量子隐形传态
Experimental quantum teleportation
Bouwmeester,D; Pan,JW; Mattle,K; et al.
Unconditional quantum teleportation
Furusawa,A; Sorensen,JL; Braunstein,SL; et al.
Teleportation of continuous quantum variables
Braunstein,SL; Kimble,HJ
Deterministic quantum teleportation with atoms
Riebe,M; Haffner,H; Roos,CF; et al.
量子通信现状与展望*
吴华1,王向斌2,3,4,潘建伟1,3
1 中国科学技术大学公共事务学院,合肥230026
2 清华大学物理系低微量子物理国家重点实验室,北京100084
3 量子信息与量子科学前沿协同创新中心,合肥230026
4 济南量子技术研究院,济南250101
量子信息研究进展
李传锋,郭光灿
热点追踪
量子隐形传态
·编者按·
日前,中国科学技术大学潘建伟院士研究小组在国际上首次成功实现多自由度量子体系的隐形传态,这是自1997年国际上首次实现单一自由度量子隐形传态以来,科学家们经过18年努力在量子信息实验领域取得的又一重大突破,为发展可扩展的量子计算和量子网络技术奠定坚实基础.2015年2月26日,国际权威学术期刊《自然》以封面标题形式发表了这一重大成果,被称为是处于当前量子光学和量子信息领域里的一个伟大的成就.2010年清华大学和北京师范大学研究组在国际上提出了第一个包含两个自由度的多自由度量子体系的隐形传态的理论方案,文章发表在《物理评论A》上,得到了国内外同行关注.2015年3月6日,国际权威物理学期刊《物理评论快报》发表了中国科学技术大学多方量子通信方案,该方案在实用化、远距离多方量子通信方面迈出了重要的一步.
量子通信基于量子力学原理,将微观世界的物质特性运用到通信技术上,在高速传输和高可靠保密通信方面具有优势,成为当今通信技术领域的研究热点之一.量子通信的基本思想主要由Bennett等人于20世纪80年代起相继提出,是利用量子相干叠加、量子纠缠效应进行信息传递的一种新型通信技术,由量子论和信息论相结合而产生,主要包括量子密钥分发(quantum key distribution,QKD)、量子秘密共享(Quantum secret sharing,QSS)、量子安全直接通信(Quantum secure direct communication,QSDC)、量子密集编码和量子隐形传态(quantum teleportation,QT).从物理学角度看,量子通信是在物理极限下利用量子效应现象完成的高性能通信,从物理原理上确保通信的绝对安全,解决了通信技术无法解决的问题,是一种全新的通信方式.从信息学角度看,量子通信是利用量子不可克隆、量子测量塌缩或者量子隐形传态等量子特性,借助量子测量的方法实现两地之间的信息数据传输.量子通信中传输的既有0,1这样的经典信息,也有量子迭加态、纠缠态这样的量子信息,是未来通信技术的重要发展方向.
近十几年来,量子通信的距离和速率都有了飞跃式的提升,一些小规模的量子通信试验网已经建成,验证了量子通信技术网络化的可行性.欧盟已提出将重点发展量子中继和卫星量子通信,实现千公里量级的量子密钥分发;日本国立信息通信研究院计划到2040年建成极限容量、无条件安全的广域光纤与自由空间量子通信网络;美国洛斯阿拉莫斯国家实验室过去几年中则一直在悄悄创建一套辐射状的量子互联网.我国在该领域的发展起步晚,但起点高,进展快,在应用研究的多个方面已经达到世界先进水平.可以预想,随着量子通信技术的产业化和广域量子通信网络的实现,在不久的将来,作为保障未来信息社会通信安全的关键技术,量子保密通信将有望走向大规模应用,成为电子政务、电子商务、电子医疗、生物特征传输和智能传输系统等各种电子服务的驱动器,为当今信息化社会提供基础的安全服务和最可靠的安全保障.
本专题得到了龙桂鲁教授(清华大学物理系)的大力支持.
·热点数据排行·
截至2015年3月20日,中国知网(CNKI)和Web of Science(WOS)的数据报告显示,以量子通信的分支“量子隐形传态(Quantum Teleportation)”为词条可以检索到的期刊文献分别为427与644条,本专题将相关数据按照:研究机构发文数、作者发文数、期刊发文数、被引用频次进行排行,结果如下.
