Therapeutic effect of Liyan Baidu decoction combined with oxygen spray on radioactive stomatitis in patients with nasopharyngeal carcinoma
Zi-Wei Qi, Xiang-Kun Yuan, Jian-Wei Hu, Jun-Jun Miao, Lei Gao, Yong-Xia Zhang,Guang-Ying Hou, Mang-Mang Cui
1Cangzhou Hospital of Integrated Traditional Chinese and Western Medicine, Hebei 06100, China.
Abstract
Key words:Radioactive mouth pharyngitis, Oxygen spray, New rehabilitation,Clinical observation
Introduction
Radiotherapy is a preferred treatment for nasopharyngeal carcinoma because of its concealed location and a narrow lumen, the surrounding structure is complex and 90% of nasopharyngeal carcinoma belongs to poorly differentiated squamous cell carcinoma and undifferentiated carcinoma.It is sensitive to radiotherapy and chemotherapy.Radioactive stomatitis is one of the common complications during radiotherapy in patients with nasopharyngeal carcinoma.Free radicals and reactive oxygen species generated by radiation can damage basal cells, preventing basal cell division and proliferation,migration to the surface, and keratinization.Radiation damage to capillaries can lead to local circulatory disorders, congestion, and edema on the surface of the mucosa, which can cause pain in the nerve endings.When the parotid gland is damaged, it will lead to bifurcation disorders of the parotid gland.In severe cases, there may even be ulcer hemorrhage and necrosis.[3-4].At present, Western medicine does not have a unified recommendation for the prevention and treatment of radioactive stomatitis in patients with nasopharyngeal carcinoma.
In the present study, 50 patients with radioactive stomatitis in patients with nasopharyngeal carcinoma admitted to our department at 2015.03-2017.05 were randomly divided into the treatment group (27 cases)and the control group (23 cases).Patients in the treatment group were treated with Liyan Baidu Decoction combined with oxygen spray, and patients in the control group were treated with Fukangxin oral solution.The result showed that Liyan Baidu Decoction combined with oxygen spray, had a better therapeutic effect on radioactive stomatitis.Liyan Baidu Decoction combined with oxygen spray may be a new strategy to treat radioactive stomatitis in the clinic.
Methods
Diagnostic criteria
Diagnostic criteria for acute radiation stomatitis were according to the diagnostic criteria of GBZ162-2004 radioactive stomatitis of the People's Republic of China:1, Irradiated dose: The radiation dose of the head and neck is 20-30Gy per exposure.2, clinical manifestations:within 6 months after irradiation or after exposure,mucosal congestion, edema, flaky mucositis,inflammatory or bloody secretions, ulcers, accompanied by pain and other symptoms; lesions involving the throat can cause difficulty breathing and eating disorders; increased purulent secretions when combined with mold infection.
Inclusion criteria
1, Pathological diagnosis of nasopharyngeal carcinoma,pathological type of poorly differentiated squamous cell carcinoma and according to clinical TNM staging M stage is M0; 2, The patient has a radiotherapy indication and is receiving radiation therapy for the first time.; 3,age > 18 years old, ≤ 70 years old; 4, Carlisle score >60 points; 5, The expected survival time is more than 3 months; 6, Patients signed informed consent, agreed to participate in the study, with good compliance, and can be followed up.
Exclusion criteria
(1), allergic or allergic to research drugs; (2), patients with malignant tumors of other pathological types of non-sickly differentiated squamous cell carcinoma of the nasopharyngeal carcinoma; (3), patients with primary malignant tumors other than nasopharyngeal carcinoma; (4), Patients with cardiovascular diseases,liver, kidney, hematopoietic system and other serious primary diseases; (5), patients with active tuberculosis and other serious infectious diseases; (6), previous and current mental illness and disturbance of consciousness cannot understand the content of the questionnaire and the terminally ill patients; (7), pregnant patients; 8, age<18 years old, >70 years old.
Treatment methods
Patients in both groups were treated with image-guided intensity-modulated radiation therapy (1.8-2Gy per time,5 times/week).The cumulative dose of primary lesions was 68-76 Gy, and the cervical lymph nodes were 60-70 Gy.
