水环境中PPCPs检测技术及风险评价研究进展
姚晶晶,吴东海,陆光华,,周 超,沈兴厚
(1.西藏农牧学院水利土木工程学院,西藏 林芝 860000;2.河海大学环境学院,江苏 南京 210098;3.河南省水文水资源局,河南 郑州 450004)
药物及个人护理品(pharmaceuticals and personal care products,PPCPs)广泛应用于医药、工业、畜牧业、农业、水产养殖等领域[1]。由于PPCPs大量使用以及城市污水处理厂现有工艺处理不彻底[2],近年来PPCPs已在江河湖泊[3-4]、地下水[5]、市政污水[6-7]、水源水[8-9]中被频繁检出,虽然其浓度大多在ng/L至μg/L,但这些物质长期赋存可能对生态系统产生潜在危害[10]。如双氯芬酸、舍曲林和氟西汀等在水体中残留会抑制斑马鱼胚胎三磷酸腺苷酶活性,影响某些外排转运蛋白的正常工作[11]。已有研究表明,诺氟沙星和磺胺甲恶唑类抗生素会对鱼类的生长和繁殖产生不利影响[12],罗红霉素能够诱导鱼类生化指标发生变化[13]。Arpin-Pont等[14]发现在海洋中残留的PPCPs会对海洋生物的代谢活动产生一定危害,进而通过生物累积对人类健康产生影响。
目前PPCPs已成为环境领域的研究热点,近十年来已有大量相关文献报道,其中尤以天然水体中低浓度PPCPs的定量分析和风险评价更受关注。本文从水样前处理方法和仪器分析技术两方面总结分析了PPCPs定量检测技术的发展,在此基础上阐述了水环境中PPCPs的健康风险和生态风险的评价方法以及取得的研究进展,最后对本领域研究局限性及未来的发展方向作了总结和展望。
1 水环境中PPCPs检测技术
由于PPCPs在天然水体中的含量通常很低,现有分析仪器无法直接对水样进行定量检测。因此,水环境样品中PPCPs的分析检测技术通常由样品前处理技术和仪器定量分析技术两部分组成。通过水样前处理技术,能够浓缩富集被测的痕量组分,降低检测限,并改善方法的灵敏度,而高效灵敏、适应性高的分析仪器保证了PPCPs检测结果的精确性。

表2 水环境中PPCPs的常用仪器分析技术原理及优缺点
1.1 样品前处理方法
常用的PPCPs样品前处理方有液液萃取法(liquid-liquid extraction,LLE)、分散液液微萃取(dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction,DLLME)、固相萃取(solid-phase extraction,SPE)、固相微萃取法(solid-phase microextraction,SPME)等。表1总结了目前PPCPs前处理常用方法的原理及其优缺点[6, 15-20]。近年来,SPME与气相、液相能够匹配,并可实现在线联用,适合于分析水样中挥发性、半挥发性、难挥发的物质,已被广泛应用于水环境中样品的富集。
1.2 仪器分析技术
