北斗导航系统走进“新时代”
Chen, He-Chin; Huang, Yu-Sheng;CChiang, Kai-Wei; et al.
BeiDou navigation satellite system and its time scales
Han, Chunhao; Yang, Yuanxi; Cai, Zhiwu; et al.
Initial assessment of the COMPASS/BeiDou-2 regional navigation satellite system
Montenbruck, Oliver; Hauschild, Andre;Steigenberger, Peter; et al.
BeiDou inter-satellite-type bias evaluation and calibration for mixed receiver attitude determination
Nadarajah, Nandakumaran; Teunissen, Peter J. G;Raziq, Noor; et al.
北斗卫星导航系统安全和完好性监测现状与发展
庄钊文,王飞雪,欧钢,孙广富,李峥嵘
北斗卫星导航系统的进展、贡献与挑战
杨元喜
北斗导航系统走进“新时代”
·编者按·
作为世界上三大卫星导航系统之一,遨游在地球轨道上的北斗卫星导航系统,受到了越来越多国家的关注。自2012年12月27日,中国政府宣布北斗区域导航系统正式提供区域服务以来,北斗系统服务亚太地区,亮出了一张新时代的“国家名片”。如今,伴随着北斗三号系统的两颗卫星升空,北斗系统开始走向全球。
目前,北斗系统已经覆盖了巴基斯坦、沙特、缅甸、埃及、印尼等近30个“一带一路”沿线国家。北斗系统服务全球既是我国发展北斗导航系统的神圣使命和庄重承诺,又是北斗系统发展的必由之路。在东盟,从2013年到2016年,北斗系统先后为文莱、老挝、泰国、马来西亚、柬埔寨、印度尼西亚提供导航与位置服务产品。在阿盟,2017年4月,北斗/全球卫星导航系统应用研讨会在沙特阿拉伯举行,北斗系统首次大规模走进对导航产品和应用有巨大需求的沙特市场。2017年5月,首届中阿国家北斗合作论坛召开,中国卫星导航管理办公室签署了《建立卫星导航合作机制》的谅解备忘录,北斗系统落地阿拉伯国家的工作全面推开。
北斗建设的提速和北斗“走出去”的强劲步伐,吸引了越来越多的国家的目光。2013年,北斗海外监测站在巴基斯坦顺利建成并开通运行;2016年,斯里兰卡在该国建设48个北斗地基增强基站;同年,首次中俄“一带一路”卫星导航联合测试——中方测试工作正式启动。据相关资料报道,2018年将要发射18颗北斗三号组网卫星,覆盖“一带一路”沿线国家;到2020年,将发射30多颗卫星,向全球提供服务。中国的北斗,世界的北斗。如今,北斗系统走进了全球组网的新时代,打开了应用与产业发展的新局面,开始书写国际合作的新篇章。
本专题得到杨元喜研究员(陕西省西安测绘研究所)、李子申副研究员(中国科学院光电研究院/中国科学院卫星导航总体部)、武子谦博士(中国科学院上海天文台)的大力支持。
·热点数据排行·
截至2017年10月20日,中国知网(CNKI)和Web of Science(WoS)的数据报告显示,以“北斗卫星导航系统(BeiDou Navigation Satellite System, BDS)”为词条可以检索到的期刊文献分别为2946条与322条,本专题将相关数据按照:研究机构发文数、作者发文数、期刊发文数、被引用频次进行排行,结果如下。

研究机构发文数量排名(CNKI)
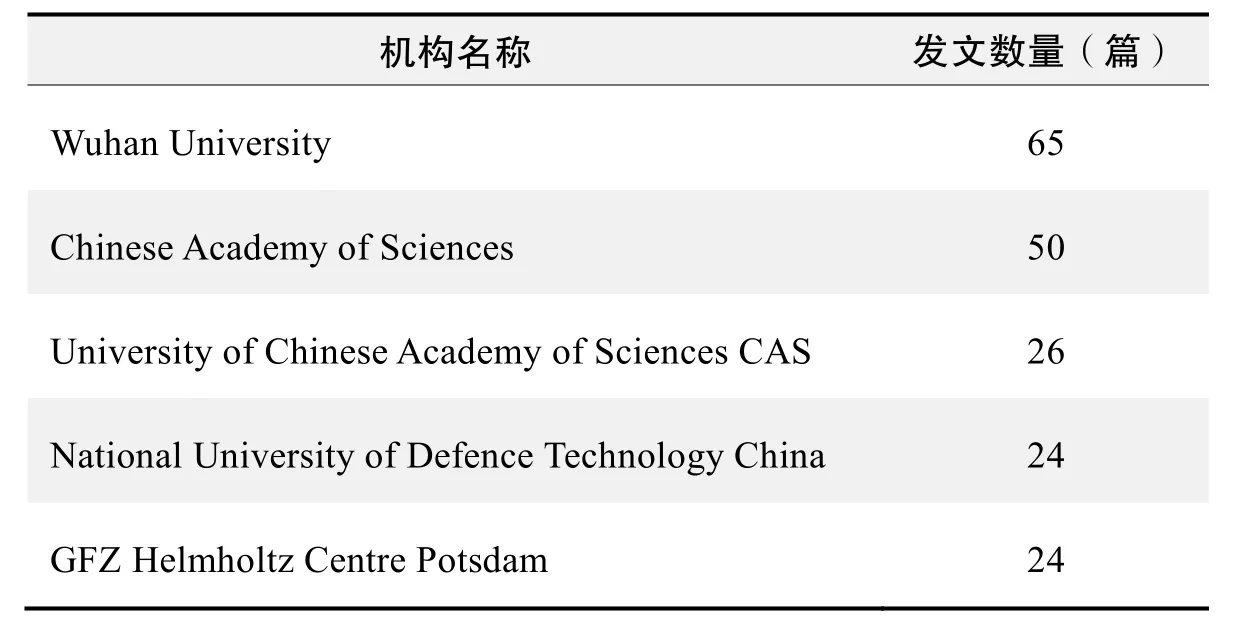
研究机构发文数量排名(WoS)
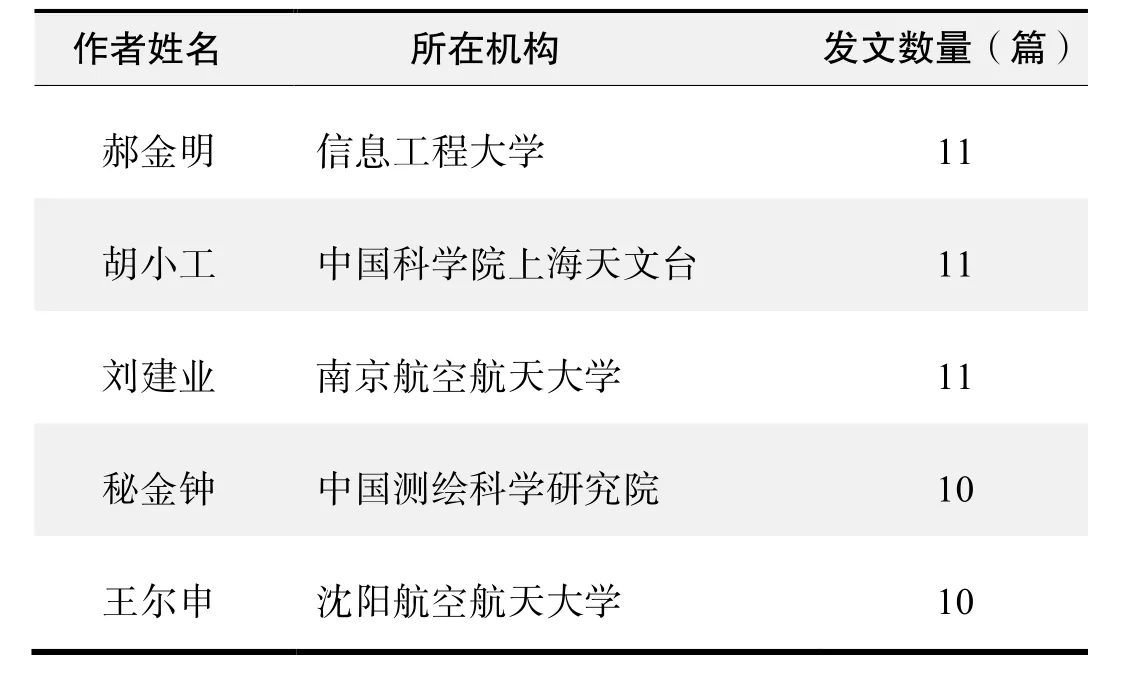
作者发文数量排名(CNKI)

作者发文数量排名(WoS)
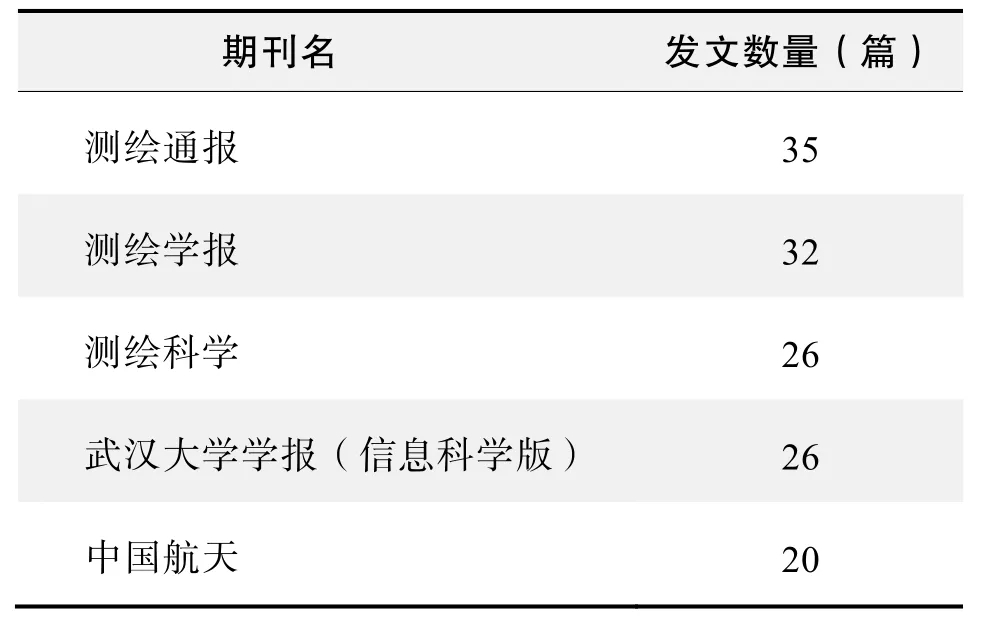
期刊发文数量排名(CNKI)

期刊发文数量排名(WoS)
根据中国知网(CNKI)数据报告,以“北斗卫星导航系统(BeiDou Navigation Satellite System,BDS)”为词条可以检索到的高被引论文排行结果如下。

国内数据库高被引论文排行
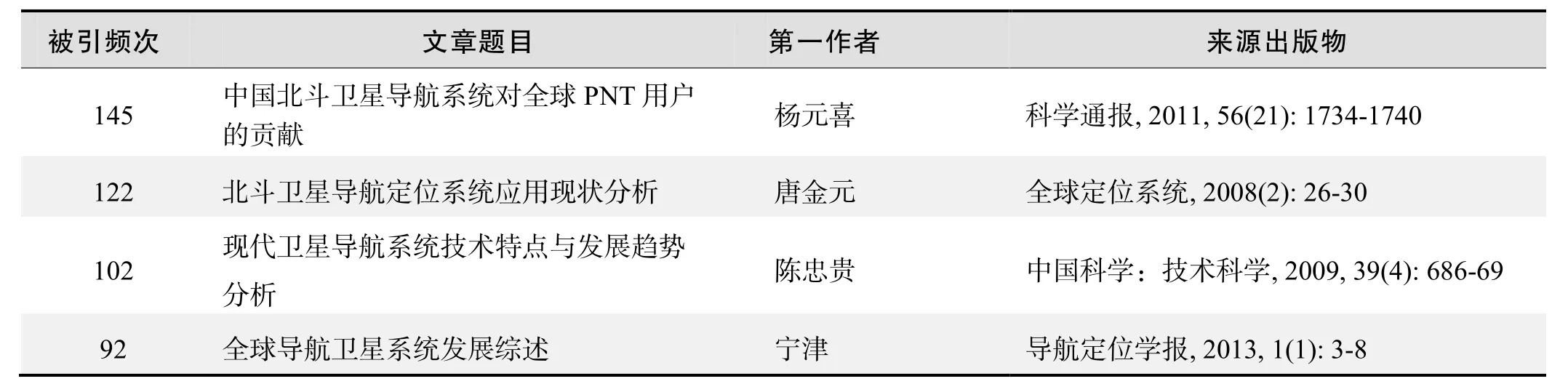
国内数据库高被引论文排行(续表)
根据Web of Science统计数据,以“北斗卫星导航系统(BeiDou Navigation Satellite System, BDS)”为词条为词条可以检索到的高被引论文排行结果如下。
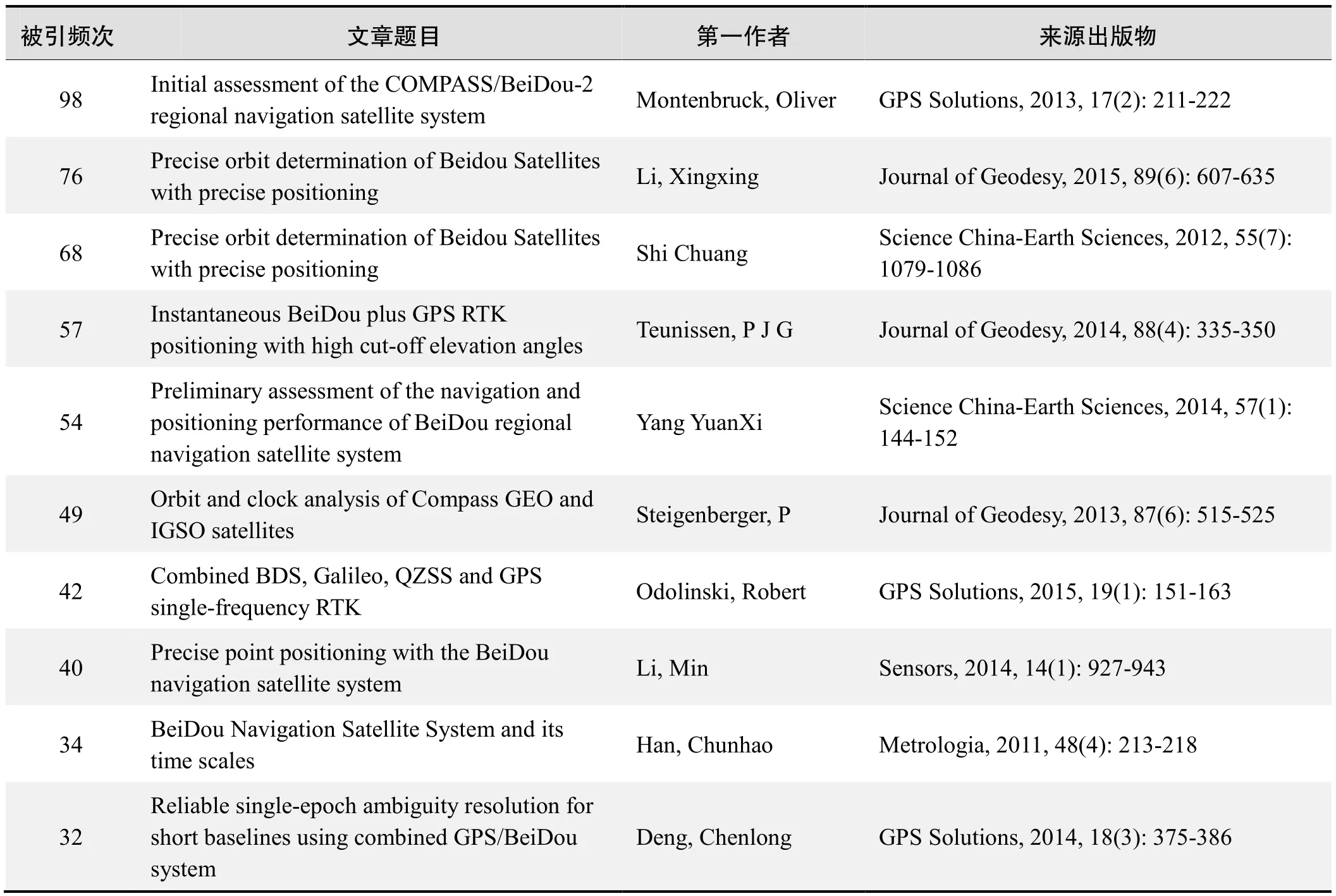
国外数据库高被引论文排行
·经典文献推荐·
基于Web of Science检索结果,利用Histcite软件选取LCS(Local Citation Score,本地引用次数)TOP50文献作为节点进行分析,得到本领域推荐的经典文献如下。
来源出版物:Advances in Space Research, 2007, 39(10):1552-1558
The performance comparison between GPS and BeiDou-2/compass: A perspective from Asia
Chen, He-Chin; Huang, Yu-Sheng;CChiang, Kai-Wei; et al.