Treatment group: starting from the first day of radiation therapy, after oral treatment with sterile saline,the oral cavity was cleaned, and 70%~75% alcohol humidified oxygen was used to connect the self-made high-pressure spray gun to the oral cavity at 4~5 L/min,20~30 min/time, 2 times a day.(The direct current oxygen spray device was made by our department and has obtained the national patent, patent number:ZL201220228057.3) [5-6].Subsequently, patients in the treatment group were given Liyan Baidu Decoction orally.The composition of the decoction: 15g ofHerba Patriniae(Baijiangcao), 15g ofHouttuynia cordata(Yuxingcao), 30g ofHerba Hedyotis(Baihuasheshecao), 20g ofradix glehniae(Beishashen),15g ofRadix Ophiopogonis(Maidong), 15g ofhoneysuckle(Jinyinhua), 15g ofscrophularia ningpoensis(Xuanshen), 15g ofFritillaria thunbergii Miq(Zhebeimu), 5g ofpeppermint(Bohe), 10g oftokyo violet herb(Zihuadiding), 15g ofRadix Rehmanniae Recens(Shengdihuang), 10g of the root ofred-rooted salvia(Danshen).The dose of the drug can be adjusted according to the patient's symptoms and taken twice a day.
Control group: From the first day of radiation therapy, after oral administration, the oral cavity was cleaned with sterile saline, and the Kangfuxin oral solution was taken orally, 10 ml/time, 2 times a day.
Clinical management of patients in the two groups before, during and after radiotherapy
In the two groups, serious adverse reactions occurred during the treatment, and the same method was used for symptomatic treatment.
(1) Oral treatment: remove tartar before radiotherapy,repair the heel, remove metal braces, treat gingival inflammation,et al., and maintain good oral hygiene.
(2) Pain management: Before the radiotherapy analgesia, the pain relief treatment was given according to the WHO stepwise analgesic program for relieving cancer pain.Mild, moderate, and severe pain was treated with ibuprofen sustained-release tablets,tramadol hydrochloride tablets, and morphine hydrochloride tablets, respectively.If necessary,tramadol hydrochloride injection and morphine hydrochloride injection were used for analgesia.
(3) Leukopenia was administered subcutaneously with 150 μg of G-CSF (recombinant human granulocyte colony stimulating factor).
Observation indicators
The time of oral mucosal reaction and the cumulative radiation dose, the degree of radioactive oral mucosal reaction, the degree of radioactive salivary gland damage and the change of KPS score were compared between the two groups.
(1) Acute radioactive oral mucosal response scoring standard.According to the "Acute Radiation Response Scoring Criteria (SOMA1995)", it is divided into 5 grades including 0, I, II, III, IV.Grade 0: no change;Grade I: erythema/slight pain without painkillers;Grade II: plaque mucosal inflammatory serous exudation/moderate pain requiring painkillers; Grade III:fusion fibromyositis/severe pain requiring anesthetics Grade IV: ulcer, bleeding or necrosis.
(2) Acute radioactive salivary gland injury scoring standard.According to the "Acute Radiation Response Scoring Criteria (SOMA1995)", it is divided into 5 grades including 0, I, II, III, IV.Grade 0: no change;Grade I: slight dry mouth, slightly thick slight change in taste, such as metallic sensation, these changes do not cause changes in eating behavior, increase water intake when eating; Grade II: moderate to severe dry mouth,Saliva is thick, obvious taste changes; grade III:complete dry mouth; grade IV: acute salivary gland necrosis.
(3) Quality of life evaluation criteria.Karnofsky scoring criteria: improvement: Karnofsky score increased by≤ 10 points; stability: Karnofsky score change < 10 points; decreased: Karnofsky score decreased by ≤10 points.Compare the quality of life of patients before and after treatment.
Statistical Analysis
The collected case data were analyzed by SPSS16.0 software.The measurement data were analyzed by t-test;the count data were analyzed by Chi-square analysis.If the normal distribution was not met, the rank sum test was used.
Results
Radiation therapy was performed in the Yinzhou Chinese Medicine and Western Medicine Hospital during the period of 2015.03-2017.05, and 50 patients with radioactive stomatitis were diagnosed.Both signed an informed consent form.The random number table method was divided into 27 cases in the treatment group and 23 cases in the control group.There were no significant differences in gender, age, and radiation dose between the two groups (P> 0.05) (Table 1).