近年来发展迅速、应用较多的PPCPs仪器分析技术有二维气相色谱法(two-dimensional gas chromatography, GC×GC)、高效液相色谱法(high performance liquid chromatography,HPLC))、气相色谱质谱联用(gas chromatography with mass spectrometry,GC-MS)、高效液相色谱质谱联用(high performance liquid chromatography with mass spectrometry,HPLC-MS/MS)等。表2概括了水环境中PPCPs的常用仪器分析技术原理及优缺点[21-28]。目前对于水环境中PPCPs的仪器分析方法大多是在气相色谱(GC)和高效液相色谱(HPLC)基础上改进和创新而来的,通过优化色谱、质谱条件和减少基质效应等来提高分离能力和灵敏度。
样品前处理将向着绿色环保、高效、小型便携化和自动化等方向发展;样品仪器分析则朝着快速检测、高选择性、高灵敏等方向发展。表3列举了目前受到重点关注的水环境中典型PPCPs的检测技术及方法可靠性[15,20,29-34]。多种方法联用检测技术的快速发展为研究人员更好地分析PPCPs在水环境中的赋存和风险提供了技术支持。
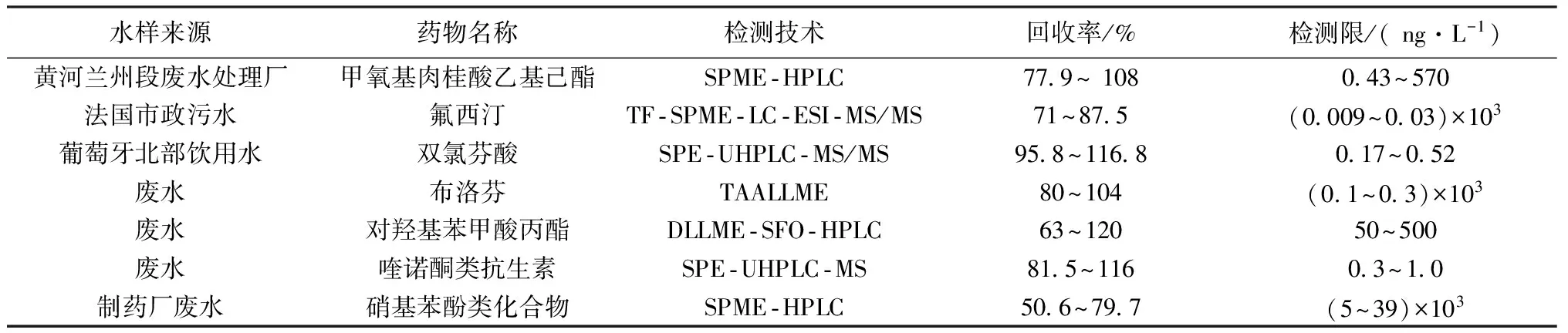
表3 水环境中典型PPCPs的检测方法及可靠性
2 水环境中PPCPs的风险评价
PPCPs风险评价中关于人体健康风险和生态风险的评价基准缺少公认的标准,不同研究人员采取不同的风险评价基准,可能会导致风险评价结果不尽相同。基于美国国家科学院和美国环保署提出的风险评价“四步法”主要包括危害鉴定、剂量效应关系评价、暴露评估和风险表征[35],作为实施风险评价的主要指南,已被中国、法国、日本等多个国家所采用。目前水环境中关于PPCPs的风险评价主要基于这种评价方法。
水环境中PPCPs的风险评价可分为人体健康风险评价和生态风险评价。人体健康风险评价的侧重点在人群的健康风险,而生态风险评价的主体是生态系统或者水环境中的生物群体。
2.1 人体健康风险评价
1986年美国国家环保署根据风险评价的四步法发布了《致癌风险评价指南》《致畸风险评价指南》《发育毒物的健康风险评价指南》《暴露风险评价指南》,1988年又颁布了《男女生殖性能风险评价指南》等一系列指导人体健康风险评价的技术性文件。2006年我国颁布的GB 5749—2006《生活饮用水卫生标准》,通过各种水样的合格标准来定性评估人体健康风险。
近年来,对PPCPs的人体健康风险研究取得了一定进展。张芹等[4]运用美国环保署的风险熵法,定性评价了表层水体中32种PPCPs对从婴幼儿到成人不同年龄段人群的健康风险,发现整体上呈现随年龄增长风险降低的趋势。Chen等[36]进行了农村污水中PPCPs的健康风险评价,发现布洛芬及其转化产物出现在下游饮用水水源中,对人体健康具有潜在危害。李勇等[37]调查舟山岛水库抗生素残留特征时,发现呋喃唑酮在岑港水库上游水样中最高,质量浓度为53.73 ng/L,呋喃唑酮及其代谢产物对人体有致畸胎和诱发癌症的作用,存在潜在的高风险。Archer等[38]通过基于最敏感生物的慢性毒性数据,研究发现双氯芬酸、克拉霉素和其代谢转化产物通过生物累积可能会使人体内分泌系统发生紊乱。Prosser等[39]报道了用PPCPs类污染废水灌溉的食用植物对人体健康影响,将人体每日摄入量估计值与可接受的每日摄入量进行比较,以确定累积在植物组织中的PPCPs是否对人体健康构成危害,结果发现三氯生和磺胺二甲嘧啶对人体健康具有中等风险。Harrison等[40]研究发现人体长期食用含PPCPs的蛋、肉后,在人体中产生了耐药基因。
