菠菜霜霉病菌快速分子检测方法研究
李 京,张祥林,王 翀,李亚伟,张小菊
(1.新疆出入境检验检疫局,乌鲁木齐830063;2.新疆农业大学农学院,乌鲁木齐830052)
菠菜霜霉病菌快速分子检测方法研究
李 京1,2,张祥林1,王 翀1,李亚伟1,张小菊1
(1.新疆出入境检验检疫局,乌鲁木齐830063;2.新疆农业大学农学院,乌鲁木齐830052)
摘要:【目的】菠菜霜霉病,由专性寄生病原菌Peronospora farinosa f. sp. Spinaciae引起,是世界上菠菜Spinacia oleracea种植中最为重要的经济型病害。建立菠菜霜霉病菌快速分子检测方法。【方法】将菠菜霜霉病菌进行显微镜的形态鉴定;提取DNA、PCR扩增、克隆、酶切、测序、序列比对与分析;采用巢式PCR技术检测菠菜霜霉病:第一轮采用通用引物ITS1/ITS4,第二轮采用特异性引物SMPF/SMPR。【结果】该菌与霜霉属的形态特征描述一致,确定菠菜患有霜霉病;测序结果经Blast比对分析与Peronospora effusa同源性达100%;巢式PCR技术也特异性的检测到了菠菜霜霉病菌。【结论】建立针对菠菜霜霉病的快速分子检测技术。
关键词:菠菜霜霉病、酶切、巢式PCR
0引 言
【研究意义】菠菜霜霉病是由专性寄生菌Peronosporafarinosaf. sp.Spinaciae引起,该病在全世界的菠菜种植中都是一种毁灭性的病害[1,2]。菠菜霜霉病是一种多发性真菌病害,尤其在气候冷且多雨的情况下发病率高,传播速度快[3]。【前人研究进展】对于菠菜霜霉病分子方面的研究国外报道较多,Young-Joon CHOI等[4]对引起菠菜霜霉病的病原Peronosporaeffusa以及霜霉属的其他种结合病原的形态特征做了同源性分析。Klosterman, S. J.等[5]采用了ASP-PCR的方法成功将引起菠菜霜霉病的病原Peronosporaeffusa与引起甜菜霜霉病的病原Peronosporaschachtii检测出来。【本研究切入点】国内对于菠菜霜霉病的分子检测技术目前还没有相关报道,大部分报道是针对菠菜霜霉病的形态特征及防止措施。【拟解决的关键问题】采用通用性引物ITS1/ITS4扩增ITS区,进而设计出针对菠菜霜霉病菌的特异性引物SMPF/SMPR。通过巢式PCR的方法来检测引物的特异性。
1材料与方法
1.1 材 料
1.1.1 主要试剂
实验所用PCR试剂、所用引物与探针均购于北京鼎国昌盛生物技术有限责任公司,植物基因组DNA提取试剂盒、凝胶回收试剂盒、质粒提取试剂盒均购于天根生物科技(北京)有限公司,PMD18-T载体购于大连宝生物工程公司,实验所有的测序均在北京鼎国昌盛生物技术有限责任公司完成。
1.1.2供试菌株(表1)
表1供试材料、寄主和来源
Table 1Materials,hosts and their sources

序号NO分类地位寄主来源SequencenoClassificationstatusHostSource1A.tenuissima(Fr.)Wiltshire枣新疆出入境检验检疫局2A.triticinaPrasada小麦新疆出入境检验检疫局3PhomamacdonaldiiBoerma向日葵新疆出入境检验检疫局4Peronospora.variabilis藜新疆伊犁尼勒克县5Bremialactucae莴笋新疆乌鲁木齐市大棚蔬菜基地6Peronosporaeffusa菠菜新疆乌鲁木齐市三坪农场
1.1.3形态鉴定
用灭过菌的手术刀轻轻刮取菠菜霜霉病叶片背面的灰色霉层或者用灭菌的解剖针挑取霉层, 观察孢囊梗及孢子囊的形态特征。
1.2 菠菜霜霉病的分子鉴定
1.2.1DNA提取
用试剂盒(Plant Genomic DNA Kit)提取菠菜霜霉病叶、正常菠菜叶片以及供试材料的核酸,并使用分光光度计ND-1000测定核酸的浓度。
1.2.2rDNA-ITS区通用引物扩增
采用真菌核糖体内转录间隔ITS区通用引物ITS1/ITS4[6,7],对提取的核酸进行PCR扩增,引物序列如下:
ITS1: 5’- CTTGCGTTGATTACGTCCC- 3’。
ITS4 :5’- TCCTCCGCTTATTGATATGC- 3’。
PCR反应体系总体积20 μL,其中2×TaqPCR Green Mix 12.5 μL,10 μM上、下游引物各0.5 μL,ddH2O 9.5 μL,模板2 μL。扩增程序:94℃预变性4 min,94℃变性 1 min,55℃ 退火40 s,72℃延伸 90 s,共35个循环,72℃延伸10 min[8]。
