Mean Values of the Hardy Sum
WANG Xiao-ying,YUE Xia-xia
(School of Mathematics,Northwest University,Xi’an 710127,China)
Mean Values of the Hardy Sum
WANG Xiao-ying,YUE Xia-xia
(School of Mathematics,Northwest University,Xi’an 710127,China)
Let p≥5 be a prime.For any integer h,the Hardy sum is defined by
which is related to the classical Dedekind sum.The mean values of the Hardy sum in short intervals are studied by using the mean value theorems of Dirichlet L-functions.
Dedekind sum;Hardy sum;mean value;Dirichlet L-function
§1.Introduction
For integers h and k>0,the classical Dedekind sum is defined by

The sum S(h,k)plays an important role in the transformation theory of the Dedekind η function(see[1]and Chapter 3 of[2]for details).
In[3]Berndt studied the following Hardy sum
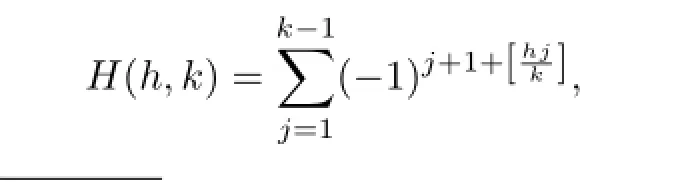
which is related to the classical Dedekind sum and obtained some arithmetic properties(see[4]). Sitaramachandrarao[5]and Pettet[6]expressed the Hardy sum in terms of the Dedekind sum as follows

For k=p being an odd prime,Zhang and Yi[7]studied the 2m-th power mean of H(h,p) and proved the following formula
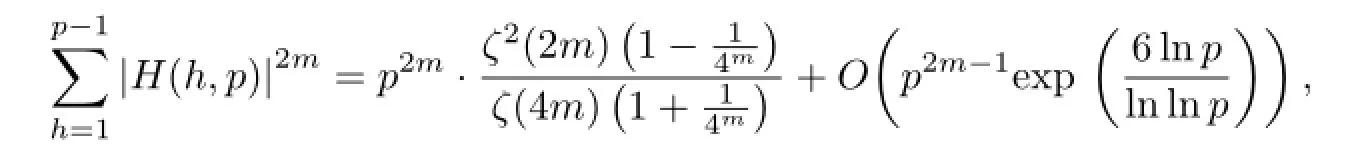
where m is a positive integer and ζ(s)is the Riemann zeta function.
Xu and Zhang[8],studied the mean values of the Hardy sums in short intervals and showed some asymptotic formula.
Proposition 1.1Let p≥5 be a prime and let b denote the multiplicative inverse of b modulo p.We have

where ε is any fixed positive number.
By using the ideas of[8],Liu[9]also studied the mean values of the Hardy sums in short intervals.
Proposition 1.2Let p≥5 be a prime.Then

We continue the study on the mean values of the Hardy sums and give some formulae.Our main results are the following
Theorem 1.1Let p≥5 be a prime.We have


§2.Identities Involving Certain Dirichlet Series


Then we have

ProofNoting that r(n)is a multiplicative function,we get

It is easy to show that

From Euler product formula,we can get
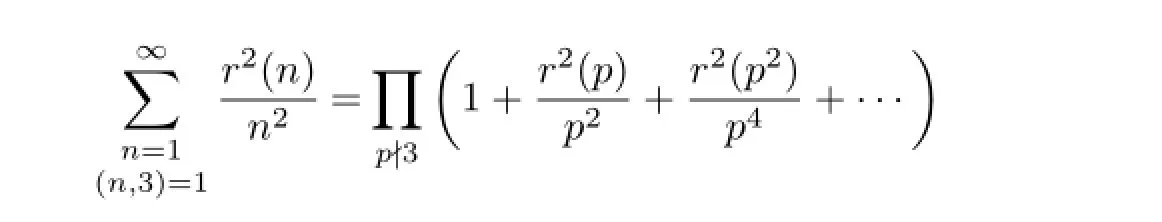
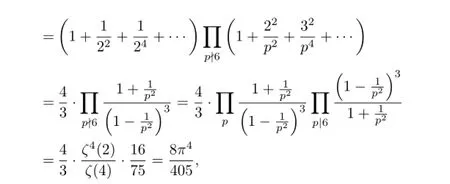

