MRI与MR关节造影诊断腕三角纤维软骨撕裂准确性的Meta分析
孟祥虹 MENG Xianghong王 植 WANG Zhi万业达 WAN Yeda
MRI与MR关节造影诊断腕三角纤维软骨撕裂准确性的Meta分析
孟祥虹1MENG Xianghong
王 植1WANG Zhi
万业达2WAN Yeda
作者单位 1.天津市天津医院放射2科 天津 300211 2.天津市天津医院放射1科 天津 300211
目的正确诊断腕三角纤维软骨(TFC)有无撕裂及评价撕裂程度对合理治疗至关重要,目前多采用MRI进行诊断。本文采用Meta分析评价MRI和MR关节造影(MRA)对TFC撕裂的诊断价值。资料与方法检索万方、维普数据库及CNKI等中文数据库,Cochrane图书馆、Medline、Embase及PubMed等英文数据库,搜集符合纳入标准的文献,提取文献的一般信息,使用诊断试验准确性研究质量工具进行文献质量评价。检验文献的异质性,计算MRI及MRA诊断TFC撕裂的汇总敏感度、特异度,并绘制汇总受试者工作特征曲线。结果共获取符合纳入标准的文献15篇,其中中文2篇,英文13篇,各研究间存在异质性。MRI诊断TFC撕裂的汇总加权敏感度、特异度分别为0.66(95% CI 0.61~0.71)、0.75(95% CI 0.69~0.81),而MRA诊断TFC撕裂的汇总加权敏感度、特异度分别为0.80(95% CI 0.73~0.87)、0.86(95% CI 0.74~0.93)。MRI诊断TFC撕裂的汇总受试者工作特征曲线下面积、Q*指数分别为0.8566、0.7875,而MRA诊断TFC撕裂的汇总受试者工作特征曲线下面积、Q*指数分别为0.9123、0.8446。结论MRA诊断TFC撕裂的准确性高于MRI,常规MRI诊断TFC撕裂不明确时,可考虑采用MRA进一步检查。
腕三角纤维软骨;撕裂;磁共振成像;磁共振关节造影; Meta分析
腕三角纤维软骨(triangular fibrocartilage,TFC)是腕尺侧部的重要结构[1],TFC撕裂会引起患者腕尺侧部慢性疼痛、下尺桡及尺腕关节失稳等症状[2]。临床上主要依靠MRI平扫及MR关节造影(magnetic resonance arthrography,MRA)诊断TFC撕裂,并评价撕裂的部位和程度[3-4]。MRA可以发现常规MRI检查不能显示的TFC撕裂[5]。本研究拟收集国内外公开发表的相关文献进行系统性评价和Meta分析,探讨MRI及MRA对TFC撕裂的诊断准确性。
1 资料与方法
1.1 文献检索 本研究主要检索中文数据库万方数据、维普数据库及CNKI,英文数据库Cochrane图书馆、Medline、Embase及Pubmed,发表时间为1990年1月—2014年12月。中文检索词为“三角纤维软骨盘”、“三角纤维软骨复合体”、“磁共振成像”、“MR”、“磁共振关节造影”、“MRA”;英文检索词包括“triangular fibrocartilage”“TFC”“triangular fibrocartilage complex”、“TFCC”、“Magnetic Resonance”、“MR”、“magnetic resonance arthrography”、“MR arthrography”、“MRA”、“wrist”、“wrist joint”。
1.2 文献筛选 纳入标准:①1990年1月—2014年12月公开发表的文献;②英文及中文文献;③研究目的为评价MRI和(或)MRA对腕三角纤维软骨或三角纤维软骨复合体撕裂的诊断准确性;④研究对象均进行MRI和(或)MRA检查,并以关节镜或开放手术为“金标准”进行诊断及治疗;⑤文献研究类型为前瞻性或回顾性研究;⑥研究对象≥10例;⑦能直接或间接获得MRI和(或)MRA检查腕三角纤维软骨撕裂的真阳性值、假阳性值、真阴性值、假阴性值。排除标准:①非英文文献;②研究对象<10例;③研究对象为尸体、动物及儿童的文献;④文摘、综述、讲座、述评及其他非论著的文献。
1.3 文献质量评价及纳入研究信息提取 由1名主治医师及1名主任医师对纳入文献使用Cochrane 协作网的诊断试验准确性研究质量(quality assessment of diagnostic accuracy studies,QUADAS)工具[6-7]进行评价,并提取所需要的纳入研究信息,意见不同时讨论达成一致意见。
