传染性胰坏死病毒的生物学研究进展
贺文斌,赵景壮,卢彤岩,尹家胜,徐黎明
(1.中国水产科学研究院黑龙江水产研究所,黑龙江 哈尔滨 150070;2.上海海洋大学水产与生命学院,上海 201306)
传染性胰坏死病毒的生物学研究进展
贺文斌1,2,赵景壮1,卢彤岩1,尹家胜1,徐黎明1
(1.中国水产科学研究院黑龙江水产研究所,黑龙江 哈尔滨 150070;2.上海海洋大学水产与生命学院,上海 201306)
传染性胰坏死病(infectious pancreatic necrosis,IPN)是一种危害多种水产动物的急性传染性疫病,能造成鲑鳟稚鱼大量死亡,造成世界范围内鲑鳟养殖业重大经济损失。IPN的病原为双链RNA病毒科(Birnaviridae)水生双链RNA病毒属(Aquabirnavirus)的传染性胰脏坏死病毒(infectious pancreatic necrosis virus,IPNV)。本文概述了该病原的基因组结构、生物学特征、诊断技术及免疫防治等研究进展,以期为IPN的防治提供参考。
传染性胰坏死病毒(IPNV);水生双链RNA病毒;基因型;血清型;鲑鳟
传染性胰坏死病毒(Infectious pancreatic necrosis virus,IPNV)主要感染鲑鳟稚鱼,一般在春季暴发,水温10℃时最易感染[1]。由于毒株、宿主和环境因素的不同,IPNV可造成虹鳟Oncorhynchus mykiss 10%~90%的死亡率[2,3]。病鱼常具有食欲减退、体色发黑、眼球突出、腹部肿胀、肛门红肿等症状,解剖后可见胰腺坏死、肾脏肿大、肠内有粘液状渗出物、腹水等症状。晚期病鱼的肝脏和鳃上皮组织严重出血,肝脏和胰脏细胞核固缩,出现空泡变性,胰腺中有炎症细胞浸润的脂肪组织发生弥散性坏死。感染IPNV幸存的鱼可不再发病,但是终生携毒,依然能传染病毒。IPNV可通过携带病毒的水体、网具、容器、染病鱼的排泄物和精液进行水平传播,也可由亲代通过受精卵(无症状的携病毒鱼卵或怀卵鱼被病毒感染)对子代进行垂直传播。
1 IPNV基因组结构
IPNV病毒颗粒呈20面体,无囊膜,有92个壳粒,直径67nm[4]。衣壳内有由2个片段组成的双股RNA基因,片段A编码一个多聚蛋白,包括VP2、VP3、VP4,并通过间隔的ORF编码一个非结构蛋白VP5;片段B编码一个依赖于RNA的RNA聚合酶(VP1)[5]。VP2蛋白是IPNV的主要外衣壳蛋白,含有病毒的主要抗原决定簇,并含有病毒特异性中和抗原表位[6],经常用于病毒的诊断、血清型分类及疫苗设计。
2 IPNV生物学特征
2.1 基因型分型
用MegAlign软件分析基因型,以VP2基因片段为目标基因,同GenBank收录的其他国家IPNV分离株及部分水生双RNA病毒进行VP2核苷酸序列同源性分析。Blake等[7]证明,IPNV病毒基于VP2氨基酸序列可分为6个基因组genogroups(1-6)。一些研究者认为,海洋双RNA病毒应该形成一个新的基因组genogroup7[8,9],Ji等[10]对一株分离于虹鳟的中国IPNV毒株ChRtm213采用邻位相邻法构建了IPNV的系统进化树(图1)。该进化树清晰地将目前水生双RNA病毒分为7个基因组。
2.2 血清分型
