苯溴马隆与非布司他在治疗2型糖尿病伴高尿酸血症的获益及安全性
商雪莹,邓 霖,宋雨凌,韩玲玲
苯溴马隆与非布司他在治疗2型糖尿病伴高尿酸血症的获益及安全性
商雪莹*,邓 霖,宋雨凌,韩玲玲
目的 评价苯溴马隆与非布司他在治疗2型糖尿病伴高尿酸血症的获益及安全性。方法 将85例已确诊的2型糖尿病伴尿酸升高的患者随机分为苯溴马隆组(A组,44例)和非布司他组(B组,41例)。两组均给予饮食控制、口服降糖药和(或)胰岛素治疗,A组给予苯溴马隆50 mg/d口服,B组给予非布司他40 mg/d口服,疗程为3个月。结果 与苯溴马隆比较,非布司他能够更快、更有效地降低血尿酸水平(P<0.05),但最终达标率比较差异无统计学意义(P>0.05)。两组均出现不同程度的不良反应,B组痛风发作率较高,而A组发生其他不良反应较多。治疗后两组患者HbA1c均改善(P<0.05),两组比较差异无统计学意义(P>0.05)。治疗前、后两组空腹C肽水平比较差异无统计学意义(P>0.05)。治疗3个月后,A组患者120分C肽水平得到改善(P<0.05),但非布司他组未见明显改善(P>0.05)。结论 在2型糖尿病合并高尿酸血症的患者中,应用非布司他及苯溴马隆治疗均能有效降低血尿酸水平,改善患者血糖。苯溴马隆能改善餐后C肽水平。
苯溴马隆;非布司他;2型糖尿病;高尿酸血症
0 引言
随着人们生活水平的提高及饮食结构的改变,高尿酸血症呈现高流行、年轻化的趋势已得到专家的共识[1]。血尿酸升高作为2型糖尿病发生发展的独立危险因素,在糖尿病的治疗过程中越来越得到重视[2]。相关荟萃分析显示,尿酸每升高1 mg/dL,糖尿病发生的相对危险度增加1.17倍[3]。有研究证实,血尿酸增高能够显著增加糖尿病视网膜病变、糖尿病肾病等糖尿病并发症的风险[4]。因此,在2型糖尿病患者中,降尿酸治疗越来越得到重视。苯溴马隆、非布司他作为2种通过不同途径降尿酸的药物,现广泛应用于临床降尿酸治疗[1]。但尚无研究评估两者在伴尿酸增高的2型糖尿病患者中的获益及安全性,故本文对此进行了研究。
1 资料与方法
1.1 受试对象 选择2015年6月至2016年4月于我院就诊的符合WHO 2型糖尿病诊断标准的糖尿病患者85例。年龄≥18岁,性别、病程长短均不限,血糖控制尚可(空腹4.4~8 mmol/L,餐后6~10 mmol/L),存在血尿酸升高(正常嘌呤饮食状态下,非同日2次空腹血尿酸水平:男性>420 μmol/L,女性>360 μmol/L),并未系统降尿酸治疗,实验前半年未应用影响尿酸代谢药物,如氢氯噻嗪、呋噻米、吡嗪酰胺、小剂量阿司匹林等。排除人群:重度肝肾功能不全、存在不稳定的心脏疾病患者、血液系统疾病、妊娠及哺乳期妇女。
1.2 方法 本实验为随机、双盲、对照研究。将符合试验标准并且获得知情同意后的患者,通过计算机编码随机分为苯溴马隆组(A组)及非布司他组(B组)。A组给予苯溴马隆50 mg/d 口服,B组给予非布司他40 mg/d 口服,疗程为3个月。
1.3 评价指标 入组后均对患者行糖尿病及高尿酸血症教育,并嘱患者低嘌呤糖尿病饮食。原降糖方案不变。每月对患者进行1次评估,评估关节疼痛情况,记录血压、心率、血常规、血尿酸水平、肝肾功能,在入组及3个月结束时,除检测上述指标外,加测HbA1c、空腹及餐后2 h C肽。
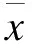
2 结果
