颈部超声、甲状腺球蛋白诊断复发分化型甲状腺癌
徐景竹,王兴华,吴 琼,杨 筱,朱沈玲,张 波
1.山西医科大学第二附属医院超声科,山西 太原 030000;2.中国医学科学院北京协和医院基本外科,北京 100730;3.中国医学科学院北京协和医院超声医学科,北京 100730
颈部超声、甲状腺球蛋白诊断复发分化型甲状腺癌
徐景竹1,2,王兴华1,吴 琼3,杨 筱3,朱沈玲3,张 波3
1.山西医科大学第二附属医院超声科,山西 太原 030000;2.中国医学科学院北京协和医院基本外科,北京 100730;3.中国医学科学院北京协和医院超声医学科,北京 100730
[摘要]背景与目的:颈部超声与血清甲状腺球蛋白(thyroglobulin,Tg)是分化型甲状腺癌(diferentiated thyroid carcinoma,DTC)术后随访的主要方法。刺激性Tg对分化型甲状腺癌的诊断价值已被充分证实,但抑制性Tg对DTC复发转移的诊断价值鲜有报道。该研究分析颈部超声及抑制性Tg对DTC复发转移的诊断价值。方法:回顾性分析2010年8月—2014年12月在北京协和医院行2次或以上手术,临床怀疑复发的DTC患者196例。选择其中入院前行甲状腺全切术后和(或)131I清甲治疗术后超声怀疑复发转移的患者共62例。分析转移性淋巴结超声特征以及抑制性Tg对DTC复发转移的诊断价值。结果:经病理证实,62例患者中59例为淋巴结转移,1例为局部复发,2例术后未发现明确复发转移。超声发现可疑淋巴结共121个,经病理证实转移性淋巴结92个,非转移性淋巴结25个,纤维组织3个,横纹肌组织1个。淋巴结内无回声、高回声及强回声对转移性淋巴结的阳性预测值均为100%,皮质内无回声及血流信号杂乱在转移性淋巴结和非转移淋巴结中差异有统计学意义。抑制性Tg阳性者(Tg≥0.2 ng/mL)49例,阴性者(Tg<0.2 ng/mL)13例,抑制性Tg诊断颈部复发转移的准确率为82.3%,灵敏度为81.7%,特异度为100%。结论:皮质内无回声及血流信号杂乱是鉴别复发DTC颈部转移性淋巴结与非转移性淋巴结特异度较高的指标,抑制性Tg(Tg≥0.2 ng/mL)对DTC的复发转移有较高的诊断价值,颈部超声检查可发现血清Tg为阴性患者的复发转移病灶。
[关键词]分化型甲状腺癌;复发转移;颈部超声;甲状腺球蛋白
Cervical ultrasound and thyroglobulin in diagnosis of recurrence of diferentiated thyroid carcinoma
XU Jingzhu1,2, WANG Xinghua1, WU Qiong3, YANG Xiao3, ZHU Shenling3, ZHANG Bo3
(1.Department of Ultrasound, the Second A ffi liated Hospital of Shanxi Medical University, Taiyuan 030000, Shanxi Province, China; 2.Department of Clinical Laboratory, Peking Union Medical College Hospital, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences, Beijing 100730, China; 3.Department of Ultrasound, Peking Union Medical College Hospital, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences, Beijing 100730, China)
Correspondence to:ZHANG Bo E-mail:zora19702006@163.com
[Abstract]Background and purpose:This study investigated the value of cervical ultrasound and TSH-suppressed thyroglobulin in the diagnosis of recurrence or metastasis of diferentiated thyroid carcinoma(DTC).Methods:This study analyzed the data on 196 thyroid carcinoma patients who underwent neck dissection after clinically suspecious recurrence of DTC in Peking Union Medical College Hospital from Aug.2010 to Dec.2014.Among the 196 patients, 62 patients sonographically suspecious recurrence after total thyroidectomy and/or radioactive iodine ablation therapy were enrolled in this study.The ultrasonic features of lymph node involvement were retrospectively analyzed.The value of the ultrasonic features in the diagnosis of lymph node involvement and a TSH-suppressed serum Tg level in the diagnosis of recurrence or metastasis of DTC was also evaluated.Results:Of the 62 patients, 59 were pathologically con fi rmed with lymph node involvement, 1 case with local recurrence and 2 cases without recurrence or metasta-sis.There were 121 ultrasonographically suspected lymph nodes, con fi rmed by pathology, 92 were metastatic ltsions, 25 were non-metastatic, 3 were fi brous tissue and 1 was striated muscle.The positive predictive rate of cyst, calci fi cation or hyper-echogenicity in cortex was 100% in the diagnosis of lymph node involvement.There was a signi fi cant diference in disordered vascularity and cyst in cortex between metastatic and non-metastatic lymph nodes.Forty-nine patients were positive for Tg, whereas 13 were negative.The accuracy, sensitivity and speci fi city of TSH-suppressed serum Tg in the diagnosis of recurrence or metastasis of DTC were 82.3%, 81.7% and 100%.Conclusion:The disordered vascularity and cyst in cortex of the lymph node are highly speci fi c indexes in diagnosing lymph node involvement.TSH-suppressed serum Tg level has high diagnostic value for detection of recurrence or metastasis of DTC.Cervical ultrasound can identify recurrent or metastatic lesions in both Tg-positive and Tg-negative patients.