Abstract:The next decade promises drastic improvements to global navigation satellite systems. The USA is modernizing GPS, Russia is refreshing GLONASS, Europe is moving ahead with its own Galileo system, and The People's Republic of China is expanding its BeiDou-1 system from a regional navigation system to a full constellation global navigation satellite system known as BeiDou-2/Compass, which consists of thirty five satellites including geostationary satellites, MEO satellites and geosynchronous satellites in the coming year. Extra satellites will make possible improved performance for all applications, and especially where satellite signals can be obscured, such as in urban canyons, under tree canopies or in open-pit mines. The benefits of the expected extra satellites and their signals can be evaluated in terms of availability, accuracy, continuity, and reliability issues. The advent of a hybrid GNSS constellation has drawn a lot of attention to study compatibility and interoperability. A number of performance analyses have been conducted on a global scale with respect to availability, reliability,accuracy and integrity in different simulated scenarios(such as open sky and urban canyons) for each system individually as well as for combined systems with all the possible combinations. Since the BeiDou-2/Compass has gained more attention from GNSS communities, the main objective of this paper is to study the performance of BeiDou-2/Compass comparied to GPS in the greater Asia region; and also to explore whether the combination of BeiDou-2/Compass with GPS would yield performance improvements in this region. The performance analysis can be analyzed by either the signal or the geometrical conditions. However, the scope of this study is limited to investigating the impact of current and future GNSS based on geometrical conditions. Therefore, the satellite visibility and DOP (Dilution of Precision) values of each system or possible combinations between them are used as the major indices for performance evaluation with the emphasis on the addition of Compass. In addition, those indices are further analyzed in terms of their spatial and temporal distributions with the emphasis on the greater Asia region.Moreover, the spatial performance analyses are conducted on both global and regional scales to provide more insightful comparisons to illustrate the importance of future Compass for users in the greater Asia region.
Keywords:global navigation satellite systems; compass;dilution of precision; GPS
来源出版物:Journal of the Chinese Institute of Engineers,2009, 32(5): 679-689
BeiDou navigation satellite system and its time scales
Han, Chunhao; Yang, Yuanxi; Cai, Zhiwu; et al.
Abstract:The development and current status of BeiDou Navigation Satellite System are briefly introduced. The definition and realization of the system time scales are described in detail. The BeiDou system time (BDT) is an internal and continuous time scale without leap seconds. It is maintained by the time and frequency system of the master station. The frequency accuracy of BDT is superior to 2×10-14and its stability is better than 6×10-15/30 days.The satellite synchronization is realized by a two-way time transfer between the uplink stations and the satellite. The measurement uncertainty of satellite clock offsets is less than 2 ns. The BeiDou System has three modes of time services: radio determination satellite service (RDSS)one-way, RDSS two-way and radio navigation satellite service (RNSS) one-way. The uncertainty of the one-way time service is designed to be less than 50 ns, and that of the two-way time service is less than 10 ns. Finally, some coordinate tactics of UTC from the viewpoint of global navigation satellite systems (GNSS) are discussed. It would be helpful to stop the leap second, from our viewpoint, but to keep the UTC name, the continuity and the coordinate function unchanged.
来源出版物:Metrologia, 2011, 48(4): 213-218
Initial assessment of the COMPASS/BeiDou-2 regional navigation satellite system
Montenbruck, Oliver; Hauschild, Andre;Steigenberger, Peter; et al.
Abstract:An initial characterization and performance assessment of the COMPASS/BeiDou-2 regional navigation system is presented. Code and carrier phase measurements on up to three frequencies have been collected in March 2012 with a small regional network of monitoring stations. The signal and measurement quality are analyzed and compared with the Japanese Quasi Zenith Satellite System. A high level of stability is demonstrated for the inter-frequency carrier phase biases,which will facilitate the application of triple-frequency undifferenced ambiguity resolution techniques in future precise point positioning applications. The performance of the onboard Rubidium frequency standards is evaluated in comparison to ground-based hydrogen masers and shown to be well competitive with other GNSS satellite clocks. Precise orbit and clock solutions obtained in post-processing are used to study the presently achievable point positioning accuracy in COMPASS/BeiDou-2-only navigation. Finally, the benefit of triple-frequency measurements and extra-wide-lane ambiguity resolution is illustrated for relative positioning on a short baseline.
来源出版物:GPS Solutions, 2013, 17(2): 211-222
BeiDou inter-satellite-type bias evaluation and calibration for mixed receiver attitude determination
Nadarajah, Nandakumaran; Teunissen, Peter J. G;Raziq, Noor; et al.
Abstract:The Chinese BeiDou system (BDS), having different types of satellites, is an important addition to the ever growing system of Global Navigation Satellite Systems (GNSS). It consists of Geostationary Earth Orbit(GEO) satellites, Inclined Geosynchronous Satellite Orbit(IGSO) satellites and Medium Earth Orbit (MEO) satellites.This paper investigates the receiver-dependent bias between these satellite types, for which we coined the name inter-satellite-type bias (ISTB), and its impact on mixed receiver attitude determination. Assuming different receiver types may have different delays/biases for different satellite types, we model the differential ISTBs among three BeiDou satellite types and investigate their existence and their impact on mixed receiver attitude determination. Our analyses using the real data sets from Curtin's GNSS array consisting of different types of BeiDou enabled receivers and series of zero-baseline experiments with BeiDou-enabled receivers reveal the existence of non-zero ISTBs between different BeiDou satellite types. We then analyse the impact of these biases on BeiDou-only attitude determination using the constrained (C-)LAMBDA method, which exploits the knowledge of baseline length. Results demonstrate that these biases could seriously affect the integer ambiguity resolution for attitude determination using mixed receiver types and that a priori correction of these biases will dramatically improve the success rate.
Keywords:Global Navigation Satellite Systems (GNSS);BeiDou system (BDS); inter-satellite-type biases; attitude determination; multivariate constrained integer leastsquaresMC-LAMBDA); carrier phase ambiguity resolution
来源出版物:Sensors, 2013, 13(7): 9435-9463
·推荐综述·
北斗卫星导航系统安全和完好性监测现状与发展
庄钊文,王飞雪,欧钢,孙广富,李峥嵘
卫星导航系统是以人造地球卫星为导航台的星基无线电导航系统,系统的定位精度高,服务范围广,可提供全天时、全天候、连续的导航定位服务,已成为时空定位领域国家重大基础设施,是大国地位和战略利益重要支撑,也是国家经济社会发展和国防与军队信息化建设的重要基石。围绕卫星导航技术发展和系统建设,国际竞争日益激烈。美国和俄罗斯正紧锣密鼓开展全球定位系统(GPS)、格洛纳斯系统(GLONASS)现代化升级,中国和欧盟正加紧北斗卫星导航系统(BDS)、伽利略系统(Galileo)建设,印度和日本正在建设的印度无线电导航卫星系统(IRNSS)、准天顶系统(QZSS),其中GPS,GLONASS,BDS,Galileo是全球导航卫星系统(GNSS),而IRNSS,QZSS是区域导航卫星系统。
