醛固酮腺瘤和单侧肾上腺增生导致醛固酮增多症腹腔镜手术效果比较
朱平

[摘 要] 目的:观察醛固酮腺瘤和单侧肾上腺增生导致醛固酮增多症腹腔镜手术效果。方法:以我院2013年3月—2014年3月收治的50例醛固酮增多症患者为研究对象,醛固酮腺瘤组38例、单侧肾上腺增生组12例,均行腹膜后腹腔镜手术,肿瘤体积较大且与周围组织界限清晰者行肾上腺部分切除,其他患者行肾上腺全切。观察围术期指标及术后症状变化,比较肾上腺部分切除与肾上腺全切手术情况。随访1年,比较疗效及复发情况。结果:肾上腺全切的醛固酮腺瘤手术时间显著高于肾上腺部分切除的醛固酮腺瘤及单侧肾上腺增生,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05),各组患者术中出血量、术后住院时间比较,差异无统计学意义(P>0.05)。2组患者术后1个月收缩压、舒张压、血浆醛固酮、醛固酮/肾素比值均显著降低,血钾、血浆肾素活性均显著升高,与术前比较差异有统计学意义(P<0.05)。患者术后1年均未见复发,单侧肾上腺增生、肾上腺全切醛固酮腺瘤、肾上腺部分切除醛固酮腺瘤治愈率分别为66.7%、64.7%、61.9%,组间比较差异无统计学意义(P<0.05)。结论:腹腔镜手术治疗醛固酮增多症两种亚型均有良好的疗效及安全性,对符合肾上腺部分切除指征患者,术中应尽可能保留患侧肾上腺组织。
[关键词] 醛固酮腺瘤;单侧肾上腺增生;醛固酮增多症;腹腔镜
中图分类号:R737.11 文献标识码:B 文章编号:2095-5200(2016)04-044-03
DOI:10.11876/mimt201604017
Comparison of the effects of laparoscopic surgery in treatment of aldosteronism caused by aldosterone adenoma and unilateral adrenal hyperplasia ZHU Ping. (Department of general surgery,Xian Fifth Hospital,Xian 710082,China)
[Abstract] Objective: To observe the effects of laparoscopic surgery in treatment of aldosteronism caused by aldosterone adenoma and unilateral adrenal hyperplasia. Methods: 50 cases of patients with aldosteronism treated in our hospital from March 2013 to March 2014 were chosen for this study, 12 cases included in unilateral adrenal hyperplasia group and 38 cases in aldosterone adenoma group, both groups underwent retroperitoneal laparoscopic surgery, the patients with larger tumor volume and well-circumscribed surrounding tissues underwent partial adrenalectomy, others with total adrenalectomy. Perioperative indexes and postoperative change in symptoms were observed, the conditions of patients with partial adrenalectomy and total adrenalectomy were compared. With1-year follow-up, the efficacy and recurrence were compared between two groups. Results: The operation time of aldosterone adenoma with total adrenalectomy was significantly higher than those of aldosterone adenoma and unilateral adrenal hyperplasia with partial adrenalectomy, the differences were statistically significant (P<0.05), the amount of bleeding and postoperative hospital stay were compared between two groups, the differences were not statistically significant (P>0.05). The ratios of systolic blood pressure, diastolic blood pressure, plasma aldosterone to renin of two groups at 1 months after surgery were significantly increased, serum potassium and plasma renin activity were significantly elevated compared with the preoperative indexes, the differences were statistically significant (P<0.05). No recurrence was found in all the patients, cure rates of unilateral adrenal hyperplasia, aldosterone adenomas with total adrenalectomy, aldosterone adenoma with partial adrenalectomy were 66.7%, 64.7%, 61.9%, respectively, the intergroup differences were not statistically significant (P<0.05). Conclusions: Laparoscopic surgery has good efficacy and safety in the treatment of two subtypes of aldosteronism, and ipsilateral adrenal tissue should be retained as far as possible in the surgery as for patients meeting the indications of partial adrenalectomy.