将PCR产物在1.5%琼脂糖凝胶,1×TAE电泳缓冲液,90V电压条件下电泳35 min,置凝胶成像系统中观察分析。
1.2.3克隆及测序
为了能胶回收成功,在电泳时将胶的浓度增大,电压调低,电泳时间延长,能将片段大小差距不大的条带分开,然后在紫外透射仪下将目的片段切下,按照胶回收试剂盒的步骤将所需片段回收,克隆到PMD18-T载体并转化到感受态细胞中,经蓝白斑筛选,挑菌、摇菌,最后按照质粒小提试剂盒的步骤从摇的菌液中提取质粒,并将质粒进行酶切及PCR电泳检测。
1.2.4质粒酶切鉴定
酶切体系:3 dH2O 11 μL,10×Buffer 2 μL,重组质粒6 μL,EcoRⅠ 0.5 μL,HindШ 0.5 μL。37℃水浴过夜,1.5%琼脂糖凝胶电泳检测。
1.2.5测 序
将阳性重组质粒送北京鼎国昌盛生物技术有限责任公司测序。
1.2.6特异性引物的设计与合成
将测序结果在NCBI上进行BLAST比对分析,利用生物学软件DNAMAN与Primer设计针对菠菜霜霉病的特异性引物,然后再次进行Genbank blast数据库的特异性比对设计出引物SMPF和SMPR。合成的引物配成100m母液,使用时稀释10倍,引物保存于-20℃冰箱里。
1.3 菠菜霜霉病巢式PCR检测
1.3.1特异性引物PCR退火温度的优化
用特异性引物SMPF/SMPR进行PCR扩增,将退火温度设置6个梯度:55、56、57、58、59和60℃。
1.3.2巢式PCR检测
供试材料菠菜霜霉病叶、莴苣霜霉病叶、藜霜霉病叶、枣黑斑病菌、小麦叶疫病菌、向日葵黑茎病菌、菠菜正常叶片,按照上述核酸提取的方法来提取核酸,用引物ITS1/ITS4进行第一轮PCR扩增,引物SMPF/SMPR进行第二轮PCR扩增。将PCR扩增产物进行电泳检测。
PCR反应体系总体积20 μL: 2×TaqPCR Green Mix 12.5 μL,10 μM上、下游引物各0.5 μL,ddH2O 9.5 μL,模板2 μL。扩增程序:94℃预变性4 min,94℃变性 30 s,55℃退火30 s,72℃延伸 1 min,共35个循环,72℃延伸10 min。
2结果与分析
2.1 形态鉴定结果
经显微镜观察并拍照可以看出:孢囊梗为二叉状锐角分支3~8次,末端尖锐,孢子囊为卵圆形或椭圆形,大小(13.8~32.7 )μm×(10.4~22.3 )μm。图1

A:孢囊梗;B:卵孢子;C、D:孢子囊
A:sporangiophore;B: Oospore;C、D: sporangia
图1菠菜霜霉病菌镜检形态
Fig.1 The morphology of Spinach Downy Mildew Pathogen through microscopy
2.2 菠菜霜霉病分子鉴定
2.2.1通用引物ITS1/ITS4 PCR扩增结果
采用通用引物ITS1和ITS4分别对菠菜病叶、菠菜正常叶片DNA进行PCR。电泳结果显示:菠菜正常叶片出现一条500 bp左右的条带,菠菜霜霉病叶出现一条800 bp左右的条带和一条500 bp左右的条带,由此可知800 bp左右的条带为菠菜霜霉病菌的DNA条带[9]。图2

M:DL2000 Marker;1-2:菠菜正常叶片DNA;3-5:菠菜霜霉病叶;6:空白
M:DL2000 Marker; 1-2:the DNA of health spinach leaf; 3-5: the DNA of spinach downy mildew leaf;6: blank
图2ITS1/ITS4引物扩增结果
Fig.2The PCR amplified result by primer ITS1/ITS4
2.2.2 重组质粒的鉴定结果
经蓝白斑筛选、PCR扩增及EcoRⅠ、HindШ双酶切鉴定,筛选出含有正确插入片段的重组质粒。从实验结果可以得出:菠菜霜霉病菌DNA重组质粒经PCR扩增,可以得到800 bp左右的片段。大小与插入片段相同,重组的质粒EcoRⅠ、HindШ双酶切,在Marker 2 000上方出现与PMD18-T质粒大小(2 692 bp)大致相同。下方得到800 bp左右的片段,片段大小与插入片段大小大致相同。图3,图4

M:DL2000 Marker;1:菠菜霜霉病菌;2:空白
M:DL2000 Marker; 1:the DNA of spinach downy mildew pathogen; 2: blank