2.1 基础情况比较 纳入100例患者,其中15例由于依从性不佳未完成3个月的治疗。最终A组完成44例,B组完成41例。两组患者的平均年龄、性别比例、BMI、高血压例数、血脂异常例数、血尿酸、HbA1c、C肽比较差异均无统计学意义(P>0.05),具有可比性。见表1。
2.2 两种药物的降尿酸效果比较 根据痛风指南及专家共识,将尿酸达标水平设定为<360 μmol/L。治疗3个月后,A组、B组患者的血尿酸控制情况达标率分别为86.4%、95%。由图1可见,B组患者达标率的上升速度快于A组。由图2可见,两种药物均能够有效地降低血尿酸浓度,并且A组每个月的平均尿酸水平略高于B组(P>0.05)。
2.3 不良事件发生率 本实验所用2种药物均存在不同程度的不良反应。痛风发作时,在予以患者加用止痛药物的同时,并未停止降尿酸药物治疗。在治疗中,A组退出6例,2例因不能耐受胃肠道反应,4例因严重的肝功能异常,其余患者不良反应均为轻度,继续治疗至3个月;B组中有9例中途退出治疗,均为不能耐受痛风发作,其余患者在加用止痛药物的基础上继续以原方案治疗。见表2。
2.4 对2型糖尿病的影响 治疗3个月后,两组患者HbA1c比较差异无统计学意义(P>0.05);A组、B组患者的HbA1c均有改善(P<0.05)。治疗前、后两组患者的0分C肽水平比较差异无统计学意义(P>0.05)。治疗后,A组120分C肽有所改善(P<0.05),但B组120分C肽水平与治疗前比较差异无统计学意义(P>0.05)。见表3。
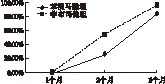
图1 两组尿酸达标率比较
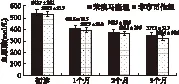
图2 两组患者血尿酸水平比较表1 两组一般资料比较(例)
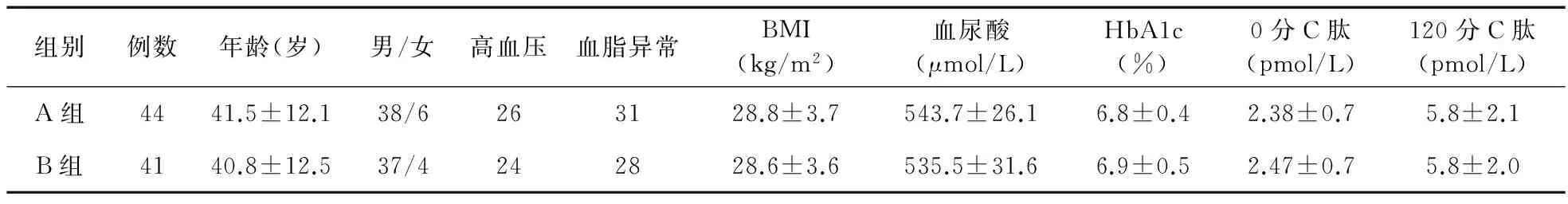
组别例数年龄(岁)男/女高血压血脂异常BMI(kg/m2)血尿酸(μmol/L)HbA1c(%)0分C肽(pmol/L)120分C肽(pmol/L)A组4441.5±12.138/6263128.8±3.7543.7±26.16.8±0.42.38±0.75.8±2.1B组4140.8±12.537/4242828.6±3.6535.5±31.66.9±0.52.47±0.75.8±2.0
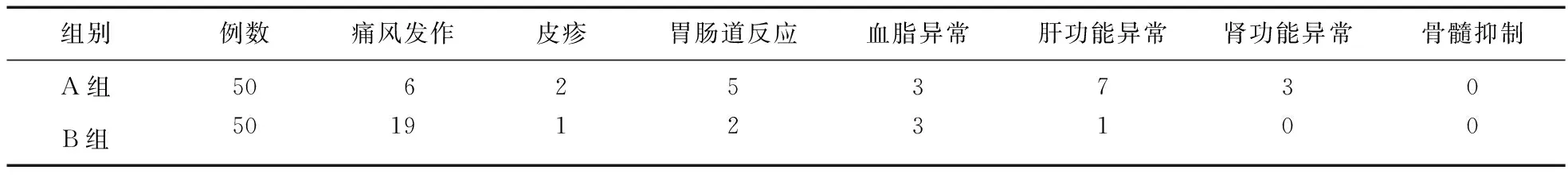
表2 两组患者不良反应比较(例)

表3 两组糖化及C肽水平比较
3 讨论
尿酸为体内嘌呤分解代谢终产物,主要由黄嘌呤和次黄嘌呤在黄嘌呤氧化酶催化下生成[5]。目前研究显示,尿酸可能通过多种机制影响患者血糖。已有报道,PDK2基因rs2728109不同基因型携带者血糖水平有明显差异,尿酸相关基因SFl rs606458与2型糖尿病不相关,SLC2A9 rsll722228与2 h血糖、2 h胰岛素和胰岛素分泌相关[6-7]。其次,有研究显示,尿酸是与胰岛素抵抗密切相关的独立危险因子,甚至认为其可以作为评判胰岛素抵抗的标志物之一[8]。并且尿酸可通过多种氧化应激通路影响胰岛B细胞的增殖/凋亡[9-10]。非布司他是一种通过抑制尿酸合成而降尿酸的药物,其作为一种非嘌呤类黄嘌呤氧化酶选择性抑制剂,常规治疗剂量下不会抑制其他参与嘌呤和嘧啶合成与代谢的酶[11]。对于轻中度肾功能不全的患者,该药物无须减量,并有研究显示其能够阻止肾功能的进一步下降[12-13]。苯溴马隆作为一种苯并呋喃衍生物,在肾脏近曲小管进行尿酸-阴离子有效且可逆性的交换,从而阻断肾小管对尿酸的重吸收,降低血尿酸。已有动物实验研究显示,苯溴马隆能够通过抑制脂肪结合蛋白4降低血糖水平[14],并且具有纠正糖负荷或胰岛素负荷下血糖的异常[15]。