目前大多数的PPCPs人体健康风险评价研究从定性角度和生物累积来推测人体健康风险,这方面发展既需要长期的实验研究作为数据支持,也需要评价方法的改进。
2.2 生态风险评价
水环境中PPCPs的生态风险评价不仅要求有环境调查,还要求大量的模拟试验研究以及合适的评价模型论证等。目前水环境中的PPCPs生态风险评价是以风险熵法(risk quotient,RQ)为基础来评价PPCPs对水环境的影响程度。RQ值不小于1.0时,认为是高风险;介于0.1~1.0,认为是中风险;介于0.01~0.1,认为是低风险。表4列出了当前国内外研究较多的PPCPs生态风险评价方法及评价结果[4,8,18,41-49]。
利用单一风险熵法评价水环境中PPCPs风险程度时,局限于预测浓度和其对水环境无影响的最大浓度两者的比值,需要有长期稳定的水环境监测数据作为支撑,评价结果的可比性差。运用混合风险熵或叠加指数法,虽然考虑了水中多种PPCPs共存的情况,但是没有考虑污染物之间的交互作用。多种模型和评价体系应用于水环境的风险评价,例如利用改进决策树模型[50]考虑污染物浓度和时效性等因素对饮用水水源地水进行环境健康风险评价;罗慧萍等[51]建立了风险源-风险受体响应的水源地综合风险评价体系,对泰州市第三自来水厂饮用水水源地水进行环境风险评价。综合使用专家评价结合层次分析法、参数分级评分叠加指数法和物种敏感分布法等方法,将有利于对水环境中PPCPs的生态风险程度进行更为客观、合理的评价。
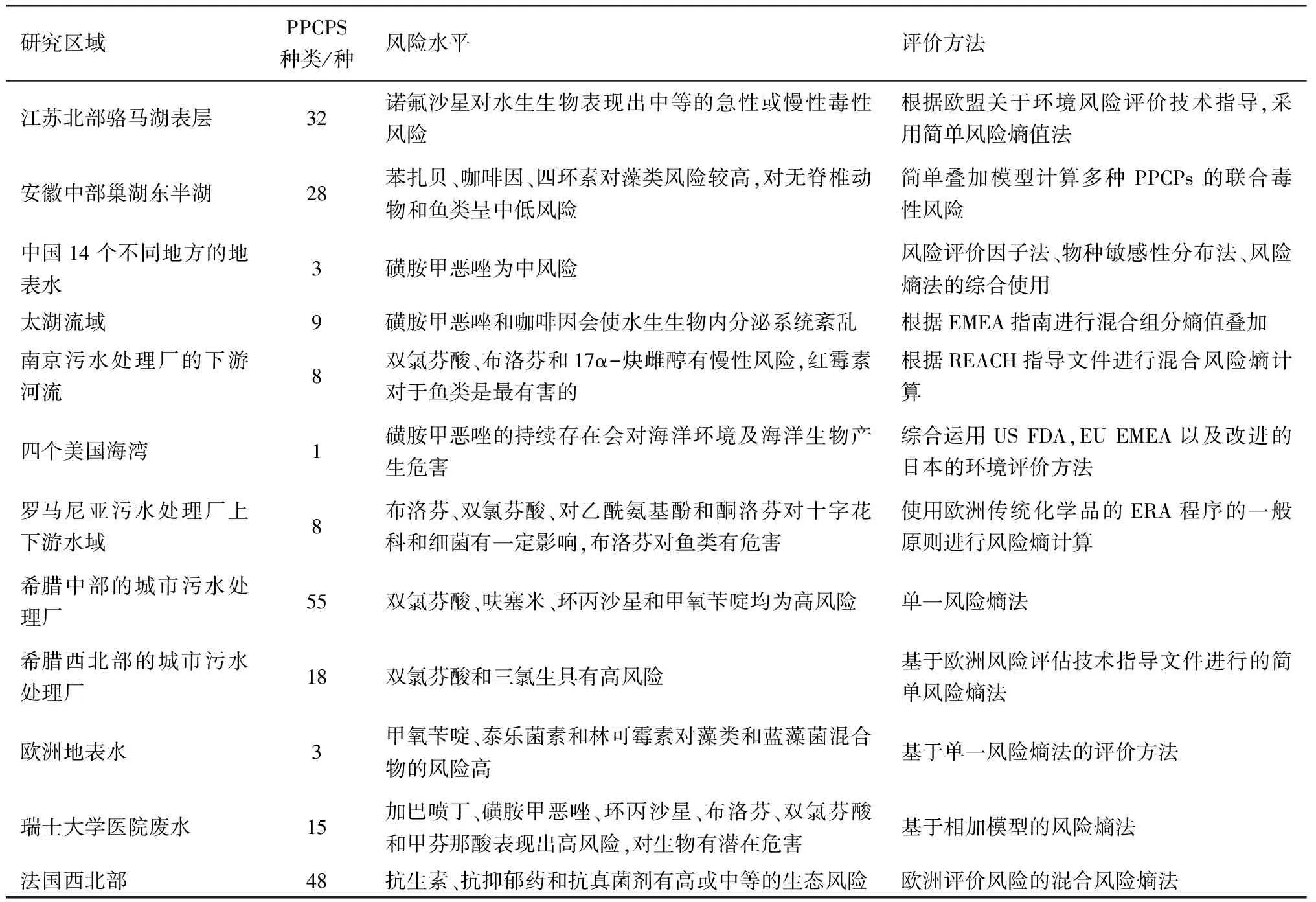
表4 水环境中PPCPs的生态风险评价方法及结果
3 结语与展望
在过去几十年中,随着科学的进步和技术的不断革新,涌现出越来越多用于浓缩富集、分析检测环境痕量污染物的新技术,使得水环境中的PPCPs污染表征和污染源识别成为可能。然而,对于水环境中超痕量PPCPs的定量分析技术和风险评价方法的发展亟待加强。
在SPE和SPME基础上改进的样品前处理方法广泛应用于低浓度的水环境样品的富集浓缩,且效率高,可同时萃取多种不同物质。在GC和HPLC基础上不断创新的仪器分析技术越来越多用于水环境中超痕量PPCPs的定量分析且灵敏度高,自动化程度高。但水环境中PPCPs具有不同的物理化学性质和复杂的基体,对其精准定量分析的研究依旧薄弱,因此,未来研究应更多地开发便携高效、灵敏度高的前处理方法,以及实现在线前处理-分析仪器检测的联合使用,以便精准定量水环境中超痕量的PPCPs。
PPCPs的风险评价大多是以美国环境保护署或欧盟环境风险评价为技术指导进行风险熵值的计算,人体健康风险主要是通过简单的单一风险熵或动物暴露实验推测而来;生态风险评价则趋向于采用混合风险熵或叠加指数法。然而对于多种PPCPs及其衍生转化产物的风险研究尚少,因此,急需发展针对水环境中共存PPCPs及其转化产物的综合风险评价方法。
[1]杨晓凡,陆光华,万杰,等.水环境中药物污染、检测及去除研究进展[J].水资源保护,2012,28(2):1-7.(YANG Xiaofan,LU Guanghua,WAN Jie,et al.A review of residue,detection,and removal of pharmaceuticals in aquatic environment[J].Water Resources Protection,2012,28(2):1-7.(in Chinese))
