Investigation and Analysis on the Physical and Mental Health Status of Intern Nurses in a Hospital, Gansu Province
Dong-Mei YAN, Dan-Lin LI, Hui-Hui ZHAO, Meng-Yao SHI
School of Nursing, Gansu University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Lanzhou 730000, China
Abstract
Key words: Nursing students; SCL-90; Norm; Comparative analysis
Background
With the awakening of people’s health consciousness,the concept of “three-point treatment and seven-point care” has gradually been accepted by people, which has brought about tremendous changes in the content and responsibilities of nursing work. At the same time, the demand for nursing work in the society is being improved constantly. In recent years, the relationship between doctors and patients has been quite tense, and vicious incidents such as violent injuries have frequently staged.Studies[1-3]have shown that nursing workers are five times more likely to be exposed to violence than other occupations, resulting in increasing nurses’ work pressure.The heavy work tasks and tremendous work pressures make the nurses’ physical and mental health face a severe test, making them a susceptible group of various psychological problems[4,5]. As a special group of medical services, nursing students play the dual role of nurses and students. They are under pressure from schools, medical environment, patients, and clinical teachers. We should pay more attention to their physical and mental health ,in order to provide innovative methods and ideas for the management of nursing interns in schools and hospitals.
Materials and methods
Research object
Students who practiced in a hospital in Gansu Province from July 2018 to March 2019 were selected as research objects. Inclusion criteria: Intems who voluntarily accept the questionnaire survey of this study. Exclusion criteria:Interns who could not be normally on duty during the study period; they are unwilling to cooperate with the investigators. A total of 146 questionnaires were distributed and 129 copies were collected. The recovery rate of the questionnaires was 88.36%. After eliminating invalid questionnaires, 121 valid questionnaires were obtained, with an effective rate of 93.80%.
Methods
Assessment tools: A questionnaire survey was conducted using the Symptom Checklist scale (SCL-90)[6]compiled by the American psychologist LRDero-gatis in 1973 to assess the mental health status of nursing students,and to Model[7], the national youth norm[8], college students norm[9]for comparative analysis. SCL-90 is an effective scale for clinical evaluation of mental health status of various populations. It contains a wide range of psychiatric symptoms, including feelings, emotions,thoughts, consciousness, behaviors, living habits,interpersonal relationships, eating and sleeping[10]. SCL-90 contains 90 items, each item is divided into five levels(from 0 to 4), 0 indicates no, 1 indicates mild, 2 indicates moderate, 3 indicates quite heavy, 4 indicates serious, the positive threshold for each entry is 0, that is to say, >0 indicates the presence of adverse psychological indicators in this aspect[11]. Ten factors, including somatization,obsessive-compulsive symptoms, interpersonal sensitivity,depression, anxiety, hostility, terror, paranoia, psychosis,and others (reflecting sleep and diet), All respondents to 90 projects were defined as valid questionnaires.
Survey methods: Questionnaires are used for questionnaire surveys. The questionnaires are distributed by the researchers. After the unified training investigators explain the purpose and requirements of the survey, the respondents fill out the questionnaires themselves and fill them out by anonymous means. The surveys are completed within 30 minutes and collected on the spot.
Statistical methods
All data were statistically analyzed using SPSS 19.0 statistical software. The measurement data were expressed as (± s), and the t test was used to compare with the norm score. P<0.05 was considered statistically significant.
Results
The scores of each factor of SCL-90 compared with the national youth norm
Compared with the norm of the youth group, the scores of the four factors such as somatization, obsessivecompulsive symptoms, terror, and anxiety in nursing students in a hospital in Gansu Province are higher than the norm of the national youth group (P<0.01), and the remaining factors are lower than the norm (P<0.01). See Table 1.
The scores of the factors of SCL-90
Compared with the national adult norm, the mental health status of nursing students in a hospital in Gansu Province was extremely significant (P<0.01), and the scores of six factors (somatic, obsessive-compulsive symptoms, depression, anxiety, horror, and psychosis)in the psychological test were higher than the national adult norm, and the difference was statistically significant(P<0.01). See Table 2.
SCL-90 scores of various factors
Compared with the national college norm, all the factors were extremely significant (P<0.01), among which the somatization factor was higher than the college norm, and the rest were lower than the norm. See Table 3.
