核能安全
ENDF/B-VII.0: Next generation evaluated nuclear data library for nuclear science and technology
Chadwick, M. B.; Oblozinsky, P; Herman, M; et al.
Design and development of the AHWR: The Indian thorium fuelled innovative nuclear reactor
Sinha RK; Kakodkar A
Deliberately small reactors and the second nuclear era
Ingersoll, D. T.
Economic potential of modular reactor nuclear power plants based on the Chinese HTR-PM project
Zhang, Zuoyi; Sun, Yuhang
中国核电发展战略研究
叶奇蓁
大型集成多功能中子学计算与分析系统Visual BUS的研究与发展
吴宜灿,李静惊,李莹,等
核能安全
·编者按·
原子的发现和核能的开发利用给人类社会发展带来新的动力,极大增强人类认识世界和改造世界的能力。核能发展伴随着核安全风险和挑战。人类要更好地利用核能、实现更大发展,必须确保核安全、做好核应急。核安全是核能事业持续健康发展的生命线,核应急是核能事业持续健康发展的重要保障。
20世纪50年代中期,中国创建核工业。60多年来,中国致力于和平利用核能事业,发展推动核技术在工业、农业、医学、环境、能源等领域广泛应用。中国坚持发展与安全并重原则,执行安全高效发展核电政策,采用最先进的技术、最严格的标准发展核电。伴随着核能事业的发展,核安全与核应急同步得到加强。中国的核设施、核活动始终保持安全稳定状态,特别是核电安全水平不断提高。面对核能事业发展新形势新挑战,中国核应急在技术、装备、人才、能力、标准等方面还存在一定不足,这也是其他国家在开发利用核能进程中面临的共同课题。中国将通过理念创新、科技创新、管理创新,不断强化国家核应急管理,把核应急提高到新水平。
中国始终把核安全放在和平利用核能事业首要位置,坚持总体国家安全观,倡导理性、协调、并进的核安全观,秉持为发展求安全、以安全促发展的理念,始终追求发展和安全2个目标有机融合。半个多世纪以来,中国人民奋发图强、历尽艰辛,创建发展核能事业并取得辉煌成就。同时,不断改进核安全技术,实施严格的核安全监管,加强核应急管理,核能事业始终保持良好安全记录。
核事故影响无国界,核应急管理无小事。总结切尔诺贝利核事故、福岛核事故的教训,中国更加深刻认识到核应急的极端重要性,持续加强和改进核应急准备与响应工作,不断提升中国核安全保障水平。中国在核应急法律法规标准建设、体制机制建设、基础能力建设、专业人才培养、演习演练、公众沟通、国际合作与交流等方面取得巨大进步,既为自身核能事业发展提供坚强保障,也为推动建立公平、开放、合作、共赢的国际核安全应急体系,促进人类共享核能发展成果作出积极贡献。
本专题得到陈妍教授(环境保护部核与辐射安全中心)的大力支持。
·热点数据排行·
截至2016年 8月 26日,中国知网(CNKI)和Web of Science(WOS)的数据报告显示,以“核能(nuclear energy)”“核安全(nuclear safety)”“核安全文化(nuclear safety culture)”“核应急(Nuclear emergency)”为词条可以检索到的期刊文献分别为1166条、9617条。本专题将相关数据按照:研究机构发文数、作者发文数、期刊发文数、被引用频次进行排行,结果如下。
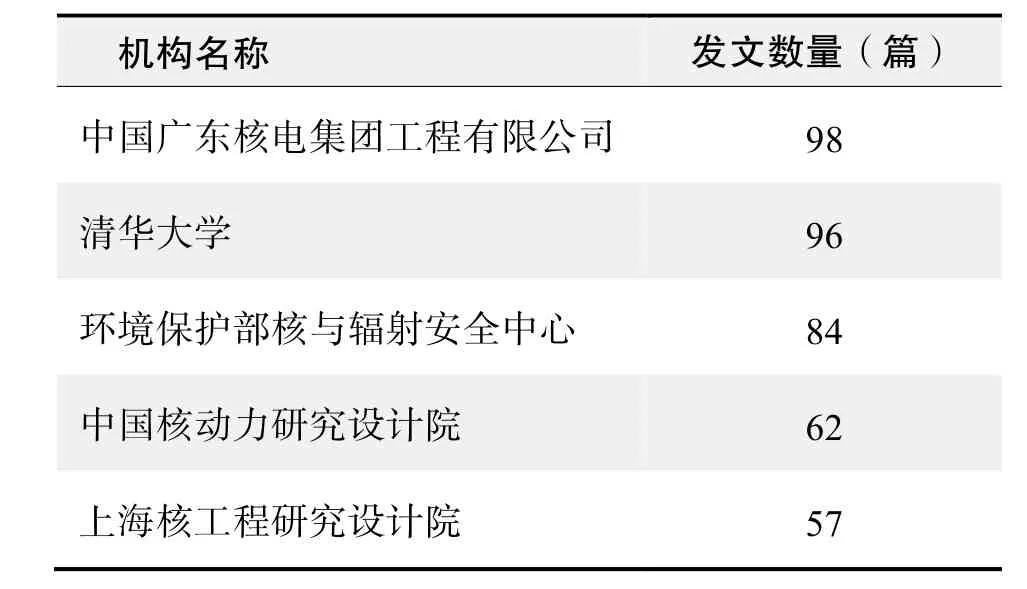
研究机构发文数量排名(CNKI)
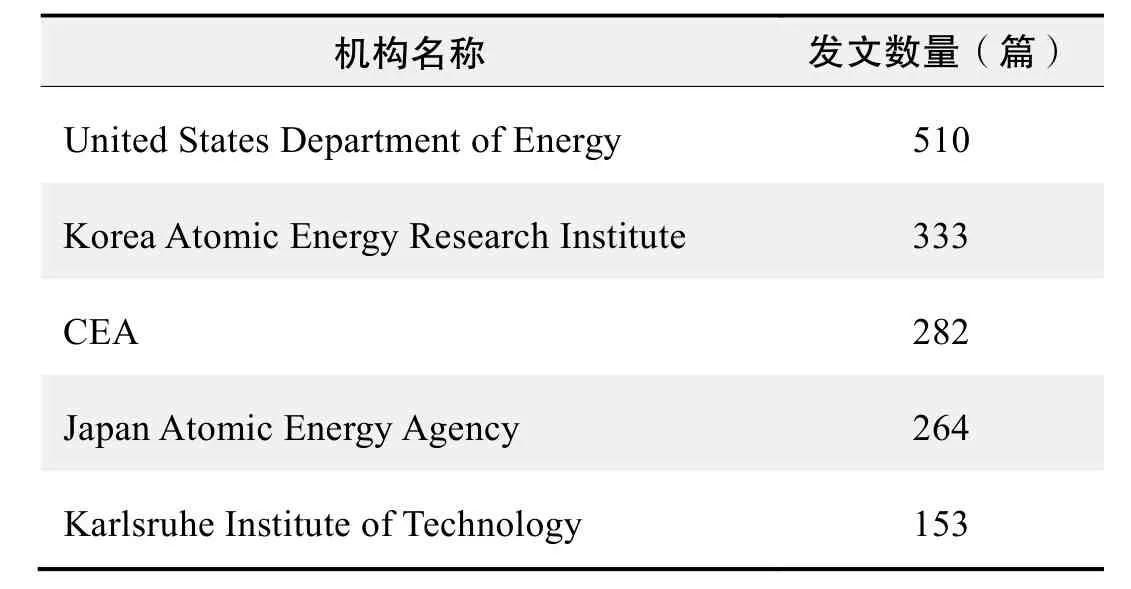
研究机构发文数量排名(WOS)

作者发文数量排名(CNKI)

作者发文数量排名(WOS)

期刊发文数量排名(CNKI)
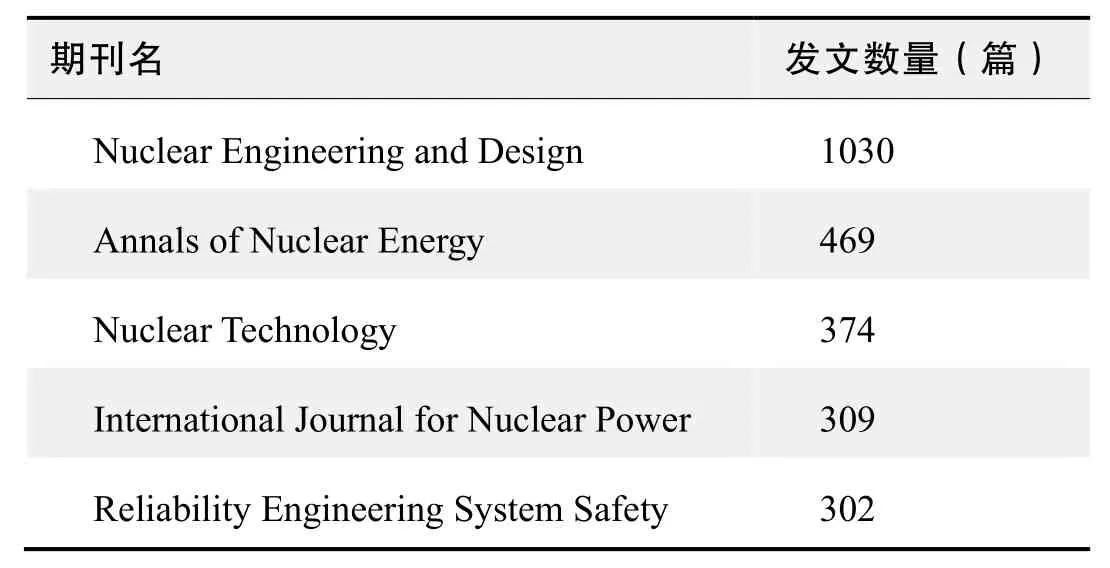
期刊发文数量排名(WOS)
根据中国知网(CNKI)数据报告,以“核能(nuclear energy)”“核安全(nuclear safety)”“核安全文化(nuclear safety culture)”“核应急(Nuclear emergency)”为词条可以检索到的高被引论文排行结果如下。
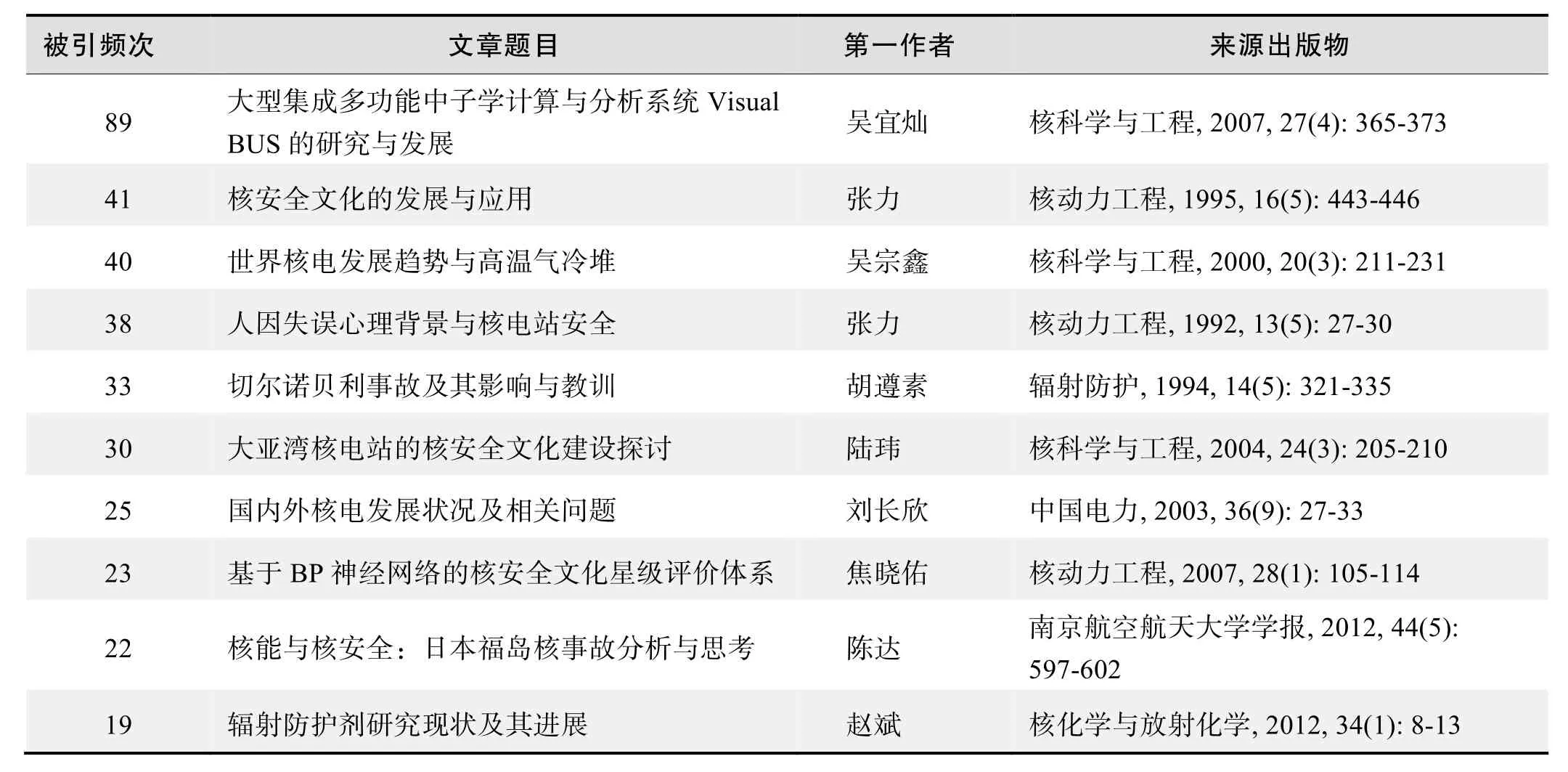
国内数据库高被引论文排行
根据Web of Science统计数据,以“核能(nuclear energy)”“核安全(nuclear safety)”“核安全文化(nuclear safety culture)”“核应急(Nuclear emergency)”为词条可以检索到的高被引论文排行结果如下。
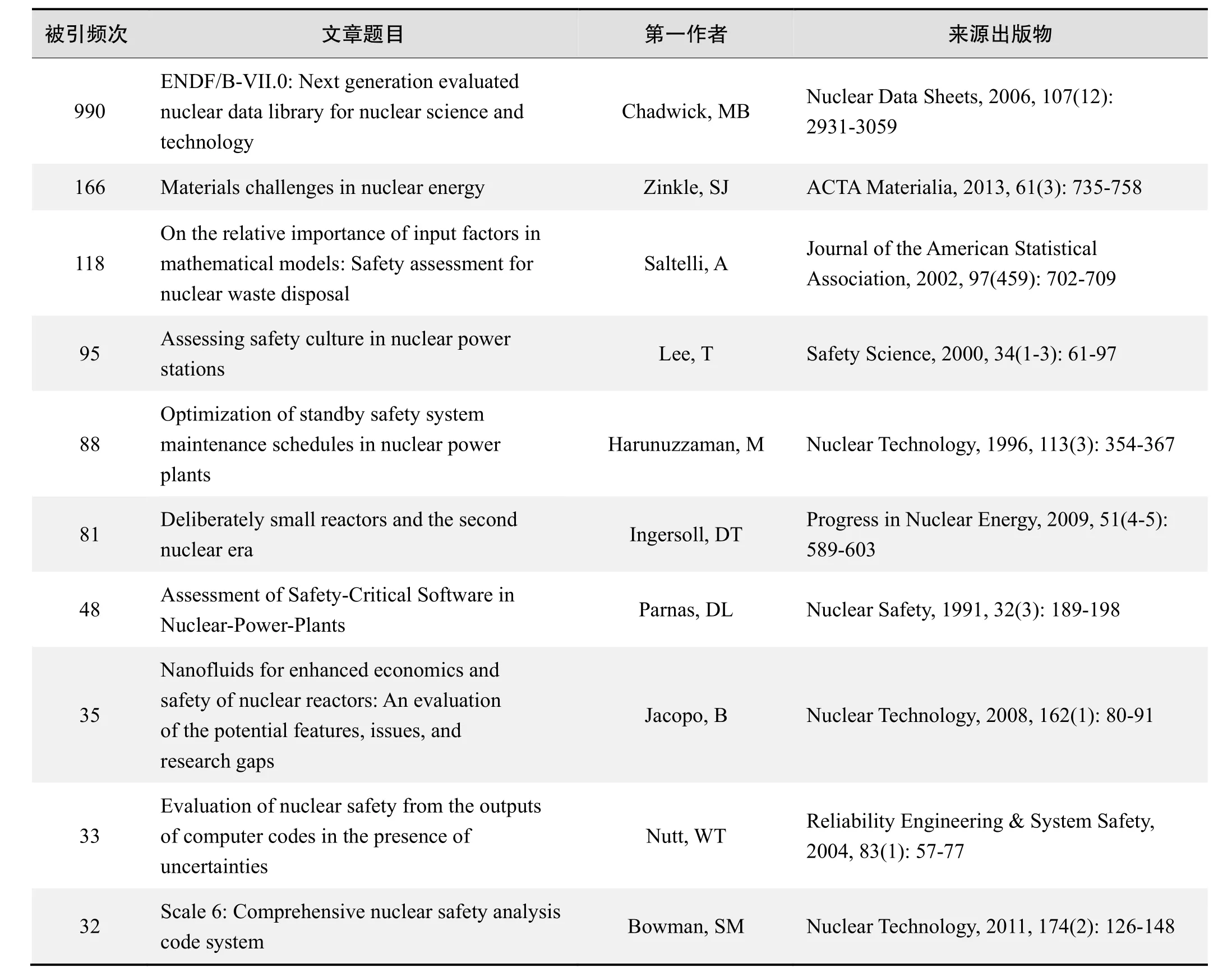
国外数据库高被引论文排行
·经典文献推荐·
基于Web of Science检索结果,利用Histcite软件选取LCS(Local Citation Score,本地引用次数)TOP50文献作为节点进行分析,得到本领域推荐的经典文献如下。
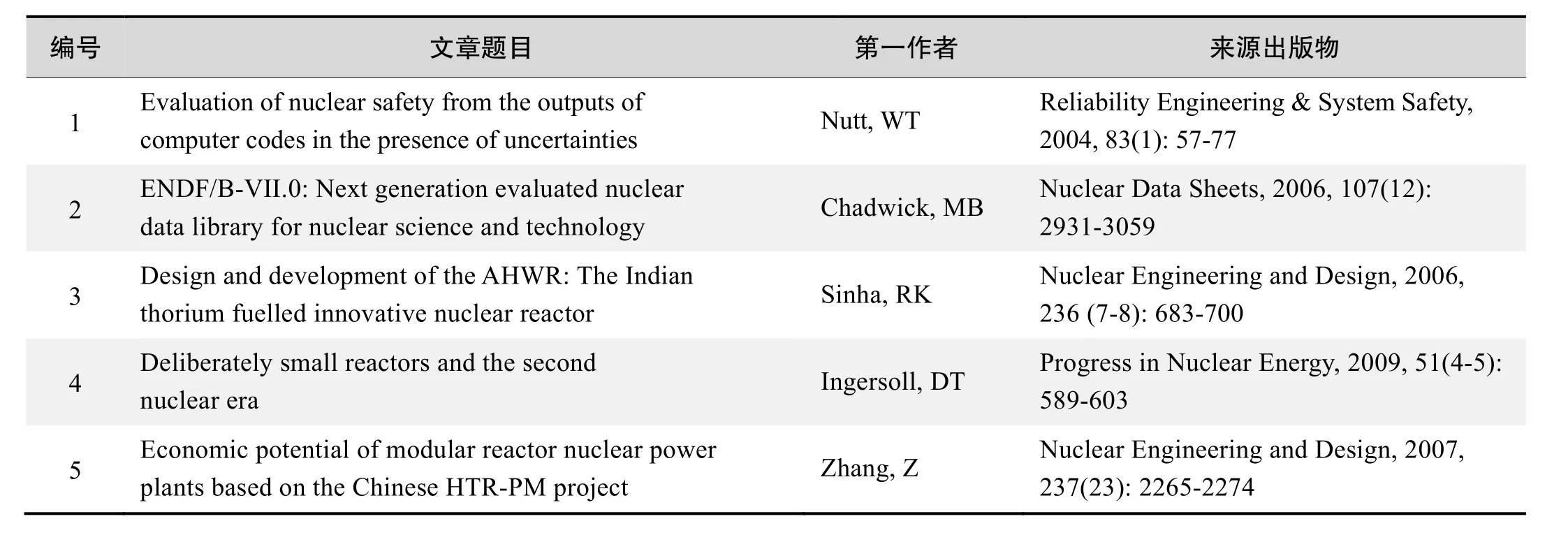
本领域经典文献
来源出版物:Reliability Engineering & System Safety,2004, 83(1): 57-77
ENDF/B-VII.0: Next generation evaluated nuclear data library for nuclear science and technology
Chadwick, M. B.; Oblozinsky, P; Herman, M; et al.
