Effects of Progressive Muscle Relaxation Training Combined with Emotion Nursing of Traditional Chinese Medicine on Motor Function and Quality of Life in Patients with Cerebral Stroke Complicated with Hemiplegia
Liu Yun (刘 云)
Rehabilitation Medicine Department, Suzhou Municipal Hospital, Suzhou 234000, China
ABSTRACT
OBJECTIVE: To explore the effects of progressive muscle relaxation training combined with emotion nursing of traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) on the motor function and quality of life in patients with cerebral stroke complicated with hemiplegia. METHODS: A total of 100 cases of patients with cerebral stroke complicated with hemiplegia who were admitted to Rehabilitation Medicine Department of Suzhou Municipal Hospital from May 2016 to May 2017 were selected and randomly divided into study group (50 cases) and control group (50 cases), and they were nursed for 1 month. Control group was given routine nursing, and study group was given progressive muscle relaxation training combined with TCM emotion nursing on the basis of routine nursing. The scores of all items were obtained by nurses through questionnaires, and the motor function and quality of life were analyzed and compared between the 2 groups.RESULTS: After nursing, the scores of muscle strength, Barthel index (BI) and Fugl-Meyer motor function scales in study group were higher than those in control group (P < 0.05). The facing scores of coping style in study group were higher than those in control group, and the avoidance score and yielding score were lower than those in control group(P < 0.05). The scores of depression and anxiety in study group were lower than those in control group (P < 0.05). The scores of items in SF-36 life scale in study group were higher than those in control group (P < 0.05). CONCLUSION:Progressive muscle relaxation training combined with TCM emotion nursing is conducive to the recovery of motor function and improvement of quality of life in patients with cerebral stroke complicated with hemiplegia.
KEYWORDS: Progressive muscle relaxation training; Emotion nursing of traditional Chinese Medicine; Cerebral stroke complicated with hemiplegia; Rehabilitation therapy
In China, there are about 2.5 million new patients with cerebral stroke every year, of which about 75% are disabled[1]. While in western developed countries, stroke has become disease with the third highest disability rate and the highest mortality rate[2]. Hemiplegia is the most common disabiling complication of stroke, and about 33% of patients suffer from depression[3]. Studies have shown that the best time for recovery after hemiplegia is within 3 months after the onset of the disease, and the earlier the rehabilitation is carried out, the better the effects of body function recovery in the later stage will be[4]. With the improvement of the current medical level,rehabilitation treatment can effectively improve the longterm survival rate and reduce the disability rate, but it is not effective in improving the depression after cerebral stroke. On this basis, the team of Rehabilitation Medicine Department of Suzhou Municipal Hospital believes that progressive muscle relaxation training and emotion nursing of traditional Chinese medicine can be combined to treat the depression of patients and promote the process of rehabilitation. The research results are as follows.
DATA AND METHODS
Clinical data
From May 2016 to October 2017, a total of 50 cases of patients with the first attack of cerebral stroke complicated with hemiplegia who were hospitalized in Rehabilitation Medicine Department of Suzhou Municipal Hospital were selected and were randomly divided into study group (50 cases) and control group (50 cases).And the onset time was within 3 months. All the patients included met the clinical diagnostic criteria of stroke complicated with hemiplegia. There were 16 males and 9 females in the control group, aged 45-73 years old, with an average age of 64.52 ± 5.23 years old; and course of hemiplegia ranged from 25 to 82 days, with an average course of 48.25 ± 6.49 days; and the complications included 13 cases of hypertension, 7 cases of diabetes, and 6 cases of hyperlipidemia. There were 15 males and 10 females in the control group, aged 42-75 years old, with an average age of 65.43 ± 5.51 years old; and course of hemiplegia ranged from 30 to 84 days, with an average course of 50.22 ± 6.76 days; and the complications included 12 cases of hypertension, 9 cases of diabetes, and 8 cases of hyperlipidemia. Before the study, there was no significant difference in general clinical data between the 2 groups (P > 0.05).
Inclusion criteria
(1) The diagnosis of cerebral stroke was confirmed by CT or MRI, which accorded with the diagnostic criteria adopted by the Fourth National Cerebrovascular Conference in 1995. The diagnosis of hemiplegia conforms to the criteria of Examination and Evaluation of Hemiplegia after Stroke[6]; (2) it was the first onset without obvious consciousness, mental or hearing impairment; (3)the patients had basic listening and speaking and reading comprehension ability, and voluntarily signed informed consent; (4) there were no stressful life events recently.
