Exploring Urban Population Forecasting and Spatial Distribution Modeling with Artificial Intelligence Technology
Yan Zou , Shaoliang Zhang and Yanhai Min
Abstract: The high precision population forecasting and spatial distribution modeling are very important for the theory and application of population sociology, city planning and Geo-Informatics.However, the two problems need to be solved for providing the high precision population information.One is how to improve the population forecasting precision of small area (e.g., street scale); another is how to improve the spatial resolution of urban population distribution model.To solve the two problems, some new methods are proposed in this contribution.(1) To improve the precision of small area population forecasting, a new method is developed based on the fade factor and the slide window.(2) To improve the spatial resolution of urban population distribution model, a new method is proposed based on the land classification, public facility information and the artificial intelligence technology.For validation of the proposed methods, the real population data of 15 streets in Xicheng district, Beijing, China from 2010 to 2016, the remote sensing images and the public facility data are collected and used.A number of experiments are performed.The results show that the spatial resolution of proposed model reaches 30m*30m and the forecasting precision is better than 5% using the proposed method to forecast the population of 15 streets in Xicheng district in the next four years.
Keywords: Population forecasting, spatial distribution, cellular automata, multi-agent system.
1 Introduction
Urban population forecasting and spatial distribution can provide important information to local governments, businesses and academics for various purposes.The inaccurate urban population information will lead to the failure of city planning, economic investment and public resource allocation.In contrast, the high precision population information can improve the urban sustainable development and the utilization efficiency of public resources.Therefore, many scholars have investigated different methods to urban population forecasting and spatial distribution [Clark (1951); Wu and Murray (2005); Wilson (2015); Zou, Zhang and Wang (2018)].
In general, there are two kinds of population forecasting models.One is the demographic model which is known as the “golden models”, such as double-region model, multiregion model, queue group element model, Hamilton-Perry model [Isserman (1993); Smith and Tayman (2003); Renski and Strate (2013)].The demographic model can obtain the high precise results of the large area population forecasting (such as a country, a province, a state), where Mean Absolute Percentage Error (MAPE) will be less than 6% [Wilson (2016)].However, it is not suitable for the small area population forecasting since the small area is lack of the necessary population statistical information, such as birth rate, death rate, migration rate, etc.Another is the pure mathematic model, such as linear model, exponential model, mixed model, gray model, autoregressive model [Armstrong (2001); Baker, Ruan, Alcantara et al.(2008); Deng (2010)].These models are often used to forecast population of small areas, such as a district, a block, a street [Chi and Voss (2011)].However, the population forecasting precisions of these pure mathematic models are poor, where MAPE is about 10% [Zou, Zhang and Wang (2018)].Tab.1 shows the merits and demerits of demographic model and pure mathematic model.
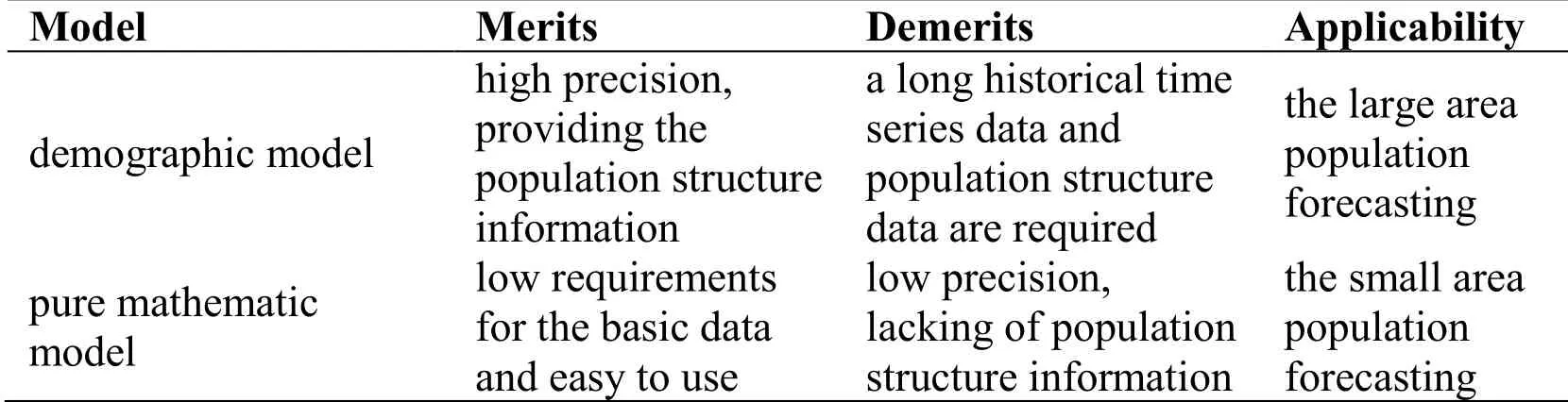
Table 1: Comparison between demographic model and pure mathematic model
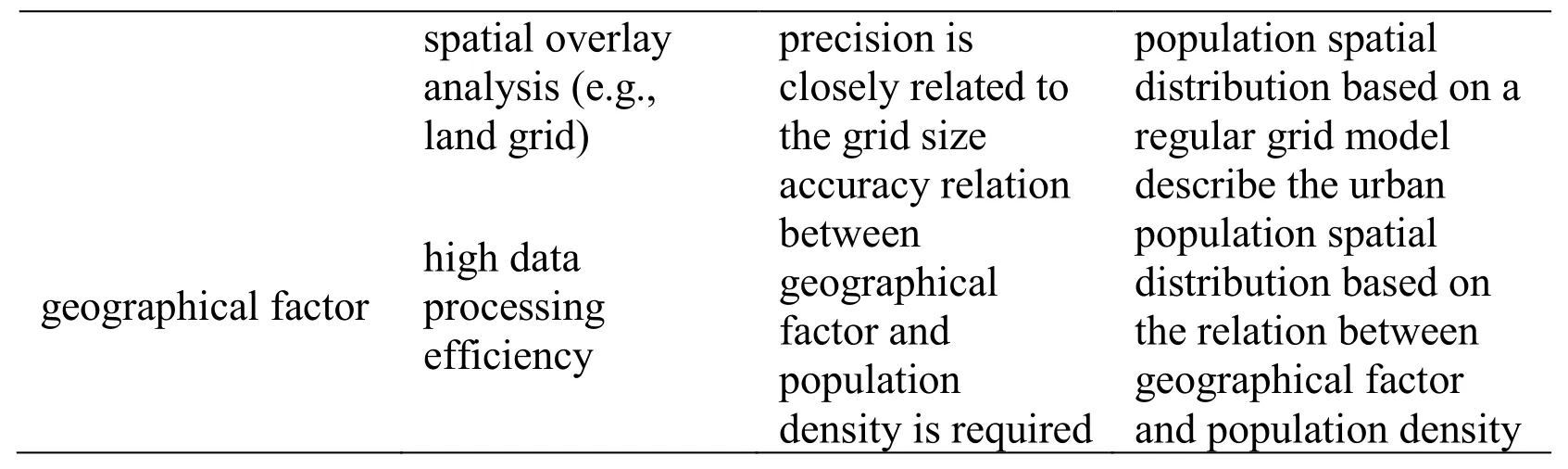
