组织芯片检测凋亡抑制蛋白Livin在前列腺癌中的表达及意义
朱永锋,张春霆
组织芯片检测凋亡抑制蛋白Livin在前列腺癌中的表达及意义
朱永锋1,张春霆2
目的:检测凋亡抑制蛋白Livin在前列腺癌中的表达及其与临床病理特征的关系。方法:采用组织芯片技术构建71例前列腺癌和37例前列腺增生组织的64点阵石蜡组织芯片,用免疫组化SP法检测该芯片中凋亡抑制蛋白Livin的表达,分析其与前列腺癌临床病理特征的关系。结果:凋亡抑制蛋白Livin在前列腺癌组织中的阳性表达率为60.94%,在前列腺增生组织中阳性表达率为2.70%(P<0.01)。Livin表达与前列腺癌Gleason评分和临床分期有关,Livin在Gleason<7分的阳性表达率为41.67%,Livin在≥7分的表达率为85.71%,在前列腺癌Ⅰ~Ⅱ期和Ⅲ~Ⅳ期阳性表达率分别为53.66%和82.61%(P<0.05)。结论:凋亡抑制蛋白Livin表达与前列腺癌的发生进展关系密切。
前列腺癌;Livin;组织芯片;免疫组织化学
前列腺癌已经成为严重危害我国男性健康的疾病之一[1],其发生进展是一个多因素多阶段的过程,涉及多个基因的表达异常。Livin基因为凋亡抑制蛋白家族(IAPs)的凋亡抑制基因。研究发现,Livin的异常表达与多种肿瘤的发生进展有关,包括肾癌[2],膀胱癌[3],肺癌[4],肝癌[5]等。本研究采用组织芯片检测71例前列腺癌和37例前列腺增生组织Livin蛋自的表达,分析Livin在前列腺癌中的表达状况及其与临床病理特征的关系。
1 资料与方法
1.1一般资料71例前列腺癌组织标本来自浙江省金华市人民医院2001—2011年病理组织库标本,患者年龄54~78岁,平均(65.5±6.4)岁。前列腺增生组织取自同期非肿瘤患者。前列腺癌根据Gleason评分系统标准,Gleason评分<7分的39例,Gleason评分≥7分的32例。临床分期按照2002年AJCC的TNM分期标准,Ⅰ~Ⅱ期41例,Ⅲ~Ⅳ期30例。前列腺癌患者术前均未接受放疗、化疗和内分泌治疗。经院伦理委员会批准,患者或其家属均签署疾病知情同意书。
1.2实验方法构建2个8×8点阵的组织芯片,一个用于免疫组化染色,一个用于阴性对照。标本经10%甲醛溶液固定,石蜡包埋,3μm厚连续切片。对制成芯片的所有组织进行点阵(SP试剂盒和DAB显色剂均为北京中杉生物技术公司产品)。根据标记,利用点阵仪对标记完成的组织进行打点取样,黏附于涂有多聚赖氨酸的载玻片上。每例前列腺癌标本和前列腺增生组织标本均取1个点。烤片6 h,芯片制作完成。根据试剂盒说明书进行免疫组化实验过程。前列腺癌组织常规切片后,由二甲苯进行脱蜡,依次经梯度乙醇依次水化。加入兔抗人Livin一抗(浓度1∶100)4℃孵育过夜,PBS洗3次,每次5 min;滴加二抗(生物素标记)室温孵育30 min。PBS洗3次,每次5 min。经DAB进行显色,苏木素进行复染,最后封片、光镜观察。使用PBS缓冲液代替Livin一抗作为阴性对照组。