水生双RNA病毒含有10个血清型,包括A组血清型 A1 (West Buxton,WB)、A2(Spajarup,Sp)、A3(Abild,Ab)、A4(Hecht,He)、A5(Tellina,Te)、A6(Canada1,C1)、A7(Canada2,C2)、A8(Canada3,C3)和 A9 (Jasper,Ja),B 组 血 清 型 B1(Tellinavirus,TV-1)。根据IPNV的多聚蛋白氨基酸序列,可将IPNV分为 6个基因簇(Genogroup 1-6),其中Genogroup1对应血清型为A3,Genogroup 2为A5和A6,Genogroup3 为 A2,Genogroup 4 为 A7 和 A8,Genogroup5 为 A1 和 A9,Genogroup6 为 A4[11,12],见表1。血清型A1主要出现在美国,血清型A6-A9主要出现在加拿大,血清型A2-A5和B1多出现在欧洲和亚洲[13]。中国早期IPNV分离株血清型均为A2(Sp),病毒滴度高,具有很高的致死性[14]。刘淼等[15]于2013年从云南某虹鳟养殖场的发病鱼分离出一株IPNV(命名为ChRtm213)。系统发育分析结果表明,该ChRtm213分离株属于Genogroup5基因型,与A1(Ja)血清型的美国的VR299、西班牙的2310株的VP2具有较高相似度。上述研究结果说明,目前中国至少有两种血清型的IPNV毒株。
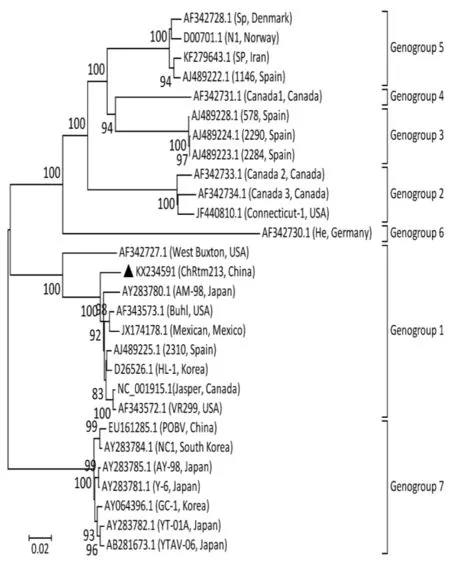
图1 基于ChRtm213与其他水生双RNA病毒A片段基因组序列同源性分析构建的进化树Fig.1 Phylogenetic relationship of ChRtm213 and other reference aquabirnaviruses strains based on complete genome of segment A using the neighborjoining method
3 IPNV诊断技术
3.1 聚合酶链式反应(Polymerase Chain Reaction,PCR)
逆转录聚合酶链式反应法(Reverse transcription Polymerase Chain Reaction,RT-PCR)根据特定病毒的核苷酸序列设计特异性引物,然后扩增核酸以检测病毒[16]。吴斌等[17]针对IPNVA片段VP5基因和VP3基因分别设计了两对特异性引物,建立了成熟的IPNV RT-PCR检测法。荧光定量RT-PCR检测法是一种对PCR反应中的循环产物荧光信号的实时检测和对起始模板进行定性定量分析的高灵敏检测方法。徐晔等[18]建立了Taqman探针荧光定量RT-PCR检测IPNV的方法,引物和探针只与IPNV的核酸特异性结合,与鲤春病毒血症病毒(Spring viraemia ofcarp virus,SVCV)、病毒性出血性败血症病毒(Viral hemorrhagic septicemia virus,VHSV)、传染性造血器官坏死病毒(Infectious hematopoietic necrosis virus,IHNV)、草鱼草鱼呼肠孤病毒(Grass carp reovirus,GCRV)和流行性造血器官坏死病毒(Epizootic haematopoietic necrosis virus,EHNV)均无交叉反应。
