秸秆双层覆盖对盐碱地水盐运动影响初步研究*
王曼华 陈为峰 宋希亮 李贤红 胡 琴 邓 从
(山东农业大学资源与环境学院,山东泰安 271018)
秸秆双层覆盖对盐碱地水盐运动影响初步研究*
王曼华 陈为峰†宋希亮 李贤红 胡 琴 邓 从
(山东农业大学资源与环境学院,山东泰安 271018)
采用室内土柱模拟的方式,研究了秸秆双层覆盖对盐碱土的改良效应及机制,以期对盐碱地的改良提供理论依据。结果表明:1)与对照相比,不同的秸秆覆盖模式均能降低土壤水分的累积蒸发量,T4处理(土表与土表下35~40 cm处覆盖秸秆量之比为2∶1)在45 d内土壤水分累积蒸发量较CK(无秸秆覆盖的对照)低36.73 mm,抑蒸率为65.89%,抑蒸率最大,对土壤水分蒸发的抑制效果最好。2)秸秆处理均在不同程度上抑制了土壤返盐,其中T4处理返盐率最小,远低于对照处理。3)土壤水分累积蒸发量与土壤累积含盐量存在高度正相关关系。4)秸秆双层覆盖对土壤水分蒸发和土壤返盐的抑制效果大于秸秆表层覆盖和秸秆深层覆盖,并且,在不同的秸秆双层覆盖的处理中,T4处理的控盐保水效果最好,是一种较好的改良盐碱土的方法。
秸秆;表层覆盖;深层覆盖;双层覆盖;蒸发量;盐分
土壤中过量的盐分能够导致土壤物理和化学性质的改变,进而导致大部分作物生长环境的退化。根据“盐随水来,盐随水去”的原理,只要能够减少土壤水分的蒸发,理论上就可以减轻土壤盐分的表聚,降低土壤对作物的盐害[1-3]。在各种调控水盐运动的措施中,秸秆覆盖可抑制或减少土壤水分蒸发,有效减轻盐分表聚。农作物秸秆量很大,来源广泛,因此,通过秸秆覆盖措施改良盐碱地,一直是研究热点之一。研究表明[4-9],土壤盐分表聚性是土壤发生盐渍化的重要因素。秸秆表层覆盖可有效控制土壤水分的蒸发,抑制盐分的表聚,减轻土壤表层的盐渍化程度,进而达到改良盐碱地的目的[10-14]。地表秸秆覆盖措施的抑盐效果主要体现在土壤表层,如秦嘉海[15]研究结果表明,留茬秸秆覆盖措施主要降低了0~20 cm耕层的土壤含盐量;孙博等[16]研究结果也显示,采用秸秆覆盖处理能够明显地抑制盐分的表聚,并可明显地降低0~10 cm土层处的土壤含盐量。也有学者[17]提出,可通过增加秸秆覆盖的深度来控制更深土层的土壤含盐量,在地表下20 cm或30 cm处覆盖小麦或玉米秸秆可切断土壤毛管,有效抑制水盐上行,降低深层土壤水分蒸发,减轻盐分表聚,防止根层盐化。随着根茬—心土混合犁[18]、深层心土还田装备的应用[19-20],秸秆深层还田设备也已经逐渐成熟。但乔海龙等[3]研究指出,秸秆深层覆盖减少了深层土壤盐分向表层的运移,在土表下20 cm处埋设秸秆隔层能够减少隔层以下的土壤盐分向上迁移,但是,土壤表层仍然出现盐分表聚的现象,甚至表层含盐量略高于秸秆表层覆盖;虎胆·吐马尔白等[21]研究结果也表明,不同地下水埋深条件下,地表以下30 cm处秸秆覆盖的土壤含盐量大于地表表层秸秆覆盖的土壤含盐量。还有部分学者[22]对地膜覆盖结合秸秆深层覆盖措施进行了研究,效果尚可,但是,地膜覆盖会产生一定的污染。综上,目前,对表层秸秆覆盖的效应争议不大,但对秸秆深层覆盖具体技术及效果尚需进一步研究。
本研究提出集上盖(地表覆盖)和下隔(地下埋设秸秆隔层)为一体的盐渍土改良新方法,采用室内土柱模拟试验的方法,研究双层秸秆覆盖还田对盐渍土的改良效应及机制,以期为盐渍土改良提供理论依据。
1 材料与方法
1.1 试验材料
本试验于2016年10月在山东农业大学资源与环境学院试验站进行。试验使用直径30 cm、高1 m的聚氯乙烯(PVC)管做土柱试验。装土前,先在土柱底部装填干净的砂石层作为反滤层,厚度约为10 cm,可为入渗过程提供一个气流顺畅的入渗环境。土柱底部用纱布封闭,放置盛有10 g L-1咸水的塑料盆中,用来模拟地下水环境。试验装置如图1所示。
实验前将玉米秸秆剪碎。土壤采自山东省东营市河口区汀罗镇渤海农场,土壤类型为滨海盐土(潮湿正常盐成土),土柱所装土壤基本化学性质如表1所示。
1.2 试验方法
将采集的盐化潮土混匀后装入土柱。试验设6个处理:表层覆盖玉米秸秆(T1)、土表下35~40 cm处玉米秸秆(T2)、土表与土表下35~40 cm处覆盖秸秆量之比为1∶1(T3)、土表与土表下35~40 cm处覆盖秸秆量之比为2∶1(T4)、土表与土表下35~40 cm处覆盖秸秆量之比为1∶2(T5)、无秸秆覆盖的对照(CK)。秸秆总覆盖量为900 g m-2。试验土柱设置在遮雨棚下,防止降雨对实验的影响。
试验开始时,采用200 mm淡水定额洗盐[23],待水分全部入渗完毕,从土柱土面用土钻开始取土,取样位置分别为距土表0~20 cm、20~40 cm、40~60 cm、60~80 cm,用于测定土壤含盐量。试验开始后,设置空的PVC管作为对照,同步测定试验过程中水面蒸发强度,每隔5 d对土柱进行称重[24],利用前后两次的差值来计算土壤水分蒸发量;同时每隔10 d对土柱进行取样,取样位置同样分别为距土表0~20 cm、20~40 cm、40~60 cm和60~80 cm,用来测定土壤盐分。在试验过程中,定期向土柱底部的塑料盆中加10 g L-1的咸水,以保持土柱底部相对稳定的咸水环境。取样后,将土壤烘干后磨碎、过2 mm筛,以1∶5的土水比浸提土壤溶液,用烘干法测定土壤含盐量。

