Artemis影响人肝癌细胞BEL-7402/5-FU化疗药物敏感性的研究
李宇婷,张 雪,范 芳,李大玉,余春波,陈佳瑜,刘 云,李长福
(1.遵义医学院 生物化学教研室,贵州 遵义 563099;2.遵义医学院 医学与生物学研究中心,贵州 遵义 563099)
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is a common malignant solid tumor and leads the 2nd cancer mortality amongst all malignancies of the world[1].Chemotherapy is a common choice for managing patients with or without surgery.However,multidrug resistance (MDR) is almost unavoidable,and almost every HCC case shows disease progression after chemotherapy[2].The mechanisms correlated with the development of drug resistance are complicated,and one of them is DNA damage repair[3],related to the drug resistance of hepatocarcinoma cell line BEL-7402/5-FU cells as reported in previous studies[4].Commonly,DNA damage stress response prompts histone modification near the site of DNA damage,especially histone H2AX phosphorylated to γ-H2AX[5].Thus,γ-H2AX was detected as an indicator of DNA damage in this research with Mitomycin (MMC).
Recently,Artemis,a nuclease with specific structure that participates in the non-homologous end joining (NHEJ) repair of DSBs[6],was approved that its phosphorylation by DNA-dependent protein kinase catalytic subunit (DNA-PKcs) was involved in DNA damage repair of BEL-7402/5-FU cells[7].Ataxia-Telangiectasia Mutated Protein (ATM),a protein kinase,has been shown to maintain the functional integrity of cells under DNA damage stress situation[8].However,far too little attention has been paid to whether Artemis is involved in multidrug resistance of BEL-7402/5-FU cells and whether this effect is associated with ATM.
To further the understanding of role of Artemis in the development of MDR in BEL-7402/5-FU cells,we knock downed Artemis gene in BEL-7402/5-FU cells and explored the sensitivity and resistance to 5-fluorouracil,MMC and sorafenib,respectively.We hypothesized that chemotherapy sensitivity is correlated with Artemis and ATM in BEL-7402/5-FU cells.
1 Materials and methods
1.1Cell culture and transfectionThe human hepatocellular carcinoma cell lines BEL-7402 and BEL-7402/5-FU were purchased from KeyGenBiotech (Nanjing,China) with satisfactory authentication.Both cell lines were maintained in RPMI-1640 (Gibco; Thermo Fisher Scientific,Inc.) supplemented with 10% fetal bovine serum (FBS) (Gibco; Thermo Fisher Scientific,Inc.) at 37 ℃ and 5% CO2.shArtemis group of BEL-7402/5-FU cells,in which Artemis was knocked down,were transfected with pSGU6/GFP/Neo/shArtemis interference plasmids from Sangon (Shanghai,China) using Lipofectamine®2000 from Invitrogen (NY,USA),according to the manufacturer’s recommended protocol.The equivalent amounts of pSGU6/GFP/Neo or Lipofectamine®2000 were complexed to use as negative reference control which grouped into shNC group and LIP2000 group,respectively.BEL-7402/5-FU cells without any treatment were Control group.Cells within the logarithmic growth phases and 60%~70% confluency were utilized.GFP expression was visualized to calculate transfection efficiency by using an Olympus IX3 fluorescence microscope (Tokyo,Japan).
1.2RNA isolation and Real-time PCRAfter 24 h incubation with DNA-lipid complex,the medium was removed and the transfected cells were washed three times with sterile 1 × PBS.Total RNA was extracted from the cells using RNAiso Plus kit from TaKaRa (Tokyo,Japan).Complementary DNA (cDNA) was synthesized with PrimeScriptTMRT-PCR Kit (Tokyo,Japan).Artemis and P-glycoprotein (P-gp) mRNA levels were verified by Real-time PCR by using SYBR® Premix Ex TaqTMII (Tokyo,Japan) on a CFX96 system (Bio-Rad; CA,USA).Primers (Tab 1) were designed and purchased from Sangon.The relative gene expression level was calculated by the Ct value method with the 2-ΔΔCtformula.