本研究显示,在2型糖尿病患者中,无论是苯溴马隆或非布司他均能够有效降低血尿酸水平,并且非布司他能够更快更有效地降低血尿酸;并且两种药物均未出现严重的不良反应,但非布司他组出现痛风发作的例数较多,苯溴马隆组其他不良反应,如皮疹、胃肠道反应、肝肾功能异常的例数更多;两种药物均能改善患者HbA1c,且两组无显著差异;苯溴马龙能够改善120分C肽水平,但非布司他组120分C肽治疗前后无显著差异。在2型糖尿病合并尿酸升高的患者中,应用非布司他及苯溴马隆均能有效地降低尿酸,并改善血糖情况。但苯溴马隆能改善餐后C肽水平。因此,2型糖尿病伴尿酸升高的患者应用苯溴马隆降尿酸是否更合适,仍需进一步研究。
[1] 中华医学会内分泌学分会.高尿酸血症和痛风治疗的中国专家共识[J].中华内分泌代谢杂志,2013,29(11):913-920.
[2] Wang T,Bi Y,Xu M,et al.Serum uric acid associates with the incidence of type 2 diabetes in a prospective cohort of middle-aged and elderly Chinese[J].Endocrine,2011,40:109-116.
[3] Kodama S,Saito K,Yachi Y,et al.Association between serum uric acid and development of type 2 diabetes[J].Diabetes Care,2009,32(9):1737-1742.
[4] Chuengsamarn S,Rattanamongkolgul S,Jirawatnotai S.Association between serum uric acid level and microalbuminuria to chronic vascular complications in Thai patients with type 2 diabetes[J].J Diabetes Complications,2014,28(2):124-129.
[5] Huang J,Wang S,Zhu M,et al.Effects of genistein,apigenin,quercetin,rtin and astilbin on serum uric acid levels and xanthine oxidase activities in normal and hyperuric emicmice[J].Food Chem Toxicol,2001,49(9):1943-1947.
[6] Ren YC,Jin TB,Sun XD,et al.PDK2 and ABCG2 genes polymorphisms are correlated with blood glucose levels and uric acid in Tibetan gout patients[J].Genet Mol Res,2016,15(1).
