自适应实时压缩感知跟踪算法*
自适应实时压缩感知跟踪算法*
0引言
【研究意义】目标跟踪技术在计算机视觉研究领域中有着非常重要的地位,已被广泛应用在车辆导航、视频监视以及人机交互等方面[1]。近几十年来,学者们提出了许多有效的目标跟踪算法,并且取得很大的突破[2-9],但是目标跟踪仍然是一个具有挑战性的课题,制约跟踪效果的因素包括目标姿态和形状等内因变化,以及相机视角、纹理、光照和遮挡等外因变化。理想的目标跟踪算法是指该算法在鲁棒性和实时性两个方面达到平衡。【前人研究进展】早期的目标跟踪算法有均值滤波、卡尔曼滤波、粒子滤波、光流法和模板匹配法等。目前实时跟踪的热点方法是将跟踪问题看成是在线的二值分类问题,一类属于背景,一类属于目标,其任务是将目标从背景中分离出来。在跟踪的过程中通过结合背景和前景(目标)信息来实时更新目标模型的分类器,从而提高跟踪性能。Aviclan[10]提出的集成跟踪算法(Ensembl Tracker),是利用Adboost 算法将在线训练得到的多个弱分类器合成一个强分类器,然后用这个强分类器标记下一帧的像素,用以对像素进行目标和背景分类。Grabner等[11]提出的在线提升(Online Boosting)算法,是将当前跟踪结果作为正样本,并在跟踪结果周围采集负样本,与上面方法的思想类似,利用Adboost算法进行在线特征选择。该方法能有效地解决跟踪过程中遇到的目标姿态、纹理及光照变化等问题。后来Grabner等[5]又在上述理论的基础上进一步提出了一种半监督学习方法,克服了模型更新带来的漂移问题,但由于该方法是用带有误差的次优样板更新训练分类器,因此,随着时间的推移误差逐渐积累,最终将会导致跟踪失败。为了解决上述问题,Babenko等[12-13]提出在线多实例学习MIL(Multiple Instance Learning) 算法,该方法将多个样本放到一个集合里面,并给它们赋一个标签。当这个集合里面的样本存在一个或者一个以上的正样本时,这个标签就为正,否则为负。在多实例学习算法中,通过寻找集合中最正确的示例确定跟踪目标,解决了样本可能使得分类器产生迷惑的问题。Zhang等[14-15]提出一种简单高效的实时压缩感知跟踪算法,该算法通过一个利用符合压缩感知约束等距性(RIP)条件的、特别稀疏的投影矩阵去提取目标和背景的广义harr-like特征,分别作为在线学习更新分类器的正、负样本,并用朴素贝叶斯分类器进行背景和目标的分类,该方法的实时性很高。【本研究切入点】但是该方法由于分类器更新的过程中引入了更新程度参数λ,且在实际中λ需要提前给定,若给定的值过大会使得分类器更新过程无法适应目标外观的变化,过小则容易使分类器“过学习”。因此,必须解决实时压缩感知跟踪算法分类器无法适应目标外观变化及过更新的问题。【拟解决的关键问题】提出一种自适应实时压缩感知跟踪算法,根据当前跟踪结果目标模型的哈希指纹与上一帧目标模型的哈希指纹间的汉明距离(Hamming distance)d,在线实时调整分类器更新程度参数λ。实验结果表明,在背景中存在与前景目标有一定相似性的物体,且目标姿态、纹理变化和光照变化较大等情况下,自适应实时压缩感知跟踪算法仍然能够对目标进行实时准确地跟踪。
1实时压缩感知跟踪
压缩感知理论[16]指出:只要信号是可压缩的或者在某个变换域是稀疏的,那么就可以用一个与变换基不相关的投影矩阵,将原始的高维信号投影到一个低维空间上,然后通过求解一个优化问题就可以从这些少量的投影中以高概率重构出原始信号。在该理论框架下,采样速率很大程度上取决于两个基本准则:稀疏性和等距约束性,或者稀疏性和非相关性。文献[15]中的实时压缩感知跟踪算法提出了一个满足RIP条件非常稀疏的随机投影矩阵R,用这个投影矩阵将高维原始信号投影到一个低维压缩子空间上,该子空间可以很好地保留原始图像的特征信息,利用基于压缩感知提取特征,该算法的数学表达式如下:
V=RX,
(1)
其中,X∈Rm×1为原始高维信号,V∈Rm为压缩后特征,R∈Rn×m(n≪m)为稀疏随机投影矩阵,满足RIP条件,其矩阵元素定义如下:

(2)
其中,s随机取2或者3,新的特征vi由原始图像特征通过rij加权求和得到,新特征压缩提取如图1所示。

图1特征压缩提取示意图
Fig.1Diagram of feature extraction by compression
