Analysis of International Commercial Space Market and Policy
GONG Yukun,QIN Tong,WEI Wei,MOU Yu
Beijing Institute of Astronautical Systems Engineering,Beijing 100094
Abstract:At present,in the world the development of space is undergoing profound changes brought by commercial space,from the traditional government-driven development to the joint government and market promotion.This paper analyzes the current status of both foreign and domestic commercial space markets and policies,and then put forward the ideas and inspirations for the development of China’s commercial space market.
Key words:commercial space,market,space policy
1 INTRODUCTION
From the general definition,commercial space refers to commercial activities carried out by adopting a market-oriented mechanism with the primary goal of obtaining commercial profits.At present,in the world the development of space is undergoing profound changes brought about by commercial space,from the traditional government-driven development to the joint government and market promotion.SpaceX,Blue Origin,Oneweb and other commercial space companies have risen in a short time and joined the competition in the world’s space market.As the domestic commercial space market is at its early stage,the current status of the development of the foreign commercial space market becomes an important reference to guide the future development of China’s commercial space market.
2 FOREIGN COMMERCIAL SPACE MARKET AND POLICY STATUS
Discussing the commercial space market requires clarifying the scale of the commercial space market.According to the statistics from the US company Bryce,the total output value of the world’s space industry in 2018 was about $360 billion,of which satellite-related industries accounted for $277.4 billion(among which,launch services accounted for $6.2 billion,satellite production accounted for $19.5 billion,ground equipment accounted for $125.2 billion,and satellite services accounted for $126.5 billion),satellite-related industries are a major component of the space market.[1]
According to the 2018 annual report of the Federal Aviation Administration (FAA),the FAA has summarized the historical data of various commercial launches from 2008 to 2017,and forecasted commercial launches from 2018 to 2027.According to FAA data,the main classifications of commercial space launches include communications satellites,remote sensing satellites,commercial transport,and other commercial launches.As the largest three classifications are the top three,and commercial transport,that is,transporting people and cargo to the International Space Station is not affected by commercial market impact,the following discussion focuses on communications satellites and remote sensing satellites.[2]
2.1 Development Trend of Commercial Space Market
1)Decreasing number of high-orbit communications satellites
According to FAA’s forecast data in 2018,the number of launches and demand for synchronous orbit communications satellites is slowly decreasing.The manufacturing market for commercial high-orbit communications satellites has also been declining.According to China Great Wall Industry Corporation News,the total numbers of the world’s orders for high-orbit communications satellites in 2017 and 2018 were 8 and 7,while the numbers were 18 and 15 in 2015 and 2016,respectively.
2)Outbreak of small orbiting satellites
According to FAA’s forecast data for 2018,the number of launches of asynchronous orbit communications satellites and remote sensing satellites will increase significantly.It is worth noting that the 2018 report has not yet predicted the 12,000 Starlink low-orbit communications satellites planned by SpaceX,otherwise its predicted number of launches would increase more significantly.
Among the increasing number of asynchronous orbit communications satellites and remote sensing satellites,the proportion of low-orbit small satellites has increased in recent years.According to the statistics of Bryce,from 2012 to 2018,the proportion of small satellites in the total number of satellites launched each year has increased year by year.Between 2012 and 2018,the total number of small commercial satellite launches reached 663,of which 532 were remote sensing satellites,accounting for 80% of the total small commercial satellites,followed by technology verification satellites and communications satellites,with 71 and 53 satellites,respectively[3].

Figure 1 FAA’s predictions 2018-2027 for the launch of synchronous orbit communications satellites[2]

Figure 2 FAA’s predictions for satellite launches from 2018 to 2027 [2]

Figure 3 FAA’s prediction of remote sensing satellite launches from 2018 to 2027 [2]

Figure 4 Statistics of launched satellite weights from 2012 to 2018 [3]
The development of low-orbit internet constellations and remote sensing constellations is the main reason for the continuous rise in the number of commercial small satellite launches.Representatives of low-orbit internet constellations include the Iridium NEXT (75,completed network),Oneweb (expected about 600 satellites),Starlink (12,000 have been applied for,of which about 300 have been launched so far),and remote sensing constellations include Planet,Spire,HawkEye360,etc.It can be said that the rise of LEO constellations is a hot spot in the commercial space market.
