高压氧治疗重型颅脑损伤的临床效果
马党捐,康彦智,韦明炯,刘雨峰
·适宜技能·
高压氧治疗重型颅脑损伤的临床效果
马党捐,康彦智,韦明炯,刘雨峰
目的 观察高压氧治疗重型颅脑损伤的临床效果。方法 选取2012—2015年陕西省第二人民医院收治的重型颅脑损伤患者146例,其中失访29例,实际纳入患者117例,采用随机数字表法分为对照组53例与观察组64例。对照组患者予以常规治疗,观察组患者在对照组基础上予以高压氧治疗;两组患者均连续治疗8周。比较两组患者治疗前后血肿面积、Loewenstein认知评定量表(LOTCA)评分。结果 治疗前两组中脑挫裂伤、硬膜外出血、硬膜下出血、蛛网膜下腔出血患者血肿面积比较,差异无统计学意义(P>0.05);治疗后观察组中脑挫裂伤、硬膜下出血、蛛网膜下腔出血患者血肿面积小于对照组中脑挫裂伤、硬膜下出血、蛛网膜下腔出血患者(P<0.05),但两组中硬膜外出血患者血肿面积比较,差异无统计学意义(P>0.05)。治疗前两组患者定向评分、知觉评分、视组织运动评分、思维运作评分、注意与集中评分比较,差异无统计学意义(P>0.05);治疗后观察组患者定向评分、知觉评分、视组织运动评分、思维运作评分、注意与集中评分高于对照组(P<0.05)。结论 高压氧治疗重型颅脑损伤的临床效果确切,可有效缩小血肿面积,改善患者认知功能。
颅脑损伤;高压氧;计算机断层扫描;治疗结果
马党捐,康彦智,韦明炯,等.高压氧治疗重型颅脑损伤的临床效果[J].实用心脑肺血管病杂志,2017,25(7):74-77.[www.syxnf.net]
MA D J,KANG Y Z,WEI M J,et al.Clinical effect of hyperbaric oxygen therapy on severe craniocerebral injury[J].Practical Journal of Cardiac Cerebral Pneumal and Vascular Disease,2017,25(7):74-77.
颅脑损伤是指因暴力直接或间接作用于头部引起的脑组织损伤,其中脑损伤后昏迷>6 h或再次昏迷者为重型颅脑损伤,临床表现为意识障碍、头痛、恶心、呕吐、癫痫发作、肢体瘫痪、感觉障碍、失语及偏盲等。近年来,随着交通、运输业的发展,颅脑损伤发生率呈逐年上升趋势,严重影响人们的生命健康和生活质量。
高压氧可有效改善重型颅脑损伤患者临床症状,减轻患者脑水肿,促进昏迷患者清醒,具有较好的临床效果[1-2]。计算机断层扫描(CT)具有扫描时间快、图像清晰等特点,是临床常用的影像学检测方法[3-5]。本研究旨在探讨高压氧治疗重型颅脑损伤患者的临床效果,现报道如下。
1 资料与方法
1.1 一般资料 选取2012—2015年陕西省第二人民医院收治的重型颅脑损伤患者146例,其中失访29例,本研究实际纳入患者117例,经颅脑CT或磁共振成像(MRI)检查确诊。纳入标准:(1)有明确创伤史;(2)格拉斯哥昏迷量表(GCS)评分3~8分;(3)病程<1个月。排除标准:(1)存在严重多发伤者;(2)存在心、肺、肝、肾等重要脏器功能不全者;(3)昏迷时间<6 h或GCS评分>8分者;(4)临床明确诊断为植物状态者;(5)存在高压氧治疗禁忌证者。采用随机数字表法将所有患者分为对照组53例与观察组64例。两组患者性别、年龄、损伤类型比较,差异无统计学意义(P>0.05,见表1),具有可比性。本研究经陕西省第二人民医院医学伦理委员会审核批准,患者家属均签署知情同意书。
1.2 方法 对照组患者予以常规治疗,包括护脑、脱水、降颅压、抗感染以及对症处理等。观察组患者在对照组基础上予以高压氧治疗,仪器为YC3200型空气加压舱,治疗期间压力维持0.2 MPa,升压15~20 min,稳压70~80 min,减压20~25 min,1次/d,4周为1个疗程;对意识障碍患者予以头罩直接供氧,意识清醒且能配合治疗患者采用面罩吸氧。两组患者均连续治疗8周。
1.3 观察指标 (1)血肿面积:两组患者治疗前后采用西门子SomotonBR 3型CT仪进行扫描,电压设定为125 kV,电流设定为350 mA,层厚设定为8 mm,间距设定为8~10 mm;检查结果由放射科医师集体读片后写出报告。(2)Loewenstein认知评定量表(LOTCA)评分:治疗前后采用LOTCA评估两组患者认知功能,包括定向、知觉、视组织运动、思维运作、注意与集中5方面,LOTCA评分越高表明患者认知功能越好。
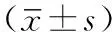