文献[15]的跟踪过程是在上一帧目标区域的周围采样n个区域作为候选区域,然后利用(1)式对这n个区域进行特征压缩提取,得到n个低维特征向量v=(v1,v2,v3,…,vn)T,最后通过朴素贝叶斯分类器H(v)进行前景目标和背景目标分离,选取n个区域中H(v)值最大的区域作为当前帧跟踪到的目标,朴素贝叶斯分类器H(v)公式如下:


(3)
其中,y=0表示负样本,y=1表示正样本,两个类先验概率相等p(y=1)=p(y=0)=0.5,分类器H(v)中的条件概率p(v1|y=1)和p(vi|y=0)服从高斯分布,其均值和标准差分别为μ1,σ1和μ0,σ0。得到当前帧目标后,对这4个参数进行增量更新:
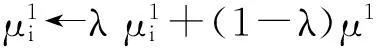


(4)
式中,λ为更新程度参数,取值范围是0<λ<1,其取值影响更新速度的学习率,λ值越小更新速度越快,反之越慢。
该算法在背景中存在与目标有一定相似性的物体,目标姿态、纹理变化和光照变化较大等情况下容易发生漂移或者跟丢目标,如图2中蓝色虚线矩形框所示。

图2实时压缩感知跟踪结果
Fig.2Tracking result of real-time compressive tracking
2感知哈希算法
感知哈希算法[17-18]是哈希算法的一类,主要用来做相似图片的搜索工作。它的原理是对每张图片生成一个“指纹”(fingerprint)字符串,然后比较不同图片的指纹。结果越接近说明图片越相似。 下面用最简单的步骤来说明感知哈希算法的原理:
1)缩小尺寸:快速去除高频和细节,只保留结构、明暗等基本信息的方法。将图片缩小到8×8的尺寸,总共64个像素。摒弃不同尺寸、比例带来的图片差异。
2)简化色彩:将8×8的小图片转为64级灰度,即所有像素点总共只有64种颜色。
3)计算平均值:计算所有64个像素的灰度平均值。
4)比较像素的灰度:将每个像素的灰度,与平均值进行比较,大于或等于平均值,记为1;小于平均值,记为0。
5)计算哈希值:将上一步比较结果组合在一起构成一个64位的整数,即为该图片的指纹。组合的次序不重要,只要保证所有图片都采用同样次序即可。
若要比较两个图片的相似性,首先要计算这两张图片的哈希指纹,即64位1或0值,然后计算出不同位的个数,理论上,这等同于计算“汉明距离”。汉明距离等于0,说明这两张图片非常相似;汉明距离小于5,说明图片略有不同,但比较相似;汉明距离大于10,说明两张图片完全不同。
3自适应实时压缩感知跟踪算法
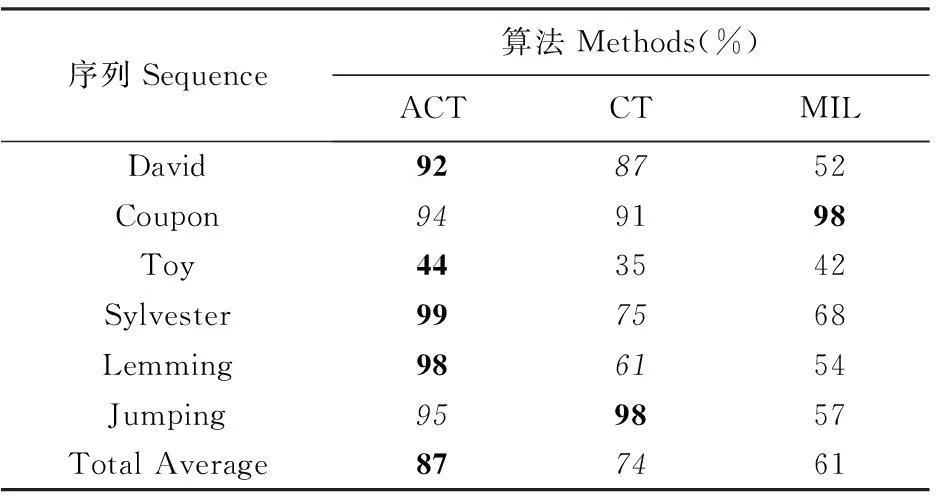
本文在实时压缩感知跟踪的基础上,利用压缩感知哈希算法计算当前帧跟踪结果目标模型的哈希指纹与上一帧目标模型的哈希指纹之间的汉明距离,在线实时调整朴素贝叶斯分类器,使得分类器能够根据目标外观变化快慢,自适应调整更新程度参数λ。具体思想:首先设置高阈值和低阈值,H=10为高阈值,L=5为低阈值,计算当前一帧跟踪结果目标模型的哈希指纹与上一帧目标模型的哈希指纹间的汉明距离d。当d>H时,说明背景中存在与前景目标有一定相似性的物体或者目标姿态、纹理变化、光照变化较大等,发生目标跟踪漂移或者跟丢,这时候,贝叶斯分类器的更新主要依赖于上一帧目标模型,若更新程度参数λ太小,则容易引起分类器过更新,这时要适当调大λ值;当d≤L时,说明目标外观变化缓慢,这时候,贝叶斯分类器的更新主要依赖于当前帧的目标模型,若更新程度参数λ太大,会造成分类器更新过程中无法适应目标外观的变化,这时要适当调小λ值;当L (5) 本文在文献 [15]实时压缩感知跟踪算法的基础上,提出自适应实时压缩感知跟踪算法,其流程如下: 输入:第t帧图像 1)以t-1帧目标位置的lt-1为中心,γ为半径采集候选目标样本集Dγ={z|‖l(z)-lt‖<γ},然后利用公式(1)对目标样本集进行特征提取,得到集合的特征向量v,计算t-1帧跟踪目标的哈希指纹Hat-1并保存; 2)使用公式(3)中的H(v)贝叶斯分类器对上述集合的特征向量v进行分类,将目标从背景中分离出来,具有最大H(v)值的候选区即为当前帧跟踪的目标,其位置记为lt,计算当前帧跟踪目标的哈希指纹Hat并保存; 3)计算当前帧跟踪目标的哈希指纹Hat与上一帧跟踪目标的哈希指纹Hat-1间的汉明距离d,将d与高低阈值进行比较,自适应调整更新程度参数λ; 4)采集目标样本和背景样本:以当前目标位置lt为中心,α为半径采集目标样本集Da={z|‖l(z)-lt‖ 5)利用公式(1)对目标样本和背景样本进行特征提取,代入公式(4)来更新分类器参数μ1,σ1和μ0,σ0。 