3.2 环介导等温扩增法(Loop-mediated isothermal amplification,LAMP)
LAMP是一种新型体外等温扩增特异核酸片段的技术[19]。与常规PCR相比,不需要对模板进行热变性、温度循环、电泳及紫外观察过程。不用专门的仪器设备就可实现现场高通量快速检测,具有简单、快速、特异性强的特点。在LAMP的基础上可使用逆转录LAMP(RT-LAMP)对特异RNA分子进行等温快速扩增。Soliman[20]将RT-LAMP引入到病毒检测中,并向反应产物中添加SYBR Green I荧光染料,建立了IPNV的RT-LAMP可视化检测方法。
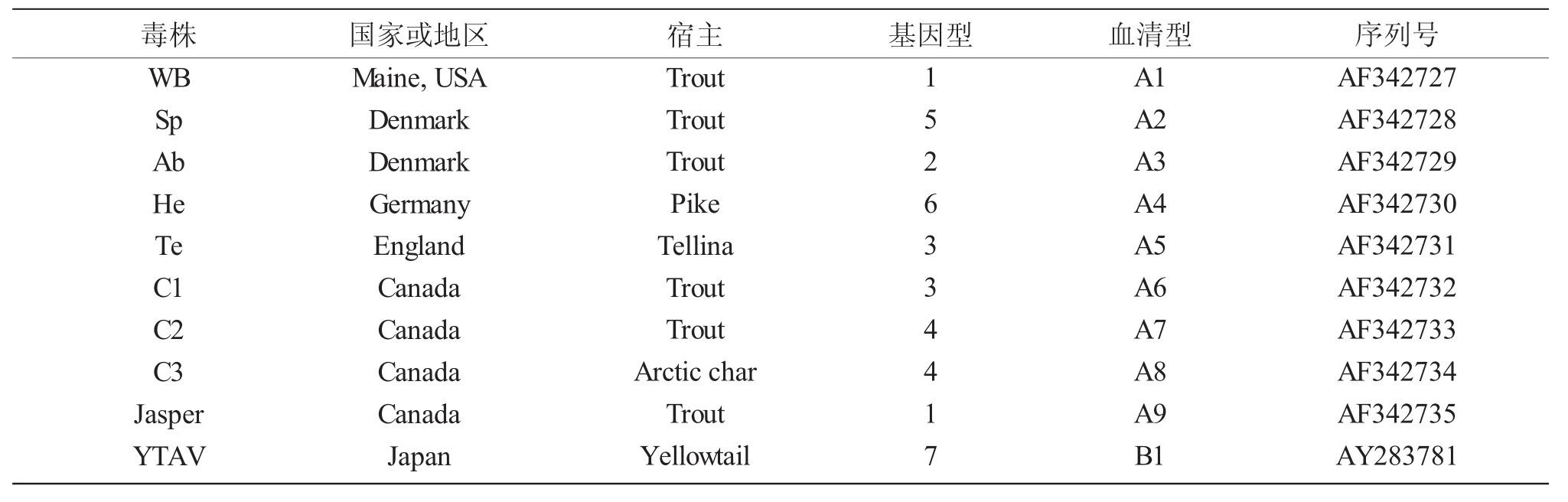
表1 水生双RNA病毒的生物学分类Tab.1 Biological classification of aquabirnaviruses
3.3 酶联免疫吸附测定法(enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay,ELISA)
以上方法灵敏度高,但需要检测仪器,存在变异性,用于检测临床样本的稳定性较低。相比较,单克隆抗体具有均质性好和易于标准化生产的优点。王健楠等[21]扩增了IPNV-ZYX分离株结构蛋白VP2的抗原表位区基因(616 bp),命名为IPNV VP2 COE,VP2 COE蛋白可作为IPNV的诊断抗原,为间接免疫荧光检测IPNV方法的建立提供了更加现实的理论依据。连科讯等[22]利用纯化的IPNVVP2 COE重组蛋白作为免疫原免疫小鼠,将小鼠的脾细胞与骨髓瘤SP2/0细胞融合,采用间接ELISA筛选杂交瘤细胞,制备的特异性单抗可应用于间接免疫荧光法检测IPNV。
单克隆抗体法检测IPNV病毒为更深入研究奠定了基础。张琳琳等[23]利用鼠抗IPNV VP2单抗及兔抗IPNV VP2建立了双抗体夹心ELISA检测法。试验中获得抗体较纯,克服了同属抗体之间的交叉反应及同株抗体捕获抗原能力弱的缺点,提高了检测的特异性,减少了假阳性结果。该方法适合于基层现场检验需要,已应用于动物疫病的临床诊断。
3.4 免疫荧光法(immunological fluorescence as-say test,IFAT)
用荧光抗体示踪或检查相应抗原的方法称荧光抗体法,也叫免疫荧光法。Xu等[24]采用抗原抗体共表达的显示技术,配合使用流式细胞仪检测荧光信号,便捷而准确地获得IPNV ChRtm213的单链抗体(single-chain antibodyfragment,scFv)。实验证明,该scFv可以特异性识别IPNV ChRtm213,能作为诊断试剂检测IPNVChRtm213。
3.5 核酸探针与基因芯片
核酸探针是继免疫学诊断技术之后发展起来的新技术。有用32P标记的寡核苷酸DNA探针[25]、多核苷酸cDNA探针[26]和用生物素标记的寡核苷酸DNA探针[27]等快速检测IPNV的研究。基因芯片是一种生物芯片,将大量探针分子固定后与标记的样品分子进行杂交,通过检测探针分子的杂交信号强度来获取样品分子的数量和序列信息。王胜强等[28]建立的基因芯片检测技术能够在一个微阵列中与7种病毒10个基因的标记扩增产物同时杂交,可以同步检测包括IPNV在内的7种重要的养殖鱼类病毒,具有通量高、特异性强的优势。
