七自由度整车半主动悬架仿真研究
王孝鹏,刘建军,吴 龙
(1. 三明学院 机电工程学院,福建 三明 365004;2. 机械现代设计制造技术福建省高校工程研究中心,福建 三明 365004;3. 绿色铸锻及其高端零部件制造福建省2011协同创新中心,福建 三明 365004 ;4. 福建省铸锻零部件工程技术研究中心,福建 三明 365004)
七自由度整车半主动悬架仿真研究
王孝鹏1,2,3,4,刘建军1,2,吴 龙1,2
(1. 三明学院 机电工程学院,福建 三明 365004;2. 机械现代设计制造技术福建省高校工程研究中心,福建 三明 365004;3. 绿色铸锻及其高端零部件制造福建省2011协同创新中心,福建 三明 365004 ;4. 福建省铸锻零部件工程技术研究中心,福建 三明 365004)
通过MATLAB软件建立整车七自由度的动力学仿真模型。半主动悬架采用双模糊控制器,将计算出的刚性车身与悬架连接处的速度、动行程与俯仰角参数作为主动悬架控制的输入量;前轴左右车轮,悬架与车身连接处的速度与其期望值的误差及其变化率作为第一控制力输入量,刚性车身质心俯仰角速度与其期望值的误差及其变化率作为第二控制力输入量;后轴左右车轮,车悬架与车身连接处的速度与其期望值的误差及其变化率作为第一控制力输入量,悬架动行程与其期望值的误差及其变化率作为第二控制力输入量。计算结果表明:采用双模糊控制器能明显改善整车行驶的舒适性与稳定性,系统综合特性较好,刚性车身的垂向加速度、俯仰角加速度、前后悬架动行程性能提升明显,分别提升27.2%, 19.6%, 95.5%, 33.8%。
七自由度;半主动悬架;双模糊控制
Keywords:seven degree-of-freedom(DOF);semi-active suspension;double fuzzy control
0 引言
在对悬架系统的研究中,二自由度悬架模型与四自由度1/2整车模型在文献中引用较多[1-5]。二自由度模型能较好地反映系统的垂向震动特性,四自由度1/2整车模型在二自由度悬架模型的基础上增加车身的俯仰特性。整车在运行过程中,各系统之间的机理特性较为复杂。采用七自由度整车模型能较全面体现整车的运动特性。七自由度模型包括刚性车身的垂向运动、俯仰运动、侧倾运动及4个车轮的垂向运动。