[2]郑少奎,李晓锋.城市污水处理厂出水中的药品和个人护理品[J].环境科学,2013,34(8):3317-3327.(ZHENG Shaokui,LI Xiaofeng.Pharmaceuticals and personal care products (PPCPs)in the effluent of sewage treatment plants[J].Environmental Science,2013,34(8):3317-3327.(in Chinese))
[3]陈月,王风贺,陆建刚,等.长江流域药品和个人护理用品污染状况的研究进展[J].工业水处理,2016,36(7):11-15.(CHEN Yue,WANG Fenghe,LU Jiangang,et al.Research progress in pharmaceutical and personal care products (PPCPs)in the Yangtze River Valley,China [J].Industrial Water Treatment,2016,36 (7):11-15.(in Chinese))
[4]张芹,张圣虎,汪贞,等.骆马湖表层水体中32种PPCPs类物质的污染水平、分布特征及风险评估[J].环境科学,2017,38(1):163-170.(ZHANG Qin,ZHANG Shenghu,WANG Zhen ,et al.Pollution level,distribution characteristics and risk assessment of 32 PPCPs in surface water of Luomahu Lake[J].Environmental Science,2017,38(1):163-170.(in Chinese))
[5]YAO L,WANG Y,TONG L,et al.Occurrence and risk assessment of antibiotics in surface water and groundwater from different depths of aquifers:a case study at Jianghan Plain,central China[J].Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety,2017,135:236-242.
[6]LOOS R,CARVALHO R,ANTóNIO D C,et al.EU-wide monitoring survey on emerging polar organic contaminants in wastewater treatment plant effluents[J].Water Research,2013,47(17):6475-6487.
[7]PRABHASANKAR V P,JOSHUA D I,BALAKRISHNA K,et al.Removal rates of antibiotics in four sewage treatment plants in South India[J].Environmental Science and Pollution Research,2016,23(9):8679-8685.
