大气主要污染物与儿童呼吸系统疾病住院率关系调查研究
胡继宏,靳利梅,赵 翊,陈 丽,李金娟,李 欣,马彦平,魏晋林,刘家基
·调查研究·
大气主要污染物与儿童呼吸系统疾病住院率关系调查研究
胡继宏1*,靳利梅1,赵 翊1,陈 丽1,李金娟1,李 欣1,马彦平1,魏晋林2,刘家基2
背景 儿童呼吸系统疾病发病率呈上升趋势,大气污染对儿童健康的影响越来越受重视。目的 比较兰州市2014年和2015年大气主要污染物对1~5岁儿童呼吸系统疾病住院率影响的差异。方法 于2016年5—6月通过“中国空气质量在线监测平台”收集2014—2015年兰州市大气主要污染物〔PM2.5、PM10、二氧化硫(SO2)、二氧化氮(NO2)、臭氧(O3)〕每月平均污染水平的数据,并通过“甘肃省卫生系统疾控机构进医院信息平台”收集同时段兰州市1~5岁儿童呼吸系统疾病每月住院率数据。采用Pearson相关分析大气主要污染物与住院率及污染物之间的关系,并采用线性回归分析大气主要污染物对住院率的影响。结果 2014年和2015年PM2.5、PM10、SO2、O3水平比较,差异均无统计学意义(P>0.05);2015年NO2水平、儿童呼吸系统疾病住院率高于2014年(P<0.05)。2014年,PM2.5、PM10、SO2、NO2水平与住院率呈正相关(P<0.05),O3水平与住院率呈负相关(P<0.05)。2015年,PM10和NO2水平与住院率无直线相关性(P>0.05),PM2.5和SO2水平与住院率呈正相关(P<0.05),O3水平与住院率呈临界负相关(P=0.050)。多元线性回归分析结果显示,2014年,PM2.5〔t=3.79,P=0.004,方差膨胀因子(VIF)=1.45〕和NO2(t=2.64,P=0.027,VIF=1.45)是住院率的影响因素(P<0.05);2015年,SO2(t=3.01,P=0.013,VIF=1.00)是住院率的影响因素(P<0.05)。结论 兰州市2015年儿童呼吸系统疾病住院率高于2014年,可能是由于2015年影响住院率的因素(SO2)与2014年(PM2.5和NO2)不同造成。
呼吸道疾病;空气污染物;儿童,学龄前;住院率
急性呼吸系统疾病是发展中国家5岁以下儿童死亡的主要原因[1]。大气污染已经成为严重影响居民健康的危险因素之一,儿童呼吸系统的发育、结构和生理特点决定了其对大气污染危害效应的敏感性[2]。有研究表明,大气污染能够对儿童造成多方面的不良影响[3]。各地污染程度不同,同一地区不同时间污染物也有差别,引起的危害也不尽相同。兰州市是全国大气污染较严重的城市之一[4],近年兰州市通过洒水工程改善环境,有关大气污染与儿童呼吸系统疾病关系的研究主要进行了区域比较[5-6],并没有直接观察大气污染物与呼吸系统疾病的关系。为此,本研究初步分析比较2014年和2015年大气主要污染物对儿童呼吸系统疾病住院率相关性的差异,为确定大气污染重点防治的污染物提供依据。
1 资料与方法
1.1 数据收集 于2016年5—6月通过“中国空气质量在线监测平台”收集2014—2015年兰州市大气主要污染物〔PM2.5、PM10、二氧化硫(SO2)、二氧化氮(NO2)、臭氧(O3)〕每月平均污染水平的数据,并通过“甘肃省卫生系统疾控机构进医院信息平台”收集同时段的兰州市1~5岁儿童呼吸系统疾病每月住院率数据。