However,the planned development of the commercial space market will not be fully realized as expected.On November 13,2019,according to Spacenews,LeoSat,which originally planned to launch 78 to 108 satellites to implement high-speed internet services,ceased operations due to lack of investment.LeoSat had received verbal promises of $2 billion from users,saying that it will use the company’s internet service,but these intentions did not translate into investor participation.Another example is Oneweb.As one of the low-orbit internet constellations with the best commercial prospects at present,Oneweb is currently unable to set up ground receiving stations in Russia,India and other countries to establish future internet services due to potential commercial risks,cyber security and military security threats.Therefore,it remains to be seen whether the development of the commercial space market will be as smooth as planned.[4]
2.2 Competition in the Commercial Launch Market
According to Bryce’s statistics,the total output value of the space industry in 2018 was $360 billion,and the total output value of launch services accounted for only $6.2 billion.In the commercial space market,although the launch of rockets has attracted much public opinion,the limitation of the total economic proposition has led to more fierce competition.
2.2.1 Competition between emerging commercial rockets and traditional commercial rockets
SpaceX’s Falcon series (Falcon 9 and Falcon heavy)rockets and Rocket Lab’s Electron rockets are currently the best among emerging commercial rockets.In 2018,these two rocket companies launched 20 and 3 times respectively,and in 2019,13 and 6 times respectively.In contrast,many traditional rockets that perform commercial launches,such as the Proton,Antares,and Zenit-3SL (effected by Russia-Ukraine relations),have had very few commercial launches.In the commercial launch market,emerging commercial rocket companies have taken the bigger share.Launch cost is the most important factor affecting launch mission orders.Falcon 9’s lower launch cost per kilogram and the lower single launch cost of Electron are the main reasons for obtaining strong market competitiveness.ESA is actively promoting the retirement of Ariane 5 and the succession of Ariane 6.The fierce competition in the price of international launch services is an important driving factor.
2.2.2 Excessive small launch vehicles and market reality
According to a report by Northrop Grumman at the 2019 International Astronautical Congress,there are currently more than 140 small launch vehicle projects in the international arena,and more than 40 projects might be“already dead”,but new small launch vehicle projects continue to emerge.The commercial space market has fueled the emergence of the small launch vehicle,but the total economic volume of the commercial launch market means that most companies cannot truly grow into launch service providers.In August 2019,Vector Space,one of the leaders in the small carrier industry,announced that the company had suspended operations.On December 13,the company filed for bankruptcy.The Vector Space company had obtained a DARPA launch contract before the suspension of operations,and had completed one sub-orbital test launch and several engine tests.By the end of 2018,it had raised about$100 million.Vector Space was one of the best companies in the industry for funding and development,but it collapsed quickly due to the sudden withdrawal of venture capital in July 2019.At SATELLITE 2019 in May 2019,the vice president of Firefly,a small rocket company in the United States,believed that only five or six of the many small launch vehicle projects might survive in the end,while the head of Vega Division in Arianespace believed that only three could survive.[5]
In fact,the small satellite launch market targeted by commercial small launch vehicles not only needs to face competition from other small launch vehicles,but also the competition from medium-sized and large launch vehicles.The multi-satellite launch represented by PSLV with 104 satellite and SpaceX’s new Rideshare“space shuttle”launch service have attracted a large number of small satellite projects who choose medium and large launch vehicles to complete their launches.At present,the majority of small launch vehicles do not have the ability to perform on-orbit launch missions.Only a few of the commercial small launch vehicle companies will be the lucky ones that can secure enough orders to survive in the fierce competition.