Tab1ThePrimersofArtemis,P-gp,β-actin

PrimersSequenceProduct lengthArtemisForward5'-GTGGTTTGGAGAAAGGAGCA-3'134 bpReverse5'-CGTTCACAGGACAGAGGTAGC-3'P-gpForward5'-GGAGATAGGCTGGTTTGATGTG-3'316 bpReverse5'-ACAAGAAAGTCAGTTACCGTTG-3'β-actinForward5'-TGACGTGGACATCCGCAAAG-3'203 bpReverse5'-GGAGCGACAGGTGGAAGGTC-3'
1.3MTT assayBriefly,parental cells BEL-7402 and 5-FU resistant cells BEL-7402/5-FU cells were seeded into a 96-well plate at a density of 8×103cells/well with six replicate wells for each group cultured in the regular condition overnight.BEL-7402/5-FU cells which were transfected with and without pSGU6/GFP/Neo/shArtemis were grouped into BEL-7402/5-FU group and BEL-7402/5-FU+shArtemis group.BEL-7402 group was BEL-7402 cells without any transfection.The groups were treated with various concentrations of 5-fluorouracil (5-FU; 3,6,12,24,48,96,192 μg/ml),mitomycin (MMC; 0.62,1.25,2.5,5.0,10.0 μg/ml) and sorafenib (0.5,1,2,4,8,16,32 μg/ml) (Solarbio; Beijing,China) for 48 h.The supernatant was removed before adding 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide (MTT; 0.5 mg/ml) from Solarbio (Beijing,China),with incubation of 4 h at 37 ℃.Dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO; 200 μL/well) was then added to stop the reaction and solubilize formazan crystals for 10 min.The absorbance was measured with a microplate reader from Bio-Rad (CA,USA) at 490 nm wavelength.The values of the half maximal inhibitory concentration (IC50) and the resistance index (RI) were calculated in triplicate on GraphPadPrism6 (CA,USA).
1.4Protein extraction and Western-blotTo determine γ-H2AX and Artemis protein changes after treatment of inhibitor of ATM,KU55933 (Abcam; USA),BEL-7402/5-FU cells were exposed to KU55933 (10 mmol/ml) 1.0 μl with MMC for 48 h.p-Artemis and ataxia-telangiectasia mutated protein (ATM) protein regulation were detected after the transfection of pSGU6/GFP/Neo/shArtemis.Before protein isolation,all the cells were washed with 1×PBS three times,lysed in RIPA buffer (Solarbio; Beijing,China) and total protein concentrations were measured with BCA assay kit (Beyotime; Haimen,China).After separation by electrophoresis on 10% SDS-PAGE (Beyotime; Haimen,China) for p-Artemis,ATM and Artemis and 15% SDS-PAGE for γ-H2AX,proteins were transferred onto PVDF membranes (Bio-Rad; CA,USA) where they were fixed and readily accessible for immunological analyses for identification of proteins.Then these PVDF membranes were incubated with primary antibodies p-Artemis (1∶1 000),ATM (1∶1 000),Artemis (1∶800) (Proteintech),γ-H2AX (1∶1000) (ABGENT) and β-actin (1∶1 000) (Abcam) at 4 ℃ overnight,and the secondary antibodies from Proteintech were incubated for 2 h at room temperature.The ClarityTMWestern ECL Substrate (Bio-Rad; CA,USA) was used for the detection of the immunoblotting bands.Proteins bands pictures were ultimately visualized by ChemiDocTMtouch imaging System and optical densities quantified by ImageJ software (NIH; USA).
1.5Statistical analysisData were expressed as the mean±standard deviation (SD) of at least three independent experiments.SPSS 17.0 (Chicago,IL,USA) was used for statistical analysis using the one-way ANOVA and Student's t-test (two-tailed).P<0.05 was considered to indicate a statistically significant difference.
2 Results
2.1pSGU6/GFP/Neo/shArtemis is processed to Artemis-siRNA in human hepatic carcinoma cell line BEL-7402/5-FU and effectively knocks down Artemis levelTo examine whether Artemis in shArtemis group,BEL-7402/5-FU cells transfected with pSGU6/GFP/Neo/shArtemis for 24 h,was knocked down.We evaluated the relative expression of Artemis mRNA in shArtemis group.The results indicated that Artemis expression was decreased effectively after transfection (P<0.05) compared to Control group (Tab 2,Fig 1).The Artemis silencing rate was 63.80%.