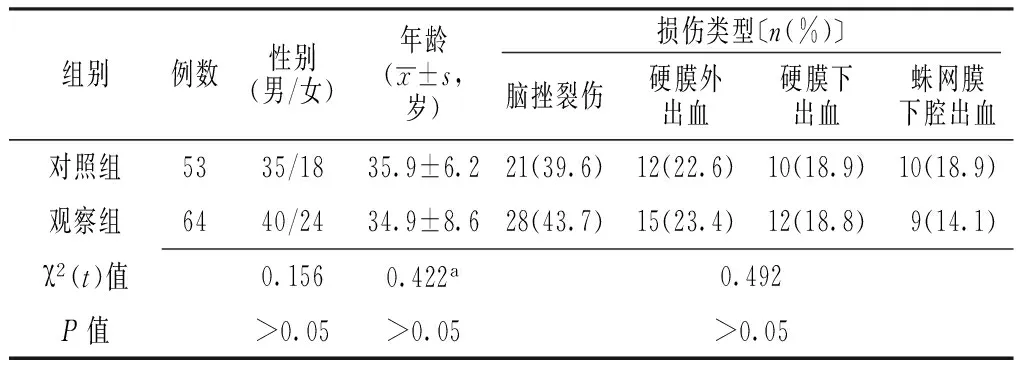
表1 两组患者一般资料比较
注:a为t值
2 结果
2.1 血肿面积 治疗前两组中脑挫裂伤、硬膜外出血、硬膜下出血、蛛网膜下腔出血患者血肿面积比较,差异无统计学意义(P>0.05);治疗后观察组中脑挫裂伤、硬膜下出血、蛛网膜下腔出血患者血肿面积分别小于对照组中脑挫裂伤、硬膜下出血、蛛网膜下腔出血患者,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05),但两组中硬膜外出血患者血肿面积比较,差异无统计学意义(P>0.05,见表2)。
2.2 LOTCA评分 治疗前两组患者定向评分、知觉评分、视组织运动评分、思维运作评分、注意与集中评分比较,差异无统计学意义(P>0.05);治疗后观察组患者定向评分、知觉评分、视组织运动评分、思维运作评分、注意与集中评分高于对照组,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05,见表3)。

表2 两组不同类型颅脑损伤患者治疗前后血肿面积比较
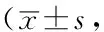
表3 两组患者治疗前后LOTCA评分比较分)
3 讨论
重型颅脑损伤是临床常见的急危重症,其会影响血-脑脊液屏障功能导致颅内压升高,造成脑水肿、坏死,进而引发微循环障碍、脑组织缺血缺氧,且随着病情进展可能发生脑疝,严重威胁患者的生命安全[6-7]。因此,及时、有效地纠正重型颅脑损伤患者脑组织缺血、缺氧可预防脑组织出现不可逆损伤。
研究表明,高压氧治疗重型颅脑损伤的临床效果较好[8-10]。高压氧治疗可通过提高重型颅脑损伤患者血氧张力及血氧含量、增加有效弥散距离而改善缺血、缺氧脑组织供血及微循环,促进毛细血管再生和侧支循环形成,进而发挥保护病灶区及周围神经元的作用[11];同时,重型颅脑损伤患者早期予以高压氧治疗,一方面可通过收缩脑血管、增强血管阻力、降低血管通透性而减轻脑水肿,另一方面可通过提高血液、脑组织及脑脊液氧分压而降低颅内压,从而切断脑缺氧-脑水肿-代谢障碍恶性循环,最大限度地促进脑组织功能恢复;高压氧治疗还能促进重型颅脑损伤患者脑神经干细胞释放,从而加速脑功能重组[12-16]。
本研究结果显示,治疗后观察组中脑挫裂伤、硬膜下出血、蛛网膜下腔出血患者的血肿面积小于对照组中脑失传裂伤、硬膜下出血、蛛网膜下腔出血患者,但两组中硬膜外出血患者的血肿面积间无差异,提示高压氧治疗可减少重型颅脑损伤患者的血肿面积。本研究利用CT对重型颅脑损伤患者高压氧治疗前后血肿面积进行评估,对早期诊断和提高重型颅脑损伤患者预后具有重要意义;且由于CT检查具有准确率较高、操作方便快捷等优点,故CT检查可能在诊断和评估重型颅脑损伤方面具有广泛应用前景。本研究结果还显示,观察组患者定向评分、知觉评分、视组织运动评分、思维运作评分、注意与集中评分高于对照组,与相关研究结果一致[17-18],提示高压氧治疗可改善重型颅脑损伤患者的认知功能。
综上所述,高压氧治疗重型颅脑损伤的临床效果确切,可有效缩小血肿面积,改善患者认知功能,值得临床推广应用。但本研究样本量较小,观察指标较少,结果结论仍有待扩大样本量、增加观察指标等进一步研究证实。
[1]XU Y,JI R,WEI R,et al.The Efficacy of Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy on Middle Cerebral Artery Occlusion in Animal Studies:A Meta-Analysis[J].PLoS One,2016,11(2):e0148324.DOI:10.1371/journal.pone.0148324.
[2]HADANNY A,EFRATI S.The efficacy and safety of hyperbaric oxygen therapy in traumatic brain injury[J].Expert Rev Neurother,2016,16(4):359-360.DOI:10.1586/14737175.2016.1157018.