[7] Sun X,Zhang R,Jiang F,et al.Common variants related to serum uric acid concentrations are associated with glucose metabolism and insulin secretion in a Chinese population[J].PLoS One,2015,10(1):e0116714.
[8] Osgood K,Krakoff J,Thearle M.Serum uric acid predicts both current and future components of the metabolic syndrome[J].Metab Syndr Relat Disord,2013,11(3):157-162.
[9] Jia L,Xing J,Ding Y,et al.Hyperuricemia causes pancreatic β-cell death and dysfunction through NF-κB signaling pathway[J].PLoS One,2013,8(10):e78284.
[10]Zhang Y,Yamamoto T,Hisatome I,et al.Uric acid induces oxidative stress and growth inhibition by activating adenosine monophosphate activated protein kinase and extracellular signal regulated kinase signal pathways in pancreatic B cells[J].Mol Cell Endocrinol,2013,375(1-2):8906.
[11]Khanna D,Khanna PP,Fitzgerald JD,et al.2012 American College of Rheumatology guidelines for management of gout.Part 2:therapy and antiinflammatory prophylaxis of acute gouty arthritis[J].Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken),2012,64(10):1447-1461.
[12]Hosoya T,Tatsuo H,Ohno I,et al.A repeated oral administration study of febuxostat (TMX-67),a non-purine-selective inhibitor of xanthine oxidase,in patients with impaired renal function in Japan:pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic study[J].J Clin Rheumatol,2011,17(4 Suppl 2):S27-S34.
[13]Whelton A,MacDonald PA,Chefo S,et al.Preservation of renal function during gout treatment with febuxostat:a quantitative study[J].Postgrad Med,2013,125(1):106-114.
[14]Cai HY,Wang T,Zhao JC,et al.Benzbromarone,an old uricosuric drug,inhibits human fatty acid binding protein 4 in vitro and lowers the blood glucose level in db/db mice[J].Acta Pharmacol Sin,2013,34(11):1397-1402.
[15]万盟,张倩,杨小红,等.别嘌醇与苯溴马隆对高尿酸小鼠糖代谢的影响[J].中国医药导报,2014,11(25):18-21.
Benefit and safety of benzbromarone and febuxostat in the treatment of type 2 diabetes with hyperuricemia
SHANG Xue-ying*,DENG Lin,SONG Yu-ling,HAN Ling-ling
(Department of Endocrinology,the 4th Affiliated Hospital of China Medical University,Shenyang 110032,China)
Objective To evaluate the benefit and safety of benzbromarone and febuxostat in the treatment of type 2 diabetes with hyperuricemia.Methods Totally 85 patients who had been diagnosed with type 2 diabetes with hyperuricemia were divided into benzbromarone group (group A,n=44) and febuxostat group (group B,n=41).Both groups received diet control,oral hypoglycemic agents and (or) insulin therapy.Patients in group A took benzbromarone (50 mg/d) orally,and the patients in group B took febuxostat (40 mg/d) orally for 3 months.Results Compared with benzbromarone,febuxosta could reduce the uric acid levels more quickly and effectively (P<0.05),but there was no significant difference in the eventual success rates between the two groups (P>0.05).Both groups had adverse reactions,group B had higher rate of gout,while group A had higher rate of other adverse reactions.After treatments,the HbA1c in both groups was improved (P<0.05),and there was no significant difference between the two groups (P>0.05).There was no significant difference in fasting C-peptide levels between the two groups before and after treatment (P>0.05).The 120-min C-peptide levels was improved in group A at 3 months after treatment (P<0.05),but there was no significant difference in group B (P>0.05).Conclusion Both febuxostat and benzbromarone can effectively reduce the blood uric acid level of the patients of type 2 diabetes with hyperuricemia,and improve the blood glucose level.Benzbromarone can improve the postprandial C-peptide levels.
Benzbromarone;Febuxostat;Type 2 diabetes;Hyperuricemia
2016-08-26
中国医科大学附属第四医院内分泌科,沈阳 110032
*通信作者
10.14053/j.cnki.ppcr.201704010