[8]潘潇,强志民,王为东.巢湖东半湖饮用水源区沉积物药品和个人护理品 (PPCPs)分布与生态风险[J].环境化学,2016,35(11):2234-2244.(PAN Xiao,QIANG Zhimin,WANG Weidong.Distribution and ecological risk of sedimentary PPCPs in the eastern drinking water source area of Chaohu Lake[J].Environmental Chemistry,2016,35 (11):2234-2244.(in Chinese))
[9]金磊,姜蕾,韩琪,等.华东地区某水源水中13 种磺胺类抗生素的分布特征及人体健康风险评价[J].环境科学,2016,37 (7):2515-2521.(JIN Lei,JIANG Lei,HAN Qi,et al.Distribution characteristics and health risk assessment of thirteen sulfonamides antibiotics in a drinking water source in east China[J].Environmental Science,2016,37 (7):2515-2521.(in Chinese))
[10]PAPAGEORGIOU M,KOSMA C,LAMBROPOULOU D.Seasonal occurrence,removal,mass loading and environmental risk assessment of 55 pharmaceuticals and personal care products in a municipal wastewater treatment plant in Central Greece[J].Science of the Total Environment,2016,543:547-569.
[11]CUNHA V,BURKHARDT-MEDICKE K,WELLNER P,et al.Effects of pharmaceuticals and personal care products (PPCPs)on multixenobiotic resistance (MXR)related efflux transporter activity in zebrafish (Danio rerio)embryos[J].Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety,2017,136:14-23.
[12]YAN Z,LU G,YE Q,et al.Long-term effects of antibiotics,norfloxacin,and sulfamethoxazole,in a partial life-cycle study with zebrafish (Danio rerio):effects on growth,development,and reproduction[J].Environmental Science and Pollution Research,2016,23(18):18222-18228.