目前,四大GNSS系统处于“一超+三强”的基本格局。美国GPS是投人运行最早、一直稳定工作、技术发展最完善、用户数量最多的GNSS系统;且GPS不断进行创新和改进,先后经历了区域系统、全球系统阶段,正在进行现代化改造。俄罗斯GLONASS建设历程与GPS类似,几乎与GPS同时建成并投人使用,也正在进行现代化改造;但受接人方式、卫星寿命、用户设备等因素影响,用户数量很少,难以对GPS领先地位产生冲击。欧洲从20世纪90年代开始,先后启动欧洲地球同步导航重叠服务(EGNOS)广域增强系统和GALILEO全球系统建设,预计在2020年完成建设。中国BDS系统起步于20世纪90年代,先后完成了北斗一号、北斗二号和北斗全球系统试验星工程建设,是第3个拥有独立自主卫星导航系统的国家;BDS工程建设已全面展开,2018年将向“一带一路”沿线及周边国家用户提供基本服务,2020年将向全球用户提供开放服务。
从技术代系看,建设中的BDS与Galileo系统和现代化后的GPS与GLONASS系统处于同一代系,系统性能也相当。与当前GPS和GLONASS系统相比,到2020年,四大GNSS系统将全面提升系统安全性和完好性,具体包括:1)显著提升系统安全与导航战能力;2)利用增加频率、采用二进制偏移载波(BOC)调制等手段实现军民信号分离;3)将增加星间链路、提升原子钟性能和系统测量精度,提高定轨精度和卫星自主运行能力;4)将增加系统完好性监测功能;5)通过采用GNSS系统共用频率、增加无数据调制导频信号等手段,可支持多GNSS信号兼容接收和弱信号接收。
近年来,瞄准GNSS现代化和卫星导航长远发展目标,中国在北斗全球系统建设、导航装备与应用产业化等方面取得了重大业绩,尤其在系统安全与抗干扰、系统完好性监测等方面更是取得了长足进步,为提升系统服务性能和提高国际竞争力打下了良好的基础。
1 系统安全与完好性内涵
1.1 卫星导航系统安全
在GPS现代化中,导航战包括保护、阻止和保持3个方面的内容。保护就是提升己方系统的抗干扰能力和复杂环境下的生存能力;阻止包含对敌方导航系统实施干扰和阻止敌方使用己方系统进行导航定位,其实质就是提升系统对抗与反利用能力;保持就是保持战区外的民用导航不受战争的影响。除对敌实施干扰外,其他方面均与系统安全相关,具体包括卫星导航系统抗干扰、反利用和卫星自主运行等。
李峥嵘等人从保证星地、星间、站间链路畅通的角度出发,提出了从信号传输体制、卫星系统、地面运控系统和地面应用系统构建抗干扰体系的构想。其中,信号传输体制抗干扰通过优化多路接人方式、伪随机码生成、信号调制方式、导航电文编排等提升体制级抗干扰能力;卫星系统抗干扰通过采用卫星防辐照、抗干扰上行接收、增强卫星发射功率等措施提升卫星抗干扰能力;地面运控系统抗干扰通过增强上行信号发射功率、提高运控终端抗干扰与防摧毁、优化注人策略与地面运控站选址等措施提升地面运控抗干扰能力;地面应用系统抗干扰通过采用干扰抑制、长码直捕、弱信号接收、辅助导航、组合导航等措施提升用户机抗干扰能力。
由于军用信号采用长周期高速伪码,抗破译能力强,敌方最可能是使用己方系统民用信号进行定位,阻止敌方接收己方民用信号是反利用的重点内容,主要采用关闭己方部分卫星信号或对己方卫星信号实施干扰两种方法。分析了关闭部分卫星信号阻止目标点使用定位服务的可行性,分析表明关闭部分信号会导致全球49%以上地区的用户无法使用普通民用定位服务。因此,针对GNSS民用信号最可能的反利用方式是在信号上叠加干扰,而不是通常所认为的直接关闭部分民用信号。
当前,各大GNSS系统均需要依赖运行控制段,通过运行控制系统周期性地向卫星注人导航数据保证系统连续稳定运行。一旦运行控制段发生故障,将严重影响系统的服务性能。同时,周期性注人也为对卫星实施电磁干扰提供了可能。为减小上行注人频度,可采用星间链路或X射频脉冲星自主导航等技术降低卫星对地面的依赖,实现一定时间内的自主运行,从而提升整个系统的生存能力。
1.2 卫星导航系统完好性监测
完好性是指导航系统发生故障或误差超出了允许的范围时,自动向用户提供及时告警的能力。完好性直接关系到卫星导航定位服务的安全可靠性,对航空、航海等对安全系数要求很高的应用领域尤为重要;服务的完好性得不到保障,将会导致用户重大损失甚至出现灾难。
影响系统完好性的因素既广又多,通常由卫星导航系统各类故障所引起,包括地面运控系统故障、卫星系统故障、传播环境异常、用户接收处理故障等。应对各类故障有不同的完好性监测方法,这些单一的方法均存在不同的优缺点,需要通过建立多层次、全方位的完好性监测体系,实时监测各类故障并传送给用户;监测体系的建立凸显了不同监测方法之间的互补性,较好地保证不了同用户对导航服务的完好性需求。
2 关键技术突破与技术进展
2.1 BDS信号传输体制设计
北斗全球系统无线电导航卫星业务(RNSS)采用与GPS相同的直接序列扩频一码分多址(DS-CDMA)体制,扩频码采用伪随机码序列,分为长码和短码两种。长码又称精密测距码(P码)或军码(M码),码周期超过1个月甚至更长,难以被破译,安全性高。短码又称民码或粗捕码(C码或C/A码),其周期1 ms。因短码周期1 ms,其频谱是间隔为1 kHz的线状谱或梳状谱,易被破译,且信号频带内谱线强度波动可达10~15 dB,选择适当的干扰频率,较小功率的单频干扰能造成较大的载噪比损耗。GPS C码接收机与P码接收机单频干扰损耗对比情况,分析时两种接收机均未采用抗干扰措施,干信比是干扰强度与信号强度之比,信号强度为133 dBm。P码接收机的抗干扰性能明显优于C码接收机。
与现代化之前的GPS类似,北斗二号系统也采用二相移相键控(BPSK)或正交移相键控(QPSK)调制方式,C码信号和P码信号分别调制到QPSK的I通道和Q通道上,两者中心频率相同。随着GNSS现代化概念的深人,通过采用点波束功率增强技术,可使局地军用信号较民用信号强几百倍(或20多dB),信号频带内军用信号强度已与噪声强度相当甚至更强,可引起几dB的民用信号损耗。现代化GPS和欧洲Galileo均采用BOC调制方式,使军用信号频谱分开到中心频率两边,从而使军民信号分离和避免相互干扰。针对BOC调制及其复用技术,中国已开发了双正交移相键控和类双正交移相键控调制方法并申请了专利,可支撑北斗全球系统调制方式的确定。
导航电文是由导航卫星播发给用户的描述导航卫星运行状态参数的电文,包括系统时间、星历、历书、卫星时钟的修正参数、导航卫星健康状况和电离层延时模型参数等内容,并以一定格式和信息速率进行传送。分析表明,信息速率越低,电文解调时所需的载噪比越小,系统和抗干扰余量越大;但所需传送的电文信息总量是确定的,需要尽量对电文进行高效编排。在对比分析GPS NAV与CNAV电文、GLONASS电文、Galileo F/NAV与I/NAV的基础上,提出了一种基于页面流的电文编排方法,优化电文后的首次定位时间和首次定位时间最短的Galileo I/NAV电文相当,而优化电文后的数据资源利用率与Galileo F/NAV的相当。另外,良好的纠错编码方式也可获取较大的译码增益,可提高电文解调灵敏度和系统与抗干扰余量。传统信道编码有汉明码、卷积码、BCH码等,随着以低密度奇偶校验(LDPC)码和Turbo码为代表的高增益信道编码的发展,可通过提高编码增益获得更高的电文解调灵敏度;而LDPC码具有更好的错误平层性能和不受专利保护,可替代传统的信道编码方法。信息分组长度与编码效率约束的高增益、低编译码实现复杂度的LDPC码,可满足对抗干扰和弱信号接收的需求。此外,为了提高导航接收机弱信号接收能力,现代化GPS LS频点、Galileo ESa与ESb无电文调制的导频通道,通过改进捕获和跟踪算法,可将接收机灵敏度提高20 dB以上。
上述研究为提升北斗全球系统抗干扰能力和确定信号传输体制提供了依据。
2.2 BDS频率规划与协调
有业界人士多次提到:“卫星导航的竞争是星座与信号的竞争,是技术体制的竞争。”由于国际电联(ITU)分配给卫星导航RNSS业务的频谱资源非常有限,频率资源是卫星导航系统最重要的资源之一。2000年世界无线电大会(WRC-2000)上新增1260~1300 MHz为RNSS业务频率,使得RNSS业务下行信号达到4个L频段和1个C频段;由于1215~1260 MHz传统导航频段已被GPS和GLONASS系统先期使用,新增的1260~1300 MHz频段成为中国BDS和欧洲Galileo竞争的焦点。自北斗系统第一颗飞行试验星发射以来,中欧历经4次频率磋商会谈,于2015年1月16日达成频率共用、在国际电联框架下完成卫星导航频率协调的意见,结束了长达8年的频率协调工作。统计表明,中国L频段可使用频率近70 MHz,比GPS和Galileo分别少12 MHz和2 MHz。但是在2012年世界无线电大会(WRC-2012)上,将无线电测定卫星业务(RDSS)的下行频段(即S频段的2483.5~2500 MHz)作为RNSS主要业务进行全球划分,而中国已先期使用该频段,具有优先使用权限。至此,中国BDS RNSS下行频率总计约86 MHz,与GPS,Galileo相当,在频率协调方面取得较大的成果。
2.3 BDS抗干扰体系建设
中国北斗系统曾遭受各类干扰的威胁,全国多地在S频段、C频段、上行L频段转C人站频段、下行L频段等频点上出现了干扰信号。另外,北斗二号首颗卫星发射后不久,就曾遭受强烈干扰而信号中断,严重影响了星地测量与数据传输。面临如此复杂的信号环境,国防科大卫星导航工程中心结合系统建设和应用,突破了卫星抗干扰、地面运控抗干扰和用户机抗干扰等一系列关键技术。
在卫星抗干扰方面,针对北斗二号卫星遭受的强干扰,经努力攻关,于2008年初突破星上抗干扰的一系列关键技术,并成功研制出具有强抗干扰能力的卫星载荷,极大地保证了系统建设进度。截至2016年8月,先后有17颗北斗卫星加装了该载荷,为提升复杂电磁环境下的系统生存能力提供了保障。在2015年3月开始发射的5颗北斗全球系统卫星中,又进一步提升了载荷的高精度、抗干扰、抗辐照等性能,干扰抑制能力进一步提升了100倍。至此,北斗二号和北斗全球系统22颗在轨工作卫星全部加装的抗干扰载荷设备,卫星抗干扰技术达到国际领先水平。另外,针对我国北斗系统的星座特点,详细研究了卫星导航系统功率增强策略及其对区域导航定位性能的影响,可为北斗全球系统功率增强方案提供依据。
在地面运控抗干扰方面,针对下行L频段干扰,结合北斗二号监测接收机的研制,成功开发了时延约束的干扰检测与抑制技术,目前已广泛应用到全国监测站中,并即将在中国领海和海外相关监测站中使用,全面支撑了北斗二号系统稳定运行和地面站选址。针对C频段干扰,结合北斗二号RDSS业务系统设备研制,成功开发了短突发、随机人站信号干扰抑制技术,解决了临近共轨卫星干扰的问题。在北斗全球系统建设中,针对运控系统各类地面站全面开展了抗干扰论证与关键技术研究,可满足复杂电磁环境下星地高精度测量需要和提升运控系统生存能力。
在用户机抗干扰方面,先后开发了长码直捕技术,时域自适应处理、变换域处理、自适应阵列天线、卫星/惯性组合导航等抗干扰技术,并结合高动态捕获与跟踪技术,成功研制了抗干扰用户终端、长码生成与长码直捕模块(类似于GPS防欺骗模块)和各类抗干扰天线,并形成了模块、天线、专用芯片等系列抗干扰产品,进一步装备应用将全面展开。
2.4 BDS星间链路
与GPS星间链路主要用于卫星自主运行相比,北斗全球系统星间链路除用于卫星自主运行外,还要用于支持全球区域内星座定轨与时间同步,着重解决海外建设监测站的不足,对链路测距和通信性能提出了更高的要求。结合北斗全球系统星间链路总体设计、星间收发信机研制,我们突破星间链路快速建立、星间精密测距、星间数据通信、抗干扰与抗辐照等关键技术。2015年7月,中国利用一箭双星技术发射了两颗中圆轨道北斗卫星,该卫星均装备了星间收发载荷,随后于2015年8月利用两颗卫星首次建立星间链路。另从第七届中国卫星导航学术年会获悉,到2016年5月,历时1年多的星间链路在轨测试圆满完成,将为北斗全球系统搭建太空桥梁。相关技术的突破,标志中国成为继美国之后第2个拥有星间链路技术的国家,也将进一步提升北斗全球系统的导航战和完好性性能。
2.5 BDS完好性监测
中国完好性监测工作启动较早,在北斗二号系统建设之时,面临的技术约束主要是难以在国外布设监测站,卫星可观测弧段小,且卫星星钟精度也不如国外系统。为保证系统精度和完好性,在国土范围了建设了20多个各类监测站。由于北斗二号监测接收机具有测距精度高、监测频带范围广、全频带实时电磁环境监测、干扰与多径抑制等功能,极大地保证了系统精度和完好性等性能指标。随着北斗二号系统应用和全球系统建设的深人,又逐步在中国领海和海外建立了若干监测站,大大扩展了监测的弧段范围,基于监测接收机的完好性监测性能进一步提升。
在开展地面完好性监测同时,北斗全球系统建设中专门安排了卫星自主完好性监测(SAIM)任务,主要目的是保证卫星自身能够完成下行导航信号的自主完好性监测,并具备对关键导航载荷工况的完好性监测告警能力。目前,在部分北斗全球系统卫星中加装了SAIM载荷设备,并完成相关在轨测试验证。另外,北斗全球系统星间链路也已完成在轨测试,可利用星间链路完成卫星自主完好性监测,进一步提升监测性能。
因此,中国已初步建成了星地一体的北斗全球系统完好性监测系统,取得了较为突出的成绩。
3 展望与讨论
从卫星导航系统发展看,今后10~15年卫星导航技术发展的主要趋势包括:1)进一步提升系统性能;2)大力加强导航战能力;3)在国家PNT体系结构的框架下发展未来卫星导航系统。
在进一步提升系统性能方面,主要包括提高系统的精度、完好性和弱信号接收能力等,有待突破的关键技术包含星间链路、高精度星载原子钟、BOC类调制与军民信号分离、增加民用三频与军用双频、系统兼容与互操作、增加导频通道、增强完好性监测等,以满足实时高精度、可靠航空应用和复杂环境下信号接收等需要。
在大力加强导航战能力方面,主要是实现保护、阻止与保持3大目标,技术上的指导思想主要是将导航战上升到国家安全政策层面、军用频谱独占与共用相结合,加强卫星抗干扰与自主运行能力,提升地面运控系统抗干扰能力,强化军用信号的安全性和易用性,高度重视民用基础设施的导航定位授时安全性,全面提升用户终端抗干扰能力,及提升军用信号区域增强能力等。
在国家综合定位导航与授时(PNT)体系建设方面,当前与今后很长一段时间内,作战武器系统和平台越来越信赖卫星导航系统提供的高精度位置和时间信息;由于卫星导航存在易受干扰、在城区、茂密丛林、水下、地下等无法正常接收等问题,难以完全满足现代化战争需要。因此,国家PNT体系必须以北斗系统为主体,融合陆基无线电、惯性、微器件(含芯片级原子钟、微惯导等)、视觉、数据库匹配(含地磁、重力场、地形等)等全源导航定位手段,为全域内的军民载体提供定位导航与授时服务,这将成为未来导航定位技术发展的必然趋势。
4 结论
自1994年启动北斗一号系统建设以来,中国卫星导航系统发展经历了北斗一号试验系统、北斗二号区域系统和北斗全球系统试验星工程三个阶段,与现代化GPS处于同一代系的北斗全球系统即将于2020年建成并向全球开放服务,工程建设将在系统安全性和完好性方面实现重大跨跃。
当前,在系统安全方面,已完成北斗系统抗干扰信号传输体制设计与实现,初步建成了包含卫星抗干扰、地面运控抗干扰、地面应用抗干扰在内天地一体化的北斗抗干扰体系建设,取得了以长码设计与直捕、系统反利用、卫星抗干扰、中欧频率协调等一系列成果,极大提升了在复杂电磁环境下的系统生存能力。
在系统完好性方面,已初步建成了包含卫星自主完好性监测(SAIM)、导航增强与全球连续监测评估、接收机自主完好性监测(RAIM)在内的星地一体化完好性监测系统,取得了星间链路、SAIM载荷、监测接收机等一系列成果,提升了卫星自主运行和完好性监测能力。
总体而言,中国北斗全球系统发展与世界卫星导航主要发展趋势一致,已取得了令世人瞩目的突破;预计2020年系统建成之时,包含安全性、完好性在内的系统性能将达到国际先进水平,并将在国际合作和全球GNSS竞争方面掌握技术主导权与话语权。
·高被引论文摘要·
被引频次:691
北斗卫星导航系统的进展、贡献与挑战
杨元喜
卫星导航发展已进入百花齐放、群星争艳的时代。主要评述我国北斗卫星导航系统的发展、应用、贡献及面临的挑战。介绍北斗卫星导航系统的建设原则和建设步骤;介绍我国北斗卫星导航系统在兼容与互操作框架下在频率、坐标系统、时间系统方面的兼容与互操作实现概况;描述北斗导航系统在冗余度概念下的主要贡献;简要说明北斗导航验证系统的重要应用和面临的主要挑战。
北斗卫星导航系统;进展;挑战
来源出版物:测绘学报, 2010, 39(1): 1-6
被引频次:322
北斗卫星导航系统的发展与思考
谭述森
摘要:从世界卫星导航发展史出发,评述了中国北斗卫星导航系统从中获得的有益启示,阐明了中国北斗卫星导航系统小幅起步的研制建设思路。在分析国际卫星导航系统发展趋势的基础上,论述了北斗全球系统的必要性、可行性和战略价值,提出了北斗GNSS的发展思路。
关键词:卫星导航;GNSS;北斗卫星导航系统
来源出版物:宇航学报, 2008, 29(2): 391-396
被引频次:180
北斗区域卫星导航系统基本导航定位性能初步评估
杨元喜,李金龙,王爱兵,等
摘要:北斗区域卫星导航系统(也称北斗2代1期)于2012年12月27日正式开始运行,系统由14颗卫星组成,包括5颗地球静止轨道卫星、5颗倾斜地球同步轨道卫星和4颗中圆地球轨道卫星。本文初步评估了北斗区域卫星导航系统建成运行后的基本导航定位性能,包括卫星可见性、位置精度衰减因子、伪距和载波相位观测量精度、单点定位和差分定位精度以及模糊度解算性能等。通过实验分析可知:北斗伪距和载波相位测量精度已与GPS处在同一水平,伪距测量精度约为33 cm,载波测量精度约为2 mm;北斗伪距单点定位水平精度优于6 m,高程精度优于10 m,已满足设计要求;北斗区域卫星导航系统已具备独立的双频RTK定位能力,其单历元双频模糊度解算成功率几乎与GPS相当;北斗载波相位差分定位精度与GPS相位差分定位处在同一水平,超短基线情况下,定位精度优于1 cm,而在短基线情况下优于3 cm;北斗与GPS组合定位时,模糊度解算的固定率和可靠性均显著提高;在短基线情况下,北斗/GPS组合载波相位差分动态定位精度相对于单一的GPS定位的改善可达20%以上;北斗单频伪距差分定位精度优于2.5 m,与GPS相比仍存在较大差距,其主要原因可能为北斗GEO卫星伪距多路径误差较大。
关键词:北斗卫星导航系统;服务区域;位置精度衰减因子;伪距和载波相位测量精度;单点定位;伪距差分定位;模糊度解算;载波相位差分定位
来源出版物:中国科学:地球科学, 2014, 44(1): 72-81
引频次:169
北斗卫星导航系统的精密定轨与定位研究
施闯,赵齐乐,李敏,等
摘要:我国北斗卫星导航系统已建成由8颗导航卫星组成的区域导航星座,初步形成了亚太地区的导航定位服务能力。本文采用“北斗卫星观测实验网”实测数据和我国自主研制的精密数据处理软件PANDA,实现了北斗导航卫星系统的高精度定轨,静态精密单点定位、相对定位,以及动态伪距差分、相位差分定位。研究成果显示:北斗卫星精密定轨径向精度优于10 cm,静态精密单点定位精度达到厘米级、基线相对定位达到毫米级;动态伪距差分定位精度达到2~4 m、RTK定位精度达到5~10 cm,接近目前GPS所能实现的精密定位水平。本研究验证了北斗卫星导航系统在地面参考站网的支持下,具备广域米级至分米级的精密定位,以及区域厘米级精密定位服务能力。可为北斗系统在我国精密导航定位领域的推广应用和科学研究提供技术积累和重要参考。
关键词:北斗卫星导航系统;PANDA;精密定轨;北斗差分
来源出版物:中国科学:地球科学, 2012, 42(6): 854-861
引频次:169
北斗卫星导航系统发展综述
吕伟,朱建军
摘要:在系统回顾“北斗一号”卫星导航系统工作原理、性能指标和存在不足的基础上,结合国内外建设卫星导航系统的经验教训,从健康高效运营角度出发,对“北斗二号”卫星导航系统的建设提出了几点建议。
关键词:北斗一号;北斗二号;卫星导航系统;原理;建议
来源出版物:地矿测绘, 2007, 23(3): 29-32
被引频次:149
基于时空系统统一的北斗与GPS融合定位
高星伟,过静珺,程鹏飞,等
摘要:我国的北斗卫星导航定位系统目前已经发射9颗北斗卫星,北斗区域卫星导航系统的基本系统已建设完成,正开展星地联调和测试评估工作,已经具备我国范围内的初步三维定位导航能力。本文研究北斗和GPS的时间系统/坐标系统的统一、卫星广播星历与卫星位置计算,以及二者的高精度定位算法,并实现了北斗和GPS载波相位的数据融合和高精度联合定位,最后通过2011-09-29的实测数据和处理结果证明了本文方法的正确性,同时为北斗二号系统的调试提供了相关试验与结果。
关键词:北斗卫星导航系统;全球定位系统;融合定位
来源出版物:测绘学报, 2012, 41(5): 743-748, 755
被引频次:145
中国北斗卫星导航系统对全球PNT用户的贡献
杨元喜,李金龙,徐君毅,等
摘要:北斗卫星导航系统作为全球四大卫星导航系统之一,不仅增加中国及周边地区定位、导航和授时(PNT=Positioning, Navigation and Timing)用户的卫星可见性和可用性,而且也将提高全球用户的PNT精度。在全球导航卫星系统(GNSS)兼容与互操作条件下,分析全球导航定位定时用户的卫星可见性和精度衰减因子改善情况;利用仿真数据分析北斗卫星导航系统对全球用户的贡献,侧重分析北斗卫星导航系统与GPS,GLONASS和Galileo多卫星导航系统组合模式下用户获得的收益。
关键词:北斗卫星导航系统;定位;导航;授时;精度衰减因子;卫星可见性
来源出版物:科学通报, 2011, 56(21): 1734-1740
被引频次:122
北斗卫星导航定位系统应用现状分析
唐金元,于潞,王思臣
摘要:北斗卫星导航定位系统是国家信息基础设施之一,是实现社会信息化的重要工具。北斗系统的应用涉及到国家各个领域。分析了北斗卫星导航定位系统的应用特点和应用现状,指出了制约该系统应用发展的主要因素,并对如何推进该系统在民用领域的产业化发展提出了一些具体建议。
关键词:北斗卫星;导航定位;应用;现状;发展;建议
来源出版物:全球定位系统, 2008(2): 26-30
被引频次:102
现代卫星导航系统技术特点与发展趋势分析
陈忠贵,帅平,曲广吉
摘要:简要介绍了美国GPS系统、俄罗斯GLONASS系统、欧洲Galileo系统、中国北斗卫星导航系统、以及日本和印度的区域卫星导航系统的发展状况。重点研究了GPS系统星座维持、有效载荷、自主导航、信号调制和地面站改造等最新技术特征,以及GPSⅢ系统技术及研究进展,分析论证了卫星导航系统技术的发展趋势,为我国卫星导航系统建设规划提供参考。
关键词:卫星导航系统;星座维持;自主导航;星间链路;导航信号调制
来源出版物:中国科学:技术科学, 2009, 39(4): 686-69
被引频次:92
全球导航卫星系统发展综述
宁津,姚宜斌,张小红
摘要:全球导航卫星系统及其应用领域在不断地扩大和深化。本文着重介绍了当前全球卫星导航系统及其应用技术的现状、发展趋势和应用前景。同时,对这几种导航系统进行综合对比,分析了全球背景下我国北斗卫星导航系统所面临的机遇和挑战,并对未来工作提出一些建议。
关键词:GNSS;GNSS定位技术;GNSS-R技术;GNSS掩星技术;组合导航技术;多频多系统联合定位技术
来源出版物:导航定位学报, 2013, 1(1): 3-8
被引频次:98
Initial assessment of the COMPASS/BeiDou-2 regional navigation satellite system
Montenbruck, Oliver; Hauschild, Andre;Steigenberger, Peter; et al.
Abstract:An initial characterization and performance assessment of the COMPASS/BeiDou-2 regional navigation system is presented. Code and carrier phase measurements on up to three frequencies have been collected in March 2012 with a small regional network of monitoring stations. The signal and measurement quality are analyzed and compared with the Japanese Quasi Zenith Satellite System. A high level of stability is demonstrated for the inter-frequency carrier phase biases,which will facilitate the application of triple-frequency undifferenced ambiguity resolution techniques in future precise point positioning applications. The performance of the onboard Rubidium frequency standards is evaluated in comparison to ground-based hydrogen masers and shown to be well competitive with other GNSS satellite clocks. Precise orbit and clock solutions obtained in post-processing are used to study the presently achievable point positioning accuracy in COMPASS/BeiDou-2-only navigation. Finally, the benefit of triple-frequency measurements and extra-wide-lane ambiguity resolution is illustrated for relative positioning on a short baseline.
来源出版物:GPS Solutions, 2013, 17(2): 211-222
被引频次:76
Precise orbit determination of Beidou Satellites with precise positioning
Li, Xingxing; Ge, Maorong; Dai, Xiaolei; et al.
Abstract:In this contribution, we present a GPS+GLONASS+BeiDou+Galileo four-system model to fully exploit the observations of all these four navigation satellite systems for real-time precise orbit determination, clock estimation and positioning. A rigorous multi-GNSS analysis is performed to achieve the best possible consistency by processing the observations from different GNSS together in one common parameter estimation procedure. Meanwhile, an efficient multi-GNSS real-time precise positioning service system is designed and demonstrated by using the multi-GNSS Experiment,BeiDou Experimental Tracking Network, and International GNSS Service networks including stations all over the world. The statistical analysis of the 6-h predicted orbits show that the radial and cross root mean square (RMS)values are smaller than 10 cm for BeiDou and Galileo, and smaller than 5 cm for both GLONASS and GPS satellites,respectively. The RMS values of the clock differences between real-time and batch-processed solutions for GPS satellites are about 0.10 ns, while the RMS values for BeiDou, Galileo and GLONASS are 0.13, 0.13 and 0.14 ns,respectively. The addition of the BeiDou, Galileo and GLONASS systems to the standard GPS-only processing,reduces the convergence time almost by 70 %, while the positioning accuracy is improved by about 25 %. Some outliers in the GPS-only solutions vanish when multi-GNSS observations are processed simultaneous. The availability and reliability of GPS precise positioning decrease dramatically as the elevation cutoff increases. However, the accuracy of multi-GNSS precise point positioning (PPP) is hardly decreased and few centimeter are still achievable in the horizontal components even with 40 elevation cutoff.At 30 and 40 elevation cutoffs, the availability rates of GPS-only solution drop significantly to only around 70 and 40 %, respectively. However, multi-GNSS PPP can provide precise position estimates continuously (availability rate is more than 99.5%) even up to 40 elevation cutoff (e.g., in urban canyons).
Keywords:Multi-GNSS constellation; Real-time precise point positioning; Precise orbit and clock determination;GPS, GLONASS, BeiDou and Galileo
来源出版物:Journal of Geodesy, 2015, 89(6): 607-635
被引频次:68
Precise orbit determination of Beidou Satellites with precise positioning
Shi Chuang; Zhao Qile; Li Min; et al.
Abstract:Chinese Beidou satellite navigation system constellation currently consists of eight Beidou satellites and can provide preliminary service of navigation and positioning in the Asia-Pacific Region. Based on the self-developed software Position And Navigation Data Analysis (PANDA) and Beidou Experimental Tracking Stations (BETS), which are built by Wuhan University, the study of Beidou precise orbit determination, static precise point positioning (PPP), and high precision relative positioning, and differential positioning are carried out comprehensively. Results show that the radial precision of the Beidou satellite orbit determination is better than 10 centimeters. The RMS of static PPP can reach several centimeters to even millimeters for baseline relative positioning. The precision of kinematic pseudo-range differential positioning and RTK mode positioning are 2-4 m and 5-10 cm respectively, which are close to the level of GPS precise positioning. Research in this paper verifies that, with support of ground reference station network,Beidou satellite navigation system can provide precise positioning from several decimeters to meters in the wide area and several centimeters in the regional area. These promising results would be helpful for the implementation and applications of Beidou satellite navigation system.
Keywords:compass/Beidou; PANDA; precise orbit determination (POD); Beidou difference
来源出版物:Science China-Earth Sciences, 2012, 55(7):1079-1086
被引频次:57
Instantaneous BeiDou plus GPS RTK positioning with high cut-off elevation angles
Teunissen, P J G; Odolinski, R; Odijk, D
Abstract:As the Chinese BeiDou Navigation Satellite System (BDS) has become operational in the Asia-Pacific region, it is of importance to better understand as well as demonstrate the capabilities that a combination of BeiDou with GPS brings to positioning. In this contribution, a formal and empirical analysis is given of the single-epoch RTK positioning capabilities of such a combined system.This will be done for the single- and dual-frequency case, and in comparison with the BDS and GPS-only performances. It will be shown that with the combined system, when more satellites are available, much larger than the customary cut-off elevations can be used. This is important, as such measurement set-up will significantly increase the GNSS applicability in constrained environments,such as e.g. in urban canyons or when low-elevation multipath is present.
Keywords:BeiDou (BDS); GPS; Multi-GNSS; integer ambiguity resolution; real time kinematic (RTK) positioning;cut-off elevation
来源出版物:Journal of Geodesy, 2014, 88(4): 335-350
被引频次:54
Preliminary assessment of the navigation and positioning performance of BeiDou regional navigation satellite system
Yang Yuanxi; Li Jinlong; Wang Aibing; et al.
Abstract:BeiDou regional navigation satellite system(BDS) also called BeiDou-2 has been in full operation since December 27, 2012. It consists of 14 satellites,including 5 satellites in Geostationary Orbit (GEO), 5 satellites in Inclined Geosynchronous Orbit (IGSO), and 4 satellites in Medium Earth Orbit (MEO). In this paper, its basic navigation and positioning performance are evaluated preliminarily by the real data collected in Beijing,including satellite visibility, Position Dilution of Precision(PDOP) value, the precision of code and carrier phase measurements, the accuracy of single point positioning and differential positioning and ambiguity resolution (AR)performance, which are also compared with those of GPS.It is shown that the precision of BDS code and carrier phase measurements are about 33 cm and 2 mm,respectively, which are comparable to those of GPS, and the accuracy of BDS single point positioning has satisfied the design requirement. The real-time kinematic positioning is also feasible by BDS alone in the opening condition, since its fixed rate and reliability of singleepoch dual-frequency AR is comparable to those of GPS.The accuracy of BDS carrier phase differential positioning is better than 1 cm for a very short baseline of 4.2 m and 3 cm for a short baseline of 8.2 km, which is on the same level with that of GPS. For the combined BDS and GPS,the fixed rate and reliability of single-epoch AR and the positioning accuracy are improved significantly. The accuracy of BDS/GPS carrier phase differential positioning is about 35% and 20% better than that of GPS for two short baseline tests in this study. The accuracy of BDS code differential positioning is better than 2.5 m. However it is worse than that of GPS, which may result from large code multipath errors of BDS GEO satellite measurements.
Keywords:BeiDou navigation satellite system; service area; dilution of precision; precision of code and carrier phase measurement; single point positioning; code differential positioning; ambiguity resolution; carrier phase differential positioning
来源出版物:Science China-Earth Sciences, 2014, 57(1):144-152
被引频次:49
Orbit and clock analysis of Compass GEO and IGSO satellites
Steigenberger, P; Hugentobler, U; Hauschild, A; et al.
Abstract:China is currently focussing on the establishment of its own global navigation satellite system called Compass or BeiDou. At present, the Compass constellation provides four usable satellites in geostationary Earth orbit (GEO) and five satellites in inclined geosynchronous orbit (IGSO). Based on a network of six Compass-capable receivers, orbit and clock parameters of these satellites were determined. The orbit consistency is on the 1-2 dm level for the IGSO satellites and on the several decimeter level for the GEO satellites. These values could be confirmed by an independent validation with satellite laser ranging. All Compass clocks show a similar performance but have a slightly lower stability compared to Galileo and the latest generation of GPS satellites. A Compass-only precise point positioning based on the products derived from the six-receiver network provides an accuracy of several centimeters compared to the GPS-only results.
Keywords:GNSS; BeiDou-2; satellite orbits; allan deviation
来源出版物:Journal of Geodesy, 2013, 87(6): 515-525
被引频次:42
Combined BDS, Galileo, QZSS and GPS single-frequency RTK
Odolinski, Robert; Teunissen, Peter J. G; Odijk, Dennis
Abstract:We will focus on single-frequency single-baseline real-time kinematic (RTK) combining four Code Division Multiple Access (CDMA) satellite systems.We will combine observations from the Chinese BeiDou Navigation Satellite System (BDS), European Galileo,American Global Positioning System (GPS) and the Japanese Quasi-Zenith Satellite System (QZSS). To further strengthen the underlying model, attention will be given to overlapping frequencies between the systems. If one can calibrate the inter-system biases, a common pivot satellite between the respective systems can be used to parameterize double-differenced ambiguities. The LAMBDA method is used for ambiguity resolution. The instantaneous (single-epoch) single-frequency RTK performance is evaluated by a formal as well as an empirical analysis, consisting of ambiguity dilution of precision (ADOP), bootstrapped and integer least-squares success rates and positioning precisions. The time-tocorrect-fix in some particular cases when instantaneous RTK is not possible will also be analyzed. To simulate conditions with obstructed satellite visibility or when lowelevation multipath is present, various elevation cut-off angles between 10 and 40 A degrees will be used. Four days of real data are collected in Perth, Western Australia.It will be shown that the four-system RTK model allows for improved integer ambiguity resolution and positioning performance over the single-, dual- or triple-systems,particularly for higher cut-off angles.
Keywords:Inter-system biases (ISBs); Real-time kinematic(RTK); Multi-global navigation satellite system (GNSS);integer ambiguity resolution; LAMBDA
来源出版物:GPS Solutions, 2015, 19(1): 151-163
被引频次:40
Precise point positioning with the BeiDou navigation satellite system
Li, Min; Qu, Lizhong; Zhao, Qile; et al.
Abstract:By the end of 2012, China had launched 16 BeiDou-2 navigation satellites that include six GEOs, five IGSOs and five MEOs. This has provided initial navigation and precise pointing services ability in the Asia-Pacific regions. In order to assess the navigation and positioning performance of the BeiDou-2 system, Wuhan University has built up a network of BeiDou Experimental Tracking Stations (BETS) around the World. The Position and Navigation Data Analyst (PANDA) software was modified to determine the orbits of BeiDou satellites and provide precise orbit and satellite clock bias products from the BeiDou satellite system for user applications. This article uses the BeiDou/GPS observations of the BeiDou Experimental Tracking Stations to realize the BeiDou and BeiDou/GPS static and kinematic precise point positioning(PPP). The result indicates that the precision of BeiDou static and kinematic PPP reaches centimeter level. The precision of BeiDou/GPS kinematic PPP solutions is improved significantly compared to that of BeiDou-only or GPS-only kinematic PPP solutions. The PPP convergence time also decreases with the use of combined BeiDou/GPS systems.
Keywords:BeiDou navigation satellite system; Position and Navigation Data Analyst (PANDA); BeiDou Experimental Tracking Stations (BETS); Precise Point Positioning (PPP)
来源出版物:Sensors, 2014, 14(1): 927-943
被引频次:34
BeiDou Navigation Satellite System and its time scales
Han, Chunhao; Yang, Yuanxi; Cai, Zhiwu; et al.
Abstract:The development and current status of BeiDou Navigation Satellite System are briefly introduced. The definition and realization of the system time scales are described in detail. The BeiDou system time (BDT) is an internal and continuous time scale without leap seconds. It is maintained by the time and frequency system of the master station. The frequency accuracy of BDT is superior to 2 × 10-14and its stability is better than 6 × 10-15/30 days.The satellite synchronization is realized by a two-way time transfer between the uplink stations and the satellite. The measurement uncertainty of satellite clock offsets is less than 2 ns. The BeiDou System has three modes of time services: radio determination satellite service (RDSS)one-way, RDSS two-way and radio navigation satellite service (RNSS) one-way. The uncertainty of the one-way time service is designed to be less than 50 ns, and that of the two-way time service is less than 10 ns. Finally,some coordinate tactics of UTC from the viewpoint of global navigation satellite systems (GNSS) are discussed.It would be helpful to stop the leap second, from our viewpoint, but to keep the UTC name, the continuity and the coordinate function unchanged.
来源出版物:Metrologia, 2011, 48(4): 213-218
被引频次:32
Reliable single-epoch ambiguity resolution for short baselines using combined GPS/BeiDou system
Deng, Chenlong; Tang, Weiming; (Liu, Jingnan
Abstract:GNSS single-epoch real-time kinematic (RTK)positioning depends on correct ambiguity resolution. If the number of observed satellites in a single epoch is insufficient, which often happens with a standalone GNSS system, the ambiguity resolution is difficult to achieve.China’s BeiDou Navigation Satellite System has been providing continuous passive positioning, navigation and timing services since December 27, 2012, covering China and the surrounding area. This new system will increase the number of satellites in view and will have a significant effect on successful ambiguity resolution.Since the BeiDou system is similar to GPS, the procedure of data processing is easier than that for the Russian GLONASS system. We briefly introduce the time and the coordinate system of BeiDou and also the BeiDou satellite visibility in China, followed by the discussion on the combined GPS/BeiDou single-epoch algorithm. Experiments were conducted and are presented here, in which the GPS/BeiDou dual-frequency static data were collected in Wuhan with the baseline distance varying from 5 to 13 km, and processed in separate and combined modes. The results indicate that, compared to a standalone GPS or BeiDou system, the combined GNSS system can increase the successful ambiguity fixing rate for single epochs and can also improve the precision of short baselines determination.
Keywords:GPS/BeiDou; ambiguity resolution; single epoch; short baselines
来源出版物:GPS Solutions, 2014, 18(3): 375-386
·推荐论文摘要·
北斗/GPS组合定位方法
吴甜甜,张云,刘永明,等
摘要:随着北斗卫星导航系统的逐渐完善,有关北斗系统定位的研究越来越深入,为了对比分析北斗系统和全球定位导航系统(GPS)定位的差异性,充分利用北斗地球静止轨道卫星(GEO)和倾斜地球同步轨道卫星(IGSO)高轨道卫星的特殊性,本文提出一种新的组合选星方法,选取卫星数较少且Position Dilution of Precision(PDOP)最小的北斗/GPS组合,分别对比分析北斗系统、GPS系统及其组合系统在楼顶开放环境和楼间恶劣环境下的定位效果。实验结果表明:北斗比GPS有更加稳定的定位效果,依据本文组合选星方法,利用少量卫星即可获得较好的定位精度。
关键词:北斗系统;GPS;组合定位;PDOP;楼间恶劣环境
来源出版物:遥感学报, 2014, 18(5): 1087-1097
多GNSS融合的北斗卫星精密定轨
刘伟平,郝金明,李建文,等
摘要:提供高精度的精密轨道产品对北斗卫星导航系统的推广应用具有重要意义。本文给出一种基于模糊度固定的北斗卫星多系统融合非差精密定轨方法,重点推导并论述模糊度固定的实现方法,结合实测数据,对其精密定轨效果进行了分析。初步分析结果表明:利用本文方法,北斗GEO、IGSO、MEO卫星三维定轨精度分别达到1.263 m、0.214 m、0.134 m,3类卫星径向定轨精度平均优于10 cm,IGSO和MEO已经基本优于5 cm;模糊度固定以后,北斗卫星三维定轨精度平均提高了21.8%,轨道切向精度改善最为明显,其中又以GEO卫星改进最大。
关键词:北斗卫星导航系统;模糊度固定;非差精密定轨;多系统融合;激光观测数据
来源出版物:测绘学报, 2014, 43(11): 1132-1138
北斗卫星导航系统及其于民航导航的应用
王艳红,赵文智,杨明
摘要:卫星导航是未来航行系统的重要组成部分,在我国对民航星基导航的学术研究较少情况下,介绍北斗卫星导航系统,从我国民航导航的角度分析了民航导航对北斗卫星导航系统的需要;对北斗卫星导航系统在民航导航中的应用做了初步的探析,结论表明北斗卫星导航系统在区域导航、进离场RNP、进近着陆导航三方面对民航导航的变革有重要意义;结合欧美国家在发展全球卫星导航系统中所遇到的问题,给出我国北斗卫星导航系统民航应用的紧迫性和前瞻性启发。
关键词:航空运输;卫星导航;综合探析;民航导航;北斗卫星导航系统
来源出版物:计算机测量与控制, 2014, 22(2): 496-498
北斗导航系统与GPS精密单点定位精度的对比分析
王阅兵,游新兆,金红林,等
摘要:基于架设在山东荣成、云南下关、宁夏盐池、河北唐山和河南郑州的UNICORECOMM UR370型北斗接收机接收到的北斗和GPS信号,利用武汉大学自主研发的PANDA软件,对比分析了北斗导航系统与GPS精密单点定位精度。结果显示,北斗导航精密单点定位精度在水平方向为1~2 cm,垂直方向为3~4 cm;GPS精密单点定位精度在水平为亚cm级,垂直方向约为1~2 cm。虽然北斗导航系统的精密单点定位精度要低于GPS 50%,但已经能应用在定位精度要求几个cm或更低精度的领域。
关键词:北斗导航系统;GPS;精密单点定位;PANDA;地壳形变
来源出版物:大地测量与地球动力学, 2014, 34(4):110-116
BDS/GPS/GLONASS组合的双频单历元相对定位性能对比分析
汪亮,李子申,袁洪,等
摘要:随着我国北斗卫星导航系统(BeiDou Navigation Satellite System, BDS)的建成与运行,目前具备独立服务能力的系统包括GPS,GLONASS和BDS,多系统组合已成为GNSS导航定位发展的必然趋势。基于伪距或载波相位的相对定位是目前利用GNSS实现高精度定位的主要技术手段之一。本文重点分析对比了BDS/GPS/GLONASS单系统、双系统以及三系统组合共7种模式下双频伪距和单历元载波相位相对定位性能。结果表明:1)BDS/GPS/GLONASS组合伪距和单历元载波相位相对定位时,三系统观测值误差比分别设为1∶1∶2和1∶1∶1较合适;2)BDS/GPS组合的性能要优于GPS/GLONASS以及BDS/GLONASS组合,BDS/GPS/GLONASS三系统组合较双系统组合可进一步改善定位性能;3)短基线条件下(<20 km),BDS/GPS/GLONASS组合伪距和单历元载波相位相对定位精度较单BDS,GPS,GLONASS系统分别提高了48.4%,31.7%,65.7%和6.1%,12.5%,39.4%。
关键词:北斗;BDS/GPS/GLONASS;相对定位;单历元RTK
来源出版物:科学通报, 2015, 60(9): 857-868
北斗/GPS组合伪距单点定位性能测试和分析
唐卫明,徐坤,金蕾,等
摘要:讨论了北斗/GPS伪距单点定位联合解算的数学模型,并根据北京、武汉两地的北斗/GPS双系统实测数据,在多种模拟遮挡环境下将北斗/GPS联合解算结果与北斗、GPS单系统在可见卫星数、PDOP值、定位精度、定位可用性等方面进行了对比分析。结果表明,相对于单系统伪距单点定位,北斗/GPS组合定位大大增加了可见卫星数,减小了PDOP值,并在观测条件较差的环境下有效地改善了定位精度,显著提高了系统定位可用性。
关键词:北斗卫星导航系统;GPS;伪距单点定位;联合解算;可用性
来源出版物:武汉大学学报:信息科学版, 2015, 40(4):529-533
北斗区域导航系统的PPP精度分析
朱永兴,冯来平,贾小林,等
摘要:北斗卫星导航系统的开放运行为其在高精度领域的应用提供了可能,系统精密单点定位性能受到了极大关注。本文首先介绍了北斗区域导航系统的星座和BDS/GPS跟踪网,分析了基于国内布站定轨的北斗卫星精密轨道和钟差精度。在此基础上研究了北斗区域导航系统静态、动态精密单点定位精度,并与GPS定位结果进行比较。实测算例表明:北斗精密单点定位可以实现静态厘米级、动态分米级的定位精度,达到目前GPS精密单点定位水平。
关键词:北斗卫星导航系统;BDS/GPS跟踪网;精密定轨;精密单点定位;精度分析
来源出版物:测绘学报, 2015, 44(4): 377-383
GNSS互操作若干问题
杨元喜,陆明泉,韩春好
摘要:GNSS兼容与互操作是国际卫星导航领域的热点议题,也是用户实现多系统融合导航必须具备的条件。本文首先介绍了兼容与互操作的基本概念;简要分析了多GNSS系统互操作的基本趋势及GNSS4大核心系统信号互操作的现状;分析了现有北斗卫星导航系统(BDS)在信号互操作方面存在的问题,指出其对用户接收机制造商和多GNSS用户的影响;分析了坐标基准和坐标框架在互操作方面存在的问题及其可能带来的影响,指出坐标系统的实现、维持甚至更新策略带来的误差都可能给多GNSS互操作及导航定位结果带来影响;讨论了时间基准互操作存在的问题,以及可能的解决措施。最后归纳了本文的主要结论。
关键词:北斗;兼容与互操作;频率;坐标系统;时间基准
来源出版物:测绘学报, 2016, 45(3): 253-259
北斗在极区导航定位性能分析
杨元喜,徐君毅
摘要:北极蕴藏着丰富的资源,冰川融化使得夏季北极地区的航行成为可能,北极地区战略地位凸显。为了保障北极地区活动的安全性,精确导航定位是重要基础保障,本文分析了我国北斗卫星导航系统当前星座及未来全球星座在极区的可用性。详细分析了利用北斗卫星导航系统在极区进行导航、定位服务的基本性能,分析其优缺点,并提出了可能的应对方法。
关键词:北极;GNSS;北斗;极区导航
来源出版物:武汉大学学报:信息科学版, 2016, 41(1):15-20
北斗卫星导航系统的毫米级精度变形监测算法与实现
肖玉钢,姜卫平,陈华,等
摘要:研究了北斗卫星导航系统(BeiDou Navigation Satellite System, BDS)毫米级精度变形监测算法。首先改进了TurboEdit方法,以能够探测到1周的小周跳;针对BDS星座结构给出更为高效的独立双差观测值搜索方法;对于模糊度固定,采用决策函数和序贯模糊度固定相结合的方法。在此基础上,研制了BDS变形监测软件。最后,利用变形监测试验平台的实测数据,从星座分布、解算精度等方面分析了BDS在变形监测中应用的可行性。结果表明,目前在试验区域内BDS与GPS在卫星几何分布等方面基本相当。BDS的短基线解算精度略低于GPS,但仍可达到平面1 mm以内、高程2 mm以内的精度水平。
关键词:北斗卫星导航系统;变形监测;软件实现;精度分析
来源出版物:测绘学报, 2016, 45(1): 16-21
基于卫星共视的远程时间频率校准系统
陈瑞琼,刘娅,李孝辉
摘要:随着北斗卫星导航系统的投入运行,基于北斗卫星的远程时间频率比对成为可能。国家授时中心基于北斗卫星共视时间比对方法,搭建了一套远程时间频率校准系统,由远程时间比对基准终端、远程时间比对校准终端和数据分析处理中心组成,可在远程恢复出UTC(NTSC)的时间频率信号。远程时间比对基准终端测量UTC(NTSC)与北斗卫星钟的钟差;远程时间比对校准终端测量本地原子钟与北斗卫星钟的钟差,并在本地驾驭生成与UTC(NTSC)同步的时频信号;数据分析处理中心处理来自远程时间比对基准终端和远程时间比对校准终端的数据。该系统摒弃了传统的不连续观测方法,以10 min作为1个观测周期,实现了时间频率的连续比对。试验结果表明,该系统配送UTC(NTSC)的不确定度为3.74 ns,配送信号的频率天稳定度达到1.97×10-14。
关键词:北斗卫星;共视;远程时间校准
来源出版物:电子测量与仪器学报, 2016, 30(1): 38-44
北斗卫星导航系统用于东北地区高精度变形监测性能分析
郭睿,胡小工,唐波,等
摘要:截至2015年1月,我国北斗区域卫星导航系统已正式运行满2年。目前北斗卫星导航系统的星座组网尚未完成,只可为亚太地区特别是低纬度地区提供较好的服务,即服务拓展到南北纬55°,东经55°至180°。由于我国东北地区所处纬度较高,可能会受到北斗星座不完善的影响。为了分析我国北斗卫星导航系统在东北地区高精度变形监测中的监测性能,本文在哈尔滨地区搭建了北斗变形监测数据采集平台并研制了北斗高精度变形监测软件。通过对连续10 d的实测数据进行处理,测试评估了北斗在变形监测中的数据质量与精度。试验结果表明,东北地区短基线变形监测条件下,北斗变形监测多个测段对应基线N、E分量重复性优于7 mm,U分量重复性优于1 cm。
关键词:北斗卫星导航系统;东北地区;高精度;变形监测;数据质量
来源出版物:测绘通报, 2016, (4): 33-37
北斗新一代试验卫星星钟及轨道精度初步分析
陈金平,胡小工,唐成盼
摘要:北斗卫星导航系统新一代试验卫星星座由2颗高轨倾斜地球同步轨道卫星和3颗中轨地球轨道卫星组成,2016年2月全部发射入轨,其任务是验证北斗系统从目前区域导航定位授时服务走向全球服务的新技术体制设计及指标性能。导航卫星星载原子钟是最重要载荷之一,负责星上时间频率基准信号维持和产生,本文利用星地双向时频传递设备观测的星地钟差数据,评估了试验星配置的新型高精度铷钟和被动型氢钟的实际性能,定量比较了相对于北斗区域系统卫星钟的性能提升。结果表明新一代试验星与北斗区域系统卫星钟差预报精度相比较有较大提高,地球倾斜静止卫星(Inclined Geosynchronous Orbit, IGSO)短期预报误差从0.65 ns减小到0.30 ns,中轨道卫星(Medium Orbit, MEO)短期预报误差从0.78 ns减小到0.32 ns,IGSO/MEO卫星中期预报误差均从2.50 ns减小到约1.50 ns。星间链路(Inter-Satellite Link,ISL)是北斗全球系统最重要的技术体制设计之一,本文评估了试验卫星实现的星间伪距测量对提升空间信号精度,即轨道和钟差的贡献,得到在地面监测网无法连续覆盖到的境外弧段,高精度星间链路测量对轨道确定和钟差测定精度的提升尤为明显。加入星间伪距测量,MEO卫星重新入境时钟差预报误差由3 ns减小至1 ns以内。采用星地星间联合定轨方法估计的卫星轨道径向重叠弧段互差优于0.1 m,三维位置重叠互差优于0.5 m,预报24 h径向重叠弧段互差优于0.2 m,三维位置重叠互差优于1 m,均较区域监测网L波段定轨结果有较大提升。为解决多星定轨处理时卫星钟差与轨道高度耦合问题,本文提出了卫星钟差半约束模式定轨处理方法。用户等效距离误差分析结果表明采用卫星钟差半约束的定轨模式,卫星轨道预报4 h用户等效距离误差由1.04 m减小至0.82 m。
关键词:北斗卫星导航系统;星载原子钟;星间链路;卫星钟差;卫星定轨;空间信号精度;星地双向时频传递
来源出版物:中国科学:物理学 力学 天文学, 2016,46(11): 119502
GPS/北斗组合卫星导航系统快速选星算法
刘帅,赵国荣,高超,等
摘要:为实现GPS/北斗组合卫星导航系统的快速选星,提出一种基于几何布局的快速选星算法。根据最优选星方案的卫星分布特点,利用卫星高度角和方位角信息实现卫星的区域划分,应用代价函数法对中仰角区域的卫星进行筛选,得到最终的选星方案。与最优选星算法相比,该算法计算量明显减小;仿真结果表明,该算法能将几何精度因子(GDOP)控制在小于2.5的范围内,具有较好的选星效果。综合考虑算法复杂度和选星效果,基于几何分布的快速选星算法能够满足航空航天等对精度和实时性要求较高的领域的需求。
关键词:组合导航;选星算法;几何布局;代价函数;北斗导航系统
来源出版物:电光与控制, 2017, 24(3): 32-35
北斗卫星导航系统服务精度评估
王威,胡英男
摘要:精度是北斗卫星导航系统(BeiDou Navigation Satellite System,BDS)服务指标体系的重要内容。给出了北斗卫星导航系统精度指标的含义及精度指标的评估方法,利用实测数据分析了北斗系统实际实现的精度指标,并将其与GPS系统实际实现的精度指标作比较分析。DOP(几何精度因子)值由卫星导航系统空间星座分布决定,是影响用户定位授时精度的重要因素,比较了北斗与GPS在中国区域DOP值分布的差异。GPS系统PDOP(定位几何精度因子)分布均匀,随用户经度和纬度变化不大,在1.0-2.0之间。而受混合星座影响,北斗系统PDOP分布随着测站经度和纬度变化较大,变化范围为1.5-5.0;且随测站纬度增加而变大,由中心经度(东经118°)向两侧不断变大。对于影响用户等效距离误差的空间信号精度进行了比较分析。利用IG(国际GNSS服务组织)提供的事后精密轨道、激光跟踪数据和北斗双向时频传递测量的卫星钟差评估了北斗基本导航电文的精度。结果表明:北斗IGSO(倾斜地球同步轨道)卫星和MEO(中轨道)卫星轨道径向误差约为0.5 m,大于GPS卫星轨道小于0.2 m的径向误差。北斗GEO(地球同步轨道)卫星激光残差约为65 cm,IGSO卫星和MEO卫星激光残差约为50 cm。受卫星钟差数据龄期影响,MEO卫星钟差参数误差明显大于IGSO卫星和GEO卫星,约为0.80 m。最后,采用MGEX(多GNSS系统试验项目)多模接收机进行了定位试验,分析了北斗系统和GPS在定位精度上的差异。结果表明:受星座构型影响,北斗卫星导航系统定位精度与GPS系统定位精度相比有所差异,但满足水平定位精度优于10 m、高程定位精度优于10 m的设计要求,双系统组合定位精度好于单一系统定位精度。
关键词:天体测量与天体力学;空间飞行器;历书;方法;数据分析
来源出版物:天文学报, 2017, 58(2): 1-10
北斗卫星全球激光测距观测及数据应用
张忠萍,程志恩,张海峰,等
摘要:卫星轨道精确测定是卫星导航系统提供导航服务的基础。北斗卫星导航系统是我国自主研发的新一代卫星导航系统,卫星上均装载了激光反射器,以厘米或毫米级精度卫星激光测距作为北斗卫星精密测轨与微波测量系统的独立外部标校手段。为增强北斗卫星的激光观测能力,上海激光测距站在白天光束监视、望远镜精跟踪、噪声滤波等方面进行了性能改进,在国际激光联测台站中首先实现同步轨道卫星白天激光观测;基于国际激光联测机制,组织国际激光测距站开展北斗卫星全球激光观测实验,获取了28个台站对北斗卫星的激光观测数据,弥补了国内台站地域局限性,为国内卫星获取国外台站观测数据提供了途径。利用全球台站激光观测数据开展了北斗卫星激光独立定轨、广播星历精度检核等研究,并将结果应用于北斗卫星导航系统性能评估。
关键词:测量;卫星激光测距;激光数据应用;全球激光联测;北斗卫星;激光反射器
来源出版物:中国激光, 2017, 44(4): 0404004
北斗卫星导航系统安全和完好性监测现状与发展
庄钊文,王飞雪,欧钢,等
摘要:随着导航现代化概念研究的深化,安全和完好性已成为全球导航卫星系统(GNSS)至关重要的性能指标。本文从导航战角度讨论了系统安全的内涵及组成,以及系统完好性监测的必要性和监测评估方法。结合北斗卫星导航系统建设,着重介绍了在信号传输体制设计、频率规划与协调、抗干扰体系建设、星间链路和完好性监测方面取得的关键技术突破和研究成果。最后,讨论了卫星导航发展趋势。
关键词:北斗卫星导航系统;系统安全;完好性监测;导航战;信号传输体制;抗干扰体系;星间链路
来源出版物:科技导报, 2017, 35(10): 13-18
基于北斗卫星导航系统的远距离海洋工程高精度定位技术
刘宏,万立健,陆亚英
摘要:随着远距离海洋工程项目的不断展开,对北斗高精度的定位需求越来越迫切,而远海地区常规地基增强建设及差分传输方式无法实施。为解决远海北斗高精度定位的难题,本文采用北斗卫星导航系统(BDS)的短报文功能进行精密单点定位误差改正数的播发,向观测用北斗卫星终端发送精度较高的卫星钟误差、星历误差改正值,实现了北斗卫星改正信息的远程传输,传输距离被大大拓展,不再受地域的限制,并大大提高了北斗系统定位精度,为北斗技术在海洋工程中的应用拓展了空间。
关键词:北斗卫星;差分播发;远距离;海洋工程;高精度定位
来源出版物:测绘通报, 2017, (5): 62-66
引入国家基准站的北斗导航卫星精密定轨
韩德强,党亚民,王虎,等
摘要:卫星精密轨道的确定是北斗卫星导航系统位置与服务的核心技术之一,而国家基准站是影响卫星轨道精度的一个重要因素。本文基于中国测绘科学研究院国际GNSS监测与评估中心自主开发的软件计算国家基准站和MGEX站对北斗卫星精密定轨的影响。得出结果:加上国家基准站后GEO卫星轨道精度平均能达到2.0 m,比没有国家基准站时提高约14%,在GEO切向方向改善最为明显,大约提高30%。IGSO和MEO卫星也有所提高。加上国家基准站后,三类卫星的轨道重复弧段的径向精度优于5 cm。有了国家基准站数据BDS精密轨道会有明显的改善。国家基准站的建立使我国北斗导航卫星的服务能力有很大提高。
关键词:国家基准站;北斗;精密轨道
来源出版物:测绘通报, 2017, (8): 1-6
Multipath analysis of code measurements for BeiDou geostationary satellites
Wang, Guangxing; de Jong, Kees; Zhao, Qile
Abstract:Having non-negligible impact on the code range observables, multipath delay is one of the error sources that limit GNSS positioning accuracy. Due to the relatively stationary geometry, multipath effects for signals from geostationary earth orbit (GEO) satellites are even more difficult to mitigate by merely increasing the observing periods or averaging over multiple epochs. To investigate the characteristics of code, multipath effects for the BeiDou Navigation Satellite System (BDS) GEO satellites,a linear combination of observations reflecting code multipath was employed and BDS multipath time series over long periods were analyzed with the Fourier transform,correlation and wavelet transform. The amplitudes of GEO multipath series vary from < 1.0 m to around 2.0 m, and the periods of the dominant daily repeating components fall between 86130 and 86280 s. The low-frequency components were extracted, and most cross-correlation coefficients between the low-frequency components of two consecutive days are larger than 0.7. When the lowfrequency components of the first day are subtracted from the multipath time series of the second day, a decrease of more than 25 % is found in terms of the code standard deviations. By correcting the observables with lowfrequency multipath of the previous day, the precisions of code-only single-point positioning using ionosphere-free linear combination of BDS first and second or first and third frequencies can be improved. Precision improvements in north, east and up components for two stations in Perth,Australia were shown to be 0.2, 0.5 and 0.4 m, and 0.3, 0 and 0.5 m, respectively.
Keywords:multipath; BDS; GEO; single-point positioning;low frequency
来源出版物:GPS Solutions, 2015, 19(1): 129-139
Combined BDS, galileo, qzss and GPS single-frequency RTK
Odolinski, Robert; Teunissen, Peter J. G; Odijk, Dennis
