Effect of Auricular Piont Pressing Combined with Thunder-Fire Moxibustion on Abdominal Distension and Constipation After Thoracic Compression Fracture
Xue-Jian ZHANG, Ling TANG, Jing ZHANG, Li-Li DING, Si-Ting LIU, Ya-Li XIAO, Yue TANG
1Department of Limbs and Spine; 2Nursing Department; 3Department of Minimally Invasive Surgery, The Third Affiliated Hospital of Beijing University of Chinese Medicine, Beijing 100029, China
Abstract
Key words: Thunder-fire moxibustion; Auricular piont pressing; Abdominal distension; Constipation; Thoracic compression fracture
Introduction
Spinal fractures are very common traumas in orthopedics department, of which thoracic vertebral compression fractures account for more than 90%[1]. After thoracic vertebral compression fractures, patients suffers from severe pain, activity disorders, abdominal distension and constipation, which seriously affects their quality of life. Some studies have found that the degree of compression of the vertebral body is highly correlated with abdominal distension and constipation. The more severe the degree of vertebral compression, the more severe the abdominal distension and constipation will be.The probability of abdominal distension and constipation after simple thoracolumbar fracture is more than 60%[2].These complications usually appear 12 h after fracture,may last more than 5 days in the acute phase[3], but are easily overlooked in the early stage. However, when these symptoms appear, the intervention methods are extremely limited, and the curative effects are not satisfactory, so the related problems need to be solved urgently. In order to explore prevention and relief of abdominal distension and constipation after thoracic compression fracture to reduce the patient’s pain and improve patient’s comfort and quality of life, the application of auricular point pressing combined with thunder-fire moxibustion therapy for clinical intervention was studied, in order to clarify its clinical efficacy and application value.
Materials and Methods
Subjects
Totally 100 patients with thoracic compression fractures in our hospital from January 2015 to March 2017 were selected as subjects.
Inclusion criteria: (1) Patients who were diagnosed as thoracic vertebral compression fractures by CT scans and MRI, all fractures were caused by trauma; (2) Patients aged 50~80 years old, with clear consciousness; (3) Patients without serious heart, brain, liver, kidney and other important organ diseases; (4) Patients without damage on abdominal organs, blood vessels and nerve; (5) Patients agreed to participate in the study and signed informed consent forms.
Exclusion creteria: (1) Patients with other pathogenic factors (abdominal organ disease, history of habitual constipation, etc) that may cause abdominal distension and constipation; (2) Patients with poor compliance, or serious adverse events, or special physiological changes;(3) Patients unwilling to continue or give up treatment or discharge, as well as those that can not be fully followed up.
Grouping: 100 patients were randomly divided into 4 groups, the observation group 1 (n=25) which were treated with conventional nursing combined with auricular point pressing, observation group 2 (n=25)treated with conventional nursing combined with thunderfire moxibustion, observation group 3 (n=25) treated with conventional nursing combined with auricular point pressing and thunder-fire moxibustion, and the control group (n=25) adopted conventional nursing alone. In the observation group 1, there were 10 males and 15 females,with ages ranging from 56-75 (73.57±9.83) years. In the observation group 2, there were 12 males and 13 females,with ages ranging from 50-80 (71.84±8.61) years. In the observation group 3, there were 10 males and 15 females,with ages ranging from 54-78 (70.45±8.74) years. In the control group, there were 11 males and 14 females, with ages ranging from 55-82 (72.56±8.71) years. All patients underwent percutaneous kyphoplasty (PKP) and the surgical time was (45±10) min. There was no statistically significant difference in age, gender, surgical procedure and time among the four groups (P>0.05).
