15] Gu Q L,Han Y,Lan Y M,et al.Association between polymorphisms in the APOB gene and hyperlipidemia in the Chinese Yugur population[J].Brazilian Journal of Medical and Biological Research,2017,50(11):6613.
[16] Zhu X J,Lin Y J,Chen W,et al.Physiological Study on Association between Nicotinamide N-Methyltransferase Gene Polymorphisms and Hyperlipidemia[J].BioMed Research International,2016,2016(2):1-8.
[17] Einhorn D,Reaven G M,Cobin R H,et al.American College of Endocrinology position statement on the insulin resistance syndrome[J].Endocrine Practice:Official Journal of the American College of Endocrinology and the American Association of Clinical Endocrinologists,2003,9(3):237-252.
[18] Speliotes E K,Willer C J,Berndt S I,et al.Association analyses of 249,796 individuals reveal 18 new loci associated with body mass index[J].Nature Genetics,2010,42(11):937-948.
[19] Olza J,Ruperez A I,Gil-Campos M,et al.Leptin Receptor Gene Variant rs11804091 Is Associated with BMI and Insulin Resistance in Spanish Female Obese Children:A Case-Control Study[J].International Journal of Molecular Sciences,2017,18(8):1690.
[20] Niro A,Sborgia G,Sborgia A,et al.Hyperhomocysteinemia in bilateral anterior ischemic optic neuropathy after conventional coronary artery bypass graft:a case report[J].Journal of Medical Case Reports,2018,12(1):11.

