Optimization for Extraction Methods and Conditions of Polysaccharides from Trolliuschinensis
WANG Xiao-ru,DU Yun-guang,WANG Shu-hua,AN Fang
(1.Department of Pharmacy,Hebei North University,Zhangjiakou,Hebei 075000,China; 2.Graduate Faculty,Hebei North University,Zhangjiakou,Hebei 075000,China)
Optimization for Extraction Methods and Conditions of Polysaccharides fromTrolliuschinensis
WANG Xiao-ru1,DU Yun-guang1,WANG Shu-hua1,AN Fang2
(1.Department of Pharmacy,Hebei North University,Zhangjiakou,Hebei 075000,China; 2.Graduate Faculty,Hebei North University,Zhangjiakou,Hebei 075000,China)
Objective To determine the optimum extraction method and condition of polysaccharides fromTrolliuschinensis(TCP).Methods With the yield of TCP as index and water as solvent,reflux extraction,ultrasonic extraction and supercritical CO2extraction were employed to determine the efficient extraction method of TCP.Moreover,the conditions of reflux extraction were optimized by single factor test and orthogonal test.The content of polysaccharide was measured with phenol-sulfuric acid method.Results The data displayed that the crude polysaccharide (CPS) yield of regular reflux extraction was (11.7±0.12)%,superior to ultrasonic extraction and supercritical CO2extraction.The optimum conditions of reflux extraction were as follows:extraction temperature of 95 ℃,extraction time of 3 h and the liquid-solid ratio of 20∶1.Under these conditions,the polysaccharide yield was(1.45±0.03)%,which was well in close agreement with the predicted value.Conclusion Regular reflux extraction was regarded as the optimal extraction method of TCP.The optimum conditions of reflux extraction were as follows:extraction temperature of 95 ℃,extraction time of 3 h and the liquid-solid ratio of 20∶1.
Trolliuschinensis;polysaccharide;extraction;optimization
TrolliuschinensisBunge,a member ofRanunculaceae’s family,is a perennial herb and an endemic plant widely distributed in northern China[1].Its flowers,known as jinlianhua in China and including several kinds,were used to be as traditional Chinese medicine by Chinese people in folk.It has been reported that these flowers can bear anti-inflammatory,antibacterial,antioxidant and antiviral effects[2],mainly used to treat respiratory infections,pharyngitis,tonsillitis,and bronchitis clinically[3].Studies have shown that these flowers mainly contain flavonoids such as orientin and vitexin,polysaccharides,phenolic acids as well as alkaloids[4].Recently the studies of their effective constituents inTrolliuschinensisare more confined to flavonoids and phenolic acids due to their abundance.Nevertheless,the researches on polysaccharides are less reported.
With the development of molecular biology,people have gradually recognized that polysaccharides and their complex have extremely important biological functions.Some reports indicated that polysaccharides have close relationship with immunomodulation,the recognition and substances transportaion between cells,and the diagnosis and treatment of cancer and so on[5].To the best of our knowledge,there are many studies reporting that bioactive polysaccharides isolated from herbal plants have extensive sources and low toxic and side effect,with hypoglycemic,antioxidant,and antitumor activities[6].Moreover,some studies have shown that polysaccharides can evoke stronger humoral and cell-mediated immune responses[7-8].Thus,this attractive material can be used as pharmaceutical products or health-care food and has become a hotspot in life science research.
In recent years,no specific studies on the extraction of TCP have been carried out.We therefore specifically focused on the polysaccharide fraction.In order to fully utilize the TCP,efficient extraction methods and conditions are in great need.Though the different yields of polysaccharides were obtained from different extraction methods,the common progress was water extraction and alcohol precipitation[9].The extraction methods of polysaccharides are various currently,including conventional extraction[10](such as reflux extraction) and novel extraction techniques of enzyme-assisted extraction[11],ultrasonic-assisted extraction[12],microwave-assisted extraction[13]and supercritical fluid extraction[14].However,enzyme-assisted extraction is often used to acquire specific polysaccharides by specific enzymes and greatly influenced by temperature.In addition,the microwave-assisted extraction condition is not easy to control and may lead to the reduction of bioactivies or degradation of polysaccharides.Therefore,in this study,conventional reflux extraction,ultrasonic-assisted extraction and supercritical fluid extraction were employed to extract TCP to find the optimal one and the optimization of the best method was also investigated,which is efficient and significant for research and industrialized application of TCP.