[13]LIU J,LU G,WANG Y,et al.Bioconcentration,metabolism,and biomarker responses in freshwater fish Carassius auratus exposed to roxithromycin [J].Chemosphere,2014,99(3):102-108.
[14]ARPIN-PONT L,BUENO M J M,GOMEZ E,et al.Occurrence of PPCPs in the marine environment:a review[J].Environmental Science and Pollution Research,2016,23(6):4978-4991.
[15]MARUBE L C,CALDAS S S,SOARES K L,et al.Dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction with solidification of floating organic droplets for simultaneous extraction of pesticides,pharmaceuticals and personal care products[J].Microchimica Acta,2015,182(9/10):1765-1774.
[16]CALDAS S S,ROMBALDI C,DE OLIVEIRA ARIAS J L,et al.Multi-residue method for determination of 58 pesticides,pharmaceuticals and personal care products in water using solvent demulsification dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction combined with liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry[J].Talanta,2016,146(2):676-688.
[17]曹江平,邸宏伟,周继梅,等.分散液液微萃取技术的研究进展[J].分析测试学报,2016,35(7):913-921.(CAO Jiangping,DAI Hongwei,ZHOU Jimei,et al.A review on dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction method[J].Journal of Instrumental Analysis,2016,35 (7):913-921.(in Chinese))
[18]KOSMA C I,LAMBROPOULOU D A,ALBANIS T A.Investigation of PPCPs in wastewater treatment plants in Greece:occurrence,removal and environmental risk assessment[J].Science of the Total Environment,2014,466/467:421-438.
[19]BASAGLIA G,PIETROGRANDE M C.Optimization of a SPME/GC/MS method for the simultaneous determination of pharmaceuticals and personal care products in waters[J].Chromatographia,2012,75(7/8):361-370.
[20]张军,王晶晶,彭华,等.SPME-HPLC法测定废水中硝基苯酚类化合物[J].环境监测管理与技术,2015,27 (1):35-38.(ZHANG Jun,WANG Jingjing,PENG Hua,et al.Determination of nitrophenols in waste water by solid phase microextraction and high performance liquid chromatography[J].The Administration and Technique of Environmental Monitoring,2015,27 (1):35-38.(in Chinese))
[21]OCHIAI N,IEDA T,SASAMOTO K,et al.Stir bar sorptive extraction and comprehensive two-dimensional gas chromatography coupled to high-resolution time-of-flight mass spectrometry for ultra-trace analysis of organochlorine pesticides in river water[J].Journal of Chromatography A,2011,1218(39):6851-6860.
[22]UBUKATA M,JOBST K J,REINER E J,et al.Non-targeted analysis of electronics waste by comprehensive two-dimensional gas chromatography combined with high-resolution mass spectrometry:Using accurate mass information and mass defect analysis to explore the data[J].Journal of Chromatography A,2015,1395:152-159.
[23]夏丹,高丽荣,郑明辉.全二维气相色谱分析持久性有机污染物的应用进展[J].色谱,2017,35(1):91-98.(XIA Dan,GAO Lirong,ZHENG Minghui.Recent developments in comprehensive two-dimensional gas chromatography for the anlaysis of persistent organic pollutants[J].Chinese Journal of Chromatography,2017,35(1):91-98.(in Chinese))
[24]文一,姚瑞华,孙宏亮,等.高效液相色谱法测定地下水中洛克沙胂[J].环境监测管理与技术,2016,28 (1):58-59.(WEN Yi,YAO Ruihua,SUN Hongliang,et al.Determination of roxarsone in groundwater with high performance liquid chromatography[J].The Administration and Technique of Environmental Monitoring,2016,28(1):58-59.(in Chinese))
[25]CHEN F,GONG Z,KELLY B C.Rapid analysis of pharmaceuticals and personal care products in fish plasma micro-aliquots using liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry[J].Journal of Chromatography A,2015,1383:104-111.