4 IPNV免疫防治
4.1 免疫原理
疫苗是有效防治IPNV的重要措施。IPNV病毒疫苗多基于VP2和VP3等结构蛋白的基因,VP2蛋白携带决定病毒毒力和适应细胞培养的因子[29]。以往的研究证实,VP2蛋白的217~221氨基酸残基与病毒毒力相关[30]。表达的VP2蛋白可在宿主细胞中自我组装亚病毒颗粒,对虹鳟注射纯的VP2亚病毒颗粒或喂食含有重组蛋白的载体菌,都可以引起鱼的特异性免疫反应,诱导鱼体产生抗体,降低IPNV侵染的病毒载量和患病率[31]。VP3也是IPNV重要的功能蛋白。Moon等[32]分别将VP3基因和VP2基因在大肠杆菌中表达纯化后免疫虹鳟。ELISA和中和试验检测免疫后虹鳟血清的抗体效价,发现VP3蛋白也具有很好的免疫原性。赵丽丽等[33]构建的重组质粒pET30b-VP3在大肠杆菌BL21中表达,通过Western-blotting以及ELISA检测表明,表达的融合蛋白与天然VP3蛋白一样具有免疫原性和反应原性。刘巍巍等[34]对IPNV VP3基因的分段表达及其抗原表位区域分析进一步精确定位VP3蛋白抗原表位奠定了基础。开发基于IPNV结构蛋白的多联亚单位疫苗是防控IPNV的重要方向[35]。
4.2 免疫方法
理想的疫苗应在早期接种以产生持久的保护,对幼龄鱼进行口服或浸泡免疫更适用于早期接种。而免疫效果与免疫方法和免疫剂量均有关系[36]。不同抗原运载系统疫苗的作用功效也不同[37]。de las Heras等[38]与Natalia A等[39]将IPNV的VP2疫苗包被在海藻酸盐颗粒中,口服免疫虹鳟后保护率分别达80%和78%~85.9%。Miguel Reyes等[40]将 DNA疫苗添加到饲料中口服免疫大西洋鲑Salmon salar,免疫组与非免疫组的体重和长度相近,表明该疫苗没有影响肠道功能和干扰营养吸收。Arun K Dhar等[41]将人类癌基因的抗原表位c-myc克隆后在酵母中表达,发现IPNV rVP2的SVP能耐受插入外来抗原基,不影响其蛋白质或插入的外来抗原表位的抗原表达,这为开发IPNVrVP2SVP多价疫苗奠定了基础。还有用鲑气单胞菌Aeromonas salmonicida[42]和乳酸菌Lactobacillus等表达的疫苗免疫大西洋鲑。刘敏等[43]将IPNV的VP2、VP3基因插入到乳酸菌表达载体中,构建重组干酪乳杆菌,诱导表达后口服免疫虹鳟幼鱼,诱导虹鳟局部粘膜免疫和全身免疫反应,免疫后病毒载量显著减少。
Skjesol等[44]发现,使用PKR激活促进细胞的病毒复制,而使用PKR抑制剂可减少病毒复制。免疫基因的死亡率和表达水平与病毒复制率、病毒基因序列有关。病毒基因组的快速变化可显著降低病毒的增殖可能表明了较高的易感性的保护机制,即疾病的爆发和死亡率取决于宿主防御和病毒基因组特性[45]。有些疫苗虽然能刺激机体免疫反应产生抗体,但并不能产生有效的保护作用,而在试验阶段具保护作用的免疫制剂在生产中并不能真正起保护作用,这就亟待开发疫苗免疫效果的评价体系。除了免疫防治,国内外研究者也在寻找能够抑制IPNV病毒的其他方法,如某些芳香衍生物对IPNV病毒复制具有抑制作用[46];一些乳制品蛋白质的早期酶解产物对IPNV具有一定的抗病毒活性[47]。Marroqui等[48]报道了霉酚酸(mycophenolic acid,MPA)能抑制次黄嘌呤核苷酸脱氢酶(Inosine 5′-monophosphate dehydrogenase,IMPDH) 而间接抑制细胞GMP的合成,使IPNV RNA的合成缺乏原料,抑制了IPNV的复制。