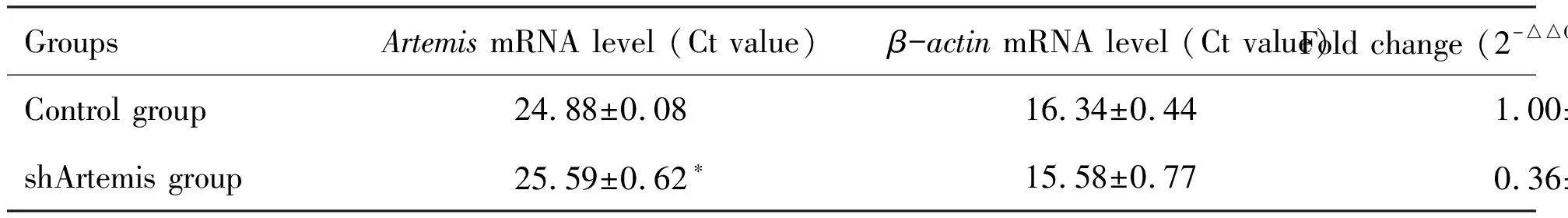
GroupsArtemis mRNA level (Ct value)β-actin mRNA level (Ct value)Fold change (2-△△Ct)Control group24.88±0.0816.34±0.441.00±0.00shArtemis group25.59±0.62∗15.58±0.770.36±0.05∗
*:Compared with Control group,P<0.05.
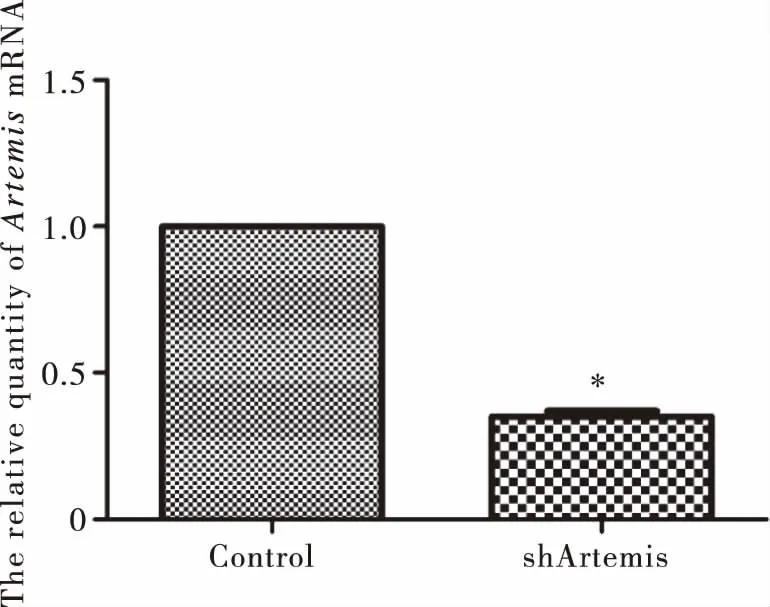
*:Compared with Control group,P<0.05. Fig 1 The relative quantity of Artemis mRNA after shArtemis interference
2.2knockdown of Artemis is effective to enhance the sensitivity of BEL-7402/5-FU to 5-fluorouracil,MMC and sorafenibGiven the important role of Artemis in DNA damage repair,one of crucial mecha-nisms of multiple drug resistance (MDR) of cancer cells,in BEL-7402/5-FU cells[7],we investigated whether knockdown of Artemis would affect the chemosensitivity of BEL-7402/5-FU cells.The results of MTT assay revealed that the IC50values of 5-fluorouracil,MMC and sorafenib were 181.80±93.38,0.60±0.056 and 0.86±0.36 μg/ml,respectively.Additionally,the RI of 5-fluorouracil,MMC and sorafenib were 1.69±1.17,1.13±0.25 and 0.50±0.13,respectively.There were significant differences in both of IC50and RI (P<0.05) (Fig 2,Fig 3,Fig 4).Furthermore,the P-gp mRNA level decreased in shArtemis group (P<0.05) (Fig 5).Together,these data indicated that knockdown of Artemis significantly enhanced the sensitivity of BEL-7402/5-FU cells to 5-fluorouracil,MMC and sorafenib by downregulating P-gp.
