鄂尔多斯盆地大牛地气田盒1段储层应力敏感性及对水平井开发的影响
陈 奎,任广磊,杨文娟,于耀南
(中国石化 华北油气分公司 勘探开发研究院,河南 郑州 450006)
鄂尔多斯盆地大牛地气田盒1段储层应力敏感性及对水平井开发的影响
陈奎,任广磊,杨文娟,于耀南
(中国石化 华北油气分公司 勘探开发研究院,河南 郑州 450006)
大牛地气田二叠系下石盒子组1段(盒1段)是典型的低渗透储层。为明确储层的应力敏感性,选取了不同类型的13块岩心开展了应力敏感性实验。结果表明,盒1段岩心普遍存在应力敏感,且存在渗透率滞后现象,这说明随净应力的增加,岩样发生了塑性变形。采用内应力敏感指数法对实验数据进行分析,结果表明物性较好的Ⅰ类储层应力敏感性较弱,Ⅱ类、Ⅲ类储层为弱~中等,13块岩心的平均内应力敏感指数为0.086,整体评价应力敏感性为弱。建立了Ⅰ-Ⅲ类储层的多级压裂水平井数值模拟模型,并将储层无因次渗透率随地层压力的变化关系加入到模型中。在定气井产量的条件下,对比应力敏感对水平井开发的影响。数值模拟结果表明:对于Ⅰ类储层,应力敏感对稳产时间和稳产期产气量影响很小,仅降低1.6%;Ⅱ类储层影响较小,降低了11.2%;Ⅲ类储层则影响较大,降低了23.6%。因此应加强Ⅱ类、Ⅲ类储层气井的配产研究和生产管理,保证开发效果。
应力敏感;低渗透;水平井;气田开发;大牛地气田;鄂尔多斯盆地
大牛地气田位于鄂尔多斯盆地伊陕斜坡北部东段,属于典型的大型低渗致密砂岩气田[1-4]。经过多年持续的产能建设,剩余未动用储量主要位于二叠系下石盒子组1段(盒1段),储层物性差、丰度低,直井开发无效益,适宜采用水平井开发。而一般认为低渗透储层比中高渗储层存在更强的应力敏感性[5-7]。国内外针对储层应力敏感的研究,主要集中在实验测试方法上。应力敏感应用研究方面,主要是在渗流模型加入应力敏感因素,评价对油气井产能的影响。对于具体区块的研究,没有针对不同类型储层进行细分。而对于应力敏感对于气藏多级压裂水平井开发指标的研究也比较少[8-17]。有鉴于此,本文在大牛地气田储层分类评价研究成果的基础上[18-19],选取盒1段不同类型储层岩心开展实验,并将外应力敏感曲线通过有效应力将其转换成内应力敏感曲线之后,评价储层的应力敏感性。再将实验结果导入气藏多级压裂水平井数值模拟模型,利用数值模拟研究应力敏感对开发指标的影响,为盒1段的开发提供指导。