图1 不同秸秆覆盖方式试验装置图Fig. 1 Sketch of the device used for the in-lab experiment on straw mulching

表1 供试土壤基本性质Table 1 Basic properties of the soil used in the experiment
1.3 数据处理
数据分析与图形绘制采用SPSS18.0、Microsoft Excel 2007和Origin 8.5软件。
2 结 果
2.1 不同秸秆覆盖方式对土柱蒸发强度的影响
2.1.1 对土壤水分日蒸发量的影响 图2为不同秸秆覆盖方式对土壤水分日蒸发量的影响。从图2可以看出,不同秸秆覆盖方式与对照处理土壤水分平均日蒸发量的变化趋势基本一致,仅是在变化幅度上存在差异性,均表现为:在试验初期日蒸发量较大,试验开始后5 d对照处理的日蒸发量显著高于其他处理,并且,不同秸秆覆盖方式的日蒸发量均小于对照处理。试验数据显示,不同秸秆覆盖方式的日蒸发量由小到大排序为T4<T5<T3<T1<T2。
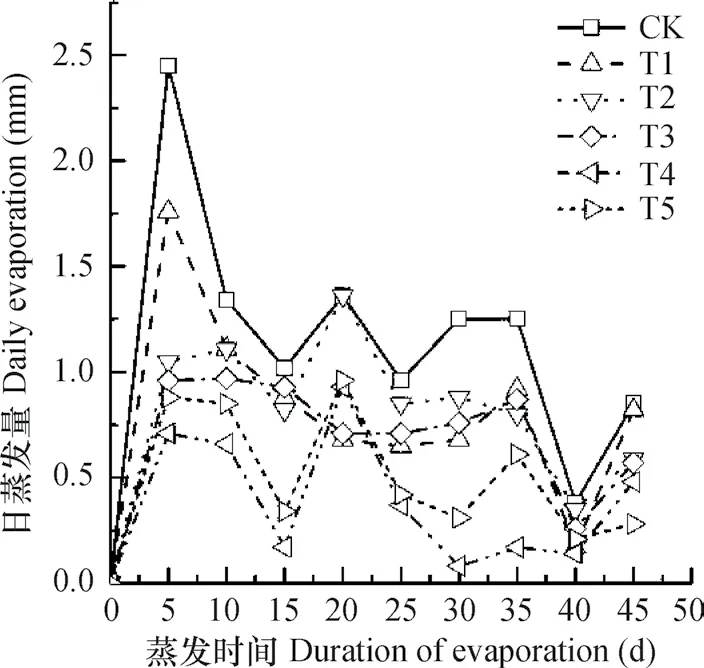
图2 不同秸秆覆盖方式的日蒸发量随时间变化Fig. 2 Temporal variation of daily soil water evaporation relative to treatment
2.1.2 对土壤水分累积蒸发量的影响 图3为不同秸秆覆盖方式对土壤水分累积蒸发量的影响。由图3可知,在同一大气蒸发条件下,不同秸秆覆盖方式对土壤水分日累积蒸发量的影响程度不同,均低于无秸秆覆盖的累积蒸发量。CK、T1、T2、T3、T4和T5处理日累积蒸发量分别为57.26 mm、40.48 mm、41.33 mm、35.81 mm、19.53 mm、26.04 mm;不同秸秆覆盖方式对土壤水分蒸发的抑制作用表现为T4>T5>T3,同时,随蒸发的进行,各处理的累积蒸发量差异更加明显。但是,在试验开始时,T2处理土柱的累积蒸发量低于T1,随着时间的推移,T2处理的累积蒸发量逐渐高于T1。

图3 不同秸秆覆盖方式的累积蒸发量随时间变化Fig. 3 Temporal variation of cumulative soil water evaporation relative to treatment
2.1.3 对土壤水分蒸发抑制率的影响 土壤水分蒸发抑制率即秸秆覆盖后累积蒸发量与对照累积蒸发量的差占对照累积蒸发量的百分数,能够更好地说明不同秸秆覆盖处理对土壤水分蒸发的影响[24]。根据图3可知,在整个蒸发过程中,CK、T1、T2、T3、T4、T5处理土柱的平均日蒸发量分别为1.27 mm d-1、0.90 mm d-1、0.92 mm d-1、0.80 mm d-1、0.43 mm d-1、0.58 mm d-1。与CK相比,T1、T2、T3、T4和T5土柱的抑蒸率分别为29.30%、27.82%、37.46%、65.89%、54.52%。其中,抑蒸率越大抑制效果越好。各处理对土壤蒸发的抑制作用明显:表层秸秆覆盖量相同时,深层秸秆覆盖量越大,抑蒸率越大,抑制效果越好;深层秸秆覆盖量相同时,表层秸秆覆盖量越大,抑蒸率越大,抑制效果越好。T4处理土柱抑蒸率最大,抑制效果最好,T2土柱抑蒸率最小,抑制效果最差。
2.2 不同秸秆覆盖方式对土壤盐分的影响
图4为不同时期不同秸秆覆盖方式对土壤剖面含盐量的影响。从图4可以看出,在蒸发作用下,底层土壤和潜水中的盐分可随水分向上迁移,导致各土柱不断积盐,不同措施的控盐抑盐效果差异明显,对土壤含盐量有明显影响。
由图4可以看出,试验开始时土柱浇淡水200 mm,在浇水后土壤上层的盐分被淋洗至土壤底层。淋洗前后,不同处理土壤盐分含量变化明显,CK、T1、T2、T3、T4和T5处理土柱0~40 cm的淋洗率分别为68.53%、70.26%、56.76%、83.36%、68.53%、76.32%,T1、T3和T5土柱的淋洗率高于CK土柱,T4土柱淋洗率与CK土柱相同,T2土柱淋洗率低于CK土柱,并且T3土柱脱盐率最高,淋洗效果最好。从图4还可以看出,在潜水蒸发阶段,土壤中的盐分随水分向土表迁移,导致各土柱不断积盐,不同秸秆覆盖方式的控盐抑盐效果差异明显。在蒸发30 d后,各土柱0~40 cm土壤返盐率分别为225.6%、75.14%、128.3%、148.4%、17.96%和122.2%。结果表明,各土柱0~40 cm土壤的返盐率均低于CK土柱;返盐率越低,控盐抑盐效果越好,T4土柱的返盐率最低,抑盐效果最好。