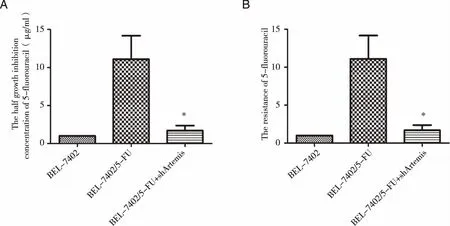
*:Compared with BEL-7402/5-FU group,P<0.05.Fig 2 Statistical analysis of IC50(A) and RI(B) of cells to 5-fluorouracil
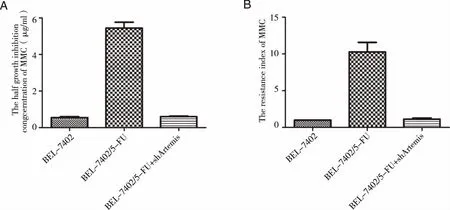
*:Compared with BEL-7402/5-FU group,P<0.05.Fig 3 Statistical analysis of IC50(A) and RI(B) of cells to MMC

*:Compared with BEL-7402/5-FU group,P<0.05.Fig 4 Statistical analysis of IC50(A) and RI(B) of cells to sorafenib
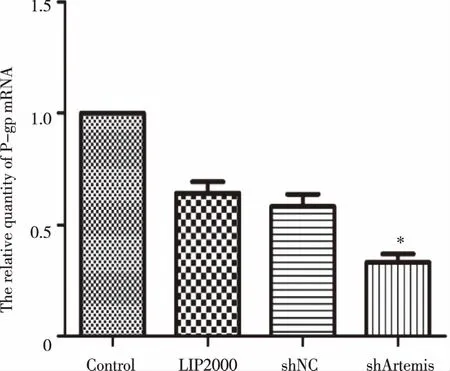
*:Compared with Control group,P<0.05. Fig 5 The relative expression of P-gp mRNA after shArtemis interference
2.3p-Artemis and ATM were involved in the regulation of chemotherapy sensitivity in BEL-7402/5-FU In the recent studies,it was demonstrated that p-Artemis,phosphorylated by ATM,was involved in homologous recombination[9]following in the G2 phase[10].Therefore,we assessed p-Artemis and ATM protein expression of shArtemis group and its reference control groups,Control group,LIP2000 group and shNC group,after treatment with MMC (5 μg/mL) for 48 h,which can induce cell DNA damage,using Western-blot.As shown in Fig 6 and Fig 7,p-Artemis and ATM protein expression of shArtemis group significantly decreased compared with Control group (P<0.05).
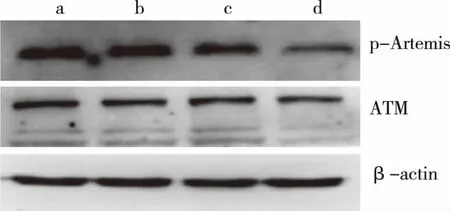
a:Control group; b:LIP2000 group; c:shNC group; d:shArtemis group; *:Compared with Control group,P<0.05. Fig 6 Expression of p-Artemis and ATM detected by Western-blot
2.5KU55933 suppressed γ-H2AX expression through the inhibition of ATM activityOur previous work has showed that knockdown of Artemis increased γ-H2AX expression[11].Therefore,we subsequently used KU55933 to assess the effect of ATM on the expression of γ-H2AX in BEL-7402/5-FU cells by Western-blot.ATM protein level was decreased following KU55933 treatment (P<0.05).The expression of γ-H2AX was significantly increased in BEL-7402/5-FU cells treated with KU55933 compared control BEL-7402/5-FU cells (P<0.05) (Fig 8 and Fig 9).

*:Compared with Control group,P<0.05.Fig 7 The relative protein quantity of p-Artemis(A) and ATM(B)

Fig 8 Expression of ATM,γ-H2AX and Artemis detected by Western-blot
However,there was no difference in Artemis protein change ware observed between inhibitor of ATM and control BEL-7402/5-FU cells (P>0.05).These findings demonstrated that ATM involved in the retardation effect of DNA damage repair with knockdown of Artemis in BEL-7402/5-FU cells.