1 Materials and methods
1.1 Materials and chemicals
The flowers ofTrolliuschinensiswere obtained from Guyuan (Zhangjiakou,Hebei Province,China) and authenticated by Professor Shulan MA from institute of materia medica of our school.Petroleum ether and acetone were bought from Tianjin Damao Chemical Reagent Factory,Tianjin,China.Phenol was produced from Shijiazhuang Organic Chemical Factory.Concentrated sulfuric acid and glucose were purchased from Tianjin Wenda Xigui Reagent Chemical Factory and Tianjin Fuchen Chemical Reagent Factory,respectively.
1.2 Pretreatment ofTrolliuschinensis
Trolliuschinensiswas washed adequately and dried to constant weight,then was homogenised in a blender and sieved through 40 mesh screen.The powder was successively degreased with petroleum ether at 40 ℃ and depigmented with acetone at 40 ℃,each for two times.Then it was treated twice with 80% ethanol (v/v) at 70 ℃ to remove monosaccharides,oligosaccharides and small molecule materials.Finally,the sample was centrifuged through a high-speed refrigerated centrifuger (Heraeu,Beckman Company,Germany) at 4 000 rpm for 20 min and the deposit was dried for 24 h at 60 ℃ to constant weight[15],sealed in glass bottle and kept at room temperature.1.3 Polysaccharide extraction ofTrolliuschinensis1.3.1 Conventional reflux extraction
Well-preparedTrolliuschinensis(100.0 g) weighing with an electronic scales (Acculab,Sartorius,Germany) was refluxingly extracted with distilled water (2.0 L) at 90 ℃ for twice and 2 h for each time.The whole extract was incorporated and filtered,then was concentrated to one-fifth of the initial volume by evaporation through a rotary evaporator (R-210D,Gongyi City Yingyu High-tech Apparatus Factory,Henan,China) at 45 ℃ under reduced pressure.The solution was precipitated with four volumes of 95% ethanol(v/v)[16].The CPS was obtained by centrifugation (4 000 rpm,20 min) and dried at 60 ℃ in vaccum through a vaccum-freeze drier (Thermo Fisher Scientific,USA),then the extraction yield was calculated with the following equation:
1.3.2 Ultrasonic Extraction
Deionised water (3.0 L) was added to 100.0 g of preparedTrolliuschinensisand stood for 2 h to fully moist,then extracted through a ultrasonic cleaner (WD-9415F,Liuyi Apparatus Factory,Beijing,China) in the power of 500 W,at 65 ℃ for twice and 25 min for each time.The extracting solution was disposed same to the conventional reflux extraction and then the extraction yield was calculated according to the method in section 1.3.1.
1.3.3 Supercritical CO2Extraction
PretreatedTrolliuschinensis(100.0 g) was put into extraction kettle of the supercritical CO2extractor (SFE-2,Applied Separations Inc.,USA) and extracted with 20% ethanol (v/v) as entrainer at 65 ℃,the pressure of 35 MPa and the flow rate of 0.5 mL·min-1for twice and 1 h for each time[17].Then the CPS was collected and the extraction yield was calculated.
1.3.4 The comparison of the three extraction methods
The CPS obtained fromTrolliuschinensisin different methods was compared by their appearance and extraction yield (Table 1),then the optical extraction method was selected.
1.4 Optimization for the conventional reflux extraction of TCP
1.4.1 Single factor experimental design
Previous investigation showed that the yield of polysaccharide is principally affected by extraction temperature,liquid-solid ratio and per extraction time[9].Consequently,the effect of extraction temperature (60,70,80,90 and 100 ℃,respectively),liquid-solid ratio (10∶1,15∶1,20∶1,25∶1 and 30∶1,respectively) and extraction time (1,1.5, 2,2.5 and 3 h,respectively) on the yield of polysaccharides were investigated by a single factor design as follows:one factor was changed while holding the other factors constant in each experiment.
1.4.1.1 Assay of different temperature on extraction yield of CTP
The choice of temperature is an important factor in the extraction process.To investigate the influence of the temperatures on the yield of CTP,we performed the extraction at different temperatures (60,70,80,90 and 100 ℃) for twice,with other conditions held constant ( liquid-solid ratio 20∶1 and extraction time 2 h) to select the optimal extraction temperature.