1 应力敏感实验
1.1实验结果
实验参照SY/T 6385—1999设计,以氮气为气体介质,根据大牛地气田储层分类评价标准[18-19],选取了分别代表了盒1段Ⅰ类、Ⅱ类和Ⅲ类储层的13块岩心进行应力敏感性实验。结果表明盒1段岩心普遍存在应力敏感。典型实验结果如图1和图2所示,在净应力增加过程中,渗透率随净应力的增加而减小,初期下降很快,当达到一定值后,下降幅度逐渐减小,趋于变缓。净应力降低过程中,渗透率逐渐恢复,但是并不能恢复到原来的大小,且净应力增加过程中的渗透率都大于对应的净应力降低过程中的渗透率值,这是渗透率滞后现象。渗透率滞后现象说明随净应力的增加,岩样发生了塑性变形。

图1 大牛地气田盒1段Ⅰ类岩样D28-6渗透率与 净应力关系Fig.1 Permeability vs. net stress of Type Ⅰ core sample(D28-6) of the 1st Member of Xiashihezi Formation in Daniudi gas field

图2 大牛地气田盒1段Ⅲ类岩样D41-37渗透率与净应力关系Fig.2 Permeability vs. net stress of type III core sample(D41-37) of the 1st Member of Xiashihezi Formation in Daniudi gas field
1.2渗透率应力敏感性评价与分析
目前常用的渗透率应力敏感性评价方法主要有行业标准法、应力敏感性系数法和应力敏感指数法。前两种方法实际上评价的是岩石渗透率对外应力(围压)的敏感程度,而实际的油气生产过程是内压不断改变的过程,所以油气藏应力敏感性评价应采用内应力敏感指数法。
应力敏感指数的表达式为:
(1)