随着微处理器在车辆中的应用逐渐普及,可控悬架可以根据整车行驶的外部信号,调整弹簧的刚度与减震器的阻尼,在一定程度上改善了悬架系统的性能,使整车行驶的舒适性与操纵稳定性得到良好的提升。控制策略对可控悬架的性能有很大的影响。模糊控制策略与其他控制策略相比,具有的优点如下:使用语言方法,不需要精确的数学模型;鲁棒性好,适合解决过程控制中的非线性、强耦合时变和滞后等问题[1-8]。
因此,本文通过建立七自由度整车模型,采用模糊控制策略对半主动悬架与被动悬架的性能进行对比分析。
1 整车模型建立
建立七自由度模型时,作如下假设:1)左右车轮受到的不平度垂直激励是不同的,左侧车轮的垂向位移为右侧车轮的2倍,用来模拟整车行驶过程中的侧倾角特性,车辆对其纵轴线左右对称[6];2)车轮及相关部件为非簧载质量,车轮在对称面中心与路面接触;3)仅考虑轮胎的刚度作用。简化后的七自由度整车模型如图1所示。图中,c为车身质心垂向位移;mc为簧载质量;l1~l4为质心到左右车轮的距离;lf为质心至前轴距离;lr为质心至后轴距离;c1~c3为簧载质量在3个不同坐标方向的位移;Ix,Iy分别为侧倾转动惯量和俯仰转动惯量;c,c, φc为簧载质量俯仰、侧倾、横摆角位移;u1~u4为编号1~4轮系处的非簧载质量位移;e1~e4为编号1~4车轮底部的路面激励;ku1~ku4为编号1~4轮胎刚度;km1~km4为编号1~4轮系处的簧载质量刚度;cη1~cη4为编号1~4轮系处的簧载质量阻尼系数;mu1~mu4为编号1~4轮系处的非簧载质量;u1~u4为编号1~4轮系处的半主动作动器的输出力。
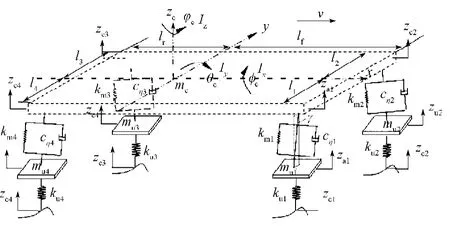
图1 整车模型Fig. 1 A full-vehicle model
根据整车模型,建立七自由度整车动力学微分方程如下。
车身垂向、俯仰、侧倾动力学方程如下。

整车参数设置如表1所示。
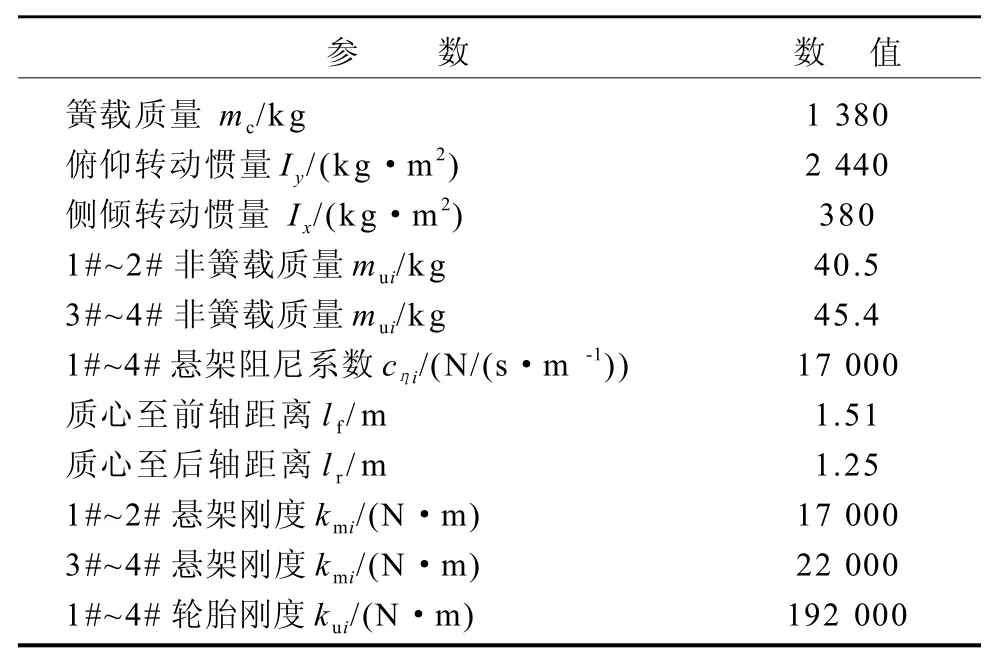
表1 整车参数设置表Table 1 Vehicle parameters table
