Applying healthcare failure mode and effect analysis to patient pain management in the anesthesia recovery period
Zho-Ping Xue,Hong-Yn Li,Rui-Tong Gun,Si Chen,*PACU,The First Hospitl of Jilin University,Chnghun,130021,ChinNursing Deprtment,The First Hospitl of Jilin University,Chnghun,130021,ChinDeprtment of Anoretl Surgery,The First Hospitl of Jilin University,Chnghun,Jilin,130021,Chin
Original article
Applying healthcare failure mode and effect analysis to patient pain management in the anesthesia recovery period
Zhao-Ping Xuea,Hong-Yan Lib,Rui-Tong Guana,Si Chenc,*aPACU,The First Hospital of Jilin University,Changchun,130021,China
bNursing Department,The First Hospital of Jilin University,Changchun,130021,China
cDepartment of Anorectal Surgery,The First Hospital of Jilin University,Changchun,Jilin,130021,China
A R T I C L EI N F O
Article history:
Received in revised from
30 April 2015
Accepted 15 December 2015
Available online 21 March 2016
Health care failure mode
Effect analysis
Pain nursing
Post anesthesia
Nursing management
ABSTRACT
Objective:To standardize pain management in the anesthesia recovery period and improve the effects of analgesia on acute postoperative pain.
Methods:Using healthcare failure mode and effect analysis(HFMEA),we analyzed the primary cause of patients'pain and subsequently determined the process and risk priority number(RPN).
Results:Actions were taken to improve patients'pain.After using HFMEA,the experimental group's visual analog scale(VAS)scores were lower than those of the control group at 1 h and at discharge from the post-anesthetic intensive care unit(PAICU).The differences were statistically significant(P<0.05).
Conclusions:The application of failure mode and effect analysis can relieve pain and improve the quality of nursing.
©2016 Shanxi Medical Periodical Press.Production and hosting by Elsevier B.V.This is an open access article under the CC BY-NC-ND license(http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/).
1.Introduction
Pain can be the worst feeling experienced by patients,and it is also among the most common and most serious forms expressing uncomfortable feelings.In nursing practice,pain is seen as the fifth key vital sign in addition to body temperature,pulse,respiration and blood pressure and is increasinglyvalued.1Statistically,obvious postoperative pain occurs in 75%of surgical patients.Poor management of postoperative pain can cause complications of the respiratory and cardiovascular systems and adversely influence postoperative rehabilitation.To reduce(alleviate)patients'postoperative pain,we applied HFMEA for patient pain management during the anesthesia recovery period.HFMEA is a team-based,systemic and prospective crisis analysis approach.As a quality improvement process,HFMEA represents a new management concept that can be described as“getting all things done at once”2to prevent failures before malfunctions occurs and eliminate or reduce the occurrence of potential failure modes to make designs and programs more secure.Identifying and analyzing the potentialcauses of the problems and then solving those problems enables the goal of quality improvement to be achieved.The American Pain Society(APS)proposed that through quality improvement,pain management can be improved.3
2.Materials and methods
2.1.General data
Onehundredtwentypatientswhounderwentelective abdominal operations under general anesthesia and tracheal intubation from February to June of 2013 were included.The inclusion criteria were as follows:patients who are 18-65 years old,ASA I-II,literate,and able to use a visual analog scale.The patients were randomly divided into an experimental group(n=60)and a control group(n=60).There were no significant differences in the age,sex,degree of education,the operation time or anesthesia time between the two groups(P>0.05).
2.2.Methods
The HFMEA management group was set up in February of 2013 and consisted of a head nurse,a pain specialist nurse,an anesthesiologist and three other nurses.The head nurse was responsiblefor training regarding HFMEA-related knowledge,guiding the team members to conduct step analysis by applying their knowledge of HFMEA,and identifying the causes of and assessing the risk factors for postoperative pain during the anesthesia recovery period. Subsequently,all team members followed the head nurse in this process.
http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.cnre.2015.12.004
2095-7718/© 2016 Shanxi Medical Periodical Press.Production and hosting by Elsevier B.V.This is an open access article under the CC BY-NC-ND license(http:// creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/).
Preventive actions were discussed,and improved solutions were developed.The pain specialist nurse organized and implemented the pain control courses for the team and supervised,audited and provided feedback about pain management.
2.2.1.The creation of a flow chart to identify the failure mode of the operation(Fig.1)
The causes of post-anesthesia pain were categorized into 3 processes according to the flowchart.Before the patient was transferred to the recovery room for the postoperative recovery period and back to the ward,every process and 8 other subprocesses were analyzed using brainstorm methods.The purpose of this analysis was to investigate the causes of the pain and the causes and effects of failures and to identify the potential modes in every process or sub-processes.