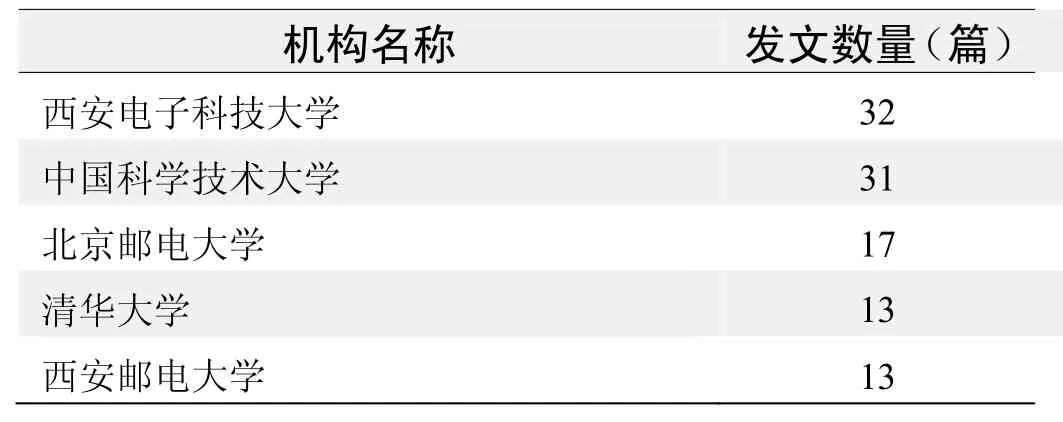
研究机构发文数量排名(CNKI)
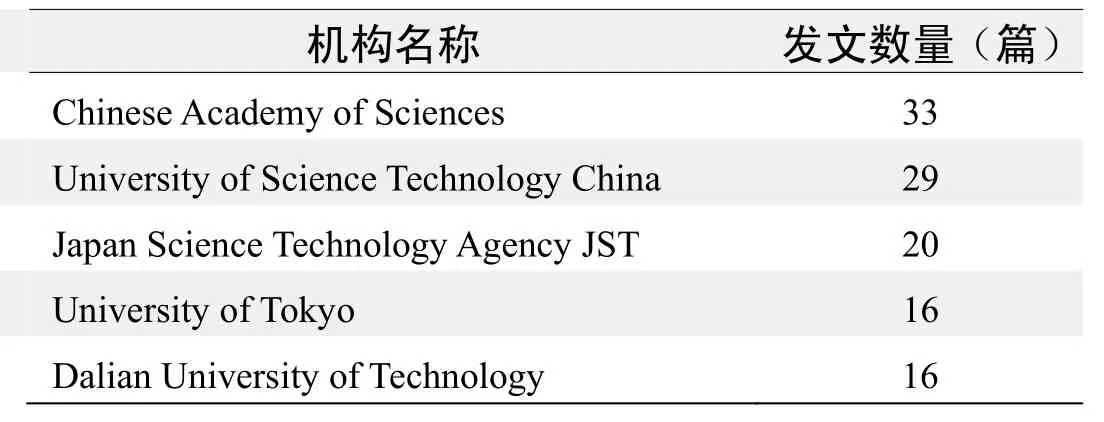
研究机构发文数量排名(WOS)
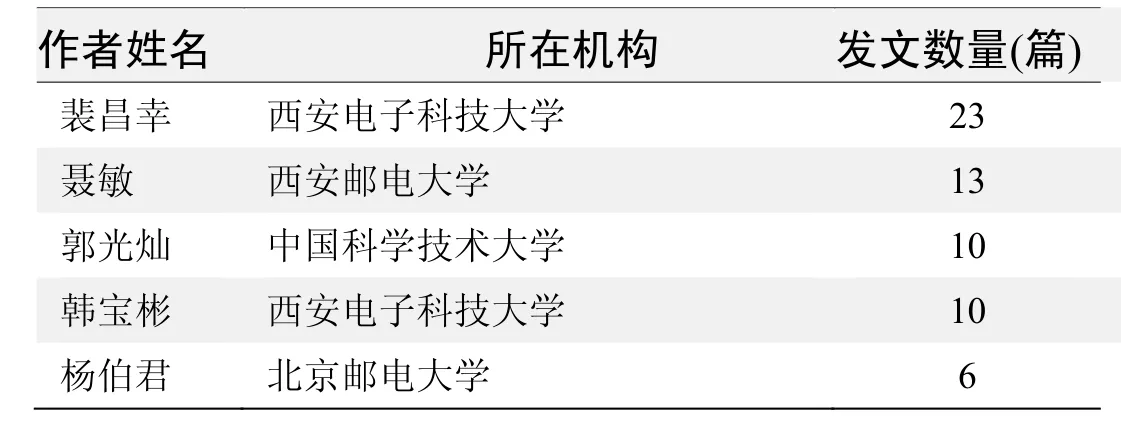
作者发文数量排名(CNKI)

作者发文数量排名(CNKI)
