Retrospect and prospect of textile raw materials in 2018
by Flora
2018 marks the year of the 40th of Chinas adoption of the reform and opening-up policy. Chinas textile industry is also faced with new changes of raw material supply, trade rules, consumption market, and investment environment.
In this year, the production capacity and consumption market center has been shifting to emerging countries, and the global industrial labor distribution layout has been reshaped.
This year has also witnessed the transfer of the industry and enterprises from product provision to experience provision, from production manufacturing to service manufacturing, from equipment provision to provision of integrated solution plans.
Retrospect
In retrospect of 2018, different sectors of Chinas textile raw materials have been forging ahead steadily. In particular, the chemical fiber industry has demonstrated a market operation environment oriented towards efficacy and quality. As the equipment and technology of the whole industry are experiencing a higher degree of automation and intelligentization, diversification of products is also accelerating to constantly cope with bottlenecks of raw materials in downstream fields, such as spinning and weaving, thus laying a solid foundation for development of the downstream apparel industries.
Annual performance of the chemical fiber industry
The chemical fiber industry has kept on deepening its supply-front structural reform primarily in the following three aspects.
Release of the new production capacity is accompanied by elimination of the backward production capacity. In 2018, chemical fiber industries, including viscose fiber, polyester, acrylic, and polypropylene, have been faced with the elimination of the production capacity. Take the chemical fiber industry for example. According to requirements of the “Regulations for Chemical Fiber Industry (2017 Version),” the viscose fiber filament industry, though whose total production capacity maintained at around 180,000 tons a year, has formed four major production bases with one in Yibing, Sichuan, one in Jilin, one in Xinxiang, Henan, and one in Nanjing, Jiangsu.
As to the viscose short fiber industry, though around 700,000 tons of the new production capacity has been released in 2018, around 300,000 to 400,000 tons of the backward production capacity would be eliminated. Elimination of the backward production capacity is resulted from not just inconsistency with relevant standards. From a deeper perspective, the new production capacity has an edge over the backward one in terms of large-scale production. Meanwhile, the automation of the new production capacity has led to a significant improvement of the production capacity. Therefore, from the perspective of cost, enterprises should take the initiative to withdraw the old equipment from the historical storage. Due to transformation of the production capacity, the viscose short fiber production line below 30,000 tons has almost disappeared. The polyester, acrylic, polypropylene and other chemical fiber industries have also exhibited a pattern in which the market-oriented elimination mechanism excels the policy-oriented elimination mechanism.
The production bases have been gradually gathering to form clusters. Large-scale groups of subsidiary industries have been sprawling, and some of them have actively distributed their overseas production bases. Take the viscose short fiber industry for example. This year, clusters have been erected in Xinjiang, Hebei, Jiangxi, Jiangsu, Shandong, Zhejiang, etc. Three of them have reached a production scale of more than 700,000 tons. The viscose fiber production capacity in Xinjiang has been close to 1 million tons, accounting for 22% of the total. Among viscose fiber enterprises in Xinjiang, Zhongtai Chemical has reached a production capacity of 930,000 tons. This means that Zhongtai Chemical has contributed around 93% to Xinjiangs viscose fiber production capacity.
In the polyester industry, enterprises represented by Hengli, Hengyi, Tongkun, Rongsheng, Shenghong and so on have developed themselves into large-scale polyester production groups. Meanwhile, groups represented by Tongkun have introduced automatic production equipment, such as mechanical arms and automatic packaging machines, to cut their labor cost and improve their production capacity. By doing so, they have increased their automation level to 80%. Evenness of their product quality has, compared with competitors in the same industry, has been significantly improved. In actively expanding the overseas project, Hengyi Industry (Brunei) Co., Ltd., a subsidiary of Hengyi Group, has been deepening its petrochemical projects in Brunei as an attempt to actively expand its overseas projects in Brunei, and Hengli Group will hopefully clinch the petroleum refining project with the Abu Dhabi government. Both Hengyi Group and Hengli Group are privately-employed enterprises. Expansion of their overseas business is both reflected as active expansion of large-scale groups to upstream refining projects so as to link the whole industrial chain from crude oil to polyester to ensure the safe layout of the whole industry.