[3]RELJIC T,MAHONY H,DJULBEGOVIC B,et al.Value of repeat head computed tomography after traumatic brain injury:systematic review and meta-analysis[J].J Neurotrauma,2014,31(1):78-98.DOI:10.1089/neu.2013.2873.
[4]MAIER D,NJOKU I Jr,SCHMUTZHARD E,et al.Traumatic brain injury in a rural and an urban Tanzanian hospital——a comparative,retrospective analysis based on computed tomography[J].World Neurosurg,2014,81(3/4):478-482.DOI:10.1016/j.wneu.2013.08.014.
[5]ALBERS C E,VON ALLMEN M,EVANGELOPOULOS D S,et al.What is the incidence of intracranial bleeding in patients with mild traumatic brain injury?A retrospective study in 3088 Canadian CT head rule patients[J].Biomed Res Int,2013:453978.DOI:10.1155/2013/453978.
[6]CHO K,YU J,RHEE H.Risk factors related to falling in stroke patients:a cross-sectional study[J].J Phys Ther Sci,2015,27(6):1751-1753.DOI:10.1589/jpts.27.1751.
[7]ALGHADIR A H,GABR S A,AL-EISA E S.Assessment of the effects of glutamic acid decarboxylase antibodies and trace elements on cognitive performance in older adults[J].Clin Interv Aging,2015,10:1901-1907.DOI:10.2147/CIA.S95974.
[8]WEE H Y,LIM S W,CHIO C C,et al.Hyperbaric oxygen effects on neuronal apoptosis associations in a traumatic brain injury rat model[J].J Surg Res,2015,197(2):382-389.DOI:10.1016/j.jss.2015.04.052.
[9]GUEDES V A,SONG S,PROVENZANO M,et al.Understanding the pathology and treatment of traumatic brain injury and posttraumatic stress disorder:a therapeutic role for hyperbaric oxygen therapy[J].Expert Rev Neurother,2016,16(1):61-70.DOI:10.1586/14737175.2016.1126180.
[10]MILLER R S,WEAVER L K,BAHRAINI N,et al.Effects of hyperbaric oxygen on symptoms and quality of life among service members with persistent postconcussion symptoms:a randomized clinical trial[J].JAMA Intern Med,2015,175(1):43-52.DOI:10.1001/jamainternmed.2014.5479.
[11]FU X,ZHU M,SUN X,et al.Hyperbaric oxygen treatment and enteral nutrition support with glutamine relieves traumatic brain injury in the rats[J].Int J Clin Exp Med,2014,7(12):5686-5690.
