糖尿病终末期肾脏病患者透析模式选择与死亡风险的分析
杜威
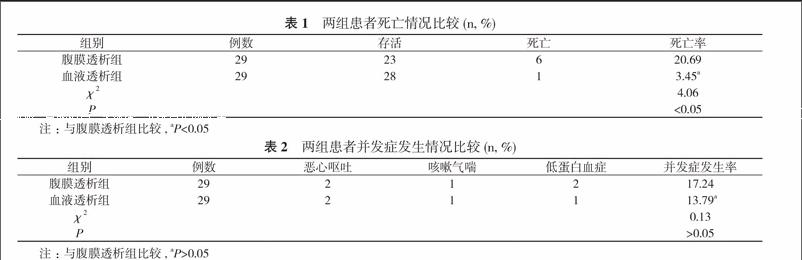
【摘要】 目的 分析糖尿病终末期肾脏病患者透析模式选择与死亡风险。方法 58例糖尿病终末期肾脏病患者, 基于患者选择的透析方式分为血液透析组与腹膜透析组, 每组29例。比较两组患者的死亡情况及并发症发生情况。结果 腹膜透析组患者死亡率为20.69%, 血液透析组患者死亡率为3.45%, 两组比较差异具有统计学意义(P<0.05)。血液透析组患者并发症发生率为13.79%, 与腹膜透析组的17.24%比较差异无统计学意义(P>0.05)。结论 糖尿病终末期肾脏病患者透析模式的选择与其死亡率具有密切联系。与腹膜透析治疗比较, 血液透析治疗糖尿病终末期肾脏病的死亡率低, 但患者治疗期间可能会出现各类并发症, 需要加以临床重点观察。
【关键词】 糖尿病终末期肾脏病;透析模式;死亡风险
DOI:10.14163/j.cnki.11-5547/r.2018.04.005
Analysis of the choice of dialysis mode and risk of death in patients with diabetic end-stage renal disease DU Wei. Department of Nephrology, Shenyang Fourth Peoples Hospital, Shenyang 110031, China
【Abstract】 Objective To analyze the choice of dialysis mode and risk of death in patients with diabetic end-stage renal disease. Methods A total of 58 patients with diabetic end-stage renal disease were divided by different dialysis modes into hemodialysis group and peritoneal dialysis group, with 29 cases in each group. Comparison were made on death condition and occurrence of complications between the two groups.
Results Peritoneal dialysis group had death rate as 20.69%, while hemodialysis group had death rate as 3.45%, and the difference was statistically significant (P<0.05). Hemodialysis group had incidence of complications as 13.79%, while hemodialysis group had incidence of complications as 17.24%, but the difference was not statistically significant (P>0.05). Conclusion Dialysis modes in patients with diabetic end-stage renal disease are closely linked to their death rate. Compared with peritoneal dialysis, the death rate of hemodialysis is lower in the treatment of diabetic end-stage renal disease, however, there may be various complications during the treatment, so patients need clinical key observation.
【Key words】 Diabetic end-stage renal disease; Dialysis mode; Risk of death
近年糖尿病患者數量呈现出不断上升的趋势, 随着糖尿病患者疾病的发展, 到终末期通常会发生肾脏疾病, 对患者生命健康带来较大威胁, 死亡率相对较高。透析治疗是延长糖尿病终末期肾脏疾病患者生存时间的重要方式, 但由于糖尿病患者血管钙化, 对实际透析治疗方式提出更高要求。本文将2016年8月~2017年8月于本院接受治疗的58例糖尿病终末期肾脏病患者作为研究对象, 基于患者所选择的透析方式将患者分为血液透析组与腹膜透析组, 比较不同透析模式选择下患者的死亡风险, 现总结内容如下。
1 资料与方法
1. 1 一般资料 将2016年8月~2017年8月于本院接受治疗的58例糖尿病终末期肾脏病患者作为研究对象, 基于患者选择的透析方式将患者分为血液透析组与腹膜透析组, 每组29例。血液透析组患者中男16例, 女13例, 年龄43~71岁,
平均年龄(56.93±4.69)岁。腹膜透析组患者中男15例, 女14例, 年龄44~71岁, 平均年龄(56.87±4.71)岁。两组患者年龄、性别等一般资料比较差异无统计学意义(P>0.05), 具有可比性。
1. 2 纳入标准 ①年龄18~80岁;②规律透析时间≥3个月;③不存在肾移植疾病史;④不存在严重心脑血管、肺功能及脑血管疾病等, 无恶性肿瘤、肝硬化疾病;⑤患者及其家属均了解实验研究内容, 签署知情同意书。
1. 3 方法 两组患者均实施透析前身体检查。血液透析组患者应用碳酸氢盐透析液实施普通血液透析治疗, 2~3次/周,endprint