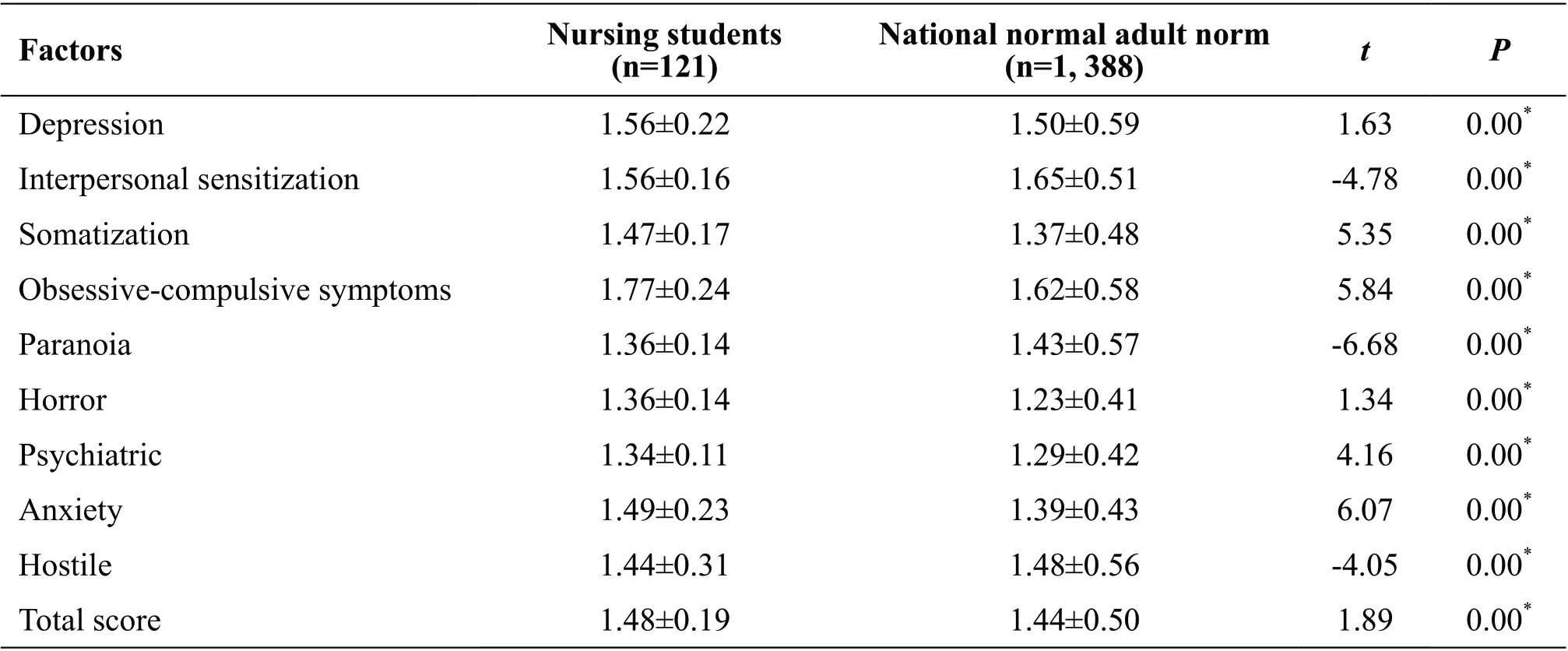
Table 1 Comparison of SCL-90 scores of nursing students in a hospital in Gansu Province with the national youth norm
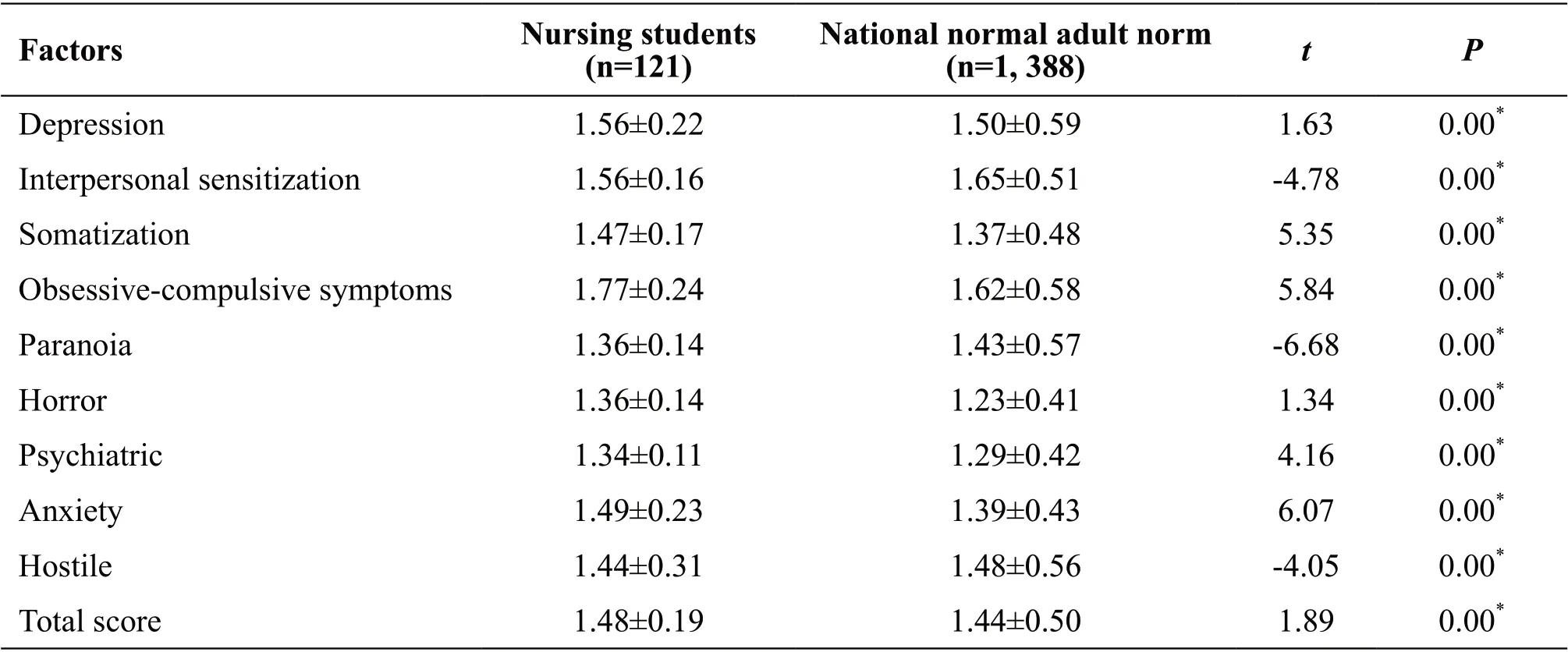
Table 2 SCL-90 scores of nursing students in a hospital in Gansu Province
Discussion
The SCL-90 scale has been introduced into China for more than 30 years. The scale has been used to study the psychological symptoms of Chinese nurses for more than 20 years. As a basic evaluation tool for researching nurses’ psychology, the scale has been widely used and the research scope is expanding. This survey shows that the mental health status of nursing students in a hospital in Gansu Province is higher than the national adult norm in the six factors of psychological testing (somatization,obsessive-compulsive symptoms, depression, anxiety,horror, and psychosis). Compared with the norm of the youth group, the scores of the four factors such as somatization, obsessive-compulsive symptoms, terror, and anxiety are higher and the remaining factors are lower.It is better than the national college students (except for somatic symptoms) (Table 1-3).
This survey shows that the symptoms of nursing students, such as somatization, compulsion, depression,and anxiety are more obvious than normal people.Somatic symptoms suggest a strong occupational fatigue tendency in the nursing population, which can also beconfirmed by some studies[12-13]. Medical staff are injured in physical illness, mainly with needle stab wounds and being beaten and scolded by patients; mental and psychological diseases are mainly insomnia and anxiety;skin system diseases are mainly acne; gynecological and obstetric system diseases are mainly dysmenorrhea and menstruation. This may be related to the overloaded work during the internship. Studies[14-15]have shown that, overload work during nursing students’ internships has affected students’ daily routines and disrupted their normal physiological laws. The reason is because the teaching teacher is ignoring the clinical nursing