1.2 疾病定义 小儿常见呼吸系统疾病主要包括急慢性上呼吸道感染、哮喘、支气管肺炎和支气管炎等。根据国际疾病分类(ICD10),各类上呼吸道感染编码为J09-J11;哮喘编码J44-J45;年龄<15岁儿童如果未指明支气管炎急慢性的情况,可假定为急性支气管炎J20;某些传染性病原体感染的疾病或外因所致的疾病,必要时可用附加编码说明(急性咽炎J02.8,腺病毒感染B97.0);支气管肺炎编码J18。

2 结果
2.1 2014年和2015年大气主要污染物水平和住院率的比较 2014年和2015年PM2.5、PM10、SO2、O3水平比较,差异均无统计学意义(P>0.05);2015年NO2水平、儿童呼吸系统疾病住院率高于2014年,差异均有统计学意义(P<0.05,见表1)。
2.2 2014年和2015年大气主要污染物水平与住院率相关性分析 2014年,PM2.5、PM10、SO2、NO2水平与住院率呈正相关(P<0.05),O3水平与住院率呈负相关(P<0.05)。2015年,PM10和NO2水平与住院率无直线相关性(P>0.05),PM2.5和SO2水平与住院率呈正相关(P<0.05),O3水平与住院率呈临界负相关(P=0.050,见表2)。
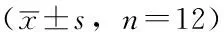
Table 1 Comparison of the levels of major air pollutants and hospitalization rate between 2014 and 2015
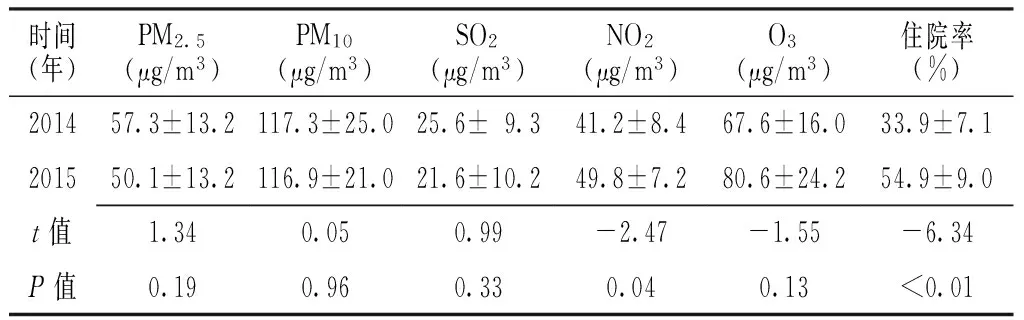
时间(年)PM2.5(μg/m3)PM10(μg/m3)SO2(μg/m3)NO2(μg/m3)O3(μg/m3)住院率(%)201457.3±13.2117.3±25.025.6±9.341.2±8.467.6±16.033.9±7.1201550.1±13.2116.9±21.021.6±10.249.8±7.280.6±24.254.9±9.0t值1.340.050.99-2.47-1.55-6.34P值0.190.960.330.040.13<0.01
注:SO2=二氧化硫,NO2=二氧化氮,O3=臭氧
表2 2014年和2015年大气主要污染物水平与住院率的相关性
Table 2 Correlation between the levels of major air pollutants and hospitalization rate in 2014 and 2015
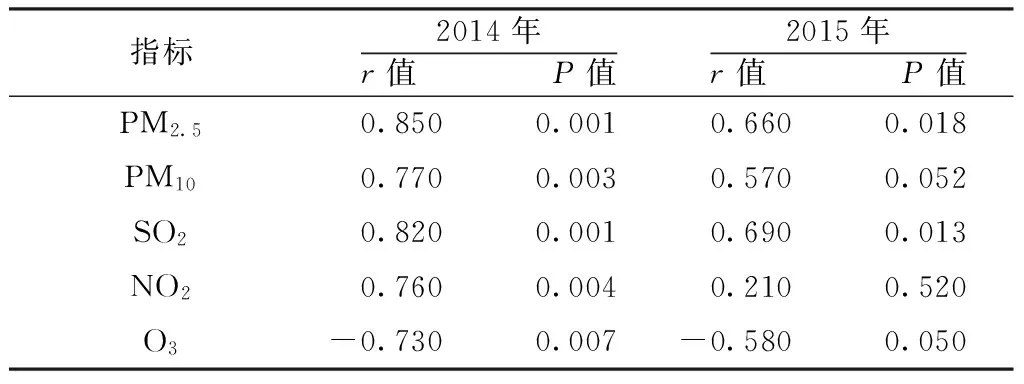
指标2014年r值 P值2015年r值 P值PM2.50.8500.0010.6600.018PM100.7700.0030.5700.052SO20.8200.0010.6900.013NO20.7600.0040.2100.520O3-0.7300.007-0.5800.050
2.3 多元线性回归分析 以住院率为因变量,以PM2.5(X1)、PM10(X2)、SO2(X3)、NO2(X4)、O3(X5)为自变量进行多元线性回归分析,结果显示,2014年线性回归方程为Y=-12.280+0.760X1+0.380X2+1.150X3,R2=0.97,F=32.87,P<0.001。多个变量存在共线性问题〔PM2.5、PM10和SO2方差膨胀因子(VIF)均>10.00〕。进一步采用逐步回归分析校正共线性问题,逐步回归方程为Y=-0.300+0.330X1+0.360X4,R2=0.84,F=23.59,P<0.001,进入方程中的PM2.5(t=3.79,P=0.004,VIF=1.45)和NO2(t=2.64,P=0.027,VIF=1.45)是住院率的影响因素,且不存在共线性。