1.4 统计学方法 采用Revman 5.3及Meta-Disc软件,异质性分析采用Cochrane Q检验,并计算I2值[8]。若I2为0~25%则异质性可忽略,I2为26%~50%提示研究间具有低度异质性,I2为51%~75%提示研究间具有中度异质性,I2>75%提示研究间具有高度异质性。若研究间存在异质性,选择随机效应模型进行Meta分析;若研究具有同质性,选择固定效应模型进行分析。计算纳入文献的汇总敏感度、特异度及95%可信区间(CI),使用森林图描述结果。使用Mantel-Haenszel回归模型绘制汇总受试者工作特征曲线(summary receiver operating characteristic,SROC)。
2 结果
2.1 纳入文献情况 根据文献标题初筛相关文献共852篇,排除重复文献后剩余303篇,经阅读标题及摘要,获得符合纳入标准的文献28篇。经仔细阅读全文,排除文献13篇,其中1篇为外文摘要翻译,6篇无“金标准”对照,3篇研究内容不符合标准,2篇研究对象为尸体,1篇不能获得原始数据。最终获得文献15篇,其中中文2篇,英文13篇,文献的基本特征见表1。
2.2 QUADAS质量评价结果 见图1。QUADAS评价结果显示,大部分研究的“金标准”和待评价试验的间隔时间不明确,“金标准”待评价试验的操作描述不清,待评价试验和“金标准”结果判读时是否互相知晓不明确。所有研究均为报告难以解释的试验结果的原因。绝大多数研究对退出研究的病例未做解释。
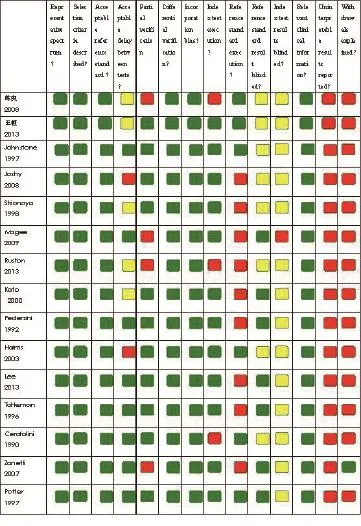
图1 15篇纳入研究的QUADAS工具评价结果。图中绿框示满足此条目,红框示不满足此条目,黄框示部分满足或从文献中无法得到
2.3 Meta分析结果
2.3.1 异质性检验 MRI诊断TFC撕裂在各研究间存在高度异质性(I2=93.3%),MRA诊断TFC撕裂在各研究间亦存在高度异质性(I2=82.7%),因此,本研究采用随机效应模型进行汇总分析。
2.3.2 MRI及MRA诊断TFC撕裂的结果见表2及图2~4。
3 讨论

表1 15 篇纳入文献的基本特征

表2 MRI和MRA诊断TFC撕裂的汇总加权敏感度、特异度及95% CI和SROC曲线的AUC和Q*指数

图2 MRI诊断TFC撕裂敏感度(A)及特异度(B)森林图

图3 MRA诊断TFC撕裂的敏感度(A)及特异度(B)森林图

图4 MRI(A)及MRA(B)诊断TFC撕裂的SROC曲线
本研究收集1990年1月—2014年12月在国内外公开发表的关于MRI及MRA对TFC撕裂诊断准确性研究的中英文文献,运用QUADAS工具对纳入文献进行系统评价,并使用Meta分析对纳入文献进行汇总统计。目前对MRI和MRA诊断TFC撕裂准确性研究的原始文献样本量一般较小,诊断效能不足,而使用Meta分析可增加样本量,提高诊断效能[20],使研究结果更加具有统计学意义。
本研究发现,MRA诊断TFC撕裂诊断的敏感度为0.80,特异度为0.86,SROC曲线下面积及Q*指数为0.9123和0.8446,均高于常规MRI检查的对应指标。因此,对临床高度可疑TFC撕裂,而常规MRI检查无明显阳性发现的患者可考虑使用MRA检查以提高诊断准确性。然而,由于MRA为有创性检查,存在伤口感染、诱发疼痛、对比剂过敏等缺陷,是否将MRA作为临床常规诊断TFC撕裂的检查方法尚存在争议。
Smith等[21]采用Meta分析对MRI和MRA诊断TFC撕裂的准确性进行评价,结果发现,MRI诊断的汇总敏感度和特异度分别为0.75和0.81,而MRA诊断的汇总敏感度和特异度分别为0.84和0.95。本研究结果显示,MRI和MRA诊断的汇总敏感度和特异度分别为0.66、0.75及0.80、0.86,均低于Smith等[21]的报道结果,推测造成结果差异的原因可能与收集文献的数据库范围、语言和年限等有关。
本研究发现,各纳入研究间研究人群、样本量、检查设备、对比剂注入部位及浓度、图像分析人员信息、诊断标准等的差别很大,造成研究间有较大的异质性:①各研究的样本量差别较大,为10~102例,研究人群的年龄多在30~40岁。②各研究所应用的MR磁场强度从0.2T到3.0T不等,多使用1.5T进行检查,而使用3.0T设备进行检查的仅有2项研究,提示还需用3.0T设备进行大样本研究才能得到符合当今MRI检查情况的较为客观、准确的数据。③部分研究对从进行MRI检查后到行关节镜手术的时间介绍不清,还有部分研究在行MRI检查后半年以上才行关节镜检查,时间间隔过长可能造成患者在此期间TFC病变已发生变化。大部分研究图像分析人员的人数、工作年限和职称不清,这些均容易对研究结果的准确性产生怀疑。④在行MRA检查时,对比剂多注入桡腕关节,也有研究将对比剂注入腕中及下尺桡关节。对比剂多使用生理盐水稀释的Gd-DTPA,但稀释的浓度及对比剂注入量在各研究间无统一标准。⑤大多数研究对关节镜操作的具体步骤描述过于简单而不能按照作者的描述进行重复操作。⑥各研究对图像分析人员和关节镜手术人员是否知晓对方检查结果的介绍不清楚或未介绍,降低了研究结果的可信程度。⑦Kato等[2]对MRI诊断TFC撕裂的敏感度、王植等[9]对MRI的诊断特异度、Magee[11]对MRA的诊断敏感度和陈爽等[8]对MRA的诊断特异度明显低于其他研究,其原因为陈爽等[8]和王植等[9]的研究所使用的磁场强度为0.2T和0.35T,低场强图像的伪影较重,信噪比低,不容易发现较小的撕裂灶,假阴性较高;而Kato等[2]和Magee[11]所制订TFC撕裂的诊断标准较为严格,降低了诊断敏感度。