按照对比护理的方式进行研究,选取我院2017年1月~2018年8月所接诊病例76例,任选组中38例,以常规方式护理,即对照组,余下38例,则给与中西医护理干预,即观察组。对照组男20例,女18例,年龄34~57岁,平均(43.12±1.08)。而观察组则由男19例,女19例,年龄31~59岁,平均(45.82±1.45)。对以上各数据对比;差异无统计学意义(P>0.05)。
2.2.2.The calculation of the RPN value
RPN includes the following 3 dimensions:the frequency of occurrence(frequency of occasion,O),and the difficulty(D)and severity(S)of the failedinspection.Each dimensionwas scored on a scale from 1 to 10;for example,a frequency of occurrence of 1 indicates“very unlikely”,whereas 10 indicates“very likely”.The RPN=O*D*S.The minimum score is 1 point,and the highest possible score is 1000 points.Higher values indicate greater potential influences of failures.The assignments were discussed by the group members as indicated in Table 1.
2.3.Develop improvement solutions
According to the failure mode risk rankings,we listed the top 6 risk factors for the failure mode and then implemented the following improvement measures:
(1)According to the degrees of pain knowledge and attitudes of
the nurses,we developed training plans.These plans included theoretical training,operation training,and training to strengthen the nurses'pain-related knowledge training.It is vitally important to master the correct pain assessment skills and analgesic treatment skills.Before that,wesought to improve the proficiency in the use of pain assessment tools and the accuracy of the assessments of pain level.It is also essential to provide corresponding treatment according to the different conditions of the patients in the meantime.
(2)The nurses spent 30 min with the patient,and then offered the patient knowledge about the surgery that he/she was going to undergo and the pain she/he was going to suffer from.Furthermore,chatting with the patient about postoperative analgesia and the possible risks can reduce her/his anxiety and fear about the operation.The nurses can also encourage the patients to express their true feelings about postoperative pain and inform them about pain assessment methods.Establishing a solid relationship of mutual trust can actually ease patients'feelings.
(3)After surgery,the patients may feel pain when they cough,change posture,or engage in behaviors that cause chest movement primarily because the wound is pulled.Nurses should instruct patients to take some preventive measures and inform them about techniques for reducing pain,such as listening to soft music to distract their attention,playing with the rhythm of light music,slow-paced breathing,Qigong and yoga,which can reduce muscle tension and relieve pain.
(6)Nurses should maintain soft lights indoors and a suitable temperature and humidity to create a comfortable environment.Simultaneously,the patients should avoid direct sunlight.To avoid noise and other environmental factors that could induce or aggravate pain,the medical care providers should use low and soft voices and gentle movements,try to avoid the effects of medical instruments,and keep the environmental noise in the recovery room below 35 dB.
2.4.The project completion report
The knowledge of HFMEA was applied during the anesthesia recovery period to identify the causes of and risk factors forpostoperative pain.We then developed improvement solutions. The project completion report should be written by the team leader.Simultaneously,the team leader should record the processes and results of the project and then generalize these experiences and propose further research projects.
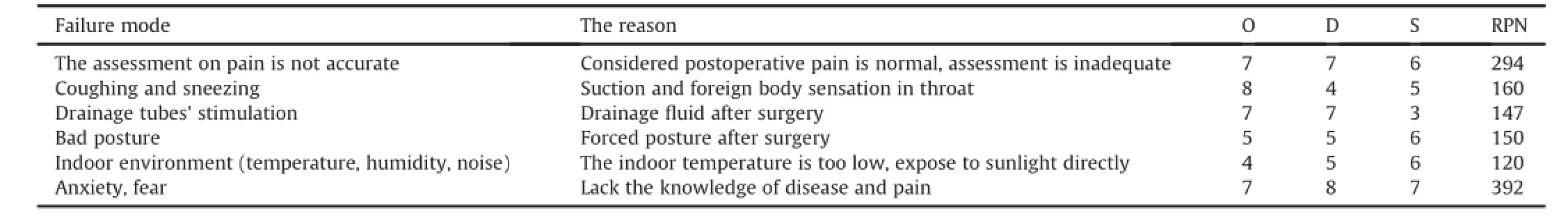
Table 1Failure mode and the reason.
Table 2
Comparison of the VAS scores of the experimental and control groups(n=60,x±s).
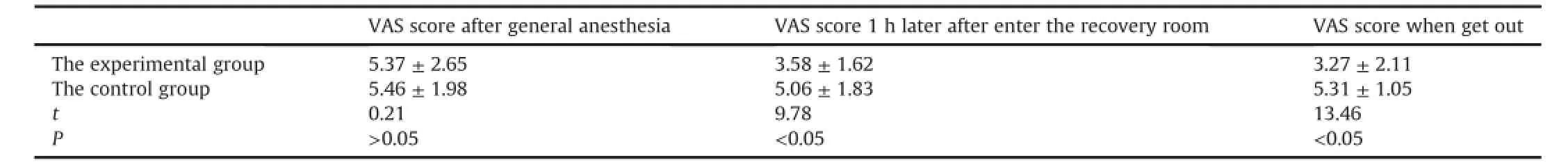
Note:VAS=visual analog scale.
