血清炎性生物学指标在支气管哮喘患者病情评估中的应用价值
朱天吉++++++张卿

[摘要] 目的 探讨血清炎性生物学指标在支气管哮喘患者中的应用价值。 方法 选择2015年1月~2016年1月内蒙古医科大学附属医院收治的急性发作期支气管哮喘患者50例(急性期组)、缓解期支气管哮喘患者50例(缓解期组)和健康成人50例(对照组)。比较三组患者免疫球蛋白E(IgE)、白细胞介素(IL)-37、IL-25、IL-27和嗜酸性粒细胞阳离子蛋白(ECP)的水平差异,并分析其与第1秒用力呼吸容积(FEV1)和呼气峰流速(PEF)的关联性。 结果 与对照组或缓解期组比较,急性期组患者IgE、IL-25、IL-27和ECP均显著增高,IL-37显著降低,差异均有统计学意义(P < 0.05)。与对照组比较,缓解期组患者IgE显著增高,IL-37显著降低,差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05)。IgE、IL-25、IL-27、ECP与FEV1、PEF均呈显著负相关(P < 0.05);IL-37与FEV1、PEF均呈显著正相关(P < 0.05)。 结论 IgE、IL-37、IL-25、IL-27和ECP与支气管哮喘患者病情严重程度紧密相关。
[关键词] 支气管哮喘;炎性生物学指标;应用价值
[中图分类号] R562.250.2 [文献标识码] A [文章编号] 1673-7210(2016)11(b)-0117-04
[Abstract] Objective To investigate the application value of serum inflammatory biological indicators in patients with bronchial asthma. Methods Fifty cases of patients with acute exacerbation of bronchial asthma (acute stage group), 50 cases with remittent stage of bronchial asthma (remittent stage group) and 50 cases with healthy adults (control group) admitted to the Affiliated Hospital of Inner Mongolia Medical University from January 2015 to January 2016 were selected. The levels of immunoglobulin E (IgE), interleukin (IL)-37, IL-25, IL-27 and eosinophile cationic protein (ECP) among the three groups were compared, and the correlation between them and forced expiratory volume in the first second (FEV1), peak expiratory flow (PEF) was analyzed. Results Compared with control group or remittent stage group, the levels of IgE, IL-27, IL25 and ECP in the acute stage group were significantly increased, and the level of IL-37 was significantly decreased, the differences were all statistically significant (P < 0.05). Compared with control group, the IgE of remittent stage group was significantly increased, while the level of IL-37 was significantly decreased, the differences were statistically significant (P < 0.05). IgE, IL-25, IL-27 and ECP were negatively correlated with FEV1 and PEF (P < 0.05); IL-37 was positively correlated with FEV1 and PEF (P < 0.05). Conclusion IgE, IL-37, IL-25, IL-27 and ECP are closely related to the severity of bronchial asthma.