Abstract: We describe the next generation general purpose Evaluated Nuclear Data File, ENDF/B-VIL0, of recommended nuclear data for advanced nuclear science and technology applications. The library, released by the U.S. Cross Section Evaluation Working Group(CSEWG)in December 2006, contains data primarily for reactions with incident neutrons, protons, and photons on almost 400 isotopes, based on experimental data and theory predictions. The principal advances over the previous ENDF/B-VI library are the following:(1) New cross sections for U, Pu, Th; Np and Am actinide isotopes, with improved performance in integral validation criticality andneutron transmission benchmark tests;(2) More precise standard cross sections for neutron reactions on H,6Li,10B, An and for235,238U fission, developed by a collaboration with the IAEA and the OECD/NEA Working Party on Evaluation Cooperation(WPEC):(3) Improved thermal neutron scattering:,(4) An extensive set of neutron cross sections on fission products developed through a WPEG collaboration;(5) A large suite of photonuclear reactions;(6) Extension of many neutron-and protoninduced evaluations up to 150 MeV:(7) Many new light nucleus neutron and proton reactions;(8) Post-fission beta-delayed photon decay spectra:,(9) New radioactive decay data:,(10) New methods for uncertainties and covariances, together with covariance evaluations for some sample cases; and(11) New actinide fission energy deposition. The paper provides an overview of this library,consisting of 14 sublibraries in the same ENDF-6 format as the earlier ENDF/B-VI library. We describe each of the 14 sublibraries, focusing on neutron reactions. Extensive validation, using radiation transport codes to simulate measured critical assemblies, show major improvements:(a) The Ion-standing underprediction of low enriched uranium thermal assemblies is removed;(b) The238U and208Pb and9Be reflector biases in fast systems are largely removed;(c) ENDF/B-VI.8 good agreement for simulations of thermal high-enriched uranium assemblies is preserved;(d) The underprediction of fast criticality of235,238U and239Pu assemblies is removed; and(e) The intermediate spectrum critical assemblies are predicted more accurately. We anticipate that the new library will play an importanrole in nuclear technology applications,including transport simulations supporting national security, nonproliferation, advanced reactor and fuel cycle concepts, criticality safety, fusion, medicine, space applications, nuclear astrophysics, and nuclear physics facility design. The ENDF/B-VII.0 library is archived at the National Nuclear Data Center, BNL, and can be retrieved from www.nndc.bnl.gov.