work,and neglecting the clinical nursing teaching work, let the students mechanically complete some simple and trivial nursing work. Students have experienced boredom,low status, decreased enthusiasm for work, decreased preparation for future work, and some even changed,resulting in a waste of nursing education resources and a large loss of nursing talents, which is unfavorable to the stability of nursing teams and the improvement of nursing quality. Therefore, it is important to help the nursing students to face the difficulties in the clinical practice internship and pay attention to their physical and mental health, especially relieving their depression and anxiety. considering the main reasons for the health of the nursing students, the research group should taken the following main measures: Firstly, emotional support:research findings[16], Family support contributed the most to the resolution of nurses’ bad psychology, followed by the support of friends, suggesting that when nursing staff have negative emotions and cannot be resolved, family,friends and relatives can get more psychological support by talking. At the same time, hospital administrators should pay attention to the mental health status of nursing students, and reserve individual psychological counseling for nursing students who have more serious psychological problems, and professional psychological counselors will conduct psychological treatment in the psychological counseling room of the hospital[17]. Secondly, improve the ability of nursing students to work: Pay attention to clinical nursing and teaching work, and work ability is the protective factor for nursing students’ anxiety.It is suggested that nursing students’ skills should be regularly trained and examined by their supervisors so as to improve their working ability and reduce their anxiety.Thirdly, occupational protection: There are mainly needle stab wounds, being beaten and scolded by patient, etc., so preventive training should be strengthened and relevant legal knowledge should be learned.