根据式(1)~(11),令作动器的输出控制力u1~u4为0,建立整车被动悬架仿真模型,如图2所示。在B级路面垂向位移输入下,计算被动悬架模型与车身连接处的车身速度、车身加速度,并将其作为控制器的输入变量。用车身加速度及悬架动行程计算预控主控力ui的大小,对主动力ui的变化范围进行界定,并用双模糊控制策略在此范围控制ui的变化。
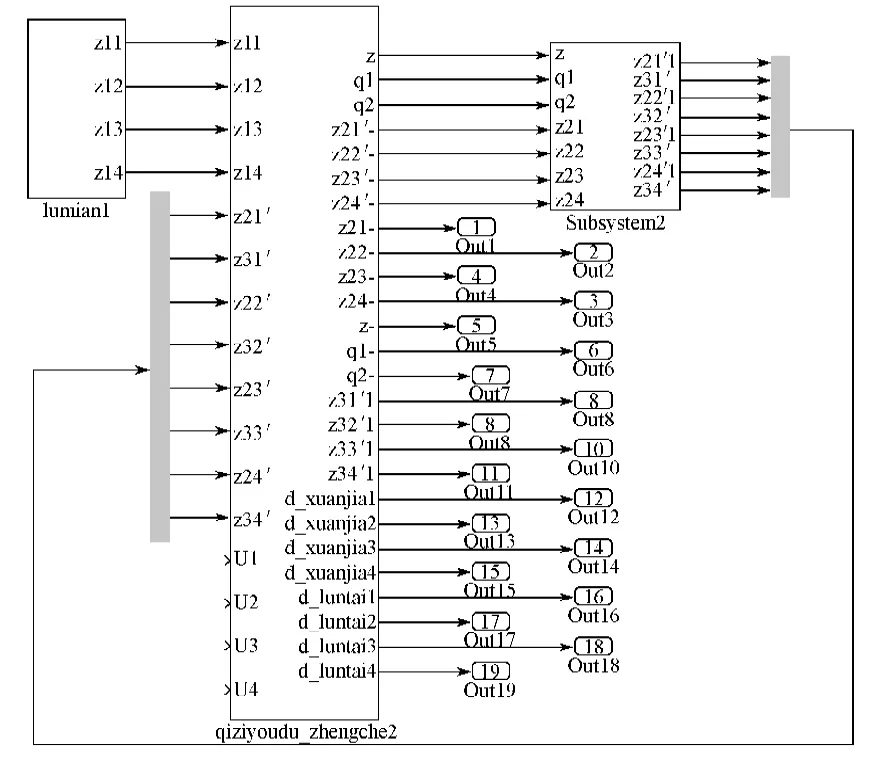
图2 整车被动悬架模型Fig. 2 A full-vehicle passive suspension model
2 路面模型
对悬架性能分析时,需输入路面模型。根据国家标准将公路等级分为8种,在不同的路段测量,很难得到2个完全相同的路面轮廓曲线。通常,将测量得到的大量路面不平度随机数据经处理后,得到路面功率谱密度。产生随机路面不平度时间轮廓有2种方法,利用积分器或成型滤波器产生白噪声。路面时域模型可用式(12)描述。考虑在实际行驶过程中,轮3与轮4和轮1与轮2接受到路面激励的时间都有相对延迟。因此对轮3与轮4加入时间延迟输入,延迟时间为t=l/v。根据式(12)建立B级路面时域仿真模型(见图3),路面垂直位移计算结果(见图4)。

式中:f0为时间频率;q(t)为路面随机激励;Gq为路面不平度系数;V为汽车行驶速;w(t)为积分白噪声。

图3 路面时域仿真模型Fig. 3 A time-domain simulation model

图4 路面垂向位移图Fig. 4 A diagram of pavement vertical displacement
3 双模糊控制器设计
3.1 仿真模型
本文采用双模糊控制器对主动控制力ui进行控制。对于前轴左右车轮,以悬架与车身连接处的速度与其期望值的误差及其变化率作为模糊控制器的输入量、ui1作为半主动悬架第一控制力输出量;以刚性车身质心角速度与其期望值的误差及其变化率作为模糊控制器的输入量,ui2作为半主动悬架第二控制力的输出量。对于后轴左右车轮,以车悬架与车身连接处的速度与其期望值的误差及其变化率作为模糊控制器的输入量、ui1作为半主动悬架第一控制力输出量;以悬架动行程ci-ui与其期望值的误差及其变化率作为第二个模糊控制器的输入量,ui2作为半主动悬架第二控制力输出量。总控制力为第一、二控制力输出量之和,即:
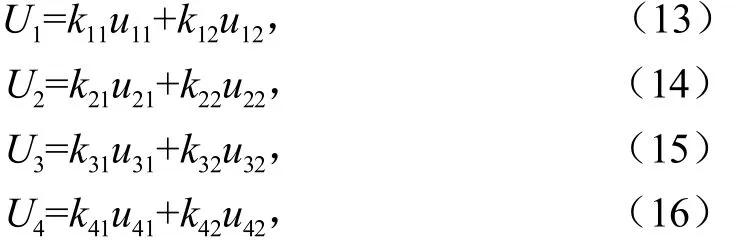
式(13)~(16)中ki1,ki2分别为第一、二控制力输出权系数。当ki1大,主控力的输出以第一控制力输出为主,主要用来降低车身的加速度,此时整车行驶在较差的路面;当ki2大,主控力以第二控制力输出为主,主要用来降低整车在行驶过程中的悬架动行程,且主控力越大,悬架动行程变化越小,此时整车行驶在较好的路面且车速较高。根据式(13)~(16),搭建了悬架系统双模糊控制器输出控制力的仿真计算模型,如图5所示。
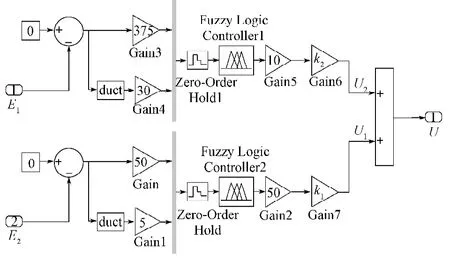
图5 悬架主控力双模糊控制器Fig. 5 A dual fuzzy controller for suspension control force
3.2 模糊控制规则
模糊控制规则是模糊控制器的核心,它用语言的方式描述了控制器输入量与输出量之间的关系。前后悬架的输入变量分别为车身质心速度及其变化量、车身俯仰角速度及其变化量、后悬架动行程及其变化量,采用7个语言变量规则来进行描述:负大(-3)、负中(-2)、负小(-1)、零(0)、正小(1)、正中(2)、正大(3)。输出变量控制力Ui同样采取7个语言模糊集来进行描述:负大(-3)、负中(-2)、负小(-1)、零(0)、正小(1)、正中(2)、正大(3)。
前轴左右车轮悬架与车身连接处的速度与其期望值的误差及其变化率的范围、量化因子分别为:

车身俯仰角速度与其期望值的误差及其变化率的范围、量化因子分别为:
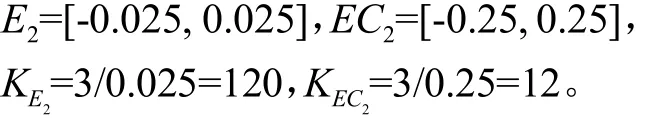
后轴左右车轮悬架与车身连接处的速度与期望值的误差及其变化率、量化因子分别为:
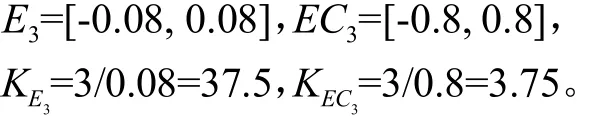
后轴左右车轮悬架车身和车身之间的动行程与其期望值的误差及其变化率、量化因子分别为:
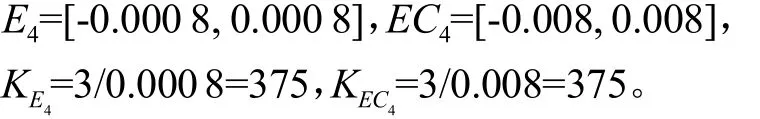
模糊化时各输入输出均采用三角形隶属函数,模糊推理采用Mandain法,解模糊采用重心法。利用MATLAB软件搭建了二维模糊控制结构子系统,模糊控制规则如表2所示。