The time of oral mucosal reaction and the relationship between cumulative radiation doses
Compared with the control group, there was a significant difference in the time of oral mucosal reaction between the treatment group and the control group (P< 0.05).The treatment group appeared later than the control group, indicating that Liyan Baidu Decoction may effectively delay the occurrence time of oral mucosal reaction in patients with nasopharyngeal carcinoma.Moreover, there was a significant difference in the cumulative radiation dose of oral mucosal reaction between the treatment group and the control group (P< 0.05).The cumulative dose of the treatment group was higher than that of the control group,indicating that Liyan Baidu Decoction can effectively prevent acute radioactive oral mucosal reactions in patients with nasopharyngeal carcinoma (Table 2).
Comparison of oral mucosal reaction index between two groups of patients with different radiotherapy doses
When the radiotherapy dose was 10Gy, 30Gy, 50Gy,and the end of radiotherapy, the oral mucosal response index was significant statistically in the treatment group compared with the control group (P< 0.05).It indicates that Liyan Baidu Decoction may effectively reduce the degree of radiation oral mucosal damage in patients with nasopharyngeal carcinoma (Table 3).
Comparison of salivary gland damage index in two groups of patients with different radiotherapy doses
When the radiotherapy dose was 10Gy, 30Gy, 50Gy,and the end of radiotherapy, the salivary gland lesions were significantly statistically in the treatment group compared with the control group (P< 0.05).It is indicated that Liyan Baidu Decoction combined with Oxygen Spray can effectively reduce the degree of oral radiation mucosa and salivary gland damage in patients with nasopharyngeal carcinoma (Table 4).
Comparison of KPS scores before and after treatment in both groups
Table 5 shows that the KPS scores of the two groups were improved compared with those before treatment,but the quality of life was higher in the Lixue Baidu Decoction combined with the Oxygen Spray group than in the control group.The difference was statistically significant (P< 0.05).
Safety evaluation
There were no obvious adverse drug reactions in 27 patients in the treatment group and 23 patients in the control group, indicating that the test drug was safe.
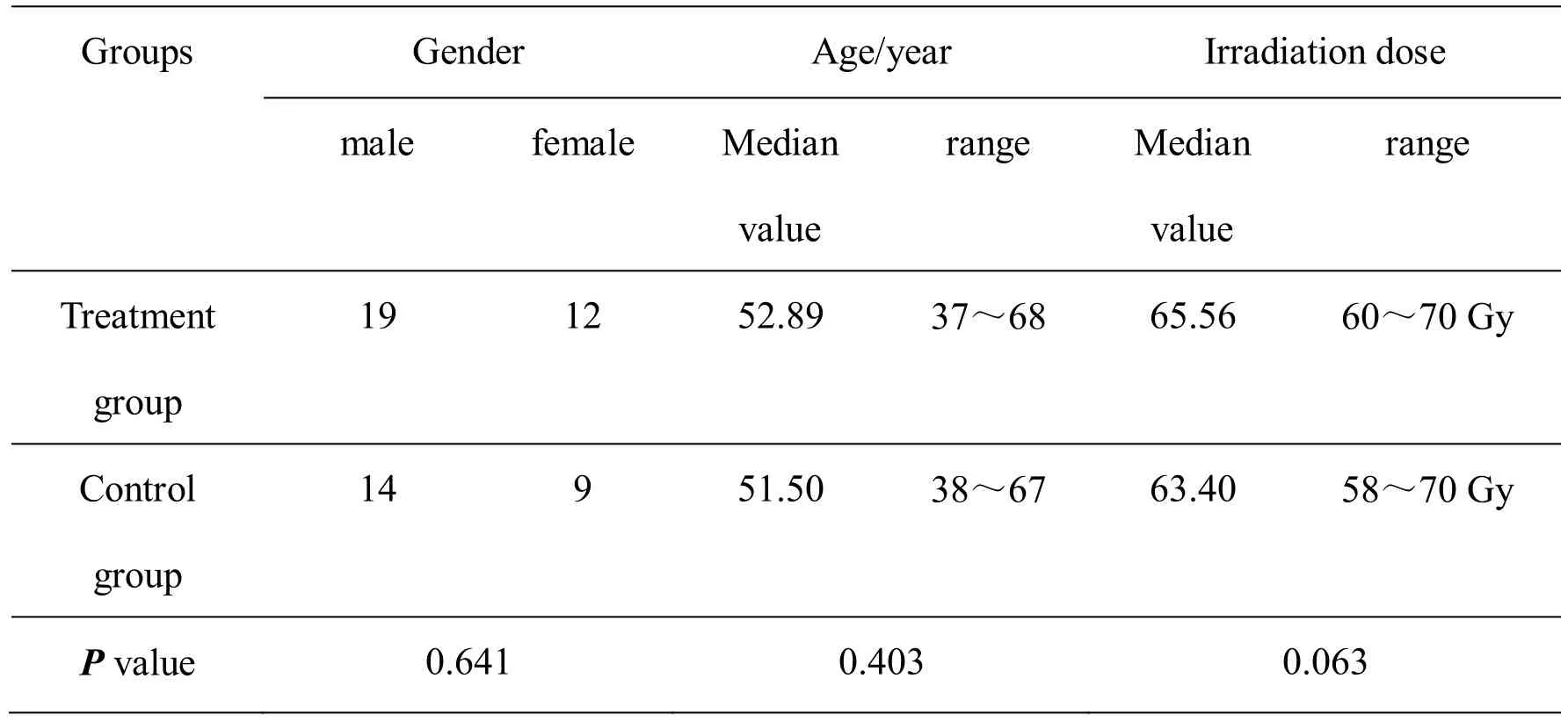
Table 1 Baseline of patient's characteristics

Table 2 The time of oral mucosal reaction and the relationship between cumulative radiation doses
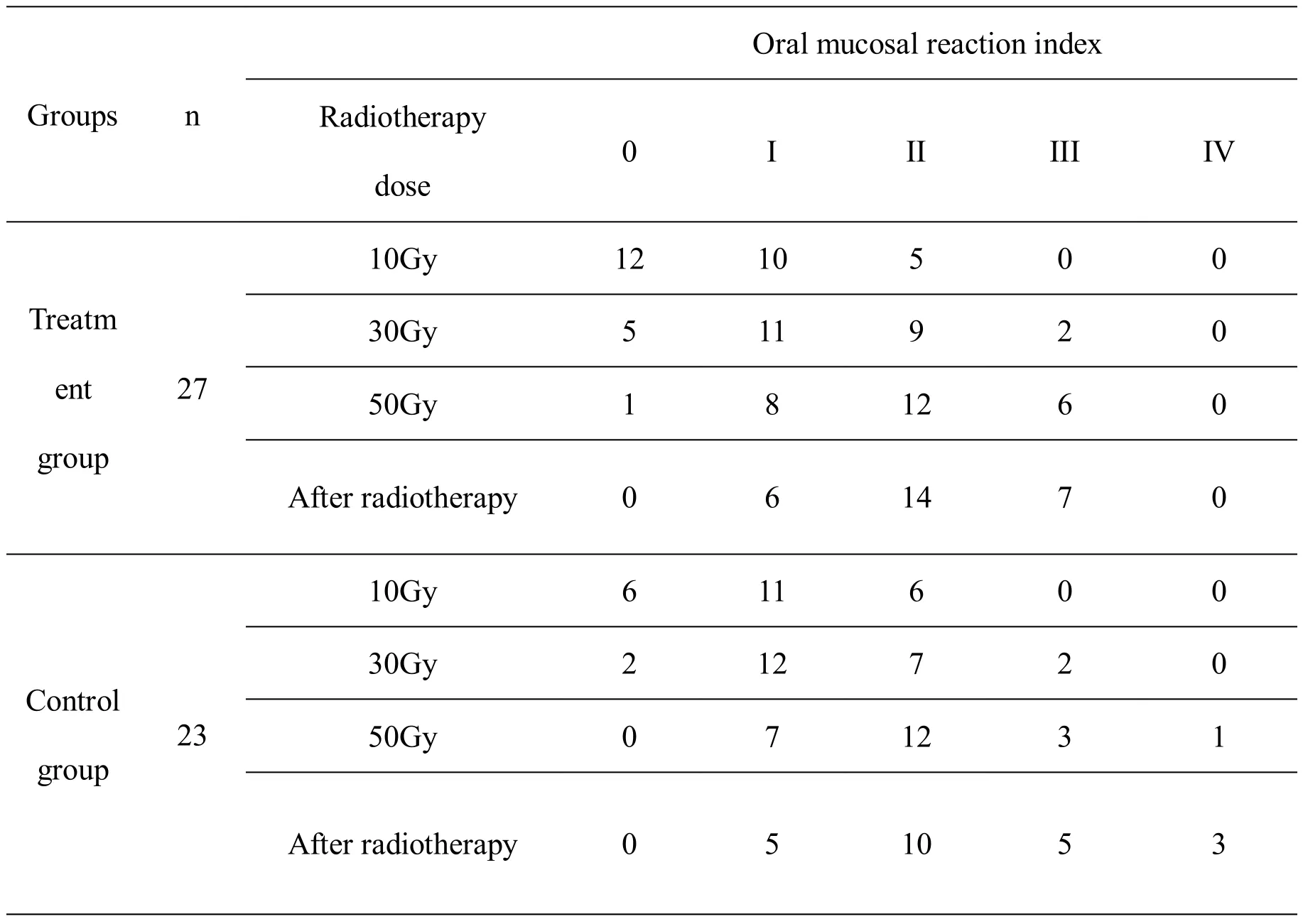
Table 3 Oral mucosal reaction index in two groups of patients
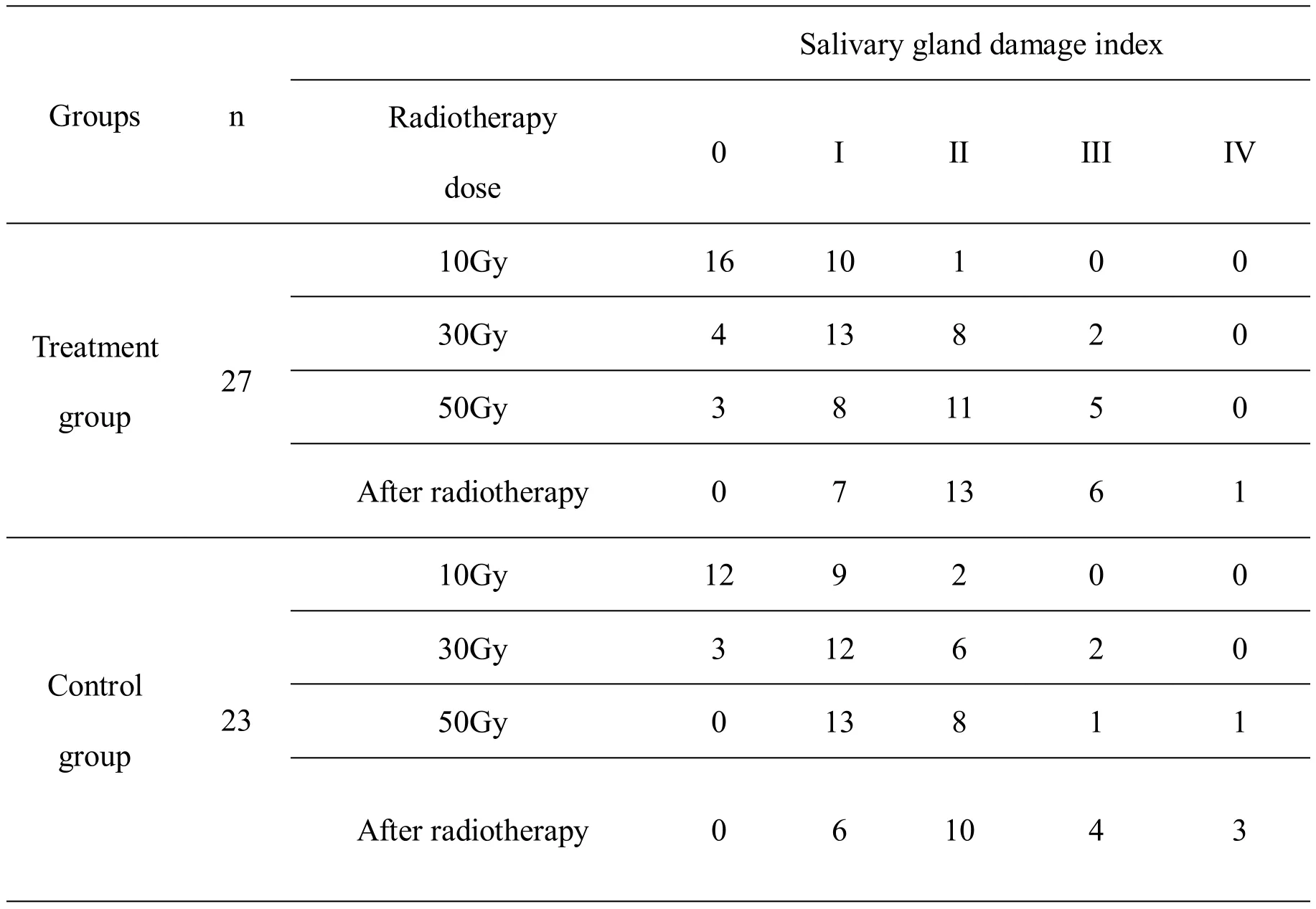
Table 4 Salivary gland damage index in two groups of patients
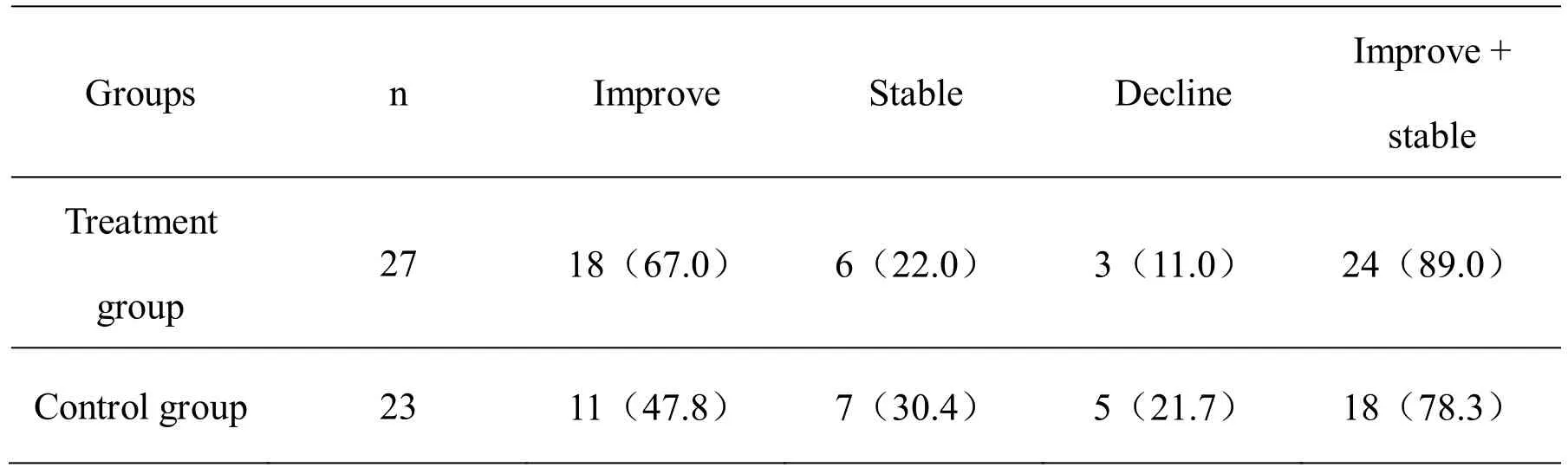
Table 5 Comparison of KPS scores before and after treatment in both groups [example (%)]
Discussion
Radioactive oropharyngeal inflammation is a side-effect of a high incidence of radiation therapy in head and neck.It is characterized by local redness, pain,mucosal damage, and even dysphagia.It seriously affects nasopharyngeal carcinoma.The quality of life of the patient may even lead to interruption or discontinuation of radiotherapy directly affecting the therapeutic effect and prognosis.Oral mucosa is very sensitive to radiation damage.After exposure to radiation, the main pathological manifestations are fibroblast degeneration and massive reduction of capillaries, telangiectasia, and local congestion, and with the progress of radiotherapy, it will further lead to abnormal proliferation, swelling, microcirculation dysfunction, insufficient blood supply, and even fibrotic changes.Studies have shown that removing superoxide anion radicals in the skin or mucosal tissue, mucosal damage caused by radiotherapy can be alleviated or avoided [7-10].Studies have shown that Kangfuxin oral solution has a significant effect on radioactive oropharyngeal, and its effect has been clinically recognized [11-12].Therefore, we chose Kangfuxin oral solution as the treatment method of the control group.
Chinese medicine believes that the radiation is "hot and poisonous evil", and the radioactive oropharyngeal inflammation is attributed to the throat category.It is believed that the radiation is the evil of smoldering heat and yin, and the yin and yang are depleted, and the qi and yin deficiency is caused by the qi and yin [13].In traditional Chinese medicine, the treatment of the cause and pathogenesis is mainly based on the treatment of Qingrejiedu, Yangyin Runfei, Yiqi Huoxue Huayu.The Liyan Detoxification Soup used in this study is the experience of our department for preventing and treating radiation oropharyngeal disease for many years.The prescriptions are based on the principle of clearing away heat and dispelling yin and nourishing yin.