式中:SI为应力敏感指数,无因次;ki为原始地层压力下的渗透率,10-3μm2;k为某个地层压力下的渗透率,10-3μm2。
本文在用常规应力敏感实验数据评价储层岩石的内应力敏感性时,首先分别通过李传亮的本体有效应力方法计算出的有效应力,将外应力敏感曲线转换成内应力敏感曲线,然后才进行内应力敏感性评价[20-22]。根据常规实验得到渗透率与净应力成乘幂关系,可统一表示为:
(2)
用本体有效应力法得到的有效应力将外应力敏感曲线转换成内应力敏感曲线后,上式即可写成:
(3)
式中:k0为初始测点对应的渗透率,10-3μm2;σ为有效应力,MPa;b为岩石的应力敏感常数,MPa-1;pc为净围压,MPa;pp为进口压力值,MPa;Φ为孔隙度,%。
为了方便对比,将原始地层压力降低10MPa时的孔隙压力和围压代入转换后的内应力敏感曲线关系,得到相应条件的渗透率值,然后根据式(1)计算出内应力敏感指数(表1)。结果表明,物性较好的Ⅰ类储层应力敏感性为弱,Ⅱ类储层应力敏感性为中等偏弱,物性差的Ⅲ类储层应力敏感性大部分为中等。说明储层越好,应力敏感性越弱。
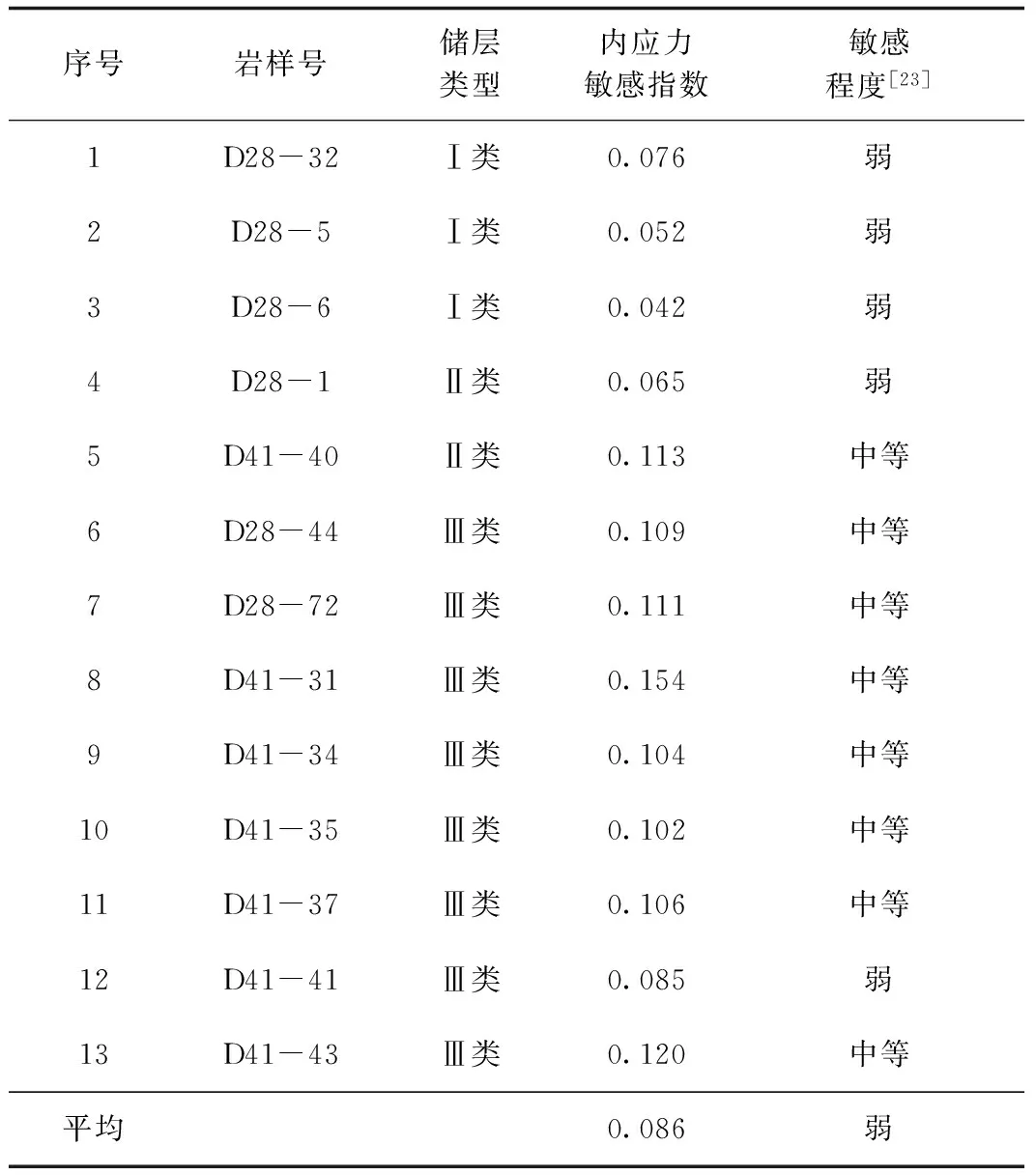
表1 大牛地气田盒1段岩样内应力敏感指数Table 1 Internal stress sensitivity index of core samples of the 1st Member of Xiashihezi Formation in Daniudi gas field
2 应力敏感对水平井开发的影响
根据应力敏感实验结果,结合储层实际上覆岩层压力以及实际地层流体压力,将实验曲线转换到地下储层渗透率随地层流体压力的变化关系。气藏Ⅰ类、Ⅱ类和Ⅲ类储层无因次渗透率随地层压力的变化关系见表2。
根据储层分类,建立不同类型储层的典型数值模拟模型,将表2数据加入模型,进行应力敏感数值模拟动态预测并对比分析,储层参数取值见表3。水平井及分段压裂参数为:水平段长度为1 100 m,采用局部加密网格模拟压裂缝,压裂段数11段,压裂有效半缝长25 m,裂缝导流能力30×10-3μm2·m。