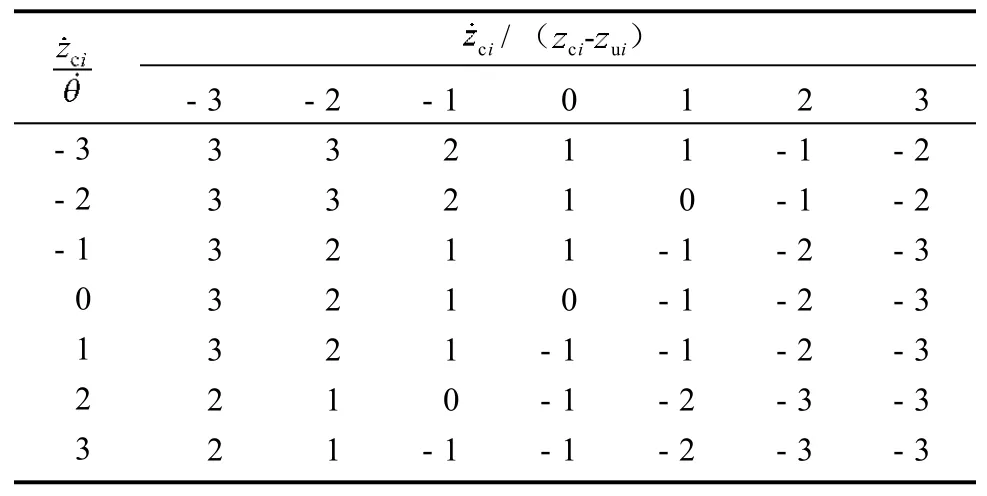
表2 模糊控制规则Table 2 Fuzzy control rules
4 仿真分析
根据整车七自由度被动悬架仿真模型与双模糊控制器模型,搭建的整车主动悬架仿真模型如图6所示。仿真步长为0.005 s,仿真时间为10 s。车身质心处的垂向加速度、俯仰角加速度、侧倾角加速度、悬架动行程、轮胎动行程仿真结果对比曲线如图7~11所示。系统具体性能参数变化如表3所示。
从仿真结果可以得到如下结论。
1)从有效值计算结果可以看出:刚性车身的垂向加速度、俯仰角加速度、悬架1和2动行程、悬架3和4动行程性能提升明显,分别提升27.2%, 19.6%, 95.5%, 33.8%;轮胎动位移改善效果不明显。
2)从最大幅值计算结果可以看出:刚性车身的侧倾角加速度相对被动悬架最大幅值较大,控制效果较差,但有效值性能提升33.3%。刚性车身垂向加速度、俯仰角加速度幅值改善不明显。
3)从多次调试系统仿真结果可以看出:悬架动行程改善较明显,随着第二控制力权系数的增加,悬架动行程改善较积极,符合控制系统位移跟踪控制的特点,但刚性车身垂向加速度增加。此时整车操纵性能有较好的提升,但舒适性较差。

图6 整车主动悬架仿真模型Fig. 6 A simulation model for the active suspension system
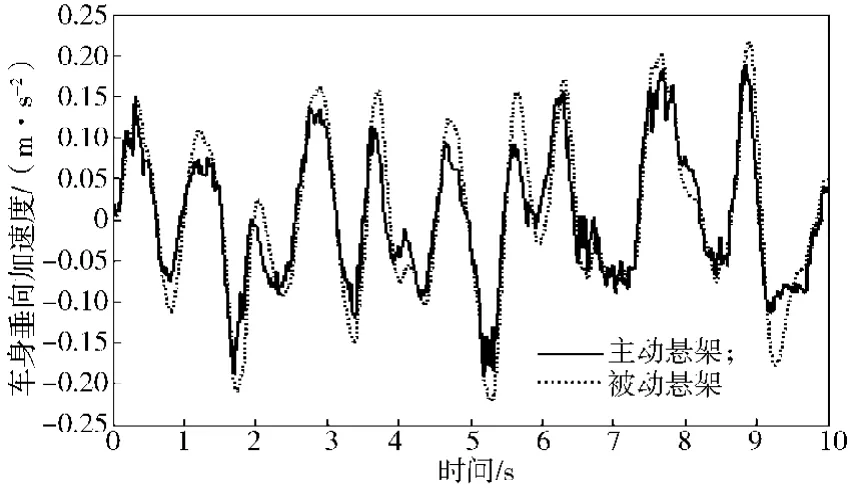
图7 车身垂向加速度Fig. 7 Body vertical acceleration
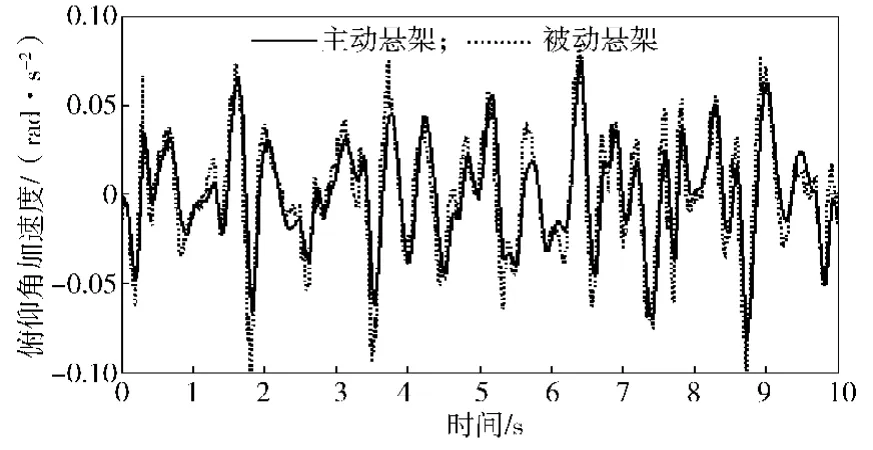
图8 车身俯仰角加速度Fig. 8 Body pitch angular acceleration
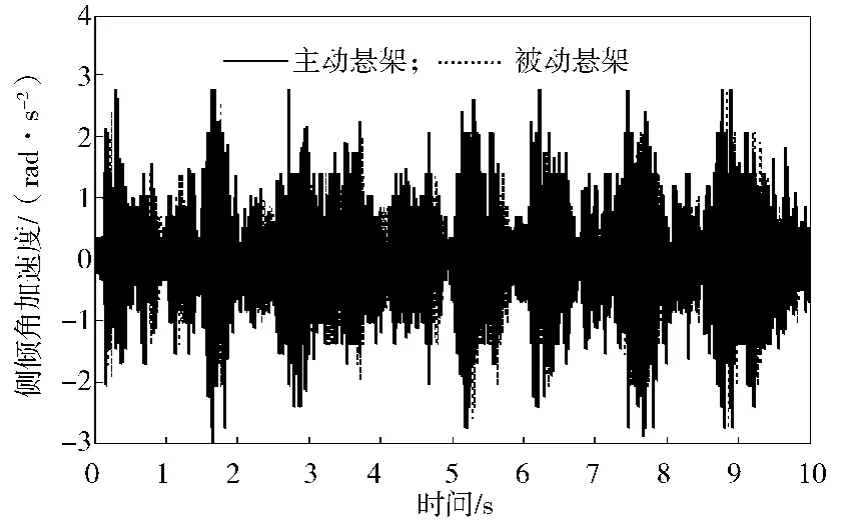
图9 车身侧倾角加速度Fig. 9 Body roll angular acceleration
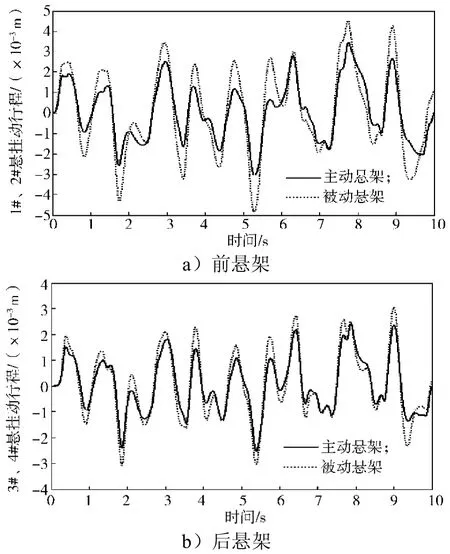