[Key words] Bronchial asthma; Inflammatory biological indicators; Application value
支气管哮喘是我国成人较为常见的疾病之一,其发病率高居不下[1-2],严重危害了患者的身心健康[3]。研究认为支气管哮喘与患者免疫功能失调相关[4-5]。免疫球蛋白E(immune globulin E,IgE)、白细胞介素(IL)-37、IL-25、IL-27和嗜酸性粒细胞阳离子蛋白(eosinophile cationic protein,ECP)等是细胞免疫中重要的细胞因子,阎昱升等[6]研究显示,IL-25和IL-27與支气管哮喘患者严重程度呈正比。IL-37是近年来新发现的细胞因子,由Th1细胞产生[7]。IgE、ECP可以通过趋化嗜酸性粒细胞,进而导致组织中嗜酸性粒细胞浸润[8]。第1秒用力呼吸容积(FEV1)和呼气峰流速(PEF)是评价支气管哮喘严重度和疗效的重要指标,可以反映患者的气流受限程度,支气管哮喘发作时其水平降低,与支气管哮喘严重度具有较好的正相关性。分析血清炎性指标与FEV1和PEF的相关性,可以反映血清炎性指标与支气管哮喘患者病情严重度的关联性。
1 资料与方法
1.1 一般资料
选择2015年1月~2016年1月内蒙古医科大学附属医院收治的急性发作期支气管哮喘患者50例、缓解期支气管哮喘患者50例和健康成人50例,分别设为急性期组、缓解期组和对照组。纳入标准:①支气管哮喘;②年龄18~65岁;③入院时处于急性发作期或缓解期;④入院前7 d内未接受过激素、支气管舒张剂等特殊治疗;⑤可以配合完成检查。排除标准:①入院时1个月内使用免疫抑制剂;②脏器功能不全;③急性感染;④自身免疫性疾病;⑤结缔组织病;⑥妊娠期;⑦研究期间转院。急性期组男32例,女18例,年龄21~58岁,平均(45.38±12.48)岁;缓解期组男30例,女20例,年龄20~57岁,平均(45.69±10.49)岁;健康成人男31名,女19名,年龄20~59岁,平均(45.92±11.59)岁。三组研究对象性别和年龄比较差异无统计学意义(P > 0.05),具有可比性。所有研究对象均知情同意并签署知情同意书,本研究通过医院伦理委员会批准。
1.2 诊断标准
支气管哮喘:①反复发作的喘息、气急、胸闷或咳嗽,多与接触变应原、冷空气、物理、化学性刺激以及病毒性呼吸道感染、运动等有关。②发作时双肺可闻及散在或弥漫性、以呼气相为主的哮鸣音,呼气相延长。③上述症状和体征可经治疗缓解或自行缓解。④除外其他疾病所引起的喘息、气急、胸闷和咳嗽。⑤临床症状不典型者,支气管试验或运动激发试验阳性;支气管舒张试验阳性FEV1增加12%以上,FEV1增加绝对值200 mL以上;呼气流量峰值日内(或2周)变异率在20%以上。符合①~④或④~⑤即可诊断为支气管哮喘。
支气管哮喘急性发作期:喘息、气促、咳嗽、胸闷等症状突然发生或急剧加重,可伴有呼吸困难、呼气流量降低为特征。
支气管哮喘缓解期:经过治疗或未经治疗症状、体征消失,肺功能恢复到急性发作前水平,持續3个月以上[9]。
1.3 治疗方法
根据2008年《支气管哮喘防治指南》[9],对于支气管哮喘患者给予吸氧、支气管舒张剂、氨茶碱及β2受体激动对症支持治疗,必要时给予人工通气;对于缓解期患者,给予β2受体激动进行家庭治疗。
1.4 观察指标及检测方法
首要观察指标包括三组研究对象血清IgE、IL-37、IL-25、IL-27和ECP水平,次要观察指标包括急性期组患者FEV1、PEF水平,并分析其与IgE、IL-37、IL-25、IL-27和ECP的关联性。
入组后即抽取各组研究对象肘静脉血5 mL,3000 r/min离心10~15 min后取上层血清,置于-80°C冷柜中保存待检。分别使用IgE、IL-37、IL-25、IL-27和ECP酶联免疫吸附测定(ELISA)试剂盒检测研究对象相关指标水平,ELISA试剂盒均购自美国R&D公司,操作过程参照ELISA试剂盒说明书进行。
1.5 统计学方法
采用SPSS 22.0完成本研究中所有数据的分析,计数资料采用χ2检验,计量资料采用均数±标准差(x±s)表示,多组计量资料比较采用ANOVA检验,组间两两比较采用t检验;相关性使用Pearson检验。以P < 0.05为差异有统计学意义。
2 结果
2.1 三组炎症因子和ECP水平比较
与对照组或缓解期组比较,急性期组患者IgE、IL-25、IL-27和ECP均显著增高,IL-37显著降低,差异均有统计学意义(P < 0.05)。与对照组比较,缓解期组患者IgE显著增高,IL-37显著降低,差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05)。见表1。
2.2 支气管哮喘急性发作期各炎症因子、ECP与FEV1、PEF的关联性
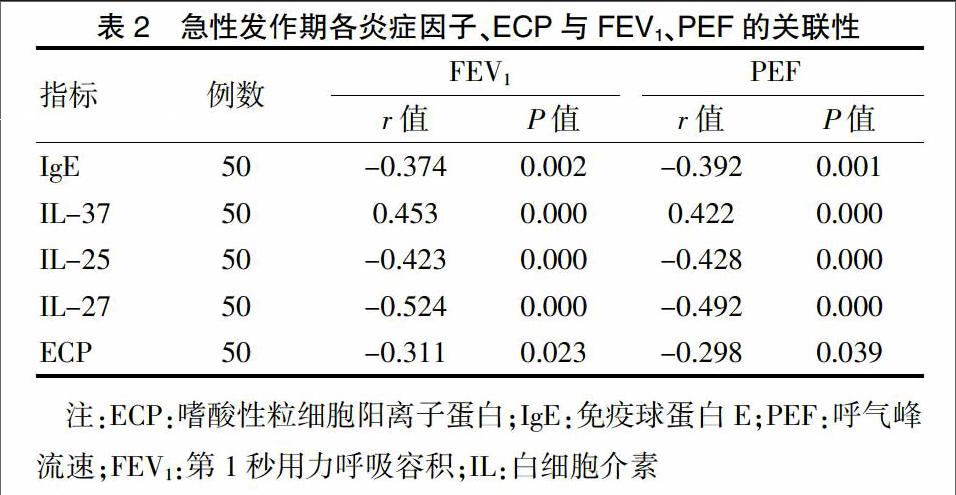
支气管哮喘患者FEV1和PEF分别为(1.89±0.35)L和(2.13±0.53)L/s。IgE、IL-25、IL-27、ECP与FEV1、PEF均呈显著负相关(P < 0.05),IL-37与FEV1、PEF均呈显著正相关(P < 0.05)。见表2。
3 讨论
导致支气管哮喘反复发作的原因是慢性气道炎症,炎症细胞和炎性细胞因子共同参与了其发病过程。IgE、IL-37、IL-25、IL-27和ECP是人体血清中重要的炎性细胞因子,这些炎性因子与Th1/Th2细胞、嗜酸性粒细胞等存在紧密的关联性[10-12]。Kumar等[13]研究表明支气管哮喘患者Th1/Th2细胞免疫平衡失调。Tang等[14]研究一样显示支气管哮喘患者与Th1/Th2平衡失调显著相关,并最终促进患者支气管哮喘的发作。T淋巴细胞是控制炎症的主要细胞[15],在支气管哮喘的患者中,Th1/Th2的平衡失调主要表现为Th1/Th2细胞免疫向Th2细胞漂移[16],Th1细胞主要介导细胞免疫,而Th2细胞主要介导体液免疫,支气管哮喘患者Th2细胞免疫亢进,可导致支气管黏膜中长期慢性炎症,进而促进其发生和发展过程[17-18]。IgE、IL-37、IL-25、IL-27和ECP等血清细胞因子是体液免疫的重要组成部分,可以介导Th1、Th2细胞功能,促进炎症因子和嗜酸性粒细胞聚集。因此,血清中IgE、IL-37、IL-25、IL-27和ECP等生物学指标可能与支气管哮喘的发生有关。为探讨此问题,2016年Salter等[19]纳入了10例变态性支气管哮喘患者,结果显示支气管哮喘患者IL-25水平显著升高,且伴随着Th2细胞免疫的失调,Farahani等[20]、Yao等[21]研究同样显示IL-25与支气管哮喘的发生紧密相关。Fujita等[22]研究则显示IL-27在支气管哮喘患者中显著升高。同样有研究显示IgE、ECP等因子在支气管哮喘患者中显著升高[23-24]。上述研究与本研究类似,本研究显示IgE、IL-25、IL-27和ECP在支气管哮喘患者中均显著升高,且与患者FEV1和PEF水平呈负相关(P < 0.05)。IgE、IL-25、IL-27和ECP导致支气管哮喘气道慢性炎症的机制可能是通过促进气道慢性炎症的持续,诱导趋化因子的聚集和嗜酸性粒细胞等在气道中的浸润,进而参与了支气管哮喘的发生。IgE是正常人血清中含量最少的免疫球蛋白,可以引起Ⅰ型超敏反应。lgE有能够与肥大细胞和嗜碱性粒细胞结合的免疫功能。ECP可以通过趋化嗜酸性粒细胞,进而导致组织中嗜酸性粒细胞浸润[8]。IL-27属于IL-6/IL-12家族的细胞因子,具有免疫促进和免疫抑制双重特点,其在支气管哮喘患者中具体作用尚待进一步研究证实。IL-25是一种促炎因子,联合IgE和ECP等参与了嗜酸性粒细胞等炎症细胞对组织的浸润过程。IL-37又称IL-1F7,是一种抗炎因子,Sakai等[25]研究显示IL-37在保护肝脏缺血再灌注损伤中具有很好的作用,其机制可能是通过抑制C-JUN等酶,进而降低体内炎性细胞因子和趋化因子。作为IL-1家族成员,IL-37对I/R损伤、炎症性肠道疾病和类风湿关节炎等均有较好的保护作用,周梦晨等[26]研究同样显示IL-37可以抑制细胞凋亡,抑制IL-6和CXCL2等炎症因子的过度表达。本研究显示支气管哮喘急性发作期IL-37水平显著降低,说明其抗炎能力下降,进而可能参与了支气管哮喘的发生过程。
綜上所述,IgE、IL-37、IL-25、IL-27和ECP与支气管哮喘患者病情严重度紧密相关。但目前相关研究尚少,需要进一步的研究证实。
[参考文献]
[1] O'Toole J,Mikulic L,Kaminsky DA. Epidemiology and pulmonary physiology of severe asthma [J]. Immunol Allergy Clin North Am,2016,36(3):425-438.
[2] Piccirillo AL,Packnett ER,Cowan DN,et al. Epidemiology of asthma-related disability in the U.S. Armed Forces:2007-2012 [J]. J Asthma,2016,53(7):668-678.
[3] Glick AF,Tomopoulos S,Fierman AH,et al. Disparities in mortality and morbidity in pediatric asthma hospitalizations,2007 to 2011 [J]. Acad Pediatr,2016,16(5):430-437.
[4] Best LG,O'Leary RA,O'Leary MA,et al. Humoral immune factors and asthma among American Indian children:a case-control study [J]. BMC Pulm Med,2016,16(1):93-102.
[5] Marusyk UI. Immune and atopic status of school-age children with asthma,given the asthma phenotype [J]. Lik Sprava,2014,7(8):10-14.
[6] 阎昱升,汤渝玲.支气管哮喘患者血清IL-25、ECP、IL-27的测定及临床意义[J].免疫学杂志,2013,29(10):912-914.
[7] Zhang G,Tang C,Tan J,et al. IL-37 inhibits the proliferation,invasion and migration of SMMC-7721 cells in vitro [J]. Xi Bao Yu Fen Zi Mian Yi Xue Za Zhi,2015,31(10):1301-1305.
[8] Huang Y,Zhang Y,Li C,et al. Immunoregulation effect of crude extract of C. elegans on allergic asthma [J]. Int J Clin Exp Med,2014,7(4):886-892.
[9] 中华医学会呼吸病学分会哮喘学组.支气管哮喘防治指南(支气管哮喘的定义、诊断、治疗和管理方案)[J].中华哮喘杂志:电子版,2008,2(1):3-13.
[10] Wang B,Bian R,Wei C,et al. Cefodizime increases peripheral blood CD4/CD8 and Th1/Th2 ratios in senile patients with bacterial pneumonia [J]. Xi Bao Yu Fen Zi Mian Yi Xue Za Zhi,2015,31(4):528-531.
