扩散峰度成像在正常成人脑组织中可重复性的研究
鲍道亮,张梅芳,苏丽清,肖友平,曹喜生,姚逸琦,陈韵彬
扩散峰度成像在正常成人脑组织中可重复性的研究
鲍道亮,张梅芳,苏丽清,肖友平,曹喜生,姚逸琦,陈韵彬*
目的对正常成人脑组织进行扩散峰度成像(DKI)的可重复性研究。材料与方法选取年龄在31~66岁的正常成人志愿者26例,采用b值为0、500、1000、1500、2000 s/mm2多参数和多方向的DKI序列进行头部扫描,经2名观察者(放射科医师)分别独立在不同的时间,测量相同区域的扩散系数(MD)和扩散峰度系数(MK)值并记录。运用SPSS 19.0进行统计学分析评估DKI扩散系数(MD)和扩散峰度系数(MK)值观察者内、观察者间一致性。结果经2名观察者在不同的时间点测量得到胼胝体膝部、胼胝体压部、内囊前肢、内囊后肢及丘脑等部位的MD和MK值。同一观察者两次所测得值(观察者内)之间差异无统计学意义(P>0.05);2名观察者分别所测得值(观察者间)之间差异无统计学意义(P>0.05)。结论脑组织扩散峰度成像(DKI)具有良好的可重复性,可应用于反映脑组织微观结构变化特点。
扩散峰度成像;扩散系数;扩散峰度系数;可重复性测定
扩散峰度成像(diffusion kurtosis imaging,DKI)是扩散张量成像(diffusion tensor imaging,DTI)技术的延伸,是DWI的扩展[1-2],其主要用来探查组织非高斯分布的水分子扩散特性[3],同时反映组织微观结构的变化[4]。DKI能同时推导出扩散系数(MD)和扩散峰度系数(MK),可提高MR探测神经组织结构变化的敏感度和特异度[5]。
本研究目的是对健康成人脑组织进行DKI扫描,通过DKI图像选择健康成人脑组织中的胼胝体膝部、胼胝体压部、内囊前肢、内囊后肢、丘脑等五个部位为测量点,并经2名观察者分别在不同的时间段,测量其各部位点的扩散系数(MD)值和峰度系数(MK)值。一方面可反映大脑不同区域的扩散分布特征及其微观结构特点;另一方面可供分析研究大脑不同区域DKI参数值测量的可重复性,对今后脑部疾病的诊断和研究提供参考依据。
1 材料与方法
1.1 一般资料
收集福建省肿瘤医院正常健康成人志愿者26例,年龄范围约31~66岁,中位年龄为45.3岁,其中男女比例各占一半,均为13例。所有受检者均无精神系统症状及脑部异常MRI影像表现。本研究实验获我院伦理委员会批准,志愿者经本人同意均签署知情同意书。
1.2 设备及参数
采用荷兰飞利浦超导型磁共振成像仪(Philips Achieva 3.0 T TX MR),和头颈联合16通道相控阵线圈作为接收线圈。受检者仰卧位,头先进,正中矢状线与扫描床的中线相一致,头颅双侧用垫片固定牢。先进行常规序列扫描,包括轴面T1WI、T2WI FLAIR、DWI扫描,排除颅脑器质性病变,然后采用单次激发自旋-平面回波(SEEPI)的轴面DKI序列,对本研究的对象进行脑部扫描。其中,DKI序列扫描参数统一为:TR 3970 ms,TE 81 ms,IR 240 ms,层厚5 mm,间隔1 mm,扫描野240 mm×240 mm,矩阵112 ×198,激励次数1,体素2.2 (RL)×1.25 (AP),启用5个扩散梯度场(b=0、500、1000、1500、2000 s/mm2),扩散梯度同时取x、y和z三个方向。
1.3 图像及数据处理
扫描所得DKI图像通过Permeability软件(PRIDE Permeability Processing Tool by Philips healthcare,DWI-TOOL R1.5)进行后处理分析和参数值测量。实验中选择Levenberg-MarquardttE线性拟合优化方法,经2名右利手的观察者(观察者1和观察者2)各自独立,要求在不同的时间段,并以DKI图中显示解剖部位较为清晰b值=0的图像,作为选择部位和测量点。对同一名受检者必须选择相同的层面、相同的部位和测量点以及相同大小的感兴趣区(ROI)进行DKI参数值测量(其ROI面积大于或等于25 pixels)(图1~3)。然后分别对大脑不同区域胼胝体膝部、胼胝体压部、内囊前肢、内囊后肢、丘脑五个部位的对应点,进行点对点测量其各点的扩散系数(MD)和扩散峰度系数(MK)值并记录。
1.4 统计学方法
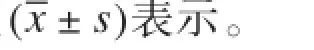
2 结果
本研究获得的脑组织DKI图像均具有较高的图像质量和分辨率。在Permeability软件上,并按图1~3所示的部位,在DKI图像上选取相对应点,即正常健康志愿者大脑的胼胝体膝部、胼胝体压部、内囊前肢、内囊后肢及丘脑等5个区域,作为观察和参数值测量的目标(图4~9)。本组研究资料均由2名不同的观察者,分别独立于不同时间段,对其同一的被检者按上述所选的区域分别进行两次MD值和MK值的测量。同一观察者两次所测得值之间的比较,即为观察者内参数值测量一致性的比较,结果两次测量所得参数值的差异不具有统计学意义(P>0.05)。不同观察者分别所测得值之间的比较,即为观察者间参数值测量一致性的比较,结果两者之间差异也不具有统计学意义(P>0.05),结果详见表1,2。
3 讨论
国际标准化组织定义的可重复性为测试状态尽可能保持一致[6],即在同一个实验室同一个操作者使用同样的设备和方法,经过一个短期的时间间隔进行同一项检测,获取独立的测试结果。因此,可重复性是一个测试系统能否对一个固定的测试对象提供稳定的结果[7]。
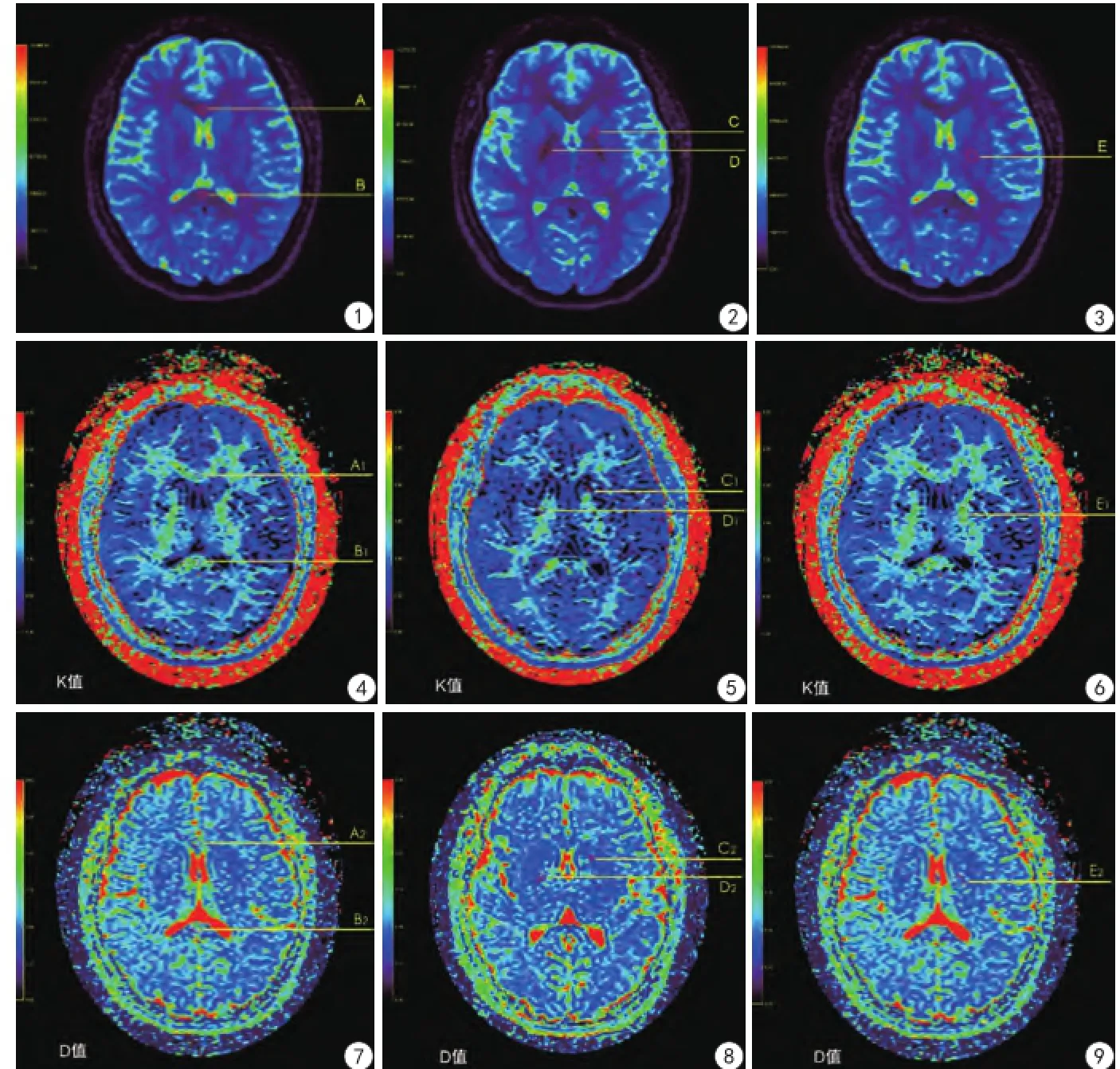
图1A:胼胝体膝部的测量选择区域; B:胼胝体压部的测量选择区域图2C:内囊前肢的测量选择区域;D:内囊后肢的测量选择区域图3E:丘脑的测量选择区域图4A1:胼胝体膝部K值的测量值为1.041;B1:胼胝体压部K值的测量值为1.012图5C1:内囊前肢K值的测量值为0.981;D1:内囊后肢K值的测量值为1.346图6E1:丘脑K值的测量值为1.061图7A2:胼胝体膝部D值的测量值为1.002× 10-3mm2/s; B2:胼胝体压部D值的测量值为1.128×10-3mm2/s图8C2:内囊前肢D值的测量值为0.869×10-3mm2/s;D2:内囊后肢D值的测量值为0.882× 10-3mm2/s图9E2:丘脑D值的测量值为0.932×103mm2/sFig. 1A: The region of interests (ROI) selected for the measurement on the genu of corpus callosum. B: The ROI drawn on the splenium of corpus callosum.Fig. 2C: The ROI contoured on the anterior limb of internal capsule. D: The ROI on the posterior anterior limb of internal capsule.Fig. 3E: The ROI for the measurement of the thalamus.Fig. 4A1: The K value measured on the genu of corpus callosum was 1.041. B1: The K value calculated on the the splenium of corpus callosum was 1.012.Fig.5C1: The measured K value on the anterior limb of internal capsule was 0.981. D1: The K value of posterior limb of internal capsule was 1.346.Fig. 6E1: The K value of thalamus was 1.061.Fig. 7A2: The D value measured on the genu of corpus callosum was 1.002 ×10-3mm2/s. B2: The D value calculated on the splenium of corpus callosum was 1.128×10-3mm2/s.Fig. 8C2: The measured D value of the interior limb of internal capsule was 0.869×10-3mm2/s. D2: The D value of posterior limb of internal capsule was 0.882×10-3mm2/s.Fig. 9E2: The D value calculated on the thalamus was 0.932×10-3mm2/s.
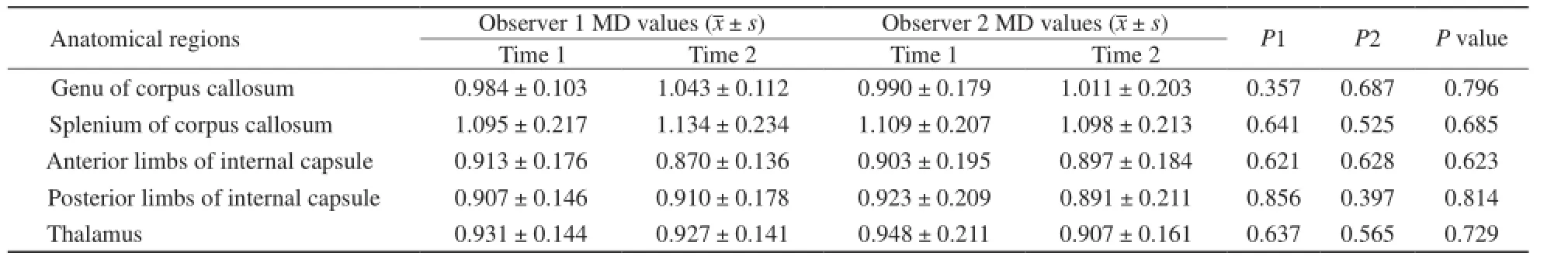
表1正常成人脑组织不同部位MD值比较Tab. 1The comparison of MD values at the different anatomical regions of brain tissues in healthy adults
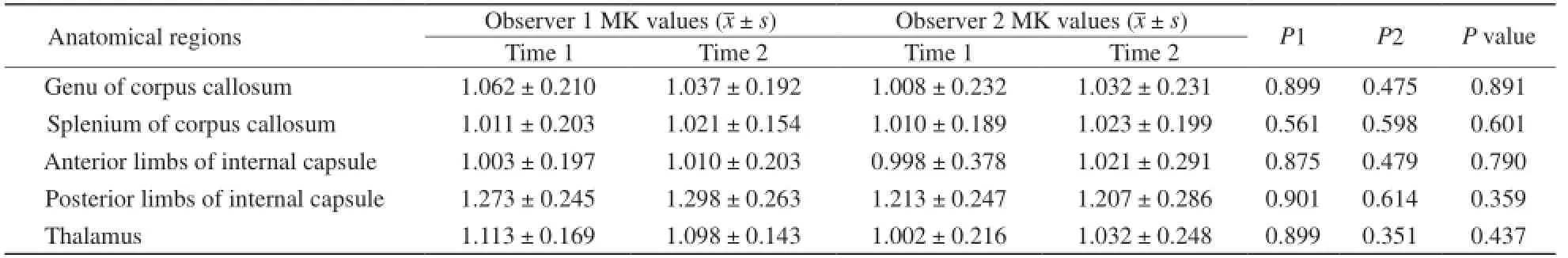
表2正常成人脑组织不同部位MK值比较Tab. 2The comparison of MK values at the different anatomical regions of brain tissues in healthy adults
本研究选择健康成人志愿者,对其脑组织进行DKI扫描成像,同时进行大脑不同区域的扩散系数(MD)值和峰度系数(MK)值测量的可重复性研究;结果发现正常成人大脑不同区域DKI参数值测量具有良好的可重复性,其参数值测量的观察者内和观察者间一致性好。
DKI由Jensen等[8]于2005年首次提出理论,并做了人脑及体模初步研究,证明其可行性,提出其广泛的研究应用前景。因此,进行脑部DKI成像和参数值测量的可重复性研究对DKI在临床,尤其是脑部疾病的应用和研究具有较高的价值和临床意义。
由于本组研究中DKI序列仅使用3个扩散方向(x、y、z),只能得到MD值和MK值,其分别表示所有方向的平均扩散系数和扩散峰度系数[9]。本组所选受检者男女比例一样,剔除性别的差异,而着重对健康成人大脑不同区域扩散系数(MD)值和峰度系数(MK)值的测量,是否存在可重复性研究。测量中由2名高龄资深医师(观察者)分别在不同时刻,对同一受检者大脑不同区域的DKI参数值进行两次测量。结果发现,同一观察者在两次不同时间测量得到的脑组织扩散系数(MD)值和峰度系数(MK)值的组间的一致性较好,具有良好的可重复性。本研究对每一健康受检者的DKI序列扫描成像图中,选择大脑中的胼胝体膝部、胼胝体压部、内囊前肢、内囊后肢、丘脑等五个区域作为测量对象,并且两次选择相应部位的ROI的大小、位置必须一致,分别测得相应区域的MD值及MK值大小并记录,其平均参数值的(观察者内)差异无统计学意义(P>0.05)。同理,对两观察者间测量的比较(观察者间),其平均参数值的差异也无统计学意义。
综上所述,脑DKI成像具有较高的稳定性,脑组织的扩散系数(MD)值和峰度系数(MK)值测量不受时间和操作者的限制,其参数值测量的一致性较高,可重复性良好。因此,脑部DKI成像在临床诊断上具有较高的可靠性和应用价值。
[References]
[1] Dang YX, Wang XM. Present research situation of diffusion kurtosis imaging and intravoxel incoherent motion of the brain. Chin J Magn Reson Imaging, 2015, 6(2): 145-150.党玉雪, 王晓明. 磁共振新技术DKI和IVIM在中枢神经系统的研究现状. 磁共振成像, 2015, 6(2):145-150.
[2] Shan Y, Lu J, Li KC. Progresses in diffusional kurtosis imaging of ischemic stroke. Chin J Med Imaging Technol, 2013, 29(12): 2046-2048.单艺, 卢洁, 李坤成. 扩散峰度成像在缺血性脑卒中的研究进展.中国医学影像技术, 2013, 29(12): 2046-2048.
[3] Jensen JH, Helpern JA. MRI quantification of non-Gaussian water diffusion by kurtosis analysis. NMR Biomed, 2010, 23(7): 698-710.
[4] Hui ES, Cheung MM, Qi L, et al. Towards better MR characterization of neural tissues using directional diffusion kurtosis analysis. Neuroimage, 2008, 42(1): 122-134.
[5] Zhang S, Yao YH, Zhang SX, et al. A study for the course of cerebral infarction with diffusion kurtosis imaging. Chin J Radiol, 2014, 6, 48(6): 443-447.张顺, 姚义好, 张水霞, 等. 脑梗死不同时期的MR扩散峰度成像表现. 中华放射学杂志, 2014, 6, 48(6): 443-447.
[6] Padhani AR, Liu G, Koh DM, et al. Diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging as a cancer biomarker: consensus and recommendations. Neoplasia, 2009,11(2): 102-125.
[7] He J, Li DY, Zhu B, et al. Repeatability and reproducibility of the apparent diffusion coefficient values of primary and metastatic hepatic carcinomas on MR diffusion-weighted imaging. J Radiol Pract, 2013, 28(2):168-172.何健, 李丹燕, 朱斌, 等. 肝脏恶性肿瘤ADC值测量的可重复性及可重现性研究. 放射学实践, 2013, 2, 28(2): 168-172.
[8] Jensen JH, Helpem JA, Ramani A, et al. Diffusional Kurtosis imaging: the quantification of non-Gaussian water diffusion by means of magnetic resonance imaging. Magn Reson Med, 2005, 53(6): 1432-1440.
[9] Xie LF, Chen SL, Liu ZY, et al. Diffusion kurtosis imaging of normal liver: study of its feasibility and reproducibility. J Clin Radiol, 2015, 34(5): 797-802.谢丽芳, 陈世林, 刘再毅, 等. 正常肝脏扩散峰度成像的可行性及可重复性研究. 临床放射学杂志, 2015, 34(5): 797-802.
The repeatability of diffusion kurtosis imaging on the brain tissue in healthy adults
BAO Dao-liang, ZHANG Mei-fang, SU Li-qing, XIAO You-ping, CAO Xi-sheng, YAO Yi-qi, CHEN Yun-bin*
Department of Radiology, Fujian Tumor Hospital, Fuzhou 350014, China
Objective:To study the reproducibility of diffusion kurtosis imaging (DKI) on the brain tissue in healthy adults.Materials and Methods:Twenty-six healthy volunteers aged from 31 to 66 years were enrolled into this present study. All enrolled subjects were scanned with the DKI sequence on their head and b-factors of 0, 500, 1000, 1500, and 2000 s/mm2were applied. Two observers (experienced radiologist) independently interpreted the acquired DKI images and conducted the measurement of diffusion coefficient (MD) and diffusion kurtosis coefficient (MK). All statistical analysis were conducted on the SPSS 19.0 software, and the inter-and intra-observer consistency of diffusion coefficient (MD) and diffusion kurtosis coefficient (MK) were tested by the repeatability measurements.Results:The MD and MK of the genu and splenium of the corpus callosum, the anterior and posterior limbs of internal capsule and thalamus were measured by two observers at the different time-points respectively. As a result, the difference between the measurements conducted by the same observer at the different times (intra-observer) was not statistically signif i cant (P>0.05), whereas the difference between the measurements between different observers (inter-observer) was also not statistically signif i cant (P>0.05).Conclusions:The parameter measurements of DKI on the brain tissues of normal adults are repeatable and may be potentially used to ref l ect the changes of the micro-structures of brain tissue.
Diffusion kurtosis imaging; Diffusion coefficient; Diffusion kurtosis coeff i cient; Repeatability
Chen YB, E-mail: yunbinchen@126.com
Received 26 July 2016, Accepted 8 Oct 2016
福建省科技厅社会发展引导性重点基金项目、国家临床重点专科建设项目和福建省临床重点专科建设项目(编号:2014Y0013)
福建省肿瘤医院放诊科,福州 350014
陈韵彬,E-mail:yunbinchen@126. com
2016-07-26
接受日期:2016-10-08
R445.2;R742
A
10.12015/issn.1674-8034.2016.11.002
鲍道亮, 张梅芳, 苏丽清, 等. 扩散峰度成像在正常成人脑组织中可重复性的研究. 磁共振成像, 2016, 7(11): 804-807.*
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTSThis study is partly supported by the Social Development Guidance Project of Fujian Province, the National Clinical Key Specialty Construction Program and the Key Clinical Specialty Discipline Construction Program of Fujian (No. 2014Y0013).