图3菠菜霜霉病菌重组质粒PCR结果
Fig.3The result that ITS1/ITS4 clones Spinach downy mildew pathogen
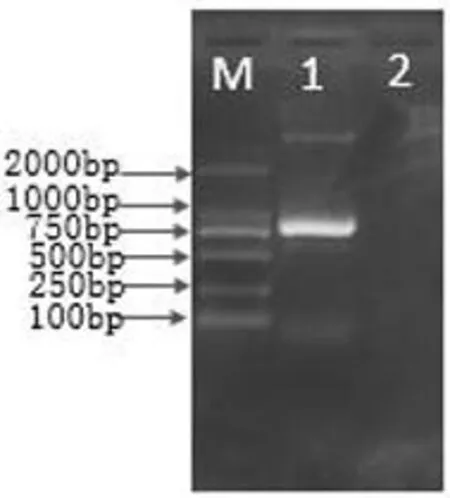
M:DL2000 Marker;1:菠菜霜霉病菌;2:空白
M:DL2000 Marker; 1:the DNA of spinach downy mildew pathogen; 2: blank
图4菠菜霜霉病菌重组质粒酶切结果
Fig.4The result that ITS1/ITS4 clones Spinach downy mildew pathogen
2.2.3测序结果
菠菜霜霉病的重组质粒测序结果显示:所克隆的目的片段的为847 bp(图6),与预期的片段大小基本一致。在NCBI上进行BLAST比对此序列与已公布的Peronosporaeffusa(AF528560.1)同源性达100%,同Genbank上公布的霜霉属其他菌的同源性高达95%以上。
2.3 特异性引物设计
将测序结果在Genbank上进行Blast比对,下载已经发布的菠菜霜霉病菌以及其他寄主的霜霉病菌ITS区序列通过DNAMAN进行多序列比对,设计出了特异性引物SMPF和SMPR。产物片段大小为414 bp。
SMPF:5’- GGGTTATCCCTGGAAGTATGC- 3’;
SMPR:5'- ATGCCACACAACCGAAGTC-3’。

M:DL2000 Marker;1:菠菜霜霉病叶;2:莴苣霜霉病叶;3:向日葵黑茎病菌;4:菠菜正常叶片;5:小麦叶疫病菌;6:藜霜霉病叶;7:枣黑斑病菌;8:空白
M:DL2000 Marker;1: the DNA of health Spinach leaf;2: the DNA of lettuce downy mildew leaf;3: the DNA of sunflower black stem pathogen;4: the DNA of health spinach leaf;5: the DNA of wheat leaf blight pathogen;6: the DNA of quinoa downy mildew leaf;7: the DNA of jujube black spot pathogen;8:blank
图5ITS1/ITS4 巢式PCR第一轮扩增结果
Fig.5The first amplification result of Nest-PCR of the primer ITS1/ITS4
2.4 巢式PCR检测
采用通用引物ITS1/ITS4进行第一轮PCR扩增,第二轮用特异性引物SMPF/SMPR进行扩增。结果显示:菠菜霜霉病叶在第一轮扩增中出现了800 bp和500 bp左右的两条条带,第二轮扩增仅出现了一条400 bp左右的条带;菠菜正常叶片第一轮扩增出现500 bp左右的条带,第二轮扩增无条带出现;莴苣霜霉病叶和向日葵黑茎病菌在第一轮扩增中均出现了一条约800 bp的条带,第二轮都无条带出现;枣黑斑病菌在第一轮扩增中出一条约500 bp的条带,在第二轮扩增中无条带出现;小麦叶疫病菌在第一轮扩增中出现了一条约700 bp的条带,在第二轮扩增中无条带出现;藜霜霉病叶第一轮扩增出现约800 bp和700 bp两条条带。图5、图6

M:DL2000 Marker;1:菠菜霜霉病叶;2:莴苣霜霉病叶;3:向日葵黑茎病菌;4:菠菜正常叶片;5:小麦叶疫病菌;6:藜霜霉病叶;7:枣黑斑病菌;8:空白
M:DL2000 Marker;1: the DNA of health Spinach leaf;2: the DNA of lettuce downy mildew leaf;3: the DNA of sunflower black stem pathogen;4: the DNA of health spinach leaf;5: the DNA of wheat leaf blight pathogen;6: the DNA of quinoa downy mildew leaf;7: the DNA of jujube black spot pathogen;8:blank
图6SMPF/SMPR巢式PCR第二轮扩增结果
Fig.6The second amplification result of Nest-PCR of the primer SMPF/SMPR