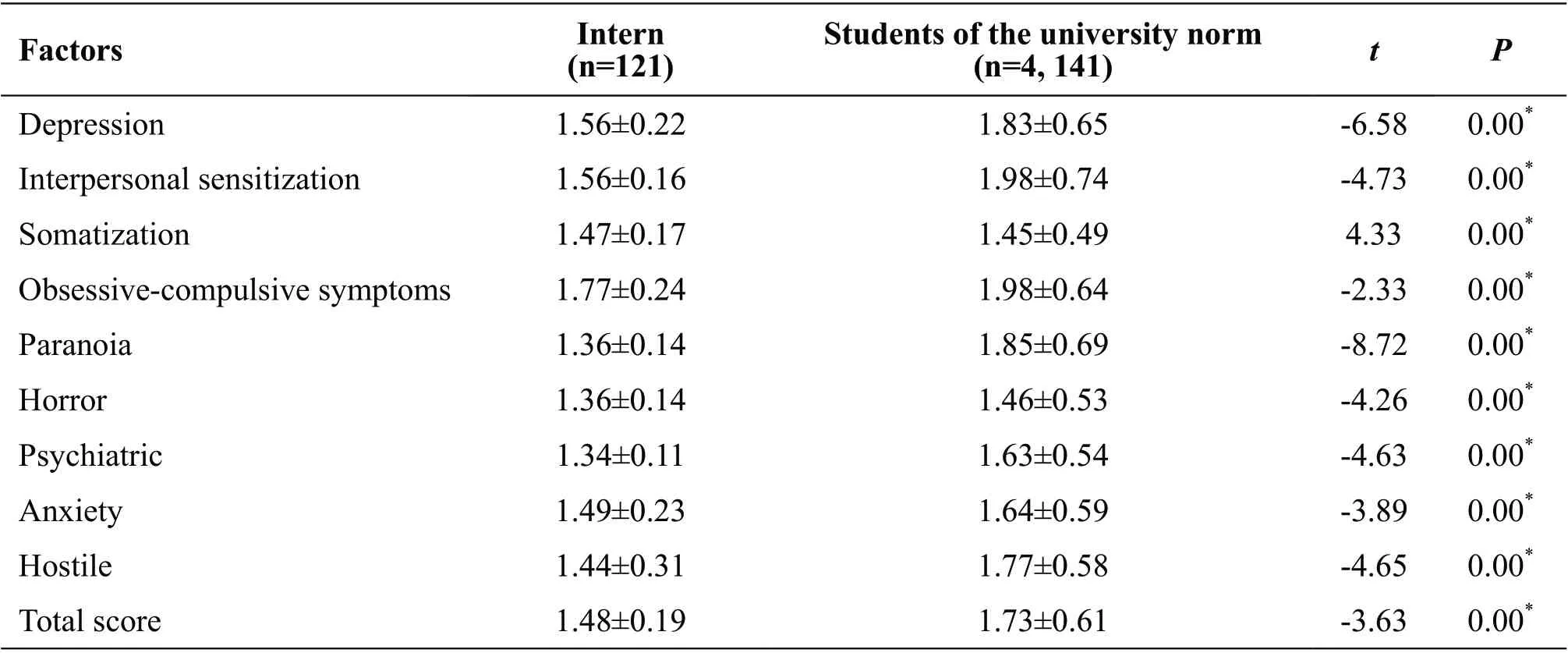
Table 3 Comparison of SCL-90 scores of nursing students in a hospital in Gansu Province with the norm of national college students
SCL-90 measures the psychological state of a person’s self-perception for a certain period of time (near a week), is susceptible to a number of factors, especially the impact of some major life events, and the nature of the nurse’s work determines the high density of stress events in the group work, therefore SCL-90 is lacking in assessing the true level of the comprehensive psychological status of nursing students, and further research is needed in the future.
Declaration
All authors of this article declare no conflict of interest.
 Journal of Integrative Nursing2019年3期
Journal of Integrative Nursing2019年3期
- Journal of Integrative Nursing的其它文章
- Correlation of Treatment Compliance, Treatment Attitude and Belief, and Quality of Life in Community Hypertensive Patients
- Five-Tone Therapy Plus Head and Face Massage Relieves Insomnia of Patients with Heart and Spleen Deficiency
- Construction of a Talent Cultivation Mode for Traditional Chinese Medicine Nursing Inheritance
- “Jianpi Tongwei Prescription”Acupoint Application Combined with Moxibustion for Gastric Retention in Elderly Patients with Nasal Feeding
- Analysis of Adaptation Process of Evidence-Based Interventions by Taking Post-Stroke Dysphagia Screening As an Example
--Based on a Series of Empirical Studies - Analysis of the Influence of Probiotics on Intestinal Micro-ecology and Related Diseases
