Application of Autologous Costal Cartilage Scaffold in Reconstruction of Microtia Ear
Xiao-nan LIAO,Xin-xin REN,Chen-yang LIU
Department of Plastic Surgery,Nanyang Central Hospital,Henan Province,Nanyang City,Henan Province,473000,China
ABSTRACT Objective To investigate the application effect and manufacturing skills of autologous costal cartilage scaffold in ear reconstruction for microtia.Methods From January 2016 to January 2019,41 patients with microtia reconstruction in our hospital were selected,all of whom were type II or type III pediatric deformities.All patients underwent auricle reconstruction and retroauricular skin expansion and autologous costal cartilage stent.The first stage of the operation is to insert a skin dilator behind the residual ear and inject water to expand.The second stage of the operation is to carve and repair the soft ribs (usually 6 or 7 ribs) from the body,make a three-dimensional auricle support for auricle reconstruction,place a negative pressure drainage tube,and follow up for 3 to 6 months to observe the three-dimensional shape of the reconstructed auricle and the formation of cranioauricular angle.Results 41 patients with microtia had good three-dimensional shape of auricle reconstruction,normal auricle position,moderate cranioauricular angle,good helix and triangular fossa structure,and good bilateral symmetry.Patients and their families were satisfied with the effect of auricle reconstruction.Conclusion Autologous costal cartilage is a good scaffold for auricle reconstruction.It is through efficient and elaborate carving and splicing that a good three-dimensional auricle structure can be formed.Combined with early flap expansion,a good postoperative appearance effect can be obtained,which is the appropriate method for auricle reconstruction at present.
KEY WORDS Microtia;Ear reconstruction;Skin expansion method;Autologous costal cartilage;Ear stent
Microtia is one of the common deformities of ear and face,mostly congenital deformities.The mechanism of its occurrence is still unclear,which may be related to the abnormal development of the first and second branchial arch or neural crest cells during embryonic period[1].Microtia is mostly manifested as structural deformity of external auricle,which affects the appearance.Severe cases may have ear canal occlusion,stenosis,middle ear deformity,etc.,which affect hearing and have a serious impact on the physical and mental health of patients[2].In recent years,with the development of plastic and cosmetic medicine,external ear plastic surgery has developed well,but external ear deformity repair is still one of the most challenging operations in plastic surgery.At present,skin and soft tissue expansion and stent implantation are mostly used in clinical practice for plastic external ear reconstruction.Autologous costal cartilage has become the first choice for clinical auricle stent due to its advantages of good plasticity,simple and convenient interception,little influence on patients,good compatibility,etc.However,due to the need for higher skills in stent plastic skills,three-dimensional structure,implantation shape adjustment and other links,the requirements for the operator are higher[3].Our hospital has accumulated certain clinical experience since carrying out auricle reconstruction with autologous costal cartilage stent.This article will summarize and analyze the sculpture combination skills of autologous costal cartilage scaffold and the clinical efficacy of autologous costal cartilage scaffold in auricle reconstruction of microtia,aiming at providing reference for clinical practice.The following reports are hereby reported.
DATA AND METHODS
General information
From January 2016 to January 2019,41 patients with microtia reconstruction in our hospital were selected as observation objects,including 25 males and 16 females.The age ranged from 16 to 41 years,with an average of 27.33.3 years.There were 19 cases of left ear malformation,21 cases of right ear and 1 case of bilateral malformation.According to the classification method of congenital microtia by Jiang Haiyue et al.[4],there were 25 cases of type II malformation and 16 cases of type III malformation.All patients underwent external ear reconstruction for the first time.Before the operation,all patients underwent thoracic rib three-dimensional scanningCT reconstruction imaging examination.All patients had no problems such as rib calcification and developmental malformation.They were willing to accept autologous costal cartilage scaffold for external ear reconstruction and signed an informed consent form.
Surgical methods
One-stage implantation of retroauricular skin dilator:shave off the patient’s hair,especially the hair around the ear,thoroughly clean the ear skin with warm soapy water,routinely disinfect the ear skin,spread aseptic towel,and make an incision with curved radian along the auricle at the postauricular hairline,with the length of about 4cm.Then bluntly separate the retroauricular skin from the fascia and extend the range to 1cm outside the pre-expansion area.After complete hemostasis,50ml or 80ml kidney-shaped dilator is selected.The controller was implanted under the separation flap,and the position of the controller was adjusted so that its upper edge was on the same horizontal line with the upper edge of the countermeasure auricle,its lower edge was parallel to the contralateral earlobe,and its anterior edge was placed on the lower edge of the residual ear cartilage.The incision was sutured in layers and drainage tube was retained.3-5 days after operation,the extraction fluid stopped,the drainage tube was pulled out,and water was injected into the dilator.The stitches were removed 2 weeks after operation,and water was injected once every 2 weeks,with 2-3ml each time.The whole expander took 3-5 months.After the expansion size reached the operation requirements,the flap was stable and maintained for 2 weeks,and the second-stage operation could be performed.The preoperative and postoperative effects are shown in Figure.1 and Figure 2.
In the second stage,the dilator was taken out,and the plastic stent of autologous costal cartilage was placed into the ear for reconstruction at the same time:the dilator was inserted into the incision in layers,the dilator and fascia were dissociated,the dilator was taken out,hemostasis was completely stopped,and the normal saline gauze was temporarily filled.According to the preoperative CT and other imaging data,all openings were made at the 6th and 7th ribs.The costal cartilage of the patient was selected for carving and divided into two parts.Some of them are about 1cm thick,and the outer contour of the auricle and the basal part of the earlobe are made according to the characteristics of the auricle.The other part is made into the internal main body of the ear bracket,the middle of the auricle is made into a wedge-shaped auricular boat,and then a section of costal cartilage is taken to make the triangular fossa of the auricle.Attention should be paid to the three-dimensional shape during the making process.See Fig.3 for the effect of making ear bracket.Take out the expanded skin flap,fill the inside with gauze,place the prepared ear directly into the expanded skin flap,wrap the skin flap,trim the direct edge and skin flap incision,adjust the direct position,place the drainage tube,and suture the skin flap layer by layer,so that the outline of the outer ear is clear,the positions are symmetrical on both sides,and the operation is over,as shown in Fig.4.One week after the operation,the drainage fluid was significantly reduced or stopped,the drainage tube was pulled out,and the stitches were removed 10-14 days after the operation.
RESULTS
All 41 patients with microtia underwent one-stage flap expansion,which met the surgical requirements.No complications such as dilator leakage,flap necrosis and infection occurred,and and the second-stage operation was successfully carried out.Autologous costal cartilage bone extraction was smooth,costal cartilage was good,and there was no calcification.The patient recovered well at the rib extraction and no complications such as chest deformity occurred.The ear bracket is lifelike in manufacture,strong in stereoscopic impression,normal in auricle position,moderate in cranial ear angle,good in helix and triangular fossa structure,and good in bilateral symmetry,as shown in Fig.5.During the follow-up for 3 to 6 months,the patients and their families were satisfied with the effect of auricle reconstruction.
DISCUSSION
Microtia is the most common ear and facial deformity,and external ear reconstruction is also one of the most delicate operations in plastic and cosmetic operations[5].The main difficulties include:① Thin ear skin,few available skin flaps,and insufficient effective skin completely wrapping the stent,which is easy to lead to stent leakage and flap necrosis.(2) The fabrication of reconstructed auricle bracket requires high materials and carving technology.The stent should not only have high plasticity and be convenient for direct combination and engraving,but also have high biological solubility to reduce the incidence of postoperative complications.The finished product of the bracket should have good supporting effect and stereoscopic impression,which is also an important basis to ensure the “natural ear”[6].(3)Accurate implantation of surgical skills and positions.In addition to ensuring the lifelike appearance of the reconstructed external ear,the implantation position of the stent is crucial to the final effect,especially the high and low symmetry and anterior and posterior symmetry of the left and right external ears.Therefore,in order to create a stent with strong stereoscopic appearance,complex structure and good supporting effect,accurate placement in place is not only the basis for natural appearance and good effect of ear reconstruction,but also a challenging and difficult operation in ear plastic surgery..
In 1920,Gilles made the first attempt to reconstruct the external ear by carving auricle supports with costal cartilage of limbs.Since then,through continuous improvement and innovation by many experts at home and abroad,a relatively mature external ear reconstruction of limb costal cartilage carving scaffold has been formed.Generally speaking,the operation is divided into two stages.The first stage is the implantation of skin dilator to cultivate sufficient skin for external ear reconstruction and reduce the extrusion of the stent due to insufficient skin,thus affecting the plastic effect and easily leading to the occurrence of adverse complications such as stent leakage.The second stage is soft rib interception and stent engraving and implantation plastic surgery,which have been widely used worldwide and achieved good clinical results,fully demonstrating the safety and popularity of this method[7].Even in recent years,with the improvement of plastic effect requirements,some scholars[8]have divided ear reconstruction into three phases.On the basis of the original two phases,the third phase of earlobe reversal reshaping was added to make the reconstructed outer ear more realistic,stereoscopic and symmetrical.Although the two-stage external ear reconstruction operation is still adopted in this study,the postoperative effect is good and has been well received by clinicians,patients and their families.The author believes that this result is closely related to the carving and implantation techniques of costal cartilage scaffolds.In particular,the costal cartilage is evaluated by making full use of image data before operation,carefully carved and well combined with costal cartilage,so that the produced external ear scaffold has realistic shape and good support stability,which becomes an important factor to ensure the success of ear reconstruction.The author has the following experience in making ear scaffold with costal cartilage.
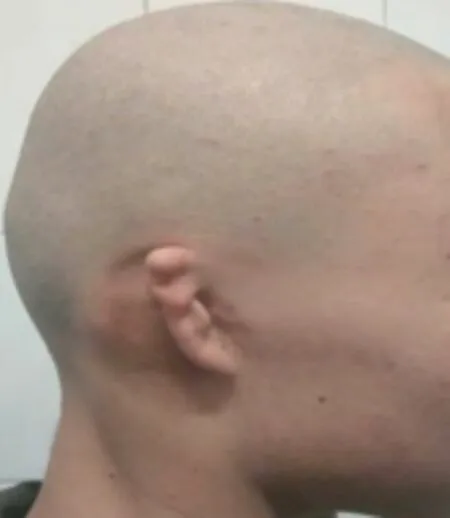
Fig.1 Preoperative side view
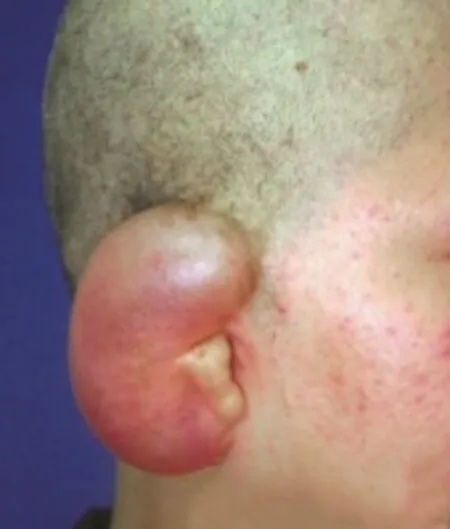
Fig.2 Posterior side view of skin expansion
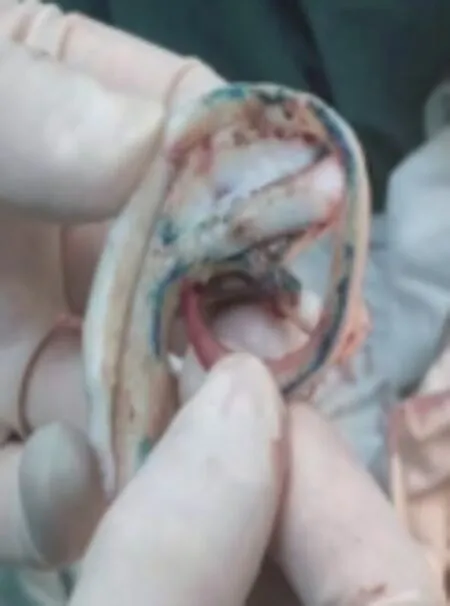
Fig.3 Engraved and formed stent
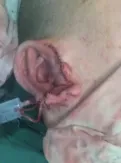
Fig.4 Postoperative stent placement
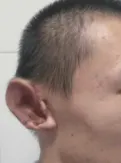
Fig.5 Lateral view 3 months after operation
Before the operation,CT and other imaging techniques were used to fully evaluate the planned costal cartilage,understand the situation of costal cartilage,remove severely calcified costal cartilage,select good cartilage,and provide good materials for scaffold fabrication.At present,there is no uniform standard for the interception of costal cartilage.In the past,three short costal cartilages were usually cut off to carve the ear bracket[9].In this study,two short costal cartilages were cut off to make the bracket,one of which was divided into two layers,and the three-layer superposition carving method was implemented to make the outer edge of the auricle thinner and the shape more vivid.Secondly,in the process of making the stent,the radian of the stent helix should be consistent with the radian of the normal outer ear on the opposite side as much as possible.If there is no deformity in both ears,keep both sides consistent.Only 2 short costal cartilages are cut off,which greatly reduces the trauma to patients,reduces the incidence of complications such as pneumothorax during and after surgery,is conducive to chest stability and accelerates postoperative rehabilitation.Moreover,the thickness of the 7th costal cartilage is close to the thickness of the auricular scaphoid base,which is conducive to a good transition between the implanted scaffold and the auricular residual bone and improves the appearance effect of the reconstructed ear[10]In addition,in the process of scaffold manufacturing,the structural characteristics of costal cartilage should be fully utilized for combined application and manufacturing,which can reach the cranioauricular fossa for one-time molding.Then,the three-dimensional impression is used for multi-level combination carving to make its smooth transition and avoid the feeling of steps.Finally,the stent placement should be accurately positioned,which not only has a close impact on the shape of the reconstructed ear,but also plays an important role in the hearing preservation of patients.The stents were placed bilaterally symmetrically to maintain the anterior cranioauricular angle.Under the guidance of the above operation points,all the reshaped ears of all patients in this study are lifelike in appearance,have no influence on hearing,and are symmetrical on both sides.They are unanimously recognized and praised by patients and their families,which fully demonstrates the scientificity,effectiveness and safety of this research method.
 Chinese Journal of Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery2019年3期
Chinese Journal of Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery2019年3期
- Chinese Journal of Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery的其它文章
- Clinical Study on Facial Rejuvenation of Non-crosslinked Small Molecule Hyaluronic Acid Combined with Filorga NCTF®BOOST135 HA
- Observation on clinical effect of botulinum toxin type A injection combined with low-energy CO2fractional laser periocular rejuvenationtreatment
- The clinical effect of frontotemporal rhytidectomy combined with botulinum toxin type A injection facial rejuvenation treatment
- Observation on the Clinical Effect of Breast Augmentation by Transplanting Concentrated Growth Factor and Autologous Fat
- Research on combination of PRP,PRF and adipose-derived stem cells for wound healing of chronic skin ulcer
- Advances in research on factors of cranioauricular angle formation after auricular reconstruction