2.3 土壤水分累积蒸发量与土壤累积含盐量的关系
本研究对土壤水分累积蒸发量与整个土体的土壤累积含盐量进行了相关性分析。由表2可以看出,土壤水分累积蒸发量与土壤累积含盐量之间的相关系数为0.848,属于高度正相关关系,即土壤水分蒸发量越大,土壤累积含盐量越大。
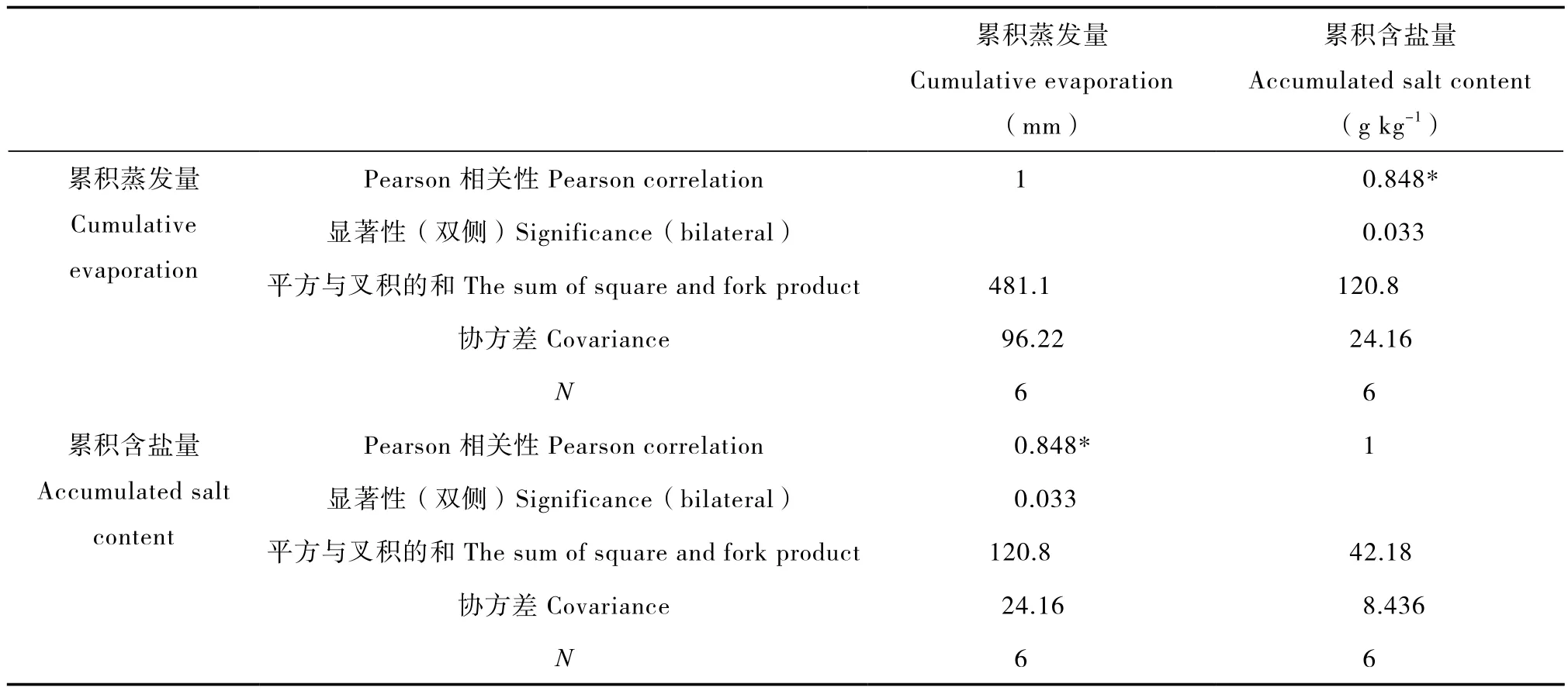
表2 土壤水分累积蒸发量与土壤累积含盐量的相关性Table 2 Correlation between cumulative evaporation and accumulated salt content in the soil
3 讨 论
本研究结果表明,秸秆双层覆盖能明显抑制土壤水分蒸发,并且,表层秸秆覆盖量与深层秸秆覆盖量之比为2∶1时,抑制效果最好。土壤中粗细不同的毛管孔隙连通一体形成复杂的毛管体系,为水分运动提供一个连续体,土壤潜水可以通过毛细管向表层运移。在地表下40 cm处埋设秸秆隔层,秸秆隔层以大孔隙居多,在土层和秸秆隔层界面形成“孔隙差异界面”[25],切断了土壤毛细管的连续性,改变了土体的通透性和导水能力的连续性,建立了一种不连续的水分运移道路,形成了土壤毛管水的上移障碍层,减弱了蒸发能力;采用地表覆盖秸秆,切断了土表与空气的接触面,降低了土壤的垂直蒸发量,上层土壤水蒸散速度减慢,从而减少了水汽扩散量,提高水分抑制率,并且表层覆盖量越大,抑制蒸发效果越明显。孙博等[16]研究表明,秸秆覆盖后,盐渍化土壤蒸发量较对照低,随着秸秆覆盖量的增加,蒸发量逐渐减少,当秸秆覆盖量为0.75 kg m-2时,日蒸发量减少幅度平缓,趋于稳定;张金珠等[24]研究结果表明,表层覆盖秸秆能明显抑制水分蒸发,秸秆量越大,日蒸发强度越小,不同秸秆覆盖量处理间累积蒸发量差异显著。乔海龙等[3]研究指出,在自然蒸发条件下,秸秆隔层可减少深层土壤水分的散失,但是表层土壤水分散失较快;Cao等[26]研究也发现,在连续一个月的蒸发过程中,秸秆隔层对深层土壤具有蓄水保墒的积极作用,但也不能完全阻隔深层土壤水分散失。本试验结合了表层秸秆覆盖和深层秸秆覆盖,达到了更好地抑制水分蒸发的效果。
本研究发现,在土表下35~40 cm处埋设秸秆隔层,对土壤返盐有较好的抑制效果。秸秆隔层切断了土壤毛细通道,破坏了土体的连续性,从而抑制盐分表聚,降低耕作层盐分含量[27-28]。但是,单一秸秆隔层的抑盐效果较秸秆表层覆盖的抑盐效果差。秸秆深层覆盖虽然降低了隔层以下土壤盐分向上返盐,但并未抑制秸秆层以上土壤盐分向土壤表层的聚集,表层土壤盐分的聚集可能是由于隔层以上土层中盐分的表聚造成的,而并非是底部毛管水支持的供给。在地表下铺设秸秆的同时结合地表覆盖,能达到更好的控盐效果,既能抑制深层土壤盐分向上层土壤的传导,也能抑制上层土壤盐分向表层聚集,明显降低土壤耕层的含盐量。赵永敢等[29]研究也曾发现,在有秸秆层的情况下,表层地膜覆盖较表层秸秆覆盖抑盐效果显著,作用时期也更持久。但是,地表覆盖地膜容易对土壤造成污染,因此,秸秆双层覆盖可能是一种更好的改良盐渍土的方法。总体而言,关于秸秆双层覆盖的研究还处于初级阶段,且多限于室内土柱试验,田间研究的报道很少。今后的研究重点应该开展田间试验,进一步深入研究本技术对盐渍土改良及增产的效果。
本试验分析了土壤水分和盐分的关系,结果表明,盐分运动与水分运动呈高度相关关系。水盐运动有着它自身的规律和特点,其中,水运动起着主导和决定性作用。水是土壤盐分的天然溶剂,水分在运动过程中溶解并携带着多种矿物质盐类,构成了一个运动着的统一物质流,“盐随水来,盐随水去”,通过抑制水分的蒸发减少盐分的积累是可行的。
4 结 论
通过室内土柱模拟试验的方法,初步研究了不同的秸秆覆盖方式对土壤水分蒸发量、盐分积累的影响,得出了以下结论:不同秸秆覆盖模式对土壤水分日蒸发量的影响有明显差异,抑制效果由大到小表现为T4>T5>T3>T1>T2。在同一大气蒸发条件下,不同的秸秆覆盖模式均能降低土壤水分的累积蒸发量,T4处理(土表与土表下35~40 cm处覆盖秸秆量之比为2∶1)效果最为明显,土壤水分累积蒸发量较CK土柱低76.13%,大幅度减弱了底层土壤水补给耕层水分蒸散损失的能力。T4处理的抑蒸率最大,对土壤水分蒸发的抑制效果最好。在水分蒸发阶段,各处理土壤中的盐分在水分蒸发作用下均不断向土壤表层聚集,每个处理均在不同程度上抑制了土壤返盐,其中,T4处理返盐率最小,远远低于对照处理。即在不同的秸秆双层覆盖处理中,T4处理的减蒸控盐效果最好。
[1] 王遵亲. 中国盐渍土. 北京:科学出版社,1993:250—311 Wang Z Q. Chinese saline soil(In Chinese). Beijing:Science Press,1993:250—311