Treatment and nursing care for control group
In control group, general nursing was performed for patients with thoracic compression fractures, which including 4 points: (1) Living care: The room was kept quiet and comfortable. The patients were guided to keep the waist and legs warm, lie on hard bed, keep the spine straight, and turn over axially every 2 hours. The ventilative thin pillow with a 3-cm thick back pad helps to restore the normal physiological curvature of the lumbar spine, relieves the patient from abdominal distension and other symptoms, and increases patients’ comforts. Instruct patients to practice bowel movements in bed[4]. (2) Diet guidance: To guide patients to eat spleen appetizer and lubricative food, such as fungus, mustard, yam, potatoes,cabbage, spinach, etc. Diet are as follows: vinegar mixed fungus, yam pumpkin porridge, melon ribs soup,chrysanthemum hawthorn tea, etc. Avoid eating spicy and irritating foods such as pepper and garlic. (3) Emotional care: Patients with fractures are prone to produce complex psychological reactions, resulting in negative emotional reactions such as anxiety, depression, and fear[5], which seriously affects the treatment effect and rehabilitation of patients. Therefore, guide patients with empathy, patient persuasion and rational enlightenment to eliminate the patient’s bad mood. (4) Functional exercise: Guide the patients to do sputum pump function exercise within 1 week after fracture, and do straight leg raising training and other functional exercises in 1-2 week after fracture.
Treatment and nursing care for observation groups
On the basis of the control group, the auricular point pressing intervention was given to the observation group 1, the thunder-fire moxibustion intervention was given to the observation of group 2, and the auricular point pressing combined with the thunder-fire moxibustion intervention was to observation group 3.
Auricular point pressing: (1) Preparation of materials:cotton swabs, ear probes, tweezers, 75% alcohol, cowherb seed, ear stickers, ear acupoint pressing record table were prepared. (1) Acupoints selection: according to the characteristics of the disease and previous clinical research methods[6-7], the acupoints were selected including the main acupoints (large intestine, small intestine, sympathetic) and auxiliary acupoints (stomach, liver, spleen). (3) Operation method: firstly detect the sensitive points of the ear with the ear probe, and determine the pressing part, disinfect the ear skin with 75% alcohol cotton ball, and then use the tweezers to pick up the seeds of cowherb stick to the detected acupoints. And give appropriate pressure until the patient feel hot, numb, bloating, pain[8]. At the end of the operation, the basic information of the patient,the operation time were recorded in the ear acupoint pressing record table. (4) Pressing time, frequency and course of treatment: According to the theory of midnightnoon ebb-flow, the period of 7am-9am, 3pm-5pm or 9pm-11pm was selected as acupoint pressing time, and the acupoint pressing is performed in one ear for 3 to 5 minutes each time, 3 times a day, and then transferred to the corresponding acupoints of the other ear after 3 days,alternative pressing between the two ears, 7 days for a course of treatment, 21 days in total.
Thunder-fire moxibustion: (1) Preparation: Zhao’s thunderfire moxibustion, curved plate, lighter, gauze, thunderfire moxibustion record table were prepared. (2) Acupoint:According to the characteristics of the disease and literature reports[9], Zhongmu, Tianshu, Shenqi, and Qihai acupoints were selected. (3) Operation method: Ignite the thunderfire moxibustion, suspend about 2 cm on the moxibustion acupoint, apply moxibustion for 10 minutes at each acupoint, until the skin presents red. After the operation,recorded the patient’s basic information, operation time,etc. in the thunder-fire moxibustion record table[8]. (4)Time to moxibustion and course of treatment: According to the theory of midnight-noon ebb-flow, the moxibustion is carried out at the period of 7am-9am, 3pm-5pm or 9pm-11pm, 7 days for a course of treatment, 21 days in total.
Observational indicators
Record the first time of exhaust and defecation.
Statistical analysis
In this study, experimental data was entered after the database was established. All measurement data are expressed as mean ± standard deviation (±s). All data were statistically analyzed using SPSS 20.0 statistical software. All groups were compared using Kruskal-Wallis One-Way ANOVA, and the pairwise comparison between groups was performed using the pairwise t-test method.P<0.05 was considered statistically significant.