[Key words] aldosterone adenoma;unilateral adrenal hyperplasia;hyperaldosteronism;laparoscopy
原发性醛固酮增多症主要包括两种亚型,即醛固酮腺瘤和结节性肾上腺增生,均由肾上腺皮质球状带病变引发[1]。该病是高血压罕见但重要的致病因素之一,手术是主要治疗方法。近年来,腹腔镜手术在原发性醛固酮增多症治疗中应用逐渐广泛[2-3]。为观察腹腔镜手术对醛固酮增多症两种亚型的治疗效果,以我院2013年3月—2014年3月收治的50例醛固酮增多症患者为研究对象,进行回顾性分析,现将手术方法与治疗效果总结如下。
1 一般资料
所有患者均接受腹膜后入路腹腔镜手术治疗,行肾上腺全切或肾上腺部分切除,病例及随访资料保存完整。排除失访、随访期间死亡或随访时间<1年者、双侧醛固酮腺瘤或肾上腺增生者、合并嗜铬细胞瘤、肾血管狭窄、肾萎缩、主动脉狭窄等其他继发性高血压影响因素患者。50例入选患者中醛固酮腺瘤组38例、单侧肾上腺增生组12例。2组患者基线临床资料如表1所示。
2 治疗方法及观察指标
单侧肾上腺增生组行肾上腺全切,醛固酮腺瘤组参照文献[4]标准,21例行肾上腺全切,17例行肾上腺部分切除。术后给予糖皮质激素、抗菌药物,密切监护呼吸、循环系统,避免肾上腺危象、低血压休克、循环衰竭等严重并发症发生[5]。
比较2组手术时间、术中出血量及术后住院时间。观察患者术前、术后1个月血压、血钾、血浆肾素活性、血浆醛固酮及醛固酮/肾素比值变化。
随访记录其醛固酮增多症复发情况,并于末次随访时进行疗效评价[6]:治愈:在不服用降压药物的前提下,血压水平处于正常范围内(<140/90 mmHg);好转:服用降压药物后,血压水平可控制在正常范围内,且降压药物剂量较术前减少50%以上;无效:术后血压水平无明显变化,或降压药物剂量较术前减少不足50%。
3 统计学分析
对所有数据采用SPSS18.0进行分析,计数资料以(n/%)表示,并采用χ2检验,计量资料以(x±s)表示,t检验,检验水准设定为α=0.05,以P<0.05为有统计学意义。
4 结果
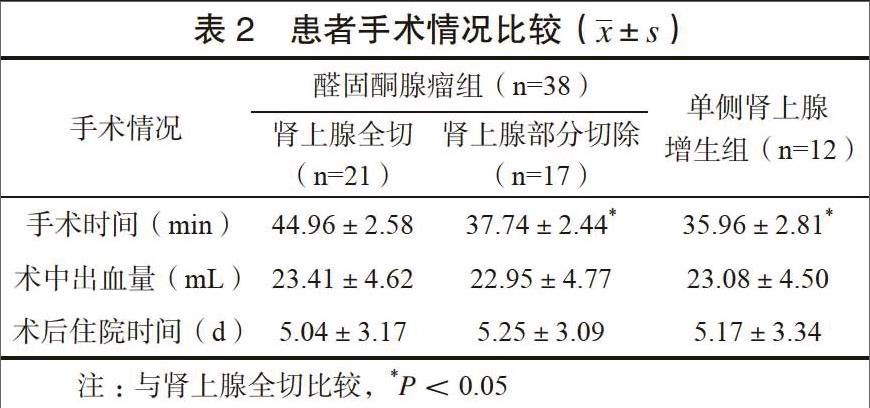
接受肾上腺全切的醛固酮腺瘤患者,其手术时间显著高于肾上腺部分切除的醛固酮腺瘤及单侧肾上腺增生患者,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05),各组患者术中出血量、术后住院时间比较,差异无统计学意义(P>0.05)。见表2。
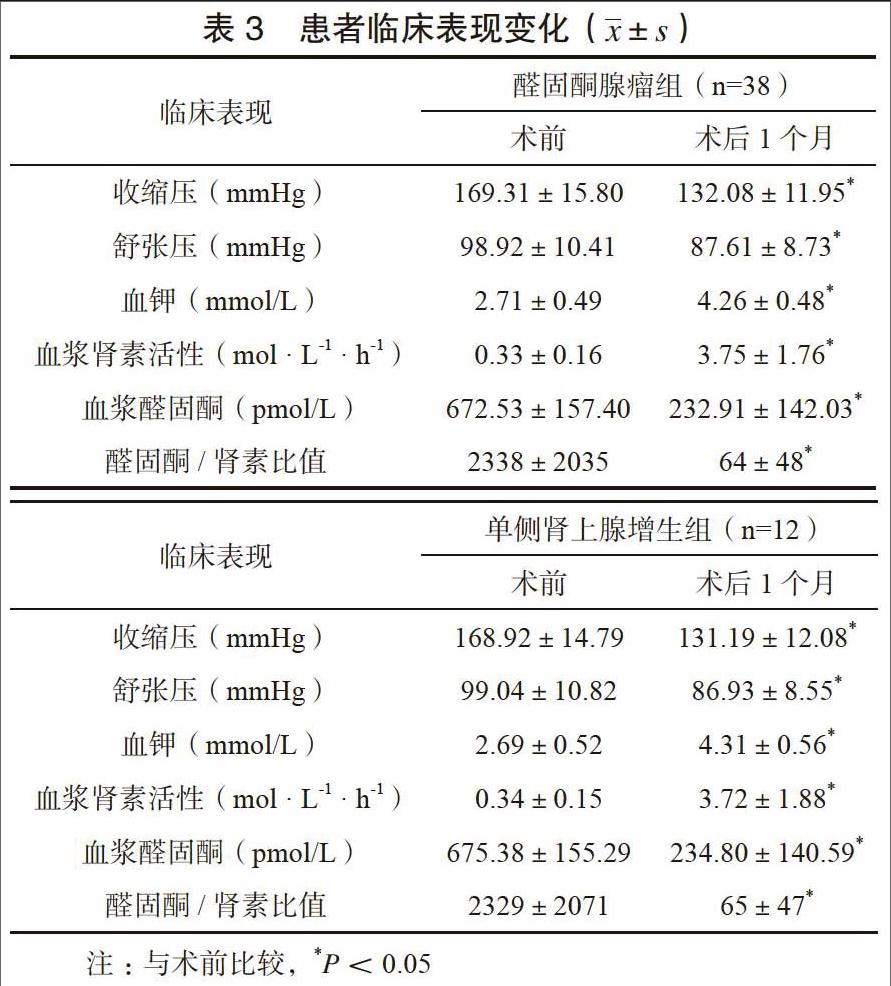
2组患者术后1个月收缩压、舒张压、血浆醛固酮、醛固酮/肾素比值均显著降低,血钾、血浆肾素活性菌显著升高,与术前比较差异有统计学意义(P<0.05)。见表3。
随访显示术后1年均未见复发,单侧肾上腺增生患者、肾上腺全切醛固酮腺瘤患者、肾上腺部分切除醛固酮腺瘤患者治愈率分别为66.7%、64.7%、61.9%,组间比较差异无统计学意义(P<0.05)。
5 讨论
随着腹腔镜微创技术推广,开腹术式在原发性醛固酮增多治疗中已退出历史舞台,特别是对于体积小、位置深、暴露困难的肾上腺,腹腔镜手术是公认的“金标准”[7-8]。