来源出版物:Nuclear Data Sheets, 2006, 107(12): 2931-3059
Design and development of the AHWR: The Indian thorium fuelled innovative nuclear reactor
Sinha RK; Kakodkar A
Abstract: India has chalked out a nuclear power program based on its domestic resource position of uranium and thorium. The first stage started with setting up the Pressurized Heavy Water Reactors(PHWR) based on natural uranium and pressure tube technology. In the second phase, the fissile material base will be multiplied in Fast Breeder Reactors using the plutonium obtained from the PHWRs. Considering the large thorium reserves in India, the future nuclear power program will be based on thorium-233U fuel cycle. However, there is a need for the timely development of thorium-based technologies for the entire fuel cycle. The Advanced Heavy Water Reactor(AHWR) has been designed to fulfill this need. The AHWR is it 300 MW, vertical, pressure tube type, heavy water moderated, boiling light water cooled natural circulation reactor. The fuel consists of(Th-Pu)O2and(Th-233U)O2pins. The fuel cluster is designed to generate maximum energy out of233U, which is bred in situ from thorium and has a slightly negative void coefficient of reactivity. For the AHWR, the well-proven pressure tube technology has been adopted and many passive safety features, consistent with the international trend, have been incorporated. A distinguishing feature which makes this reactor unique,from other conventional nuclear power reactors is the fact that it is designed to remove core heat by natural circulation. under normal operating conditions, eliminating the need of pumps. In addition to this passive feature,several innovative passive safety systems have been incorporated in the design, for decay heat removal under shut down condition and mitigation of postulated accident conditions. The design of the reactor has progressively undergone modifications and improvements based on the feedbacks from the analytical and the experimental R&D. This paper gives the details of the current design of the AHWR.
来源出版物: Nuclear Engineering and Design, 2006, 236(7-8): 683-700
Deliberately small reactors and the second nuclear era
Ingersoll, D. T.
Abstract: Smaller sized nuclear reactors were instrumental during the pioneering days of commercial nuclear power to facilitate the development and demonstration of early reactor technologies and to establish operational experience for the fledgling nuclear power industry. As the U.S. embarks on its “second nuclear era,” the question becomes: Will smaller sized plants have a significant role in meeting the nation’s needs for electricity and other energy demands?A brief review of our nuclear history is presented relativeto plant size considerations, followed by a review of several commonly cited benefits of small reactors. Several“deliberately small” designs currently being developed in the U.S. are briefly described, as well as some of the technical and institutional challenges faced by these designs. Deliberately small reactors offer substantial benefits in safety. security, operational flexibilities and economics,and they are well positioned to figure prominently in the second nuclear era.
Keywords: small medium reactors; deliberately small reactors; second nuclear era; nuclear renaissance; new reactor designs
来源出版物:Progress in Nuclear Energy, 2009, 51(4-5): 589-603
Economic potential of modular reactor nuclear power plants based on the Chinese HTR-PM project
Zhang, Zuoyi; Sun, Yuhang
Abstract: Modular reactors with improved safety features have been developed after the Three-Mile Island accident. Economics of small modular reactors compared to large light water reactors whose power output is 10 times higher is the major issue for these kind of reactors to be introduced into the market. Based on the Chinese high temperature gas-cooled reactor pebble-bed module(HTRPM) project, this paper analyzes economical potentials of modular reactor nuclear power plants. The reactor plant equipments are divided into 6 categories such as RPV and reactor internals, other NSSS components and so on. The economic impact of these equipments is analyzed. It is found that the major difference between an HTR-PM plant and a PWR is the capital costs of the RPV and the reactor internals. The fact, however, that RPV and reactor internals costs account for only 2% of the total plant costs in PWR plants demonstrates the limited influence of this difference. On the premise of multiple NSSS modules forming a nuclear power plant with a plant capacity equivalent to a typical PWR plant, an upper value and a target value of the total plant capital costs are estimated. A comparison is made for two design proposals of the Chinese HTR-PM project. It is estimated that the specific costs of a ready-to-build 2 × 250 MWth modular plant will be only 5% higher than the specific costs of one 458 MWth plant. When considering the technical uncertainties of the latter, a 2 × 250 MWth modular plant seems to be more attractive. Finally, four main points are listed for MHTGRs to achieve economic viability.
来源出版物:Nuclear Engineering and Design, 2007, 237(23): 2265-2274
·推荐综述·
中国核电发展战略研究
叶奇蓁
1核能在中国能源可持续发展中的地位
1.1中国能源资源状况分析
中国能源资源有3个基本特点。能源资源品种丰富,但人均占有量较少,在己探明储量中煤炭占世界人均的56%、石油占11%,天然气占4.6%。能源资源结构不尽合理,煤炭、水能相对丰富,而优质化石能源(石油)相对不足。能源资源分布与生产力布局不平衡,经济发达地区在东南沿海,而水力资源在西部和西南部,煤炭主要在北方。
目前,我国能源发展面临4个基本问题。即经济社会发展中的能源供需总量平衡问题。长期以煤为主的能源结构,造成的环境、生态问题。西气东运、北煤南运、西电东输的能源输运问题,我国煤炭运输占铁路运量的40%,占沿海和长江中下游水运1/3。对国外资源依存的能源供应安全问题。
核电的基本特性决定了在应对能源挑战中有能力发挥无可替代的重要作用。核电不排放SO2等污染物和温室气体CO2,对环境后果实行严格管理,因此属于清洁能源。而核电的安全可靠性正在不断提高。核电对煤电具有较强经济竞争力和替代能力,目前二代改进型核电站的电价大都与当地的标杆电价相当。核电燃料运输量小。因此,我国在现阶段发展核电是调整源布局的有效途径。
1.2中国核能发展的技术路线
我国核能发展的技术路线是走热堆、快堆、聚变堆三步发展的道路。在近期发展己经成熟的热中子堆核电站,满足当前和近期核电发展的需要。第二步发展快中子增殖堆核电站及配套的核燃料循环体系,充分利用铀资源,实现裂变核能的可持续发展。第三步发展核聚变堆核电站,有望最终解决人类的能源供应问题。
目前,在热堆核电发展阶段,逐步实现由二代向三代过渡。在2020年以前,适度发展我国己经掌握技术的二代改进型压水堆核电站。抓紧引进三代核电技术的消化吸收再创新,掌握技术、实现自主化,尽快实现三代核电的批量化建设。
1.3核电产业发展的目标
根据有关研究部门的预测,2020年我国电力总装机将达到15亿kW,核电总装机容量将达到7000万kW,核电容量占总容量的4.6%,占总发电量的7.0%左右。考虑能源结构调整的要求,2030年我国总发电装机容量将达到20亿kW,核电总装机容量将达到2亿kW,核电装机容量占10%,占总发电量的15%。2050年我国将进入中等发达国家行列,以人均1.56 kW计算,总发电装机容量将达到25亿kW,核电总装机容量将达到4亿kW,核电占总装容量的16%,占总发电量的22%。
2中国核电已形成规模化批量化发展格局
我国大陆投入商运的核电机组共有 11台,总装机容量为910万kW,机组负荷因子达85%~92%,各项运行指标均高于世界平均水准,处于世界中上等水平以上。在全球441座核电站中,大多进入前50~60名。即将建成的岭澳二期核电站和秦山核电二期扩建均进展良好,预期在2010—2011年将陆续投产发电。目前己有22台二代改进型压水堆核电站取得了路条,并己有7台机组浇灌了第一罐混凝土。主设备己实现了批量采购,有的制造厂己签订了数台或十余台长周期设备。而核电站设计的标准化规范化工作也正在积极进行当中。
当前我国二代改进型压水堆核电站己具备系列化规模化发展的有利条件。二代改进型压水堆属于成熟的堆型,设计经过验证,自主化程度较高。有相当丰富的自主建设和自主运行经验,平均建设周期小于5 a。设备国产化率超过70%,除主循环泵(目前己有3家制造厂在研制)外,主要的核电设备己具备坚实的国产化基础。我国己建成的核电站的运行经验表明,核电站的运行是安全的,没有温室气体和有害气体排放,放射性废物的排放远低于国家标准。
2.1二代改进型压水堆核电站自主化能力分析
二代改进型压水堆核电站随着技术的发展和运行经验的反馈,逐步引入新的成熟技术,使核电站的安全性得到进一步的提高。新设计建设的二代改进型压水堆降低了堆芯功率密度,使热工安全余量大于15%;加大稳压器容量,增加了核电站运行的稳定性;增设附加应急柴油发电机系统,提高了供电的可靠性;增设安全壳过滤卸压排放系统,防止安全壳超压失效,并防止放射性外泄;应用概率安全分析技术以及风险管理技术,防止核电站出现严重事故;引入严重事故预防和缓解措施:如非能动氢复合系统防止氢爆、稳压器卸压排放系统防止高压熔堆、田湾核电站还设计了堆芯捕集器用以在堆芯熔融时防止熔融物熔穿透安全壳底板;广泛采用数字化仪控技术和先进控制室,改善了人机界面;汽轮发电机采用半速机组,提高了出力和热效。
二代改进型压水堆核电站在自主设计能力方面,形成了专业配套、结构合理的研究设计队伍。
在项目管理能力方面,按国际通用项目管理模式管理,己基本与国际接轨。
在设备制造能力方面,3大集团都将基本具备每年提供2~3台百万千瓦级机组设备的能力。
在建设安装能力方面,己经具有4个项目8台机组的建设实践。
在营运管理能力方面,根据世界核电运行者协会WANO的9项性能指标,3项进入前1/4的先进行列,有5项超过中值水平,只有1项略低于中值水平。
在安全监管能力方面,建立了与国际接轨的核安全管理和监督的法规制度,具备了全过程全方位监督管理的能力。
2.2大力堆进内陆核电建设
国际上大部分核电站建设在内陆。法国有65.1%的核电站建设在内陆,美国亦有75.7%的核电站建设在内陆。有些内陆国家,比如瑞士,5座核电站都在内陆的江河边上,5座核电站总发电功率为3220 MW,占总发电量的37%,其他将近60%的发电量由水电提供。因此,国外其他国家的经验表明,在内陆建核电站是完全可行的。
我国内陆地区经济有了很大发展,电网容量亦有很大发展,但部分省份同样存在缺乏煤炭和水力资源。2009年初南方各省发生了大面积、长时间的雪灾,造成了广大地区长时间的断电,带来了严重的后果。因此,仅依靠远距离输电和长途运煤是难以保障用电安全的。这样,除提高电网的抗灾害能力,建设紧急情况下不依赖燃料运输的核电站是很有必要的。
从安全和环保要求看,内陆核电站和沿海核电站没有本质的差别。目前成熟的核电站设计和建造技术完全可用到内陆核电。内陆江河流量多半不够大,可采用冷却塔闭式循环带走余热,以减轻温排水对环境的影响。目前,百万千瓦级核电站一机一塔要求塔高200 m,淋水面积16000 m2时,我国己能设计160 m,12000 m2冷却塔,正在开展超大型冷却塔的设计。因此按照核电规范选择的厂址是能够保证核电站的安全的。