In response to tightening of the governments environmental protection policies, enterprises have been investing more and more in environmental protection, which has inevitably increased the cost of the chemical fiber industry. The “National Environmental Protection Review” action launched in the second quarter of 2018, though failing to exert a huge impact on the chemical fiber industry itself, has significantly influenced the upstream and downstream of the whole chemical fiber industry, and such influence is expanding to the whole chemical fiber industry. For example, chemical product enterprises committed to producing caustic soda, sulfuric acid and other auxiliary chemicals of the viscose short fiber have been shut down. The shutdown percentage in Shandong, Jiangsu and so on even reached above 40%. This has seriously influenced the auxiliary chemical raw material supply in Shandong, Jiangsu, Zhejiang, etc. A solid evidence for the serious influence is the sharp rise in the manufacturing cost of viscose short fiber plants in these three provinces. Meanwhile, projects like changing the fuel from coal to gas have led to a rapid increase of cost of viscose short fiber plants. Among the downstream water-jet weaving and printing industry, many dyeing and water-jet weaving plants have been rectified.
Since the upstream and downstream industries are both subject to the influence of environmental protection policies, the operating rate of various links has been inadequate. As a result, the chemical fiber price and delivery state in 2018 have been in a lukewarm state. The price increase of raw materials has led to an increasing cost of chemical fibers. At the same time, due to production limitations of downstream industries, the delivery channels of chemical fiber products have been blocked. Under the condition, the price of chemical fibers, though experiencing a major rise in the third quarter, is still restricted by downstream delivery channels. In the fourth quarter, the commodity price of the whole chemical fiber industry and cotton industry has both undergone a fall after rise.
Annual performance of the cotton spinning industry
With the escalation of Sino-US trade frictions from March of the first quarter, the employment confidence in the cotton spinning industry has been weak. A main reason is that the emergence of new situations to the international trade pattern has caused a misconception that Sino-US trade frictions in 2018 would be more severe than the financial crisis in 2008, thus holding back many traders from receiving orders. Influenced by such a mentality, the annual performance of the cotton spinning industry is as below:
Before receiving a new order, the trader is concerned about the currency exchange rate, financial and cargo safety. In 2018, the exchange rate of RMB shows a trend of “first appreciation and then depreciation,” which is just contrary to that in 2017, which was“first depreciation and then appreciation.” The appreciation of the RMB exchange rate will trigger losses of export enterprises upon settlement of exchange. Therefore, foreign trade enterprises who just suffered losses in this aspect dare not receive too many orders in the appreciation stage of RMB exchange rate in the first half of 2018. After June 2018, the RMB exchange rate starts depreciating. A majority of foreign traders in the cotton spinning industry still dare not receive orders. The status has continued to the third quarter. When RMB demonstrates a strong depreciation signal, foreign trade enterprises also have the courage to receive orders as usual. Nevertheless, the aggravation of the Sino-US trade frictions and the worldwide geopolitics have aroused many Chinese foreign trade enterprises concern about receiving orders. In spite of that, the data released by the Customs show that the annual export data of the cotton spinning industry are still dominated by a growing trend on the whole. The only change is that the export destinations have been transferred from European or American countries to Southeast Asian and African countries.
Structural adjustment of the cotton spinning product types happens on a frequent basis. Considering the high price and frequent price fluctuations of chemical fiber products, the downstream cotton spinning plants have adopted two measures. First, proceed from the order perspective to purchase raw materials to make conventional yarns. Second, make use of the low-cost textile raw materials for new product development. For example, in early 2018, the price of cotton and polyester is relatively cheap. Additionally, the expectation of a lower output of cotton has led to the expectation of a rising crude oil price. Therefore, many textile enterprises have adjusted their product structure to adopting cotton or polyester as raw materials for spinning. Due to that, the cotton and polyester industry have achieved a considerable increase of their price as raw materials in the second and third quarters. Pitifully, because of the surge in the price of these two raw materials, the downstream spinning plants have started adopting viscose short fiber or other relatively cheap raw materials for spinning. This can well explain the slump of the cotton and polyester price in the fourth quarter.