图10 悬架动行程Fig. 10 Suspension dynamic displacement
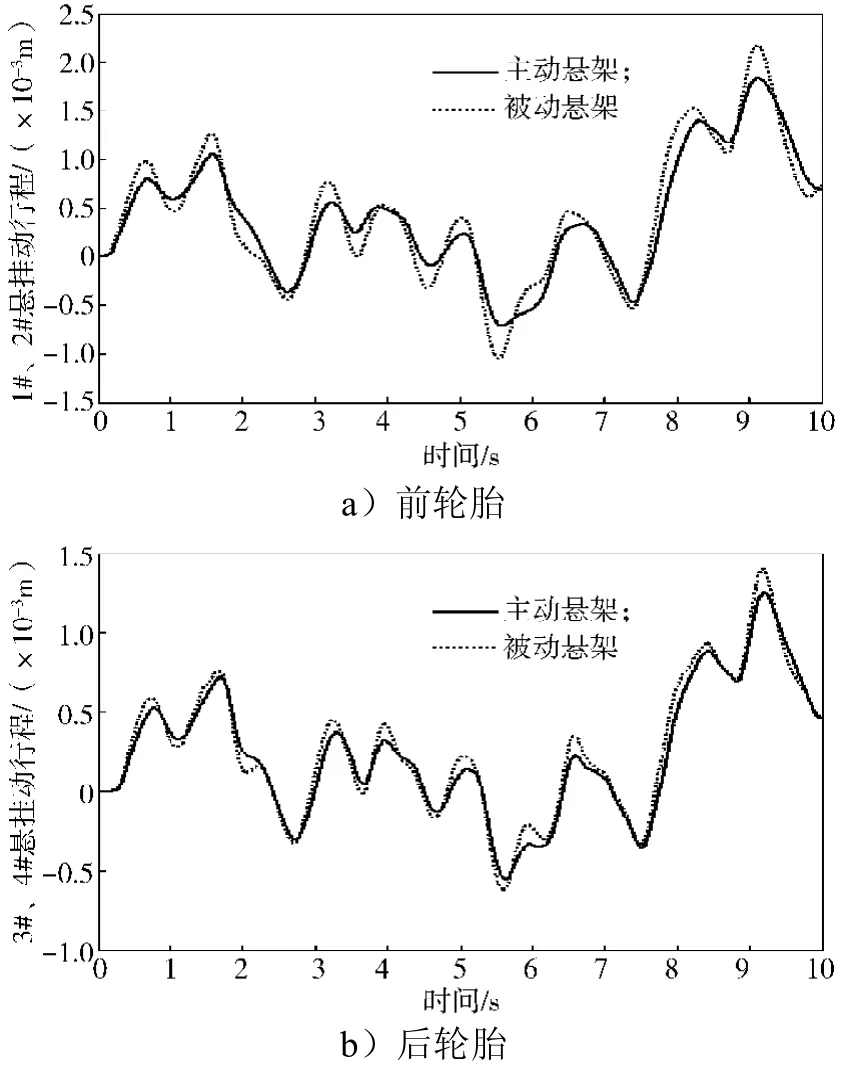
图11 轮胎动行程Fig. 11 Tire dynamic displacement
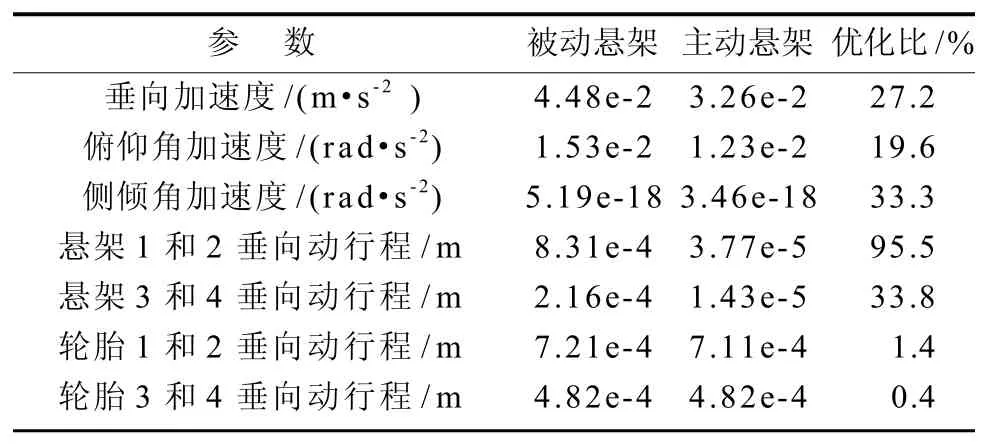
表3 性能均方根值对比Table 3 Contrast between performance RMS values
5 结语
本文提出了双模糊控制策略,建立了整车七自由度主动悬架仿真模型。双模糊控制器控制主动控制力。总控制力为第一、二控制力输出量之和,调整加权系数可以调节第一、二控制力在总控制力中的比重。通过仿真分析,可得如下结论:1)车身质心处的垂向加速度、俯仰角加速度及侧倾角加速度、车轮1~4悬架动行程、车轮1~4悬架垂向加速度都有改善,其中车身垂向加速度、俯仰角加速度、侧倾角加速度、悬架1和2动行程、悬架3和4动行程改善非常明显,分别提升27.2%, 19.6%, 33.3%, 95.5%, 33. 8%;2)相比传统模糊控制器,双模糊控制器对整车参数不敏感,系统的综合特性较好,鲁棒性强。
[1]张 昆,习文辉,邓文华,等. 基于CarSim-Simulink联合仿真的整车半主动悬架模糊控制仿真研究[J]. 昆明理工大学学报(自然科学版),2015,40(1) :39-44. ZHANG Kun,XI Wenhui,DENG Wenhua,et al. Fuzzy Control Simulation of Full Vehicle Semi-Active Suspension Based on Carsim-Simulink Co-Simulation[J]. Journal of Kunming University of Science and Technology(Natural Science Edition),2015,40(1) :39-44.