本研究50例患者均采用腹膜后径路手术,该径路不受腹腔粘连影响,入路直接且不会对腹腔脏器造成明显损伤,有利于患者术后胃肠功能的早期恢复[9]。本研究各组患者手术时间均控制在50 min以内,术中出血量不足30 mL,证明腹腔镜操作的安全性。接受肾上腺全切的醛固酮腺瘤患者手术时间偏长,与肿瘤体积较小、与周围组织粘连较重,增加了手术操作复杂性有关。St?lberg等[10-11]指出,肾上腺部分切除术对肾上腺组织的保留,能够促进患者术后血浆醛固酮浓度及皮质醇浓度的早期恢复,促进患者临床症状的改善,而肾上腺全切则多于包膜下实施肿瘤剜除,不可避免地会造成肿瘤组织残留,易增加术后醛固酮腺瘤复发风险,影响医疗质量。本研究各组患者术后1年随访均未见疾病复发,考虑与随访时间较短、样本量较小有关,关于手术治疗对患者远期预后的影响,有待日后大样本长期随访加以明确。总体而言,建议对符合肾上腺部分切除指征患者,术中应尽可能保留患侧肾上腺组织,杜绝随意扩大切除范围;若患者醛固酮腺瘤呈多发特点,且合并小卫星灶,则不应一味实施肾上腺部分切除,为保证病灶完全清楚,建议采取肾上腺全切术式[12]。
随着多层CT的发展与推广,近年来单侧肾上腺增生的检出率也有所提高,有效避免了传统肾上腺静脉采血特异性低、并发症率发生高的弊端[13]。对于单侧肾上腺增生患者,我们同样以腹膜后径路入路腹腔镜手术,治愈率达到66.7%,仅有1例患者治疗无效,治愈率与Pirvu等[14]研究结果相仿。
本次研究虽然2组患者术后1个月血压、血钾水平均较术前有所改善,但仍未恢复正常水平,考虑与患者病程较长,长期高血压及高血浆醛固酮浓度导致的心肌肥厚、血管僵硬、肾脏血管改建等状态无法在短时间内恢复有关[15]。该结果表明,患者应在确诊后即尽早实施手术,降低心肌梗死、脑梗死、动脉粥样硬化、代谢综合征等并发症的发生风险。
综上所述,经腹膜后径路腹腔镜手术治疗醛固酮增多症两种亚型均可取得良好的临床疗效,根据患者临床指征选择合适的切除范围有助于手术时间和术中出血量控制,进一步提高手术的安全性。
参 考 文 献
[1] 李明川,姜永光,李青,等.原发性醛固酮增多症的后腹腔镜治疗[J].临床泌尿外科杂志,2011,26(9):652-654.
[2] 郭瑞敏.原发性醛固酮增多症代谢异常及基因分型研究[D].上海:上海交通大学,2007.
[3] JIANG SB,GUO XD,WANG HB,et al. A retrospective study of laparoscopic unilateral adrenalectomy for primary hyperaldosteronism caused by unilateral adrenal hyperplasia[J]. Int Urol Nephrol,2014,46(7):1283-1288.
[4] SIGURJONSDOTTIR H A,GRONOWITZ M,ANDERSSON O,et al. Unilateral adrenal hyperplasia is a usual cause of primary hyperaldosteronism. Results from a Swedish screening study[J]. BMC Endocr Disord,2012,12(1):17.
[5] 胡斌. 原发性醛固酮增多症52例回顾性分析[D].南宁:广西医科大学,2007.
[6] VOLPE C,HAMBERGER B,H??G A,et al. Primary aldosteronism: functional histopathology and long-term follow-up after unilateral adrenalectomy[J]. Clin Endocrinol, 2015, 82(5): 639-647.