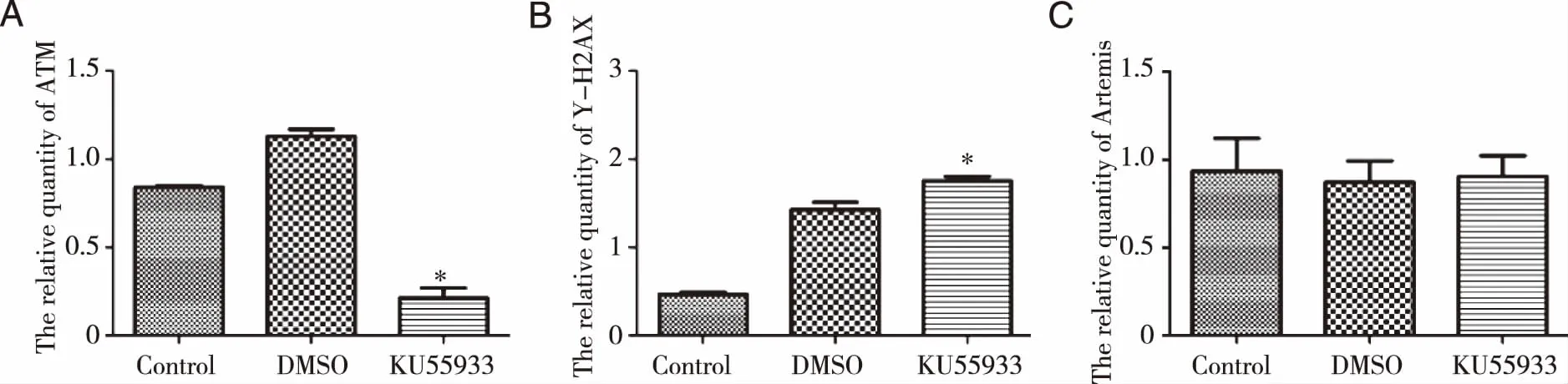
*:Compared with Control group,P<0.05.Fig 9 The relative protein quantity of ATM(A),γ-H2AX(B) and Artemis(C)
3 Discussion
Our findings of the changes of the sensitivity to 5-fluorouracil,MMC and sorafenib after knockdown of Artemis in BEL-7402/5-FU suggest that the expression level of Artemis influences the MDR pathway of BEL-7402/5-FU progression.Moreover,combination therapeutic strategies,such as directly decreasing the expression of Artemis before 5-fluorouracil or MMC or sorafenib treatment,might be effective to overcome chemoresistance of HCC/5-FU.
We found that knockdown of Artemis significantly enhanced the sensitivity of BEL-7402/5-FU cells to 5-fluorouracil,MMC and sorafenib.Moreover,the IC50and RI declined dramatically with the decreased expression of P-gp mRNA.It is indicated that the significantly enhanced the sensitivity of BEL-7402/5-FU cells to 5-fluorouracil,MMC and sorafenib after knockdown of Artemis may be associated with downregulating P-gp.And P-gp, MDR-related protein,play a vital role in pharmacokinetics,whose inhibition can attenuate the resistance of some chemotherapeutic drugs[12].As one of the biggest obstacles to cancer treatment,MDR,whose mechanisms include promoting DNA damage repair[13].The non-homologous end joining (NHEJ) pathway acts as a prominent repairing mechanism of DNA double strand breaks (DSBs) in mammalian cells[14].Therefore,interference to DNA repair efficiency by blocking DNA repair-associated proteins of NHEJ pathway may promote tumor cell apoptosis and death,and increase cellular sensitivity to radiation[14]and chemotherapy[15].Here we focus on Artemis,one of best identified regulatory factors in the NHEJ family,to understand more about this useful tool to modulate BEL-7402/5-FU cells chemosensitivity.
Artemis,with endonuclease activity,is involved in modifying DNA blunted ends due to DNA damage and promotes the linkage of DSBs.Meanwhile,Artemis deficiency leads to unrepaired DSBs and immunodeficiency[6]combined severe sensitivity to radiation[16].As shown in previous study,Artemis can be recruited and activated by DNA-PKcs[7]which can be regulated by ATM through phosphorylation in NHEJ[17].In addition,p-Artemis,phosphorylated by ATM,with ATM participate in homologous recombination (HR) in G2[10]and NHEJ in G0/G1[18]following oxidative damage or endogenous damage for DSBs repair[19-20].
Our data showed that p-Artemis and ATM protein expression were significantly decreased following Artemis knockdown.Therefore,ATM was suggested to be an important mediator of DSBs repair.Subsequently,we found that ATM inhibition can increase γ-H2AX expression but didn't have any effect on Artemis expression.It is implied that Artemis may act as a new molecular switch in DSB repair.We speculated that chemotherapy-induced Artemis phosphorylation required ATM,which is consistent with the observation[14]that ATM is the upstream molecule of Artemis and is dependent on radiation-induced Artemis hyperphosphorylation which joins approximately 10% of DSBs.Moreover,according to the ATM signaling pathway,even though Artemis is not essential for cell cycle checkpoint function,it is required particularly for DSBs repair process.Hence,Artemis phosphorylation was inhibited simultaneously following ATM inhibition so that Artemis expression was unaffected.
In summary,we demonstrate that Artemis is a RNAi therapeutic target of BEL-7402/5-FU multiple drug resistance Further investigations are still needed to clarify more mechanism about the effect of Artemis on chemotherapy sensitivity.