Exclusion criteria
(1) Those who were with severe heart failure and severe liver and kidney diseases were excluded; (2) those with dementia were excluded; (3) those who were unable to sign the informed consent independently were excluded.
Methods
After admission, the control group received routine nursing treatment, such as morning and evening nursing, dietary guidance, medication nursing, defecation nursing, psychological nursing and health education.Rehabilitation training guidance was given according to the patient's condition.
On the basis of routine nursing, the study group adopted progressive muscle relaxation training combined with emotion nursing of traditional Chinese medicine.The nursing time of both groups was one month. The specific methods were as follows.
Progressive muscle relaxation training method:According to Benston's Progressive Relaxation Training Manual, first keep the ward quiet, and patients should evacuate before training, and then let them wear headphones to assist guidance through downloaded audio lessons. The patient should lie on his back, close his eyes,concentrate his attention, take a deep breath, and slowly feel the tension of the muscles from hands, to arms, biceps brachii, forehead, eyes, neck and throat, and to shoulder,back, chest, abdomen, buttocks, and last to thigh, leg and feet. After 5 seconds, the patient should expel air and relax the muscles for 15 seconds. At the same time, the patient should slowly feel the feeling of muscle relaxation.Alternate each part of the muscle relaxation at least 2 times,and then repeat the training for those muscles that are not completely relaxed. Each training time should be about 30 minutes, and twice a day in the morning and evening.
Emotion nursing methods of traditional Chinese medicine: (1) Emotion counseling method: nurses should talk with patients while visiting the wards, listen patiently to the problems and difficulties they encountered in the course of treatment, understand their psychological state and needs, inform the effects of their emotions on the recovery of the disease, and help them cooperate with the treatment with calm and peaceful emotions; (2) emotion transferring method: arrange patients with similar interests in the same ward, organize them to listen to songs, watch operas and discuss recent social events during non-treatment time, and increase social activities to reduce their negative emotions caused by loneliness and anxiety during hospitalization;(3) emotion substitution method: with the guidance of the nurses, the patient would recall the happy and interesting fragments of his past life, or tell about his areas of expertise to promote his sense of pride, thus helping him overcome depression, and strengthening his confidence in the treatment of diseases; (4) differential care method: for the introverted patients, encourage him or her to speak more about his feelings. For the sensitive, discussion of unfavorable conditions in front of them should be avoided and they should be praised more often. For the extroverted, explain the significance of retraining to them to keep the family rehabilitation training after discharging from hospital.
Evaluation standards
The score of muscle strength was measured by six-level test of American Medical Research Council, with a score of 0-6. The higher the score was, the better the muscle strength would be. The score of BI was calculated by Barthel index, with a score of 0-100. The higher the score was, the better the self-care ability would be. The score of Fugl-Meyer[7]motor function scale was divided into upper limb motor function score 0-66 and lower limb motor function score 0-66. The higher the score was, the better the motor function of limbs would be. Coping style was scored by 1-4 grade of medical questionnaire, which contained 20 items, including facing, avoidance and yielding. The higher the facing score was, the stronger the coping ability would be, and the lower the avoidance score and yielding score would be. The anxiety and depression scores were evaluated by self-rating anxiety scale and self-rating depression scale, with 20 items in each set of questionnaires, and the score was multiplied by the integral part of 1.25 after adding the scores.The higher the scores were, the higher the anxiety and depression level would be; the quality of life score was evaluated by some items of the SF-36 scores including body function, body role, social function, body pain,vitality, social function, emotion role and mental health.The higher the score was, the better the situation would be.
Table 1. Comparison of motor function score before and after nursing between the 2 groups
Notes: Compared with before nursing, ①P < 0.05; compared with the control group after nursing, ②P < 0.05.
Upper limb (point) Lower limb(point)Study group Before nursing 2.81±0.61 53.31±5.32 21.31±5.57 10.25±4.65 After nursing 4.45±0.62①② 71.84±4.96①② 42.42±5.63①② 20.35±5.63①②Control group Before nursing 2.84±0.54 54.45±5.51 20.22±4.56 11.24±5.21 After nursing 3.41±0.78① 64.23±5.56① 35.55±5.12① 15.36±6.31①Group categories Time Scores of muscle strength (point) BI (point)
Statistical methods
SPSS17.0 software was used to analyze the data collected before and after nursing. The measurement data were expressed by (x–±s). Paired t-test was used for intragroup comparison and independent t-test was used for inter-group comparison. P < 0.05 suggested that there was statistical significance.