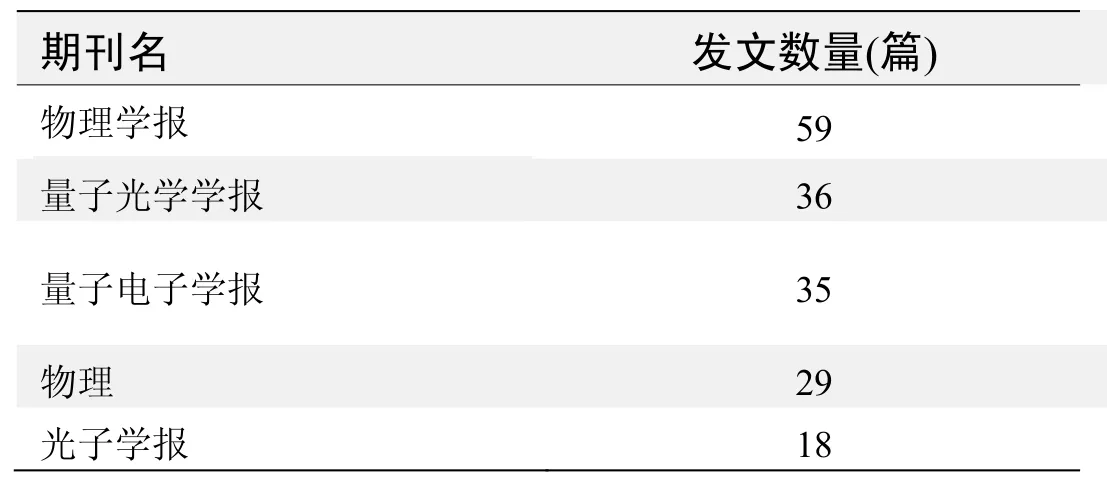
期刊发文数量排名(CNKI)

期刊发文数量排名(WOS)
根据中国知网(CNKI)数据报告,以量子隐形传态为词条可以检索到的高被引论文排行结果如下.
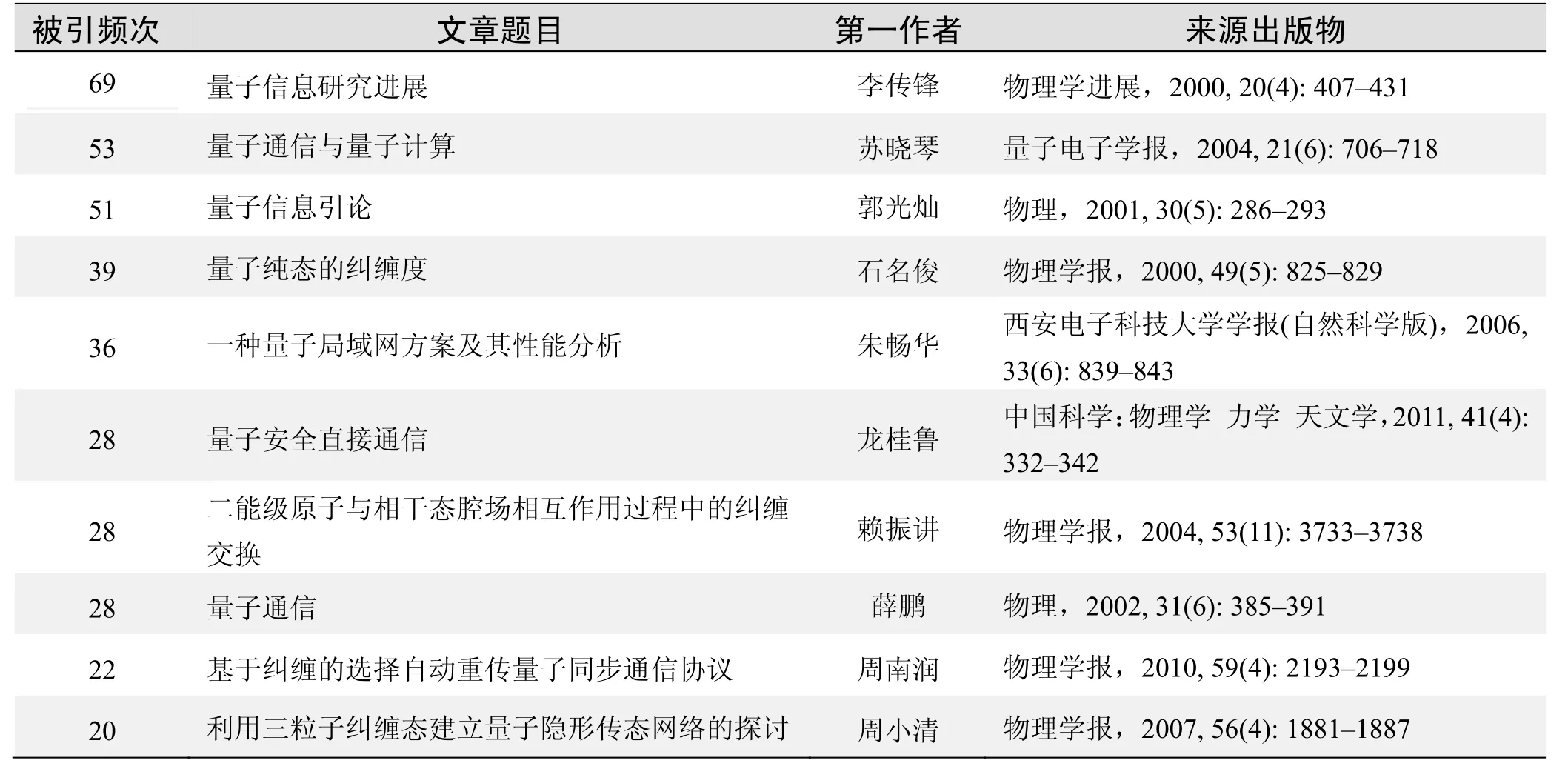
国内数据库高被引论文排行
根据Web of Science统计数据,以量子隐形传态(Quantum