Results
A single factor variance analysis was used for the overall comparison of four groups, and the results showed that there was significant difference among four groups with regard to the first exhaust time (F=4.890, P=0.007) and the first release time (F=11.182, P=0.000). The efficacy of observation group 3 was significantly better than that of observation group 2, observation group 1, and control group (P<0.001), regarding the first exhaust time or the first defecation time. Observation group 2 and observation group 1 were also superior to the control group (P<0.05),but there was no statistical difference between observation groups 1 and 2 (P>0.05) (Figure 1, 2). The results clearly indicated that the auricular point pressing combined with thunder-fire moxibustion intervention for thoracic compression fractures had obvious effects on abdominal distension and constipation.
Discussion
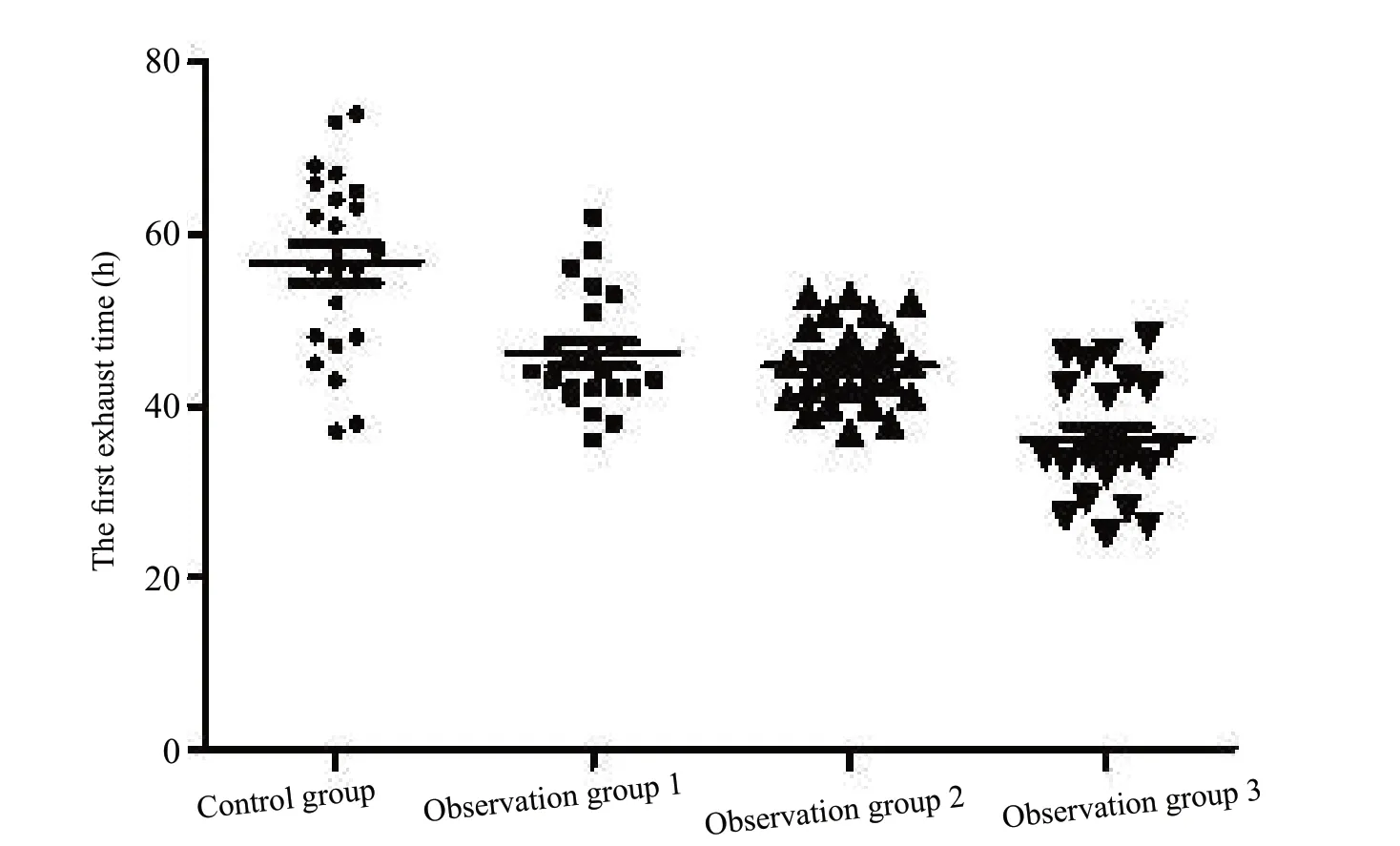
Figure 1 A scatter plot of the first exhaust time for each groupNotes: Observation group 1 vs. Control group, t=3.906, P=0.0003; Observation group 2 vs. Control group, t=4.716, P<0.0001; Observation group 3 vs. Control group; t=7.508, P<0.0001; Observation group 2 vs. Observation group 1, t=0.753, P=0.4552; Observation group 3 vs. Observation group 1, t=4.782, P<0.0001; Observation group 3 vs. Observation group 2, t=4.653, P<0.0001.