2.2.1放射性液态流出物的排放控制
内陆厂址与沿海厂址相比,液态流出物中要考虑放射性物质到达人体的途径及饮用水和灌溉等途径。目前,我国江河、湖泊污染事件屡有发生,国家主管部门和公众对于河流的排放控制均持高度关注和审慎的态度。核电厂环境辐射防护规定液态流出物排放的放射性总量每年≤200 GBq(不包括氚),URD文件中对先进压水堆核电站规定每年≤1.85 GBq(不包括氚),EUR文件中对先进压水堆核电站规定每年≤10 GBq(不包括氟)。从秦山二期2002—2006年统计的数据,年液态流出物排放的放射性总量为2~5 GBq。因此,目前设计的液态流出物处理系统完全能满足国标要求,而实际运行水平远低于国标要求,并与先进压水堆核电站的要求相当。
2.2.2液态放射性流出物排放浓度控制
我国的《生活饮用水卫生标准》(GB57492006)中规定总β放射性小于1 Bq/L。《核动力厂环境辐射防护规定》(GB6249)提出核动力厂排放口下游1 km处受纳水体中总月放射性浓度不得超过1 Bq/L,这就是要求在排放口下1 km处满足生活饮用水标准。GB-14587—修订版的征求意见稿,提出了100 Bq/L的排放罐出口浓度控制值。因此,经过适当的稀释,核电厂液态放射性流出物排放浓度就可达到天然放射性本底水平。
内陆核电站由于采用冷却塔闭式循环带走余热,没有循环冷却水对放射性废液的稀释。滨海压水堆核电站液态流出物排放的内部实际控制值为≤1000~2000 Bq/L(不包括氚),经循环冷却水对放射性废液的稀释 1000倍后,其浓度己相当低,一般≤1 Bq/L。俄罗斯滨河核电站要求液态流出物排放的浓度控制值为≤18 Bq/L(不包括氚)。所以,改进目前沿海核电站的液态放射性废物的处理技术,是完全能满足内陆核电站对液态放射性废物处理和排放的要求的。
2.2.3液态放射性废物处理技术
俄罗斯核电站放射性废液处理采用了双蒸发器处理系统,处理后的液体再经二级离子交换处理,净化系数从10E3提高到10E5。美国采用反渗透废液处理技术,实现废水回用,以满足“零液体排放”要求,并可针对某些元素进行高纯度净化或去除。美国 Comanch Peak核电站用于去除放射性,特别是Co胶体,CS和I到监测不到水平,净化系数达 5.7×104。美国德赖斯登核电站用超级过滤+反渗透+去离子技术处理废液。内陆核电站的含氟废水,在废水处理后,排入冷却塔循环冷却水中,通过蒸发向大气排放。
3积极消化吸收第三代核电技术
3.1第三代核电发展的背景
1979年美国发生的三里岛核电站事故和1986年前苏联发生的切尔诺贝利核电站事故,使公众要求进一步提高核电的安全性。1990年EPRI根据主要电力公司意见出版了“电力公司要求文件(URD)”共 3卷。1994年欧洲联盟出版了“欧洲电力公司要求(EUR)”共 4卷。这些文件对未来压水堆和沸水堆核电站提出了电力公司明确和完整的要求,更高的安全要求和经济要求,涉及各个技术和经济领域。
第三代核电机组要有更高安全目标。即堆芯热工安全裕量>15%,堆芯损坏概率<10-5/堆年,大量放射性外泄<10-6/堆年。第三代核电机组要有更好的经济性,具体表现在机组额定功率为1000~1500 MWe,可利用因子>87%,换料周期18~24月,电站寿命60 a,建设周期48~52月,电价要能与联合循环的天然气电厂相竞争。因此,第三代核电机组在技术上更先进。
3.2AP1000核电站的特点
AP1000核电站采用非能动安全系统。具体表现在采用非能动安注、多级非能动自动卸压系统、非能动余热排放系统和非能动安全壳冷却系统。AP1000核电站引入了严重事故预防和缓解措施,如堆腔淹没技术、安全壳内氢点火和氢复合系统、堆芯熔融物反应堆压力容器内保持。同时,AP1000采用双层安全壳和全数字化仪控系统。采用模块化施工使建设工期缩短到 48个月。
AP1000核电站的反应堆冷却剂系统(如图1所示)采用屏蔽式电泵,取消了机械密封,采用在上部堆芯测量以及大容量稳压器,焊接结构的堆内构件和压力容器活性区及法兰接管段大型整体锻件。
AP1000核电站的非能动堆芯冷却系统,不依赖外部电源,采用非能动余热导出、非能动安全注入以及非能动安全壳冷却可以保证长时间的安全停堆,还可以保证大于72 h不用操作员干预。
3.3ERP核电站的特点
EPR核电站的主要特点有以下几个。EPR核电站功率高,达到1500~1700 MWe。采用4通道安全系统和双层安全壳。引入了严重事故预防及缓解措施,如稳压器卸压、堆芯扑集器和非能动氢复合器。同时EPR核电站也采用全数字化仪控和模块化施工。
3.4AP1000的关键技术
AP1000的关键技术是采用非能动安全系统,特别是非能动安全壳冷却系统。AP1000核电站引入了严重事故的预防和缓解措施,包括自动卸压系统久(ADS),抑制氢爆的氢复合系统(氢点火器和非能动氢催化复合),以及堆芯熔融物压力容器内保持(IVR)等技术。同时AP1000核电站大容量屏蔽泵的设计和制造,爆破膜的设计和制造,以及大尺寸园柱形钢安全壳的设计和建造也存在技术难点和需攻克的关键技术。
3.5重视三代核电引进中技术风险经济风险的规避
AP1000的技术风险主要在于缺少首堆工程整体验证的实践证明,AP1000的设计认证尚未真正通过,而且还有一系列涉及安全的设计验证工作未做,设计方案尚未固化,从美国条件的设计直接移植到中国,还需要作适应性修改。
AP1000核电站也存在一定的经济风险。最近西屋公司与美国几个电力公司签订在美国新建AP1000的总承包协议,比投资是我国自主建设核电的 2~3倍,也是招标引进时申报的2~3倍。
4铀资源的保障
我国己探明一定数量铀资源可以满足近期核电发展的需要。国内铀资源勘测有较好发展前景。理论预测铀矿资源比较丰富,预测铀资源总量超过几百万吨,加之我国相当范围国土未经详细勘查,因此扩大老矿区、加强深层勘查,开辟新基地前景看好。我国目前己探明储量,加上海外采购和合作开采的天然铀,足以保障2020年核电对天然铀的需求。因此加大铀资源的国内勘查力度,同时开拓国外铀资源的供应,我国核电发展的铀资源是一定能得到保证的。
从长期来看,到 2030—2050年我国的人口将达到顶峰16亿,按平均每人消耗电力1.56 kW来计(相当于发达国家的中等水平),就需要25亿kW的电力供应,其中16%为核电(相当于目前世界核电的平均份额),即4亿kW的核电。到2050年我国对于天然铀资源需求相当大,如果核电的比例比16%还要大,则对天然铀资源的需求将更大。
5开发快中子增殖堆核电站、构建核燃料循环体系
5.1钠冷快堆SFR
快中子增殖反应堆的主要特点在于它能增殖核燃料,即它每燃耗一个燃料原子,就可以生产出多于一个燃料原子,这样一来,在理论上说,它可以将全部铀资源都转化为可燃烧的燃料并加以利用。采用适当增殖比的快中子堆,可以将铀资源的利用率由普通的热堆的不足 1%,提高到 60%~70%,从而有效防止铀资源枯竭的威胁。
快中子增殖反应堆中等规模的电功率为 150~500 MWe,一般采用热冶金金属燃料后处理循环。大型规模的电功率为500~1500 MWe,一般采用先进水法氧化燃料后处理循环。堆出口温度可达 550℃。快中子增殖反应堆用钠作为冷却剂,主要分为池式或环路式2种。
5.2快中子反应堆在中国的发展
我国己在“十一五”期间建成实验快中子堆。计划2020年前后将建成原型快中子堆核电站,通过引进技术建设第一个快中子堆示范工程。2035年前后完成商用快中子堆核电站及核燃料循环系统的建设。此时,不仅可利用0.7% U—235,通过快中子堆增殖,还可利用大量的U—238(经快中子反应堆转换的Pu)。
5.3加快商用后处理厂的建设和快堆燃料循环技术
的研发
近期目标主要是实现 2025年开式循环向闭式循环转变,减缓天然铀资源的消耗,并为快中子堆提供核燃料,在 2020年前后建成大型商用后处理厂是关键核心环节。建成年处理800 t重金属乏燃料规模是适当的,但与2020年7000万kW核电装机规模相比还稍小。远期目标主要是在2035年前后实现快堆核能系统的商化,快堆燃料制备和快堆乏燃料后处理的研究开发应与快堆同步进行。
5.4突破放射性废物最小化和安全处置的关键技术
乏燃料管理和高放废物处置仍然是核工业关键的挑战。必须开展利用快堆进行放射性废物擅变研究实现MA(次婀系核素)和LLFP(长寿命裂变产物)的彻底焚烧。要积极推进高放废物安全处置的研究,我国高放废物处置地下实验室应于2020年建成,争取在2040—2050年建成地质处置库并投入运行。
【作者单位:中国核工业集团公司】
(摘自《电网与清洁能源》2010年1期)
·高被引论文摘要·
被引频次:89
大型集成多功能中子学计算与分析系统Visual BUS的研究与发展
吴宜灿,李静惊,李莹,等
中子学计算与分析是反应堆物理与辐射防护设计、燃料循环管理优化和核安全分析的基础。在广泛深入调研国内外中子学程序发展现状和趋势的基础上,采用国际上先进的中子学模拟计算技术和现代计算机软件技术,设计和研发了基于网络的大型集成多功能中子学计算与分析软件系统Visual BUS,可用于裂变、聚变和各类混合次临界反应堆系统以及加速器等辐射装置的计算与分析。一系列国际基准校验计算和实际应用表明了该系统的正确性和有效性。本文重点介绍该系统的研发概况、技术特点和测试与应用情况。
中子学;计算;建模;可视化;Visual BUS
来源出版物:核科学与工程, 2007, 27(4): 365-373
被引频次:41
核安全文化的发展与应用
张力
摘要:安全文化已对核能企业的安全性产生了重大影响。本文分析了核安全文化产生的背景,介绍了核安全文化在一些国家和组织应用发展的状况,提出了推行安全文化过程中应注意的几个问题,讨论了评价安全文化绩效的原则。
关键词:安全文化;核电站;核安全
来源出版物:核动力工程, 1995, 16(5): 443-446
被引频次:40
世界核电发展趋势与高温气冷堆
吴宗鑫,张作义
摘要:核能的发展面临经济竞争力、核安全、核废物的最终处置及防止核武器材料扩散的挑战。为改善公众的可接受性,核电厂的安全性进一步改进。电力市场体制的非管制化改革加剧了电力技术的竞争。环境保护意识增强使核废物的处置倍受关注。80年代中期以来发展的先进轻水堆核电厂如ABWR,System 80+,EPR,AP600等是今后一段时期内商用核电的主力堆型。进入2000年之际,美国能源部正在规划发展第四代先进核能系统,目标是在2020年或之前,向市场提供经过验证的成熟的第四代核电厂技术,以替代美国退役的核电容量。球床高温气冷堆被认为是第四代先进核能系统的优选技术。南非ESKOM电力公司选择了球床高温气冷堆作为今后核电发展的堆型。清华大学承担设计和建设的10 MW高温气冷实验堆计划在2000年内临界。通过10 MW高温气冷堆的建造,我国已形成了高温气冷堆技术的自主知识产权,初步具备了自主设计、制造和建造的能力。
关键词:核能科学与工程;高温气冷堆
来源出版物:核科学与工程, 2000, 20(3): 211-231
被引频次:38
人因失误心理背景与核电站安全
张力
摘要:人因失误是造成核电站事故的主要因素之一,而现场的心理背景在诱发人因失误的过程中起着十分重要的作用。本文分析了人行为时心理背景的结构,总结了几种典型的人误心理背景。最后指出,消除不利于安全的心理背景之根本途径是建立企业安全文化,并提出了核安全文化的基本特征。
关键词:人的行为;人因失误;心理因素
来源出版物:核动力工程, 1992, 13(5): 27-30
被引频次:33
切尔诺贝利事故及其影响与教训
胡遵素
摘要:本文从核安全与辐射防护的角度出发,根据几年来国际的研究与报道以及现场访问所了解的情况,对前苏联切尔诺贝利核电站事故发生的原因、影响及其教训进行了简要回顾。内容包括对切尔诺贝利核电站的简单描述、事故发生的过程、事故后的应急行动与防护措施、健康与环境影响以及事故的原因与经验教训。从安全角度看,该电站的型反应堆的空泡正反应性系数、反应性余量不足、控制棒从最高位置开始下落时有一个反应性增长区以及没有有效的围封等是在设计上使此次事故得以发生并酿成灾难性后果的根本原因。操作人员把几个“极不可能事件”组合在一起,是引发事故的直接“导火线”。这次事故暴露的最大问题是前苏联在核安全管理方面的缺陷。笔者认为,提高核能安全性的关键在于健全管理体制和提高安全文化水平。
关键词:核电站;事故;切尔诺贝利;核安全;设计;管理;安全文化
来源出版物:辐射防护, 1994, 14(5): 321-335
被引频次:30
大亚湾核电站的核安全文化建设探讨
陆玮,唐炎钊
摘要:论述了核电站管理中安全文化的概念及安全文化的发展阶段。重点分析了大亚湾核安全文化形成的背景及过程,阐述了大亚湾核安全文化的核心理念,提出了核电站安全文化指标,总结了大亚湾核电站实施核安全文化的主要措施 ;描述了透明度的普及,并对大亚湾核电站核安全文化实施的效果进行了系统分析。
关键词:大亚湾;核电站;核安全文化;企业文化建设
来源出版物:核科学与工程, 2004, 24(3): 205-210
被引频次:25
国内外核电发展状况及相关问题
刘长欣
摘要:介绍国内外核电发展的最新情况,并就与核电有关的若干问题进行讨论。中国是世界主要的核大国,但核电对我国的电力贡献还很少,仅占全国发电量的1.43%。国家主管部门将于近期批准新的核电项目,并有可能就 2020年前的核电发展做出规划,中国的核电发展即将步入快速、稳定的发展之路。
关键词:核电;可用率;自主化;核安全;高放废物;核扩散
来源出版物:中国电力, 2003, 36(9): 27-33
被引频次:23
基于BP神经网络的核安全文化星级评价体系
焦晓佑,宋守信,吴俊勇
摘要:为了加强核电安全文化建设,本文提出了一种对核电安全文化进行科学、全面评价的方法。并根据核电安全文化的特点,以SMART准则为依据,从安全意识、安全价值观、安全行为、安全现状等方面确立了24项安全文化评价指标,提出了安全文化星级划分标准,并在Visual Basic 6.0平台上建立了基于BP神经网络的安全文化星级评价体系。通过泛化能力测试,该体系能准确地评价出核电安全文化发展到了什么阶段,具有良好的可行性和有效性,操作简便,易于推广。
关键词:核电安全文化;星级评价;BP神经网络
来源出版物:核动力工程, 2007, 28(1): 105-114
被引频次:22
核能与核安全:日本福岛核事故分析与思考
陈达
摘要:核能是当今人类社会不可或缺的重要能源,日本福岛核事故危害巨大并再次将核能利用推向风口浪尖。本文从世界核能发展及中国能源需求出发,阐述了发展核能的重要性和必要性;对日本福岛核事故基本情况进行了简单介绍,并对事故原因作深入分析;从福岛核事故对世界核电发展的影响、中国核电发展规划、核电站选址、核电站设计运行、核电技术研发、核安全文化及核电人才培养等方面进行了分析思考,吸取经验、总结教训,切实把核安全摆在核电发展首位。
关键词:核能;核安全;福岛核事故;分析与思考
来源出版物:南京航空航天大学学报, 2012, 44(5): 597-602
被引频次:19
辐射防护剂研究现状及其进展
赵斌,张军帅,刘培勋
摘要:近年来,随着世界核安全形势的紧张以及放射治疗的迅速发展,尤其是日本福岛核电站发生核泄漏事故后,辐射防护剂的研究再一次引起人们的关注。辐射损伤防治药物是救治与防护最为有效和直接的手段之一,在接触放射性物质前使用,能预防射线对人体的损伤,受到照射后使用,能减轻放射病的临床症状,促进早期恢复。自1949年Patt报道半胱氨酸能预防急性放射损伤以来的半个多世纪里,很多国家对辐射损伤的药物预防进行了比较详细的、深入的研究。本工作简述了辐射防护剂的研究简史、化学分类及其作用机理,并就其研究方向作了展望。
关键词:辐射防护剂;研究简史;化学分类;作用机制
来源出版物:核化学与放射化学, 2012, 34(1): 8-13
被引频次:990
ENDF/B-VII.0: Next generation evaluated nuclear data library for nuclear science and technology
Chadwick, M. B.; Oblozinsky, P; Herman, M; et al.