输出:第t帧跟踪到的目标位置lt、自适应更新程度参数λ及更新后的分类器参数。 4算法验证 为了验证本文提出的自适应实时压缩感知跟踪算法(简称ACT算法)在视频目标跟踪中的鲁棒性和有效性,使用David、Coupon、Toy、Sylvester、Lemming和Jumping这6个标准视频序列进行测试,并且与文献[15]的 Compressive Tracking算法(简称CT算法)、文献[13]的Multiple Instance Learning算法(简称MIL算法)进行比较。为保证公平设置参数时每个算法处于最优跟踪性能,在CT算法中正样本采集半径α=4,产生45个正样本,负样本采集内半径ζ=8,外半径β=30,在圆环中随机选择50负样本,目标候选区域γ=20,产生约1100个候选区域样本,更新程度参数λ=0.85。在ACT算法中正样本采集半径α=4,产生45个正样本,负样本采集内半径ζ=8,外半径β=30,在圆环中随机选择50负样本,目标候选区域γ=20,产生约1100个候选区域样本,哈希指纹间的汉明距离d在高低阈值H、L不同范围内的自适应更新程度参数为λ1=0.85,λ2=0.35,λ3=0.15。在MIL算法中,正样本采集半径r=25,产生一个45个正样本的正包,负样本采集半径β=50,在负样本集中随机选择65个负样本组成负包,候选弱分类器的个数M=250,从中挑选出响应最大的弱分类器个数为K=50,弱分类器更新学习率ρ=0.85。 4.1定性分析 定性分析,即通过视觉对比,能够对算法进行直观地比较。图3给出3个算法在David、Coupon、Toy、Sylvester、Lemming和Jumping这6个标准视频序列中的跟踪结果。 (a)David视频序列中,跟踪的目标是David的脸部,视频包含光照变化、目标姿势、尺度变化等挑战。由于MIL算法的外观更新公式较粗糙,(a)视频的第290帧光照和目标姿势剧烈变化时,MIL算法跟踪目标失败。CT算法在跟踪过程中出现跟踪漂移,而ACT算法却能准确地跟踪目标,在该视频中取得最佳表现。 (b)Coupon视频序列中,跟踪的目标是一张赠券,背景干扰和遮挡增加了跟踪目标的难度,在该视频中由于没有光照、目标姿态的较大变化,在3个算法中MIL算法能够最优地跟踪目标,由于具有自适应调整更新程度参数的能力,ACT算法比CT算法要好一些。 (c)Toy视频序列中,跟踪的目标是玩偶的正脸,玩偶在跟踪过程中快速运动、多尺度变化和旋转,在(c)视频的第3帧中MIL算法跟丢目标,此时ACT和CT算法还可以准确跟踪目标,到了第82帧CT算法跟踪出现漂移,ACT算法仍能很好地跟踪目标,在本视频序列中ACT算法最佳,CT算法次佳。 (d)Sylvester视频序列中,跟踪的目标是一个玩偶,视频包含光照变化和目标旋转的干扰。ACT算法表现最佳,能准确地跟踪目标,CT在跟踪过程中发生漂移,MIL算法在第959帧中完全跟丢目标。 图36个测试序列的抽样跟踪结果 Fig.3Sampled tracking results of 6 tested sequences (e)Lemming视频序列中,跟踪的目标是玩偶旅鼠,视频包含背景杂乱、遮挡、旋转、序列较长的因素,在目标发生遮挡时,3个算法的表现并不理想。跟踪过程中ACT算法由于目标被遮挡,导致目标跟丢,但快速调整后能重新准确跟踪目标,而CT算法和MIL算法在目标遮挡时,发生目标跟丢后不能很好地调整,导致跟踪失败。在该视频中ACT算法表现最佳。 (f)Jumping视频序列中,跟踪的目标是跳绳男子的上半身,视频包含模糊运动和快速运动因素,CT算法和ACT算法表现较好,而MIL算法在跟踪目标的过程中出现漂移。 