[26]张祥民.色谱-质谱技术在生物分析研究中的最新进展[J].色谱,2017,35(1):138-140.(ZHENG Xiangmin.Recent advances in chromatography-mass spectrometry in bioanalytical research [J].Chinese Journal of Chromatography,2017,35 (1):138-140.(in Chinese))
[27]周弛,王斐,张会强,等.HPLC和HPLC-MS/MS 测定地表水中酚类化合物[J].环境监测管理与技术,2016,28(4):46-49.(ZHOU Chi,WANG Fei,ZHANG Huiqiang,et al.Determination of phenols in surface water by high performance liquidchromatography-diode array detection and high performance liquidchromatography-tandem mass spectrometry [J].The Administration and Technique of Environmental Monitoring,2016,28(4):46-49.(in Chinese))
[28]LING J,YU Y,ZHU J,et al.A highly sensitive HPLC-MS/MS method for quantification of 20 (S)-protopanaxadiol in human plasma and its application in phase IIa clinical trial of a novel antidepressant agent[J].Journal of Chromatography B :Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci,2016,1031:214-220.
[29]HAI-XIA L I U,YAO-XIA Y,MA M G,et al.Self-assembled gold nanoparticles coating for solid-phase microextraction of ultraviolet filters in environmental water[J].Chinese Journal of Analytical Chemistry,2015,43(2):207-211.
[30]TOGUNDE O P,CUDJOE E,OAKES K D,et al.Determination of selected pharmaceutical residues in wastewater using an automated open bed solid phase microextraction system[J].Journal of Chromatography A,2012,1262:34-42.
[31]BARBOSA M O,RIBEIRO A R,PEREIRA M F R,et al.Eco-friendly LC-MS/MS method for analysis of multi-class micropollutants in tap,fountain,and well water from northern Portugal[J].Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry,2016,408(29):8355-8367.
[32]BAZREGAR M,RAJABI M,YAMINI Y,et al.Tandem air-agitated liquid-liquid microextraction as an efficient method for determination of acidic drugs in complicated matrices[J].Analytica Chimica Acta,2016,1429:14-21.
[33]顾海东,尹燕敏,秦宏兵.超高效液相色谱三重四级杆质谱联用法测定水中喹诺酮类抗生素[J].环境监测管理与技术,2013,25(3):34-37.(GU Haidong,YIN Yanmin,QIN Hongbing.Determination of quinolone in water samples by solid phase extraction-ultra performance liquid chromatographelectrospray tandem mass spectrometry [J].The Administration and Technique of Environmental Monitoring,2013,25(3):34-37.(in Chinese))
[34]谢正鑫,陆光华,孙丽莎,等.水环境中药物及个人护理品(PPCPs)的生物降解研究进展[J].水资源保护,2013,29(4):5-11.(XIE Zhengxin,LU Guanghua,SUN Lisha,et al.A review of biodegradation of pharmaceuticals and personal care products (PPCPs)in aqueous environment[J].Water Resources Protection,2013,29(4):5-11.(in Chinese))
[35]EPA (US Environmental Protection Agency).Framework for ecological risk assessment.EPA630-R-92-001[R].Office of Research and Development,Washington D C,USA,1992.
[36]CHEN Y,VYMAZAL J,BEZINOVá T,et al.Occurrence,removal and environmental risk assessment of pharmaceuticals and personal care products in rural wastewater treatment wetlands[J].Science of the Total Environment,2016,566/567:1660-1669.
[37]李勇,蒋婷婷,景龙飞,等.舟山岛水库有机农药和抗生素残留特征及潜在风险评估[J].水资源保护,2014,30(3):31-37.(LI Yong,JIANG Tingting,JING Longfei,et al.Characteristics of residual organic pesticides and antibiotics in reservoirs of Zhoushan Islands and potential risk evaluation[J].Water Resources Protection,2014,30(3):31-37.(in Chinese))
[38]ARCHER E,PETRIE B,KASPRZYK-HORDERN B,et al.The fate of pharmaceuticals and personal care products (PPCPs),endocrine disrupting contaminants (EDCs),metabolites and illicit drugs in a WWTW and environmental waters[J].Chemosphere,2017,174:437-446.