Therefore
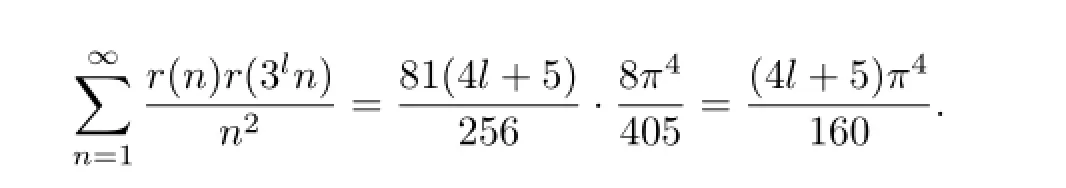
This proves(2.1).
Similarly we have


This proves(2.2).
By the Euler product formula we also get


This completes the proof of(2.3).
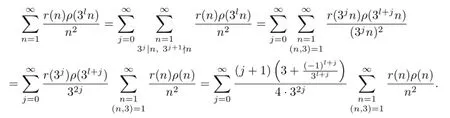
It is not hard to show that

Therefore

This proves(2.4).
Similarly we have
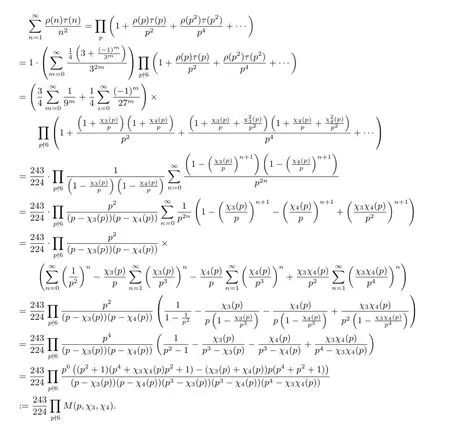
It is not hard to show that


This completes the proof of(2.5).
§3.Mean Values of the Dirichlet L-functions
In this section,we shall prove some mean values of the Dirichlet L-functions,which will be used to prove Theorem 1.1.
Theorem 3.1 Let p≥5 be a prime and let k and l be fixed non-negative integers.Then we have

all odd Dirichlet characters modulo p.
Proof Let N be an integer with p≤N<p4.By Abel’s identity we have


From the P´olya-Vinogradov inequality we get

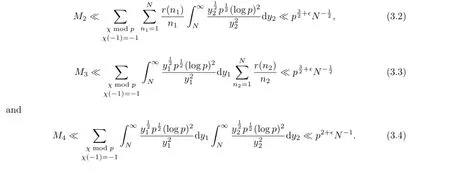
So we haveNow from(3.1)~(3.4)and the orthogonality relations for characters we get