Abstract:We will focus on single-frequency singlebaseline real-time kinematic (RTK) combining four Code Division Multiple Access (CDMA) satellite systems. We will combine observations from the Chinese BeiDou Navigation Satellite System (BDS), European Galileo,American Global Positioning System (GPS) and the Japanese Quasi-Zenith Satellite System (QZSS). To further strengthen the underlying model, attention will be given to overlapping frequencies between the systems. If one can calibrate the inter-system biases, a common pivot satellite between the respective systems can be used to parameterize double-differenced ambiguities. The LAMBDA method is used for ambiguity resolution. The instantaneous (singleepoch) single-frequency RTK performance is evaluated by a formal as well as an empirical analysis, consisting of ambiguity dilution of precision (ADOP), bootstrapped and integer least-squares success rates and positioning precisions. The time-to-correct-fix in some particular cases when instantaneous RTK is not possible will also be analyzed. To simulate conditions with obstructed satellite visibility or when low-elevation multipath is present,various elevation cut-off angles between 10 and 40A degrees will be used. Four days of real data are collected in Perth, Western Australia. It will be shown that the foursystem RTK model allows for improved integer ambiguity resolution and positioning performance over the single,dual or triple-systems, particularly for higher cut-off angles.
Keywords:Inter-system biases (ISBs); Real-time kinematic (RTK); Multi-global navigation satellite system(GNSS); integer ambiguity resolution; LAMBDA
来源出版物:GPS Solutions, 2015, 19(1): 151-163
Analysis on the long-term dynamical evolution of the inclined geosynchronous orbits in the Chinese BeiDou navigation system
Zhao, Chang-Yin; Zhang, Ming-Jiang;Wang, Hong-Bo; et al.
Abstract:Five inclined geosynchronous orbit (IGSO)satellites with the inclination of about 55 degrees in the Chinese BeiDou navigation system have been put in orbit until now. The Inter-Agency Space Debris Coordination Committee (IADC) has defined a geosynchronous orbit(GEO) protected region and recommended that the GEO satellite should be maneuvered to a disposal orbit high enough at end-of-mission to remain above the GEO protected region. The recommended disposal altitude is at least 235 km + (1000. C-R . A/M) higher than the perigee altitude of the GEO satellite, where C-R and A/M are radiation pressure coefficient and area-to-mass ratio respectively. Whether this recommendation is also adequate for the disposal of these IGSO satellites in the Chinese BeiDou navigation system at end-of-mission? And if not, is there any other possible strategy to do? In view of these considerations, the long-term dynamical evolution of these IGSO satellites is investigated by both theoretical analysis and numerical computation methods in this paper.Some qualitative orbital evolution characteristics and quantitative result of variation ranges of the semi-major axis a, the inclination i and the eccentricity e are presented respectively. Based on these results, a possible mitigation strategy to reduce the orbital lifetime of the IGSO satellites after end-of-mission is proposed.
Keywords:long-term dynamical evolution; inclined geosynchronous orbit; Chinese BeiDou navigation system;mitigation strategy
来源出版物:Advances in Space Research, 2015, 56(3):377-387
Precise point positioning with quad-constellations:GPS, BeiDou, GLONASS and Galileo
Cai, Changsheng; Gao, Yang; Pan, Lin
Abstract: Multi-constellation GNSS precise point positioning (PPP) first became feasible back to 2007 but with only two constellations, namely GPS and GLONASS.With the availability of more satellites and precise orbit and clock products from BeiDou and Galileo, it is possible now to investigate PPP with four constellations, namely GPS, BeiDou, GLONASS and Galileo. This research aims at investigating the quad-constellation PPP for position determination and analyzing its positioning performance. A quad-constellation PPP model is developed to simultaneously process the observations from all the four GNSS systems. The developed model is also applicable to the PPP processing with observations from single, dual or triple constellations. The analysis on PPP accuracy and convergence time is conducted based on data processing results from both static and kinematic tests of single-constellation and multi-constellations. The three-hour static positioning results indicate that the BeiDou-only PPP accuracy is worse than the GPS-only PPP.The RMSs of position errors for BeiDou-only PPP are 5.2 cm, 2.7 cm and 8.3 cm in east, north and up directions while the ones for GPS-only PPP are 3.9 cm, 1.6 cm and 5.7 cm. The GPS/BeiDou PPP improves the positioning accuracy by 28%, 6% and 7% and reduces the convergence time by 26%, 13% and 14% over the GPS-only PPP in three coordinate components, respectively. The GPS/GLONASS PPP achieves slightly better performance than the GPS/BeiDou PPP. The triple-constellation PPP further increases the positioning accuracy and decreases the convergence time over the dual-constellation PPP. The improvement of positioning performance is not significant after adding Galileo due to currently limited number of satellites. Similar to the static positioning, the quadconstellation kinematic PPP also significantly improves the positioning performance in contrast with singleconstellation and dual-constellations. The time varying characteristics of the time differences between the four systems are also investigated. The results indicate that the system time differences of GPS with BeiDou, GLONASS and Galileo are very stable over time with STD values of better than 1.1 ns.
Keywords:quad-constellation;precise point positioning;convergence time; positioning accuracy
来源出版物:Advances in Space Research, 2015, 56(1):133-143
Multiangle BSAR imaging based on BeiDou-2 navigation satellite system: Experiments and preliminary results
Zeng, Tao; Ao, Dongyang; Hu, Cheng; et al.
Abstract:This paper analyzes the multiangle imaging results for bistatic synthetic aperture radar (BSAR) based on global navigation satellite systems (GNSS-BSAR). Due to the shortcoming of GNSS-BSAR images, a multiangle observation and data processing strategy based on BeiDou-2 navigation satellites was put forward to improve the quality of images and the value of system application.Twenty-six BSAR experiments were conducted and analyzed in different configurations. Furthermore, a regionbased fusion algorithm using region-of-interest (ROI)segmentation was proposed to generate a high-quality fusion image. Based on the fusion image, typical targets such as water area, vegetation area, and artificial targets were compared and interpreted among single/multipleangle images. The results reveal that the multiangle imaging method was a good technique to enhance image information, which might extend the applications of GNSS-BSAR.
Keywords:bistatic synthetic aperture radar (BSAR);global navigation satellite system (GNSS); image fusion;image interpretation; multiangle
来源出版物:IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2015, 53(10): 5760-5773
Estimation of differential code biases for Beidou navigation system using multi-GNSS observations:How stable are the differential satellite and receiver code biases?
Xue, Junchen; Song, Shuli; Zhu, Wenyao; et al.
Abstract:Differential code biases (DCBs) are important parameters that must be estimated accurately and reliably for high-precision GNSS applications. For optimal operational service performance of the Beidou navigation system (BDS), continuous monitoring and constant quality assessment of the BDS satellite DCBs are crucial. In this study, a global ionospheric model was constructed based on a dual system BDS/GPS combination. Daily BDS DCBs were estimated together with the total electron content from 23 months’ multi-GNSS observations. The stability of the resulting BDS DCB estimates was analyzed in detail. It was found that over a long period, the standard deviations(STDs) for all satellite B1-B2 DCBs were within 0.3 ns(average: 0.19 ns) and for all satellite B1-B3 DCBs, the STDs were within 0.36 ns (average: 0.22 ns). For BDS receivers, the STDs were greater than for the satellites,with most values 2 ns. The DCBs of different receiver families are different. Comparison of the statistics of the short-term stability of satellite DCBs over different time intervals revealed that the difference in STD between 28-and 7-day intervals was small, with a maximum not exceeding 0.06 ns. In almost all cases, the difference in BDS satellite DCBs between two consecutive days was 0.8 ns. The main conclusion is that because of the stability of the BDS DCBs, they only require occasional estimation or calibration. Furthermore, the 30-day averaged satellite DCBs can be used reliably for the most demanding BDS applications.
Keywords:differential code bias; GNSS; Beidou navigation system; global ionospheric model
来源出版物:Journal of Geodesy, 2016, 90(4): 309-321
BDS/GPS Dual Systems Positioning Based on the Modified SR-UKF Algorithm
Kong, JaeHyok; Mao, Xuchu; Li, Shaoyuan
Abstract:The Global Navigation Satellite System can provide all-day three-dimensional position and speed information. Currently, only using the single navigation system cannot satisfy the requirements of the system’s reliability and integrity. In order to improve the reliability and stability of the satellite navigation system, the positioning method by BDS and GPS navigation system is presented, the measurement model and the state model are described. Furthermore, the modified square-root Unscented Kalman Filter (SR-UKF) algorithm is employed in BDS and GPS conditions, and analysis of single system/multi-system positioning has been carried out,respectively. The experimental results are compared with the traditional estimation results, which show that the proposed method can perform highly-precise positioning.Especially when the number of satellites is not adequate enough, the proposed method combine BDS and GPS systems to achieve a higher positioning precision.