[2]周 兵,赵保华. 汽车主动悬架自适应模糊PID控制仿真研究[J]. 湖南大学学报(自然科学版),2009,36(12) :27-30. ZHOU Bing,ZHAO Baohua. Simulation Study of Self-Adaptive Fuzzy-PID Control of Active Suspension[J]. Journal of Hunan University(Natural Sciences),2009,36(12) :27-30.
[3]刘 静. 带天棚阻尼的1/2车辆主动悬架仿真研究[J]. 公路与汽运,2015,166(3) :15-20,80. LIU Jing. A Simulation Research on Half-Car Active Suspension System with Skyhook Damper[J]. Highways & Automotive Applications,2015,166(3) :15-20,80.
[4]杨礼康. 基于磁流变技术的车辆半主动悬挂系统理论与试验研究[D]. 杭州:浙江大学,2003. YANG Likang. The Theoret1ea1 and Experimental Investigation on Semi-Aet1ve Vehiele Suspension Emp1oying Magneto-Rheologieal Teehnology[D]. Hangzhou:Zhejiang University,2003.
[5]唐志桥. 二分之一车辆悬架系统的动力学仿真研究[J]. 公路与汽运,2015(1) :5-8,56. TANG Zhiqiao. Dynamics Simulation of Half Vehicle Suspension System[J]. Highways & Automotive Applications,2015(1) :5-8,56.
[6]HUANG Chen,CHEN Long,JIANG Haobin,et al. Fuzzy Chaos Control for Vehicle Lateral Dynamics Based on Active Suspension System[J]. Chinese Journal of Mechanical Engineering,2014,27(4) :793-801.