1.4.1.2 Assay of liquid-solid ratio on extraction yield of CTP
The extraction conditions were set as follows:extraction temperature 90 ℃ and extraction time 2 h.The yield of TCP was determined for two times by changes of different liquid-solid ratios (10∶1,15∶1,20∶1,25∶1,30∶1) to provide basis for the subsequent experiments.
1.4.1.3 Assay of extraction time on extraction yield of CTP
We extracted the polysaccharides for twice at different extraction time (1,1.5,2,2.5 and 3 h) and other conditions remained constant (liquid-solid ratio 20∶1 and extraction temperature 90 ℃).Thus,the extraction time could be selected by the comparison of extraction yield of polysaccharides.
1.4.2 Orthogonal experimental design
This experiment showed that several factors exhibit great influence on the extraction process from TCP. Based on the results of single factor experiment,the orthogonal array (3 factors and 3 levels) (Table 2 and 3) was carried out to improve the extraction yield of TCP,which could reduce number of experimental trials and learn more about the mutual influence between the factors.
1.5 The determination of polysaccharides content fromTrolliuschinensis
1.5.1 The preparation of standard curve
Accurately weigh 0.0500 g of glucose,which was dried to constant weight at 105 ℃,then made into standard solution of 1.0 mg·mL-1.Take different volumes (0.02,0.04,0.06,0.08,0.10 and 0.12 mL,respectively) of glucose standard solution precisely into volumetric flask and dilute to 1.0 mL with distilled water.After that,0.5 mL of 5% phenol solution and 2.5 mL of concentrated suifuric acid were successively added to the sample,mixed evenly and left to stand for 20 min at room temperature[18].Then the absorbance of the resulting solution was read at 490 nm against a corresponding blank with a UV-Vis Spectrophotometer (UV-3900,Hitachi,Japan).Finally,regression equation was obtained,the absorbance and the concentration of glucose asXandYaxis respectively,which wasY=0.0166X-0.0004,and the correlation coefficiency was 0.9998,showing a good linear relationship within the scope of 0.02~0.12 mg·mL-1.1.5.2 The determination of polysaccharides content
Weigh 10 mg of CPS sample,which was configured to the concentration of 1.0 mg·mL-1sample solution.Suck up 0.3 mL of the solution and the absorbance was measured same to the item of 1.5.1.According to the standard curve,we calculated the polysaccharides content of CPS sample,and then calculated the yield of polysaccharides with the following equation:
1.6 Statistical Analysis
Measurements were carried out in triplicate for all experiments.All the data were expressed as the mean of three replicate extractions.SPSS 16.0 software was used for statistical calculation and analysis,standard deviation(SD) were all below 0.15%.
2 Results
2.1 Comparisons of three extraction methods fromTrolliuschinensis
The results were shown in Table 1,which revealed that the CPS obtained fromTrolliuschinensisby the refluxing extraction and ultrasonic extraction were both tawny,in powder shape. However,the CPS by supercritical CO2extraction was white,in amorphous shape.Moreover,extraction yield of CPS from the reflux extraction was much higher than that of ultrasonic extraction or supercritical CO2extraction.Thus,we selected the refluxing extraction as the optimum method for extraction of TCP.
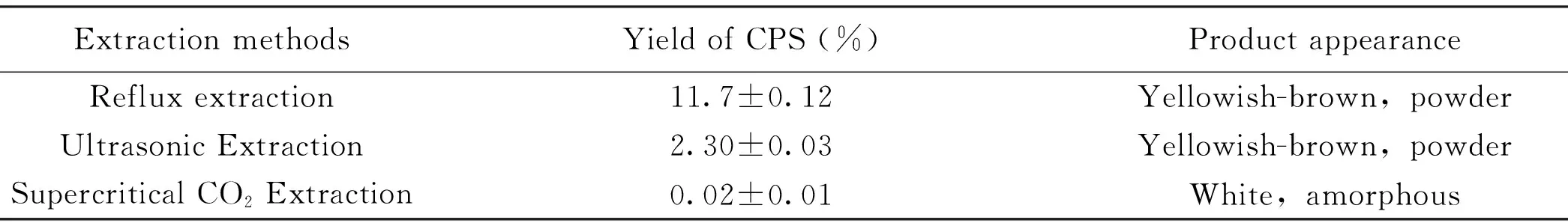
Table 1 Comparisons of three extraction methods

Fig 1 Effect of extraction temperature on polysaccharide yield
2.2 Optimization for the conventional reflux extraction of TCP
2.2.1 Effect of different temperature on the yield of TCP
The yield of TCP,as shown in Fig 1,reached a maximum at 90 ℃.On the whole,the yield increased apparently first and then declined when it surpassed the optimum temperature.Thereby,the refluxing temperature set around 90 ℃ would be optimum in this experiment.2.2.2 Effect of liquid-solid ratio on the yield of TCP
The increase of TCP yield was exhibited along with the increase of liquid-solid ratio from 10∶1 to 20∶1.When increasing to a certain extent,there was a little decline in the yield because of no increase in mass-transfer power (Fig 2).It was considered that the increase of water volume would prolong the solvent recycling time and raise the operation cost,the optimum liquid-solid ratio was considered to be 20∶1.