First we consider M11.We have

It is not hard to show that
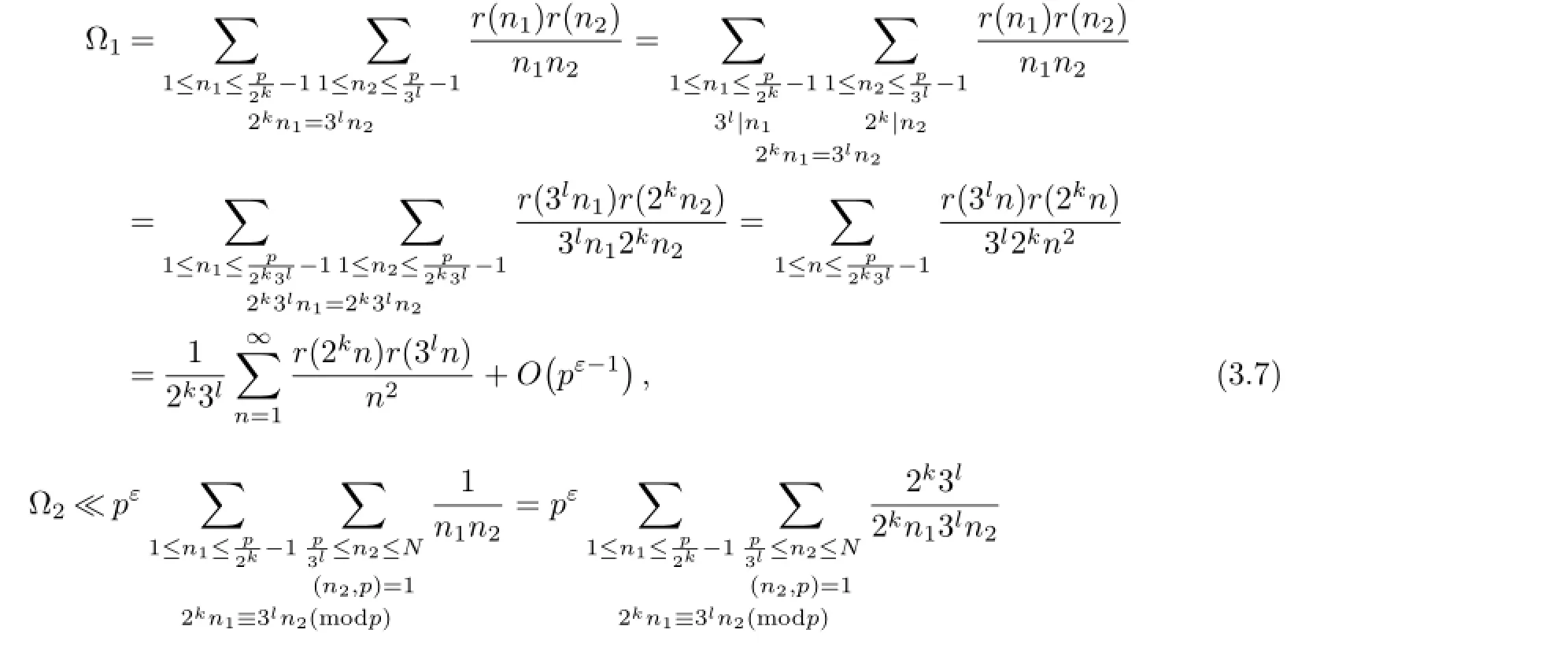

Then from(3.6)~(3.10)we have

Similarly we can get

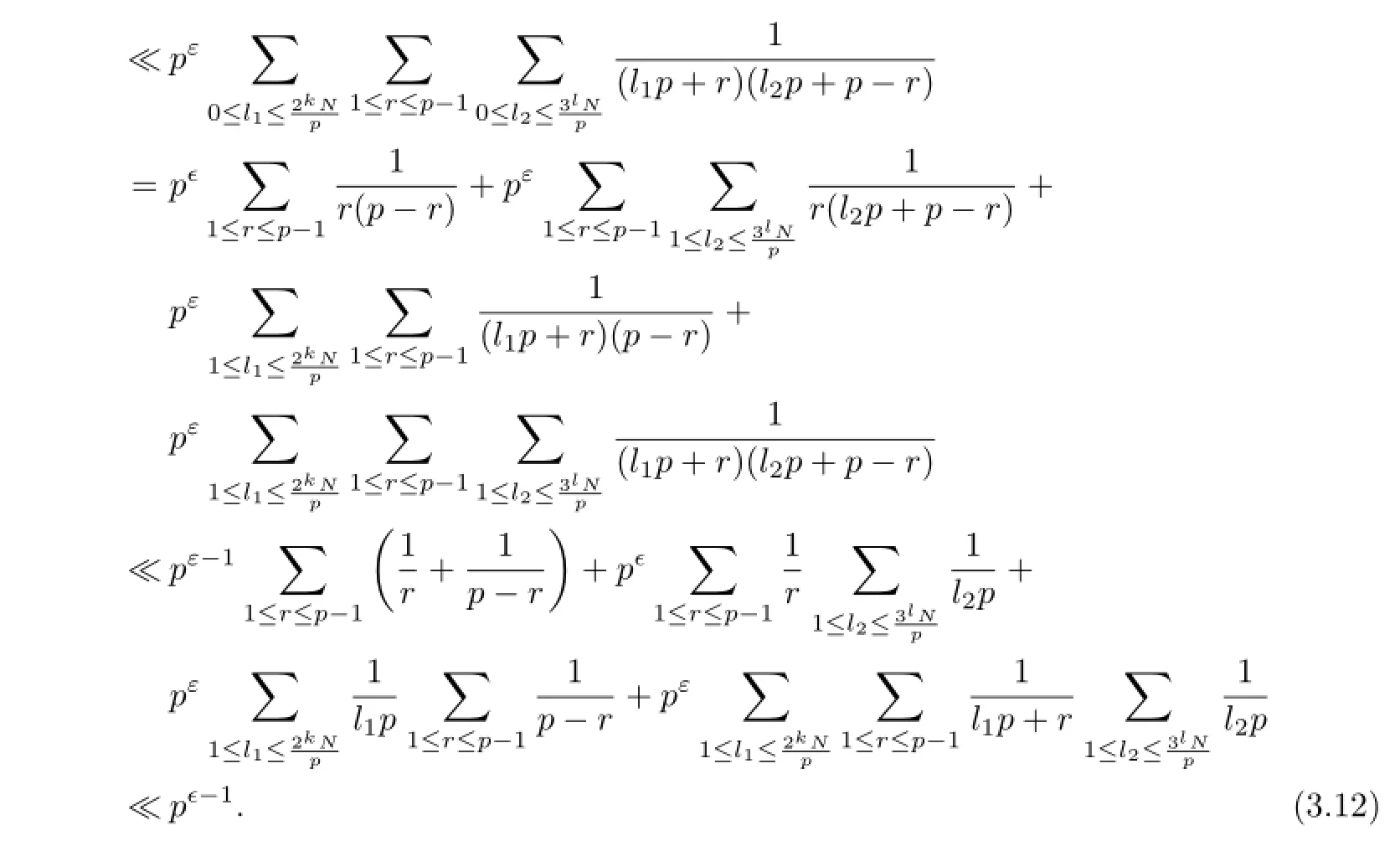
Now taking N=p3and combining(3.5),(3.11)~(3.12),we have

Note that r(2kn)=r(n).Thus from Theorem 2.1 we immediately get

Similarly we have

Theorem 3.2Let p≥5 be a prime and let k and l be fixed non-negative integers. Suppose that χ3is the non-principal character modulo 3 and χ4is the non-principal character modulo 4.Then we have


Proof Note that
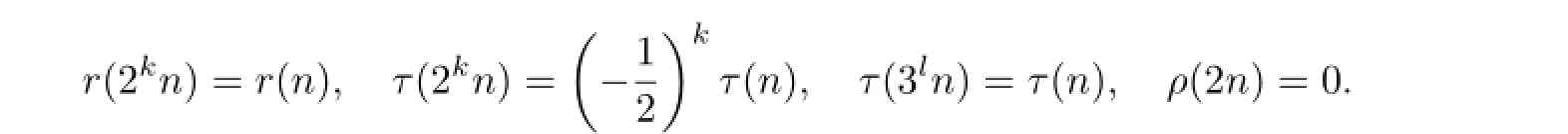
Thus from Theorem 2.1 and the methods of Theorem 3.1,we have


