Prospects for Satellite Services
Pacome Revillon Euroconsult
Disruptive Environment of the Space Ecosystem
There are four dimensions driving very profound changes in space activities.
Government will continue to play a key role both as a driver for the investment in both R&D in terms of regulation, policy, and ambition, and in terms of supporting the development of space industries.Government will also remain a key user of essentially all the services delivered by satellite assets.Innovation is certainly a key word in space activities. I think innovation has never been as fast and strong as in recent years, and the industry is very much transformed by digitization and all the changes applying to the IT sector which also greatly impacts space activities.
Investors come from an increasing number of organizations around the world. This can be public investors in many places, but also strategic companies from inside or outside the space sector, taking positions to benefit from innovation and the new developments in space, as well as a broad community of financial investors, from launcher capital firms to more established financial investors.
In terms of the markets, with both the complimentarity and combination of the satellite ground-based solutions,we see many changes in what customers/users require from space activity and services, whereby it can create some tensions on some historical or legacy solutions,but also opens new opportunities for development of new types of services, and the possibility to open to new communities of users.
Government Space Investment
In 2017, government space investment represented approximately $60 billion around the world, and it is now over 70 countries having active investments to develop their own space activities, which makes international space cooperation highly relevant.
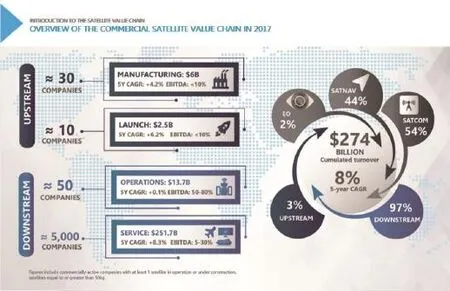
Commercial Space Revenues
Aggregating all activities, we see a current global space market of over $274 billion, of which a large part corresponds to the services being delivered for a variety of public and private users around the world, for the benefit of both professional activities and ultimately citizens. As part of that,the most mature value chain and commercial activity (54%) remains in the domain of satellite communications, but with satellite navigation(44%) also being a large component, and Earth observation (2%)progressively growing and opening as a commercial space sector.
Satellite Communications – The Path to Broadband
Speaking about satellite communications, the driving concept is certainly about how to deliver broadband and increasingly as well IOT and services that can be a full part of the future communications landscape including as part of the 5G development of the coming years.
Welcome to the Terabit Satellite Era
If you look at how much capacity is leased from satellite systems around the world, we just passed in 2017 1 terabit/second being leased over satellite systems, which would represent a growth of approximately 20%, with this growth being primarily supported by new-generation broadband satellite systems, also called “HTS.”
Revenues of Wholesale Operators Still being Adjusted
One of the challenges, if you look at the economics of the sector, is that the industry of commercial satellite operators, which has been a growing industry over the last 20 years, is going through a transition period, where the historical assets face difficulties in maintaining prices and their competitiveness, while the operators work at developing new markets with new broadband satellite systems. And in that transition period, as in any breakthrough innovation period, we see a combination of historical companies, partly suffering and adapting to the change, and a number of startup organizations or new companies trying to enter the sector and bringing new competition.
HTS Supply Expansion to Accelerate Through 2023
If you think of the capacity that will be available, we believe that the total capacity available around the world could be multiplied by approximately 5 in the next 5 years, which would represent over 10 terabit/second being delivered. A good part of that should continue to be through geostationary satellite systems,but much emphasis is also currently on the development of broadband constellations in the low Earth orbit(LEO). You could have approximately at least 1 terabit/second made available in all parts of the world for the land masses and countries, but also for oceanic areas in support of maritime or aeronautic services.
Satcom Ecosystem – Integrate/Deliver More Value?
This transformation is not just about capacity, it's also about how organizations will adapt to bring services to their clients. Today we see new trends for new vertical integration, changes in the way services get delivered between satellites and the ground segment, and the optimization of services down to the end-user. This results in a combination of different businesses, either through strategic partnerships or even certain mergers and acquisitions around the world.
Capacity Pricing to Support New Business Cases
New systems bring the ability to provide more bandwidth for the same price. All of us are more than happy to enjoy 4G services today or 5G services tomorrow, but we don't want to pay much more for our monthly subscription for our mobile devices. And the same applies largely to the satellite sector. Most of the users want to use more data and deliver data-rich services, including video services for example, but this is only possible if the new satellite systems become more efficient and can deliver much more attractive pricing to the end-users against the data being delivered.We believe that the ability to have much more efficient systems should drive an enlargement of the community of users around the world in the direction of universal access to communications, in the ability to provide what is today first connectivity and would be tomorrow video streaming capacity to all passengers on a ship or a plane,and on top of that contribute to the fast-growing IOT industry carrying and delivering data between various assets, and especially smart or automated vehicles or machines around the world.
Satellite Solutions for Bridging Digital Divide
In the context of bringing universal access, this new efficiency could greatly increase the volume of capacity and services being delivered, either directly to provide broadband to households, currently a few million users,or through WiFi community networks.
