D-二聚体在肝硬化、肝癌患者中的临床价值
樊和斌,陈彩云,杨东亮,李 智,孙 洁,严福明,吴娟娟
1. 中国人民解放军第一六一医院感染科,湖北 武汉 430010;2. 中国人民解放军火箭军武汉干休所;3. 华中科技大学同济医学院协和医院感染科
D-二聚体在肝硬化、肝癌患者中的临床价值
樊和斌1,陈彩云2,杨东亮3,李 智1,孙 洁1,严福明1,吴娟娟1
1. 中国人民解放军第一六一医院感染科,湖北 武汉 430010;2. 中国人民解放军火箭军武汉干休所;3. 华中科技大学同济医学院协和医院感染科
目的 探讨肝硬化、肝癌患者血浆D-二聚体水平与肝脏疾病的严重程度的相关性。方法 回顾性分析2005年1月-2013年12月中国人民解放军第一六一医院感染科收治的肝硬化及肝癌患者,采用美国贝克曼库尔特公司的原装试剂进行D-二聚体的测定,根据患者的临床特点、生化结果进行Child-Pugh分级,并根据肝癌的大小、分期、是否有门静脉癌栓及是否伴有腹水进行分组,分析D-二聚体与肝脏疾病严重程度的相关性。结果 肝硬化患者Child-Pugh A、B、C级的D-二聚体值分别为(2.218±0.54)μg/ml、(6.03±0.76)μg/ml、(10.536±0.664)μg/ml,差异有显著统计学意义(P=0.000)。肝癌的大小、分期、门静脉癌血栓有无及是否伴有腹水的D-二聚体值差异均有统计学意义(P=0.000)。结论 肝脏疾病越严重,血浆D-二聚体含量越高,因而D-二聚体是反映肝脏疾病严重程度的标志物之一。
肝硬化;肝细胞癌;Child-Pugh;D-二聚体
D-二聚体是交联纤维蛋白特异的降解产物,它的生成或增高反映了凝血和纤溶系统的激活,可作为体内高凝状态和纤溶亢进的分子标志物之一[1]。目前已被广泛应用于血栓性疾病(如DIC、肺栓塞、深静脉血栓、急性心肌梗塞、冠心病、肿瘤等)的诊断、鉴别诊断、病情监测及预后判断中[2-3]。有研究[4]表明,肝脏疾病(尤其是肝硬化失代偿期)存在不同程度凝血、纤溶的功能异常。近年来研究发现D-二聚体与腹水有相关性[5]。我们检测了肝硬化、肝癌患者的血浆D-二聚体水平,旨在探讨不同阶段肝病患者D-二聚体的变化及其临床意义。
1 资料与方法
1.1 一般资料 2005年1月-2013年12月在中国人民解放军第一六一医院感染科住院的肝硬化患者628例,男417例,女211例,年龄39~75岁,诊断符合2000年西安第10次全国病毒性肝炎及肝病学术会议制定的标准进行诊断分型[6]。根据肝硬化患者的生化指标、临床特征等进行Child-Pugh分级。排除标准为患者存在深静脉血栓、中央静脉血栓、抗凝治疗、合并有其他肿瘤者及同时合并有两种或两种以上并发症者。肝癌患者66例,男42例,女24例,年龄42~65岁。肝癌的诊断及分期按2001年9月在广州召开的第八届全国肝癌学术会议上正式通过了“原发性肝癌的临床诊断与分期标准”执行[7]。根据肿瘤的大小、TNM分期、有无腹水、是否存在门静脉癌栓分组,比较D-二聚体的含量水平。本研究经过本院的伦理研究委员会批准,所有患者签署知情同意书。
