不同类型心房颤动患者心脏结构及B型钠尿肽水平的变化
刘运龄,赵艳淑,刘恩照,赵珺,刘彤,许纲
(天津医科大学第二医院心脏科,天津300211)
论著
不同类型心房颤动患者心脏结构及B型钠尿肽水平的变化
刘运龄,赵艳淑,刘恩照,赵珺,刘彤,许纲
(天津医科大学第二医院心脏科,天津300211)
目的:比较不同类型心房颤动(AF)患者血浆中B型钠尿肽(BNP)水平及心脏结构变化。方法:顺序入选阵发性AF患者35例,持续性AF患者30例,另设无房颤患者30例作为对照组。详细记录各组患者基线资料、血浆BNP水平以及超声心动图测量数据。结果:持续性AF组患者血浆BNP平均水平明显高于阵发性AF组(P<0.001),且这两组患者血浆BNP平均水平均明显高于对照组患者(P<0.001)。3组患者间左心房内径(LAD)(P<0.001)及右心室舒张末期内径(RVDd)(P=0.023)存在显著差异。血浆BNP水平与超声指标LAD呈正相关(r=0.419,P<0.001)。结论:血浆BNP水平随AF进展而升高,并与AF患者LAD呈显著正相关。
心房颤动;B型钠尿肽;左房内径;左室射血分数
心房颤动(房颤,AF)是临床最常见的心律失常之一。钠尿肽家族主要由5个成员组成[1],根据其氨基酸的排列顺序不同分为:A型钠尿肽 (ANP)、B型钠尿肽(BNP)、C型钠尿肽(CNP)、V型钠尿肽(VNP)和D型钠尿肽(DNP),其中BNP与房颤关系最为密切。BNP在心力衰竭、瓣膜疾病、先天性心脏疾病等多种情况下可见升高[2],有报道称房颤患者血浆BNP水平升高,其左心房内径(LAD)显著大于非房颤者,且BNP可作为房颤患者经导管消融转复为窦性心律后房颤是否复发的独立预测因子[3-6]。本研究拟探讨不同类型房颤患者BNP水平及心脏结构变化。
1 资料与方法
1.1 临床资料 本研究顺序入选2013年3月-7月于天津医科大学第二医院心脏科住院治疗的不同类型房颤患者65例,其中持续性房颤30例、阵发性房颤35例,另设30例无房颤患者作为对照组,平均年龄为(67±11)岁,64.21%为男性。所有入选患者符合ESC房颤指南和诊断标准,阵发性房颤指能在7 d内自行转复为窦性心律者,一般持续时间小于48 h;持续性房颤指持续7 d以上,需要药物或电击才能转复为窦性心律者。对照组为既往无房颤病史的高血压、稳定型冠状动脉粥样硬化型心脏病、室性期前收缩、阵发性室上性心动过速患者。排除标准:(1)排除可逆性病因引起的房颤患者。(2)排除入院时有血流动力学改变或恶性心律失常者。(3)排除心功能Ⅲ~Ⅳ级患者。(4)排除合并房颤并发症患者。(5)排除肺栓塞、周围血管疾病患者。(6)排除明显肝脏、肾脏原发疾病及严重感染、恶性肿瘤、急慢性血液病、活动性出血患者。(7)排除难以控制的高血压患者(收缩压≥160 mmHg或舒张压≥100 mmHg)。
1.2 方法
1.2.1 经胸超声心动图(TTE)检查 详细记录左室舒张末期内径(LVDd)、左室收缩末期内径(LVDs)、室间隔厚度(IVST)、左室后壁厚度(LVPWT)、左房内径(LAD)、右室舒张末期内径(RVDd)、左室射血分数(LVEF)数值。房颤患者各项测量数据均需多次测量(至少3个心动周期)后取平均值,阵发性房颤在患者房颤转复后进行检查。
1.2.2 血BNP的测量 持续性房颤患者取血时间为入院次晨7点,阵发性房颤患者取血时间为入院处于房颤节律时。使用Triage B型脑钠肽仪测定BNP水平,具体操作步骤严格按照产品说明书进行。
1.3 统计学方法 所有数据的统计分析均采用统计软件SPSS 17.0完成,连续变量采用±s差的方式进行统计描述,应用t检验进行均值比较。通过χ2检验明确3组样本间各观测变量是否有显著的统计学差异。相关分析用于评估患者血浆BNP水平与其他变量间线性相关程度的强弱。以显著性水平P<0.05为具有统计学意义。
2 结果
2.1 临床特点比较 3组患者间各基线临床特点均无显著统计学差异(P>0.05)。见表1。
2.2 经胸超声心动图结果比较 3组患者间LAD(P<0.001)及RVDd(P=0.023)存在显著差异。持续房颤组患者LAD高于阵发性房颤组和对照组,阵发性房颤组患者LAD亦高于对照组。持续性房颤组患者RVDd高于阵发性房颤组和对照组。持续房颤组LVEF低于阵发性房颤组和对照组。见表2。