[39]PROSSER R S,SIBLEY P K.Human health risk assessment of pharmaceuticals and personal care products in plant tissue due to biosolids and manure amendments,and wastewater irrigation[J].Environment International,2015,75(75C):223-233.
[40]HARRISON E M,PATERSON G K,HOLDEN M T,et al.Whole genome sequencing identifies zoonotic transmission of MRSA isolates with the novel mecA homologue mecC [J].Embo Molecular Medicine,2013,5(4):509-515.
[41]汪涛,杨再福,陈勇航,等.地表水中磺胺类抗生素的生态风险评价[J].生态环境学报2016,25(9):1508-1514.(WANG Tao,YANG Zaifu,CHEN Yonghang,et al.Ecological risk assessment for sulfonamides in surface waters [J].Ecology and Environmental Sciences,2016,25 (9):1508-1514.(in Chinese))
[42]YAN Z,YANG X,LU G,et al.Potential environmental implications of emerging organic contaminants in Taihu Lake,China:comparison of two ecotoxicological assessment approaches[J].Science of the Total Environment,2014,470/471:171-179.
[43]LIU J,LU G,XIE Z,et al.Occurrence,bioaccumulation and risk assessment of lipophilic pharmaceutically active compounds in the downstream rivers of sewage treatment plants[J].Science of the Total Environment,2015,511:54-62.
[44]HOYETT Z,OWENS M A,CLARK C J,et al.A comparative evaluation of environmental risk assessment strategies for pharmaceuticals and personal care products[J].Ocean & Coastal Management,2016,127:74-80.
[45]GHEORGHE S,PETRE J,LUCACIU I,et al.Risk screening of pharmaceutical compounds in Romanian aquatic environment[J].Environmental Monitoring and Assessment,2016,188(6):1-16.
[46]PAPAGEORGIOU M,KOSMA C,LAMBROPOULOU D.Seasonal occurrence,removal,mass loading and environmental risk assessment of 55 pharmaceuticals and personal care products in a municipal wastewater treatment plant in Central Greece[J].Science of the Total Environment,2016,543(Pt A):547-569.
[47]GUO J,SELBY K,BOXALL A B A.Assessment of the risks of mixtures of major use veterinary antibiotics in european surface waters[J].Environmental Science & Technology,2016,50(15):8282-8289.
[48]DAOUK S,CHèVRE N,VERNAZ N,et al.Dynamics of active pharmaceutical ingredients loads in a Swiss university hospital wastewaters and prediction of the related environmental risk for the aquatic ecosystems[J].Science of the Total Environment,2016,547:244-253.
[49]MINGUEZ L,PEDELUCQ J,FARCY E,et al.Toxicities of 48 pharmaceuticals and their freshwater and marine environmental assessment in northwestern France[J].Environmental Science and Pollution Research,2016,23(6):4992-5001.
[50]程斌,王菲凤,张江山.改进决策树模型支持下的饮用水水源地健康风险评价[J].水资源保护,2013,29(1):27-31.(CHENG Bin,WANG Feifeng,ZHANG Jingshan.An improved decision tree model for health risk assessment of drinking water source[J].Water Resources Protection,2013,29(1):27-31.(in Chinese))
[51]罗慧萍,逄勇,罗缙,等.泰州市第三自来水厂饮用水水源地水环境风险评价[J].河海大学学报(自然科学版),2015,43(2):114-120.(LUO Huiping,PANG Yong,LUO Jing,et al.Water environment risk assessment of Taizhou Three Waterworks drinking water source area[J].Journal of Hohai University(Natural Sciences),2015,43(2):114-120.(in Chinese))