1.2 检测方法 所有研究对象均在清晨采集空腹静脉血1.8 ml,注入含有0.2 ml的枸橼酸钠抗凝试管中,在1∶9抗凝充分混匀后,3 000 r/min离心20 min,采用美国贝克曼库尔特公司的原装试剂进行D-二聚体的测定,测定过程完全按照厂家提供的说明书严格操作。

2 结果
2.1 628例肝硬化患者的基本特征及不同组别肝硬化病因的比较 628例患者中乙肝肝硬化304例(48.4%),丙肝肝硬化141例(22.5%),酒精性肝硬化71例(11.3%),血吸虫性肝硬化48例(7.6%),自身免疫性肝硬化32例(5.1%),不明原因性肝硬化32例(5.1%)。
2.2 628例肝硬化患者Child-Pugh分级的血浆D-二聚体含量(μg/ml) 628例患者中,Child-Pugh A级225例,D-二聚体为(2.218±0.54)μg/ml;Child-Pugh B级172例,D-二聚体为(6.03±0.76)μg/ml;Child-Pugh C级231例,D-二聚体为(10.536±0.664)μg/ml。三组两两比较,差异有统计学意义(P=0.000)。
2.3 不同分组66例肝癌患者D-二聚体水平 肝癌的大小、TNM分期、门静脉癌血栓有无及是否伴有腹水的D-二聚体值比较差异均有统计学意义(P=0.000,见表1)。
表1 不同程度肝癌患者D-二聚体的比较
Tab 1 Comparison of D-dimer in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma
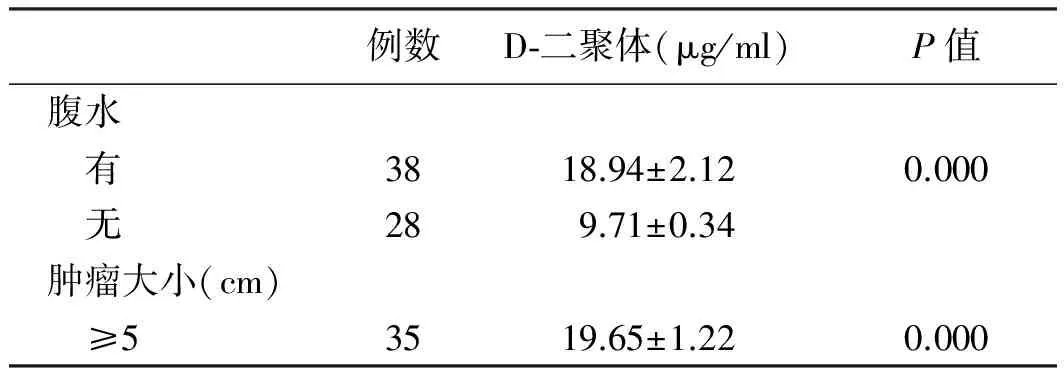
例数D⁃二聚体(μg/ml)P值腹水 有3818.94±2.120.000 无289.71±0.34肿瘤大小(cm) ≥53519.65±1.220.000
续表1
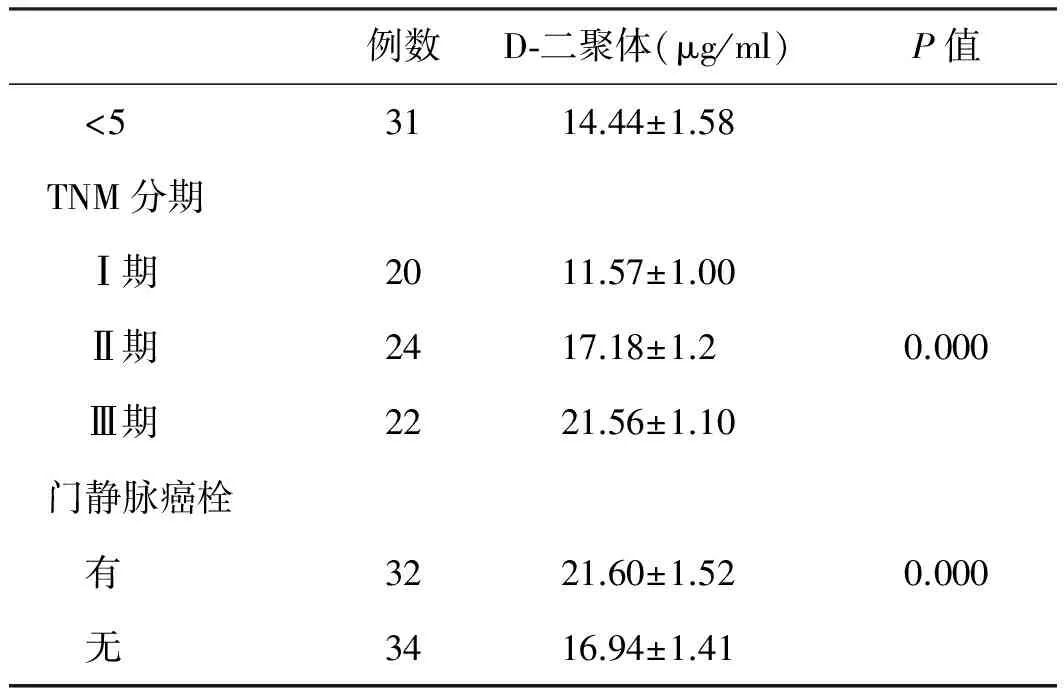
例数D⁃二聚体(μg/ml)P值 <53114.44±1.58TNM分期 Ⅰ期2011.57±1.00 Ⅱ期2417.18±1.20.000 Ⅲ期2221.56±1.10门静脉癌栓 有3221.60±1.520.000 无3416.94±1.41
3 讨论