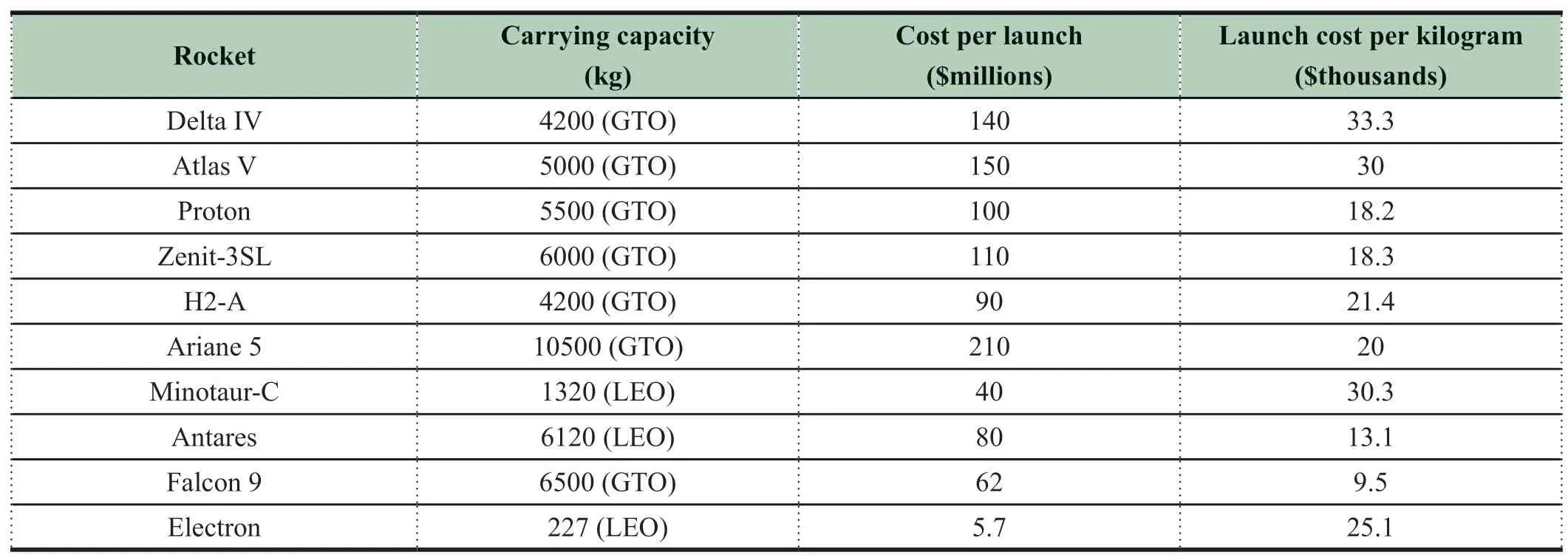
Table 1 Statistics of launch costs for major foreign commercial rockets
2.3 Government Policies for Commercial Space
Due to the characteristic of large funding requirements and technical difficulties in the space industry,the development and growth of commercial space companies is more difficult than in other industries.In order to promote the development of domestic commercial space,different countries,the United States for instance,in recent years have given development support at various levels.
2.3.1 Policy guidance and reform
The United States has the most complete legal and regulatory system in commercial space.In 2010,the United States promulgated“Title 51 National and Commercial Space Programs”,which fully absorbed the previous commercial space laws,and made technical modifications and adjustments.It has important significance for promoting the development of the U.S.commercial space market.In 2015,the United States passed the“Commercial Space Launch Competitiveness Act”,which covers commercial space launches,commercial remote sensing,a commercial space management agency name changes and functional enhancements,plus exploration and utilization of outer space resources.It helped to further promote the innovation and entrepreneurship of U.S.commercial space companies and enhance their international competitiveness.
On March 23,2018,the White House issued a statement saying that the Trump administration has formulated a National Space Strategy,which is the first“space strategy”in the history of the United States (the Obama administration only promulgated the“National Security Space Strategy”).The new strategy emphasizes the need to make the three areas,national security space,commercial space and civil space more dynamic,while strengthening cooperation amongst the three.The United States will work with the business community to ensure that U.S.companies remain world leaders in aerospace technology.The new national aerospace strategy prioritizes regulatory reforms to unleash the vitality of the U.S.industry and ensure that the United States maintains its position as the world’s leading provider of space services and technology.
On May 24,2018,adhering to the concepts of the National Aerospace Strategy,President Trump signed the Space Policy Directive 2 (SPD-2).SPD-2 requires measures to simplify the regulation and promotion of commercial space,and ensure the leading status of U.S.commercial space.The directive puts forward specific requirements from six aspects,including policy,launch and re-entry licensing,commercial remote sensing,reorganization of the Department of Commerce,radio frequency spectrum,and licensing regulations.
Under the requirements of SPD-2,relevant US government agencies have begun reforms of various aspects.On the organization side,the FAA has begun restructuring the Office of Commercial Space Transportation (AST)to maximize the efficiency of the simplified new regulations.In terms of launch licensing,the FAA is revising the launch license approval procedure.Rocket Lab has become a beneficiary of the approval reform.The company has received a five-year permit to launch the Electron rocket in October 2019,without having to apply for licenses multiple times.In terms of satellite licensing,the US Federal Communications Commission (FCC)has simplified the application procedures for small satellites.The license application fee has been reduced from $472,000 to $30,000,and 10 satellites can be applied for at one time.Clear regulatory and policy reforms have played a positive role in guiding the development of the US commercial space market.