Teleportation)为词条可以检索到的高被引论文排行结果如下.
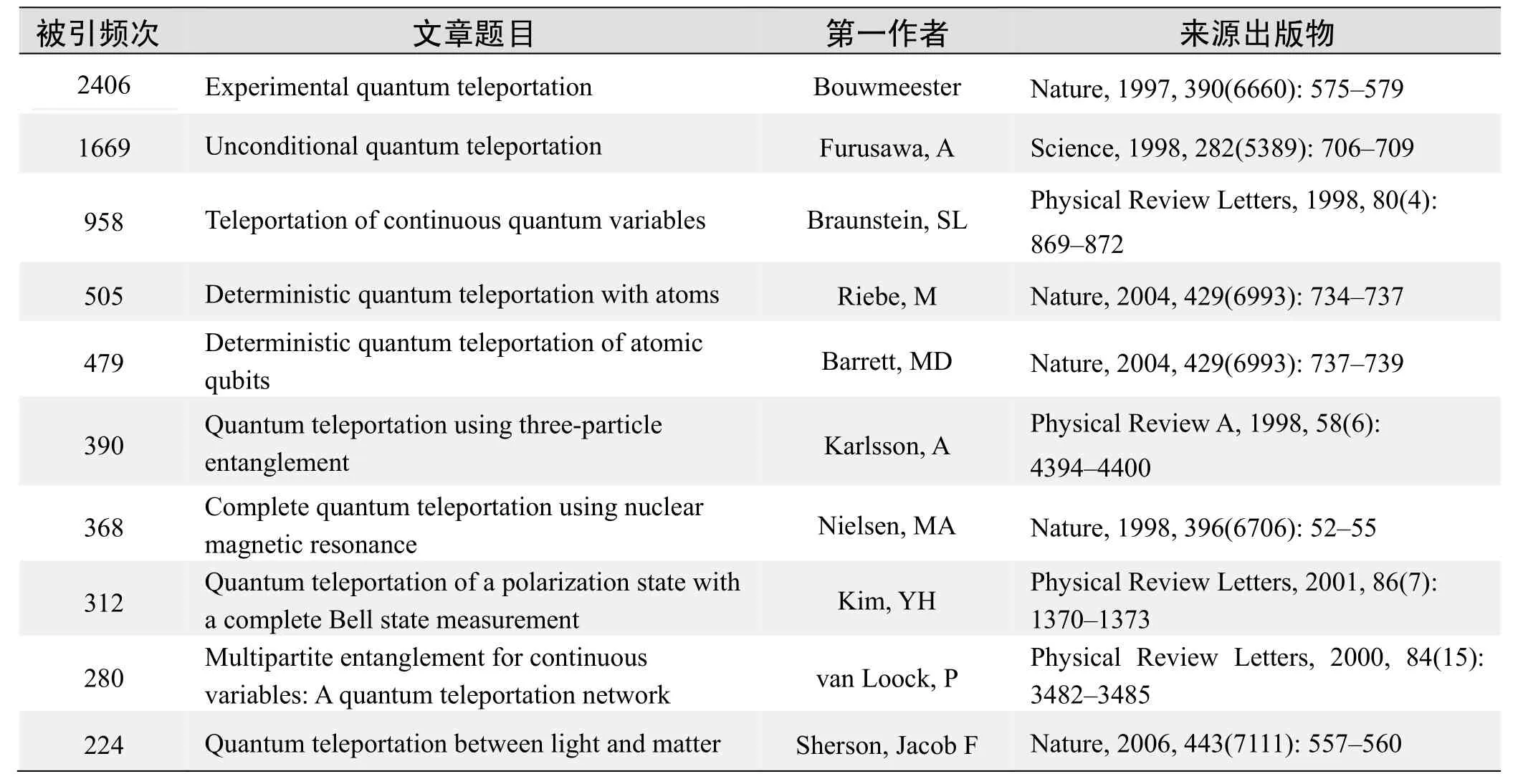
国外数据库高被引论文排行
·经典文献推荐·
基于Web of Science检索结果,利用Histcite软件选取LCS(Local Citation Score,本地引用次数)TOP 30文献作为节点进行分析,得到本领域推荐的经典文献如下.