肝硬化尤其伴有并发症时,肝脏清除t-PA能力下降,同时合成纤溶抑制物减少,导致患者体内继发性纤溶或同时存在原发性纤溶亢进,最终引起D-二聚体的升高[8]。本研究结果显示,肝硬化患者Child-Pugh评分越高,D-二聚体含量越高。肝硬化患者纤溶亢进可能系低水平的弥漫性血管内凝血,而弥漫性血管内凝血多继发于肠道菌群移位,肝硬化终末期肝病更容易发生肠道菌群移位,说明病情及肝功能损伤越严重,血浆D-二聚体含量越高,因而D-二聚体是反映肝硬化活动水平及程度的标志物之一。
肝硬化患者纤溶亢进的发生率为19%~95%,往往导致严重出血。其发生纤溶亢进的机制除了上述肝脏合成及灭活功能减退外,有研究[9-10]发现血浆及腹水中D-二聚体的升高,血浆及腹水之间存在凝血及纤溶蛋白互换,因此推测肝硬化腹水也是其发生纤溶亢进的机制之一。本研究发现肝癌也有类似现象,伴腹水患者D-二聚体水平高于无腹水组。
本研究也发现,进展快、预后差的肝癌患者其D-二聚体明显升高。因此,D-二聚体可以作为肝脏疾病严重程度的一个生化指标,监测其变化,对疾病的预后有重要的临床意义。
[1]郭世杰, 王林. D-二聚体的目前认识与临床应用[J]. 天津医科大学学报, 2013, 5(1): 82-85.
Guo SJ, Wang L. Current knowledge and clinical application of D-dimer [J]. Journal of Tianjin Medical University, 2013, 19(1): 82-85.
[2]Bates SM. D-dimer assays in diagnosis and management of thrombotic and bleeding disorders [J]. Semin Thromb Hemost, 2012, 38(7): 673-682.
[3]Lecumberri R, Pegenaute C, Paramo JA. Clinical use of D-dimer in patients with cancer [J]. Med Clin (Barc), 2011, 137(10): 453-458.
[4]Drolz A, Horvatits T, Roedl K, et al. Coagulation parameters and major bleeding in critically ill patients with cirrhosis [J]. Hepatology, 2016, 64(2): 556-568.
[5]杨乃珍, 何小礼. 肝硬化患者凝血功能指标及D-二聚体变化与Child-Pugh肝功能分级的关系[J]. 检验医学与临床, 2012, 9(1): 49-51.