From Tab.1, it is known that neither the demographic model nor the pure mathematic model can provide the spatial distribution information of urban population.However, it is very significant for government, business and individual to make a practical policy, planning and investment that the high precision spatial distribution information of urban population.Therefore, it is attracting more and more research interests of the urban population spatial distribution modeling [Vidyattama and Tanton (2010)].Currently, there are three kinds of urban population spatial models: a) population density model [Clark (1951); Tanner (1961); Smeed (1961); Anderson (1985)]; b) spatial interpolation model [Tober (1979); Lam (1983)]; c) geographical factor model [Harvey (2002); Tian, Chen, Yue et al.(2004); Xu, Mei and Han (1994); Zhuo, Chen, Shi et al.(2005)].Tab.2 summarizes the characters and applicability of these urban population spatial distribution models.
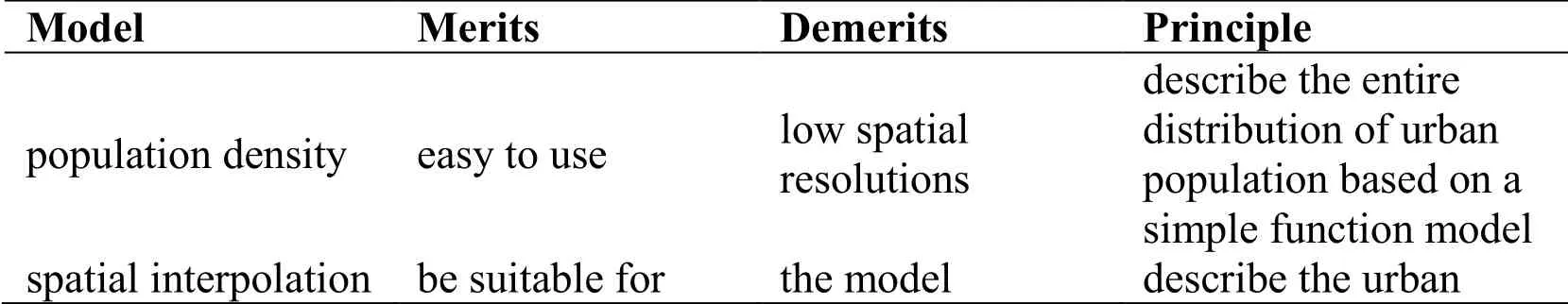
Table 2: Characters of current urban population spatial distribution models
spatial overlay analysis (e.g., land grid) precision is closely related to the grid size population spatial distribution based on a regular grid model geographical factor high data processing efficiency accuracy relation between geographical factor and population density is required describe the urban population spatial distribution based on the relation between geographical factor and population density
From Tab.2, the population density model is easy to use, but its spatial resolution is low.The spatial interpolation model can reach a high spatial resolution if the mesh is sufficiently dense that the numerical approximation is an accurate one, but the additional computational burden may not be tolerable.The geographical factor can improve the data processing efficiency, but it is very difficult to accuracy establish the function relation between geographical factor and population density.Therefore, it is necessary to develop a high spatial resolution and easy-to-use urban population distribution model.
In this study, the methods of high precision small area population forecasting and high spatial resolution urban population distribution modeling are investigated.To improve the precision of small area population forecasting, a new method is developed based on the fade factor and the slide window; and to improve the spatial resolution of urban population distribution model, a new method is proposed based on the land classification, city public facility information and the artificial intelligence technology.For validation of the proposed methods, the real population data of 15 streets in Xicheng district, Beijing, China from 2010 to 2016, the remote sensing images and the public facility data are collected and used.The results show that the spatial resolution of proposed model reaches 30 m*30 m and the forecasting precision of each street population is better than 5%.In the following, Section 2 introduces the study area, data and methods in this study; Section 3 presents the experimental results and analysis; Section 4 summarizes the main points and contributions of this paper.
2 Study area, data and methods
2.1 Study area
The study area is the Xicheng district, Beijing city, China.Beijing is the capital of the People's Republic of China.There are 16 districts in Beijing city and the Xicheng district is the center of Beijing, where the state council of China and the other important administrative organizations of China are located in Xicheng district.Therefore, the population density of Xicheng district is the largest in the 16 districts of Beijing, which reaches 28,793 people per km2in 2016, and the registered population is counted and the unregistered population is not included.Actually, the number of unregistered population is very large in Xicheng district.Therefore, the real population density of Xicheng district is larger than the above value.It is noted that the administrative area of Xicheng district was adjusted in 2010, where the Xuanwu district was merged into the Xicheng district.Therefore, the study area of this paper means the merged Xicheng district.The Fig.1 shows the population spatial distribution of 16 districts of Beijing city and 15 streets of Xicheng district in 2016.