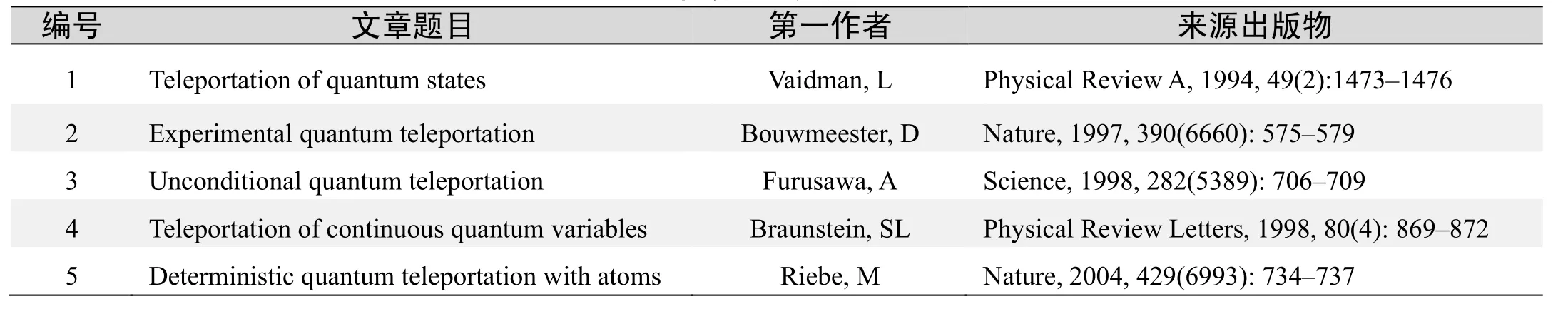
本领域经典文献
来源出版物:Physical Review A,1994,49(2):1473-1476
Experimental quantum teleportation
Bouwmeester,D; Pan,JW; Mattle,K; et al.
Abstract: Quantum teleportation-the transmission and reconstruction over arbitrary distances of the state of a quantum system-is demonstrated experimentally. During teleportation,an initial photon which carries the polarization that is to be transferred and one of a pair of entangled photons are subjected to a measurement such that the second photon of the entangled pair acquires the polarization of the initial photon. This latter photon can be arbitrarily far away from the initial one. Quantum teleportation will he a critical ingredient for quantum computation networks.
来源出版物:Nature,1997,390(6660): 575-579
Unconditional quantum teleportation
Furusawa,A; Sorensen,JL; Braunstein,SL; et al.
Abstract: Quantum teleportation of optical coherent states was demonstrated experimentally using squeezed-state entanglement. The quantum nature of the achieved teleportation was verified by the experimentally determined fidelity F-exp=0.58+/-0.02,which describes the match between input and output states. A fidelity greater than 0.5 is not possible for coherent states without the use of entanglement. This is the first realization of unconditional quantum teleportation where every state entering the device is actually teleported.
Keywords: podolsky-rosen paradox; sub-poissonian light; continuous-variables; atomic-state; realization; conversion; cavity
来源出版物:Science,1998,282(5389): 706-709
Teleportation of continuous quantum variables
Braunstein,SL; Kimble,HJ
Abstract: Quantum teleportation is analyzed for states of dynamical variables with continuous spectra,in contrast to previous work with discrete(spin)variables. The entanglement fidelity of the scheme is computed,including the roles of finite quantum correlation and nonideal detection efficiency. A protocol is presented for teleporting the wave function of a single mode of the electromagnetic field with high fidelity using squeezed-state entanglement and current experimental capability.