2015年线性回归方程为Y=71.135-0.920X4,R2=0.82,F=5.44,P=0.031。多个变量存在共线性问题(PM2.5、SO2和O3VIF均>10.00或接近10.00)。进一步采用逐步回归分析校正共线性问题,逐步回归方程为Y=-41.690+0.611X3,R2=0.48,F=9.04,P=0.013,进入方程中的SO2(t=3.01,P=0.013,VIF=1.00)是住院率的影响因素,且不存在共线性(见表3)。
表3 2014年和2015年大气主要污染物对1~5岁儿童呼吸系统疾病住院率影响的多元线性回归分析
Table 3 Multivariate linear regression analysis on the effect of major air pollutants for hospitalization rate of respiratory diseases among children aged 1-5 years in 2014 and 2015
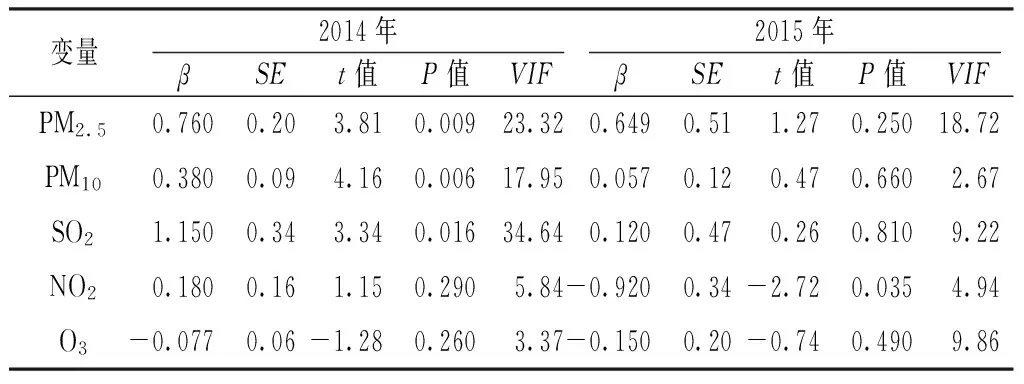
变量2014年2015年βSEt值P值VIFβSEt值P值VIFPM2.50.7600.203.810.00923.320.6490.511.270.25018.72PM100.3800.094.160.00617.950.0570.120.470.6602.67SO21.1500.343.340.01634.640.1200.470.260.8109.22NO20.1800.161.150.2905.84-0.9200.34-2.720.0354.94O3-0.0770.06-1.280.2603.37-0.1500.20-0.740.4909.86
注:VIF=方差膨胀因子
2.4 2014年和2015年大气主要污染物之间的相关性 进一步对造成共线性的变量进行相关性分析,结果显示,2014年,PM2.5与SO2、NO2、O3存在强相关(r>0.800),SO2与O3存在强相关,可能是造成共线性的原因;2015年,PM2.5与SO2存在强相关,PM10与SO2、NO2存在强相关,可能是造成共线性的原因(见表4)。
3 讨论
近年来儿童呼吸系统疾病有明显增加的趋势,其原因除了儿童自身免疫系统特点,也与近年来空气污染加重等有关[7-8]。本研究分析比较了兰州市2014年和2015年大气主要污染物与1~5岁儿童呼吸系统疾病住院率之间的相关关系,发现兰州市2015年1~5岁儿童呼吸系统疾病住院率显著高于2014年,其原因可能与两年的大气主要污染物不同、不同污染物的效应不同有关。通过比较发现,2015年大气主要污染物NO2水平显著高于2014年,O3水平与2014年比较无统计学差异,但数值上高于2014年,推测可能NO2和O3是造成2015年住院率高于2014年的主要原因。本研究进一步进行了相关性分析和多元线性回归分析,结果显示,2015年与住院率相关性最强的为SO2,其次为PM2.5,住院率影响因素为SO2(且为危险因素);2014年,PM2.5、PM10、SO2、NO2与住院率呈正相关,住院率影响因素为PM2.5和NO2(且为危险因素)。