2.3.2 Funding support
SpaceX’s growth process received considerable funding support from NASA.According to the data from the FAA,when SpaceX did not have the ability to fulfill the enter into orbit criteria,NASA awarded a contract for up to $396 million for SpaceX’s Dragon cargo spacecraft.After the successful first flight of SpaceX in September 2008,NASA immediately awarded SpaceX another $1.6 billion contact for 12 Dragon missions.[2]According to statistics from the US company Space Angels,US government agencies supported 67 commercial space companies from 2000 to 2018 with a total of $7.2 billion,of which SpaceX and Blue Origin accounted for 6.7 billion.In addition to support for companies like SpaceX,agencies such as NASA and the United States Air Force also have special funding support for small business innovation research (SBIR)and small business technology transfer (STTR)for start-up commercial space companies.From 2000 to 2018,US government agencies awarded a total of 345 SBIR and STTR projects with a total funding of$133.7 million[6].
Affected by the successful experience of the United States,since 2018,many countries have proposed special funds,funded by the government,to support the development of domestic commercial space.The UK has proposed the“Cosmic Capital”venture fund of approximately $126 million to support startup space companies.Japan has set up a $1 billion fund to support domestic space startups and formed a“space business investment pairing platform”.Luxembourg has established a$250 million special fund to support aerospace mining companies[8].

Figure 5 FAA’s statistics on commercial crew and cargo contracts awarded by NASA in 2018 [2]

Figure 6 Statistics on commercial space investment by U.S.government agencies from 2000 to 2018 [6]
2.3.3 Infrastructure support
In order to support the growth of commercial space companies,countries have also given considerable support in terms of infrastructure construction,mainly in the construction of launch sites.SpaceX leased the existing launch pad at Vandenberg Air Force Base and Cape Canaveral for the launch of Falcon rockets,thus saving SpaceX’s development funds.In order to expand its launch capabilities,Rocket Lab sought to build a new launch site in the United States in addition to the existing New Zealand launch site,and received strong support from the Virginia government.The Virginia government provided $5 million in grants for Rocket Lab to build an LC-2 launch facility on Wallops Island,and provided additional support in the form of labor.
In order to support the development of commercial space companies and restore local launch capabilities,the British government is also actively investing in the construction of British space launch sites,including the Sutherland Spaceport for the Orbex’s Prime rocket and Cornwall Spaceport in England for the Virgin Orbit's Launcher One air-launched rocket.
3 DOMESTIC COMMERCIAL SPACE MARKET AND POLICY STATUS
In recent years,commercial space companies such as SpaceX have taken a demonstration role in the area of commercial space development.The“Guiding Opinions on Encouraging Social Investment,Investment and Financing Mechanisms in Innovative Key Areas”was issued by the State Council in 2014.It is the first time to encourage private capital to participate in national civil space Infrastructure construction,to develop,launch and operate commercial remote sensing satellites,to provide market-oriented and professional services,and to participate in the construction of satellite navigation ground application systems.Because of these reasons,the domestic commercial space market has begun to develop.
At present,the development of domestic commercial space mainly depends on the input of social capital.According to the research report of iResearch on the development of China’s commercial space,from 2015,domestic investment institutions began to gradually invest in commercial space.The number of investment institutions increased from 24 in 2017 to 90 in 2018.The specific financing situation shows that investment institutions are currently more enthusiastic about investing in companies providing commercial launch services.[7]

Table 2 Financing of some domestic emerging commercial space companies
In terms of launch vehicles that provide commercial launch services,private rocket companies generally choose the route of developing small solid rockets and then liquid rockets,and the launch capacity is mainly aimed at the small satellite launch market.The main reason for choosing to prioritize the development of solid rockets is that the development of solid rockets is relatively easy and the development cycle is relatively short,which is convenient for the private companies to quickly seize the small satellite launch market,conduct launch missions early,complete the commercial closed loop,and promote further financing.JD-1 liquid oxygen methane engine from i-Space,TQ-12 liquid oxygen methane engine from LandSpace,and other self-developed liquid engines have completed their test of the complete system,indicating that these company's liquid rocket research and development is also gradually progressing.However,the failure of the first flight of ZQ-1 and OS-M shows that due to the lack of technical accumulation,the private company will face more difficulty in the process of research and development of private rockets.