Figure 1: Population spatial distribution of 16 districts of Beijing city (a) and that of 15 streets of Xicheng district (b) in 2016
It is known that the population distribution of Beijing like a group of concentric rings from the Fig.1(a), where the population densities of central areas (I, II) are the largest, and that of outer suburbs (XII, XIII, XIV, XV, XVI) are the smallest.This kind of population spatial distribution was described by Clark, see Clark [Clark (1951)].However, it is only suitable for modeling the population distribution of large area (e.g., Beijing city).The population spatial distribution of small area (e.g., Xicheng district) is different in the Fig.1(b), which is effected by various kinds of factors, such as land type, public facility, house price, etc.Therefore, the high spatial resolution model should be developed to describe the real distribution of urban population.
2.2 Data
In this study, there are three kinds of data are collected and used: a) the population data of 15 streets in Xicheng district, Beijing from 2010 to 2016; b) the remote sensing images of Xicheng district, Beijing from Landsat in 2016; c) the spatial distribution of public facilities of Xicheng district, Beijing from 2010 to 2016.The special information of three kinds of data is listed in the Tab.3.

Table 3: Study data type, content and source

c Public Facility digital map of subway station, school, hospital, shop center in Xicheng district 2010-2016 www.openstreetmap.org
2.3 Methods
2.3.1 Population forecasting method
The purpose of this study is that constructing a high precision and high resolution population spatial distribution model of Xicheng district, Beijing city, China.Therefore, the total number of populations of each street should be obtained in different year firstly.The population data of 15 streets in 2010 and 2012 is taken as the basic data, and the population of 15 streets in the next 4 years is forecasted, respectively.Six forecasting models are used and the population data of 15 streets (2013-2016) from Beijing Municipal Bureau of Statistics are taken as the true values to validate the forecasting precision of each model.The forecasting models include linear model, improved index model [Baker, Ruan, Alcantara et al.(2008)], grey model [Deng (2010)], sharing model of the population scale constant, constant model of the population growth rate difference [Davis (1995)] and sharing model of population growth variable [Wilson (2015)], of which the first three models are pure mathematical model, and the latter three models are the forecasting models with total population constraint information.And a new method based on the fade fact and slide window is adopted to improve the precisions of these models for small-area population forecasting [Zou, Zhang and Wang (2018)].The concrete formula is as follows:
① Linear model (LIN):

Where, Pi(t), Pi(t+1) and riare the population and the average annual growth rate of population of the ithstreet in the tthand (t+1)thyear respectively.
② Improved exponential model (MEX):

When ri≥0, Kiis five times the population of the ithstreet in the tthyear; when ri<0, Kiis 1/5 of the population of the ithstreet in the tthyear.
③ Grey model (GM)