3讨 论
虽然易建平等[10]提出了挑取孢子在解剖镜下压碎后提取核酸的方法[10],但是为了能够快速有效的提取菠菜霜霉菌的核酸实验采用了提取患病叶片的核酸,在克隆过程中通过胶回收来获得菠菜霜霉菌的DNA[11,12]。
目前国内对于菠菜霜霉病的分子形态学研究还处于初级阶段,针对菠菜霜霉病的分子检测方法还没有建立,实验采用巢式PCR方法建立了常规分子检测方法,实现了菠菜霜霉病的快速分子检测。实验只涉及到常规PCR检测技术,但在实时荧光PCR检测技术方面还有很大发展的空间。
4结 论
通过镜检确定了该病菌为霜霉病菌,通过分子鉴定(实验采用巢式PCR的方法)出菠菜霜霉病菌与Peronosporaeffuse的同源性最高,更进一步确定了该霜霉病的种类。扩增ITS区实现了菠菜霜霉病的快速检测。
参考文献(References)
[1] Irish, B. M., Correll, J. C., Feng, C., Bentley, T., & Reyes, B. G. D. L. (2008). Characterization of a resistance locus (pfs-1) to the spinach downy mildew pathogen (peronospora farinosa f. sp. spinaciae) and development of a molecular marker linked to pfs-.Phytopathology, 98(8):894-900.
[2] Feng, C., Correll, J. C., Kammeijer, K. E., & Koike, S. T. (2014). Identification of new races and deviating strains of the spinach downy mildew pathogen peronospora farinosa f. sp. spinaciae.PlantDisease, 98(1):145-152.
[3]李金堂,默书霞,杨子亮,等. 菠菜霜霉病的识别及防治[J]. 长江蔬菜,2013,(9):46-47.
LI Jin-tang, MO Shu-xia, YANG Zi-liang, et al. (2013). Identification and prevention of spinach downy mildew [J].JournalofChangjiangVegetables, (9):46-47. (in Chinese)
[4] Choi, Y. J., Hong, S. B., & Shin, H. D. (2007). Re-consideration of peronospora farinosa infecting spinacia oleracea as distinct species, peronospora effusa.MycologicalResearch, 111(Pt 4):381-391.
[5] Klosterman, S. J., Amy, A., Neil, M. R., Koike, S. T., Subbarao, K. V., & Hermann, V., et al. (2014). Coupling spore traps and quantitative pcr assays for detection of the downy mildew pathogens of spinach (peronospora effusa) and beet (p. schachtii).Phytopathology, 104(12):1,349-1,359.
[6]赵杰. ITS序列分析及其在植物真菌病害分子检测中的应用[J].陕西农业科学,2004,(4):35-37.
ZHAO Jie. (2004). The ITS sequence analysis and application in molecular detection of plant fungal diseases [J].ShaanxiJournalofAgriculturalSciences, (4):35-37. (in Chinese)
[7]刘艳,沙爱华,陈海峰,等.大豆霜霉病菌rDNA ITS区的分子探针的设计与应用[J].华北农学报,2012,27(2):230-233.