On the other hand,the two major state-owned aerospace groups,China Aerospace Science and Technology Corporation(CASC)and China Aerospace Science and Industry Corporation (CASIC)have used existing mature technologies to develop small solid commercial rockets such as SD-1 and Kuaizhou-1A to participate in commercial competition,and have released piggyback launch opportunities of the Long March series launchvehicles.The action by the state-owned space groups indicates that they will continue to be an important part in the commercial space market.[8]

Table 3 Domestic major commercial launch vehicles
In terms of policy,China’s space laws and regulations are mainly industrial administrative laws,mostly separate laws and regulations,hence lack systemic laws and regulations.In 2019,the State Administration for Science,Technology and Industry for National Defense and the Equipment Development Department of the Central Military Commission jointly issued the“Notice on Promoting the Orderly Development of Commercial Launch Vehicles,”which included content related to commercial rocket and weaponry equipment research plus production licenses,space launch declarations,work in launch sites and test sites,security and export control.This notice has played a certain role in the orderly development of commercial space.However,in terms of policy guidance and commercial space management systems,such as management policies for social capital entering the space field,management of commercial launch permits,review of commercial launch activities involving national security,public safety,space debris,etc.,plus the commercial policy of using space infrastructure,there are still some gaps in domestic policies.The state needs to develop the relevant top-level commercial space policies and improve commercial space laws and regulations.[9]
4 THOUGHT AND INSPIRATION
4.1 Balance in Commercial Space Regulatory Standards
Appropriate regulation can help the development of commercial space.Excessive regulation can hinder innovation and the growth of commercial space,while the lack of regulation may bring chaos and disrupt the market.The rapid development of low-orbit small satellites in recent years has brought many new problems.For example,the launch of SpaceX’s Starlink satellites have not only severely disturbed ground astronomical observations around the world,but has also caused ESA’s“Aeolus”satellite conducting orbital maneuvers to avoid collisions due to active satellites for the first time in history.In January 2018,four small satellites of the Swarm company were successfully launched by PSLV rocket without the FCC’s approval.[10]How to find a suitable regulatory scale is the issue that requires space managers around the world to think about.With the increasing number of domestic commercial satellite production companies and commercial launch providers,the regulation of the domestic commercial launch market needs to be established early to cope with the future development of the domestic commercial space market.
4.2 Market Rules For the Commercial Space Market
As mentioned before,the plans proposed by commercial satellite companies are not necessarily becoming reality,and the vast majority of more than 140 commercial small launch vehicle projects cannot really survive.On December 6,2019,the last first-generation Iridium satellite Iridium 97 withdrew from operation.As we all know,the failure of the first-generation Iridium was not a technical failure,but a failure in commercial operations.Commercial space,like other commercial areas,has commercial risks.The development of the commercial space market requires commercial thinking to guide its development and reduce blind and repetitive investment and construction.Domestic commercial space companies and investment institutions should face business risks rationally,not simply by cash-burning competition,but by finding a suitable business operational mode,and finding a commercial operational method suitable for the Chinese space market.
4.3 Commercial Space Is Still a Competition For Space
Orbital and frequency band resources are an important part of space resources.With the boom of commercial space,competition for orbital and frequency band resources has become increasingly fierce.The International Telecommunication Union proposed in November 2019 that after the first satellite in the constellation begins to operate,the satellite operator must complete 50% of the constellation deployment within 5 years and complete all deployment within 7 years,otherwise the approved spectrum rights will be reduced.This new regulation is in response to the fierce competition for frequency band resources.[11]In addition to competition for space resources,the development of commercial space is also an important part of the development of the national air and space strategy.Therefore,commercial space is not just a commercial market,but a new force that competes in international space sector on behalf of its country.The development of commercial space still needs a strategy that serves the country.Relevant domestic departments should actively face and guide the development of domestic commercial space companies,and provide useful supplements for the overall development of China’s total space industry.
5 CONCLUSIONS
This paper analyzes the current status of foreign commercial space markets and policies by summarizing the development trends of foreign commercial space markets,competition in commercial launch markets,commercial space policies of various countries,and analyzes the current status of domestic commercial space markets and policies,then puts forward the thoughts and inspirations for the development of China’s commercial space market.China’s commercial space development is still in its early stage,and there are still many uncertain factors from the market to the policy.It requires the efforts of all parties in the space industry to actively promote its development.
- Aerospace China的其它文章
- LM-4B Launches GF-7 and 3 Other Satellites into Orbit
- China Announces Open Sharing of GF Data
- LM-3B Completes the Launches of All BeiDou IGSO Satellites
- China Launched Shijian 20 Satellite Atop a LM-5
- Develop Highly Reliable and Low-Cost Technology for Access to Space,Embrace the New Space Economy Era
- LM-6 Launches Five Satellites on Its First Low-Inclination Launch