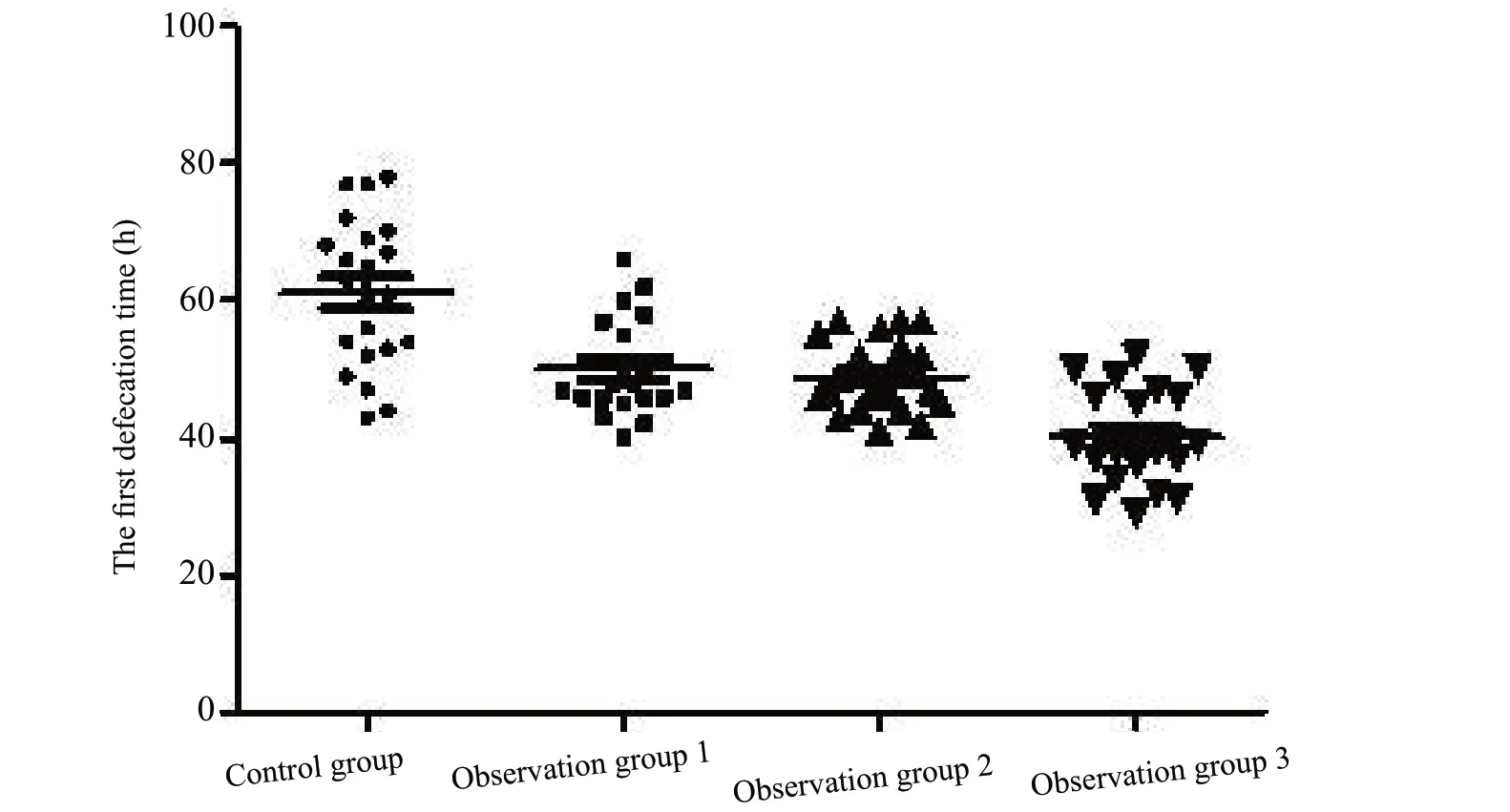
Figure 2 A scatter plot of the first defecation time in each groupNotes: Observation group 1 vs. Control group, t=4.079, P=0.0002; Observation group 2 vs. Control group, t=4.830, P<0.0001; Observation group 3 vs. Control group; t=7.674, P<0.0001; Observation group 2 vs. Observation group 1, t=0.673, P= 0.504; Observation group 3 vs. Observation group 1, t=4.759, P<0.0001; Observation group 3 vs. Observation group 2, t=4.674, P<0.0001.
One of the most common early complications of patients with thoracic fractures is abdominal distension and constipation. Patients with simple thoracolumbar fractures have symptoms of abdominal pain and difficulty in bowel movements when being hospitalized, but the degree is mild, the patient feels mild discomfort, and then the degree of abdominal distension gradually aggravates, which
has a significant impact on patient comfort[2]. Traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) believes that thoracolumbar vertebral compression fractures hurt the Du meridian and bladder meridians, which leads to qi and blood disorders,and then blood stasis, qi stagnation, and dryness in the intestines, thus obstructing the intestines. Modern medicine believes that after thoracolumbar fracture, the formation of retroperitoneal hematoma, stimulation or even oppression of autonomic nerves can cause lost of the self-control ability of the anal sphincter and rectal bowel movements,slowing intestinal peristalsis, and even paralysis. The feces stay in the intestines for too long, and the water is absorbed, which makes the stool dry and difficult to be passed[10]. At present, for abdominal distension and constipation caused by thoracolumbar fractures, modern medicine uses oral laxative drugs, Kaisailu glycerin enema, anal canal exhaust, diet adjustment