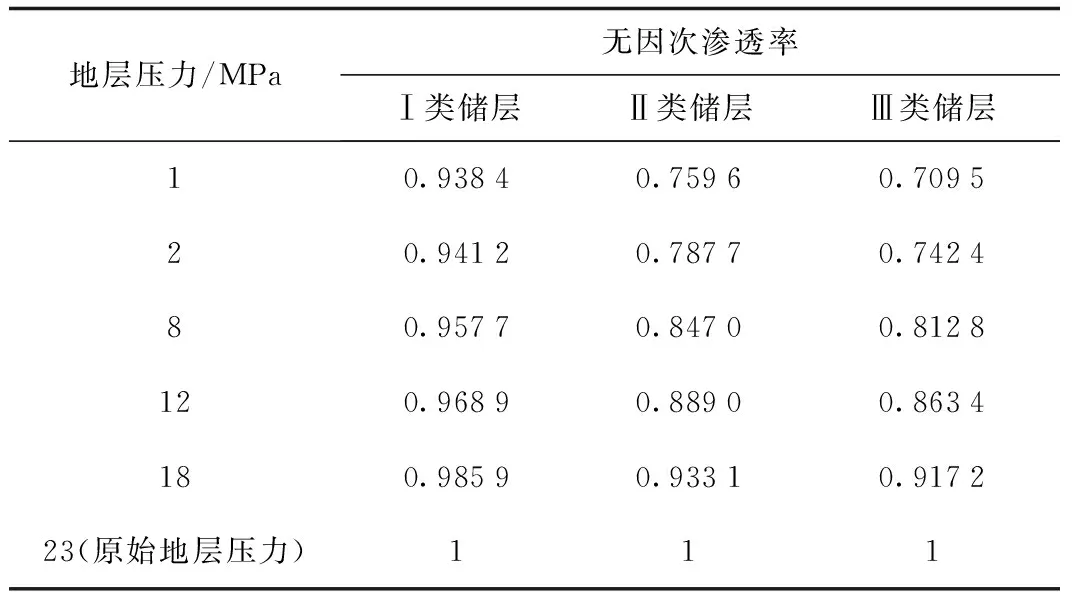
表2 大牛地气田盒1段不同类型储层无因次 渗透率随地层压力变化关系Table 2 Dimensionless permeability vs. formation pressure of different reservoir types of the 1st Member of Xiashihezi Formation in Daniudi gas field
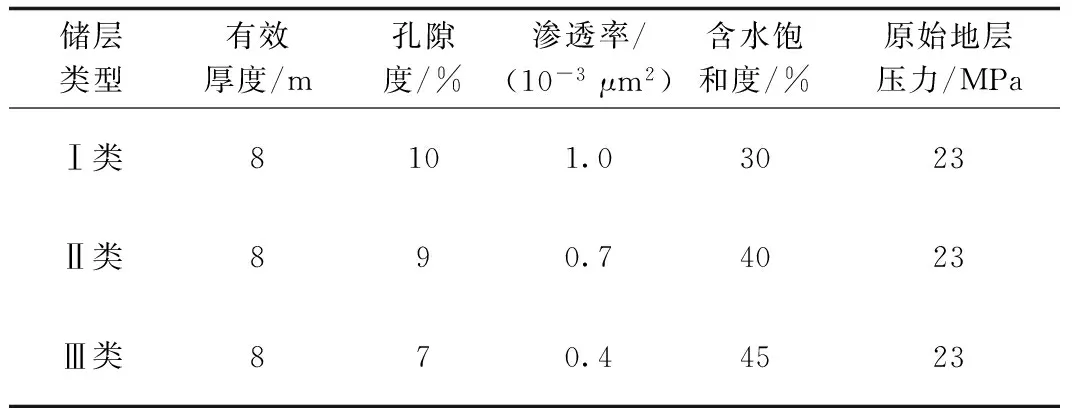
表3 大牛地气田盒1段水平井单井数值模拟储层参数Table 3 Reservoir parameters for horizontal well numerical simulation of the 1st Member of Xiashihezi Formation in Daniudi gas field
为了便于对比,气井生产制度统一设定为2.2×104m3/d。计算结果表明,Ⅰ类储层不考虑应力敏感可稳产6.22年,而考虑应力敏感后稳产时间降低到6.12年,降低0.1年,降低幅度只有1.6%,应力敏感对开发的影响很小。Ⅱ类储层不考虑应力敏感可稳产3.39年,而考虑应力敏感后稳产时间降低到3.01年,降低0.38年,降低幅度11.2%,应力敏感对开发的影响也比较小。Ⅲ类储层不考虑应力敏感可稳产0.89年,而考虑应力敏感后稳产时间降低到0.68年,降低0.21年,降低幅度23.6%,应力敏感对开发的影响较大,如表4、图3、图4和图5。因此Ⅲ类储层气井的产量不宜过高,以免较大的应力敏感影响稳产期累产气量。
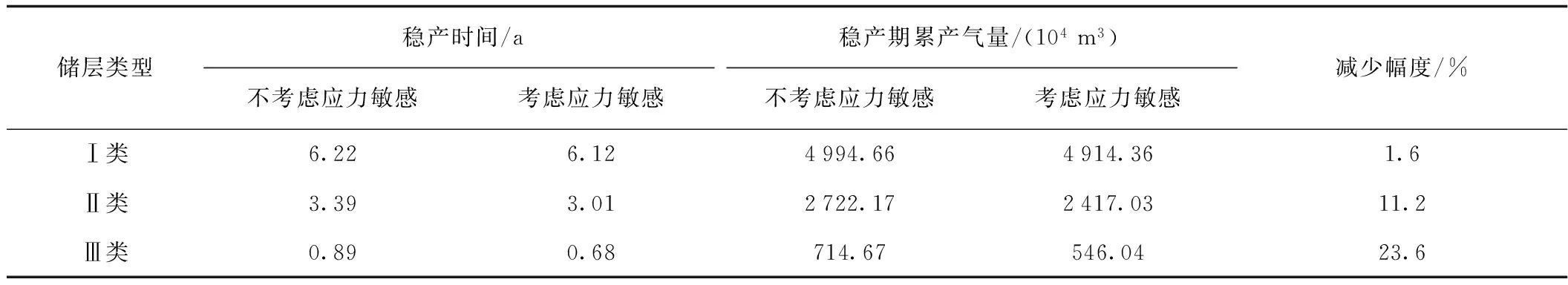
表4 大牛地气田盒1段应力敏感对不同类型储层影响Table 4 Influences of stress sensitivity on different reservoir types of the 1st Member of Xiashihezi Formation in Daniudi gas field