In the field of covering yarn, acrylic fiber covering yarns have gradually replaced viscose short fiber covering yarns to become a mainstream covering yarn in the market. At the same time, the covering cores dyeing is under environmental protection. Some spinning plants have started developing the colorful polyester covering corn made up of the colorful, modified polyester short fibers. These changes have enriched the species of textile products in 2018, which are much more than those in 2017.
The product prevailing period has been shortened, and the e-commerce marketing channels have made great strides. Diversity of yarns has facilitated the development of textile terminal products, including garments and home textiles. The prevalence period of a style might be automatically shortened along with community output. This is partially attributable to shortening of the terminal product period. Moreover, textile apartments have taken a growing percentage on large-scale network platforms, such as Taobao.com, Tianmao.com, Jingdong.com and Suning.com. Appearance of new platforms has included the textile garments. For example, following startup of pinduoduo, a Chinese e-commerce platform which allows users to participate in group buying, many textile individual businesses have appeared. Therefore, the establishment speed of e-commerce channels for textile products in 2018 is much faster than that in 2017. During the “November 11 Shopping Festival” of Taobao. com, the total turnover reached 213.5 billion yuan, rising by 26.93% compared with 168.2 billion yuan in 2017. Among the large trading volume, sales of knitted blouses, socks and trousers, made a considerable contribution.
Review of multiple indexes
Here, three textile raw materials with a wide range of applications and adequate production capacity in the target market, including synthetic fibers, viscose short fibers and cottons, are adopted to analyze the textile raw material market operation status in 2018.
Output
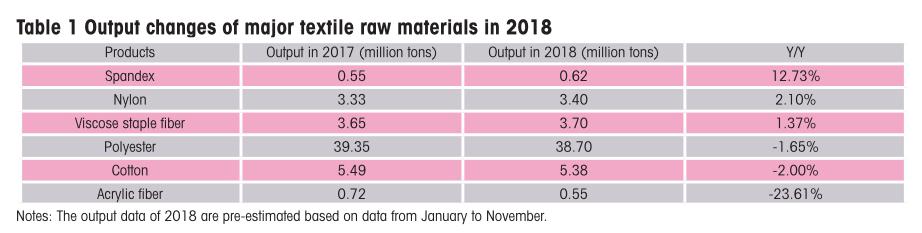
From Table 1, one can observe that increase and decrease coexist in the output of major textile raw materials of 2018. Among them, the output of spandex, nylon and viscose staple fiber is on an increasing trend. Meanwhile, spandex ranks No. 1 as to its output, registering a year-on-year increase of 12.73% compared with that in 2017. The increasing output of nylon mainly benefits the growing output of cotton bale ammonia and rayon ammonia. In order to turn out more comfortable and fit fabrics, more spandex should be added into differ-ent fabrics. The total output of spandex this year is expected to reach 620,000 tons, which might be even higher than that of acrylic fibers, known as “man-made wool”.
Growth of nylon and viscose staple fiber cannot be separated from popularity of covering core with these two fabrics as raw materials in 2017. Currently, nylon and viscose staple fiber still constitute primary raw materials of covering core. In 2018, the covering core has diversified its types from the purely “28S imitated rabbit hair” to “imitated rabbit hair”, “rainbow core covering”, “imitated mink cashmere” and so on. The favorable hand feel and fur look of the said covering cores has directly resulted in a declining output of conventional acrylic fibers. Besides, though the covering core made up of acrylic fibers has gained a solid foothold in the yarn market of 2018, acrylic fibers are sold at an exorbitant price. Consequently, the lower yarn clients and knitwear clients do not have a strong demand for acrylic fibers. Besides, the output of acrylonitrile with acrylic fiber as the raw material is still limited. This is also partially responsible for a sharp shrinking in the output and use of acrylic fibers in 2018. In 2018, the total output of acrylic fibers is expected to reach 550,000 tons, decreasing by 23.61% compared with that in 2017.