1.3结果判定Livin染色主要是细胞浆出现蓝褐色颗粒为阳性染色,细胞膜及细胞核表达很少,根据阳性表达细胞数区分表达等级。(-)为阳性表达细胞数<10%,(+)为阳性表达细胞数10%~25%,(++)为阳性表达细胞数26%~50%,(+++)为阳性表达细胞数51%~75%。(++++)为阳性表达细胞数>75%,阳性表达细胞数>10%阳性表达,阳性表达细胞数≤10%为阴性表达。
1.4统计学处理运用SPSS 18.0软件进行统计学分析,对染色结果用成组设计两样本阳性率比较进行χ2检验(或者Fisher概率法),以P<0.05认为差异具有统计学意义。
2 结果
2.1Livin在前列腺癌中的表达免疫组化染色结果发现,Livin主要表达在细胞浆,而在胞膜及胞核中表达不明显(见图1)。
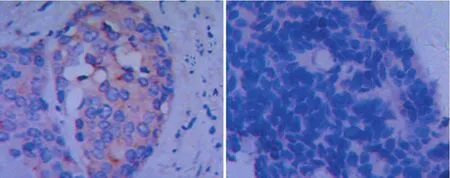
图1 Livin在前列腺癌组织中的表达(×400)
2.2Livin在前列腺癌和前列腺增生组织中的表达
Livin在前列腺癌中呈高表达,染色强度及阳性细胞数明显增高,在前列腺癌组织中表达的阳性率为60.94%(48/71),在前列腺增生组织中阳性表达率为2.70%(1/37)。见表1。
2.3Livin表达与前列腺癌Gleason评分和临床分期之间的关系 Livin在39例前列腺癌<7分的阳性表达率为41.67%(22/39),Livin在32例前列腺癌≥7分的表达率为85.71%(26/32),两者之间比较有差异。在前列腺癌临床分期中,Ⅰ~Ⅱ期表达率53.66%(23/ 41)和Ⅲ~Ⅳ期阳性表达率为82.61%(25/30),两者相比有明显差异(见表1)。
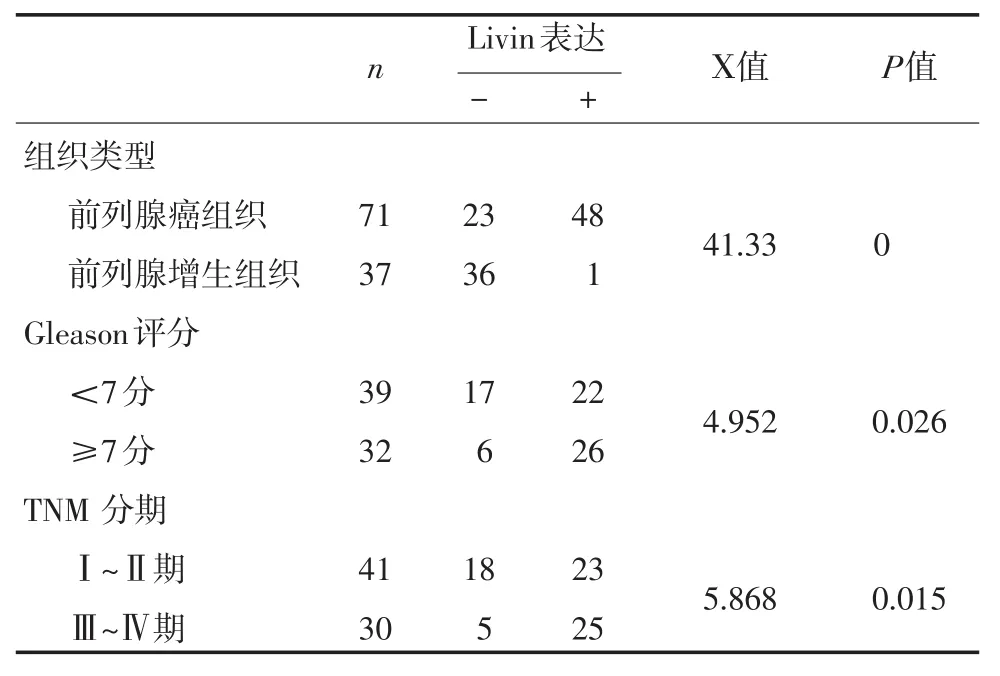
表1 Livin在前列腺癌和前列腺增生组织中的表达
3 讨论
虽然多基因参与了前列腺癌的发生进展,但前列腺癌的发生进展与细胞的增殖和凋亡功能紊乱有关。细胞凋亡可由多种因子、多条信号通路调控,其中凋亡抑制蛋白家族在其调控过程中具重要作用。Livin是一个新发现的凋亡抑制基因.是IAPs成员之一,是人类的一种重要的内源性抗凋亡蛋白,该基因包括两个亚型Livinα和Livinβ[6]。Livin包含一个独特的凋亡抑制蛋白(IAP)结构域重复序列及杆状病毒IAP重复序列(BIR)和一个环指状结构域,Livin基因BIR结构域的突变大大增加了它的不稳定性,BIR结构域的改变可能会出现的抑制活性下降,抑制半胱天冬酶激活因子导致Caspase-3和Caspase-7酶的水解从而抑制了细胞的凋亡[7]。
Livin基因在多种恶性肿瘤和恶性肿瘤细胞中的异常表达,包括恶性黑色素瘤[8]、白血病[9]、膀胱癌、肝细胞癌、肾癌等[10-11]。本实验使用组织芯片和免疫组化SP法对Livin在前列腺癌和增生前列腺组织中的表达状况进行了研究,结果显示,Livin在前列腺增生组织内极少表达。而在前列腺癌内呈现高表达,在前列腺增生组织中表达率为2.78%,在前列腺癌中表达率为67.61%,两者比较差异有统计意义。进一步研究发现,前列腺癌中39例Gleason评分<7分的阳性表达率为56.41%(22/39),在32例前列腺癌Gleason评分≥7分的表达率为82.05%(26/ 32),两者之间比较有差异。在对前列腺癌临床分期中,Ⅰ~Ⅱ期表达率56.10%(23/41),Ⅲ~Ⅳ期阳性表达率为83.33%(25/30),两者相比有明显差异(P<0.05)。