Keywords:Global Navigation Satellite System (GNSS);positioning algorithm; modified square-root Unscented Kalman filter (modified SR-UKF); BeiDou navigation System (BDS)
来源出版物:Sensors, 2016, 16(5): 35
Integrated solution for anomalous driving detection based on BeiDou/GPS/IMU measurements
Sun, Rui; Han, Ke; Hu, Jun
Abstract:There has been an increasing role played by Global Navigation Satellite Systems (GNSS) in Intelligent Transportation System (ITS) applications in recent decades.In particular, centimeter/decimetre positioning accuracy is required for some safety related applications, such as lane control, collision avoidance, and intelligent speed assistance. Lane-level Anomalous driving detection underpins these safety-related ITS applications. The two major issues associated with such detection are (1)accessing high accuracy vehicle positioning and dynamic parameters; and (2) extraction of irregular driving patterns from such information. This paper introduces a new integrated framework for detecting lane-level anomalous driving, by combining Global Positioning Systems (GPS),BeiDou, and Inertial Measurement Unit (IMU) with advanced algorithms. Specifically, we use Unscented Particle Filter (UPF) to perform data fusion with different positioning sources. The detection of different types of Anomalous driving is achieved based on the application of a Fuzzy Inference System (FIS) with a newly introduced velocity-based indicator. The framework proposed in this paper yield significantly improved accuracy in terms of positioning and Anomalous driving detection compared to state-of-the-art, while offering an economically viable solution for performing these tasks.
来源出版物:Transportation Research Part C-Emerging Technologies, 2016, 69: 193-207
GNSS multi-carrier fast partial ambiguity resolution strategy tested with real BDS/GPS dual- and triple-frequency observations
He H; Li J; Yang Y; et al.
Abstract:The regional constellation of BeiDou navigation satellite system (BDS) has been officially in operation since December 27, 2012, and real-time kinematic positioning using BDS and GPS multi-frequency observations is feasible. A heavy computational problem arises when resolving ambiguities in the case of multi-system with multi-frequency observations. A multi-carrier fast partial ambiguity resolution strategy is developed with the property that the extra-wide-lane and wide-lane ambiguities in the multi-frequency case can be resolved reliably in advance. Consequently, the technique resolves ambiguities sequentially instead of the usual batch ambiguity resolution (AR) mode so as to improve the computational efficiency of AR significantly. The strategy is demonstrated with real BDS/GPS dual- and triplefrequency observations. The results have shown that the probability of correct AR by the proposed method is comparable to that of the batch AR. Experimentally, the new method is about 2.5 times as fast as the batch AR in the dual-frequency case, 3 times in the mixed dual and triplefrequency case and 3.5 times in the triple-frequency case.
Keywords:BeiDou; Geostationary Earth Orbit (GEO);Solar Radiation Pressure (SRP); Precise Orbit Determination(POD)
来源出版物:Advances in Space Research, 2016, 57(1):234-244
Applications of two-way satellite time and frequency transfer in the BeiDou navigation satellite system
Zhou, ShanShi; Hu, XiaoGong; Liu, Li; et al.
Abstract:A two-way satellite time and frequency transfer(TWSTFT) device equipped in the BeiDou navigation satellite system (BDS) can calculate clock error between satellite and ground master clock. TWSTFT is a real-time method with high accuracy because most system errors such as orbital error, station position error, and tropospheric and ionospheric delay error can be eliminated by calculating the two-way pseudorange difference.Another method, the multi-satellite precision orbit determination (MPOD) method, can be applied to estimate satellite clock errors. By comparison with MPOD clock estimations, this paper discusses the applications of the BDS TWSTFT clock observations in satellite clock measurement, satellite clock prediction, navigation system time monitor, and satellite clock performance assessment in orbit. The results show that with TWSTFT clock observations, the accuracy of satellite clock prediction is higher than MPOD. Five continuous weeks of comparisons with three international GNSS Service (IGS) analysis centers (ACs) show that the reference time difference between BeiDou time (BDT) and golbal positoning system(GPS) time (GPST) realized IGS ACs is in the tens of nanoseconds. Applying the TWSTFT clock error observations may obtain more accurate satellite clock performance evaluation in the 104s interval because the accuracy of the MPOD clock estimation is not sufficiently high. By comparing the BDS and GPS satellite clock performance, we found that the BDS clock stability at the 103s interval is approximately 10-12, which is similar to the GPS IIR.
Keywords:BDS; TWSTFT; satellite clock; prediction accuracy; system reference time; Allan variance
来源出版物:Science China-Physics Mechanics &Astronomy, 2016, 59(10): 109511
Performance evaluation of single-frequency point positioning with GPS, GLONASS,BeiDou and Galileo
Pan, L; Cai, C; Santerre, R; et al.
Abstract:The single point positioning (SPP) mode has been widely used in many fields such as vehicle navigation,Geographic Information System and land surveying. For a long period, the SPP technology mainly relies on GPS system. With the recent revitalisation of the GLONASS constellation and two newly emerging constellations of BeiDou and Galileo, it is now feasible to investigate the performance of quad-constellation integrated SPP (QISPP)with GPS, GLONASS, BeiDou and Galileo measurements.As a satellite-based positioning technology, the QISPP is expected to improve the accuracy and availability of positioning solutions due to the increased number of visible satellites and the improved satellite sky distribution.In this study, a QISPP model is presented to simultaneously process observations from all four Global Navigation Satellite System (GNSS) constellations. Datasets collected at 47 globally distributed Multi-GNSS Experiment(MGEX) stations on two consecutive days and a kinematic experimental dataset are employed to fully assess the QISPP performance in terms of positioning accuracy and availability. Given that most navigation users are using single-frequency receivers, only the observations on a single frequency are utilised. The results indicate that the QISPP improves the positioning accuracy by an average of 16%, 13% and 12% using the MGEX datasets, and 43%, 31% and 51% using the kinematic experimental dataset over the GPS-only case in the east, north and up components, respectively. The availability of the QISPP solutions remains 100% even for a mask elevation angle of 40 degrees, whereas it is only 37% for the GPS-only case.All these results are achieved using geodetic-type receivers and they are possibly optimistic for users who use navigation-type receivers.
Keywords:single point positioning; GPS; GLONASS;BeiDou; Galileo
来源出版物:Survey Review, 2017, 49(354): 197-205
Sea level change from BeiDou Navigation Satellite System-Reflectometry (BDS-R): First results and evaluation
Jin, Shuanggen; Qian, Xiaodong; Wu, X; et al.
Abstract:Sea level changes affect human living environments, particularly ocean coasts. The tide gauges(TG) can measure sea level change, while it is the relative variations with respect to the land. Recently, GPSReflectometry (GPS-R) has been demonstrated to measure sea level change as an altimetry. With the rapid development of China’s BeiDou Navigation Satellite System (BDS), it may provide a new possible opportunity to monitor sea level changes with three frequencies (L2, L6 and L7). In this paper, BDS-Reflectometry (BDS-R) is the first time used to estimate the sea level changes based on Signal-to-Noise Ratio (SNR) data and triple-frequency phase and code combinations, which are compared to tide gauge observations. Results show that sea level changes from BDS SNR and phase combination have a good agreement with correlation coefficients of 0.83-0.91 and RMSEs of less than 0.6 m, while BDS code combination is not as good as others. Furthermore, a new negative linear model between phase and code peak frequencies and tide gauge observations is further obtained and analyzed, which improves the results from three-frequency phase and code combinations with the RMSE of about 10 cm and 18 cm.
来源出版物:Global and Planetary Change, 2017, 1149:20-25
The Multi-GNSS Experiment (MGEX) of the International GNSS Service (IGS):Achievements, prospects and challenges
Montenbruck, Oliver; Steigenberger, Peter;Prange, Lars; et al.
Abstract:Over the past five years, the International GNSS Service (IGS) has made continuous efforts to extend its service from GPS and GLONASS to the variety of newly established global and regional navigation satellite systems.This report summarizes the achievements and progress made in this period by the IGS Multi-GNSS Experiment(MGEX). The status and tracking capabilities of the IGS monitoring station network are presented and the multi-GNSS products derived from this resource are discussed. The achieved performance is assessed and related to the current level of space segment and user equipment characterization. While the performance of orbit and clock products for BeiDou, Galileo, and QZSS still lags behind the legacy GPS and GLONASS products,continued progress has been made since launch of the MGEX project and already enables use of the new constellations for precise point positioning, atmospheric research and other applications. Directions for further research are identified to fully integrate the new constellations into routine GNSS processing. Furthermore,the active support of GNSS providers is encouraged to assist the scientific community in the generation of fully competitive products for the new constellations.
Keywords:IGS; MGEX; BeiDou; Galileo; QZSS; Orbit and clock
来源出版物:Advances in Space Research, 2017, 59(7):1671-1697
BeiDou Signal Acquisition with Neumann-Hoffman Code Modulation in a Degraded Channel
Zhao, Lin; Liu, Aimeng; Ding, Jicheng; et al.
Abstract:With the modernization of global navigation satellite systems (GNSS), secondary codes, also known as the Neumann-Hoffman (NH) codes, are modulated on the satellite signal to obtain a better positioning performance.However, this leads to an attenuation of the acquisition sensitivity of classic integration algorithms because of the frequent bit transitions that refer to the NH codes. Taking weak BeiDou navigation satellite system (BDS) signals as objects, the present study analyzes the side effect of NH codes on acquisition in detail and derives a straightforward formula, which indicates that bit transitions decrease the frequency accuracy. To meet the requirement of carriertracking loop initialization, a frequency recalculation algorithm is proposed based on verified fast Fourier transform (FFT) to mitigate the effect, meanwhile, the starting point of NH codes is found. Then, a differential correction is utilized to improve the acquisition accuracy of code phase. Monte Carlo simulations and real BDS data tests demonstrate that the new structure is superior to the conventional algorithms both in detection probability and frequency accuracy in a degraded channel.
Keywords:BeiDou; acquisition; bit transition; differential coherent integration
来源出版物:Sensors, 2017, 17(2): 323
Kinematic Precise Point Positioning Using Multi-Constellation Global Navigation Satellite System (GNSS) Observations
Yu, Xidong; Gao, Jingxiang
Abstract:Multi-constellation global navigation satellite systems (GNSSs) are expected to enhance the capability of precise point positioning (PPP) by improving the positioning accuracy and reducing the convergence time because more satellites will be available. This paper discusses the performance of multi-constellation kinematic PPP based on a multi-constellation kinematic PPP model,Kalman filter and stochastic models. The experimental dataset was collected from the receivers on a vehicle and processed using self-developed software. A comparison of the multi-constellation kinematic PPP and real-time kinematic (RTK) results revealed that the availability,positioning accuracy and convergence performance of the multi-constellation kinematic PPP were all better than those of both global positioning system (GPS)-based PPP and dual-constellation PPP. Multi-constellation kinematic PPP can provide a positioning service with centimetre-level accuracy for dynamic users.
Keywords:multi-constellation; PPP; convergence time;positioning accuracy
来源出版物:ISPRS International Journal of Geo-Information, 2017, 6(1): 6
Improving the ionospheric delay correction of satellite-based augmentation systems in equatorial regions
Huang, Z.; Yuan, H
In 2005, China designed and constructed independent satellite systems ‘Beidou II’, which indicated the start of a new area in Chinese space-based positioning,navigation and timing systems. It is necessary and important to investigate the performance of ionospheric delay correction in the region of China. In this paper, a new algorithm of satellite-based augmentation systems (SBAS)ionospheric delay correction is proposed and tested using observational data at 18 GPS stations. The data are used during periods from January 4 to 23, 2000. The computing results show that precision is high for user stations in the higher mid-latitudes with the average root mean square(RMS) of around 0.4 m. The precision is relatively lower for the lower latitude, which is more prominent for the equatorial region from latitude 20 degrees N to 25 degrees N and from longitude 100 degrees E to 120 degrees E.Quite a few prediction errors surpass 2 m, and the worst case reaches a maximum of 3 in.
Beidou; GPS; satellite-based augmentation system (SBAS); the ionospheric delay; IRI model
文章题目第一作者来源出版物1 Improving the ionospheric delay correction of satellite-based augmentation systems in equatorial regions Huang, Z Advances in Space Research, 2007, 39(10):1552-1558 2 The performance comparison between GPS and Chen, He-Chin Journal of the Chinese Institute of Beidou-2/compass: A perspective from Asia Engineers, 2009, 32(5): 679-689 3 BeiDou navigation satellite system and its time scales Han, Chunhao Metrologia, 2011, 48(4): 213-218 4 Initial assessment of the COMPASS/BeiDou-2 regional Montenbruck,GPS Solutions, 2013, 17(2): 211-222 navigation satellite system Oliver 5 BeiDou inter-satellite-type bias evaluation and calibration for Nadarajah,Sensors, 2013, 13(7): 9435-9463 mixed receiver attitude determination Nandakumaran
国防科学技术大学电子科学与工程学院卫星导航定位技术工程研究中心】
(摘自《科技导报》2017年10期)
卫夏雯