3.Results and analysis
After general anesthesia,the nurses will make baseline pain assessments based on a VAS in both the experimental group and control group.During this assessment,the patients were asked to grade their pain level on a 10 cm ruler(0 cm indicates pain-free,and 10 cm indicates the most severe pain).Then,the nurse should reassess 1 h after entering the recovery room and right before discharging the patient from the PACU.According to the statistical analyses of the 3 assessments mentioned above using SPSS 17.0 software,we found that the data fit the normal distribution and applied t tests.The results are described below(Table 2).
4.Discussion
Since July of 2001,based on the frequent alert events that were periodically published by the Joint Commission on the Accreditation of Healthcare Organizations(JCAHO),all hospitals that are certified by the JCAHO are required to conduct an annual prospective risk assessment using EMAP.Domestic scholars who are certified by the JCAHO are required to conduct annual prospective risk assessments and reduce the occurrence of adverse obstetrical events.Simultaneously,this process can ensure the safety of oral drugs.4-6
Generally,anesthesia and surgery can lead to severe postoperative pain,which can cause stress responses,including the induction of the secretion of catecholamine;increases the respiratory frequency,pulse,blood pressure and blood glucose;greater oxygen consumption;and others.Eventually,these responses can interrupt the stability of the internal environment,affect the functionality of multiple systems of the body,and delay patient recovery from surgery.7,8
By applying HFMEA,studies that focus on the risk factors that might cause postoperative pain can develop improved preventive measures.Nursing staff should be given full freedom of subjective initiative and strive to formulate improved preventive measures that are related to postoperative pain.By providing preoperative education to the patients and creating a pleasant and relaxing atmosphere in the PACU,the proper relaxing measures can effectively alleviate postoperative pain and the VAS scores can be effectively reduced at 1 h after entering the recovery room as well as immediately prior to discharge from the PACU.Finally,the effects of analgesia are efficaciously improved,and true continuous quality improvement can be achieved.
5.Conclusions
Even in the control group,pain can be eased by the use of the routine nursing process.However,the results of the investigation suggested that the analgesic effects were effectively enhanced in the experimental group.This difference was significant(P<0.05).
Conflicts of interest
All contributing authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
1.Li XH,Shang SM.Basic Nursing Science.Beijing:People’s Medical Publishing House.2012:430.
2.Estorillo C,Posso RK.The reduction of irregularities in the use of‘process FMEA’. Int J Qual Rel Manag.2010;27:721-733.
3.Go'on GB,Polomano RC,Pellion TA,et al.Revised American Pain Society Patient Outcome Questionnaire(APS-POQ-R)for quality improvement of pain management in hospitalized adults:preliminary psychometric evaluation.J Pain. 2010;11:1172-1186.
4.Jiang GF,Peng LL.Application of healthcare failure mode and effect analysts in the prevention of falls among hospitalized elderly parents.Chin J Nurs.2011;46:273-274(in Chinese).
5.Liu XL,Ding XH.Application of FMEA on the management of adverse nursing event in Obstetrics department.Int J Nurs.2012;31:1917-1919(in Chinese).
6.Jiang H,Huang Y,Huang GE.Application of health care failure mode and effect analysis in the construction and evaluation of hospital oral administration security system.Chin J Nurs.2010;45:394-396(in Chinese).
7.Witt JK,Linkenauger SA,Bakdash JZ,Augustyn JS,Cook A,Proffitt DR.The long road of pain:chronic pain increases perceived distance.Exp Brain Res.2009;192:145-148.
8.Baliki MN,Chialvo DR,Geha PY,et al.Chronic pain and the emotional brain:specific brain activity associated with spontaneous fluctuations of intensity of chronic back pain.J Neurosci.2006;26:12165-12173.
27 January 2015
*Corresponding author.
E-mailaddresses:1643961393@qq.com(Z.-P.Xue),875182831@qq.com (S.Chen).
Peer review under responsibility of Shanxi Medical Periodical Press.
- Frontiers of Nursing的其它文章
- GUIDE FOR AUTHORS
- Aims and Scope
- Study of the effect of humanistic nursing care model wards in Children Caring Ward School on the nurses'caring ability☆
- Analysis of risk factors and the establishment of a risk model for peripherally inserted central catheter thrombosis
- Nurses'perception of risk factors for infusion phlebitis:A cross-sectional survey
- Tai Chi as an intervention to reduce falls and improve balance function in the elderly:A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials