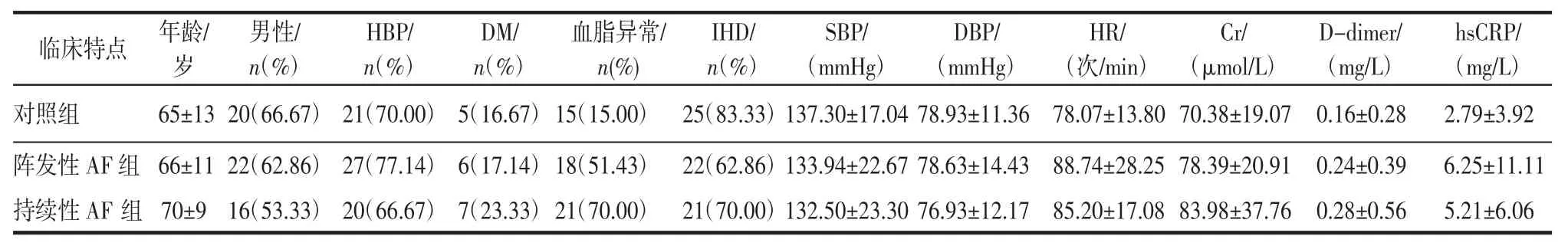
表1 各组间临床特点比较Tab 1 Comparison of the clinical characteristics of each group
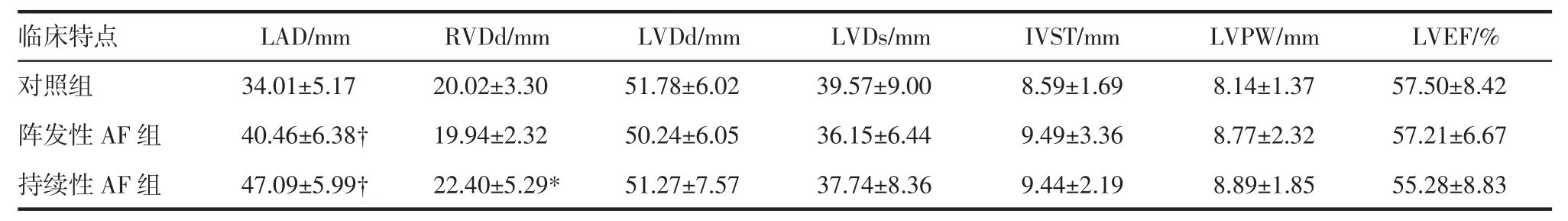
表2 各组间心脏超声指标比较Tab2 Comparison of cardiac ultrasound parameters among groups
2.3 各组间BNP水平比较 对照组BNP平均水平为(63.93±69.78)pg/mL,阵发性房颤组BNP平均水平为(215.17±212.66)pg/mL,持续性房颤组BNP平均水平为(397.70±335.91)pg/mL,3组患者血浆BNP水平存在显著性差异(P<0.001),持续性房颤组患者血浆BNP水平明显高于阵发性房颤组,二者血浆BNP水平均明显高于对照组(P<0.001)。
2.4 患者BNP水平与心脏超声指标相关性比较 将3组患者血浆BNP水平与各超声指标进行相关性分析,结果显示患者血浆BNP水平与LAD呈正相关(r=0.436,P<0.001),与LVEF呈负相关(r=-0.477,P<0.001)。见图1、2。

图13 组患者血浆BNP水平与LAD的关系Fig 1 The relationship between plasma BNP levels and LAD levels in 3 groups
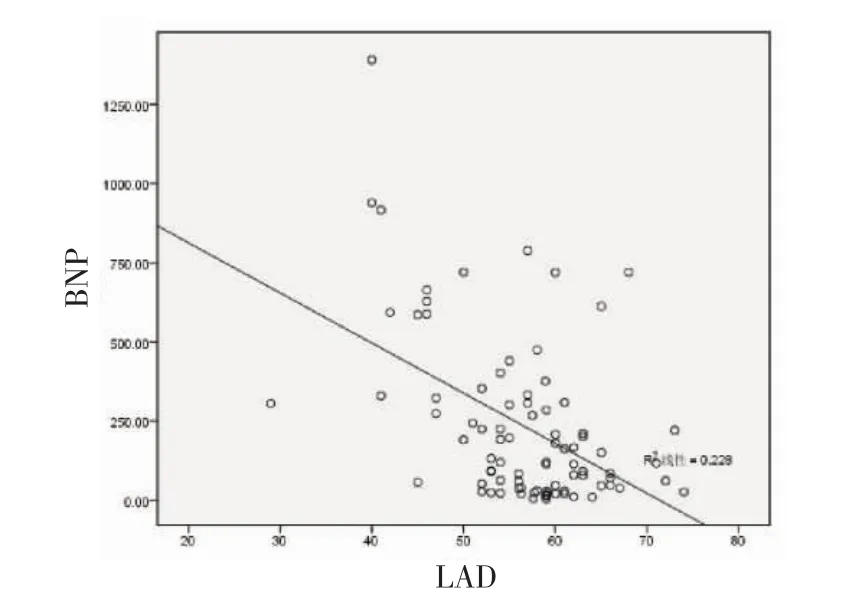
图23 组患者血浆BNP水平与LVEF的关系Fig 2 The relationship between plasma BNP levels and LVEF levels in 3 groups
3 讨论
多项研究证实房颤可引起心脏重构,在房颤时由于心房的不规律且快速的活动,导致左心房舒张晚期的收缩功能消失,血液在心房内淤滞造成心房容量超负荷、压力升高,无收缩或收缩降低的心脏节段易受被动性伸展的影响,造成心房被动增大[8-9]。此外房颤时心房内血流储备减少,但是代谢需求增加[10],心房肌细胞为了适应这种变化,自身结构会发生明显的变化。研究还表明心房容积的大小与房颤的稳定性呈显著正相关[11]。本研究比较持续性房颤、阵发性房颤及对照组左房内径数据发现:持续性房颤组患者LAD高于阵发性房颤组,且两组患者LAD高于对照组。随着房颤持续时间的延长及发生频率的增加,左心房内部结构会发生明显的变化,这与Dittrich等[12]证实的房颤发病时间越长,左心房扩大越明显的结果相一致。
既往研究发现房颤患者血浆BNP水平较窦性节律者显著升高,且房颤患者转复为窦性心律后血浆BNP水平下降,进行导管消融后复发的房颤患者血浆BNP水平较高[14]。Silvet等[15]也证实慢性房颤患者的血奖BNP水平显著高于无房颤患者。本研究中,持续性房颤患者血浆BNP平均水平明显高于阵发性房颤患者,且两组均明显高于对照组,与之前研究结果相一致。房颤患者BNP的分泌及其精确调节机制,至今尚未完全明了。BNP分泌主要来自心室肌[16-17],心室压力、心室容量和心脏负荷是BNP分泌的主要刺激因素。房颤可导致心房收缩不规则、心室充盈能力下降、心肌细胞能量利用不足等病理生理性改变,最终引发心室功能的变化,进一步引发BNP释放入血,血浆BNP水平升高[18]。另有研究显示[19-20],左心室功能正常的房颤患者较非房颤患者的BNP分泌增高。还有研究认为[21-23],心房肌细胞亦可分泌少量BNP,而心房的增大和容量负荷的上升亦导致心肌纤维化的发生,促使心房肌细胞BNP分泌上升。
本研究还证实房颤患者血浆BNP水平与左房内径呈正相关,可能机制为:房颤时心房扩大和容积负荷增大作为刺激因子促使BNP释放[24-25]。本研究中患者血浆BNP水平随LVEF升高而降低,这与既往研究表明房颤患者血浆BNP水平的升高与心功能不全相关一致。
本研究结果提示,房颤类型可影响患者的血浆BNP水平,BNP可反应房颤患者心脏结构变化。
[1]赵丽,吴学思.B型利钠肽在心血管疾病中的作用研究进展[J].中国急救医学,2003,(5):41
[2] Yilmaz M B,Erbay A R,Balci M,et al.Atrial natriuretic peptide predicts impaired atrial remodeling and occurrence of late postoperative atrial fibrillation after surgery for symptomatic aortic stenosis[J].Cardiology,2006,105(4):207
[3] Sanghamitra M,Prasant M,Luigi D B,et al.Baseline B-Type natriuretic peptide:a gender-specific predictor of procedureoutcome in atrial fibrillation patients undergoing catheter ablation [J].J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol,2011,22(8):858
[4] Stephan D,Sarah V,Henrike F,et al.Predictive value of B-type natriuretic peptide levels in patients with paroxysmal and persistent atrial fibrillation undergoing pulmonary vein isolation[J].J Interv Card Electrophysiol,2011,30(3):217
[5] Tang Y,Yang H,Qiu J.Relationship between brain natriuretic peptide and recurrence of atrial fibrillation after successful electrical cardioversion:a meta-analysis[J].J Int Med Res,2011,39 (5):1618
[6] Phang R,Isserman S,Karia D,et al.Echocardiographic evidence of left atrial abnormality in young patients with lone paroxysmal atrial fibrillation[J].Am J Cardiol,2004,94(4):511
[7] Rostagno C,Olivo G,Comeglio M,et al.Left atrial size changes in patients with paroxysmal lone at rial fibrillation.An echocardiographic follow-up[J].Angiology,1996,47(8):797
[8] Bosch R F,Grammer J B,Kuhlkamp V,et al.Electrical remodeling in atrial fibrillation—cellular and molecular mechanisms[J].Z Kardiol,2000,89(9):795
[9] Leistad E,Aksnes G,Verburg E,et al.Atrial contractile dysfunction after short-term atrial fibrillation is reduced by verapamil but increased by BAY K8644[J].Circulation,1996,93(9):1747
[10]White C W,Kerber R E,Weiss H R,et al.The effects of atrial fibrillation on atrial pressure-volume and flow relationships[J].Circ Res,1982,51(2):205
[11]Verhorst P M,Kamp O,Welling R C,et al.Transesophageal echocardiographic predictors for maintenance of sinus rhythm after electrical cardioversion of atrial fibrillation[J].Am J Cardiol,1997, 79(10):1355
[12]Thamilarasan M,Klein A L.Factors relating to left atrial enlargement in atrial fibrillation:“Chicken or the egg”hypothesis[J].Am Heart J, 1999,137(3):381[13]Kallel S,Jarrya A,Triki Z,et al.The use of N-terminal pro-brain natriuretic peptide as a predictor of atrial fibrillation after cardiac surgery[J].J Cardiovasc Surg(Torino),2013,54(3):403
[14]Francia P,Ricotta A,Frattari A,et al.Atrial natriuretic Peptide single nucleotide polymorphisms in patients with nonfamilial structural atrial fibrillation[J].Clin Med Insights Cardiol,2013,7: 153
[15]Silvet H,Young-Xu Y,Walleigh D,et al.Brain natriuretic peptide is elevated in outpatients with atrial fibrillation[J].Am J Cardiol, 2003,92(9):1124
[16]Vanderheyden M,Vrints C,Verstreken S,et al.B-type natriuretic peptide as a marker of heart failure:new insights from biochemistry and clinical implications[J].Biomark Med,2010,4(2):315
[17]Tosa S,Watanabe H,Iino K,et al.Usefulness of plasma BNP levels as a marker of left ventricular wall stress in obese individuals[J].Int Heart J,2009,50(2):173
[18]Mandalenakis Z,Eriksson H,Welin L,et al.Atrial natriuretic peptide as a predictor of atrial fibrillation in a male population study.The Study of Men Born in 1913 and 1923[J].Int J Cardiol, 2014,171(1):44
[19]Cheung B M,Kumana C R.Natriuretic peptides--relevance in cardiovascular disease[J].JAMA,1998,280(23):1983
[20]Jourdain P,Bellorini M,Funck F,et al.Short-term effects of sinus rhythm restoration in patients with lone atrial fibrillation:a hormonal study[J].Eur J Heart Fail,2002,4(3):263
[21]郭俊晓,张玉龙,刘志平,等.先天性心脏病伴不同程度肺动脉高压患儿血浆脑钠肽及氨基末端脑钠肽前体的变化[J].中国医药,2015,10(11):1577