5 展望
IPN造成虹鳟高死亡率,严重威胁鲑鳟养殖业的健康发展,开发有效的疫苗是最有效的预防方法,需继续对IPNV的感染机理、鱼类免疫反应[49-51]等开展更加深入的研究。更加丰富的研究方法对IPN的防治技术也有重大意义,如用基因工程技术将抗原蛋白与受体结合蛋白、转运蛋白以及信号肽融合,使抗原能够精确定位到效应细胞[52],通过流式细胞术分析病毒感染后体内白细胞的变化,掌握病毒在体内的不同感染时期[53],采取针对性地的治疗措施。
[1]王旭,颜其贵,雷燕.鱼类传染性胰腺坏死病的病毒学特征诊断及防治研究[J].水产科学,2010,29(9):559-562.
[2]EBiering,SVilloing,ISommerset,etal.Updateon viralvaccinesforfish[J].DevelopmentsinBiologicals,2005:121-113.
[3]RJ Roberts and MD Pearson.Infectious pancreatic necrosis in Atlantic salmon,Salmo salar L[J].Journal of Fish Diseases,2005,28(7):383-390.
[4]P Dobos P,B J Hill,R Hallett,et al.Biophysical and biochemical characterization of five animal viruses with bisegmented double-stranded RNA genomes[J].Journal of Virology,1979,32(2):593-605.
[5]葛均青,龚晖,陈超.水生动物双RNA病毒的研究进展[J].武夷科学,2014(30):162-167.
[6]A Pyde,W T Melvin and A L Munro.Nucleotide sequence analysis of the serotype-specific epitope of infections pancreatic necrosis virus[J].Arch Virol,1993,129(1-4):287-293.
[7]S Blake,J Y Ma,D A Caporale,et al.Phylogenetic rela-tionships of aquatic birnaviruses based on deduced amino acid sequences of genome segment A cDNA[J].Diseases ofaquatic organisms,2001,45(2):89-102.
[8]T Isshiki,T Nagano and S Suzuki.Infectivity of aquabirnavirus strains to various marine fish species[J].Diseases ofAquatic Organism,2001,46(2):109-14.
[9]S J Jung,S R Kim,I Y Joung,et al.Distribution of Marine Birnavirus in Cultured Olive Flounder Paralichthys olivaceus in Korea[J].Journal of Microbiology,2008,46(3):265-273.
[10]F Ji,J ZZhao,MLiu,et al.Complete genomic sequence of an infectious pancreatic necrosis virus isolated from rainbow trout(Oncorhynchus mykiss) in China[J].Virus Genes,2016:215-225.
[11]L Zhu,X Wang,K Wang,et al.Outbreak of infectious pancreatic necrosis virus(IPNV)in farmed rainbowtrout in China[J].Acta Tropica,2017,170:63-69.
[12]R A Manríquez,T Vera,M V Villalba,et al.Molecular characterization of infectious pancreatic necrosis virus strains isolated from the three types of salmonids farmed in Chile[J].VirologyJournal,2017,14(1):14-17.
[13]MDadar,R Peyghan and H R Memari.Evaluation of the Bioaccumulation of Heavy Metals in White Shrimp(Litopenaeus vannamei)Along the Persian Gulf Coast[J].Bulletin of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology,2014,93(3):339-343.
[14]孙颖杰,陈文义,夏德昌,等.虹鳟鱼传染性胰脏坏死病毒的分离与鉴定[J].水产学杂志,1993,6(1):50-56.
[15]刘淼,徐黎明,赵景壮,等.虹鳟传染性胰脏坏死病毒的分离鉴定及聚类分析[J].大连海洋大学学报,2017(1):56-61.
[16]江育林,徐伯亥,李伟,等.虹鳟传染性胰脏坏死病毒(IPNV)的初步研究[J].水生生物学报,1989,13(4):353-358.
[17]吴斌,肇慧君,李叶,等.传染性胰脏坏死病毒逆转录聚合酶链式反应法(RT-PCR)的研究[J].中国动物检疫,2012,29(9):46-48.
[18]徐晔,段宏安,周毅,等.实时荧光定量RT-PCR检测鱼类传染性胰脏坏死病病毒方法的建立[J].安徽农业科学,2011,39(31):19224-19226.
[19]TNotomi,H Okayama,H Masubuchi,et al.Loop-mediated isothermal amplification of DNA[J].Nucl Acids Res,2000,28(12):E63.
[20]H Soliman,P J Midtlyng and M EI-Matbouli.Sensitive and rapid detection of infectious pancreatic necrosis virus byreverse transcription loop mediated isothermal amplification[J].Journal of Virological Methods,2009,158(2):77-83.
[21]王健楠,赵丽丽,刘立月,等.传染性胰腺坏死病病毒分离株VP2基因抗原表位区融合表达及免疫特性的分析[J].水产学报,2012,36(11):1770-1775.
[22]连科迅,赵丽丽,张琳琳,等.传染性胰腺坏死病毒VP2 COE蛋白使用单克隆抗体的制备与初步应用[J].水产学报,2013,37(8):1229-1235.
[23]张琳琳,连科迅,张英,等.传染性胰坏死病毒双抗体夹心 ELISA检测方法的建立[J].淡水渔业,2014,44(4):57-72.
[24]L MXu,J Z Zhao,MLiu,et al.Recombinant scFv antibodies against infectious pancreatic necrosis virus isolated byflowcytometry[J].JournalofVirologicalMethods,2016,237:204-209.
[25]E Rimstad,R Krona,E Hornes,et al.Detection of infectious pancreatic necrosis virus RNA by hybridization with an oligonucleotide DNA probe[J].Veterinary Microbiology,1990,23(1-4):211.
[26]C P Dopazo,F M Hetrick and S K Samal.Use of cloned cDNA probes for diagnosis ofinfectious pancreatic necrosis virus infectious[J].Journal of Fish Diseases,2006,17(1):1-16.
[27]周建玲,宫云浩.用生物素标记寡核苷酸DNA探针快速检测鱼传染性胰脏坏死病病毒IPNV[J].水产学报,1995,19(4):310-314.
[28]王胜强,耿伟光,李晋,等.基因芯片检测鱼类病毒的方法建立与优化[J].中国动物检疫,2015,32(7):77-84.
[29]HongJ R,GongH Y,Wu J L,et al.A novel Anti-apoptosis gene of the Bcl-2 family,regulates Mcl-l and viral protein expression[J].Virology,2002,295(2):217-229.
[30]H Song,N Santi,Øystein Evensen,et al.Molecular determinants of infectious pancreatic necrosis virus virulence and cell culture adaptation[J].Journal of Virology,2005,79(16):10289-10299.
[31]A J McBeath,M Snow,C J Secombes,et al.Expression kinetics ofinterferon and interferon-induced genes in Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar)following infection with infectious pancreatic necrosis virus and infectious salmon anaemia virus[J].Fish and Shellfish Immunology,2007,22(3):230-241.
[32]C H Moon,J W Do,S J Cha,et al.Comparison of the immunogenicity of recombinant VP2 and VP3 of infectious pancreatic necrosis virus and marine birnavirus[J].Archive ofVirology,2004,149(10):2059-2068.
[33]赵丽丽,刘敏,哈卓,等.传染性胰腺坏死病毒VP3蛋白的原核表达及抗原性分析[J].水产学报,2010,34(4):604-610.
[34]刘巍巍,赵丽丽,赵永欣,等.传染性胰腺坏死病毒VP3基因的分段表达及其抗原表位区域分析[J].淡水渔业,2011,41(4):61-65.
[35]A K Dhar,R MBowers,C G Rowe,et al.Expression of a foreign epitope on infectious pancreatic necrosis virus VP2 capsid protein subviral particle(SVP)and immunogenicity in rainbowtrout[J].Antiviral Research,2010,85(3):525-531.
[36]R BShivappa,P E McAllister,GH Edwards,et al.Development of a subunit vaccine for infectious pancreatic necrosis virus usinga baculovirus insect/larvae system[J].Developments in Biologicals,2005,12(121):165.
[37]Hetron M,Munang′andu,Børge N,et al.Comparison of vaccine efficacy for different antigen delivery systems for infectious pancreatic necrosis virus vaccines in Atlantic salmon(Salmo salar L)in a cohabitation challenge model[J].Vaccine,2012,30(27):4007-4016.
[38]Heras AIDL,Saint-Jean S R and Pérez-Prieto S I.Immunogenic and protective effects of an oral DNA vaccine against infectious pancreatic necrosis virus in fish[J].Fish and Shellfish Immunology,2010,28(4):562-570.
[39]Ballesteros N A,Saint-Jean S S,Encinas P A,et al.Oral immunization of rainbow trout to infectious pancreatic necrosis virus (Ipnv)induces different immune gene expression profiles in head kidney and pyloric ceca[J].Fish&Shellfish Immunology,2012,33(2):174-85.
[40]Miguel Reyes,Cesar Ramírez,Ivan Ñancucheo et al.A novel“in-feed”delivery platform applied for oral DNA vaccination against IPNV enables high protection in Atlantic salmon(Salmon salar)[J].Vaccine,2017,35(4):626-632.
[41]Dhar A K,Bowers R M,Rowe,C G,et al.Expression of a foreign epitope on infectious pancreatic necrosis virus VP2 capsid protein subviral particle(SVP)and immunogenicity in rainbowtrout[J].Antiviral Research,2010,85(3):525-531.
[42]Kumari J,B agwald J and Dalmo R A.Vaccination Aeromonas salmonicida and infectious pancreatic of Atlantic salmon,Salmo salar L necrosis virus(IPNV)showed a with mixed Thl/Th2/Treg response[J].Journal ofFish Diseases,2013,36(10):881-886.
[43]刘敏,赵丽丽,葛俊伟,等.传染性胰腺坏死病毒VP3蛋白的干酪乳杆菌表达系统构建[J].淡水渔业,2008,38(5):30-34.
[44]A Skjesol,T Hansen,C Y Shi,et al.Structural and functional studies of STAT1 from Atlantic salmon(Salmo salar)[J].BMCImmunology,2010,11(1):17.
[45]A Skjesol,I Skjæveland,MElnæs,et al.IPNV with high and low virulence:host immune responses and viral mutations during infection[J].Virology Journal,2011,8(1):396.
[46]B Modak,A MSandino,L Arata,et al.Inhibitory effect of aromatic geranyl derivatives isolated from Heliotropium filifolium on infectiouspancreatic necrosis virus replication[J].VeterinaryMicrobiology,2010,141(1-2):53-58.
[47]S S Rodríguez,S I Pérez Prieto,I Lópezexpósito,et al.Antiviral activity of dairy proteins and hydrolysates on salmonid fish viruses[J].International Dairy Journal,2012,23(10):24-29.
[48]L Marroqui,A Estepa and L Perez.Inhibitory effect of mycophenolic acid on the replication of infectious pancreatic necrosis virus and viral hemorrhagic septicemia virus[J].Antiviral Research,2008,80(3):332-338.
[49]H MMunang′Andu,S Mutoloki and Ø Evensen.Acquired immunity and vaccination against infectious pancreatic necrosis virus of salmon[J].Developmental and Comparative Immunology,2014,43(2):184.
[50]H M Munang′Andu,B N Fredriksen,S Mutoloki,et al.The kinetics of CD4+gene expression correlate with protection in Atlantic salmon(Salmo solar)CD8+T cell vaccinated against infectious pancreatic necrosis[J].Vaccine,2013,31(15):1956-1963.
[51]A Kamil,A Raae,P G Fjelldal,et al.Comparative analysis ofIgMsub-variants in salmonid fish and identification ofa residue in μ3 which is essential for MAb4C10 reactivity[J].Fish and Shellfish Immunology,2013,34(2):667-72.
[52]Kuo T,Chen G H,Wu C,et al.Subunit vaccine for aquaculture:US,US8343505[P].2013.
[53]A Rønneseth,E F Pettersen and H I Wergeland.Flowcytometry assay for intracellular detection of infectious pancreatic necrosis virus(IPNV)in Atlantic salmon(Salmo salar L)leucocytes[J].Fish and Shellfish Immunology,2012,33(6):1292-1302.
Progress on Biological Research of Infectious Pancreatic Necrosis Virus:a Review
HE Wen-bin1,ZHAO Jing-zhuang1,LU Tong-yan1,YIN Jia-sheng1,XU Li-ming1
(1.Heilongjiang River Fishery Research Institute,Chinese Academy of Fishery Sciences,Harbin 150070,China;2.College of Fishery and Life Science,Shanghai Ocean University,Shanghai 201306,China)
Infectious pancreatic necrosis (IPN)as an acute infectious disease of many aquatic animals,can cause high mortalities in worldwide salmon and trout fingerlings,whose pathogen,infectious pancreatic necrosis virus(IPNV),belongs to the Aquabirnavirus within the family Birnaviridae.This review summarizes the genomic structure,biological characteristics,diagnostic techniques and immunological control of the pathogen,in order to provide reference for the prevention and treatment of IPN.
infectious pancreatic necrosis virus (IPNV);Aquabirnavirus,aquatic double stranded RNA virus;genotype;serotype;salmon and trout
S941
A
1005-3832(2017)06-0001-06
2017-06-29
中央公益性事业单位基本科研业务费专项经费(HSY201514).
贺文斌(1992-),女,硕士研究生,从事鱼类病毒学研究.E-mail:981073106@qq.com
徐黎明,女,博士,副研究员,从事鱼类病毒学研究.E-mail:lmxu0917@163.com