Where a and b are the calculation coefficients for the model whose formula is as follows:
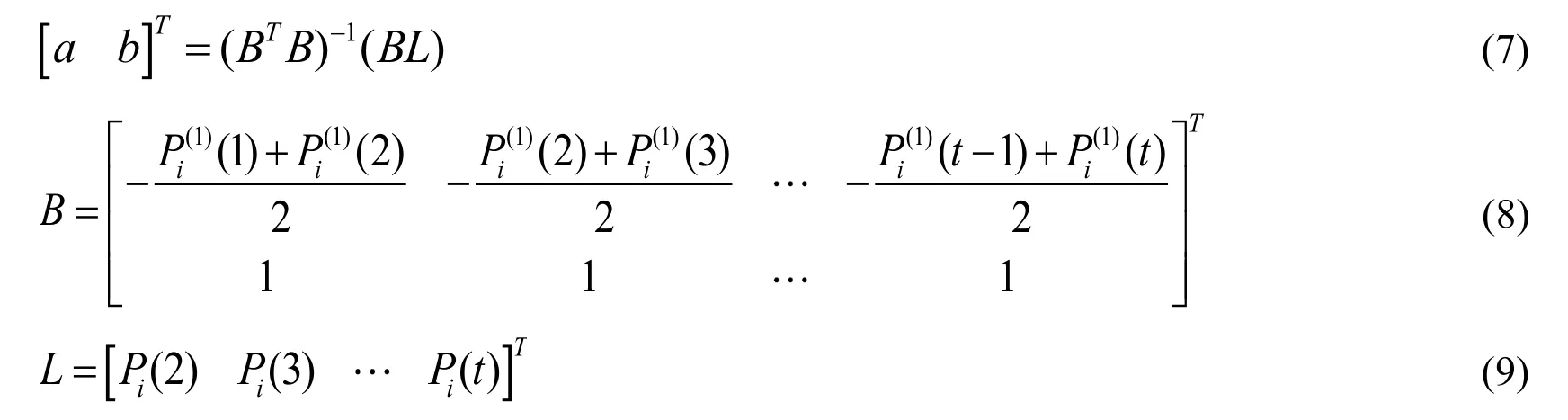
④ Sharing model of the population scale constant (CSP)

Where, Siis the average scale of the population of the ithstreet accounting for the total population of the whole district in the past t years.
⑤ Constant model of the population growth rate difference (CGD):

Where, rT(t, t+1) is the annual growth rate of the population of the whole district in the (t+1)thyear, and grdiis the average of the difference between the population growth rate of the ithstreet and that of the whole district.
⑥ Sharing model of population growth variable (VSG):
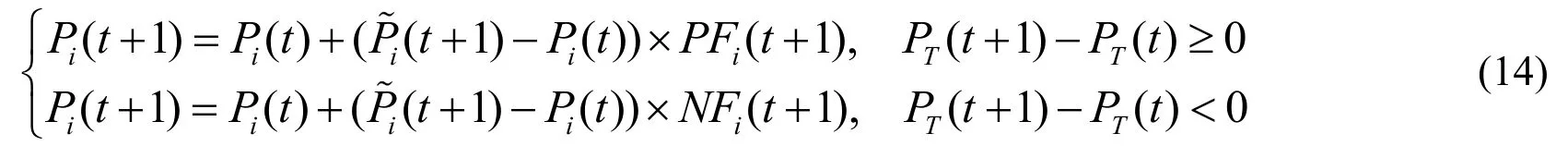

Where, m is the number of street in the district.
⑦ The method based on the fade factor and slide window:
To weaken the influence of historical information and strengthen the role of new information, a new method based on the fade factor and slide window technology is proposed [Zou, Zhang and Wang (2018)].The specific implementation steps of the method are as follows.
The calculation formula of LIN and MEX is consistent with (1) and (3), but the fading factor and sliding time window are introduced while calculating the average annual population growth rate.So (2) is adapted as follows:

Where, w is the number of times of window movement; f(j) is the fading factor; α is the weight coefficient.(16) and (17) make use of the parameter w to keep the dynamic update of ri.Due to the introduction of f(j) and α, the weight of the historical data is adjusted constantly, which will further improve the timeliness of the parameter ri.
The calculation formula of GM is basically the same as (4)-(9), butis constantly updated using moving window technology, and then matrix B and matrix L are updated.(7) is substituted into weight matrix W, and then the fading factor f(j) are introduced, the specific formula of which is as follows:

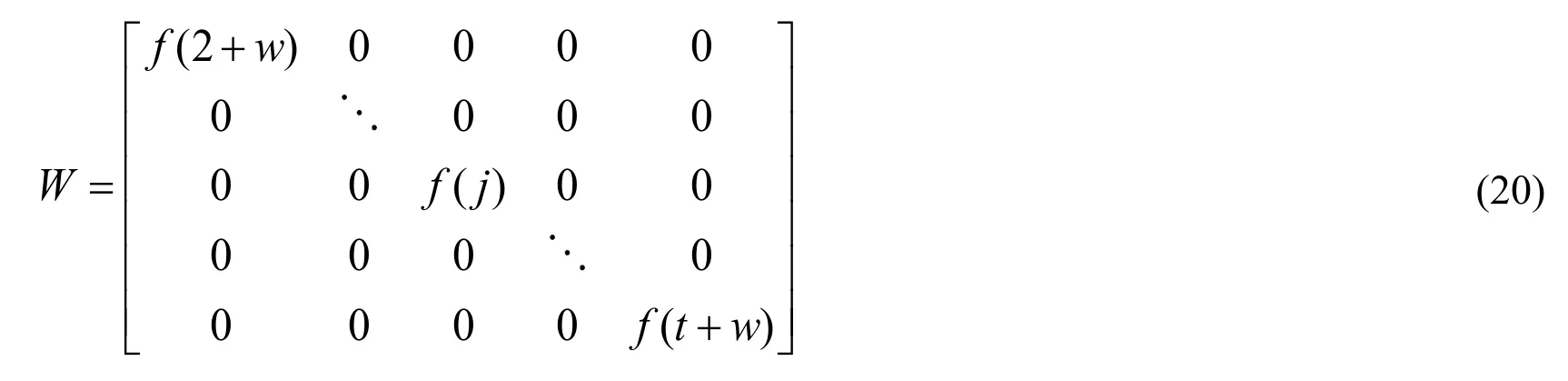
Where, the calculation formula of f(j) is the same as (17) in which t is the dimension of matrix W plus 1.After the introduction of the fading factor and sliding time window, GM becomes a weighted progressive model of equal dimension essentially.
CSP and CGD are calculated in the same way as (10)-(13), and the fading factor and sliding time window are also introduced to them.So (11) and (13) are adapted as follows:

Where, the calculation formula of f(j) is the same as (17), and the calculation formula of VSG is the same as (14) and (15).However, (16) and (17) are used in the calculation of the average annual population growth rate.Thus, the method of small-area population forecasting based on the fading factor and sliding time window is actually to add new predicted value via moving window method, keep updating parameters of the model, and meanwhile weight the modeling data using the fading factor.This method can not only improve the timeliness of model parameters, but also increase the flexibility of the prediction model, thus better adapting to the rapid and dynamic change characteristics of unstable time series data.
2.3.2 Population distribution based on land-use type
The total number of population in each street can be obtained by the above forecasting method.However, the population of each street is not distributed evenly on the whole street.For example, it is impossible for people to live on a traffic/green/water land.The people just live on the construction land [Tayman (1996); Ji, Wang, Zhuang et al.(2014)].Therefore, the land use type of each street should be accurately obtained.To solve this problem, the 30 m*30 m remote sensing image of Xicheng district from Landsat in 2016 is used and ENVI software is used for image data preprocessing and land-use classification.The special method of remote sensing image data processing is described as follows.
Firstly, the remote sensing image data from Landsat in 2016 is preprocessing, including radiative correction, atmospheric correction, geometric correction, contrast stretching, etc.Secondly, the remote sensing image is clipped according to the administrative boundaries of Xicheng district.Thirdly, the land of Xicheng district is classified into construction land, green land, water land, traffic land by the supervised classification method.Fourthly, the image of construction land is visual interpreted furtherly for ensuring the precision of construction land classification.Lastly, the construction land is vectorized for the subsequent spatial analysis.
2.3.3 Population distribution based on public facility
The population of each street is distributed on the construction land based on the result of land-use classification.However, the population on each piece of construction land is not completely equal.The population density of construction land which has a good public facility condition is larger than that of construction land which has a poor public facility condition.Therefore, the spatial locations of public facilities (subway station, school, hospital) in Xicheng district are obtained by the digital map from the OpenStreetMap.Then these public facilities are placed on the remote sensing image.It is noted that the coordinate systems of the remote sensing image and the digital map should be kept consistent.Furthermore, it becomes a key problem how to simulate the spatial distribution of population based on the spatial distribution of public facility.To solve this problem, a new method of population spatial distribution modeling is proposed based on the cellular automata (CA) and multi-agent system (MAS).The implement steps are described as follows.
Firstly, the all construction lands of Xicheng district are divided to 30 m*30 m grids and each grid is taken as a cellular automata.Secondly, three character values are assigned to each CA, including traffic, school and hospital.The calculation formula of character value is as follows.

Where Vi(k) means the kth character value of ithCA.And k is type of character value (1=traffic, 2=school, 3=hospital).The dij(k) is the Euclidean distance between the ithCA and jthpublic facility and the jthpublic facility is the nearest one to the ithCA in m facilities of kthtype of public facility.n notes the number of CA and m is the number of the kthtype of public facility.
Thirdly, the integrated score of each CA is computed by the Eq.(24).
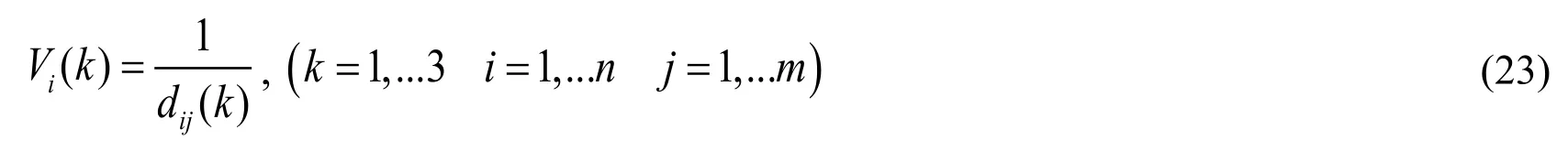
Where Tiis the integrated score of the ithCA; P(k) is the power of the kthtype of public facility.And the P(k) can be obtained by the adjustment method based on at least three year of historical population data in each street.
Fourthly, the population of each street is divided equally to each CA.Then one agent represents one person.And average score per agent (ASPA) of each CA is calculated by the Eq.(25).

Where Piis the number of population of the ithCA.If the average score per agent is high, it means that the public facility is rich and the number of population is small on this CA.In contrast, if the average score per agent is low, it notes that the public facility is poor and the number of population is large on this CA.
Fifthly, the agents live on the low ASPA of CA move to the high ASPA of CA.Then the ASPA of each CA is calculated again and it will be stopped until the differences between the new ASPA and old ASPA of all CA are less than one threshold.It means that the balance between the public resource and the number of population has been realized on all CA.The Fig.2 is the flow chart of population spatial distribution modeling based on the CA and MAS technology.