本研究的局限性在于:本研究未收集尚未发表的文献和会议摘要,有可能产生偏倚;本研究仅纳入中英文文献,无其他语言文献,也可能产生结果偏倚。
总之,MRA诊断TFC撕裂的准确度高于MRI,各研究对MRI诊断腕关节TFC撕裂的研究方法不统一,文章质量参差不齐。
[1]Johnstone DJ,Thorogood S,Smith WH,et al. A comparison of magnetic resonance imaging and arthroscopy in the investigation of chronic wrist pain. J Hand Surg Br,1997,22(6): 714-718.
[2]Kato H,Nakamura R,Shionoya K,et al. Does high-resolution MR imaging have better accuracy than standard MR imaging for evaluation of the triangular fibrocartilage complex? J Hand Surg Br,2000,25(5): 487-491.
[3]Joshy S,Ghosh S,Lee K,et al. Accuracy of direct magnetic resonance arthrography in the diagnosis of triangular fibrocartilage complex tears of the wrist. Int Orthop,2008,32(2): 251-253.
[4]Cerny M,Marlois R,Theumann N,et al. 3-T direct MR arthrography of the wrist: value of finger trap distraction to assess intrinsic ligament and triangular fibrocartilage complex tears. Eur J Radiol,2013,82(10): e582-e589.
[5]Rüegger C,Schmid MR,Pfirrmann CW,et al. Peripheral tear of the triangular fibrocartilage: depiction with MR arthrography of the distal radioulnar joint. Am J Roentgenol,2007,188(1): 187-192.
[6]Whiting PF,Weswood ME,Rutjes AW,et al. Evaluation of QUADAS,a tool for the quality assessment of diagnostic accuracy studies. BMC Med Res Methodol,2006,6: 9.
[7]Whiting P,Rutjes AW,Dinnes J,et al. Development and validation of methods for assessing the quality of diagnostic accuracy studies. Health Technol Assess,2004,8(25): iii,1-234.
[8]陈爽,徐文东,冯晓源. MR直接关节造影在腕三角纤维软骨复合体损伤中的应用. 中华放射学杂志,2008,42(3): 242-246.
[9]王植,孟祥虹,王林森,等. 腕三角纤维软骨盘损伤:STIR序列诊断与关节镜对照. 国际医学放射学杂志,2013,36(4): 311-314.
[10]Shionova K,Nakamura R,Imaeda T,et al. Arthrography is superior to magnetic resonance imaging for diagnosing injuries of the triangular fibrocartilage. J Hand Surg Br,1998,23(3): 402-405.