[7] HARVEY A,PASIEKA JL,KLINE G,et al. Modification of the protocol for selective adrenal venous sampling results in both a significant increase in the accuracy and necessity of the procedure in the management of patients with primary hyperaldosteronism[J]. Surgery,2012,152(4):643-649.
[8] DOUMA S,PETIDIS K,KAMPAROUDIS A,et al. Surgical management of primary aldosteronism. not everything that shines is gold[J]. Clin Exp Hypertens, 2012,34(1):53-56.
[9] 王楠,田刚. 原发性醛固酮增多症90例患者的临床分析[J]. 山西医科大学学报,2013,44(10):803-806.
[10] St?lberg P, Hellman P. Surgical Treatment of Unilateral Excessive Aldosterone Production[M]. Springer New York, 2014: 215-223.
[11] 赵振华, 胡卫列, 郑东升, 等. 单侧肾上腺切除治疗原发性醛固酮增多症对侧肾上腺储备功能的评价分析[J]. 现代泌尿外科杂志, 2014, 19(11): 728-731.
[12] FUJIMOTO K,HONJO S,TATSUOKA H,et al. Primary aldosteronism associated with subclinical Cushing syndrome[J]. J Endocrinol Invest,2013,36(8):564-567.
[13] HARTMANN I,GREPL M,VIDLAR A,et al. Outcomes of adrenalectomy in patients with primary hyperaldosteronism--a single centre experience[J]. Biomed Pap Med Fac Univ Palacky Olomouc Czech Repub,2014,158(4):583-590.
[14] PIRVU A,NAEM N,BAGUET JP,et al. Is adrenal venous sampling mandatory before surgical decision in case of primary hyperaldosteronism[J]. World J Surg,2014,38(7):1749-1754.
[15] Lin Y H, Huang K H, Lee J K, et al. Factors influencing left ventricular mass regression in patients with primary aldosteronism post adrenalectomy[J]. J Renin Angiotensin Aldosterone Syst, 2011, 12(1): 48-53.