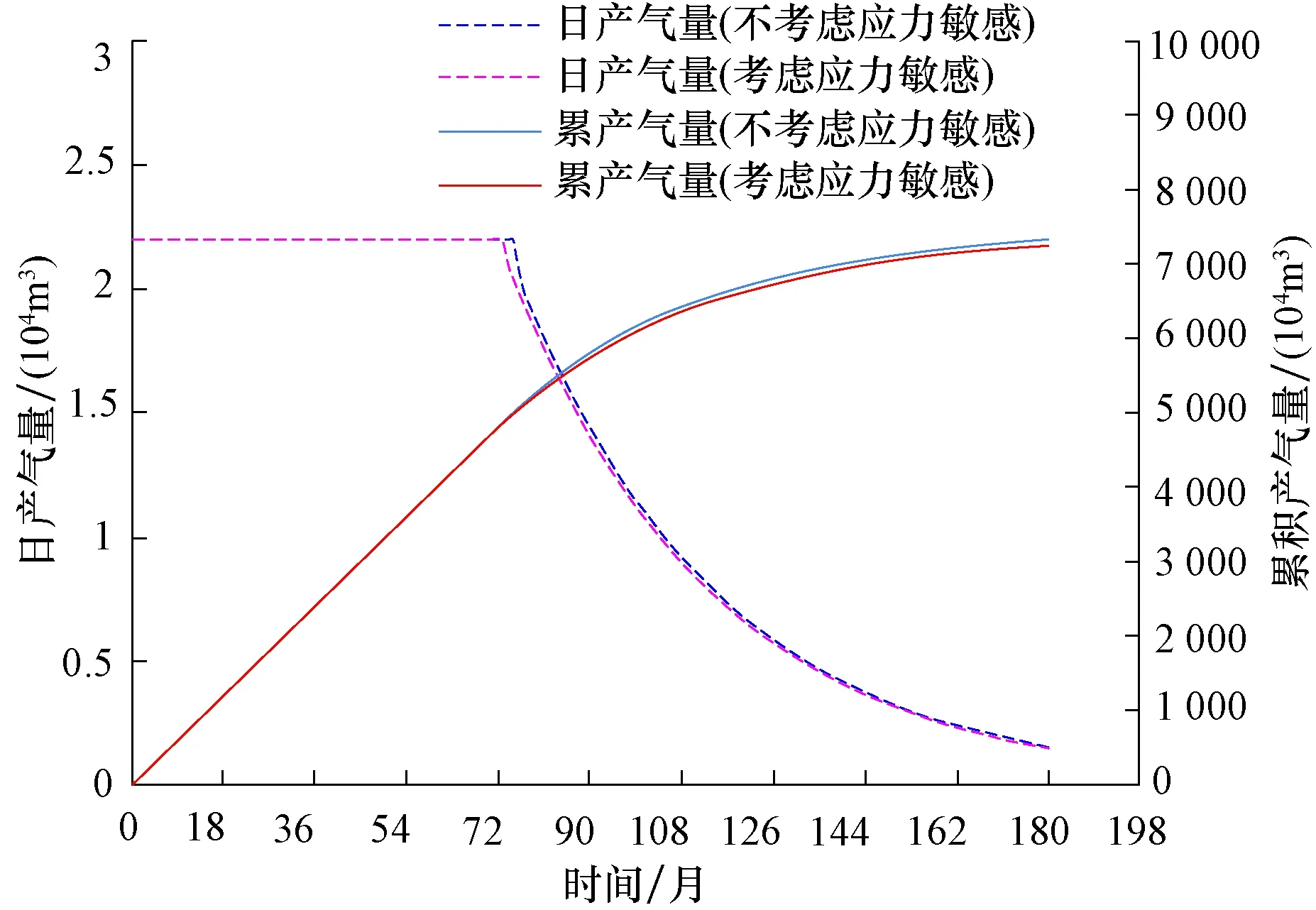
图3 大牛地气田盒1段应力敏感对Ⅰ类储层影响Fig.3 Influences of stress sensitivity on type Ⅰ reservoirs of the 1st Member of Xiashihezi Formation in Daniudi gas field
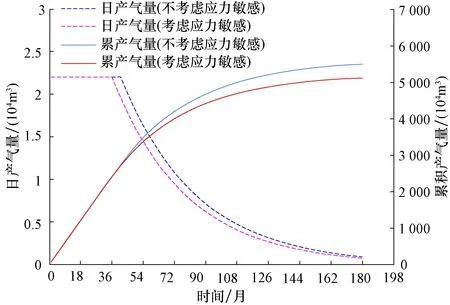
图4 大牛地气田盒1段应力敏感对Ⅱ类储层影响Fig.4 Influences of stress sensitivity on type Ⅱ reservoirs of the 1st Member of Xiashihezi Formation in Daniudi gas field
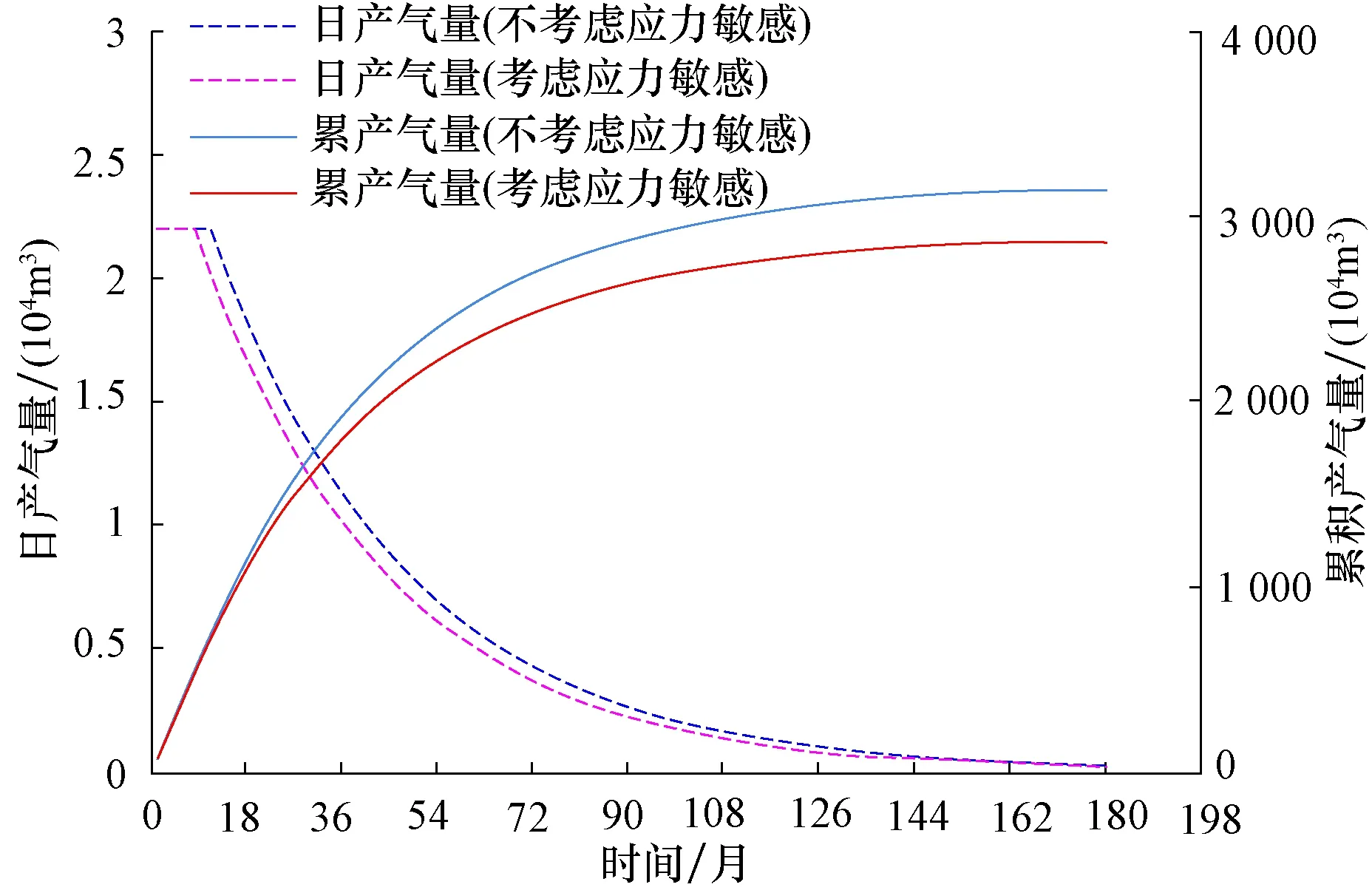
图5 大牛地气田盒1段应力敏感对Ⅲ类储层影响Fig.5 Influences of stress sensitivity on type Ⅲ reservoirs of the 1st Member of Xiashihezi Formation in Daniudi gas field
3 结论
1) 实验结果表明盒1段岩心普遍存在应力敏感。物性较好的Ⅰ类储层,应力敏感性为弱,Ⅱ类储层应力敏感性为中等偏弱,物性差的Ⅲ类储层应力敏感性大部分为中等。
2) 考虑了应力敏感的水平井开发数值模拟结果表明,Ⅰ类储层应力敏感对稳产期等指标的影响很小,Ⅱ类储层影响较小,Ⅲ类储层影响较大。
3) 盒1段Ⅲ类储层气井配产不宜过高,避免因应力敏感效应,对气井稳产期及累产气量产生较大影响。
[1]郝蜀民,惠宽洋,李良.鄂尔多斯盆地大牛地大型低渗气田成藏特征及其勘探开发技术[J].石油与天然气地质,2006,27(6):762-768.