Abstract: We describe the next generation general purpose Evaluated Nuclear Data File, ENDF/B-VIL.0, of recommended nuclear data for advanced nuclear science and technology applications. The library, released by the U.S. Cross Section Evaluation Working Group(CSEWG)in December 2006, contains data primarily for reactions with incident neutrons, protons, and photons on almost 400 isotopes, based on experimental data and theory predictions. The principal advances over the previous ENDF/B-VI library are the following:(1) New cross sections for U, Pu, Th; Np and Am actinide isotopes, with improved performance in integral validation criticality and neutron transmission benchmark tests;(2) More precise standard cross sections for neutron reactions on H,6Li,10B, An and for235,238U fission, developed by a collaboration with the IAEA and the OECD/NEA Working Party on Evaluation Cooperation(WPEC):(3) Improved thermal neutron scattering:(4) An extensive set of neutron cross sections on fission products developed through a WPEG collaboration;(5) A large suite of photonuclear reactions;(6) Extension of many neutron-and protoninduced evaluations up to 150 MeV:(7) Many new light nucleus neutron and proton reactions;(8) Post-fission beta-delayed photon decay spectra:(9) New radioactive decay data:(10) New methods for uncertainties and covariances, together with covariance evaluations for some sample cases; and(11) New actinide fission energy deposition. The paper provides an overview of this library;consisting of 14 sublibraries in the same ENDF-6 format as the earlier ENDF/B-VI library. We describe each of the 14 sublibraries, focusing on neutron reactions. Extensive validation, using radiation transport codes to simulate measured critical assemblies, show major improvements:(a) The Ion-standing underprediction of low enriched uranium thermal assemblies is removed;(b) The238U and208Pb and9Be reflector biases in fast systems are largely removed;(c) ENDF/B-VI.8 good agreement for simulations of thermal high-enriched uranium assemblies is preserved;(d) The underprediction of fast criticality of235,238U and239Pu assemblies is removed; and(e) The intermediate spectrum critical assemblies are predicted more accurately. We anticipate that the new library will play an importanrole in nuclear technology applications, including transport simulations supporting national security, nonproliferation, advanced reactor and fuel cycle concepts, criticality safety, fusion, medicine, space applications, nuclear astrophysics, and nuclear physics facility design. The ENDF/B-VII.0 library is archived at the National Nuclear Data Center, BNL, and can be retrieved from www.nndc.bnl.gov.
来源出版物:Nuclear Data Sheets, 2006, 107(12): 2931-3059
被引频次:166
Materials challenges in nuclear energy
Zinkle, S.J; Was, GS
Abstract: Nuclear power currently provides about 13% of electrical power worldwide, and has emerged as a reliable baseload source of electricity. A number of materials challenges must be successfully resolved for nuclear energy to continue to make further improvements in reliability, safety and economics. The operating environment for materials in current and proposed future nuclear energy systems is summarized, along with a description of materials used for the main operating components. Materials challenges associated with power uprates and extensions of the operating lifetimes of reactors are described. The three major materials challenges for the current and next generation of water-cooled fission reactors are centered on two structural materials aging degradation issues(corrosion and stress corrosion cracking of structural materials and neutron-induced embrittlement of reactor pressure vessels), along with improved fuel system reliability and accident tolerance issues. The major corrosion and stress corrosion cracking degradation mechanisms for light-water reactors are reviewed. The materials degradation issues for the Zr alloy-clad UO2 fuel system currently utilized in the majority of commercial nuclear power plants are discussed for normal and off-normal operating conditions. Looking to proposed future(Generation IV) fission and fusion energy systems,there are five key bulk radiation degradation effects(low temperature radiation hardening and embrittlement;radiation-induced and -modified solute segregation and phase stability; irradiation creep; void swelling; and high-temperature helium embrittlement) and a multitude of corrosion and stress corrosion cracking effects(including irradiation-assisted phenomena) that can have a major impact on the performance of structural materials.
Keywords: nuclear materials; radiation effects; stress corrosion cracking; structural alloys(steels and nickelbase); nuclear fuels
来源出版物:ACTA Materialia, 2013, 61(3): 735-758
被引频次:118
On the relative importance of input factors in mathematical models: Safety assessment for nuclear waste disposal
Saltelli, A; Tarantola, S
Abstract: This article deals with global quantitative sensitivity analysis of the Level E model, a computer code used in safety assessment for nuclear waste disposal. The Level E code has been the Subject of two international benchmarks of risk assessment codes and Monte Carlo methods and is well known in the literature. We discuss the Level E model with reference to two different settings. In the first setting, the objective is to find the input factor that drives most of the output variance. In the second setting,we strive to achieve a preestablished reduction in the variance of the model output by fixing the smallest number of factors. The emphasis of this work is on how to define the concept of importance in an unambiguous way and how to assess it in the simultaneous occurrence of correlated input factors and non-additive models.
Keywords: analysis of variance; correlated input;nonadditive model; sensitivity analysis
来源出版物:Journal of the American Statistical Association, 2002, 97(459): 702-709
被引频次:95
Assessing safety culture in nuclear power stations
Lee, T; Harrison, K
Abstract: Definitions of safety culture abound, but they variously refer to the safety-related values, attitudes,beliefs, risk perceptions and behaviours of all employees. This assembly may seem too inclusive to be meaningful,but each represents a different level of processing and the choice for measurement(or intervention) is more pragmatic than theoretical. The present study addresses mainly attitudes, but also reported behaviours. This is done using a 120-item questionnaire covering eight domains of safety in three nuclear power stations. Principal components analysis yields 28 factors - all but four of which are correlated with one or more of nine criteria of accident history. Differences by gender, age, shifts/days and work areas are revealed, but these are confounded by type of job and ANOVAS are applied to clarify the main sources of variation. The effects on safety culture of a number of organisational components are also explored. For example the role of safety in team briefings,management style, work pressure versus safety, etc. It is concluded that personnel safety surveys can usefully be applied to deliver a multi-perspective. comprehensive and economical assessment of the current state of a safety culture and also to explore the: dynamic inter-relationships of its working parts.
Keywords: safety culture; nuclear accidents; nuclear employees; nuclear power stations; safety attitudes
来源出版物:Safety Science, 2000, 34(1-3): 61-97
被引频次:88
Optimization of standby safety system maintenance schedules in nuclear power plants
Harunuzzaman, M; Aldemir, T
Abstract: A methodology and a computational scheme are developed based on dynamic programming(DP) to find the minimum cost maintenance schedule for nuclear power plant standby safety systems. Surveillance and testing are assumed to return the component to as-good-as-new condition whether accompanied by restorative maintenance only or full repair or replacement. The methodology defines component state as the number of unsurveilled and untested maintenance intervals or stages, and the optimization process is decomposed into(a) feasibility screening and(b) DP search. This approach achieves a significant reduction in the state space over which the DP search is to be performed. The application of the scheme is demonstrated on the ten-component high-pressure injection system of a pressurized water reactor. This demonstration indicates that the scheme is viable and efficient and particularly suited to exploit any economies of scale and scope that may be present.