大气主要污染物对儿童呼吸系统的影响取决于污染物本身的效应,大气污染物作为哮喘和慢性阻塞性肺疾病等下呼吸道疾病的诱因已经较为明确[9],大气污染物以巨噬细胞或上皮细胞为靶细胞,产生免疫反应和氧化损伤,而对于上呼吸道的作用可能也与之类似。SO2具有较强的刺激性,会刺激眼结膜和鼻、咽部黏膜,且易溶于水,会被上呼吸道和支气管黏膜的黏液吸收,从而作用于上呼吸道系统,损伤呼吸道及其支气管,引发气管炎和慢性阻塞性肺疾病,若长期接触低浓度SO2,会引发慢性鼻炎以及肺气肿等。NO2会侵入肺部的巨噬细胞内,然后释放出蛋白分解酶,进而破坏肺泡;PM2.5微粒小,沉降极为缓慢,在空气中停留时间长,飘散的距离远,在空气环境中可吸附大量有机物或者微生物,并可直接沉积于肺,对儿童呼吸系统造成损害,有研究提示粗颗粒物引起短期效应比细颗粒物更强[10-11]。有研究发现空气质量指数(AQI)与医院儿科呼吸系统疾病总门诊量呈正相关[12],但有些研究发现PM10、NO2与呼吸系统疾病门诊量无关联[13-14]。本研究也发现2014年和2015年并不是所有大气污染物对住院率有影响,这可能与不同时间受调查区域大气污染物水平不同有关。
另外,本研究发现无论2014年还是2015年,PM2.5与SO2均存在强相关性,2015年PM10与SO2及NO2均存在强相关性,这可能是造成共线性的主要原因。已有研究发现当SO2吸附到PM2.5表面进而进入呼吸道深处时,SO2的毒性会增加3~4倍[10],大气污染物对健康的影响可能存在联合作用。
本研究数据监测主要来源于室外,而室内污染也会影响呼吸系统疾病的住院率,儿童呼吸系统疾病发生率与家庭成员的每日吸烟量和吸烟年限呈正相关[15],家养宠物也可增加儿童呼吸系统疾病和症状发生的危险性[16],有待于进一步研究。另外,本研究属于生态学研究,存在生态学谬误。
本研究背景:
儿童好发呼吸系统疾病,大气污染是呼吸系统疾病重要的危险因素。兰州市是全国大气污染最严重的城市之一,近几年通过各种措施进行治理。目前,有关大气污染对儿童呼吸系统疾病的影响仅做了地区比较,而大气主要污染物对兰州市儿童呼吸系统疾病的影响如何,目前尚未见报道。本研究有助于对兰州市影响儿童呼吸系统疾病的重要污染物进行针对性的重点治理提供依据。

表4 2014年和2015年各大气主要污染物之间相关性分析
注:-为数据重复,未再表示
作者贡献:胡继宏进行试验设计与实施、资料收集整理、撰写论文、成文并对文章负责;靳利梅、赵翊、陈丽、李金娟、李欣、马彦平、魏晋林、刘家基进行试验实施、评估、资料收集;胡继宏进行质量控制及审校。
本文无利益冲突。
[1]陈学敏.环境卫生学[M].北京:人民卫生出版社,2004:420. CHEN X M.Environmental health[M].Beijing:People′s Medical Publishing House,2004:420.
[2]元凤丽.大气污染的儿童健康效应[J].职业卫生与病伤,2008,23(6):369-370. YUAN F L.The effect of children′s health influenced by the air pollution[J].Journal of Occupational Health and Damage,2008,23(6):369-370.