[7]YOSHIMURA T,ITARU T. Active Suspension Control of a One-Wheel Car Model Using Singlei-Nput Rule Modules Fuzzy Reasoning and a Disturbance Observer[J]. Journal of Zhejiang University-Science A:Applied Physics & Engineering,2005,6(4) :251-256.
[8]DOYNG X,YU M. Genetic Algorithm Based Fuzzy Logic Control for a Magneto-Rheological Suspension[J]. Journal of Vibration and Control,2013,20(9) :1343-1355.
[9]TAO Sun,HUANG Zhenyu,CHEN Dayue,et al. Signal Frequency Based Self-Tuning Fuzzy Controller for Semi-Activesuspension System[J]. Journal of Zhejiang University-Science A:Applied Physics & Engineering,2003,4(4) :426-432.
[10]YU Yang,WEI Xuexia,ZHANG Yongfa. Analyses and Simulation of Fuzzy Logic Control for Suspension System of a Track Vehicle[J]. Journal of Beijing Institute of Technology,2008,17(2) :164-167.
[11]XU Xing,ZHOU Kongkang,ZOU Nannan,et al. Hierarchical Control of Ride Height System for Electronically Controlled Air Suspension Based on Variable Structure and Fuzzy Control Theory[J]. Chinese Journal of Mechanical Engineering,2015,28(5) :945-953.
[12]SU Xiaojie,YANG Xiaozhan,SHI Peng,et al. Fuzzy Control of Nonlinear Electromagnetic Suspension Systems [J]. Mechatronics,2014,24(4) :328-335.
[13]LI Rui,CHEN Weimin,LIAO Changrong,et al. Fuzzy Hybrid Control of Vibration Attitude of Full Car via Magneto-Rheological Suspensions[J]. Chinese Journal of Mechanical Engineering,2010,23(1) :72-79.
[14]NGUYEN S D,CHOI S B. A Novel Minimum-Maximum Data-Clustering Algorithm for Vibration Control of a Semi-Active Vehicle Suspension System[J]. Noise & Vibration Bulletin, 2013,227(9) :1242-1254.
[15]GUAN Jifu,GU Liang,HOU Chaozhen,et al. Fuzzy Logic Control for Semi-Active Suspension System of Tracked Vehicle[J]. Journal of Beijing Institute of Technology,2004,13(2) :113-117.
(责任编辑:邓 彬)
A Simulation Research on Seven DOF Semi-Active Full Vehicle Suspension
WANG Xiaopeng1,2,3,4,LIU Jianjun1,2,WU Long1,2
(1. School of Mechanical & Electronic Engineering,Sanming University,Sanming Fujian 365004,China ;2. Engineering Research Center in Fujian Province University for Modern Mechanical Design and Manufacturing Technology,Sanming Fujian 365004,China ;3. Fujian Provincial Collaborative Innovation Center for Green Casting,Forging and Advanced Manufacturing,Sanming Fujian 365004,China ;4. Fujian Provincial Engineering Research Center for Casting and Forging Parts,Sanming Fujian 365004,China)
A dynamic simulation model of seven DOF full vehicle has been established by using MATLAB software. By adopting the dual mode fuzzy controller as the semi-active suspension, the velocity of rigid body and suspension joints, as well as the input quantity, with the dynamic displacement and pitch angle parameters being the active suspension control, are to be worked out. The front left and right wheels are to take the error between the speed of the connection linking the suspension and the body and the expected value, as well as its rate of change, as the input quantity of the first control force, and to take the error between the angular velocity of the rigid body and the expected value, as well as its rate of change, as the input quantity of the second control force. The rear left and right wheels are to take the error between the speed of the connection linking the suspension and the body and the expected value, as well as its rate of change, as the input quantity of the first control force, and to take the error between the suspension working space and the expected value, as well as its rate of change, as the input quantity of the second control force. The numerical results of the simulation show that the adoption of the dual fuzzy controller helps to greatly improve the ride comfort and stability in vehicle driving, with a better performance exhibited in the comprehensive system, and with a significant increase as high as 27.2% in the rigid body vertical acceleration, 19.6% in the pitch angular acceleration, 95.5% in the dynamic travel performance of the front suspension, and 33.8% in the dynamic travel performance of the rear suspension, respectively.
U270.1
A
1673-9833(2016)06-0012-06
10.3969/j.issn.1673-9833.2016.06.003
2016-08-15
福建省省属高校科研专项基金资助项目(JK2014048)
王孝鹏(1983-),男,山西运城人,三明学院讲师,主要研究方向为车辆系统动力学及控制,E-mail:mrxp1984@163.com