[2] Qadir M,Ghafoor A,Murtaza G. Amelioration strategies for saline soils:A review. Land Degradation and Development,2001,11(6):501—521
[3] 乔海龙,刘小京,李伟强,等. 秸秆深层覆盖对土壤水盐运移及小麦生长的影响. 土壤通报,2006,37(5):885—889 Qiao H L,Liu X J,Li W Q,et al. Effects of straw deep mulching on soil moisture infiltration and evaporation (In Chinese). Chinese Journal of Soil Science,2006,37(5):885—889
[4] 张建兵,杨劲松,李芙荣,等. 有机肥与覆盖对苏北滩涂重度盐渍土壤水盐调控效应分析. 土壤学报,2014,51(1):184—188 Zhang J B,Yang J S,Li F R,et al. Effects of farmyard manure and mulching on soil water and salinity in severes alinized tide flat soil of North Jiangsu Province(In Chinese). Acta Pedologica Sinica,2014,51(1):184—188
[5] TolkJ,Howell T,Evett S. Effect of mulch,irrigation and soil type on water use and yield of maize. Soilamp;Tillage Research,1999,50(2):137—147
[6] 侯连涛,焦念元,韩宾,等. 不同覆盖方式对土壤水分分布的影响. 灌溉排水学报,2007,26(1):47—48 Hou L T,Jiao N Y,Han B,et al. Effects of different covering methods on soil water distribution(In Chinese). Journal of Irrigation and Drainage,2007,26(1):47—48
[7] Ji S,Ungerb P W. Soil water accumulation under different precipitation,potential evaporation,and straw mulch conditions. Soil Science Society of America Journal,2001,65(2):442—448
[8] 王维,郑曙峰,路曦结,等. 农田秸秆覆盖技术研究进展. 安徽农业科学,2009,37(18):8343—8346 Wang W,Zheng S F,Lu X J,et al. Research Progress on straw mulch technology in farmland(In Chinese).Journal of Anhui Agricultural Sciences,2009,37(18):8343—8346
[9] 邓力群,陈铭达,刘兆普,等. 地面覆盖对盐渍土水热盐运动及作物生长的影响. 土壤通报,2003,34(2):93—97 Deng L Q,Chen M D,Liu Z P,et al. Effects of different ground covers on soil physical properties and crop growth on saline-alkaline soil(In Chinese).Chinese Journal of Soil Science,2003,34(2):93—97
[10] 毕远杰,王全九,雪静. 覆盖及水质对土壤水盐状况及油葵产量的影响. 农业工程学报,2010,26(S1):83—89 Bi Y J,Wang Q J,Xue J. Effects of ground coverage measure and water quality on soil water salinity distribution and helianthus yield(In Chinese).Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering,2010,26(S1):83—89
[11] Cook H F,Valdes G S B,Lee H C. Mulch effects on rainfall interception,soil physical characteristics and temperature under Zea mays L. Soil amp; Tillage Research,2006,91(1):227—235