and other nursing interventions, which is only belong to symptomatic intervention methods, unable to regulates organ function int rinsically. However, TCM nursing emphasizes that human body is an organic whole with internal organs such as viscera, meridians and qi and blood, so that we can distinguish one symptom from another.
Auricular piont pressing is effective in relieving the symptoms of abdominal distension and constipation caused by thoracolumbar fractures. As the Miscellaneous Diseases and Rhinoceros records, “The five viscera and the twelve meridians are all linked with the ear.” The ear is the place where the twelve meridians of the human body pass, intersect and terminate. Therefore, the ear is closely related to the meridians and the viscera. Any lesion in the body can be reflected through the relative meridian acupoints on the auricle. The auricular point pressing technology is based on the close relationship between the function of the meridian acupoints and the viscera of the human body, and stimulates the acupoints in the ear corresponding to the viscera to achieve the functions of dredging the meridians and regulating the blood and the internal organs[11]. In this study, pressing the large intestine and small intestine acupoints can promote intestinal peristalsis to enhance intestinal function.Pressing sympathetic acupoints can regulate the function of sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous system.Pressing liver acupoint can soothe the liver and relieve qi stagnation. Pressing the spleen and stomach acupoints can strengthen the spleen and stomach. So giving the above acupoints appropriate and effective stimulation can achieve the effect of regulating the qi movement and the internal organs, thereby effectively alleviating symptoms of abdominal distension and constipation.
Thunder-fire moxibustion also can effectively relieve the symptoms of abdominal distension and constipation caused by thoracolumbar vertebral fractures. Thunderfire moxibustion is an external treatment method based on the ancient Chinese medical law. It has been reported in the literature[12]that moxibustion can improve the symptoms of patients with constipation. The moxibustion strip contains agarwood, woody, frankincense, capillaris,scorpion, dry ginger, pangolin, musk, moxa and other drugs, possessing the characteristics of strong drug potency, fierce firepower and strong penetrability, with wide therapeutic scope[13]. When moxibustion strip burns, it generates heat and infrared radiation, forms a high-concentration drug area acting on the periphery of the lesion and the acupuncture point, and permeates into the deep tissue under the action of heat, eventually reaching the effect of invigorating qi, dispelling wind and dispersing cold, invigorating the spleen and kidney,improving peripheral blood circulation, and relieving patients’ discomfort[14]. In this study, Zhongwan acupoint were selected for strengthening the function of stomach and spleen. Tianshu acupoint can dredge large intestines,so that body fluid can pass through, Shenque point can rehabilitate the body by warming yang and rescuing patient from collapse. Qihai acupoint has the function of regulating qi, and helping to raise healthy qi. Together,through combining with acupuncture, Thunder-fire moxibustion on the above acupoints can achieve the goal of protecting the body function, and strengthening qi in the abdomen, adjusting the body weakness, enhance immunity and the defense functions, thereby effectively alleviating symptoms such as abdominal distension and constipation.
The results of this study clearly indicated that the efficacy of observation group 3 was significantly better than that of observation group 2, observation group 1 and control group (P<0.001), with regard to the first exhaust time and the first defecation time. Moreover, there was no statistical difference between the observation groups 1 and 2, and the observation groups 1 and 2 were also superior to the control group. Together, it can be seen that the auricular point pressing combined with thunder-fire moxibustion for the treatment of abdominal distension and constipation after thoracic compression fractures have clear curative effect, good feasibility, good clinical value and prospects, can be considered for application promotion.
Conclusion
TCM refers to the nursing work under the guidance of the basic theory of TCM, which integrates TCM culture and modern natural science culture. It is an important part of China’s nursing field and a unique nursing model in China[15]. TCM nursing technology has a long history.It is favored by patients for it has the advantages of simple operation, remarkable curative effects and low price, and possesses unique advantages in treating many chronic diseases, such as relieving abdominal distension and constipation. In summary, in this study, based on the close relationship between acupoints and organs and following midnight-noon ebb-flow theory, we uses auricular point pressing combined with thunder-fire moxibustion intervention, choose the large intestine and small intestine acupoints, give appropriate and effective stimulation on those acupoints to relieve the symptom of abdominal distension constipation. And by comparison to routine nursing, auricular point pressing or thunderfire moxibustion alone, it can be verified that auricular point pressing combined with thunder-fire moxibustion has better result in treating abdominal distension and constipation after thoracic compression fracture.
Declaration
The authors of this article declare no conflict of interests.
 Journal of Integrative Nursing2019年2期
Journal of Integrative Nursing2019年2期
- Journal of Integrative Nursing的其它文章
- Effect of Acupoint Massage on Cognitive Dysfunction: A Systematic Review
- The Effects of Simulation-Based Learning Using Virtual Reality in Nursing Student:A Meta-Analysis
- Application of Out-of-Hospital Extended Nursing in Brace Treatment of Patients with Idiopathic Scoliosis
- Quantitative and Qualitative Investigation of Traditional Chinese Medicine Nursing Protocols for Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
- Application of Stone Needle Therapy Based on Blood Stasis Theory in the Treatment of 36 Cases of Knee Osteoarthritis in Early and Middle Stage
- Application of Comprehensive Health Education in Nursing of Patients with Metrorrhagia and Metrostaxis Treated by Hysteroscopic Electrotomy