Keywords: podolsky-rosen paradox; nondegenerate parametric amplification; squeezed light; atomic-state; phase; spectroscopy; realization;channels
来源出版物:Physical Review Letters,1998,80(4): 869-872
Deterministic quantum teleportation with atoms
Riebe,M; Haffner,H; Roos,CF; et al.
Abstract: Teleportation of a quantum state encompasses the complete transfer of information from one particle to another. The complete specification of the quantum state of a system generally requires an infinite amount of information,even for simple two-level systems(qubits). Moreover,the principles of quantum mechanics dictate that any measurement on a system immediately alters its state,while yielding at most one bit of information. The transfer of a state from one system to another(by performing measurements on the first and operations on the second)might therefore appear impossible. However,it has been shown(1)that the entangling properties of quantum mechanics,in combination with classical communication,allow quantum-state teleportation to be performed. Teleportation using pairs of entangled photons has been demonstrated(2-6),but such techniques are probabilistic,requiring post-selection of measured photons. Here,we report deterministic quantum-state teleportation between a pair of trapped calcium ions. Following closely the original proposal(1),we create a highly entangled pair of ions and perform a complete Bell-state measurement involving one ion from this pair and a third source ion. State reconstruction conditioned on this measurement is then performed on the other half of the entangled pair. The measured fidelity is 75%,demonstrating unequivocally the quantum nature of the process.
Keywords: Podolsky-Rosen Channels; Computer; State
来源出版物:Nature,2004,429(6993): 734-737联系邮箱:Blatt,R; Rainer.Blatt@uibk.ac.at
·推荐综述·
量子通信现状与展望*
吴华1,王向斌2,3,4,潘建伟1,3
1 中国科学技术大学公共事务学院,合肥230026
2 清华大学物理系低微量子物理国家重点实验室,北京100084
3 量子信息与量子科学前沿协同创新中心,合肥230026
4 济南量子技术研究院,济南250101
1引言
“最近的16公里量子态隐形传输的成功试验表明,中国将有能力建立起卫星与地面的安全量子通信网络.”——美国《时代周刊》在“爆炸性新闻”栏目中以“中国量子科学的飞跃”为题,对2010年中国科技大学与清华大学合作完成的16公里量子态隐形传输试验进行了评论.相比于经典通信,量子通信究竟有哪些优势,有哪些应用,源于何种原理以及方法和技术手段等,无疑是大家所关心的.我们将在此介绍量子通信的基本概念与方法、技术现状,以及未来应用前景.
量子通信的基本思想主要由Bennett 等于20世纪80年代和90年代起相继提出,主要包括量子密钥分发(quantum key distribution,QKD)[1]和量子态隐形传输(quantum teleportation)[2].量子密钥分发可以建立安全的通信密码,通过一次一密的加密方式可以实现点对点方式的安全经典通信.这里的安全性是在数学上已经获得严格证明的安全性,这是经典通信迄今为止做不到的.现有的量子密钥分发技术可以实现百公里量级的量子密钥分发[3],辅以光开关等技术,还可以实现量子密钥分发网络[4;5].量子态隐形传输是基于量子纠缠态的分发与量子联合测量,实现量子态(量子信息)的空间转移而又不移动量子态的物理载体,这如同将密封信件内容从一个信封内转移到另一个信封内而又不移动任何信息载体自身.这在经典通信中是无法想象的事.基于量子态隐形传输技术和量子存储技术的量子中继器可以实现任意远距离的量子密钥分发及网络.
量子通信的实现基于量子态传输.为便于传输,现有的量子通信实验一般以光子为量子态载体,其表现形式即为光子态传输. 量子信息的编码空间以光偏振(见图1)为主.
如前所述,量子态隐形传输只是在空间转移量子信息(量子态),但并不转移量子信息的物理载体.若以光子为量子信息载体,量子态隐形传输就是把量子信息从一个光子上转移到远处另外一个光子上.这样的量子态隐形传输有一个明显的应用:在恶劣通道情况下,若直接传输光子本身进行量子通信,将会由于误码率过大而无从实现通信任务.而基于量子态隐形传输的量子通信由于无需传输光子本身,其通信质量不受物理通道影响.量子态隐形传输需要通信双方预先共享一个量子纠缠态(常用的两光子量子纠缠态又称纠缠光子对,或纠缠对).为了预先共享纠缠对,需要预先进行纠缠对分发.实际上,纠缠分发本身也可以用来实现量子密钥分发.通信双方预先共享的纠缠对的质量取决于纠缠分发时的通道状况.用于各类噪声的存在,共享纠缠对一般是不理想的.Bennett等人[1;2]的理论表明,通过对不理想纠缠对纯化可以获得高质量纠缠对.基于此可以实现高品质的量子态隐形传输.目前,量子态隐形传输[6]、纠缠光子对分发[7;8],以及纠缠纯化[9;10]都已经获得广泛实验研究.