[12] 付国占,李潮海,王俊忠,等. 残茬覆盖与耕作方式对土壤性状及夏玉米水分利用效率的影响. 农业工程学报,2005,21(1):52—56 Fu G Z,Li C H,Wang J Z,et al. Effects of stubble mulch and tillage managements on soil physical properties and water use efficiency of summer maize(In Chinese). Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering,2005,21(1):52—56
[13] MulumbaL N,Lal R. Mulching effects on selected soil physical properties. Soil amp; Tillage Research,2008,98(1):106—111
[14] 员学锋,吴普特,汪有科,等. 免耕条件下秸秆覆盖保墒灌溉的土壤水、热及作物效应研究. 农业工程学报,2006,22(7):22—26 Yuan X F,Wu P T,Wang Y K,et al. Soil moisture conserving irrigation under straw mulch with no-tillage(In Chinese). Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering,2006,22(7):22—26
[15] 秦嘉海. 免耕留茬秸秆覆盖对河西走廊荒漠化土壤改土培肥效应的研究. 土壤,2005,37(4):447—450 Qin J H. Effects of non-tillage and mulching on soil building of desertified soil in the Hexi corridor(In Chinese). Soils,2005,37(4):447—450
[16] 孙博,解建仓,汪妮,等. 秸秆覆盖对盐渍化土壤水盐动态的影响. 干旱地区农业研究,2011,29(4):181—184 Sun B,Xie J C,Wang N,et al. Effect of straw mulching on water-salt dynamic of saline soil(In Chinese). Agricultural Research in the Arid Areas,2011,29(4):181—184
[17] 范浩,李跃进,陈玉海,等. 秸秆深埋对河套盐渍土盐碱调控作用的研究. 内蒙古农业科技,2015,43(2):16—18 Fan H,Li Y J,Chen Y H,et al. Study on straw buried on saline soil saline-alkali regulation in Hetao Plain (In Chinese). Inner Mongolia Agricultural Science and Technology,2015,43(2):16—18
[18] 张春峰,贾会彬,张洪权,等. 秸秆心土还田改良沼泽化土壤排涝效果的研究. 黑龙江农业科学,2001,60(3):6—8 Zhang C F,Jia H B,Zhang H Q,et al. Effect of returning the crop stack into subsoil on improving the marsh bog soil and drainage(In Chinese).Heilongjiang Agricultural Science,2001,60(3):6—8
[19] 黄毅,毕素艳,邹洪涛,等. 秸秆深层还田对玉米根系及产量的影响. 玉米科学,2013,21(5):109—112 Huang Y,Bi S Y,Zou H T,et al. Effect of straw deep returning on corn root system and yield(In Chinese).Journal of Maize Sciences,2013,21(5):109—112
[20] 赵永敢,王婧,李玉义,等. 秸秆隔层与地覆膜盖有效抑制潜水蒸发和土壤返盐. 农业工程学报,2013,29(23):109—117 Zhao Y G,Wang J,Li Y Y,et al. Reducing evaporation from phreatic water and soil resalinization by using straw interlayer and plastic mulch(In Chinese).Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering,2013,29(23):109—117