Fig 2 Effect of liquid-solid ratio on polysaccharide yield
2.2.3 Effect of extraction time on the yield of TCP
Fig 3 displayed that the yield of TCP increased obviously range from 1 h to 2 h.However,it almost remained unchanged within 2~3 h,explaining the TCP yield in this period has reached dissolution equilibrium.Therefore,2~3 h was selected for the further optimization experiments in this work.
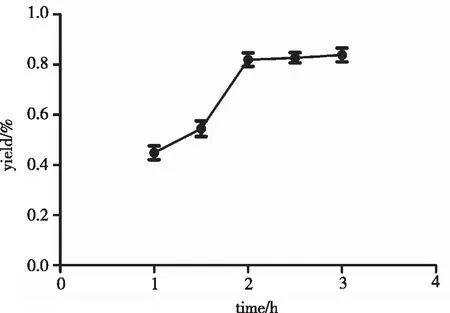
Fig 3 Effect of extraction time on polysaccharide yield
2.2.4 The determination of optimum extraction conditions of reflux extraction
As seen from Table 2,according to the R values,the effect of conditions on the TCP yield was as follows:A>C>B (temperature>liquid-solid ratio>time).The optimal combination conditions were A3C3B1,that is,the extract temperature of 95 ℃,the liquid-solid ratio of 20∶1 and the extract time of 3 h.
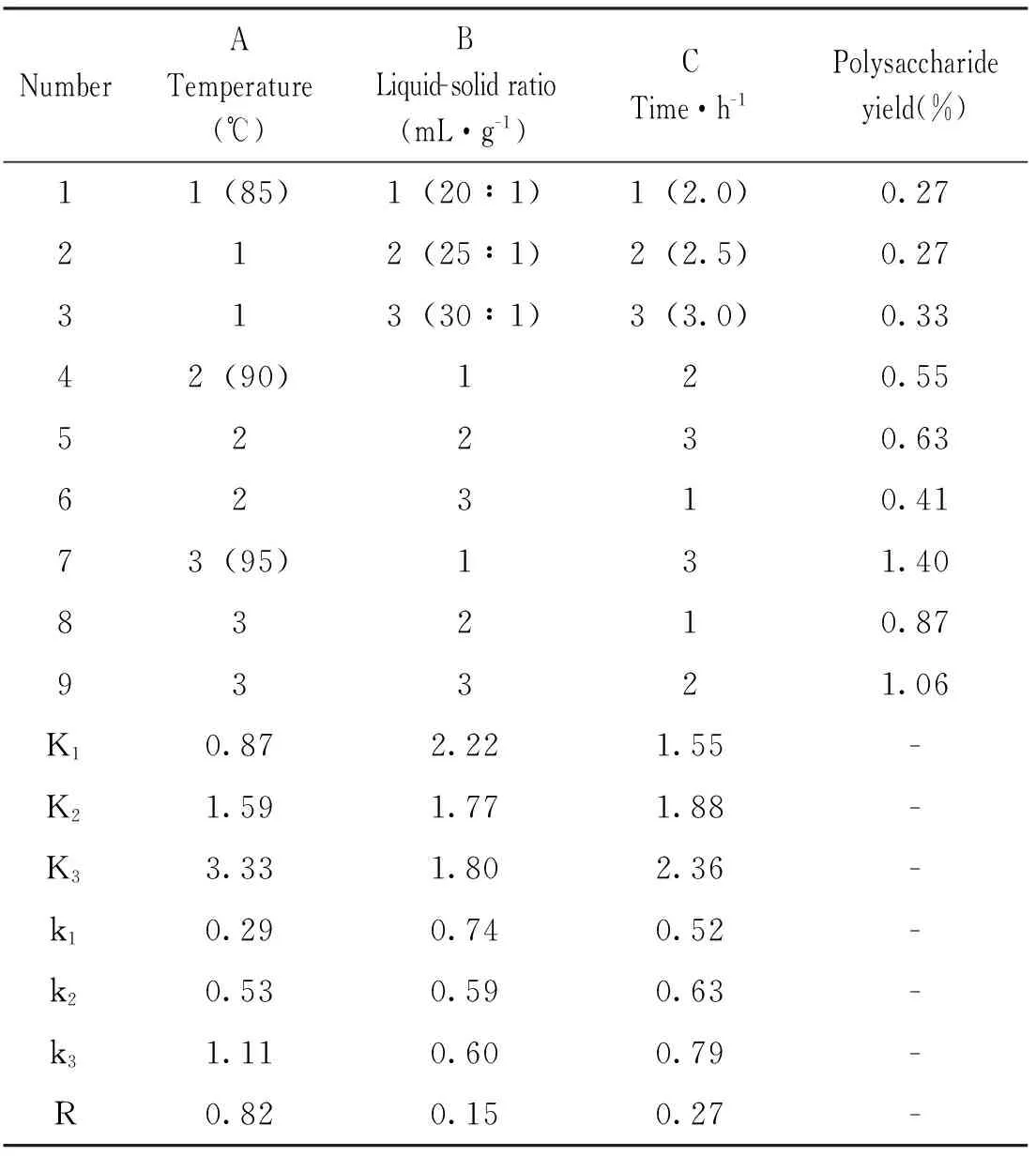
Table 2 Design and results of orthogonal test
Note:K:sum of yields of different levels;k:average yield of different levels;R:range
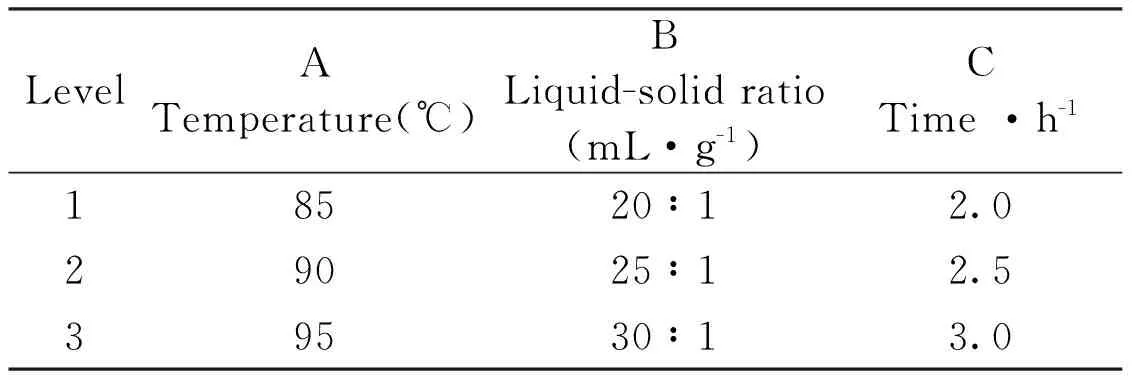
Table 3 Experimental factors and levels
2.2.5 Verification of predicted model
In order to verify whether the optimum conditions was reasonable,we extracted the polysaccharide fromTrolliuschinensison these conditions described above and determined the yield of TCP.The results indicated that the average of polysaccharide yield was maximum,which was (1.45±0.03)% (n=5),showing no significant difference from the predicted value.
3 Discussion
In general,the extraction of TCP is effected by many factors and the different yields would be obtained by different methods.Each method has its own advantages and disadvantages.In the present study,we adopted three extraction methods to obtain TCP.The experimental results demonstrated that the effect of different extraction methods on TCP yield was remarkable and the polysaccharides yield of conventional reflux extraction was the highest,which was regarded as the optical extraction method of TCP.Although reflux extraction was an original method,it is practical not only because of its simplicity,low investment cost and operability of long-time extraction in higher temperature,but also because of the accordance with the way of traditional medicine extraction[19-20].