The traditional Chinese medicine is succulent,Scutellaria, Hedyotis diffusa, and northern sand ginseng.The composition of Ophiopogon japonicus,Honeysuckle, Scrophulariaceae, Fritillaria, Peppermint,Purple Flower Ding, Shengdi and Salvia miltiorrhiza Bge., after clinical certification, can effectively reduce radiation oropharyngeal inflammation, relieve symptoms and improve quality of life.Modern pharmacological studies have found that P.sylvestris,Houttuynia cordata, Hedyotis diffusa, Honeysuckle,Viola, D.chinensis, and Salvia miltiorrhiza have anti-pathogenic microorganisms, and various pathogenic bacteria such as Staphylococcus aureus and pneumococcus Hemolytic streptococcus, Escherichia coli, pathogenic bacillus, Pseudomonas aeruginosa,Vibrio cholerae, Salmonella typhi, Paratyphoid bacillus,Mycobacterium tuberculosis,et al.have certain inhibitory effects; honeysuckle and Houttuynia have antipyretic and anti-inflammatory effects, It can inhibit the release of inflammatory factors; Hedyotis diffusa,Houttuynia cordata,et al.have antiviral effects;honeysuckle, Scrophulariaceae, Houttuynia cordata,Salvia miltiorrhiza, and peppermint can regulate immunity and improve the body's immunity [14-15].This Chinese medicine detection contains various anti-oxidant, anti-inflammatory, anti-bacterial,anti-tumor, and other active ingredients has an obvious anti-radiation effect and can activate macrophages,while macrophages can synthesize endogenous alkaline(Fibroblast growth factor).High-flow oxygen inhalation may improve local blood circulation and increase local oxygen partial pressure, thereby promoting oxygen metabolism and granulation tissue formation in wound cells, and promoting healing of ulcerated mucosa.The combination of the two can better remove superoxide anion radicals in the skin or mucosa, which is beneficial to reduce the inflammatory reaction of the wound,accelerate the growth of granulation tissue and promote wound healing [16-17].
In this study, Liyan Baidu Decoction combined with Oxygen Spray was used to treat radioactive oropharyngeal cancer of nasopharyngeal carcinoma.The time of oral mucosal reaction was significantly different between the treatment group and the control group (P< 0.05).The treatment group appeared later than the control group.It indicates that Liyan Baidu Decoction can effectively delay the time of acute radioactive oral mucosal reaction in patients with nasopharyngeal carcinoma.Compared with the control group, the cumulative radiation dose of the oral mucosal reaction was significantly different between the treatment group and the control group (P< 0.05).The cumulative dose of the treatment group was higher than that of the control group, indicating that Liyan Baidu Decoction may effectively prevent acute radiation Oral mucosal reaction in patients with nasopharyngeal carcinoma.When the radiotherapy dose was 10Gy,30Gy, 50Gy and the end of radiotherapy, the oral mucosal response index was significant statistically in the treatment group compared with the control group (P< 0.05).When the radiotherapy dose was 10Gy, 30Gy,50Gy and the end of radiotherapy, the degree of salivary gland damage was significantly statistically between the two groups (P< 0.05).It shows that Liyan Baidu Decoction may effectively reduce the degree of oral radiation mucosa and salivary gland damage in patients with nasopharyngeal carcinoma.Through this study, we can see that Liyan Baidu Decoction combined with Oxygen Spray has a significant effect on patients with nasopharyngeal carcinoma with radioactive pharyngitis, which may delay the time of acute radioactive oral mucosal reaction, reduce the oral mucosal reaction and salivary gland damage at each radiotherapy stage, and ensure the smooth progress of the radiotherapy process, and to improve the quality of life of patients, safe and no adverse reactions appear, it is worthy of clinical application.
- Cancer Advances的其它文章
- Traditional Chinese Medicine for Treatment of Apatinib-induced Hand and Foot Skin Reaction:A case report
- Immunoregulation of KangAi injection combined with chemotherapy in advanced non-small cell lung cancer:a systematic review and meta-analysis
- Anti-tumor mechanism of Angelica and its compound preparations
- Research progress on radiation-induced bystander effect
- Study on the technical specification of Miao doctor's medicinal acupuncture therapy for interventional cancer pain