Keywords:dynamicprogramming;maintenance optimization; reliability-centered maintenance
来源出版物:Nuclear Technology, 1996, 113(3): 354-367
被引频次:81
Deliberately small reactors and the second nuclear era
Ingersoll, D. T.
Abstract: Smaller sized nuclear reactors were instrumental during the pioneering days of commercial nuclear power to facilitate the development and demonstration of early reactor technologies and to establish operational experience for the fledgling nuclear power industry. As the U.S.embarks on its “second nuclear era,” the question becomes: Will smaller sized plants have a significant role in meeting the nation’s needs for electricity and other energy demands? A brief review of our nuclear history is presented relative to plant size considerations, followed by a review of several commonly cited benefits of small reactors. Several “deliberately small” designs currently being developed in the U.S. are briefly described, as well as some of the technical and institutional challenges faced by these designs. Deliberately small reactors offer substantial benefits in safety. security, operational flexibilities and economics, and they are well positioned to figure prominently in the second nuclear era.
Keywords: small medium reactors; deliberately small reactors; second nuclear era; nuclear renaissance; new reactor designs
来源出版物:Progress in Nuclear Energy, 2009, 51(4-5): 589-603
被引频次:48
Assessment of safety-critical software in nuclear-power-plants
Parnas, DL; Asmis, GJK; Madey, J
Abstract: This article outlines an approach to the design,documentation, and evaluation of computer systems. We believe that this approach allows the use of software in many safety-critical applications because it enables the systematic comparison of the program behavior with the engineering specifications of the computer system. Many of the ideas in this article have been used by the Atomic Energy Control Board of Canada(AECB) in its safety assessment of the software for the shutdown systems of the Darlington Nuclear Power Generating Station. The four main elements of this approach follow:(1) Formal Documentation of Software Requirements: Most of the details of a complex environment can be ignored by system implementers and reviewers if they are given a complete and precise statement of the behavioral requirements for the computer system. We describe five mathematical relations that specify the requirements for the software in a computerized control system.(2) Design and Documentation of the Module Structure: Complexity caused by interactions between separately written components can be reduced by applying “Information Hiding”(also known as Data Abstraction, Abstract Data Types, and Object-Oriented Programming) if the interfaces are precisely and completely documented.(3) Program Function Documentation: Software executions are lengthy sequences of state changes described by complex algorithms. The effects of these execution sequences can be precisely specified and documented with tabular representations of the program functions discussed by Mills and others. Also,large programs can be decomposed and presented as a collection of well- documented smaller programs.(4)“Tripod Approach” to Assessment: There are three basic approaches to the assessment of complex software products:(i) testing,(ii) systematic inspection, and(iii) certification of people and processes. Assessment of a complex system cannot depend on any one of these alone. The approach used on the Darlington shutdown software, which included systematic inspection as well as both planned and statistically designed random testing, is outlined. Certification of software engineers remains a difficult issue.
来源出版物:Nuclear Safety, 1991, 32(3): 189-198
被引频次:35
Nanofluids for enhanced economics and safety of nuclear reactors: An evaluation of the potential features, issues, and research gaps
Buongiorno, Jacopo; Hu, Lin-Wen; Kim, Sung Joong
Abstract: Nanofluids are engineered colloidal suspensions of nanoparticles in water and exhibit a very significant enhancement(up to 200%) of the boiling critical heat flux(CHF) at modest nanoparticle concentrations(<= 0.1% by volume). Since CHF is the upper limit of nucleate boiling,such enhancement offers the potential for major performance improvement in many practical applications that use nucleate boiling as their prevalent heat transfer mode. The Massachusetts Institute of Technology is exploring the nuclear applications of nanofluids, specifically the following three: 1. main reactor coolant for pressurized water reactors(PWRs). 2. coolant for the emergency core cooling system(ECCS) of both PWRs and boiling water reactors. 3. coolant for in-vessel retention of the molten core during severe accidents in high-power-density light water reactors. The main features and potential issues of these applications are discussed. The first application could enable significant power uprates in current and future PWRs, thus enhancing their economic performance. Specifically, the use of nanofluids with at least 32% higher CHF could enable a 20% power density uprate in current plants without changing the fuel assembly design and without reducing the margin to CHF The nanoparticles would not alter the neutronic performance of the systemsignificantly. A RELAP5 analysis of the large-break loss-of-coolant accident in PWRs has shown that the use of a nanofluid in the ECCS accumulators and safety injection can increase the peak-cladding-temperature margins(in the nominal-power core) or maintain them in uprated cores if the nanofluid has a higher post-CHF heat transfer rate. The third application can increase the margin to vessel breach by 40% during severe accidents in high-power density systems such as Westing house AP1000 and the Korean APR1400. In summary, the use of nanofluids in nuclear systems seems promising; however, several significant gaps are evident, including, most notably, demonstration of thenanofluidthermal-hydraulicperformanceat prototypical reactor conditions and the compatibility of the nanofluid chemistry with the reactor materials. These gaps must be closed before any of the aforementioned applications can be implemented in a nuclear power plant.
Keywords: nanofluids; reactor coolant; critical heat flux
来源出版物:Nuclear Technology, 2008, 162(1): 80-91
被引频次:33
Evaluation of nuclear safety from the outputs of computer codes in the presence of uncertainties
Nutt, WT; Wallis, GB
Abstract: We apply methods from order statistics to the problem of satisfying regulations that specify individual criteria to be met by each of a number of outputs, k, from a computer code simulating nuclear accidents. The regulations are assumed to apply to an ‘extent’, gamma(k),(such as 95%) of the cumulative probability distribution of each output, k, that is obtained by randomly varying the inputs to the code over their ranges of uncertainty. We use a 'bracketing' approach to obtain expressions for the confidence, 6, or probability that these desired extents will be covered in N runs of the code. Detailed results are obtained for k = 1, 2, 3, with equal extents, gamma, and are shown to depend on the degree of correlation of the outputs. They reduce to the proper expressions in limiting cases. These limiting cases are also analyzed for an arbitrary number of outputs, k. The bracketing methodology is contrasted with the traditional ‘coverage’approach in which the objective is to obtain a range of outputs that enclose a total fraction, gamma, of all possible outputs, without regard to the extent of individual outputs. For the case of two outputs we develop an alternate formulation and show that the confidence, 6, depends on the degree of correlation between outputs. The alternate formulation reduces to the single output case when the outputs are so well correlated that the coverage criterion is always met in a single run of the code if either output lies beyond an extent gamma, it reduces to Wilks’ expression for un-correlated variables when the outputs are independent, and it reduces to Wald’s result when the outputs are so negatively correlated that the coverage criterion could never be met by the two outputs of a single run of the code. The predictions of both formulations are validated by comparison with Monte Carlo simulations.
Keywords: nuclear safety; outputs of codes; regulations;non-parametric methods; bracketing; coverage; confidence来源出版物:Reliability Engineering & System Safety,
2004, 83(1): 57-77
被引频次:32
Scale 6: Comprehensive nuclear safety analysis code system
Bowman, SM
Abstract: Version 6 of the Standardized Computer Analyses for Licensing Evaluation(SCALE) computer software system developed at Oak Ridge National Laboratory, released in February 2009, contains significant new capabilities and data for nuclear safety analysis and marks an important update for this software package, which is used worldwide. This paper highlights the capabilities of the SCALE system, including continuous-energy flux calculations for processing multigroup problem-dependent cross sections,ENDF/B-VII continuous-energy and multigroup nuclear cross-section data, continuous-energy Monte Carlo criticality safety calculations, Monte Carlo radiation shielding analyses with automated three-dimensional variance reduction techniques, one- and three-dimensional sensitivity and uncertainty analyses for criticality safety evaluations, twoand three-dimensional lattice physics depletion analyses,fast and accurate source terms and decay heat calculations,automated burnup credit analyses with loading curve search, and integrated three-dimensional criticality accident alarm system analyses using coupled Monte Carlo criticality and shielding calculations.
Keywords: reactor physics; sensitivity; uncertainty;criticality safety
来源出版物:Nuclear Technology, 2011, 174(2): 126-148
·推荐论文摘要·
核电厂工程结构抗震研究进展
孔宪京,林皋
摘要:当前以及今后相当长一段时期,核电都将是中国积极发展的能源形式之一,保障核电安全是确保核电工程建设顺利实施和安全运营的关键。然而,中国幅员广阔,地质条件差异大,海域自然条件复杂;同时,中国地震活动范围广、强度大、频度高,基于标准化设计的核电工程结构在建设过程中面临着诸多问题。尤其是2011年日本大地震导致的福岛核电事故的教训,对核电工程的抗震安全提出了新的问题。结合大连理工大学十几年来在解决我国核电工程结构抗震安全中的关键问题,以及在“地震作用下核电厂工程结构的功能失效机理及抗震安全评价”研究中所取得若干进展进行综述性介绍,主要包括核岛地基抗震适应性研究和核岛安全相关工程结构抗震防灾研究。
关键词:核电厂;地基适应性;取排水构筑物;安全壳;抗震安全评价
来源出版物:中国工程科学, 2013, 15(4): 62-74
福岛核事故后核电厂安全改进行动分析
张琳,李文宏,杨红义
摘要:介绍了福岛核事故后世界上主要核电国家相继开展的核电厂安全检查、再评价行动,并得出相应的检查和测试结论。法国、美国和中国等国家分别提出了福岛核事故后改进核电厂安全的建议、要求和行动,并制定了具体工程措施:在极端外部事件的设防,严重事故预防和缓解,水、电、通风实体改进,限制严重事故下的放射性释放和应急准备等主要方面开展的安全改进行动,将会提高核电厂的安全水平并提升缓解严重事故的能力。反思福岛核事故,总结福岛核事故对核电安全技术改进的促进作用,对未来核电安全技术的发展进行了展望。
关键词:福岛核事故;核电厂;核安全;改进行动
来源出版物:原子能科学技术, 2014, 48(3): 486-491
我国内陆核电发展的环境风险可控性探析
潘自强,赵成昆,陈晓秋,等
摘要:阐述了内陆发展核电所关注的厂址安全、环境保护的几个问题。分析表明,发展内陆核电是我国绿色低碳能源发展的重要战略选择,内陆核电的核安全是有保障的,环境风险可控,我国启动内陆核电建设的条件已经成熟。
关键词:内陆核电;核安全;环境风险;绿色低碳
来源出版物:环境保护, 2014, 42(1): 10-14
核化学与放射化学的研究进展
张生栋,丁有钱,顾忠茂
摘要:在我国核能快速发展的新形势下,新型核能资源的开发、乏燃料后处理、放射性废物处理与处置等核燃料循环化学研究日益活跃。随着科学技术的不断发展,离子加速器、反应堆、各种类型的探测器和分析设备、以及计算机技术等的发展,核化学与放射化学研究的范围和成果在不断扩展和增加,如核安全、环境放射化学、放射分析化学、放射性药物与标记化合物等,研究成果对于国防建设、核能发展、核技术应用等方面具有重要支撑作用。本文综述了近年来国内在上述领域所取得的研究进展。
关键词:核燃料循环化学;核化学;放射化学;环境放射化学;放射性药物化学;核安全;核技术应用
来源出版物:化学通报, 2014, 77(7): 660-669
以核安全文化引领核能与核技术利用事业安全、健康、可持续发展——《核安全文化政策声明》解读
郭承站
摘要:《核安全文化政策声明》(以下简称《声明》)是我国政府关于核安全文化的首个政策声明。文章对新形势下加强核安全文化建设的必要性、《声明》对推动核安全文化建设的深远意义、良好核安全文化的八大特性、全行业核安全文化建设的要求等进行了深入分析和解读,并对持续推进核安全文化提出了相关倡议。
关键词:核安全文化;核安全观;核能;核技术利用
来源出版物:环境保护, 2015, 43(6): 12-15
核电厂环境风险评价框架及方法
陈妍,郑鹏,陈海英,等
摘要:目前核电厂风险评价技术分为核事故风险评价及非人类物种电离辐射防护评价。为发展一个包括非人类物种防护在内的核电厂辐射防护体系,本文借鉴环境风险评价的关键流程要素,提出包括公众健康和非人类物种的核电厂环境风险评价框架。在这一框架的危害排序环节,对所选择的各评价终点指标采用层次分析法,计算评价终点对核电厂环境风险的权重并进行排序,旨在发现对环境风险贡献较大的评价终点并在风险管理中对其优先管理控制。
关键词:环境风险评价;健康风险;生态风险
来源出版物:科技导报, 2015, 33(4): 37-43
我国内陆核电的用水安全
张爱玲,陈晓秋,刘森林,等
摘要:在介绍我国拟建内陆核电机组的安全设计和厂用水系统的基础上,分析了内陆核电的用水需求和保证率要求。结合我国水资源条件及水资源论证现状,对如何保障内陆核电取水水源的可靠性与可行性进行了探讨,并提出了内陆核电用水安全保障措施的建议。
关键词:内陆核电;用水安全;厂用水系统;水源条件;水资源论证
来源出版物:水文, 2015, 35(3): 69-73
核安全级数字化仪控系统软件可靠性评估
刘盈,杨明
摘要:采用核电厂安全审查大纲技术的分支NUREG-0800 BTP7-14分别建立基于贝叶斯(Bayes)网络的阶段评估模型以及综合评估模型。在阶段评估模型中,确立8个阶段,通过13个一级指标、74个二级指标、326个三级指标来完成对软件阶段性的实时评估。选用Hugin贝叶斯网络分析工具,针对测试对象展开预测推理及敏感性分析。经过测试后得到该软件在生命周期不同阶段对标准的符合程度,经综合评估模型推理,可得该软件在标准层面的可靠性指标是98.84%。经敏感性分析,可以定性地发现软件在生存周期中存在的薄弱环节,为评估核安全级数字化仪控系统的可靠性和安全性奠定基础。
关键词:核安全级;数字化仪控系统;软件可靠性;标准;贝叶斯网络
来源出版物:核动力工程, 2016, 37(1): 143-147
加速器辐射安全评价常见问题探讨
宋培峰,王晓峰,李恩敬
摘要:目的:探讨核技术利用加速器项目辐射安全评价应关注的问题,并提出对策。方法:查阅 2014年度国家核安全局监督管理单位相关加速器辐射安全评价申报材料审查记录,按照相关法规标准要求,对常见加速器项目申报材料中存在的问题进行整理与分析。结果:2014年度国家核安全局完成27个加速器相关项目辐射安全评价审查,约有9个项目存在执行限值模糊,12个项目存在屏蔽估算过程不完善,8个项目存在安全联锁措施描述遗漏、阐述不清晰或设置不当,5个项目存在放射性产物相关环节描述不充分等问题。结论:建议依据常见加速器项目应用类型不同采取可接受的执行限值、多方面完善屏蔽估算、全面合理评价安全联锁措施以及优化放射性产物的评价与管理,明确产物去向。
关键词:加速器;辐射安全;评价;对策
来源出版物:中国职业医学, 2016, 43(3): 361-364
A combined deterministic and probabilistic procedure for safety assessment of beyond design basis accidents in nuclear power plant: Application to ECCS performance assessment for design basis LOCA redefinition Kang, Dong Gu; Ahn, Seung-Hoon;
Chang, Soon Heung; et al.
Abstract: The concept and assessment approach of nuclear safety in nuclear power plants(NPPs) have been evolved with the technological progress and the lessons learned from the major events. Recently, studies on the integrated approach of deterministic and probabilistic method have been done. In this study, a combined deterministic and probabilistic procedure(CDPP) is proposed for safety assessment of the beyond design basis accidents(BDBAs). In the CDPP, the conditional exceedance probability obtained by the best estimate plus uncertainty method acts as go-between deterministic and probabilistic safety assessments, resulting in more reliable values of core damage frequency and conditional core damage probability. To verify applicability of the methodology,performance of the APR-1400 emergency core cooling system is assessed against large break loss of coolant accident(LOCA), under the premise that LOCAs for any breaks larger than transition break size would be regarded as BDBA. In addition, discussions are made for analysis results for allowable NPP changes of emergency diesel generator start time extension and power uprating. It is concluded that the proposed CDPP is applicable to safety assessment of BDBAs in NPPs without significant erosionof the safety margin.
来源出版物:Nuclear Engineering and Design, 2013, 260: 165-174
A survey of dynamic methodologies for probabilistic safety assessment of nuclear power plants
Aldemir, Tunc
Abstract: Dynamic methodologies for probabilistic safety assessment(PSA) are defined as those which use a time-dependent phenomenological model of system evolution along with its stochastic behavior to account for possible dependencies between failure events. Over the past 30 years, numerous concerns have been raised in the literature regarding the capability of the traditional static modeling approaches such as the event-tree/fault-tree methodology to adequately account for the impact of process/hardware/software/firmware/human interactions on the stochastic system behavior. A survey of the types of dynamic PSA methodologies proposed to date is presented,as well as a brief summary of an example application for the PSA modeling of a digital feedwater control system of an operating pressurized water reactor. The use of dynamic methodologies for PSA modeling of passive components and phenomenological uncertainties are also discussed.
Keywords: probabilistic safety assessment; probabilistic risk assessment; epistemic uncertainties
来源出版物:Annals of Nuclear Energy, 2013, 52(S1): 113-124
Extension of station blackout coping capability and implications on nuclear safety
Volkanovski, Andrija; Prosek, Andrej; et al.
Abstract: The safety of the nuclear power plant depends on the availability of the continuous and reliable sources of electrical energy during all modes of operation of the plant. The station blackout corresponds to a total loss of all alternate current(AC) power as a result of complete failure of both offsite and on-site AC power sources. The electricity for the essential systems during station blackout is provided from the batteries installed in the nuclear power plant. The results of the probabilistic safety assessment show that station blackout is one of the main and frequently the dominant contributor to the core damage frequency. The accident in Fukushima Daiichi nuclear power plants demonstrates the vulnerability of the currently operating nuclear power plants during the extended station blackout events. The objective of this paper is, considering the identified importance of the station blackout initiating event, to assess the implications of the strengthening of the SBO mitigation capability on safety of the NPP. The assessment is done with state-of-art deterministic and probabilistic methods and tolls with application on reference models of nuclear power plants. The U.S. NRC Station Blackout Rule describes procedure for the assessment of the size and capacity of the batteries in the nuclear power plant. The description of the procedure with the application on the reference plant and identified deficiencies in the procedure is presented. The safety analysis is done on reference model of the nuclear power plant. Obtained results show large decrease of the core damage frequency with strengthening of the station blackout mitigation capability. The time extension of blackout coping capability results in the delay of the core heat up for at least the extension time interval. Availability and operation of the steam driven auxiliary feedwater system maintains core integrity up to 72 h after the successful shutdown, even in the presence of the reactor coolant pumps seal leakage. The largest weighted decrease of the core damage frequency considering the costs for the modification is obtained for the modification resulting in extension of the station blackout coping capability. The importance of the common cause failures of the emergency diesel generators for the obtained decrease of the core damage frequency and overall safety of the plant is identified in the obtained results. The results of the analysis support the latest recommendations and expected revisions to the corresponding regulatory requirement by the U.S. Regulatory Commission considering the station blackout mitigation capability.
来源出版物:Nuclear Engineering and Design, 2013, 255: 16-27
Design of integrated passive safety system(IPSS)for ultimate passive safety of nuclear power plants
Chang, Soon Heung; Kim, Sang Ho; Choi, Jae Young
Abstract: The design concept of integrated passive safety system(IPSS) which can perform various passive safety functions is proposed in this paper. It has the various functions of passive decay heat removal system, passive safety injection system, passive containment cooling system, passive in-vessel retention and cavity flooding system, and filtered venting system with containmentpressure control. The objectives of this paper are to propose the conceptual design of an IPSS and to estimate the design characters of the IPSS with accident simulations using MARS code. Some functions of the IPSS are newly proposed and the other functions are reviewed with the integration of the functions. Consequently, all of the functions are modified and integrated for simplicity of the design in preparation for beyond design based accidents(BDBAs) focused on a station black out(SBO). The simulation results with the IPSS show that the decay heat can be sufficiently removed in accidents that occur with a SBO. Also, the molten core can be retained in a vessel via the passive in-vessel retention strategy of the IPSS. The actual application potential of the IPSS is high, as numerous strong design characters are evaluated. The installation of the IPSS into the original design of a nuclear power plant requires minimal design change using the current penetrations of the containment. The functions are integrated in one or two large tanks outside the containment. Furthermore, the operation time of the IPSS can be increased by refilling coolant from the containment outside into integrated passive safety tanks(IPSTs). The coolant in the IPSTs is used for various functions in accident scenarios. Also, potential problems for the realistic installation of the IPSS are proposed and the solutions to these problems are schematically described. IPSS is the design for the passive safety enhancement in preparation for a loss of AC power. Consequently, it is designed for the supplementation and enhancement of current nuclear power plants, not as a replacement. The specific optimization design for each current or future reactor will be studied as further works.
来源出版物:Nuclear Engineering and Design, 2013, 260: 104-120
Theory and implementation of nuclear safety system codes - Part I: Conservation equations,flow regimes, numerics and significant assumptions
Roth, Glenn A.; Aydogan, Fatih
Abstract: The design and analysis of the thermal/hydraulic systems of nuclear power plants necessitates system codes that can be used in the analysis of steady-state and transient conditions. Due to the dispersed development of system codes over many laboratories and universities, there are several system codes available for use. Many of the available codes have multiple similar versions developed for specific user needs. The code comparisons provided in the two parts of this article series allow users to select the appropriate system code for their specific problems. In this comparison, the governing equations for mass, momentum and energy conservation are evaluated. It will be shown that the governing equations do riot vary substantially between the codes considered. Most of them utilize a lumped approach with only two fields to represent two phase flow. Two-phase flows are divided into flow regimes based on their appearance and the flow structure. The regimes are used to select appropriate closure relationships to model heat transfer, interfacial drag, and other flow conditions. In addition, major assumptions about the governing and closure equations in these codes are compared and discussed. The most significant of the assumptions is that the governing equations can be discretized in time. The numerical approach of the codes is compared to one another since the numerical approach not only affects the speed of the system codes but also the accuracy of the results. In the second part of this article, the closure relations, their major assumptions, experimental verification and validation are discussed. The results of these articles also guide the development of these system codes, the underlying thermal/hydraulic models, and indicate areas where models must be improved to adequately address issues with new reactor design and development activities.
Keywords: system code comparison; nuclear plant analysis; relap; trace; cathare; athlet
来源出版物:Progress in Nuclear Energy, 2014, 76: 160-182:
Theory and implementation of nuclear safety system codes - Part II: System code closure relations, validation, and limitations
Roth, Glenn A.; Aydogan, Fatih
Abstract: This is Part II of two articles describing the details of thermal-hydraulic system codes. In this second part of the article series, the system code closure relationships(used to model thermal and mechanical non-equilibrium and the coupling of the phases) for the governing equations are discussed and evaluated. These include several thermal and hydraulic models, such as heat transfer coefficients for various flow regimes, two phase pressure correlations, two phase friction correlations, drag coefficients and interfacial models between the fields.These models are often developed from experimental data. The experiment conditions should be understood to evaluate the efficacy of the closure models. Code verification and validation, including Separate Effects Tests(SETs) and Integral effects tests(IETs) is also assessed. It can be shown from the assessments that the test cases cover a significant section of the system code capabilities, but some of the more advanced reactor designs will push the limits of validation for the codes. Lastly, the limitations of the codes are discussed by considering next generation power plants, such as Small Modular Reactors(SMRs), analyzing not only existing nuclear power plants,but also next generation nuclear power plants. The nuclear industry is developing new, innovative reactor designs,such as Small Modular Reactors(SMRs), High-Temperature Gas-cooled Reactors(HTGRs) and others. Sub-types of these reactor designs utilize pebbles,prismatic graphite moderators, helical steam generators,innovative fuel types, liquid metal coolants, and many other design features that may not be fully analyzed by current system codes. This second part completes the series on the comparison and evaluation of the selected reactor system codes by discussing the closure relations, validation and limitations. These two articles indicate areas where the models can be improved to adequately address issues with new reactor design and development.
Keywords: system code comparison; nuclear plant analysis; relap; trace; cathare; athlet
来源出版物:Progress in Nuclear Energy, 2014, 76: 55-72
Accurate fission data for nuclear safety
Solders, A; Gorelov, D; Jokinen, A; et al.
Abstract: The accurate fission data for nuclear safety(AIFONS) project aims at high precision measurements of fission yields, using the renewed IGISOL mass separator facility in combination with a new high current light ion cyclotron at the University of Jyvaskyla. The 30 MeV proton beam will be used to create fast and thermal neutron spectra for the study of neutron induced fission yields. Thanks to a series of mass separating elements,culminating with the JYFLTRAP Penning trap, it is possible to achieve a mass resolving power in the order of a few hundred thousands. In this paper we present the experimental setup and the design of a neutron converter target for IGISOL. The goal is to have a flexible design. For studies of exotic nuclei far from stability a high neutron flux(1012) neutrons/s) at energies 1-30 MeV is desired while for reactor applications neutron spectra that resembles those of thermal and fast nuclear reactors are preferred. It is also desirable to be able to produce(semi-)monoenergetic neutrons for benchmarking and to study the energy dependence of fission yields. The scientific program is extensive and is planed to start in 2013 with a measurement of isomeric yield ratios of proton induced fission in uranium. This will be followed by studies of independent yields of thermal and fast neutron induced fission of various actinides.
来源出版物:Nuclear Data Sheets, 2014, 119: 338-341
China’s approach to nuclear safety: From the perspective of policy and institutional system
Mu, Ruimin; Zuo, Jian; Yuan, Xueliang
Abstract: Nuclear energy plays an important role in the energy sector in the world. It has achieved a rapid development during the past six decades and contributes to over 11% of the world’s electricity supply. On the other side, nuclear accidents have triggered substantial debates with a growing public concern on nuclear facilities. Followed by the Fukushima nuclear accident, some developed countries decided to shut down the existing nuclear power plants or to abandon plans to build new ones. Given this background, accelerating the development of nuclear power on the basis of safety in China will make it a bellwether for other countries. China assigns the top priority to the nuclear safety in nuclear energy development and has maintained a good record in this field. The policy and institutional system provide the necessary guarantee for the nuclear energy development and safety management. Furthermore, China’s approach to nuclear safety provides a benchmark for the safe development and utilization of nuclear power. This research draws an overall picture of the nuclear energy development and nuclear safety in China from the policy and institutional perspective.
Keywords: nuclear energy; safety; policy; institution;China
来源出版物:Energy Policy, 2015, 76: 161-172
Coupling a CFD code with neutron kinetics and pin thermal models for nuclear reactor safety analyses
Chen, Zhao; Chen, Xue-Nong; Rineiski, Andrei; et al.
Abstract: Most system codes are based on the onedimensional lumped-parameter method, which is unsuitabletosimulatemulti-dimensionalthermal-hydraulics problems. CFD method is a good tool to simulate multidimensional thermal-hydraulics phenomena in the nuclear reactor, which can increase the accuracy of analysis results. However, since there is no neutron kinetics model and pin thermal model in current CFD codes, the application of the CFD method in the area of nuclear reactor safety analyses is still limited. Coupling a CFD code with the neutron kinetics model(PKM) and the pin thermal model(PTM) is a good way to use CFD code to simulate multi-dimensional thermal-hydraulics problems of nuclear reactors. The motivation for this work is to develop a CFD/neutron kinetics coupled code named FLUENT/PK for nuclear reactor safety analyses by coupling the commercial CFD code named FLUENT with the point kinetics model(PKM) and the pin thermal model(PTM). The mathematical models and the coupling method are described and the unprotected transient overpower(UTOP)accident of a liquid metal cooled fast reactor(LMFR) is chosen as an application case. As a general validation, the calculated results are used to compare with that of another multi-physics coupled code named SIMMER-Ill and good agreements are achieved for various characteristic parameters.
Keywords: CFD; neutron kinetics; pin thermal model;safety analysis
来源出版物:Annals of Nuclear Energy, 2015, 83: 41-49
Exploring the relationship between safety culture and safety performance in US nuclear power operations
Morrow, Stephanie L; Koves, G. Kenneth;Barnes, Valerie E
Abstract: How do nuclear power plant workers, within a single national culture, perceive safety culture within their organizations? What is the relationship between safety culture and other indicators of safety? Is the construct of safety culture useful for predicting future plant performance? These questions were addressed in the current study using a survey administered to a sample of personnel at 97% of the nuclear power plants in the United States, resulting in 2876 responses from 63 nuclear power plant sites. Exploratory and confirmatory factor analysis revealed a multi-factor structure to the safety culture survey. For each nuclear power plant, the mean score for the total survey results and the factor means were correlated with organization-level performance indicators both concurrently and one year following the survey administration.Correlationssuggestedmeaningful,statistically significant relationships between safety culture, as measured by the survey, and multiple nuclear power plant performance indicators. This study presents a unique look at safety culture across the United States nuclear power industry and takes a critical step toward establishing that safety culture is empirically related to safety performance.
Keywords: safety culture; nuclear power; safety performance;humanandorganizationalfactors;organizational culture; safety climate
来源出版物:Safety Science, 2014, 69(S1): 37-47
A strategy for the qualification of multi-fluid approaches for nuclear reactor safety
Lucas, D; Rzehak, R; Krepper, E; et al.
Abstract: CFD-simulations for two-phase flows applying the multi -fluid approach are not yet qualified to provide reliable predictions for unknown flows. Among others, one important reason is the missing agreement within the community on closure models to be used. Considering specific phenomena or not, using different models and adjustable constants, most papers presenting a model validation end up with a good agreement with experimental data. However a case by case selection of models and constants does not help to improve the predictive capabilities of such models. For this reason the definition of baseline models considering all known phenomena that could be important is proposed. In such baseline models all parameter have to be defined, i.e., there are no tuning parameters by definition. Therefore these baseline models have to be applied to many experiments with different complexity. Shortcomings of the models and our physical understanding of the complex flow phenomena have to be identified by detailed analyses on the deviations between experimental data and simulation results. A modification of the baseline model will only be done if it bases on physical considerations and improves the overall performance of the model. This requires a huge effort, but seems to be the only way to improve the situation. In particular more complete experimental data are required. Joint activities on the development of such baseline models are desirable. The paper illustrates this strategy by a baseline model for polydisperse bubbly flows which is presently developed at HZDR.
来源出版物:Nuclear Engineering and Design, 2016, 266: 2-11
Contributing to the nuclear 3S’s via a methodology aiming at enhancing the synergies between nuclear security and safety
Cipollaro, Antonio; Lomonaco, Guglielmo
Abstract: Nuclear safety, nuclear security and nuclear safeguards regimes have not historically developed at the same pace and surely have not reached the same level of maturity. Nevertheless, these aspects are of special relevance in the current global nuclear energy context when considering the numerous countries that have and will have the legitimate ambition to start a nuclear energy production programme without any or scarce previous nuclear safety, security and safeguards cultures. The future development of nuclear energy exploitation will depend more and more on the convergence of decisions from governments, from the nuclear industry, from utilities, from private and institutional investors as well as from the level of acceptance by the public opinion. Following an in-depth state-of-the-artanalysisandliteraturesearch,a methodological approach focussed on the safety and security connections is presented, as it seems a field where more commonalities and operational aspects could be possibly found and exploited.
Keywords: nuclear security; nuclear safety; 3S;vulnerability; terrorism and sabotage; critical infrastructures
来源出版物:Progress in Nuclear Energy, 2016, 86: 31-39
Molecular data of mixed metal oxides with importance in nuclear safety
Kovacs, Attila; Konings, Rudy J. M
Abstract: The gas-phase structural and spectroscopic properties of selected mixed metal oxides(Cs2CrO4, Cs2MnO4, Cs2MoO4, Cs2RuO4, BaMoO4, BaMoO3) have been calculated using Density Functional Theory(DFT). The possible structural isomers have been analyzed and for the found global minima the vibrational(IR, Raman)spectra have been predicted taking into account also anharmonic corrections. The bonding properties have been characterized by means of the Natural Bond Orbital analysis model while the low-lying excited electronic states have been calculated using time-dependent DFT. In order to assess the stability of the target species the dissociation enthalpies have been evaluated.
来源出版物:Journal of Nuclear Materials, 2016, 477: 134-138
Progress of experimental research on nuclear safety in NPIC
Gong, H; Zan, Y; Peng, C; et al.
Abstract: Two kinds of Generation III commercial nuclear power plants have been developed in CNNC(China National Nuclear Corporation), one is a small modular reactor ACP100 having an equivalent electric power 100 MW, and the other is HPR1000(once named ACP1000)having an equivalent electric power1000 MW. Both NPPs widely adopted the design philosophy of advanced passive safety systems and considered the lessons from Fukushima Daichi nuclear accident. As the backbone of the R&D of ACP100 and HPR1000, NPIC(nuclear power Institute of China) has finished the engineering verification test of main safety systems, including passive residual heat removal experiments, reactor cavity injection experiments,hydrogencombustionexperiments,andpassive autocatalytic recombiner experiments. Above experimental work conducted in NPIC and further research plan of nuclear safety are introduced in this paper.
来源出版物:Kerntechnik, 2016, 81(2): 125-133
编辑:卫夏雯
Evaluation of nuclear safety from the outputs of computer codes in the presence of uncertainties
Nutt, WT; Wallis, GB
We apply methods from order statistics to the problem of satisfying regulations that specify individual criteria to be met by each of a number of outputs, k, from a computer code simulating nuclear accidents. The regulations are assumed to apply to an ‘extent’, gamma(k),(such as 95%) of the cumulative probability distribution of each output, k, that is obtained by randomly varying the inputs to the code over their ranges of uncertainty. We use a ‘bracketing’ approach to obtain expressions for the confidence, 6, or probability that these desired extents will be covered in N runs of the code. Detailed results are obtained for k = 1, 2, 3, with equal extents, gamma, and are shown to depend on the degree of correlation of the outputs. They reduce to the proper expressions in limiting cases. These limiting cases are also analyzed for an arbitrary number of outputs, k. The bracketing methodology is contrasted with the traditional ‘coverage’approach in which the objective is to obtain a range of outputs that enclose a total fraction, gamma, of all possible outputs, without regard to the extent of individual outputs. For the case of two outputs we develop an alternate formulation and show that the confidence, 6, depends on the degree of correlation between outputs. The alternate formulation reduces to the single output case when the outputs are so well correlated that the coverage criterion is always met in a single run of the code if either output lies beyond an extent gamma, it reduces to Wilks’ expression for un-correlated variables when the outputs are independent, and it reduces to Wald’s result when the outputs are so negatively correlated that the coverage criterion could never be met by the two outputs of a single run of the code. The predictions of both formulations are validated by comparison with Monte Carlo simulations.
nuclear safety; outputs of codes; regulations;non-parametric methods; bracketing; coverage; confidence