Hao Shumin,Hui Kuanyang,Li Liang.Reservoiring features of Daniudi low-permeability gas field in Ordos basin and its exploration and development technologies[J].Oil & Gas Geology,2006,27(6):762-768.
[2]曲希玉,陈修,邱隆伟,等.石英溶解型次生孔隙的成因及其对储层的影响——以大牛地气田上古生界致密砂岩储层为例[J].石油与天然气地质,2015,36(5):804-813.
Qu Xiyu,Chen Xiu,Qiu Longwei,et al.Genesis of secondary pore of quartz dissolution type and its influences on reservoir:Taking the tight sandstone reservoir in the Upper Paleozoic of Daniudi gas field as an example[J].Oil & Gas Geology,2015,36(5):804-813.
[3]佘刚,周小鹰,戴明刚,等.波形分类技术在鄂北薄砂岩储层预测中的应用[J].石油天然气与地质,2012,33(4):536-540.
She Gang,Zhou Xiaoying,Dai Mingang,et al.Application of seismic waveform classification technique in thin sandstones reservoir prediction in northern Ordos Basin[J].Oil & Gas Geology,2012,33(4):536-540.
[4]杨辰雨,田景春,张翔,等.基于砂体构型精细刻画潮坪砂坝优质砂体——以大牛地气田D17井区太原组2段为例[J].石油与天然气地质,2015,36(2):248-254.