RESULTS
The scores of motor function before and after nursing in the 2 groups were compared. There was no significant difference between the 2 groups before nursing (P > 0.05). The scores of motor function in the study group were higher than those in the control group after nursing. The difference between the 2 groups was significant (P < 0.05). See Table 1.
Comparing depression and anxiety scores before and after nursing, there was no significant difference between the 2 groups before nursing (P > 0.05). After nursing, the anxiety score and depression score in the study group were both lower than those in control group, and the difference between the 2 groups was significant (P < 0.05). See Table 2.
Table 2. Comparison of depression and anxiety scores before and after nursing between the 2 groups

Table 2. Comparison of depression and anxiety scores before and after nursing between the 2 groups
Notes: Compared with before nursing, ①P < 0.05; compared with the control group after nursing, ②P < 0.05.
Depression scores (point)Study group Before nursing 58.93±6.21 62.71±6.08 After nursing 45.29±5.76①② 47.56±5.82①②Control group Before nursing 59.23±5.63 63.37±6.21 After nursing 50.56±5.32① 56.51±5.64①Group categories Time Anxiety scores (point)
Comparing of coping style scores before and after nursing, there was no significant difference in the scores of facing, avoidance and yielding before nursing between the 2 groups (P > 0.05). After nursing, the scores of facing in study group were higher than those of control group, while the scores of avoidance and yielding were lower than those of control group. There was significant difference between the 2 groups (P < 0.05). See Table 3.
Comparing scores of life quality before and after nursing, there was no significant difference before nursing between the 2 groups (P > 0.05). After nursing, the scores of life quality in the study group were higher than those in the control group with significant difference (P < 0.05).See Table 4.
DISCUSSION
Cerebral stroke is cerebral blood circulation disorder caused by blockage of cerebral blood vessels or suddenrupture of cerebral blood vessels, causing transient or permanent functional damage in brain tissue[8].Hemiplegia is one of the most common complications of cerebral stroke. Although the illness can be alleviated after treatment, most patients will still suffer from anxiety,depression and even lose confidence in treatment because of long time of rehabilitation training yet with difficulty and ineffective efficacy. At present, progressive muscle relaxation training has been applied in the clinical treatment of psychological diseases and in various rehabilitation abroad, most of which have achieved good results[8].Studies have shown that emotion nursing of traditional Chinese medicine can promote the psychological and physiological rehabilitation of patients with cerebral stroke complicated with hemiplegia, and improve their negative emotions[10,11]. In this study, progressive muscle relaxation training combined with emotion nursing of traditional Chinese medicine is conducive to improving the effect of rehabilitation treatment and speeding up the process of rehabilitation treatment.
Table 3. Comparison of coping style scores before and after nursing between the 2 groups

Table 3. Comparison of coping style scores before and after nursing between the 2 groups
Notes: Compared with before nursing, ①P < 0.05; compared with the control group after nursing, ②P < 0.05.
Study group Before nursing 4.55±1.21 5.21±0.96 4.74±0.95 After nursing 7.52±1.62①② 2.45±0.73①② 2.51±0.72①②Control group Before nursing 4.63±1.35 5.06±0.76 4.59±0.75 After nursing 5.24±1.46① 4.13±0.81① 3.92±0.63①
Table 4. Comparison of scores of life quality before and after nursing between the 2 groups
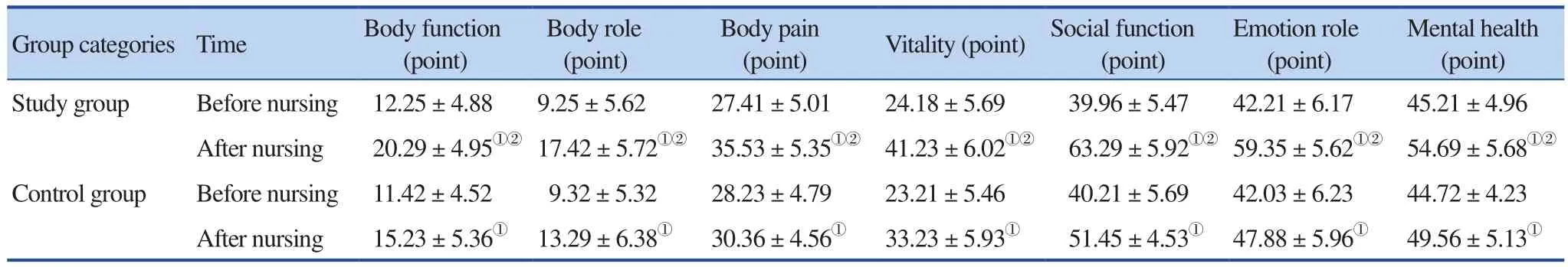
Table 4. Comparison of scores of life quality before and after nursing between the 2 groups
Notes: Compared with before nursing, ①P < 0.05; compared with control group after nursing, ②P < 0.05.