[22]蒋春英,王蕊,李旭东,等.单纯收缩期高血压患者血浆B型钠尿肽水平与左心室肥厚、舒张功能变化的关系[J].中国动脉硬化杂志,2015,23(1):73
[23]陈兴泳,张旭,雷惠新,等.急性脑梗死血N端-脑钠肽前体水平变化及临床意义[J].中国神经精神疾病杂志,2011,37(7):423
[24]饶志荣,杨友祥,王宁生,等.非瓣膜病性心房颤动患者血清CRPBNP与ET-1水平的测定及其临床意义[J].河北医学,2012,18(2):166
[25]徐颖,李广平,倪燕平,等.非瓣膜性心房颤动患者血清高敏C反应蛋白、脑钠肽、内皮素-1水平的测定及其临床意义[J].中国全科医学,2011,14(10):1095
(2016-01-31)
Relationship between plasma leves B-type natriuretic peptide and cardiac structure in patients with different types of atrial fibrillation
LIU Yun-ling,ZHAO Yan-shu,LIU En-zhao,ZHAO Jun,LIU Tong,XU Gang
(Department of Cardiology,The Second Hospital,Tianjin Medical University,Tianjin 300211,China)
Objective:To analyze the risk factors related to plasma levels of BNP in patients with different types of atrial fibrillation(AF). Methods:Sixty-five patients with AF were divided into paroxysmal AF group (n=35)and persistent AF group (n=30),and 30 patients without AF were included as control.Detailed information were recorded including the basic characteristics of patients,biochemical parameters,the levels of plasma BNP and transthoracic echocardiography indices.Results:The BNP level in patients with persistent AF group was significantly higher than that in paroxysmal AF group(BNP:397.70±335.91vs215.17±212.66,P<0.001),and the BNP level in the two groups with AF was higher than control group(63.93±69.78,P<0.001).The blood BNP levels were positively correlated with LAD (r=0.419,P<0.001).Conclusion:The plasma BNP levels tend to increase with the development of AF,and are significantly positively correlated with LAD in patients with AF.
atrial fibrillation;B-type natriuretic peptide;left atrial diameter;left ventricular ejection fraction
R541.7+5
A
1006-8147(2016)06-0522-03
刘运龄(1991-),女,硕士在读,研究方向:心血管内科;通信作者:刘恩照,E-mail:liu_ezh@126.com。