4.2定量分析 表1平均中心误差 Table 1Average center location errors 序列Sequence算法Methods(pixels)ACTCTMILDavid121723Coupon785Toy283236Sylvester4913Lemming51922Jumping7610TotalAverage101518 注:粗体数字表示最佳,斜体表示次佳 Note:Bold fonts indicate the best performance while the italic fonts indicate the second best ones 表2跟踪成功率 Table 2Success rate 序列Sequence算法Methods(%)ACTCTMILDavid928752Coupon949198Toy443542Sylvester997568Lemming986154Jumping959857TotalAverage877461 注:粗体数字表示最佳,斜体表示次佳 Note:Bold fonts indicate the best performance while the italic fonts indicate the second best ones 5结论 针对实时压缩感知目标跟踪算法在目标姿态、纹理或光线变化剧烈时,不能自适应地调整更新分类器,导致跟踪容易发生漂移、丢失目标的问题,提出自适应的实时压缩感知跟踪算法。实验结果表明,在6个具有挑战性的视频中自适应实时压缩感知跟踪算法表现较好,跟踪成功率比CT算法高出13%,比MIL算法高26%。当目标大小为40 pixel×43 pixel时,处理帧速约为37 fps,满足实时性要求。此外,ACT算法在目标运动速度非常快的情况下,跟踪效果不是很理想,这是本文后续要研究和解决的重点问题。 参考文献: [1]YILMAZ A,JAVED O,SHAH M.Object tracking:A survey[J].ACM Computing Surveys (CSUR),2006,38(4):1-45. [2]AVIDAN S,TECHNOL M V,JERUSALEM I.Sup- port vector tracking[C]//Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition.[S.l.]:IEEE,2001:184-191. [3]JEPSON A D,FLEET D J,EL-MARAGHI T F.Robust online appearance models for visual tracking,IEEE Trans[J].Pattern Anal Mach Intell,2003,25(10):1296-1311. [4]COLLINS R T,LIU Y,LEORDEANU M.Online selection of discriminative tracking features,IEEE Trans[J].Pattern Anal Mach Intell,2005,27(10):1631-1643. [5]GRABNER H,LEISTNER C,BISCHOF H.Semi-supervisedon-line boosting for robust tracking[C]//FORSYTH D,TORR P,ZISSERMAN A,eds.Computer Vision-ECCV 2008.[S.l.]:Springer Berlin Heidelberg,2008:234-247. [6]MEI X,LING H.Robust visual tracking using l1minimization[C]//Proc IEEE Int Comput Vis Conf.Sep.[S.l.:s.n.],2009:1436-1443.DOI:10.1109/ICCV.2009.5459292. [7]KWON J,LEE K M.Visual tracking decomposition [C]//Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition(CVPR),2010 IEEE Conference on.SanFrancisco,CA:IEEE,2010:1269-1276.DOI:10.1109/CVPR.2010.5539821. [8]KALAL Z,MATAS J,MIKOLAJCZYK K.P-N learning:Bootstrapping binary classifiers by structural