[Key words]Diferentiated thyroid carcinoma; Recurrence; Cervical ultrasound; Thyroglobulin
分化型甲状腺癌(differentiated thyroid cancer,DTC)主要包括乳头状癌(85%)与滤泡细胞癌(12%)[1]。手术切除是治疗DTC患者的主要方法,在接受甲状腺手术并行131I清除手术残留甲状腺组织治疗后预后效果较好,但有研究表明,DTC的复发转移率高达15%~30%[2],2015年美国甲状腺学会(American Thyroid Association,ATA)指南指出定期随访颈部超声及血清甲状腺球蛋白(thyroglobulin,Tg)是监测DTC治疗后有无复发转移最主要的检查方法。刺激性Tg(>2 ng/mL),对DTC的复发转移有高度诊断价值已被证实[3-6],但目前尚缺乏针对我国人群的抑制性Tg对DTC复发转移诊断价值的研究。本研究通过北京协和医院再次手术的DTC复发患者的颈部超声结果及抑制性Tg检测分析,研究转移性淋巴结颈部超声表现及抑制性Tg在监测DTC复发转移中的作用。
1 资料和方法
1.1 一般资料
回顾性分析2010年8月—2014年12月在北京协和医院复诊,经过2次或以上手术的DTC患者196例。所有患者均行颈部超声及抑制性Tg的检查,以石蜡病理结果为“金标准”。入选标准:① 行甲状腺全切术,常规超声检查未发现有残余甲状腺组织,甲状腺组织小于1 g被认为是甲状腺已全切[7];② 在随访过程中均常规行颈部超声检查,Tg、促甲状腺激素(thyroidstimulating hormone,TSH)和甲状腺球蛋白抗体(anti-thyroglobulin antibody,TgAb)检测;③ 颈部超声怀疑有复发或转移患者,再次行手术切除并获得石蜡病理结果。排除标准:① 结合病史及其他相关检查,排除伴有其他淋巴结原发性或继发性疾病;② 超声检查发现有残余甲状腺组织的患者;③ 存在远处转移的患者。在符合标准的62例患者中,乳头状癌60例,滤泡癌2例;男性18例,女性44例;年龄16~83岁,平均(40.48±13.3)岁。
1.2 判断标准
Tg检测诊断标准:在TSH抑制状态下(即在服用甲状腺激素替代治疗状态下)Tg≥0.2 ng/mL为阳性[8-10]。TgAb≥50 U/mL为阳性,TgAb <50 U/mL为阴性[11]。
超声诊断淋巴结转移的声像图特征[12]:① 淋巴结内出现微小钙化;② 淋巴结内出现液化或囊性区;③ 淋巴结内出现高回声;④ 皮髓质分界不清或消失;⑤ 淋巴结长短径比<2;⑥ 血流丰富或较丰富,血流分布出现边缘型或混合型。
超声诊断甲状腺床复发转移的声像图特征[13-14]:低回声,圆形或椭圆形,内部回声不均,内部可见微小钙化,血流信号丰富杂乱。
1.3 统计学处理
应用SPSS 20.0对数据进行分析,计量资料采用χ2表示,计数资料组间比较采用χ2检验及Fisher精确检验,P<0.05为差异有统计学意义。
2 结 果
2.1 超声特征
在超声提示的121个异常淋巴结中,经病理证实92个为转移性淋巴结,25个为非转性淋巴结(3个炎性反应,22个正常),3个纤维组织,1个横纹肌组织。117个淋巴结的声像图特征如表1。在灰阶超声中皮质内无回声在转移性与非转移性淋巴结中的差异有统计学意义(P=0.045),皮质内出现无回声、高回声及强回声的阳性预测值均为100%,即可认为在淋巴结内出现无回声、高回声或强回声即转移性淋巴结。比较转移性和非转移性淋巴结的彩色多普勒血流显像(color Doppler flow imaging,CDFI)声像图特征发现,血流信号杂乱在两者中的差异有统计学意义(P=0.033),而其余声像图特征(短径/长径≥0.5,皮髓质分界不清,皮质内高回声,皮质内强回声,外周血流,血流信号丰富)在两者中的差异均无统计学意义(P>0.05)。淋巴结内皮质无回声及血流信号杂乱的声像图见图1。
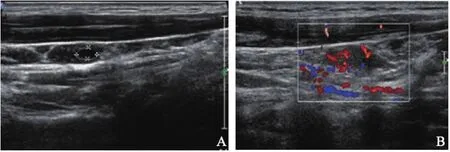
图 1 转移性淋巴结声像图Fig.1 Ultrasonography of metastatic lymph nodes