[21] 虎胆·吐马尔白,吴旭春,迪力达. 不同位置秸秆覆盖条件下土壤水盐运动实验研究. 灌溉排水学报,2006,25(1):34—37 Hudan T,Wu X C,Di L D. A study of effects of wheat straw mulch on soil water conservation(In Chinese).Journal of Irrigation and Drainage,2006,25(1):34—37
[22] 赵永敢,李玉义,胡小龙,等. 地膜覆盖结合秸秆深埋对土壤水盐动态影响的微区试验. 土壤学报,2013,50(6):1129—1137 Zhao Y G,Li Y Y,Hu X L,et al. Effects of plastic mulching and deep burial of straw on dynamicsof soil water and salt in micro-plot field cultivation(In Chinese). Acta Pedologica Sinina,2013,50(6):1129—1137
[23] 郭相平,杨泊,王振昌,等. 秸秆隔层对滨海盐渍土水盐运移影响. 灌溉排水学报,2016,35(5):22—27 Guo X P,Yang B,Wang Z C,et al. Influence of straw interlayer on the water and salt movement of costal saline soil(In Chinese). Journal of Irrigation and Drainage,2016,35(5):22—27
[24] 张金珠,王振华,虎胆·吐马尔白. 秸秆覆盖对土柱一维水分传输与蒸发的影响. 干旱区研究,2015,32(5):861—868 Zhang J Z,Wang Z H,Hudan T. Effects of straw mulch on vertical water movement and evaporation of a soil column(In Chinese). Arid Zone Research,2015,32(5):861—868
[25] 曲晨晓,王炜. 土壤剖面中砂质夹层的储水作用及机理研究. 华中农业大学学报,1997,16(5):349—356 Qu C X,Wang W. Mechanisms of water reserved by sand interlayer in soil profile(In Chinese). Journal of Huazhong Agricultural University,1997,16(5):349—356
[26] Cao J,Liu C,Zhang W,et al. Effect of integrating straw into agricultural soils on soil infiltration and evaporation. Water Science amp; Technology,2012,65(12):2213—2218
[27] 张金珠,王振华,虎胆·吐马尔白. 具有秸秆夹层层状土壤一维垂直入渗水盐分布特征. 土壤,2014,46(5):954—960 Zhang J Z,Wang Z H,Hudan T. Distribution characteristics of one-dimensional vertical infiltration water and salt in layered soil with subsurface straw layer(In Chinese). Soils,2014,46(5):954—960
[28] 李芙荣,杨劲松,吴亚坤,等. 不同秸秆埋深对苏北滩涂盐渍土水盐动态变化的影响. 土壤,2013, 45(6):1101—1107 Li F R,Yang J S,Wu Y K,et al. Effects of straw mulch at different depths on water-salt dynamic changes of coastal saline soil in North Jiangsu Province(In Chinese). Soils,2013,45(6):1101—1107
[29] 赵永敢,逄焕成,李玉义,等. 秸秆隔层对盐碱土水盐运移及食葵光合特性的影响. 生态学报,2013,33(17):5153—5161 Zhao Y G,Pang H C,Li Y Y,et al. Effects of straw interlayer on soil water and salt movement and sunflower photosynthetic characteristics in saline-alkali soils(In Chinese). Acta Ecologica Sinica,2013,33(17):5153—5161