Yang NZ, He XL. Relationship of coagulation index, D-dimer change with Child-Pugh liver function classification in patients with liver cirrhosis [J]. Lab Med Clin, 2012, 9(1): 49-51.
[6]中华医学会传染病与寄生虫病学分会、肝病学分会联合修订. 病毒性肝炎防治方案[J]. 中华肝脏病杂志, 2000, 8(6): 324-329.
Infectious Diseases and Parasitic Diseases Branch of Chinese Medical Association, Branch of Liver Disease. Prevention and treatment of viral hepatitis [J]. Chin J Hepatol, 2008, 8(6): 324-329.
[7]中国抗癌协会肝癌专业委员会. 原发性肝癌的临床诊断与分期标准[J]. 中华肝脏病杂志, 2001, 9(6): 324.
Chinese Cancer Society Cancer Association Specialized Committee. The standard of clinical diagnosis and staging of primary liver cancer [J]. Chin J Hepatol, 2001, 9(6): 324.
[8]尤德宏, 张根兴, 邓历. 肝硬化患者血浆D-二聚体的变化及其意义[J]. 现代中西医结合杂志, 2012, 21(25): 2826-2827.
You DH, Zhang GX, Deng L. The changes and significance of plasma D-dimer in patients with liver cirrhosis [J]. Modern Journal of Integrated Traditional Chinese and Western Medicine, 2012, 21(25): 2826-2827.
[9]Saray A, Mesihovic R, Gornjakovic S, et al. Association between high D-dimer plasma levels and ascites in patients with liver cirrhosis [J]. Med Arch, 2012, 66(6): 372-374.
[10]Kim HK, Lee KR, Yang JH, et al. Plasma levels of D-dimer and soluble fibrin polymer in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma: a possible predictor of tumor thrombosis [J]. Thromb Res, 2003, 109(2-3): 125-129.
(责任编辑:王全楚)
Clinical value of D-dimer in patients with liver cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma
FAN Hebin1, CHEN Caiyun2, YANG Dongliang3, LI Zhi1, SUN Jie1, YAN Fuming1, WU Juanjuan1
1. Department of Infectious Diseases, the 161th Hospital of People’s Liberation Army, Wuhan 430010; 2. Sanatorium for Wuhan Rocket Army Retire Cadres; 3. Department of Infectious Diseases, Union Hospital of Tongji Medical College, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, China
Objective To investigate the relationship between the plasma D-dimer level and severity in patients with liver cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma.Methods Liver cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma patients were analyzed retrospectively from 2005 to 2013 in the 161th Hospital of People’s Liberation Army. According to the score of Child-Pugh, patients with liver cirrhosis were divided into 3 groups (Child-Pugh A, Child-Pugh B and Child-Pugh C). D-dimer was determined by the original reagent from Backman Company, Child-Pugh was classified according to the clinical characteristics and biochemical results. Results The plasma D-dimer levels were (2.218±0.54)μg/ml, (6.03±0.76)μg/ml, (10.536±0.664)μg/ml in Child-Pugh A, B and C, respectively, there was significantly different among Child-Pugh A,B,C (P=0.000). In patients with hepatocellular carcinoma, there were significant differences in D-dimer level, compared with group≥5 cm and group<5 cm, TNM stage Ⅰ, Ⅱ and Ⅲ, with portal vein tumor thrombus group and without portal vein tumor thrombus, with ascites group and without ascites groups (P=0.000).Conclusion The liver function damage is associated with the plasma D-dimer. So the D-dimer is one of the markers reflecting the level and degree liver severity.
Liver cirrhosis; Hepatocellular carcinoma; Child-Pugh; D-dimer
樊和斌,副主任医师,博士研究生,研究方向:病毒性肝炎及感染性疾病。E-mail:296592559@qq.com
10.3969/j.issn.1006-5709.2016.08.014
R575.2;R735.7
A
1006-5709(2016)08-0889-03
2015-03-18