2.2 Tg检测结果
术前抑制性T g平均值为(6.1 6± 1 7.6 4)n g/m L,术后抑制性T g平均值为(1.38±4.24)ng/mL。Tg≥0.2 g/mL有49例患者经病理证实均存在复发转移灶,Tg<0.2 ng/mL有13例患者,其中TgAb阳性者有5例,经病理证实有11例患者存在复发转移病灶,2例病理未发现复发转移病灶(表2)。Tg对DTC复发转移诊断的准确率为82.3%,灵敏度为81.7%,特异度为100%。

表 2 Tg水平与病理结果的比较Tab.2 Comparison between the levels of Tg and pathologic fi ndings
3 讨 论
DTC患者在接受手术及131I治疗的患者预后效果较好,但DTC的复发转移率高达15%~30%[2],因此DTC术后必须长期随访。2015 年ATA指南强烈推荐DTC全切术后的患者应每6~12个月检查1次颈部超声及Tg。
本研究分析颈部可疑淋巴结的声像图发现,皮质内出现无回声、高回声及强回声的阳性预测值均为100%,即表明在淋巴结中出现无回声、高回声或强回声对转移性的淋巴结有较高灵敏度。在灰阶超声中皮质内出现无回声在转移性与非转移性淋巴结中差异有统计学意义。皮质内无回声在诊断转移性淋巴结中有较高的特异度。有研究表明在>7 mm的淋巴结中皮质内出现无回声或强回声即可认为是转移性淋巴结[12],本研究也证实了这一观点。2015 年ATA指南中指出周边血流丰富是诊断转移性淋巴结较灵敏的指标之一,但尚未对淋巴结的CDFI作具体分层。本研究将可疑淋巴结的CDFI分为周边血流、血流信号丰富和血流信号杂乱,研究发现血流信号杂乱在转移性淋巴结和非转移性淋巴结中差异有统计学意义,而周边血流、血流信号丰富的差异无统计学意义,这与之前我们研究的结果相一致[15]。血流信号杂乱可能包含周边血流与血流信号丰富,经本研究证实血流信号杂乱在诊断转移性淋巴结中的特异度更高。而皮髓质分界消失、短径/长径的比值需结合其他声像图特征才能更加准确地诊断转移性淋巴结。在可疑淋巴结中经病理证实有3个纤维组织和1个横纹肌组织,因其与转移性淋巴结有相似的特征,故易造成误诊。因此在诊断可疑淋巴结时应仔细区分淋巴结与肌纤维组织的回声,而进一步提高超声诊断转移性淋巴结的价值。
DTC患者经手术及清甲治疗后Tg是监测复发转移的特异性指标。随着现在抑制性Tg检测方法灵敏度的升高(<0.1 ng/mL)可能会代替刺激性Tg对复发转移的监测。在62例患者中,有49例患者抑制性Tg水平为阳性结果。通过与石蜡病理结果比较,差异无统计学意义(P=0.56)。Tg对复发转移诊断的正确率为82.3%,灵敏度为81.7%,特异度为100%。有文献报道抑制性Tg在0.2~0.3 ng/mL时诊断复发转移的灵敏度与特异度最高[10]。患者术前抑制性Tg的水平为6.16 ng/mL,术后抑制性Tg平均值为1.38 ng/mL,手术切除病灶后Tg水平显著降低。Tg的分泌水平受TgAb及TSH的影响,TgAb的影响作用最为显著,使血清Tg的分泌水平低于实际水平而产生假阴性的结果[16]。在13例阴性患者中,有11例为假阴性结果,其中有5例患者TgAb为阳性,降低了Tg对复发转移的诊断价值。
在颈部超声怀疑存在复发转移的62例患者中,Tg阳性者仅49例,而病理结果证实60例患者发生复发转移。颈部超声既可发现Tg阳性的复发转移病灶,也可发现Tg阴性的病灶。有研究表明,颈部超声对颈部淋巴结诊断的灵敏度为70%~100%[12]。颈部超声检查不仅可以发现复发转移病灶,而且能对其进行精准的定位,起到为手术者提供导向作用,为手术成功及减少术后的并发证提供保障[17]。虽然血清Tg对DTC术后的复发转移有较高的诊断价值,如果单纯行血清Tg的检测而未行颈部超声检查,可能有很多转移病灶会被遗漏。因此,在DTC患者术后的长期随访中,血清Tg检测应联合颈部超声检查以提高复发转移病灶的诊断水平。
[参考文献]
[1]KONDO T, EZZAT S, ASA S L.Pathogenetic mechanisms in thyroid follicular-cell neoplasia[J].Nat Rev Cancer, 2006, 6(4):292-306.