The principle of ultrasonic extraction was using the acoustic cavitation generated by ultrasonic and diffusion through the cell walls,making the release of intracellular polysaccharides[21].Previous studies reported that ultrasonic extraction,a green and environmentally friendly technique,could facilitate the acoustic cavitation with short extraction time and non corrosive solvents,as well as higher polysaccharide yield[22-23].However,that was not the case in this study.It may be influenced by ultrasonic frequency or time and the difference of plant polysaccharide structures,which required further study.Moreover,it has been reported that ultrasonic extraction may lead to the degradation of polysaccharide[24].
Supercritical CO2extraction,a new-kind technology,takes advantage of the uniquely physical and chemical properties (such as low viscosity and large diffusion coefficient and dielectric constant) of supercritical fluid to achieve the solute separation[25].Studies have shown that supercritical CO2extraction reduced the solvent consumption and extraction time and increased the yield of phytochemicals[26-27].Nevertheless,this experiment displayed that the TCP yield through supercritical CO2extraction equipment by changing extraction pressure,temperature and the entrainer amount was little and the polysaccharide can hardly be extracted, which may be the reason that polysaccharide is a kind of macromolecular polyol compound and the structural difference of plant polysaccharide.Furthermore,supercritical fluid extraction technology is still in the stage of development and remains to be used in further research.
It is well recognized that the extract yield of polysaccharide is influenced by a variety of factors.However,increasing evidence displayed that extraction temperature,liquid-solid ratio and extraction time are the most principle and important factors in the extraction process[9,28].The choice of temperature is critical due to its effects on extraction efficiency.Selecting liquid-solid ratio is necessary,and large liquid-solid ratio would prolong the solvent recycling time and raise the operation cost.In the whole extract process,dissolution equilibrium would be reached and increasing extraction time can’t improve extraction efficiency.Therefore,in this study,we selected these three factors to provide basis for subsequent experiment.Our results in orthogonal array indicated that temperature is the major factor and greatly effected on the yield.Another factor is liquid-solid ratio or extract time,which is in consistent with previous study proposed by WANG et al[29].
4 Conclusion
In conclusion,this experiment exhibited that the optical method of TCP extraction was traditional reflux extraction.And orthogonal test displayed that the optimum extraction conditions of TCP were as follows:reflux extraction twice,extraction temperature of 95 ℃,liquid-solid ratio of 20∶1 and extraction time of 3 h.Under these conditions,the yield of TCP was (1.45±0.03)%,which was close to the predicted value.However,further studies are also necessary if someone still wants to increase the polysaccharide yield.
Acknowledgement
We thank Prof.Shu-lan MA at the institute of materia medica of Hebei North University,Hebei,China,for the help with the authentication ofTrolliuschinensis.
[1]LI J,QIN PZ,HAN X,et al.Evaluation of antioxidant and antibacterial properties of extracts fromTrolliuschinensisBunge[J].Eur Food Res Technol,2015,240(2):301-310.
[2]LI H Y,LIU Y.Research progress on the extraction,purification and pharmacological action of flavonoids inTrolliuschinensisBunge[J].Applied Mechanics and Materials,2013,295:283-286.
[3]WANG R F,YANG X W,MA C M.A bioactive alkaloid from the flowers ofTrolliuschinensis[J].Heterocycles,2004,63(8):1443-1448.
[4]QIN Y H,LIANG Y Z,REN D B,et al.Separation of phenolic acids and flavonoids fromTrolliuschinensisBunge by high speed counter-current chromatography[J].J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci,2015,1001:82-89.
[5]CHEN J C,TIAN S,SHU X Y,et al.Extraction,characterization and immunological activity of polysaccharides fromRhizomagastrodiae[J].Int J Mol Sci,2016,17:7.
[6]LAN G S,CHEN H X,WANG Z S,et al.Extraction ofPolygonatumodoratumpolysaccharides using response surface methodology and preparation of a compound beverage[J].Carbohydr Polym,2011,86(3):1175-1180.
[7]CHEN Y,WANG D,HU Y,et al.Astragalus polysaccharide and oxymatrine can synergistically improve the immune efficacy of Newcastle disease vaccine in chicken[J].Int J Biol Macromol,2010,46:425-428.
[8]LIU F X,SUN S,CUI Z Z.Analysis of immunological enhancement of immunosuppressed chickens by Chinese herbal extracts[J].J Ethnopharmacol,2010,127:251-256.
[9]QUAN Y,YANG S,WAN J,et al.Optimization for the extraction of polysaccharides fromNostoccommuneand its antioxidant and antibacterial activities[J].J Taiwan Inst Chem E,2015,52:14-21.