[3]SCHWARTZ J.Air pollution and children′s health[J].Pediatrics,2004,113(4 Suppl):1037-1043.
[4]马敏劲,郭士奇,王式功.近11年兰州空气污染特征及其边界层结构影响的分析[J].兰州大学学报(自然科学版),2012,48(6):69-73. MA M J,GUO S Q,WANG S G.Analysis of the characteristics of air pollution and its boundary layer structural effect in recent 11 years over Lanzhou[J].Journal of Lanzhou University(Natural Sciences),2012,48(6):69-73.
[5]李盛,王金玉,王宇红.兰州市城关区大气污染对儿童呼吸系统疾病和症状的影响[J].环境与健康杂志,2015,32(1):46-48. LI S,WANG J Y,WANG Y H.Effects of air pollution on respiratory diseases and symptoms of school children in Chengguan district of Lanzhou,Gansu[J].Journal of Environment and Health,2015,32(1):46-48.
[6]李盛,王金玉,李守禹,等.兰州市西固区大气污染对儿童呼吸系统疾病和症状的影响[J].环境与健康杂志,2015,32(9):816-819. LI S,WANG J Y,LI S Y,et al.Effects of air pollution on respiratory system of school children in Xigu district of Lanzhou[J].Journal of Environment and Health,2015,32(9):816-819.
[7]王少利,郭新彪,张金良.北京市大气污染对学龄儿童呼吸系统疾病和症状的影响[J].环境与健康杂志,2004,21(1):41-44. WANG S L,GUO X B,ZHANG J L.Study on the effects of ambient air pollution on respiratory disease and symptoms among school-age children in Beijing[J].Journal of Environment and Health,2004,21(1):41-44.
[8]朱一丹,魏建荣,黄露,等.不同大气污染程度地区学龄儿童呼吸系统疾病及症状发生的比较[J].北京大学学报(医学版),2015(3):395-399. ZHU Y D,WEI J R,HUANG L,et al.Comparison of respiratory diseases and symptoms among school-age children in areas with different levels of air pollution[J].Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences),2015(3):395-399.
[9]施凯,刘晓菊,庞琪,等.大气细颗粒物对慢性阻塞性肺疾病患者外周血巨噬细胞吞噬功能的影响[J].中华结核和呼吸杂志,2014,37(4):229-301. SHI K,LIU X J,PANG Q,et al.Effects of fine particulate matter on phagocytosis of macrophage cell in peripheral blood of patients with COPD[J].Chinese Journal of Tuberculosis and Respiratory Diseases,2014,37(4):229-301.
[10]PENG R D,CHANG H H,BELL M L,et al.Coarse particulate matter air pollution and hospital admissions for cardiovascular and respiratory diseases among medicare patients[J].JAMA,2008,299(18):2172-2179.
[11]孙玉伟,周学华,袁琦,等.济南市秋末冬初大气颗粒物和气体污染物污染水平及来源[J].环境科学研究,2012,25(3):245-252. SUN Y W,ZHOU X H,YUAN Q,et al.Particle and gaseous pollutant levels and sources in the late fall and early winter in Ji′nan city[J].Research of Environmental Sciences,2012,25(3):245-252.
[12]马关培,邹宝兰,许振成,等.广州市某区医院呼吸系统疾病门诊人数与大气污染关系的时间序列研究[J].环境与健康杂志,2012,29(6):526-528. MA G P,ZOU B L,XU Z C,et al.Association of respiratory diseases outpatient visits and air pollution in a district,Guangzhou:a time-series study[J].Journal of Environment and Health,2012,29(6):526-528.
[13]吴彧,张衍燊,刘玲,等.郑州市空气污染对每日门诊人次影响的滞后效应和收获效应[J].环境与健康杂志,2011,28(3):233-237. WU Y,ZHANG Y S,LIU L,et al.Lag structure and harvesting effects of air pollution on daily outpatient visits[J].Journal of Environment and Health,2011,28(3):233-237.
[14]ZAMORANO A,MRQUEZ S,ARNGUIZ J L,et al.Association of acute bronchiolitis with climate factors and environmental contamination[J].Rev Med Chil,2003,131(10):1117-1122.
[15]艾勇.烟气暴露对儿童呼吸系统影响的调查研究[J].现代预防医学,2012,39(9):2177-2178. AI Y.A survey on the influence of passive smoking on children′s respiratory system disease[J].Modern Preventive Medicine,2012,39(9):2177-2178.