[2]HUNDAHL S A, CADY B, CUNNINGHAM M P, et al.Initial results from a prospective cohort study of 5583 cases of thyroid carcinoma treated in the United States during 1996.U.S.and German Thyroid Cancer Study Group.An American College of Surgeons Commission on Cancer Patient Care Evaluation Study[J].Cancer, 2000, 89(1):202-217.
[3]DAVID A, BLOTTA A, BONDANELLI M, et al.Serum thyroglobulin concentrations and(131)I whole-body scan results in patients with differentiated thyroid carcinoma after administration of recombinant human thyroid-stimulating hormone[J].J Nucl Med, 2001, 42(10):1470-1475.
[4]MAZZAFERRI E L, KLOOS R T.Is diagnostic iodine-131 scanning with recombinant human TSH useful in the followup of differentiated thyroid cancer after thyroid ablation?[J].J Clin Endocrinol Metab, 2002, 87(4):1490-1498.
[5]HAUGEN B R, RIDGWAY E C, MCLAUGHLIN B A, et al.Clinical comparison of whole-body radioiodine scan andserum thyroglobulin after stimulation with recombinant human thyrotropin[J].Thyroid, 2002, 12(1):37-43.
[6]WARTOFSKY L, rhTSH-STIMULATED THYROGLOBULIN STUDY GROUP.Management of low-risk well-differentiated thyroid cancer based only on thyroglobulin measurement after recombinant human thyrotropin[J].Thyroid, 2002, 12(7):583-590.
[7]DUREN M, YAVUZ N, BUKEY Y, et al.Impact of initial surgical treatment on survival of patients with differentiated thyroid cancer:experience of an endocrine surgery center in an iodine-deficient region[J].World J Surg, 2000, 24(11):1290-1294.
[8]HAUGEN B R M, ALEXANDER E K, BIBLE K C, et al.2015 American Thyroid Association management guidelines for adult patients with thyroid nodules and differentiated thyroid cancer[J].Thyroid, 2015.[Epub ahead of print].
[9]GIOVANELLA L, CERIANI L, SURIANO S, et al.Thyroglobulin measurement before rhTSH-aided 131I ablation in detecting metastases from differentiated thyroid carcinoma[J].Clin Endocrinol(Oxf), 2008, 69(4):659-663.
[10]SCHLUMBERGER M, HITZEL A, TOUBERT M E, et al.Comparison of seven serum thyroglobulin assays in the followup of papillary and follicular thyroid cancer patients[J].J Clin Endocrinol Metab, 2007, 92(7):2487-2495.
[11]HSIEH C J, WANG P W.Sequential changes of serum antithyroglobulin antibody levels are a good predictor of disease activity in thyroglobulin-negative patients with papillary thyroid carcinoma[J].Thyroid, 2014, 24(3):488-493.
[12]LEBOULLEUX S, GIRARD E, ROSE M, et al.Ultrasound criteria of malignancy for cervical lymph nodes in patients followed up for differentiated thyroid cancer[J].J Clin Endocrinol Metab, 2007, 92(9):3590-3594.
[13]FRASOLDATI A, PESENTI M, GALLO M, et al.Diagnosis of neck recurrences in patients with differentiated thyroid carcinoma[J].Cancer, 2003, 97(1):90-96.
[14]KAMAYA A, GROSS M, AKATSU H, et al.Recurrence in the thyroidectomy bed:sonographic findings[J].AJR Am J Roentgenol, 2011, 196(1):66-70.
[15]吴琼, 房世保, 李小毅, 等.甲状腺癌淋巴结清扫术前超声定位的作用[J].协和医学杂志,2015, 6(5):338-342.
[16]SPENCER C A.Clinical review:Clinical utility of thyroglobulin antibody(TgAb)measurements for patients with differentiated thyroid cancers(DTC)[J].J Clin Endocrinol Metab, 2011, 96(12):3615-3627.
[17]赵博, 王金锐, 胡静, 等.术前超声在分化型甲状腺癌淋巴结手术选择中的临床价值[J].中国超声医学杂志, 2014, 30(11):964-967.
收稿日期:(2015-11-18 修回日期:2015-12-30)
通信作者:张 波 E-mail:zora19702006@163.com
基金项目:国家自然科学基金(81541131);国家国际科技合作专项项目(2015DFA30440)。
中图分类号:R736.1
文献标志码:A
文章编号:1007-3639(2016)01-0097-05
DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1007-3969.2016.01.015