(责任编辑:陈荣府)
Preliminary Study on Effect of Straw Mulching and Incorporation on Water and Salt Movement in Salinized Soil
WANG Manhua CHEN Weifeng†SONG Xiliang LI Xianhong HU Qin DENG Cong
(College of Resources and Environment,Shangdong Agicultural University,Tai’an,Shandong 271018,China)
【Objective】Soil salinization is the major cause of reduction of agricultural production in Dongying of Shandong Province,China,where shallow groundwater table,high evaporation and low precipitation cause soil salt to move upwards and accumulate on the surface soil of farmlands,so that yields of the crops therein are often quite low. In the study,an indoor simulation experiment was carried out using soil columns to explore effect of the farming practice of simultaneous straw mulching and straw incorporation on soil water evaporation,salt movement and soil water and salt distribution in farmland,in an attempt to provide a theoretical basis for amelioration and utilization of the coastal saline soil in Dongying.【Method】The in-lab simulation experiment was designed to have six treatment i.e. T1(Straw mulching),T2(Straw incorporation into the 35~40 cm soil layer),T3(With the ratio of straw in mulching and incorporation set at 1∶1),T4(With the ratio set at 2∶1),T5(With the ratio set at 1∶2)and CK(No straw mulching or incorporation). Soil water evaporation and soil salt content was monitored during the experiment.【Result】It was found that:(1)The treatments varied sharply in effect on daily soil water evaporation and exhibited an order of T4 < T5 < T3 < T1 < T2 < CK. Under the same atmospheric condition,either mulching or incorporation or both reduced cumulative soil water evaporation and Treatment T4 was the most obvious in the effect,cutting the cumulative evaporation by 76.13% as compared with CK by retarding the upward movement of soil water from the bottom soil layer,thus greatly reducing soil water loss. The evaporation inhibition rate of Treatment T4 reached 65.89%,being