On the Number of Integral Ideals in Two Diff erent Quadratic Number Fields∗
Zhishan YANG
1 Introduction
Dirichlet series plays an important role in number theory.Given two Dirichlet series
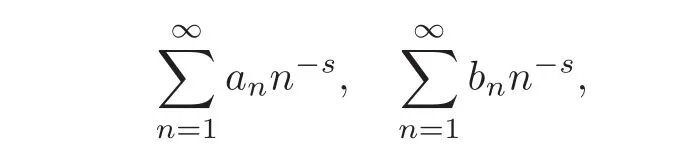
the convolution
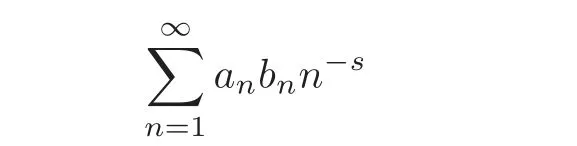
of these two series is a classical object studied by many authors,especially in the theory of automorphic forms.In connection with the multidimensional arithmetic of Hecke E.(see[7,11]),Linnik Yu.V.in[13]suggested to consider the scalar product of Hecke’s L-function associated with Größencharakters and asked whether this function can be analytically continued to the whole complex plane.This is the well-known Linnik problem.In this paper,we will consider the generalizations of the special cases of the problem connected to the Linnik problem.
Let K be an algebraic number field of finite degree d over the rational field Q.Denote the number of integral ideals in K with norm n by aK(n).Then the Dedekind zeta-function ζK(s)is defined by,for σ>1,
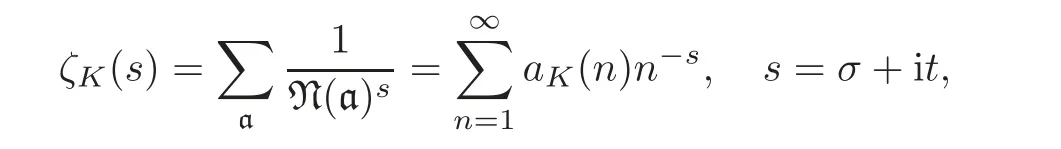
where a varies over the integral ideals of K,and N(a)denotes its norm.Obviously,the Dedekind zeta function can be seen as the convolution of Riemann zeta function ζ(s)and itself.
Chandraseknaran and Good[1]showed that aK(n)is a multiplicative function,and satisfies

where τ(k)is the divisor function,and d=[K:Q].
The number of integral ideals appeals to many authors.It was already known to Weber[21]that
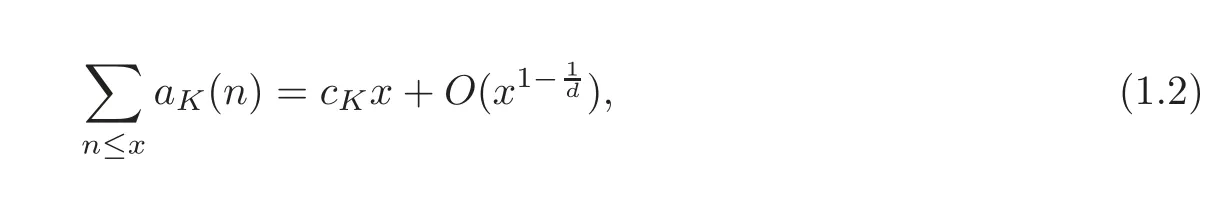
where cKis the residue of ζK(s)at its simple pole s=1.The estimate on the error term in(1.1)was improved by Landau[12]to
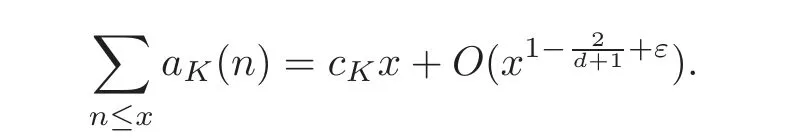
For quadratic fields,Huxley and Watt[8]established that

For cubic fields,Müller[17]proved that
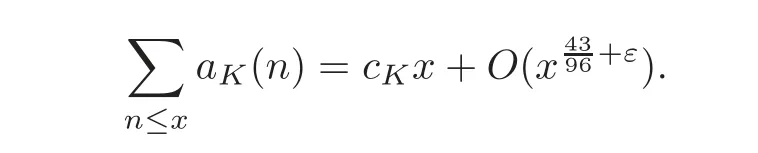
For any algebraic number field of degree d≥3,Nowak[18]made important contributions,and showed that
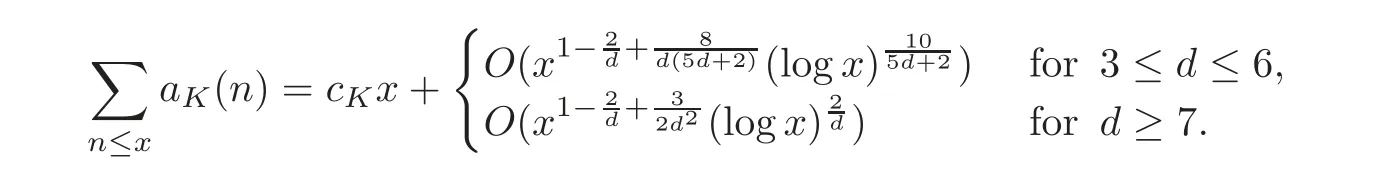
The second moment of aK(n)was first considered in[2],where it was shown that if K is a Galois extension of Q of degree d,then