[10]GAO F,YU Y L,CHEN Y J.Extraction of polysaccharides fromCordycepsmilitarisby ethanol refluxing method[J].Adv Mater Res,2011,287:2003-2007.
[11]YIN X,YOU Q,JIANG Z.Optimization of enzyme-assisted extraction of polysaccharides fromTricholomamatsutakeby response surface methodology[J].Carbohydr Polym,2011,86:1358-1364.
[12]ZHU C P,ZHAI X C,LI L Q,et al.Response surface optimization of ultrasound-assisted polysaccharides extraction fromPomegranatepeel[J].Food Chem,2015,177:139-146.
[13]THIRUGNANASA K,SIVAKUMAR V,PRAKASH M J.Microwave-assisted extraction of polysaccharides from mulberry leaves[J].Int J Biol Macromol,2015,72:1-5.
[14]KATARZYNA P,GRAZYNA W K.Extraction of tocopherol-enriched oils fromQuinoaseeds by supercritical fluid extraction[J].Ind Crop prod,2015,63:41-47.
[15]REN H N.The research on the composition and content determination method fromCoastalglehniarootpolysaccharide and monosaccharide[D].Shenyang:Shenyang Pharm Univ,2008.
[16]LIU Q G.The process study of hot water extraction onpleurotucomucopiaepolysaccharide[J].J Hebei Agri Sci,2007,11:92-93.
[17]YU J P,CHANG X,LI W Y.The extraction and content determination of polysaccharide fromLoniceraChrysanthafruitafter the treatment with supercritical CO2[J].Southwest Chin J Agri Sci,2010,23:181-183.
[18]DONG Y M,TANG X W,ZHANG S J,et al.The optimization for the content determination condition and extraction process onAcanthopanaxgiraldiiHarms polysaccharide[J].Central South pharmacy,2006,4:86-88.
[19]SAMAVATI V.Polysaccharide extraction fromAbelmoschusesculentus:optimization by response surface methodology[J].Carbohydr Polym,2013,95:588-597.
[20]QIAN Z.Extraction,characterization and biological activities of polysaccharides fromAmomumvillosum[J].Carbohydr Polym,2014,101:432-434.
[21]CAI B,PAN J,WAN P,et al.Ultrasonic-assisted production of antioxidative polysaccharides fromCrassostreahongkongensis[J].Prep Biochem Biotech,2014,44(7):708-724.
[22]YAN Y J,LI X,WAN M J,et al.Effect of extraction methods on property and bioactivity of water-soluble polysaccharides fromAmomumvillosum[J].Carbohydr Polym,2015,117:632-635.
[23]BRIJESH K T.Ultrasound:a clean,green extraction technology[J].TrAC Trend Anal Chem,2015,71:100-109.
[24]LU R J.The methods of extraction and analysis from plant polysaccharides[J].Tianjin Pharmacy,2015,27:67-68.
[25]WU J,SHI S W,HU L N.The application of supercritical CO2extraction technology on plant chemical extraction[J].Food Res Dev,2014,35:52-56.
[26]PRAKASH MARAN J,PRIYA B.Supercritical fluid extraction of oil from muskmelon(Cucumismelo)seeds[J].J Taiwan Inst Chem E,2015,47:71-78.
[27]ASTRID R,DEBORA P,YI-HSU J,et al.Supercritical CO2extraction of phytochemical compounds fromMimosapudicaLinn[J].Chem Eng Commun,2015,202:1011-1017.
[28]JIN F,HE J,JIA L Y,et al.Optimizing conditions for the extraction of polysaccharides of white tea[J].Biotechnol Biotecl Eq,2015,29(5):921-925.
[29]WANG J,ZHAO Y M,GUO C Y,et al.Ultrasound-assisted extraction of total flavonoids fromInulahelenium[J].Pharmacognosy Magazine,2012,8(30):166.
[责任编辑:李蓟龙 英文编辑:刘彦哲]
R 284.2
A
WANG Xiao-ru(1991-),Female,Xingtai City in Hebei Province,Postgraduate.
AN Fang (1965-),Male,Master,Professor,Research Field:Study of Extract and Pharmacological Activity of Traditional Chinese Medicine.
10.3969/j.issn.1673-1492.2017.08.001
From Date:2017-02-27
Fund:Major Scientific Projects of Hebei North University (No.ZD1314),Innovation Fund Project of Graduate of Hebei Province (2015-203 and 2016-288)