[12]ZHANG Y,YANG Y,TANG H,et al.Hyperbaric oxygen therapy ameliorates local brain metabolism,brain edema and inflammatory response in a blast-induced traumatic brain injury model in rabbits[J].Neurochem Res,2014,39(5):950-960.DOI:10.1007/s11064-014-1292-4.
[13]PELEG R K,FISHLEV G,BECHOR Y,et al.Effects of hyperbaric oxygen on blood glucose levels in patients with diabetes mellitus,stroke or traumatic brain injury and healthy volunteers:a prospective,crossover,controlled trial[J].Diving Hyperb Med,2013,43(4):218-221.
[14]KRAITSY K,UECAL M,GROSSAUER S,et al.Repetitive long-term hyperbaric oxygen treatment(HBOT)administered after experimental traumatic brain injury in rats induces significant remyelination and a recovery of sensorimotor function[J].PLoS One,2014,9(5):e97750.DOI:10.1371/journal.pone.0097750.
[15]EFRATI S,BEN-JACOB E.Reflections on the neurotherapeutic effects of hyperbaric oxygen[J].Expert Rev Neurother,2014,14(3):233-236.DOI:10.1586/14737175.2014.884928.
[16]YANG Y,ZHANG Y G,LIN G A,et al.The effects of different hyperbaric oxygen manipulations in rats after traumatic brain injury[J].Neurosci Lett,2014,563:38-43.DOI:10.1016/j.neulet.2014.01.002.
[17]HARCH P G.Hyperbaric oxygen therapy for post-concussion syndrome:contradictory conclusions from a study mischaracterized as sham-controlled[J].J Neurotrauma,2013,30(23):1995-1999.DOI:10.1089/neu.2012.2799.
[18]BLAKEMAN T C.Evidence for oxygen use in the hospitalized patient:is more really the enemy of good?[J].Respir Care,2013,58(10):1679-1693.DOI:10.4187/respcare.02677.
(本文编辑:李洁晨)
Clinical Effect of Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy on Severe Craniocerebral Injury
MADang-juan,KANGYan-zhi,WEIMing-jiong,LIUYu-feng
DepartmentofImageology,theSecondPeople′sHospitalofShaanxiProvince,Xi′an710005,ChinaCorrespondingauthor:LIUYu-feng,E-mail:511388645@qq.com
Objective The observe the clinical effect of hyperbaric oxygen therapy on severe craniocerebral injury.Methods A total of 146 patients with severe craniocerebral injury were selected in the Second People′s Hospital of Shaanxi Province from 2012 to 2015,thereinto 29 cases lost to follow-up,thus 117 cases enrolled into this study eventually,and they were divided into control group(n=53)and observation group(n=64)according to random number table.Patients of control group
conventional treatment,while patients of observation group received hyperbaric oxygen therapy based on conventional treatment;both groups continuously treated for 8 weeks.Hematoma area and LOTCA score were compared between the two groups before and after treatment.Results No statistically significant differences of hematoma area in patients with cerebral contusion and laceration,with extradural hemorrhage,with subdural hemorrhage or with subarachnoid hemorrhage between the groups before treatment(P>0.05);after treatment,hematoma area in patients with cerebral contusion and laceration,with subdural hemorrhage and with subarachnoid hemorrhage of observation group was statistically significantly smaller than that in patients with cerebral contusion and laceration,with subdural hemorrhage and with subarachnoid hemorrhage of control group(P<0.05),while no statistically significant differences of hematoma area in patients with extradural hemorrhage was found between the two groups(P>0.05).No statistically significant differences of orientation score,consciousness score,eyesight tissue movement score,mental operation score,attention and concentration score was found between the two groups before treatment(P>0.05),while orientation score,consciousness score,eyesight tissue movement score,mental operation score,attention and concentration score of observation group were statistically significantly higher than those of control group after treatment(P<0.05).Conclusion Hyperbaric oxygen therapy has certain clinical effect in treating severe craniocerebral injury,can effectively shrink the hematoma area and improve the cognitive function.
Craniocerebral trauma;Hyperbaric oxygenation;Computed tomography scan;Treatment outcome
刘雨峰,E-mail:511388645@qq.com
R 651
B
10.3969/j.issn.1008-5971.2017.07.017
2017-03-18;
2017-07-14)
710005陕西省西安市,陕西省第二人民医院影像科