In terms of cottons, though the planting area has seen considerable increase in 2018 compared with that in 2017, there are too many extreme weathers this year. Particularly after filling the gaps with seedlings, the cotton-growing areas have been suffering from harsh weathers. As predicted by relevant institutions, the cotton output in 2018 will be to some extent lower than that in 2017, and the decrease is expected to be around 2%. In terms of polyester, its output has been largely restricted by the gradual increase of the crude oil price from June to early October in 2018. The growing cost of polyester is mainly reflected as a rapid increase of the PTA price. In some regions, polyester plants have to limit their production or even stop it. The output of 2018, compared with that in 2018, is expected to reduce by around 1.65%.
Price
As one notices in Table 2, price of raw textile raw materials in 2018 is on an upward trend. Below are major causes:
In response to the tightening environmental protection measures, production units have transferred part of their cost to product price. Take the price of viscose staple fiber for example. Its price is around 14,606 yuan per ton on average, which is 7.49% lower than that in 2017. Nevertheless, there are two price peaks in 2018 — one happening in May and the other in September. The price peak has a close bearing on environmental protection of May and September. Coupled with the continuous improvement of prospects of the paper-making industry, the price of raw and auxiliary materials for viscose short fiber has been on the rise. From the perspective of gross profits, the whole industry or the enterprises did not see many profits, while some small enterprises even suffered losses.
The decreasing output has led to an increasing price. Though the downstream industries might reduce their use of acrylic fibers, the decreasing output of acrylic staple fibers cannot yet prevent their shortage in the market. The acrylic fiber industry suffering the sharpest decrease is mainly characterized in a strong rise. Table 2 shows that the price rise of acrylic fiber products is above 20% on average in 2018.
After June, the increasing crude oil price has resulted in a price increase of polyester and nylon product series by around 8% to 14%. The price of polyester staple fibers and polyester filament yarns, compared with that in 2017, increases by 13.99% and 8.39%, respectively. There are two reasons for the sharp price increase of polyester staple fibers. On the one hand, the price base is relatively low. On the other hand, the textile spinning plant has a growing demand for polyester staple fibers. Similarly, there are two reasons for the growing demand. First, polyester staple fibers, apart from being used to make covering cores, have also been applied to other fields. For example, the T/R blending yarn series is very popular in 2018, so its output increases by a large mar- gin compared with that in 2017. Second, the potential of the polyester-made chenille yarn market has also been further tapped in the second half of 2018 with its applications extended to the field of carpets and decorations within cars. Hence, the rising cost is just partially responsible for the price increase of the polyester series. In fact, the price increase is largely driven by a growing demand of downstream operators.
The increasing output and complexity of the external environment have jointly resulted in a price decrease. Take viscose staple fiber and polyester for example. Driven by the sharp expansion of the production capacity, the product supply of these two fibers has both been improved, which has, to some extent, upset the original supply-demand balance, thus leading to an overall price decrease. The output of cotton is mainly influenced by the obscure external environment and the national governments reduction of tax levied on imported products. In the fourth quarter of 2018, the price of imported products suffers a dramatic decline, which offsets the increase in the second quarter and the third quarter.
Profits
In 2018, the polyester series and nylon series have made profits all the year around. In contrast, vis- cose staple fibers and acrylic fibers experience one to two losses in 2018. Moreover, the loss period of the acrylic fiber series has lasted for nearly half a year. To sum up, the earning power of textile raw materials in 2018 has a close bearing on the above output and price. The bilateral correlation is mainly reflected as below:
The polyester series, though experiencing a decline in its output, has been considerable profitable, considering its price and earning power.