[16]解继胜,邓仕华,李海,等.家养皮毛宠物对儿童哮喘及哮喘样症状影响的流行病学调查[J].中国卫生统计,2010,27(2):161-162. XIE J S,DENG S H,LI H,et al.The influences of hairy pet on the children′s asthma and its syndrome in survey[J].Chinese Journal of Health Statistics,2010,27(2):161-162.
(本文编辑:贾萌萌)
Correlation of Major Air Pollutants and the Hospital Rate of Respiratory Diseases among Children
HUJi-hong1*,JINLi-mei1,ZHAOYi1,CHENLi1,LIJin-juan1,LIXin1,MAYan-ping1,WEIJin-lin2,LIUJia-ji2
1.DepartmentofEpidemiology,SchoolofPublicHealth,GansuUniversityofChineseMedicine,Lanzhou730000,China
2.LanzhouMunicipalCenterforDiseaseControl,Lanzhou730030,China
Background As the prevalence of respiratory diseases in children presents an upward trend,the influence of air pollution on children′s health is being taken more seriously.Objective To compare the influence of major air pollutants on the hospitalization rate of respiratory diseases among children aged 1-5 years between 2014 and 2015 in Lanzhou city.Methods From May to June 2016,we collected the data of monthly level of major air pollutants(PM2.5,PM10,SO2,NO2and O3) of Lanzhou in 2014 and 2015 from China′s Air Pollution Online Monitoring Platform,and the data of hospitalization rate for respiratory diseases among children aged 1-5 years in Lanzhou during the same two years from the Information Platform of Health System from CDC into Hospital in Gansu province.The Pearson correlation was used to test the correlation of major air pollutants with hospitalization rate,and that between the major air pollutants.The linear regression was used to analyze the influence of major air pollutants on hospitalization rate.Results The differences in the levels of PM2.5,PM10,SO2and O3in Lanzhou between 2014 and 2015 showed no statistical significance(P>0.05).The level of NO2was significantly higher in 2015 than it in 2014(P<0.05),and the hospitalization rate of respiratory diseases among 1-5 years old children was significantly higher in 2015 than it in 2014(P<0.05).Results of Pearson correlation showed that in 2014,PM2.5,PM10,SO2,NO2were positively correlated with the hospitalization rate(P<0.05),while O3was negatively correlated with it(P<0.05);in 2015,PM10and NO2had no linear correlation with hospitalization rate(P>0.05),PM2.5and SO2were positively correlated with the hospitalization rate(P<0.05),and O3was critically negatively correlated with hospitalization rate(P=0.050).The results of multivariate linear regression analysis showed that in 2014,PM2.5(t=3.79,P=0.004,VIF=1.45)and NO2(t=2.64,P=0.027,VIF=1.45)were significant risk factors for hospitalization rate(P<0.05);in 2015,SO2(t=3.01,P=0.013,VIF=1.00)was the significant risk factor for hospitalization rate(P<0.05).Conclusion The different air pollutants(PM2.5and NO2in 2014,and SO2in 2015) might lead to the higher hospitalization rate of respiratory diseases among children aged 1-5 in Lanzhou in 2015 than it in 2014.
Respiratory tract diseases;Air pollutants;Children,preschool;Hospitalization rate
R 725.6
A
10.3969/j.issn.1007-9572.2017.05.016
2016-10-20;
2017-01-20)
1.730000甘肃省兰州市,甘肃中医药大学公共卫生学院流行病学教研室
2.730030甘肃省兰州市疾病预防控制中心
*通信作者:胡继宏,副教授,硕士生导师;E-mail:hujihonghappy@163.com
胡继宏,靳利梅,赵翊,等.大气主要污染物与儿童呼吸系统疾病住院率关系调查研究[J].中国全科医学,2017,20(5):586-589.[www.chinagp.net]
HU J H,JIN L M,ZHAO Y,et al.Correlation of major air pollutants and the hospital rate of respiratory diseases among children[J].Chinese General Practice,2017,20(5):586-589.
*Correspondingauthor:HUJi-hong,Associateprofessor,Mastersupervisor;E-mail:hujihonghappy@163.com