Yang Chenyu,Tian Jingchun,Zhang Xiang,et al.Configuration-based fine description of high-quality sand bodies in tidal-flat bar—Taking the tight sandstone reservoir in the 2ndmember of the Taiyuan Formation in D-17 wellblock in Daniudi gasfield as an example[J].Oil & Gas Geology,2015,36(2):248-254.
[5]罗瑞兰.“对低渗储层不存在强应力敏感”观点的质疑[J].石油钻采工艺,2006,28(2):78-80.
Luo Ruilan.Queries to the viewpoint low permeability reservoirs have not the characteristics of strong stress sensitivity[J].Oil Drilling & Production Technology,2006,28(2):78-80.
[6]罗瑞兰.关于低渗致密储层岩石的应力敏感问题—与李传亮教授探讨[J].石油钻采工艺,2010,32(2):126-130.
Luo Ruilan.Discussion of stress sensitivity of low permeability and tight reservoir rocks[J].Oil Drilling & Production Technology,2010,32(2):126-130.
[7]刘晓旭,胡勇,朱斌,等.储层应力敏感性影响因素研究[J].特种油气藏,2006,13(3):18-21.
Liu Xiaoxu,Hu Yong,Zhu Bin,et al.Influential factor analysis of reservoir stress sensitivity[J].Special Oil and Gas Reservoirs,2006,13(3):18-21.
[8]张睿,宁正福,杨峰,等.页岩应力敏感实验与机理[J].石油学报,2015,36(2):224-231,237.
Zhang Rui,Ning Zhengfu,Yang Feng,et al.Shale stress sensitivity experiment and mechanism[J].Acta Petrolei Sinica,2015,36(2):224-231,237.
[9]高涛.特低渗砂岩油藏水平缝应力敏感实验研究及产能计算[D].成都:西南石油大学,2015.
Gao Tao.Experimental study on stress sensitivity and productivity calculation of horizontal seam in extra low permeability sandstone reservoir[D].Chengdu:Southwest Petroleum University,2015.
[10]肖香姣,毕研鹏,王小培,等.一种新的考虑应力敏感影响的三项式产能方程[J].天然气地球科学,2014,25(5):767-770.
Xiao Xiangjiao,Bi Yanpeng,Wang Xiaopei,et al.A new trinomial deliverability equation with consideration of stress sensitivity[J].Natural Gas Geoscience,2014,25(5):767-770.
[11]李传亮,朱苏阳.关于应力敏感测试方法的认识误区[J].岩性油气藏,2015,27(6):1-4.
Li Chuanliang,Zhu Suyang.Misunderstanding of measuring methods of stress sensibility[J].Lithologic Reservoirs,2015,27(6):1-4.
[12]李明军,马勇新,李红东,等.海上异常高压低渗透气藏应力敏感实验研究[J].钻采工艺,2014,37(1):88-90.
Li Mingjun,Ma Yongxin,Li Hongdong,et al.Stress sensitivity experiment of offshore abnormal high pressure low permeability gas reservoir[J].Drilling & Production Technology,2014,37(1):88-90.
[13]窦晶晶,修乃岭,严玉忠,等.基于应力敏感常数的致密砂岩储层应力敏感性评价研究[J].重庆科技学院学报( 自然科学版),2015,17(4):10-13.
Dou Jingjing,Xiu Nailing,Yan Yuzhong,et al.Research on tight sandstone stress sensitivity reservoir based evaluation experiments of on stress sensitivity constant[J].Journal of Chongqing University of Science and Technology(Natural Science Edition),2015,17(4):10-13.
[14]何江,付永雷,沈桂川,等.低渗砂岩储层岩石学特征与应力敏感性耦合关系——以鄂尔多斯盆地苏里格-吉尔地区下石盒子组八段下亚段为例[J].石油与天然气地质,2012,33(6):923-931.
He Jiang,Fu Yonglei,Shen Guichuan,et al.Coupling relations between the petrologic characteristics and stress-sensitiveness in low-permeability sandstone reservoirs:an example from the lower 8thmember of the Lower Shihezi Formation in Sulige-Jier area,Ordos Basin[J].Oil & Gas Geology,2012,33(6):923-931.
[15]刘峰,王裕亮,陈小凡,等.考虑应力敏感性的低渗透油藏油井产能分析[J].石油与天然气地质,2013,34(1):124-128.
Liu Feng,Wang Yuliang,Chen Xiaofan,et al.Analysis on oil well productivity of low-permeability reservoirs with stress-sensitivity being taken into considerations[J].Oil & Gas Geology,2013,34(1):124-128.
[16]杨松,刘培亮,何昶,等.塔河油田底水砂岩油藏水平井剩余油主控因素分析[J].石油实验地质,2015,37(S1): 23-28.