The nylon series, if seen from the output, price and earning power, has its price mainly driven by downstream demands. Therefore, the output changing trend of nylon is steadier than that of acrylic fiber and polyester.
In 2018, the output of acrylic fiber drops. A main reason is that the industrial losses are so serious that the acrylic fiber industry has to limit or reduce its production. It is not until the fourth quarter that the acrylic fiber industry starts to make profits.
Excluding acrylic fiber which demonstrates a vigorous increase in its earning power, the rest of fibers all have experienced a shrinking of their gross profits.
Operating rate
In terms of the operating rate of major chemical fibers, there is an industry-wide decline in the first quarter of 2018, because the Spring Festival of 2018 falls on February 16. The operating rate of nylon plummets to around 50% before and after the Spring Festival. The operating rate of the spandex, polyester filament yarn and viscose staple fiber maintains at around 77%, 66% and 73%, respectively. After the Spring Festival, the operating rate of polyester filament, nylon, spandex and viscose staple fiber hovers in the section of 75% to 88%. Comparatively, the operating rate of synthetic fibers is slightly higher than that of viscose staple fiber. In the fourth quarter, the operating rate of the viscose staple fiber industry rises to 90%, and the figure for the synthetic fiber industry ranges from 80% to 82%. The operating rate of chemical fibers in 2018 has generally taken a good turn, which cannot be separated from the downstream support of the textile industrial chain.
Inventory
From the perspective of inventory, the inventory of spandex can support more than 30 days of supply. In September, the inventory even reaches a peak, which suffices to supply for 45 days. The high-inventory operation of spandex is mainly attributable to the gradual drop of the spandex price. However, it is widely believed among spandex plants that there is the slack season and the peak season every year, and that, as long as they have adequate funds, they can let the inventory sustain from the slack season to the peak season to profit from the changing price trend. Such an idea prevails in the spandex industry, leading to a high inventory of spandex and forcing spandex operators to shift their inventory via price reduction.
The inventory of the nylon industry takes a good turn in the second half of 2018. The inventory in the first half of 2018 generally maintains at above 20 days. However, from the second half of 2018, the industrywide inventory level ranges from 15 days to 17 days.
The inventory of viscose staple fibers lasts from five days to 20 days. Of special note is that from late April to early November, the industrial inventory operates at a level of more than 15 days.
The increasing inventory of the viscose staple fiber is mainly because the new production capacity of the viscose staple fiber has been almost fully released from October to November. It takes time for the production capacity of the new line to satisfy market demand.
Prospect
Prospect of macroeconomics
The macroeconomic operation in the fourth quarter of 2018 suggests that the global economy is in a slump. With the weakening growth momentum and tightening financial status of emerging and developing economies, the prospect of the global economy growth outperforming the expected level has been weakening.
The International Monetary Fund (IMF) has also lowered the expected global economic growth speed. In fact, mainstream global institutions are not positive about macroeconomic policies in 2019. However, thanks to remarkable achievements of Chinas supplyfront structural reform, from the third quarter of 2018, the financial field has been evolved from “deleveraging” to “stabilization of leverage”. Meanwhile, from the second half of October 2018, the State Council, Peoples Bank of China, China Securities Regulatory Commission and other relevant departments have promulgated a series of policies to guarantee a minimum level. It is expected that the market bottom is expected to foster around the second quarter of 2019 under the above policy support. From the second half of 2019, Chinas macroeconomy will hopefully make a turnaround.
In October 2018, introduction of the document entitled Improvement and Promotion of the Consumption Mechanism and Institution Implementation Plan (2018 - 2020) suggested that Chinas future macroeconomic policy would stick to supply-front structural reform and consumption stimulation. In 2019, this policy is likely to be further detailed and implemented. From the demand perspective, after the implementation of the consumption mechanism and institution plan, Chinas macroeconomic growth point will shift from the supply-front to the demand-front step by step, thus embarking on a new round of normalized macroeconomic growth period.