constraints[C]//Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition(CVPR),2010 IEEE Conference on.SanFrancisco,CA:IEEE,2010:49-56.DOI:10.1109/CVPR.2010.5540231. [9]WANG Q,CHEN F,XU W L,et al.Online discriminative object tracking with local sparse representation[C]// M in Applications of Computer Vision (WACV),2012 IEEE Workshop on.[S.l.:s.n.],2012:425-432. [10]AVIDAN S.Ensemble tracking[C]//Computer Visi- on and Pattern Recognition,IEEE Computer Society Conference.[S.l.:s.n.],2005:261-271. [11]GRABNER H,BISCHOF H.On-line boosting and vision[C]//Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition,2006 IEEE Computer Society Conference on.[S.l.:s.n.],2006:260-267. [12]BABENKO B,YANG M H,BELONGIE S.Visual tracking with online multiple instance learning[C]//Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition,2009.[S.l.]:IEEE,2009:983-990. [13]BABENKO B,YANG M H,BELONGIE S.Robust object tracking with online multiple instance learning[J].Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence,IEEE Transactions on,2011,33:1619-1632. [14]ZHANG K H,SONG H H.Real-time visual tracking via online weighted multiple instance learning[J].Pattern Recognition,2013,46:397-411. [15]ZHANG K H,ZHAGN L,YANG M H.Real-time compressive tracking[C]//FITZGIBBON A,LAZEBNIK A PERONA P,et al,eds.Computer Vision-ECCV 2012.[S.l.]:Springer Berlin Heidelberg,2012:864-877. [16]DONOHO D L.Compressed sensing[J].IEEE Tran- sactions on Information Theory,2006,52 (4):1289-1306. [17]KRAWETA N.The Hacker factor blog[EB/OL]. [2015-09-22].http://www.hackerfactor.com/blog/index.php?/archives/432-Looks-Like-It.html. [18]CHEN C.感知哈希算法:找出相似的图片[EB/OL].[2015-09-12].http://www.cnblogs.com/technology/archive/2012/07/12/Perceptual-Hash-Algorithm.html. CHEN C.Perception of hash algorithm:Find the similar images[EB/OL].