基于BB84协议的量子密钥分发无需共享纠缠对资源,只需要单光子态传输.目前真实系统没有理想单光子源,采用的是近似单光子源,即强度为单光子量级的弱激光源,后简称弱光.由于传输损耗,基于弱光传输的量子密钥分发安全距离受到严重限制.另一方面,窃听者可以冒充通道损耗进行光子分数攻击(photon number splitting attack,PNS attack)[11;12].文献分析表明,现有技术的安全距离实际上不到20公里.一个行之有效的办法是采用近年发展起来的诱骗态方法(decoy-state method)[13~16],它虽然继续采用现有光源,但安全性等价于理想单光子源,距离与理想单光子源距离基本相同.
基于量子力学原理,单量子态信号不能被完全克隆放大,而通道损耗随距离呈指数增长.因此,不论光源与检测技术如何发展,单量子态的直接传输距离不可能无限发展.一般认为,其极限距离大概在数百公里量级.远程量子通信的最终实现将依赖于量子中继概念.其基本思想是:在空间建立许多站点.各相邻站点间预先共享并存储量子纠缠对.采用量子态隐形传输技术可以实现量子纠缠转换,即增长量子纠缠对的空间分隔距离.如果预先将纠缠对布置在各相邻站点,纠缠转换操作后便可实现次近邻站点间的共享纠缠.继续操作下去,原则上可以实现在很远的两个站点间建立共享纠缠,即实现远距离量子通信.基于量子中继[17;18]的量子通信距离没有原理上的限制.基于量子中继的远程量子保密通信,即便所有中继站都为敌方控制,终端间的通信依然是安全的.这是量子中继相比于经典中继(又称可信中继)的最大优势.
近年来,以BB84协议和量子态隐形传输为代表的量子通信理论与实验在以越来越快的速度朝实用化和商用化方向迅猛发展.
2量子通信的基本原理
点对点保密通信最直接的办法是让通信双方先共享一串密码,然后以此密码通过一次一密的加密方式对通信内容加密、解密.Shannon[19]于1948年已经证明,若密码是安全的,则通信内容严格安全.现有的经典协议不能确保通信双方的共享密码的安全性.例如,使用秘密信道建立共同密码的方法.经典通信不存在可证实的绝对安全的秘密信道,因为窃听者原则上总可以做到获取“秘密通道”的信息(密码)而又不留痕迹.合法用户无从知晓通过“秘密信道”发送的密钥有没有被窃听.建立密钥的另一种经典方法是基于对特定数学问题的复杂性假定.然而,现有的复杂性假定并未获得严格的数学证明,基于量子逻辑的大数分解算法[20]却从理论上证明了经典RSA通信协议不安全.下面我们重点介绍量子密钥分发理论协议的安全性问题.
2.1BB84 协议及其安全性
相比于经典通信,量子通信的一个重大优势是可以实现严格数学证明下的安全性(绝对安全性).为实现绝对安全的保密通信,Benett与Brassard于1984年提出了首个量子密钥分发协议[1](见图2),即著名的BB84协议.这种方案的安全性基于量子力学的两个基本原理:单光子的不可分割性和单光子量子态的测量塌缩性.
在BB84协议以及大多数量子信息处理中,以单量子态对应于经典二进制码(bit).基本要求是所选择的量子系统有两个基本态.在BB84协议中水平或45°偏振对应于经典比特0;竖直或135°偏振对应于经典比特1.Alice向Bob发射一系列单光子偏振态.每个光子的偏振从水平、竖直、45°或135°中随机选出.或者说,Alice随机使用了两组基,我们称之为直角基(水平,竖直偏振)及斜角基(45°偏振或135°偏振).对每个飞入光子,Bob随机选用直角或斜角基测量其偏振.Bob丢弃那些使用了错误基得到的测量结果.对于剩下的测量记录,随机抽取一部分与Alice对照,检验每组基下各态的误码率并丢弃这些公开宣布的用作检验的测量结果.再对剩余数据(我们称之为初始码)通过纠错,隐私放大而提炼出最终码.