Figure 2: Process of population spatial distribution modeling based on the CA and MAS
3 Experimental results and analysis
3.1 Population forecasting experiment
To validate the proposed method in this study, the data of introduced in the Section 2.2 and the methods of introduced in the Section 2.3 are used.In the population forecasting experiment, two experiment schemes are designed and performed.In scheme 1, the population data of 15 streets in Xicheng district from 2010 to 2012 and LIN, MEX, GM, CSP, CGD, VSG models are used to forecast the population of each street in the next 4 years.In scheme 2, the basic data and models are the same as those of scheme 1, but the fading factor and sliding time window are introduced in the forecasting models.In our experiment, the weight coefficient α of the fading factor is set as 0.5 and the length of sliding time window is set to be 3 years (basic data length).
The Fig.3 is the population forecasting precision of 15 streets of Xicheng district in the next 4 years using scheme 1 and scheme 2.The Mean Absolute Percentage Error (MAPE) is taken as the index of precision evaluation and the MAPE is calculated by (26).The Tab.2 lists the forecasting precision of each model and the average forecasting precision (AVE) of each scheme, as well as the improvement of the forecasting precision (IMP) of scheme 2 compared with scheme 1.The calculation formula of AVE and IMP are as follows.

Where, MAPEirepresents the forecasting precision of the ithmodel and m is the number of forecasting models.

Where, AVEaand AVEbrepresent the average forecasting models of the athand the bthexperimental scheme.

Figure 3: Precisions comparison of using scheme 1 and scheme 2 respectively to forecast the population of 15 streets of Xicheng district, Beijing in the next four year

Table 4: Forecasting precision and improvement using scheme 1 and scheme 2 Unit: %
From the Tab.4 and Fig.3, it can be known that (a) the forecasting precisions of the latter three population forecasting models (CSP, CGD and VSG) with total population constraint information are higher than those of the first three pure mathematical models (LIN, MEX and GM), among which VSG has the highest forecasting precision (6.32%); (b) the forecasting precision of all the six models increase significantly after using the fading factor and sliding time window technology.Compared with the scheme 1, the forecasting precision of scheme 2 is improved by 46.88%.Among these models, the forecasting precision of the optimal model VSG reaches 3.51%.
3.2 Population spatial distribution experiment based on land-use type
To improve the spatial resolution of urban population distribution modeling, the land-use type of Xicheng district is classified by ENVI software since the people just live on the construction land.The results of 2016 population forecasting from the VSG of scheme 2 are taken as the basic data.The Fig.4(a) shows the results of land classification of Xicheng district and the Fig.4(b) demonstrates the results of the population spatial distribution based on the land-use type.
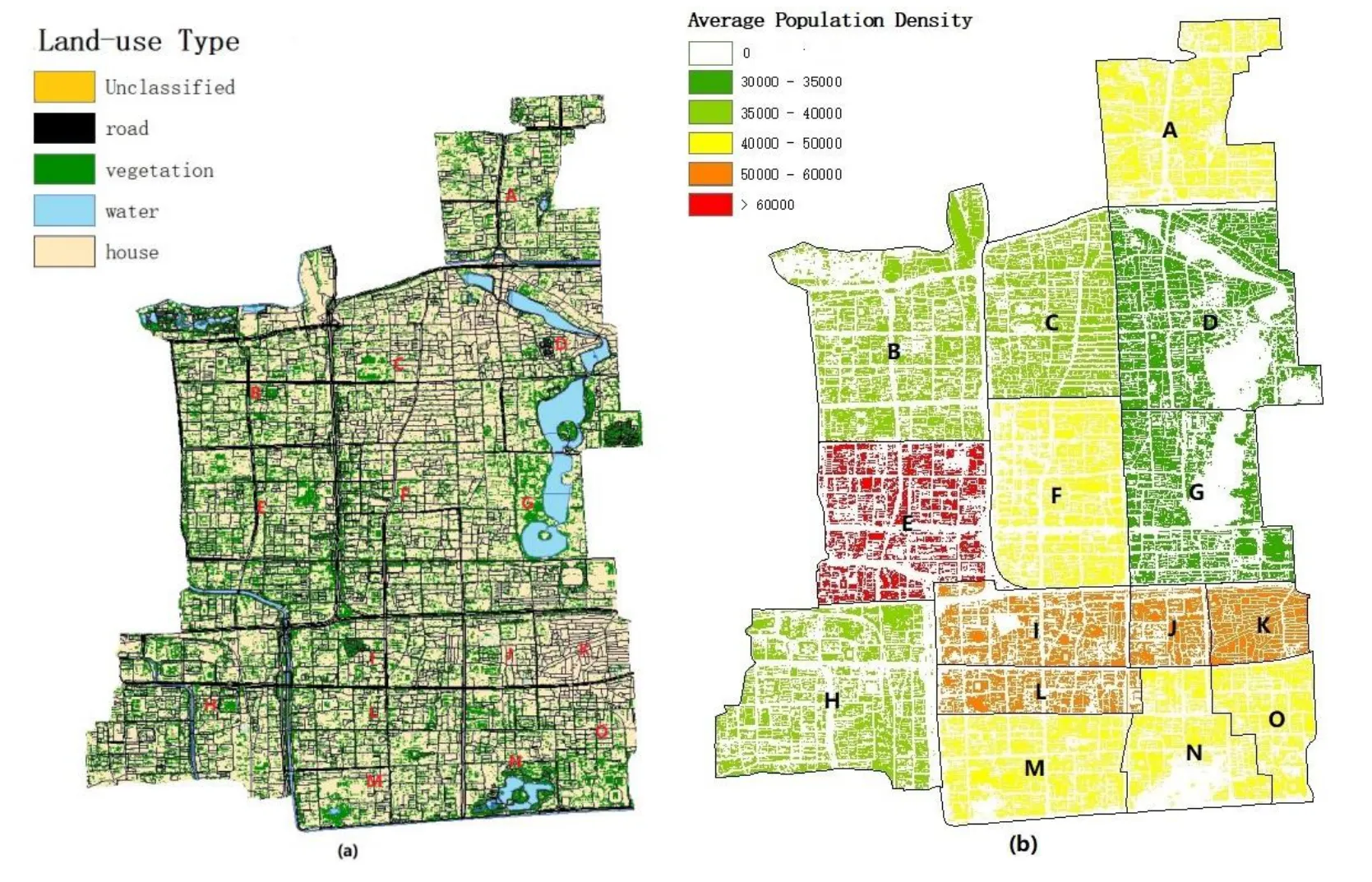
Figure 4: Results of land-use type of Xicheng district (a) and the population spatial distribution based on the land-use type (b)
From the Fig.4(a), it is can be known that the area of construction land is the largest because Xicheng district is in the center of Beijing city.The area of other unclassified land is the smallest, which means there is little undeveloped land in Xicheng district.The Fig.4(b) provides a higher spatial resolution of Xicheng district population distribution than that provides by the Fig.1(b).And it can be found that the population density of Fig.4(b) is larger than that of Fig.1(b), because the population is not allocated on all types of land but on the construction land.The population density of Dashanlan Street (K) is the largest in the Fig.1(b).However, the population density of Yuetan Street (E) becomes the largest in the Fig.4(b).The reason is that the area of un-construction land of Yuetan Street is larger than that of Dashanlan Street (see the Fig.5).Therefore, it is proved that the land-use classification is very important to model the population spatial distribution accurately.

Figure 5: Comparison of population spatial distribution of Yuetan Street and Dashanlan Street based on the results of land classification
3.3 Population spatial distribution experiment based on public facility
Although the spatial resolution of population distribution is improved by the land classification, the spatial distribution of urban population is severely affected by the public facilities distribution [Voss (2006)].Therefore, a new method is developed to simulate the effect of public facility on the spatial distribution of urban population, which is described in Section 2.3.3.The Fig.6(a) shows the spatial distribution of three kinds of public facilities (subway station, school and hospital) of Xicheng district in 2016.To simplify the data processing, only the subway station, the key schools and hospitals are considered.The Fig.6(b) is the population spatial distribution of Xicheng district based on the above public facilities, using the CA and MAS technologies.

Figure 6: Public facility spatial distribution (a) and population spatial distribution based on the CA and MAS (b)
From the Fig.6, three conclusions can be drawn: (1) the spatial resolution of population distribution can be improved significantly if the effect of public facility is considered.In the same construction land, the population is not distributed evenly, but is strongly affected by the spatial distribution of public facilities; (2) the population aggregation of the Baizhifang Street (M) is very obvious, although its population is not too large.However, it leads to the highly concentrated population because the rare public facilities; (3) the subway station shows the strongest attraction for the population in the three kinds of public facilities.It notes the traffic condition is a very important influence factor for resident decision of where they live.Therefore, it indicates that the government can guide urban population realize the even distribution by the reasonable planning and construction of city public facilities.
4 Conclusions
In this study, two key problems of urban population forecasting and modeling are investigated.One is that the population forecasting of small area (street scale) and another is that high spatial resolution modeling of urban population spatial distribution.To improve the precision of small area population forecasting, a method is proposed based on the fade factor and the slide window.To improve the resolution of population spatial distribution model, a method is developed based on the artificial intelligence technology.For validation of the proposed methods, the population data, the remote sensing images and public facility distribution data of Xicheng district, Beijing, China are used and a number of experiments are performed.Some conclusions are listed as follows.Compared with the tradition six models (LIN, MEX, GM, CSP, CGD, and VSG), the average forecasting precision can be improved by 46.88% using the proposed method to forecast the population of 15 streets of Xicheng district in the next four years.The VSG model is the best and its forecasting precision (MAPE) reaches 3.51%.The spatial resolution of population can be improved significantly using the information of land classification and public facility distribution.And the subway station has the more effect on the urban resident spatial distribution than the hospital and the school.However, more influence factors of urban population spatial distribution should be investigated and the longer time series of population data and public facility distribution data should be used to determine the power (P(k)) of each type of public facility.In addition, the population data of special resident area should be collected for validating the precision of proposed population spatial distribution model in the future study.
Acknowledgement:This research was supported by the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (No.2017XKQY071, 2017).
References
Anderson, J.(1985): The changing structure of a city: temporal changes in cubic spline urban density patterns.Journal of Regional Science, vol.25, pp.413-425.
Armstrong, J.S.(2001): Combining Forecasts.Principles of Forecasting: A Handbook for Researchers and Practitioners, pp.417-439.
Baker, J.; Ruan, X.; Alcantara, A.; Jones, T.; Watkins, K.et al.(2008): Densitydependence in urban housing unit growth: an evaluation of the Pearl-Reed model for predicting housing unit stock at the census tract level.Journal of Social and Economic Measurement, vol.33, pp.155-163.
Chi, G.; Voss, P.R.(2011): Small-area population forecasting: borrowing strength across space and time.Population, Space and Place, vol.17, pp.505-520.
Clark, C.(1951): Urban population densities.Journal of Royal Statistics Society, Series A, vol.114, pp.490-494.
Davis, H.C.(1995): Demographic Projection Techniques for Regions and Small Areas.University of British Columbia Press: Vancouver.
Deng, J.(2010): Introduction to Grey Mathematical Resource Science.Huazhong University of Science and Technology Press: Wuhan.
Harvey, J.T.(2002): Estimating census district populations from satellite imagery: some approaches and limitations.International Journal of Remote Sensing, vol.23, no.10, pp.2071-2095.
Isserman, A.M.(1993): The right people, the right rates: making population estimates and forecasts with an interregional cohort-component model.Journal of the American Planning Association, vol.59, pp.45-64.
Ji, W.; Wang, Y.; Zhuang, D.; Song, D.; Shen, X.et al.(2014): Spatial and temporal distribution of expressway and its relationships to land cover and population: a case study of Beijing, China.Transportation Research Part D, vol.32, pp.86-96.
Lam N.S.(1983): Spatial Interpolation Method: a review.The American Cartographer, vol.10, no.2, pp.129-149.
Renski, H.; Strate, S.(2013): Evaluating alternative migration estimation techniques for population estimates and projections.Journal of Planning Education and Research, vol.33, pp.325-335.
Smeed, R.J.(1961): The traffic problem in towns.Manchester Statistical Society Papers.Manchester: Norbury Lockwood.
Smith, S.K.; Tayman, J.(2003): An evaluation of population projections by age.Demography, vol.40, pp.741-757.
Tanner, J.C.(1961): Factors affecting the amount travel.Road Research Technical Paper No.51.HMSO (Department of Scientific and Industrial Research), London.
Tian, Y.Z.; Chen, S.P.; Yue, T.X.; Zhu, L.F.; Wang, Y.A.(2004): Simulation of Chinese population density based on land use.Acta Geographica Sinica, vol.59, no.2, pp.283-292.
Tober, W.R.(1979): Smooth psycnophylactic interpolation for geographical region.Journal of the American Statistical Association, vol.74, pp.519-530.
Tayman, J.(1996): The accuracy of small-area population forecasts based on a spatial interaction land-use modeling system.Journal of the American Planning Association, vol.62, pp.85-98.
Vidyattama, Y.; Tanton, R.(2010): Projecting small area statistics with Australian Spatial Microsimulation Model (SPATIALMSM).Australasian Journal of Regional Studies, vol.16, pp.99-126.
Voss, P.R.; Chi, G.(2006): Highways and population change.Rural Sociology, vol.71, pp.33-58.
Wilson, T.(2015): New evaluations of simple models for small area population forecasts.Population, Space and Place, vol.21, pp.335-353.
Wilson, T.(2016): Evaluation of alternative cohort-component models for local area population forecasts.Population Research and Policy Review, vol.35, pp.241-261.
Wu, C.S.; Murray, A.T.(2005): A cokriging method for estimating population density in urban areas.Computers, Environment and Urban Systems, vol.29, no.2, pp.558-579.
Xu, J.G.; Mei, A.X.; Han, X.P.(1994): Model of estimating population density in the residential quarter of urban.Remote Sensing of Environment China, vol.9, no.3, pp.240-243.
Zou, Y.; Zhang, S.L.; Wang, Q.X.(2018): A method of small area population forecasting based on the fading factor and sliding time window.Population and Society, 2018, vol.34, no.1, pp.1-18.
Zhuo, L.; Chen, J.; Shi, P.; Gu, Z.; Fan, Y.et al.(2005): Modeling population density of China in 1998 based on DMSP/OLS nighttime light image.Acta Geographica Sinica, vol.60, no.2, pp.266-279.
 Computer Modeling In Engineering&Sciences2019年5期
Computer Modeling In Engineering&Sciences2019年5期
- Computer Modeling In Engineering&Sciences的其它文章
- LNA Design for Future S Band Satellite Navigation and 4G LTE Applications
- The Quality Assessment of Non-Integer-Hour Data in GPS Broadcast Ephemerides and Its Impact on the Accuracy of Real-Time Kinematic Positioning Over the South China Sea
- RAIM Algorithm Based on Fuzzy Clustering Analysis
- Inferring Spatial Distribution Patterns in Web Maps for Land Cover Mapping
- Monitoring Multiple Cropping Index of Henan Province, China Based on MODIS-EVI Time Series Data and Savitzky-Golay Filtering Algorithm
- Frequency Domain Filtering SAR Interferometric Phase Noise Using the Amended Matrix Pencil Model