研究结果显示,在前列腺癌中Livin的异常表达参与了前列腺癌的发生和进展。国内宋涛等[12]采用通过RT—PCR、免疫组化SP法,检测Livin在62例前列腺癌和10例正常前列腺组织中的表达情况。62例PCa组织中Livin蛋白阳性表达共有37例(59.7%),低分化组Livin蛋白阳性表达率(83.3%),明显高于高分化组(28.6%),其差异有统计学意义。Livin蛋白阳性表达在前列腺癌T1~T2和T3~T4分别为65.0%和77.3%,亦有统计学意义(P<0.05)。本研究的结果与此大致一致。但我们对前列腺癌中Livin蛋白的表达与Gleason评分进行了研究,结果显示,前列腺癌分化程度越低,Livin蛋白阳性表达率愈高。据此推测,Livin可能参与了前列腺癌发生进展,Livin可能是前列腺癌发生和演进中的早期事件之一。
凋亡抑制基因Livin在前列腺癌中表达上调,凋亡抑制基因的表达异常增高可能是前列腺癌发生过程中的早期事件[13]。本研究结果提示,Livin基因在前列腺癌中呈现异常表达,参与了前列腺癌的发生进展。但Livin基因在前列腺癌中表达上调是通过何种机制起作用,是否通过JAK-STAT3或通过影响紧密连接蛋白表达等途径[14-15],靶向干扰Livin表达是否可以抑制前列腺癌细胞的生物学行为,尚需要进一步研究证实。
[1]叶定伟.前列腺癌的流行病学及中国的发病趋势[J].中华外科杂志,2006,44(6):362-364.
[2]Haferkamp A,Bedke J,Vetter C,et al.High nuclear livin expres⁃sion is a favourable prognostic indicator in renal cell carcinoma [J].BJU Int,2008,102(11):1700-1706.
[3]Liu HB,Kong CZ,Zeng Y,et al.Livin may serve as a marker for prognosis of bladder cancer relapse and a target of bladder cancer treatment[J].Urol Oncol,2009,27(3):277-283.
[4]Hariu H,Hirohashi Y,Torigoe T,et al.Aberrant expression and potency as a cancer immunotherapy target of inhibitor of apoptosis protein family,Livin/ML-IAP in lung cancer[J].Clin Cancer Res, 2005,11(3):1000-1009.
[5]Guo H,Gao YT,Zhang Q,et al.Expression and clinical signifi⁃cance of livin protein in hepatocellular carcinoma[J].Dis Markers, 2013,35(5):489-496.