for a suitable constant
Later,Chandraseknaran and Good[1]showed that if K is a Galois extension of Q of degree d,then for any ε>0 and any integer l≥ 2,we have

where PKdenotes a suitable polynomial of degree dl−1− 1.
In 2010,Lü and Wang[14]improved their result.If K is a Galois extension of Q of degree d,then for any ε>0 and any integer l≥ 2,we have
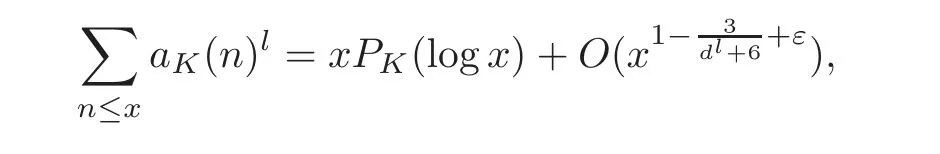
where PKdenotes a suitable polynomial of degree dl−1−1.Furthermore,for Abelian extensions K,some stronger results have also been established.
Recently,Land Yang[15]studied the average behavior of the coefficients of Dedekind zeta function over square numbers.For example,it was proved that for Galois fields of degree d which is odd,we have

whereand Pm(t)is a polynomial in t of degree m − 1.
In this paper,we will discuss the special cases of the Linnik problem in different quadratic fields.Let K1and K2be two different quadratic fields.We are interested in convolution sum
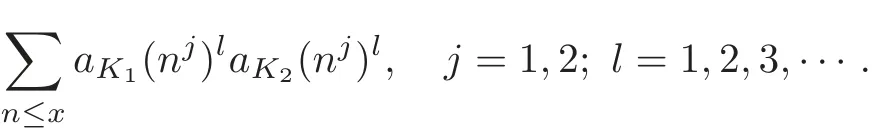
In this direction,Fomenko[3]proved that

where cK1,K2is a suitable constant.
We are able to prove the following results.
Theorem 1.1Let
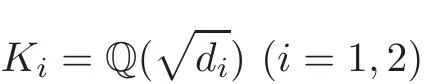
be the quadratic field of discriminantdi.Assume that(d1,d2)=1.Then for anyε>0and any integerl≥2,we have
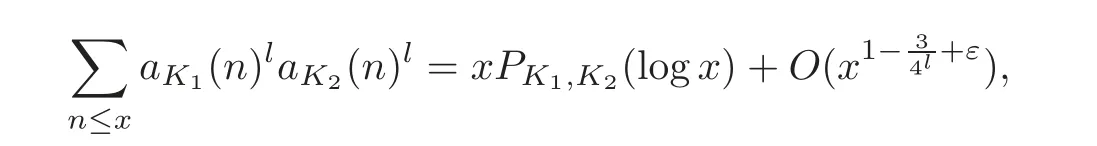
wherePK1,K2denotes a suitable polynomial of degree4l−1− 1.
Theorem 1.2Let
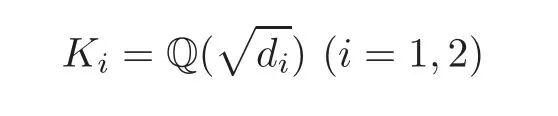
be the quadratic field of discriminantdi.Assume that(d1,d2)=1.Then for anyε>0and any integerl≥1,we have
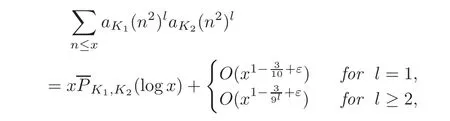
wheredenotes a suitable polynomial of degreeM2+2M,and
Remark 1.1(1)When l=1,by using our method,the result in Theorem 1.1 coincides with the result of Feomenko in[3];
(2)Under the GRH(Generalized Riemann hypothesis),we can improve the error term in the two theorems above as
As an application,we can get the distribution of the integral ideals in a quadratic field with norm of the sum of two squares.
Letbe a quadratic field with the discriminant d.aK(n)is the number of integral ideals with norm n in K.The distribution of integral ideals is important in algebraic number theory,and we are interested in the distribution of integral ideals with norm of the sum of two squares,i.e.,we consider the average sum
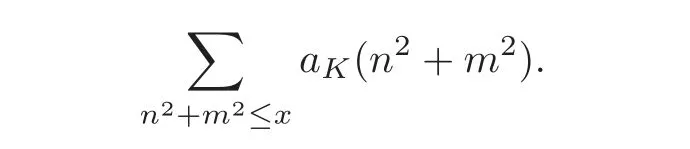
We define the function r(u)to be the number of solutions to n2+m2=u in integers n,m.Then the generating Dirichlet series for r(u)is equal to 4ζK?(s),where ζK?(s)is the zeta function of the imaginary quadratic field
On the other hand,we have
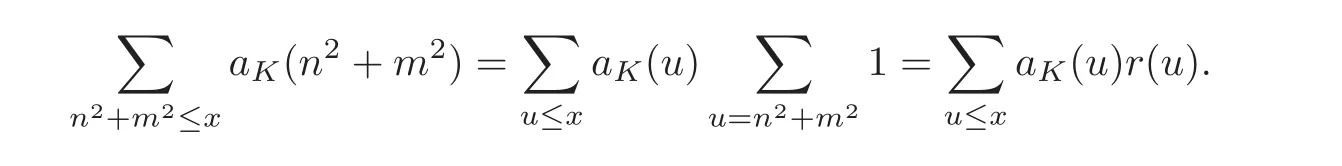
Now,let K1=K,K2=K'.According to Theorem 1.1,when l=1,we have the following corollary.
Corollary 1.1Letbe a quadratic field with discriminantd,andaK(n)thenumber of integral ideals with normn.Then we have
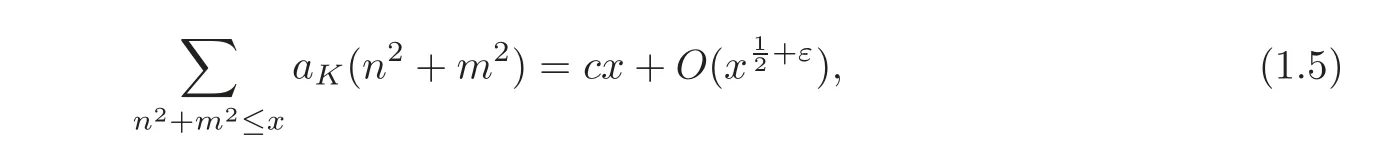
wherecis a suitable constant.
2 Proof of Theorem 1.1
For1,define
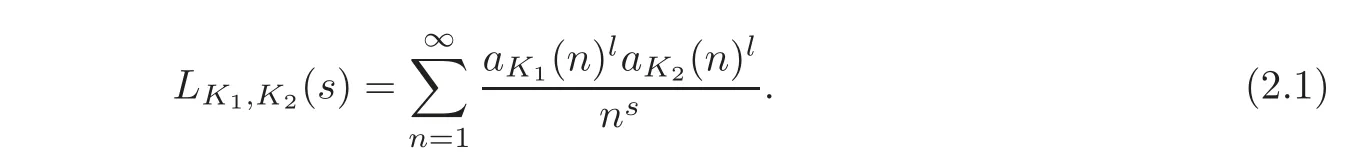
In fact,it absolutely converges in the half-plane>1 on noting(1.1).Since aK1(n)laK2(n)lis a multiplicative arithmetic function,we have
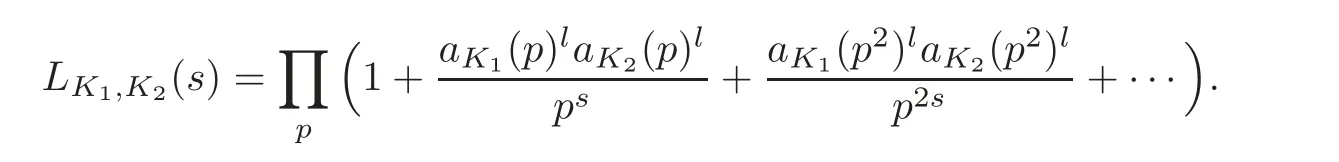
Obviously,the termdetermines the analytic properties of LK1,K2(s)in the halfplane
Let K1K2=be the composite field.K1and K2are two intermediate fields of the composite field K1K2.Let K3be another intermediate field of K1K2.Then it is well-known that
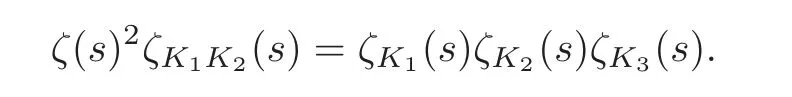
(see the formula 45 on page 64 in Swinnerton-Dyer[20]).On the other hand,we have
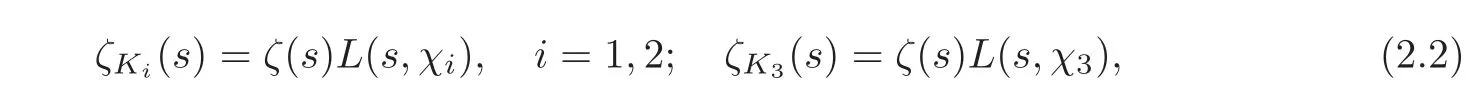
where χ1and χ2are two Dirichlet characters,and χ3= χ1χ2.Hence we have
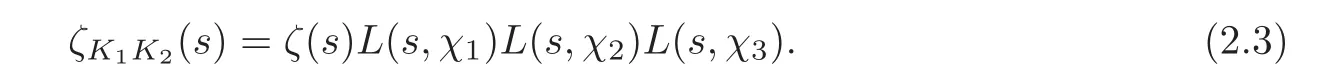
By comparing the Euler products over prime numbers of both sides in(2.2)–(2.3),we have
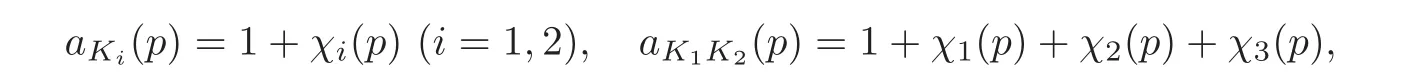
where p is prime.Hence for any prime number p,we have

The composite field K1K2is a Galois extension of degree 4 over Q.For a Galois extension K over Q of degree d,Chandraseknaran and Good[1]proved,by the well-known decomposition law of prime ideals,that except for finitely many prime numbers

where l is any positive integer.In particular,we have

By directly checking the Euler products of LK1,K2(s)and ζK1K2(s)4l−1in the region>1,we have

where U(s)denotes a Dirichlet series,which is absolutely convergent for σ>.
Now we begin to complete the proof of Theorem 1.1.By(2.4)we learn that LK1,K2(s)can be analytically continued to the half-plane?s>,where s=1 is the only pole of order 4l−1.Then by(2.1)and Perron’s formula(see Proposition 5.54 in[10]),we have

where b=1+ε and 1≤T≤x is a parameter to be chosen later.Here we have used(1.1).Next we move the integration to the parallel segment with=+ ε.By Cauchy’s residue theorem,we have
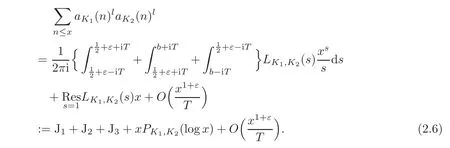
For J1,by(2.4)we have(noting that l≥2)

where we have
and
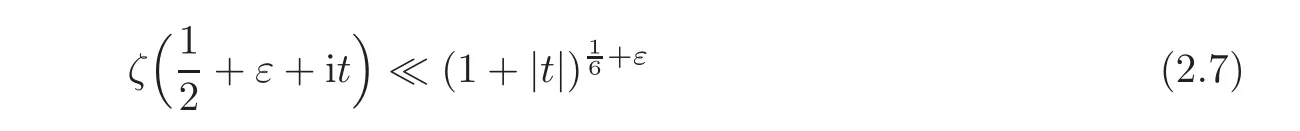
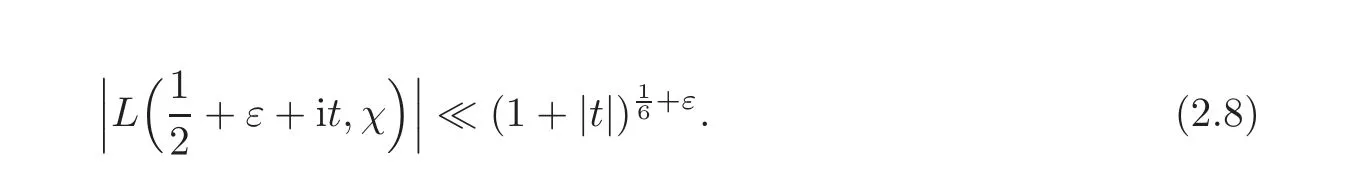
These results can be derived from the two following results:

and
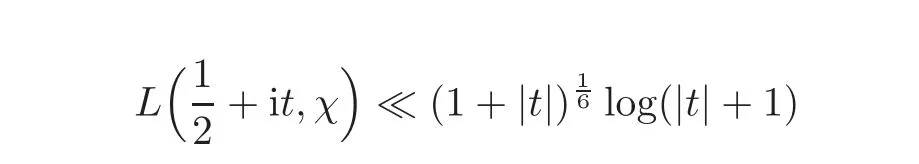
(see Theorems 24.1.1 and 24.2.1 in Pan and Pan[19])by the Phragmen-Lindelöf principle for a strip(see Theorem 5.53 in Iwaniec and Kowalski[10]).
Then we have
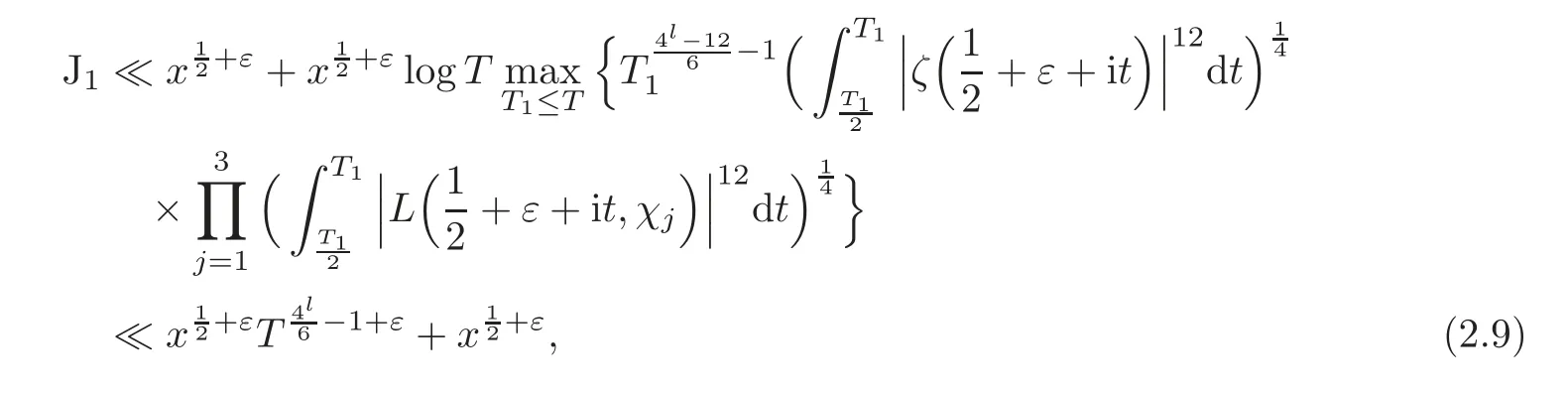
where we have used

and
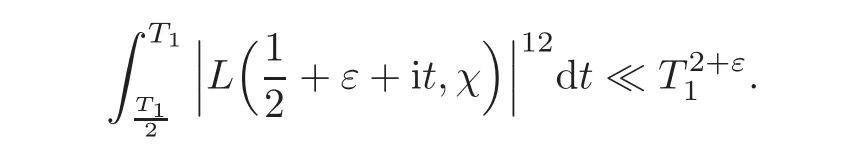
These results can be established by Gabriel’s convexity theorem(see Lemma 8.3 in Ivi´c[9]),and the results of Heath-Brown[5]and Meurman[16]respectively,which state that

and
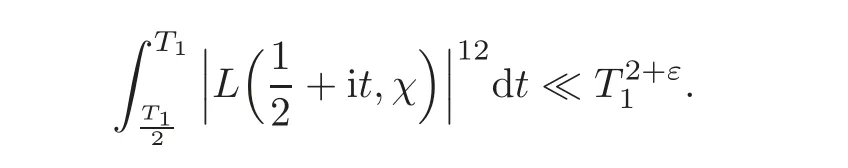
By(2.7)–(2.8),for the integrals over the horizontal segments we have
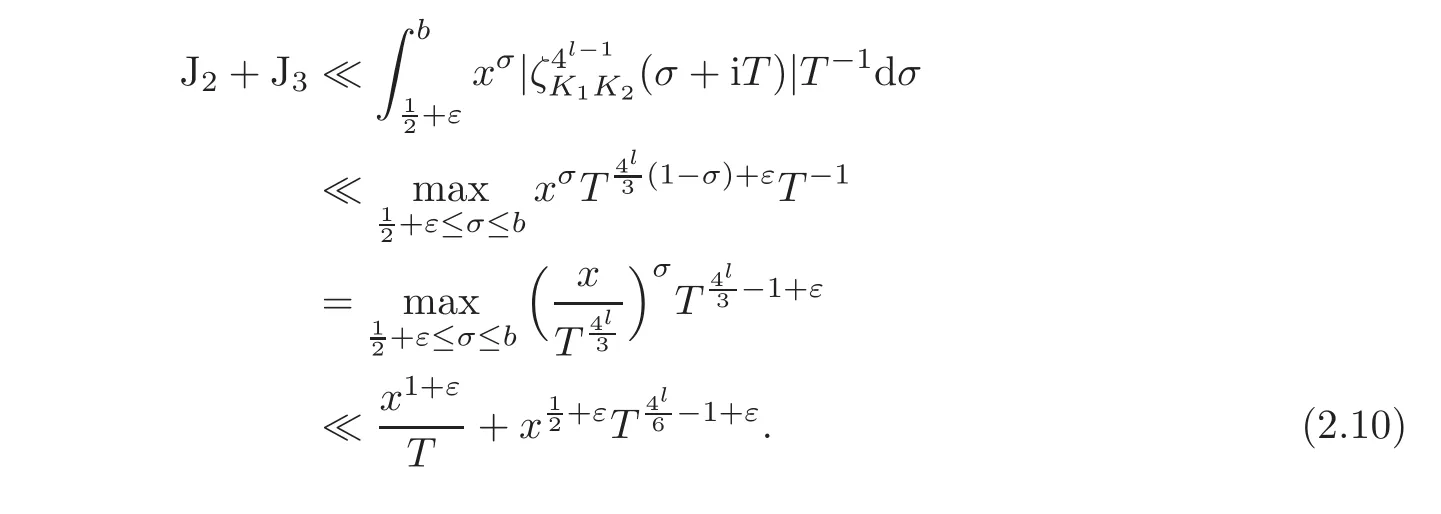
From(2.6),(2.9)–(2.10),we have
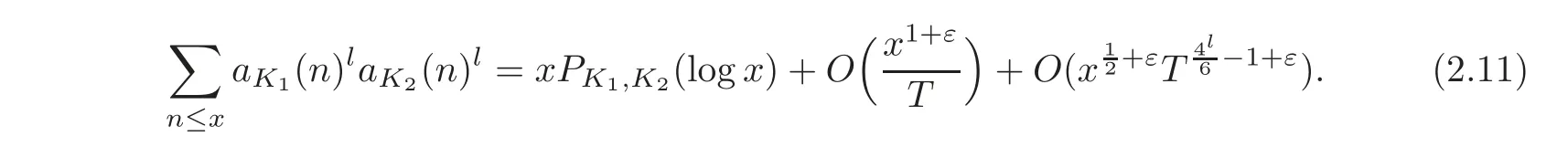
On taking T=in(2.11),we have

3 Proof of Theorem 1.2
We firstly recall some usefulresults.Let K be an algebraic number field of degree n,and then
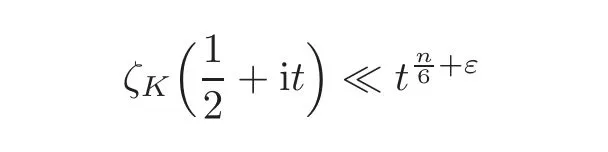
(see[6]).
By using the Phragmen-Lindelöf principle for a strip,we have that for≤ σ ≤ 1+ ε,
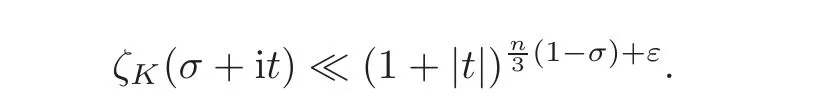
From(1.1),we can easily get

Define the series
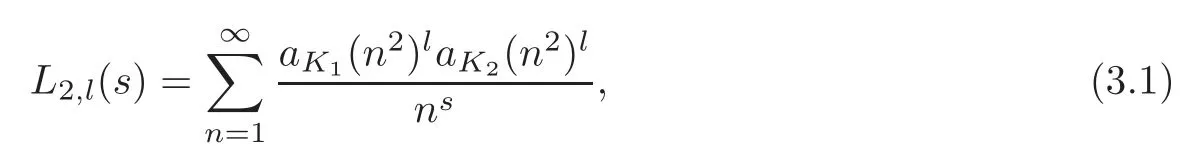
and then it is absolutely convergent in the half plane?s>1.Since aKi(n)(i=1,2)are multiplicative,so are aK1(n2)laK2(n2)l.We can rewrite L2,l(s)as

where the product runs over all primes.
For a quadratic field K,Lü and Yang[15]proved the relation
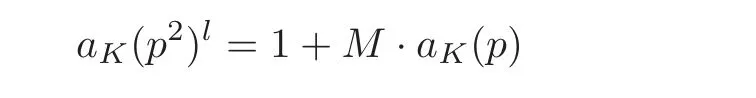
holds true for all but finitely many primes,where,and l is any positive integer.We can immediately deduce that except for finitely many primes,

By checking the Euler products of L2,l(s)andwe have

where U1(s)denotes a Dirichlet series,which is absolutely convergent for σ>
From(3.3),L2,l(s)admits a meromorphic continuation to the half-planeand only has a pole at s=1 of order(M+1)2in this region.
By applying Perron’s formula,we have

where b=1+ε and 1≤T≤x is a parameter to be chosen later.
We shift the path of integration to the vertical line
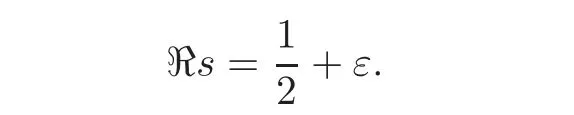
By Cauchy’s residue theorem,we get
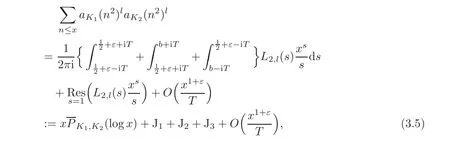
wheredenotes a suitable polynomial in t of degree M2+2M.
Case l=1
The horizontal segments contribute

where we have used that U1(s)is absolutely convergent in the regionand behaves as O(1)there.
For J1,we have
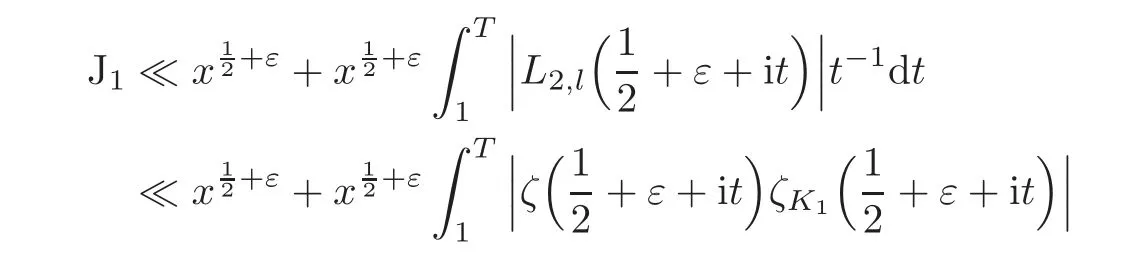
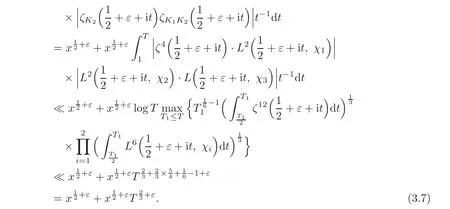
Here we have used the following estimation:

This is derived form the formulae
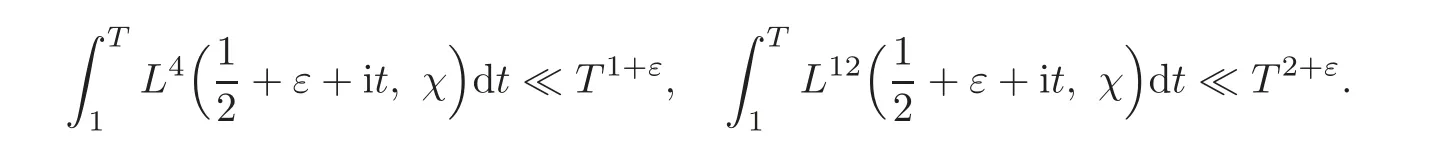
According to(3.6)–(3.7),we obtain
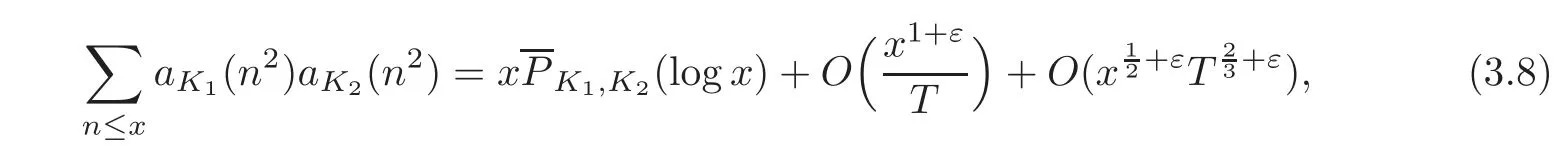
where PK1,K2(t)is a polynomial in t of degree 3.
Taking T=to formula(3.8),then
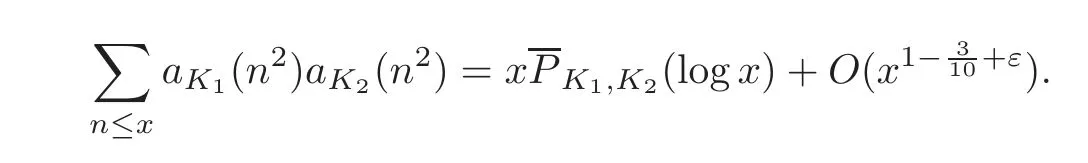
Case l≥2
For J1,by(3.3)we have
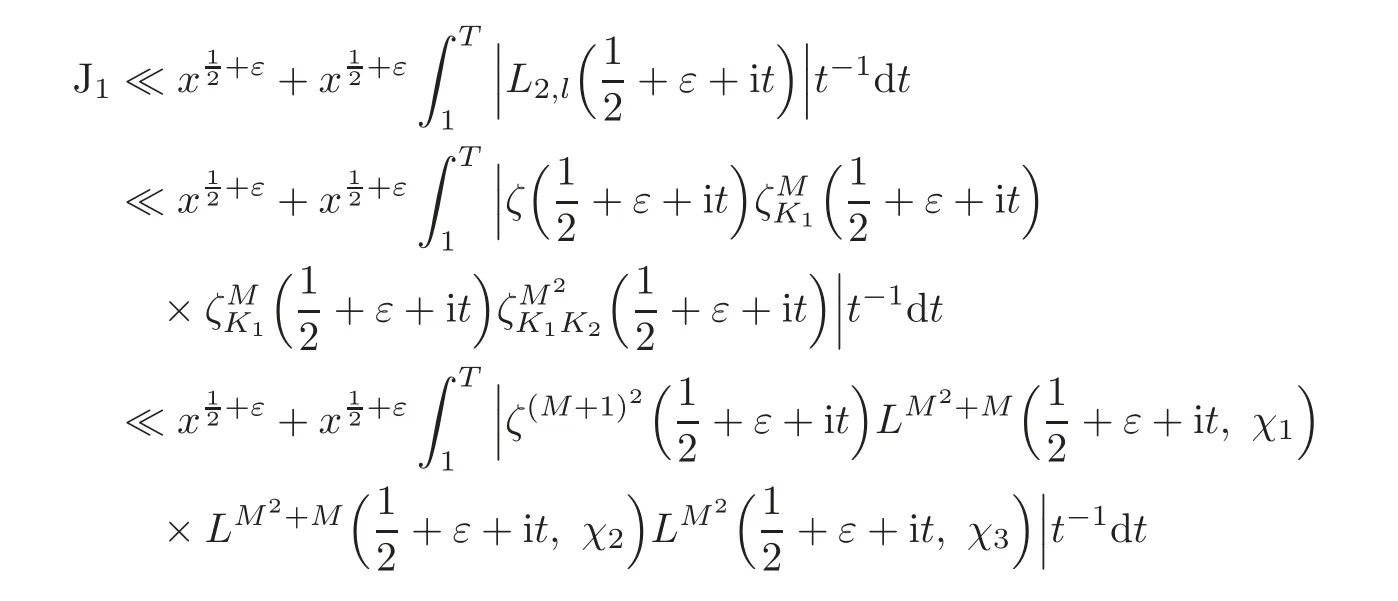