Yang Song,Liu Peiliang,He Chang,et al.Main controlling factors for remaining oils in horizontal wells in sandstone reservoirs with bottom water in the Tahe Oil Field.Petroleum[J].Geology & Experiment,2015,37(S1):23-28.
[17]雷刚,王昊,董平川,等.非均质致密砂岩应力敏感性的定量表征[J].油气地质与采收率,2015,22(3):90-94
Lei Gang,Wang Hao,Dong Pingchuan,et al.Quantitative analysis on stress sensitivity of heterogeneous tight sandstone[J].Petroleum Geology and Revovery Efficiency,2015,22(3):90-94.
[18]侯瑞云,刘忠群.鄂尔多斯盆地大牛地气田致密低渗储层评价与开发对策[J].石油天然气与地质,2012,33(1):118-128.
Hou Ruiyun,Liu Zhongqun.Reservoir evaluation and development strategies of Daniudi tight sand gas field in the Ordos Basin[J].Oil&Gas Geology,2012,33(1):118-128.
[19]郝蜀民,刘忠群,周涌沂,等.大牛地致密低渗气田水平井整体开发技术[M].北京:石油工业出版社,2015:113-114.
Hao Shumin,Liu Zhongqun,Zhou Yongyi,et al.Integrated development technology of horizontal well in Daniudi tight and low permeability gas field[M].Beijing:Petroleum Industry Press,2015:113-114.
[20]李传亮,孔祥言,徐献芝,等.多孔介质的双重有效应力[J].自然杂志,1999,21(5):288-292.
Li Chuanliang,Kong Xiangyan,Xu Xianzhi,et al.Double effective stress of porous media[J].Chinese Journal of Nature,1999,21(5):288-292.
[21]李闽,乔国安,陈昊.低渗砂岩储层岩石应力敏感实验与理论研究[J].钻采工艺, 2006,29(4):91-93.
Li Min,Qiao Guoan,Chen Hao.Experimental and theoretical study on rock stress-sensitivities in low permeability sandstone[J].Drilling & Production Technology,2006,29(4):91-93.
[22]李传亮.岩石应力敏感指数与压缩系数之间的关系式[J].岩性油气藏,2007,19(4):95-98.Li Chuanliang.A theoretical formula of stress sensitivity index with compressibility of rock[J].Lithologic Reservoirs,2007,19(4):95-98.
[23]李传亮.储层岩石的应力敏感性评价方法[J].大庆石油地质与开发,2006,25(1):40-42.
Li Chuanliang.Evaluation method for stress sensitivity of reservoir rock[J].Petroleum Geology & Oilfield Development in Daqing,2006,25(1):40-42.
(编辑张亚雄)
Stress sensitivity of the 1stMember of Xiashihezi Formation and its influences on horizontal well development of Daniudi gas field,Ordos Basin
Chen Kui,Ren Guanglei,Yang Wenjuan,Yu Yaonan
(ExplorationandDevelopmentResearchInstitute,SINOPECNorthChinaCompany,Zhengzhou,Henan450006,China)
The 1stMember of Xiashihezi Formation(H1)of Daniudi gas field is a typical low permeability reservoir in Ordos Basin.In order to clearly understand the stress sensitivity of H1,13 core samples of different types were chosen for stress sensitivity tests.The experimental results show that the core samples from H1 commonly show stress sensitivity and permeability hysteresis,indicating that the cores experience plastic deformation with the increasing of net stress.Analysis of the experimental data with internal stress sensitivity index method shows that the type Ⅰ reservoirs with better physical properties has a relatively low stress sensitivity,while the type Ⅱ and Ⅲ reservoirs have low to moderate stress sensitivity.The averaged internal stress sensitivity index of these 13 core samples is 0.086,indicating that the overall stress sensitivity is low.We built numerical simulation models of multi-stage fracturing of horizontal wells for Ⅰ-Ⅲ type reservoirs,into which the relationship between dimensionless permeability and the formation pressure was incorporated.Under a constant gas production rate scheme in the numerical model,the effects of stress sensitivity on horizontal well performance were investigated.The numerical simulation results show that the stress sensitivity has very little effect on gas rate during stable production period for type Ⅰ reservoir,which only decreased by 1.6% in comparison with that without stress sensitivity case.For type Ⅱ and Ⅲ reservoirs,the gas rate during stable production period decreased by 11.2% and 23.6%,respectively.Therefore,production allocation and management should be strengthened for type Ⅱ and Ⅲ reservoirs to guarantee well performance.
stress sensitivity,low permeability,horizontal well,gas field development,Daniudi gas field,Ordos Basin
2015-12-20;
2016-02-24。
陈奎(1980—),男,硕士,工程师,气藏工程。E-mail:1235199@qq.com。
国家科技重大专项(2011ZX05045)。
0253-9985(2016)02-0267-05
10.11743/ogg20160216
TE37
A