Theorem 3.3Let p≥5 be a prime and let k>0 be fixed integer.Then we have
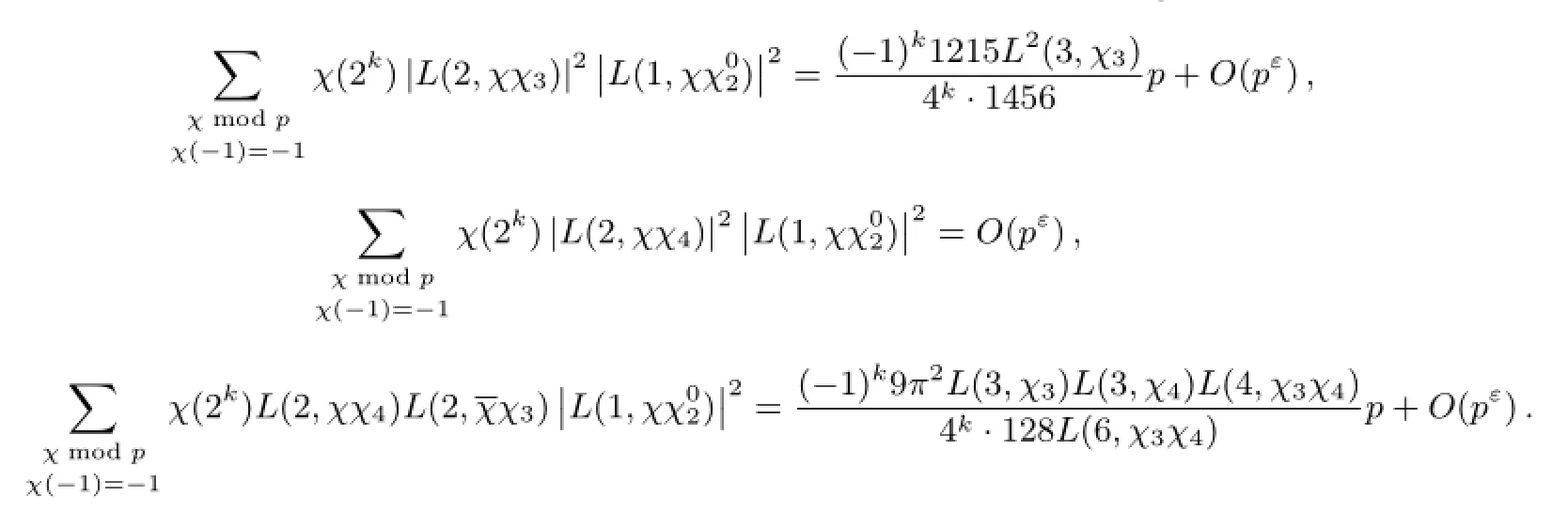
ProofNote that

Thus from Theorem 2.1 and the methods of Theorem 3.1,we have
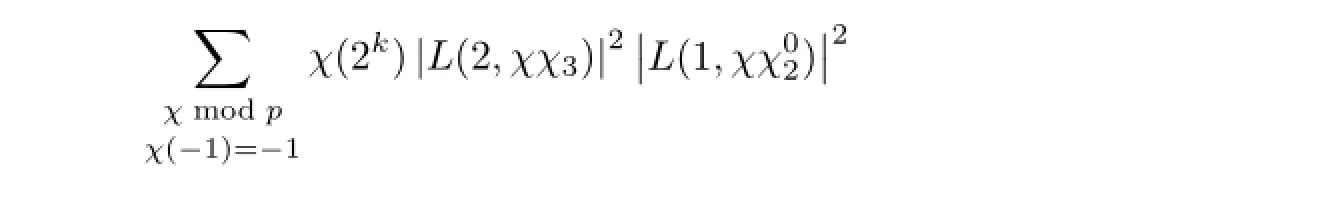

§4.Mean Values of the Homogeneous Dedekind Sums
Let q>3 be an integer and let χ be a Dirichlet character modulo q.The generalized Bernoulli numbers Bn,χare defined by

Let r be a positive integer prime to q and let k≥0 be an integer.By(6)of[10]and(2.12) of[11],we have
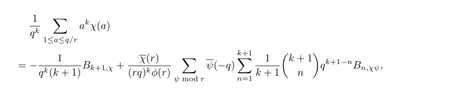
By using the above formula Liu[12]showed the following Lemma.
Lemma 4.1Let χ be a primitive character modulo q>3.Then

On the other hand,let p be a prime and a be a positive integer with(a,p)=1.By[13]we know that
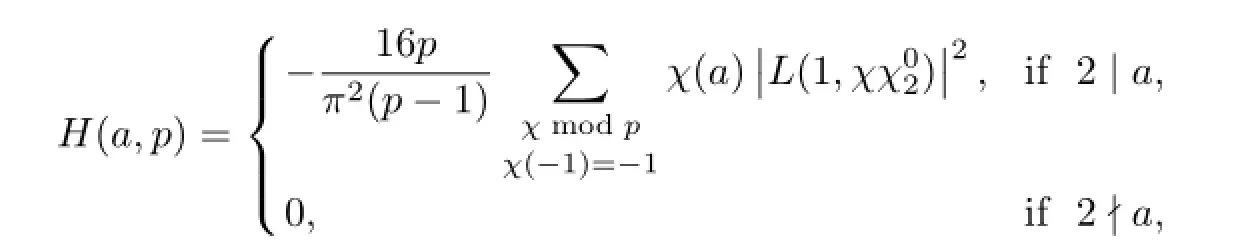