[2015-09-12].http://www.cnblogs.com/technology/archive/2012/07/12/Percept- ual-Hash-Algorithm.html. (责任编辑:陆雁) Adaptive Real-time Compressive Sensing Tracking Algorithm 梁剑平,朱晓姝 LIANG Jianping,ZHU Xiaoshu (玉林师范学院计算机科学与工程学院,广西玉林537000) (School of Computer Science and Engineering,Yulin Normal University,Yulin,Guangxi,537000,China) 摘要:【目的】解决实时压缩感知跟踪算法分类器无法适应目标外观变化及过更新的问题。【方法】根据当前跟踪结果目标模型的哈希指纹与上一帧目标模型的哈希指纹之间的汉明距离(Hamming distance),在线实时调整分类器,以提高实时压缩感知目标跟踪算法的自适应能力。【结果】自适应实时压缩感知跟踪算法的跟踪成功率比实时压缩感知跟踪算法提高13%,在目标大小为40 pixel×43 pixel时,跟踪速率为37 fps,满足实时性要求。【结论】本研究建立的方法在背景中存在与目标有一定相似性的物体,且目标姿态、纹理变化和光照变化较大等情况下,能快速获取跟踪目标,并且具有较强的鲁棒性和准确性。 关键词:压缩感知目标跟踪哈希指纹汉明距离自适应实时压缩 Abstract:【Objective】To solve the problem of real-time compressed sensing tracking algorithm,which is the inadaptability of classifier to the changes of the target appearance and the over update.【Methods】Base on Hamming distance between the Hash fingerprints of current target and original one, classifier is adjusted in real time, which improved the adaptive capacity of the real-time compressed sensing tracking.【Results】As compared with the real-time compressive sensing tracking algorithm, the proposed algorithm improves the success rate by 13%,and average computing frame rate is 37 frames when the target scale is 40 pixel×43 pixel, which satisfies the requirements of real-time tracking.【Conclusion】The proposed algorithm is tested with variant video sequences.The results show that the proposed algorithm is capable of speedily and accurately capturing the tracking target by target gestures, textures, or significant light change. Key words:compressive sensing,target tracking,Hash fingerprint,Hamming distance,adaptive,real-time compressive 中图分类号:TP391 文献标识码:A 文章编号:1002-7378(2016)01-0042-07 作者简介:梁剑平(1987-),女,助教,主要从事数字图像处理研究。 收稿日期:2015-10-14 网络优先数字出版时间:2016-01-27 网络优先数字出版地址:http://www.cnki.net/kcms/detail/45.1075.N.20160127.1616.018.html *广西高校科学技术研究项目(201204LX339和YB2014321)资助。