the highest among those of the treatments,so the treatment was the best in the experiment in inhibiting soil water loss through evaporation;(2)During the phase of water leaching and infiltration in the experiment,the treatments also varied significantly in effect on salt leaching.Treatment T3 was the best,with the soil desalination rate in the 0~40cm soil layer reaching up to 14.83%,while all the other treatments,except Treatment T2,were also found higher than CK in soil desalinization rate. During the phase of of water evaporation,all the treatments were found to have salt accumulated on the surface by a varying degree,and Treatment T4 treatment was the lowest in soil resalinization rate,and much lower than CK;(3)Treatments T3,T4 and T5 were obviously higher than Treatments T1 and T2 in effect of inhibiting soil water evaporation and soil resalinization,with Treatment T4 in particular;and(4)Correlation analysis of cumulative soil water evaporation and cumulative soil salt accumulation shows that the two were positively related,that is,the higher the cumulative soil water evaporation,the higher the soil salt accumulation.【Conclusion】Through the in-lab simulation experiment,it is found that the practice of either mulching or incorporation or both can inhibite soil water evaporation and soil resalinization to a varying extent and the practice of mulching and incorporating straw simultaneously at a ratio of 2∶1 in quantity is the best in controlling soil water evaporation and soil resalinization,so it is a good option for amelioration of salt-affected soils.
Straw;Surface mulching;In-depth incorporation;Mulching coupled with incorporation;Evaporation;Salt
S156.4
A
10.11766/trxb201705020061
* 山东省重点产业关键技术项目(2016CYJS05A02)和国家自然科学基金项目(31570522)共同资助 Support by the Shandong Province Key Industry Key Technology Projects(No.2016CYJS05A02)and the National Natural Science Foundation of China(No. 31570522)
† 通讯作者 Corresponding author,E-mail:chwf@sdau.edu.cn
王曼华(1991—),女,河北保定人,硕士研究生,主要从事盐碱地改良研究。E-mail:15552830282@163.com
2017-05-02;
2017-06-08;优先数字出版日期(www.cnki.net):2017-06-27