Group categoriesTime Body function(point)Mental health(point)Study group Before nursing 12.25±4.88 9.25±5.62 27.41±5.01 24.18±5.69 39.96±5.47 42.21±6.17 45.21±4.96 After nursing 20.29±4.95①② 17.42±5.72①② 35.53±5.35①② 41.23±6.02①② 63.29±5.92①② 59.35±5.62①② 54.69±5.68①②Control group Before nursing 11.42±4.52 9.32±5.32 28.23±4.79 23.21±5.46 40.21±5.69 42.03±6.23 44.72±4.23 After nursing 15.23±5.36① 13.29±6.38① 30.36±4.56① 33.23±5.93① 51.45±4.53① 47.88±5.96① 49.56±5.13①Body role(point)Body pain(point) Vitality (point) Social function(point)Emotion role(point)
In this study, the muscle strength score, BI score and Fugl-Meyer motor function scale score of the study group and the control group increased after nursing, and the score of the study group was higher than that of the control group (P < 0.05), indicating that progressive muscle relaxation training accelerated motor recovery faster than traditional rehabilitation training. Previous studies have shown that muscle relaxation training can relieve tension, regulate the central nervous system and promote the recovery of physiological function[12,13].Ju Shan[14]and others believe that progressive muscle relaxation training is safe and easy to master, and can be applied to various fields of nursing. The score of coping style in the study group and the control group increased,and the score in the study group was higher than that in the control group, while the scores of avoidance and yielding in the 2 groups decreased, and the score in the study group was lower than that in the control group(P < 0.05). The scores of anxiety and depression in the study group were lower than those in the control group(P < 0.05), suggesting that emotion nursing of TCM can effectively improve patients' negative emotions and promote their physical and mental health. Xue Dongqun and others believe that emotion nursing of TCM can promote the establishment of good relationship between nurse and patient, improve the quality of life, and promote the rehabilitation of diseases. The scores of body function, body role, body pain, vitality, social function,emotion role and mental health in the SF-36 life scale of the study group and the control group increased after nursing. The scores in the study group were higher than those in the control group (P < 0.05), indicating that the combination of the 2 could effectively improve the life quality of patients. The reason was that progressive muscle relaxation training and emotion nursing of traditional Chinese medicine complemented each other and benefit each other. The advantages of progressive muscle relaxation training and emotion nursing of traditional Chinese medicine in previous studies were basically consistent with the results of this study.
In conclusion, progressive muscle relaxation training combined with emotion nursing of traditional Chinese medicine is more conducive to the recovery of patients' motor function, physical and mental health,and improve the quality of life. Because the cases of the study were chosen from the Rehabilitation Medicine Department of Suzhou Municipal Hospital, and that there were some inclusion criteria for the research group and the control group, the sample size of this study was small and limitedly representative. In the later stage, the number of samples, the follow-up time would be increased to continue in-depth research and promote the application of progressive muscle relaxation training combined with emotion nursing of traditional Chinese medicine in clinical practice.
 World Journal of Integrated Traditional and Western Medicine2019年1期
World Journal of Integrated Traditional and Western Medicine2019年1期
- World Journal of Integrated Traditional and Western Medicine的其它文章
- World Federation of Chinese Medicine Societies Center for Translation
- Effects of Acupoint Massage Combined with Cupping Therapy on Postpartum Lactation and Mastitis in Puerpera
- Effects of Traditional Chinese Medicine Five-element Music Combined with Acupoint Application on Perioperative Sleep Quality in Patients Undergoing Joint Replacement Surgery
- Effects of Tanshinone Combined with Western Medicine on Clinical Symptoms and Cardiac Function in Patients with Acute Heart Failure
- Effects of Maixuekang Capsules Combined with Edaravone on Serum MMP-9, S-100β Protein Levels and Neurological Functions in Patients with Hemorrhagic Cerebral Infarction
- Clinical Comparison and Analysis of Decoction of Traditional Chinese Medicine Combined with Ear Acupoint Application and Simple Artificial Tears in the Treatment of Dry Eye Syndrome