From Lemma 4.1 we have XX


Similarly we get


This proves Theorem 1.1.
[1]RADEMACHER H,GROSSWALD E.Dedekind Sums[M].Washington:Carus Mathematical Monographs, 1972.
[2]APOSTOL T M.Modular Functions and Dirichlet Series in Number Theory[M].New York:Springer-Verlag, 1976.
[3]BERNDT B C.Analytic Eisenstein series,theta-functions,and series relations in the spirit of Ramanujan[J]. Journal F¨ur Die Reine Und Angewandte Mathematik,1978,303/304:332-365.
[4]BERNDT B C,GOLDBERG L A.Analytic properties of arithmetic sums arising in the theory of the classical theta-functions[J].SIAM Journal on Mathematical Analysis,1984,15(1):143-150.
[5]SITARAMACHANDRARAO R.Dedekind and Hardy sums[J].Acta Arithmetica,1987,48(4):325-340.
[6]PETTET M R,SITARAMACHANDRARAO R.Three-Term relations for Hardy sums[J].Journal of Number Theory,1987,25(3):328-339.
[7]ZHANG Wen-peng,YI Yuan.On the 2m-th power mean of certain Hardy sums[J].Soochow Journal of Mathematics,2000,26(1):73-84.
[8]XU Zhe-feng,ZHANG Wen-peng.The mean value of Hardy sums over short intervals[J].Proceedings of the Royal Society of Edinburgh:Section a Mathematics,2007,137(4):885-894.
[9]LIU Wei-xia.Mean value of Hardy sums over short intervals[J].Acta Mathematica Academiae Paedagogicae Ny´ıregyh´aziensis New Series,2012,28(1):1-11.
[10]SZMIDT J,URBANOWICZ J,ZAGIER D.Congruences among generalized Bernoulli numbers[J].Acta Arithmetica,1995,71(3):273-278.
[11]KANEMITSU S,LI Hai-long,WANG Nian-liang.Weighted short-interval character sums[J].Proceedings of the American Mathematical Society,2011,139(5):1521-1532.
[12]LIU Hua-ning.On the mean values of Dirichlet L-functions[J].Journal of Number Theory,2015,147: 172-183.
[13]SCHINZEL A,URBANOWICZ J,VAN WAMELEN P.Class numbers and short sums of Kronecker symbols[J].Journal of Number Theory,1999,78(1):62-84.
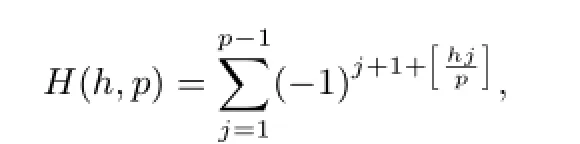
tion:11F20
:A
1002–0462(2017)01–0016–18
date:2015-11-06
Supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China(11571277);Supported by the Science and Technology Program of Shaanxi Province(2016GY-077)
Biography:WANG Xiao-ying(1964-),female,native of Changwu,Shaanxi,a professor of Northwest University,Ph.D.,engages in analytic number theory.
CLC number:O156.4
 Chinese Quarterly Journal of Mathematics2017年1期
Chinese Quarterly Journal of Mathematics2017年1期
- Chinese Quarterly Journal of Mathematics的其它文章
- A Generalized Schwarz Lemma
- Existence of Positive Solutions for Eigenvalue Problems of Fourth-order Elastic Beam Equations
- The Generalization on Inequalities of Hermite-Hadamard’s Integration
- Lvy-Prohorov Metric on the Measure Space
- Existence and Uniqueness of Solutions to Singular Higher Order Two-point BVPs on Time Scales
- The Translational Hull of Strongly Inverse Wrpp Semigroups