[6]Liu B,Han M,Wen JK,et al.Livin/ML-IAP as a new target for cancer treatment[J].Cancer Lett,2007,250(2):168-176.
[7]Zhang H,Yuan S,Chen H.Induction effects of antisense phospho⁃rothioate oligodeoxynucleotide of livin mRNA on apoptosis in MCF-7 cells[J].Int J Clin Pharmacol Ther,2004,9(12):1353-1356.
[8]Xi RC,Biao WS,Gang ZZ:Significant elevation of survivin and liv⁃in expression in human colorectal cancer:inverse correlation be⁃tween expression and overall survival[J].Onkologie,2011,34(8-9): 428-432.
[9]Ding ZY,Liu GH,Olsson B,et al.Upregulation of the antiapoptotic factor Livin contributes to cisplatin resistance in colon cancer cells [J].Tumor Biol,2013,34(2):683-693.
[10]Yan B:Research progress on Livin protein:an inhibitor of apopto⁃sis[J].Mol Cell Biochem,2011,357(1-2):39-45.
[11]Liang SR,Hu GR,Fang LJ,et al.CpG oligodeoxynucleotides en⁃hance chemosensitivity of 5-fluorouracil in HepG2 human hepato⁃ma cells via downregulation of the antiapoptotic factors survivin and livin[J].Cancer Cell Int,2013,13(1):106.
[12]宋涛,洪宝发,高江平,等.前列腺癌组织中凋亡抑制基因Livin的表达研究[J].中国男科学,2008,14(1):30-33.
[13]Ye L,Song X,Li S,et al.Livin-alpha promotes cell proliferation by regulating G1-S cell cycle transition in prostate cancer[J]. Prostate,2011,71(1):42-51.
[14]朱永锋,张春霆,张洪团,等.组织芯片检测Claudin-3在前列腺癌中的表达[J].中国中西医结合外科杂志,2013,19(6):636-638.
[15]Zhu Z,Li E,Liu Y,et al.Inhibition of Jak-STAT3 pathway en⁃hances bufalin-induced apoptosis incolon cancer SW620 cells[J]. World J Surg Oncol,2012,30(10):228.
(收稿:2014-12-06修回:2015-04-20)
(责任编辑王 丰)
Expression and Significance of Livin Protein in Prostate Cancer with Tissue Microarray
ZHU Yong-feng,ZHANG Chun-ting.Department of Urology,JinHua Profession and Technology College Affiliated JinHua People's Hospital,Jinhua(321000),China
ObjectiveTo detect expression of Apoptosis Inhibitor Protein Livin and clinical pathological characteristics of patients with prostate cancer.MethodsTissue microarray technology was performed in 71 cases of prostate cancer tissues and 37 cases of benign prostatic hyperplasia,microarray and immunohistochemi⁃cal method were used to detect expression of Apoptosis Inhibitor Protein Livin in the chip.An important relation⁃ship was found between the expression of Apoptosis Inhibitor Protein Livin,Gleason score and the clinical stag⁃es of prostate cancer.ResultsIn patients with prostate cancer,Livin positive expression rate was 60.94%,In hyperplasia tissue the expression rate was 2.70%,There was a significant difference(P<0.01).Positive expres⁃sion rate of Livin in Gleason score<7 was 41.67%,the rate of Livin expression in Gleason score≥7 was 85.71%.The positive expression rates inⅠ~ⅡandⅢ~Ⅳstages of prostate cancer were respectively 53.66% and 82.61%,and were significantly different(P<0.05).Livin expression in prostate cancer was significantly re⁃lated to Gleason score and clinical stage(P<0.05).ConclusionAbnormal expression of apoptosis inhibition protein Livin is closely related to the development of prostate cancer.
Prostate cancer;livin;tissue microarray;immunohistochemistry
R737.25
A
1007-6948(2015)03-0221-03
10.3969/j.issn.1007-6948.2015.03.003
1.浙江省金华职业技术学院附属金华市人民医院泌尿外科(金华 321000)
2.浙江大学金华医院泌尿外科(金华 321000)
张春霆,E-mail:chuntingzhang11@163.com