[11]Magee T. Comparison of 3-T MRI and arthroscopy of intrinsic wrist ligament and TFCC tears. Am J Roentgenol,2009,192(1): 80-85.
[12]Ruston J,Konan S,Rubinraut E,et al. Diagnostic accuracy of clinical examination and magnetic resonance imaging for common articular wrist pathology. Acta Orthop Belg,2013,79(4): 375-380.
[13]Pederzini L,Luchetti R,Soragni O,et al. Evaluation of the triangular fibrocartilage complex tears by arthroscopy,arthrography,and magnetic resonance imaging. Arthroscopy,1992,8(2): 191-197.
[14]Haims AH,Schweitzer ME,Morrison WB,et al. Internal derangement of the wrist: indirect MR arthrography versus unenhanced MR imaging. Radiology,2003,227(3): 701-707.
[15]Lee YH,Choi YR,Kim S,et al. Intrinsic ligament andtriangular fibrocartilage complex (TFCC) tears of the wrist: comparison of isovolumetric 3D-THRIVE sequence MR arthrography and conventional MR image at 3 T. Magn Reson Imaging,2013,31(2): 221-226.
[16]Totterman SM,Miller RJ,Mccance SE,et al. Lesions of the triangular fibrocartilage complex: MR findings with a threedimensional gradient-recalled-echo sequence. Radiology,1996,199(1): 227-232.
[17]Cerofolini E,Luchetti R,Pederzini L,et al. MR evaluation of triangular fibrocartilage complex tears in the wrist: comparison with arthrography and arthroscopy. J Comput Assist Tomogr,1990,14(6): 963-967.
[18]Zanetti M,Bräm J,Hodler J. Triangular fibrocartilage and intercarpal ligaments of the wrist: does MR arthrography improve standard MRI? J Magn Reson Imaging,1997,7(3): 590-594.
[19]Potter HG,Asnis-Ernberg L,Weiland AJ,et al. The utility of high-resolution magnetic resonance imaging in the evaluation of the triangular fibrocartilage complex of the wrist. J Bone Joint Surg Am,1997,79(11): 1675-1684.
[20]李晓翠,苗丽琼,钱靖,等. PET/CT诊断非小细胞肺癌纵隔淋巴结分期的准确性研究——Meta分析. 中国医学影像学杂志,2014,22(7): 540-546.
[21]Smith TO,Drew B,Toms AP,et al. Diagnostic accuracy of magnetic resonance imaging and magnetic resonance arthrography for triangular fibrocartilaginous complex injury. J Bone Joint Surg Am,2012,94(9): 824-832.
(本文编辑 张春辉)
MRI and MRA in Detecting Wrist Triangular Fibrocartilage Tear: A Meta-analysis
PurposeAccurate diagnosis of triangular fibrocartilage (TFC) tear is very important for treatment. MRI is most used for diagnosing TFC tear. This paper aims to evaluate MRI and MR arthrography (MRA) for diagnosing TFC tear by meta-analysis.Materials and MethodsThe articles were searched in the databases such as Wanfang,VIP,CNKI,Cochrane Library,Medline,Embase and PubMed. The QUADAS items were used to evaluate the quality of the included studies. Heterogeneity of the included articles was tested. The pooled weighted sensitivity and specificity of MRI and MRA in diagnosing TFC tear were calculated,and the pooled receiver operation curve was drawn.ResultsFifteen articles met the inclusion criteria,2 were Chinese articles and 13 were English articles. The subjects and methods of the articles were different and existed heterogeneity. The sensitivity and specificity of MRI for diagnosing TFC tear were 0.66 (95% CI 0.61-0.71) and 0.75 (95% CI 0.69-0.81),and those of MRA were 0.80 (95% CI 0.73-0.87) and 0.86 (95% CI 0.74-0.93). The area under curve and Q* index of SROC of MRI were 0.8566 and 0.7875,respectively. The area under curve and Q* index of SROC of MRA were 0.9123 and 0.8446,respectively.ConclusionThe accuracy of TFC tear avulsion for MRA are higher than for MRI,when there is unclear of TFC avulsion using MRI,MRA can be used for diagnosis.
Triangular Fibrocartilage; Tear; MRI; MRA; Meta analysis
10.3969/j.issn.1005-5185.2015.11.020
王 植
Second Department of Radiology,Tianjin Hospital,Tianjin 300211,China
Address Correspondence to: WANG Zhi E-mail: wz_13820256789@sina.com
R681.3;R445.2
2015-04-11
修回日期:2015-09-18
中国医学影像学杂志2015年 第23卷11期:865-870
Chinese Journal of Medical Imaging 2015 Volume 23(11): 865-870