[11] Miyagawa F,Hasegawa A,Imoto K,et al. Differential expression profile of Th1/Th2-associated chemokines characterizes Stevens-Johnson syndrome/toxic epidermal necrolysis(SJS/TEN)and drug-induced hypersensitivity syndrome/drug reaction with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms(DIHS/DRESS)as distinct entities [J]. Eur J Dermatol,2015,25(1):87-89.
[12] Xia T,Zheng XF,Qian BH,et al. Plasma interleukin-37 is elevated in patients with rheumatoid arthritis:its correlation with disease activity and Th1/Th2/Th17-related cytokines [J]. Dis Markers,2015,32(4):124-131.
[13] Kumar A,Das S,Agrawal A,et al. Genetic association of key Th1/Th2 pathway candidate genes,IRF2,IL6,IFNGR2,STAT4 and IL4RA,with atopic asthma in the Indian population [J]. J Hum Genet,2015,60(8):443-448.
[14] Tang F,Wang F,An L,et al. Upregulation of Tim-3 on CD4(+)T cells is associated with Th1/Th2 imbalance in patients with allergic asthma [J]. Int J Clin Exp Med,2015, 8(3):3809-3816.
[15] Gaddam RR,Fraser R,Badiei A,et al. Differential Effects of Kupffer Cell Inactivation on Inflammation and the Liver Sieve Following Caecal-Ligation and Puncture Induced Sepsis in Mice [J]. Shock,2016. [Epub ahead of print]
[16] Rogala B,Bozek A,Gluck J,et al. Prevalence of IgE-mediated allergy and evaluation of Th1/Th2 cytokine profiles in patients with severe bronchial asthma [J]. Postepy Dermatol Alergol,2015,32(4):274-280.
[17] Shim JU,Koh YI. Increased Th2-like Invariant Natural Killer T cells in Peripheral Blood From Patients With Asthma [J]. Allergy Asthma Immunol Res,2014,6(5):444-448.
[18] Pi CC,Wang HY,Lu CY,et al. Ganoderma formosanum polysaccharides attenuate Th2 inflammation and airway hyperresponsiveness in a murine model of allergic asthma [J]. Springerplus,2014,3(5):297-305.
[19] Salter BM,Oliveria JP,Nusca G,et al. IL-25 and IL-33 induce Type 2 inflammation in basophils from subjects with allergic asthma [J]. Respir Res,2016,17(5):134-142.
[20] Farahani R,Sherkat R,Hakemi MG,et al. Cytokines (interleukin-9,IL-17,IL-22,IL-25 and IL-33)and asthma [J]. Adv Biomed Res,2014,3(127):435-442.
[21] Yao X,Wang W,Li Y,et al. Characteristics of IL-25 and allergen-induced airway fibrosis in a murine model of asthma [J]. Respirology,2015,20(5):730-738.
[22] Fujita H,Teng A,Nozawa R,et al. Production of both IL-27 and IFN-gamma after the treatment with a ligand for invariant NK T cells is responsible for the suppression of Th2 response and allergic inflammation in a mouse experimental asthma model [J]. J Immunol,2009, 183(1):254-260.
[23] Jonsson UB,Hakansson LD,Jogi R,et al. Associations of ECP(eosinophil cationic protein)-gene polymorphisms to allergy,asthma,smoke habits and lung function in two Estonian and Swedish sub cohorts of the ECRHS Ⅱ study [J]. BMC Pulm Med,2010,10(36):734-742.
[24] Chung KF. Staphylococcal enterotoxin-specific IgE:a biomarker for a distinct phenotype of severe asthma [J]. Clin Exp Allergy,2016,46(3):387-389.
[25] Sakai N,Van Sweringen HL,Belizaire RM,et al. Interleukin-37 reduces liver inflammatory injury via effects on hepatocytes and non-parenchymal cells [J]. J Gastroenterol Hepatol,2012,27(10):1609-1616.
[26] 周夢晨,姜桂青,李倩倩,等.IL-37抑制缺氧诱导的细胞凋亡的研究[J].中国病理生理杂志,2016,12(8):1519-1520.