Enterprises will certainly benefit from that progress to extend their network and the ability to provide data-rich content and environments, as more enterprise companies benefit from cloud applications to support their operations. This would also include civil government programs to either bring connectivity or contribute to civil security and other dimensions.
Cellular backhaul continues to expand mobile coverage and bring new mobile broadband capabilities even in the most remote areas-landscaping, driving on any highway anywhere, serving any single village or island anywhere on Earth.
Satellite – The Dominant Technology for Mobility
In terms of transportation, this is really a transformative move that we see today; it starts by bringing connectivity to ships and aircraft, and we believe that by 2020 approximately half of the total commercial fleet of aircraft should have started to install WiFi onboard,highly supported by satellite communications.
The start of connectivity will certainly support development in the automated ship or in the smart plane that will bring much more information to and outside of the aircraft in the future, to optimize operations.
Overview of our Updated FSS Forecasts
Thanks to this broadband development, we believe that after a challenging period of transition we could expect another period of relatively sustained growth, certainly in terms of the consumption of satellite services for communications, but also in terms of market value.While the industry is currently transforming and adapting, we look forward to a new period of growth,where there will always be challenges but where we could see a larger number of organizations taking benefit from that broadband path, either at the level of the networks or at the level of the services being delivered.
Earth Observation – The Information Revolution
Previously we were speaking about communications,but we've also seen another revolution that has started even more recently, in the context of Earth observation.CNSA presented very well some of the innovative programs being driven by China today, and this resonates with innovations we see around the world.
Dynamics for EO Satellite Manufacturing
We will see an increasing number of satellites being developed and launched into orbit with a growing diversity of sensors to collect and transmit information about Earth. We expect to see a large range of small to very small satellites, or cubesats, working in constellations, and a number of constellation projects now under development should get into orbit around 2020-2022, which will bring an unprecedented volume of data being delivered to Earth about human activities and about our global environment.
On top of the satellite program, aerial and high-altitude platforms (HAPs) will be utilized to bring additional contributions to this data collection.
Not Just More Data– But New Types of Resources
This will bring two primary changeson the one side and thinking more of medium resolution systems, it will be the ability to capture any point of Earth, to a large extent,on a daily basis. In parallel to that move and to those development programs, we will have the other side of the spectrum where the increasing number of very highresolution systems would be able to do the same daily monitoring but in more selective portions of the globe.The objective of these systems will be to bring much more flexibility of use and the ability to be much more reactive to deliver services to the community of users.
Commercial Data Pricing in Transition
This should come with changes in the dynamics for the pricing of data. To have much more frequent revisits will transform the industry from more tasking and data on-demand to more subscription-based models and more change detection-type services that will be offered by the industry. While premium prices could remain for the most capable systems, we will otherwise see a decrease in the pricing of data that should benefit the development of more value-added services.
Free Data Downloads–Turning into Services?
In parallel to commercial imagery, we see a rapid increase in the download and consumption of free data and government-backed systems-these are just two examples of statistics available through the historical LANDSAT system in the U.S. and from the more recent COPERNICUS program of the European Union.In just one year, the volume of data collected from the European system is as large as that of the LANDSAT system. The data consumption and downloads keep increasing for the different types of systems; there is certainly no less appetite to collect more data and see how to transform it into applications. But a large part of the applications development and services development is still in front of us.
EO Ecosystem – Integrate/Deliver More Value?
To that extent, very much as in the communications sector, we will see a change in the ecosystem with more vertical integration and combination of businesses from organizations collecting and delivering the data to organizations providing automatized or advanced analytics, delivering software solutions even as a service,and delivering the release of final information products to a variety of clients. This will require both internal development by the companies, but also an increasing number of partnerships and cooperation to take the benefits of the EO capabilities.
Service Potential to be Fully Unlocked
This, on the side of the commercial services, leads us to a scenario where we are confident that, on top of a much larger consumption of data, the industry should continue to grow. While we have a baseline scenario, we believe that upside scenarios exist for Earth observation services,but this depends significantly on the ability to bring such services to new communities of users, such as, for example, financial services, or delivering a broader range of solutions to the development of smart cities or other types of users. This implies going from a data product to services that are easy to consume for decision makers of various organizations and to understand how they can use such materials to drive their own decision making.
Key Takeaways
Innovation is ongoing but will continue to accelerate-and certainly the entire space sector will need to innovate at a faster pace in the next decade than it ever did before. This will open new opportunities, investment options and business cases for the private sector and commercialization but will also bring challenges and the need to adapt on a continuous basis to maintain an added value to the end-users.
There is a continuity in the investment brought by historical stake-holders, but there are also emerging and new investors from both the public and private sector from around the world.
The space ecosystem is and will continue to transform-either through increasing cooperation and partnerships, or through transformation of the organizations themselves, as they take advantage of digitization of services and aim at optimizing their efficiency.