LIU Yan, SHA Ai-hua, CHEN Hai-feng, et al. (2012). Development and application of molecular probe of soybean downy mildew based on Peronospora manshurica (Naoun.) sydow Rdna ITS [J].ActaAgriculturaeBoreali-Sinica, 27(2): 230-233. (in Chinese)
[8]曹永军,程萍,喻国辉,等. 利用ITS1和ITS4通用引物扩增香蕉枯萎病菌核酸片段鉴定其生理小种[J]. 热带作物学报,2010,31(7):1 098-1 102.
CHAO Yong-jun, CHENG Ping, YU Guo-hui, et al. (2010). Using general primers ITS1 and ITS4 to amplify DNA fragment of banana fusariumt to identify their physiological small race.[J].ChineseJournalofTropicalCrops, 31(7): 1,098-1,102. (in Chinese)
[9]乾义柯,张祥林,陆平,等. 甜菜霜霉病菌形态鉴定及28S rDNA序列分析[J].新疆农业科学,2012,49(2):249-254.
QIAN Yi-ke, ZHANG Xiang-lin, LU Ping, et al. (2012). Morphological detection and sequence analysis of 28S ribosomal DNA 0f Peronospora farinosa f. sp. Betae byford [J].XinjiangAgriculturalSciences, 49(2): 249-254. (in Chinese)
[10]易建平,陶庭典,潘良文,等. 套式PCR直接检测印度腥黑穗病菌冬孢子[J]. 植物检疫,2002,16(4):197-200.
YI Jian-ping, TAO Ting-dian, PAN Liang-wen, et al. (2002). Direct deterction of Tilletia indica teliospores by nest PCR [J].PlantQuarantine, 16(4): 197-200. (in Chinese)
[11] Choi, Y. J., Hong, S. B., & Shin, H. D. (2003). Diversity of the hyaloperonospora parasitica complex from core brassicaceous hosts based on its rdna sequences.MycologicalResearch, 107(11):1,314-1,322.
[12] Belbahri, L., Calmin, G. J., & Lefort, F. (2005). Phylogenetic analysis and real time pcr detection of a presumbably undescribed peronospora species on sweet basil and sage.MycologicalResearch, 109(Pt 11):1,276-1,287.
Fund project:Supported by The Scientific Research Project of General Administration of Quality Supervision (201310091)
Rapid Detection Spinach Downy Mildew Pathogen by Molecular Method
LI Jing1,2, ZHANG Xiang-lin1, WANG Chong1, LI Ya-wei1, ZHANG Xiao-ju1
(1.XinjiangEntry-ExitInspectionandQuarantineBureau,Urumqi830063,China; 2.CollegeofAgronomy,XinjiangAgriculturalUniversity,Urumqi830052,China)
Abstract:【Objective】 Spinach downy mildew disease, caused by the obligate pathogen Peronospora farinosa f. sp. spinaciae, is the most economically important spinach (Spinacia oleracea) disease.【Objective】The purpose of this study is to establish the molecular method of rapid detection of spinach downy mildew pathogen.【Method】 First of all, the morphology of spinach downy mildew pathogen should be identified by microscope; then the second process was DNA extraction, PCR amplification, cloning, enzyme digestion, sequencing, the sequence alignment and analysis; and finally, the spinach downy mildew was detected by using nested PCR technique. The first amplification was to use the universal primer ITS1/ITS4 and the second amplification was to use the specific primer SMPF/SMPR.【Result】Microscopy results showed that the fungus were consistent with the description of Peronospora morphology, so we made sure that spinach were infected with downy mildew disease; The homology of sequencing results of the blast analysis with Peronospora effuse was 100%; nested PCR technology also specially detected spinach downy mildew pathogen.【Conclusion】This study established the rapid detection spinach downy mildew pathogen by molecular method but the technique of Real-time quantitative PCR needs more exploration.
Key words:spinach downy mildew; enzyme digestion; nested-PCR
通讯作者:张祥林(1964-),男,新疆人,研究员,研究方向为分子植物病理学,(E-mail)XL6479@163.com
作者简介:李京(1990-),女,山东人,硕士研究生,研究方向为植物检疫病害,(E-mail)13579981032@163.com
基金项目:国家质检总局科研项目(201310091)
收稿日期:2015-09-20
中图分类号:S41
文献标识码:A
文章编号:1001-4330(2016)02-0346-06
doi:10.6048/j.issn.1001-4330.2016.02.022