For the integration over horizontal segments,we have

By(3.9)and(3.10),we get
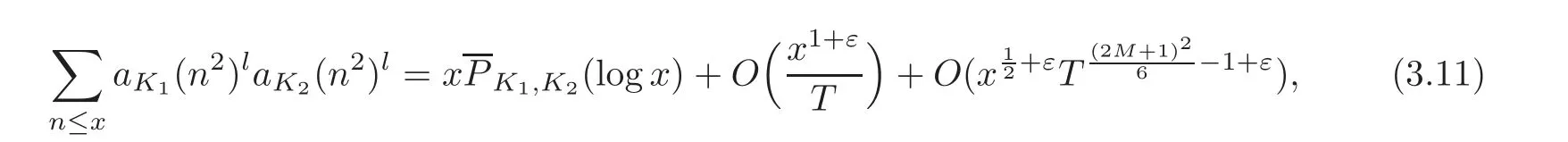
whereis a polynomial in t with degree M2+2M.
Takingin the formula(3.11),we obtain
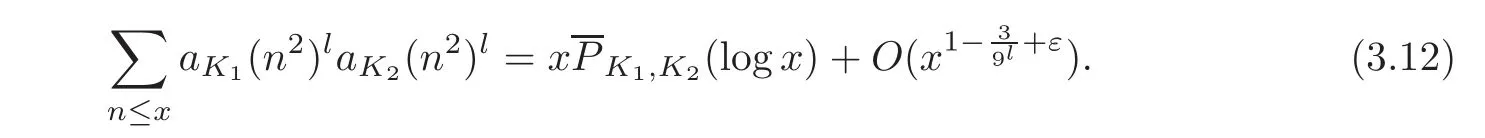
We complete the proof.
AcknowledgementsThe author would like to thank Professor Guangshi Lü for his encouragement,and is gratefulto the referee for the comments.
[1]Chandraseknaran,K.and Good,A.,On the number of integeral ideals in Galois extensions,Monatsh.Math.,95,1983,99–109.
[2]Chandraseknaran,K.and Narasimhan,R.,The approximate functional equation for a class of zetafunctions,Math.Ann.,152,1963,30–64.
[3]Fomenko,O.M.,Distribution of lattice points on surfaces of second order,J.Math.Sci.,83,1997,795–815.
[4]Fomenko,O.M.,The mean number of solutions of certain congruences,J.Math.Sci.,105,2001,2257–2268.
[5]Heath-Brown,D.R.,The twelfth power moment of the Rimeann zeta-function,Q.J.Math.,29,1978,443–462.
[6]Heath-Brown,D.R.,The growth rate of the Dedekind zeta-function on the critical line,Acta Arith.,49,1988,323–339.
[7]Hecke,E.,Eine neue Art von Zetafunktionen und ihre Beziehungen zur Verteilung der Primzahlen,Math.Z.,1,1918,357–376;6,1920,11–51.
[8]Huxley,M.N.and Watt,N.,The number of ideals in a quadratic field II,Israel J.Math.Part A,120,2000,125–153.
[9]Ivi´c,A.,The Riemann Zeta-Function,Theory and Applications,John Wiley&Sons,New York,1985.
[10]Iwaniec,H.and Kowalski,E.,Analytic Number Theory,Amer.Math.Soc.Colloquium Publ.,53,Amer.Math.Soc.,Providence,2004.
[11]Kubilus,I.P.,On some problems in geometry of prime numbers,Math.Sbornik,31,1952,507–542(in Russian).
[12]Landau,E.,Einführung in Die Elementare umd Analytische Theorie der Algebraischen Zahlen und der Ideals,Chelsea Publishing Company,New York,1949(in German).
[13]Linnik,Yu.V.,Private communications,1950.
[14]Lü,G.S.and Wang,Y.H.,Note on the number of integral ideals in Galois extensions,Science China:Mathematics,53,2010,2417–2424.
[15]Lü,G.S.and Yang,Z.S.,The average behavior of the coefficients of Dedekind zeta functions over square numbers,Journal of Number Theory,131,2011,1924–1938.
[16]Meurman,T.,The mean twelfth power of Dirichlet L-functions on the critical line,Ann.Acd.Sci.Fenn.Ser.A.,52,1984,44 pages.
[17]Müller,W.,On the distribution of ideals in cubic number fields,Monatsh.Math.,106,1988,211–219.
[18]Nowak,W.G.,On the distribution of integral ideals in algebraic number theory fields,Math.Nachr.,161,1993,59–74.
[19]Pan,C.D.and Pan,C.B.,Fundamentals of Analytic Number Theory,Science Press,Beijing,1991(in Chinese).
[20]Swinnerton-Dyer,H.P.F.,A Brief Guide to Algebraic Number Theory,London Mathematical Society Student Texts,50,Cambridge University Press,Cambridge,2001.
[21]Weber,H.,Lehrbuch der Algebra,Vol.II,Druck und Verlag von Friedrich Vieweg und Sohn,Braunschweig,1896.
 Chinese Annals of Mathematics,Series B2016年4期
Chinese Annals of Mathematics,Series B2016年4期
- Chinese Annals of Mathematics,Series B的其它文章
- Abstract Elliptic Equations with Integral Boundary Conditons
- Symmetric Periodic Orbits and Uniruled Real Liouville Domains∗
- Order Bounded Weighted Composition Operators Mapping into the Dirichlet Type Spaces∗
- Augmentation Quotients for Complex Representation Rings of Generalized Quaternion Groups∗
- Sharp Distortion Theorems for a Subclass of Biholomorphic Mappings Which Have a Parametric Representation in Several Complex Variables∗
- Symmetries and Their Lie Algebra of a Variable Coefficient Korteweg-de Vries Hierarchy∗