Chances are high that RMB exchange rate in 2019 would change with 6.85 at the center. From 2015 to early 2017, the RMB was in the depreciation stage. From 2017 to April 2018, the RMB shifted to an appreciation stage. From May 2018 to present, the RMB has been in a depreciation stage. Currently, the RMB exchange rate has touched the strategic pass of 7. However, some large-scale institutions think that chances are low for RMB exchange rate to hover around 7. Instead, the RMB exchange rate will still revolve around 6.85.
Prospect of the crude oil price
Under the background of a high supply-front elasticity (there is still a large room for improvement of the OPEC supply, and the high oil price has driven the output of shale oil) and uncertain demand (the American economy is approximating the inflection point in this round of recovery, and Chinas economic growth is faced with overwhelming pressure), the decreasing output resulted from Americas withdrawal from the Iranian Nuclear Deal can be offset by the increasing output of other oil manufacturers. The high oil price has its endogenous instability, and fluctuations resulted from short-term transaction happen now and then. However, the possibility for the oil price in the coming one year to stabilize above 100 USD is very low. Currently, the United States Energy Information Administration predicts that the crude oil price of the WTI will stay around 69.56 USD per barrel, 1.65 slightly higher than expected in 2018. The prediction is too conservative. Considering the favorable prospect of the crude oil price in the last round, the crude oil price in New York is likely to rise to 75 USD per barrel in 2019.
Prospect of the textile raw material market
By investigating the output, price, profit, operating rate and inventory of textile raw materials in the fourth quarter of 2018, the output of the whole chemical fiber industry is experiencing a further increase. In the fourth quarter of 2018, the operating rate of chemical fiber products, excluding the spandex industry with a high inventory, all maintains at a steady level or increases slightly. Meanwhile, their inventory is relatively stable. However, the inventory of the viscose staple fiber in the fourth quarter increases sharply, indicating that the new production capacity of viscose staple fiber will be finally consumed in the fourth quarter.
Seen from price and profit, the price of multiple products on the textile raw material market is dropping in the fourth quarter of 2018. On the contrary, the price of acrylic fiber, which has been in a losing state, has changed to an upward trend. As to profits of polyester, nylon, and viscose staple fiber, they are gradually offset by their growing costs. In 2019, under the condition of a high cost and a large inventory, the operating rate is expected to drop gradually. At the same time, as the product price stays at a level where profits and losses are at a balance, the operating rate will sustain for three to four months within the section. After the inventory is consumed by downstream industries, the price of three textile raw materials is likely to increase. On the whole, since the production capacity is expanding swiftly, huge price fluctuations will hardly happen under a weak balance state of the supply-and-demand relationship.
At the same time, since the price of convention product types is low, the downstream textile plants and apparel brand owners might fall into the trap of “new product R&D.;” In other words, more funds and human resources will be put in to develop yarns and fabrics for the niche market to promote the fashion trends. In the process, the textile product cycle in 2019 will be much faster than the current “one product cycle every three years.” In other words, the development pattern of “the imitating speed slower than the innovation speed” might appear, thus exerting the pressure on the inventory of yarns or fabrics for the niche market throughout the industry. This is something worth more precautions. To sum up, since the macroeconomic development is expected to be robust in the first half of 2019, enterprises in the textile raw material market might spontaneously limit their production. However, because many people are positive about the prospect of the crude oil price and macroeconomy in 2019, the textile raw material market will in the second half of 2019 hopefully get rid of the plunge of the fourth quarter of 2018 to usher in a new round of industrial cycle.
- China Textile的其它文章
- What kind of big change will the textile industry usher in?
- Focusing on textile intangible cultural heritage to promote cultural confidence
- 2018.12
- World’s primary sustainable fashion design competition launched with new industry partners to support growth in China
- Local charity REDRESS collects a recordbreaking 9 tonnes of unwanted clothing for“GetRedressed Month”
- 15 years of ISPO Beijing:A success story in the growth market of China