光子总是以一个整体出现.半个光子的事件从来不会发生BB84协议要求传输的单光子脉冲,原理上不允许窃听者通过分割光子并保留部分光子的办法进行窃听.窃听者要么获得完整光子,要么什么都没有获得.量子物理学把测量视为物理学过程的一部分.对一个量子体系观测,原则上会带来扰动.量子世界里不存在“静悄悄地偷看”,即观测而又不对被观测系统产生扰动.就是说,观测就会留下痕迹,这些构成量子密钥安全性的物理基础.
严格的安全性证明最早由Mayers[21]于1996年给出Shor与Preskill[22]于1999年给出了大为简化的证明,其主要结论是:任何窃听者对最终码的信息量大于ϭ的概率小于Ɛ,其中ϭ,Ɛ为指数接近于零点小量,如100亿分之一.最终码的产出率取决于通道误码率.就BB84方案而言量子密钥分发误码率上限值为11%.
虽然BB84方案已经被证明是绝对安全的,这并不意味着任何以该方案为基础的实验都是安全的.这是因为所进行的实验未必真正符合BB84安全性证明中所要求的前提条件.证明中假设了单光子源,由于技术难度极高,现有的实验多采用单一强度弱激光,即弱相干态光.其安全性上存在一定问题,下面我们做简要的介绍.
2.2光子数分离攻击
如前所说,单光子的不可分割性是量子密码安全性的重要物理基础.然而,多光子脉冲不再拥有不可分割性.例如,一个包含两个光子的脉冲,原则上可以被分割为两个单光子脉冲,所以其安全性基础就不复存在了,就会遭受光子数分离攻击,下面我们来具体介绍下光子数分离攻击[11;12].由于量子通信通道损耗率极大,对于100 km以上的距离,加上探测效率,整体效率将小于千分之一.根据理论证明,理想单光子源即便在高损耗通道下也是绝对安全的,可是实际系统使用的弱光在高损耗通道下则结果完全不同:窃听者可以冒充通道损耗通过光子数分离攻击而获得全部密码.如图3所示,为表述方便,我们以偏振空间为例.弱相干态脉冲实际上是单光子与多光子脉冲的概率混合.即,在所发出的非真空脉冲中,有些是单光子的,有些是多光子的(2光子,3光子,…).多光子脉冲即包含了多个全同偏振光子.窃听者可将其分离,自己留下一个,将剩余光子送到远程合法用户.对于这些多光子脉冲,窃听者可以拥有与合法用户完全一样的偏振光子而不对远程合法用户的光子偏振态造成任何扰动.即,对于多光子脉冲,窃听者可以拥有100%的信息而不被察觉.窃听者可以选择将所有单光子脉冲完全吸收而使得远程合法用户的所有比特皆由光源的多光子脉冲产生.窃听者的行为不会被合法用户察觉,因为窃听者可以对每个单独脉冲随时调整通道衰减系数,从而使得远程合法用户的探测器计数率等同于高损耗自然通道.
对于2005年以前的弱相干态密钥分发实验[20;23~27],窃听者可获取全部信息而不留下任何痕迹.事实上,量子密码发明者之一,Brassard等[11;12]早在2000年就对弱相干态量子密码实验做出批评,Brassard等在其著名论文的摘要部分指出:“Existing experimental schemes(based on weak pulses)currently do not offer unconditional security for the reported distances and signal strength”,即:“现有基于(相干态)弱脉冲的做法,据其所报告的距离及所采用的脉冲强度,并不提供绝对安全性.”Brassard的这一评论适用于2005年以前所有基于弱相干光的量子密钥分发实验[20;23~27].幸运的是,于2005年起发展起来的诱骗态量子密码理论,提供了一个基于弱相干光源的安全量子密钥分发方案.
2.3侧信道攻击和木马攻击
尽管量子通信技术在理论上具有“无条件安全性”,但理论方案安全性和实际系统安全性这两个层面之间仍存在一条狭窄但分明的缝隙.利用量子保密通信系统器件的性能缺陷进行窃听,或者针对器件的弱点进行主动攻击都可能削弱甚至破坏量子保密通信系统的安全性.自2000年以来,随着量子通信技术的逐步实用化,实用系统中的安全攻防问题变得越来越重要,并引起研究者的高度重视.针对早期方案和实验技术中的安全性漏洞,已提出了大量的攻击方案,如伪装态攻击、相位重映射攻击、定时侧信道攻击、大脉冲攻击、光学部件高能破坏攻击等.这些攻击方案,统称为侧信道攻击和木马攻击.
“木马攻击”中的木马是指实际的量子保密通信系统其信号源、接收器以及其他部件有可能存在的某种弱点,针对这种弱点,可以设计攻击方案,主动诱使系统内部信息泄露.如果不弥补器件的弱点,这种攻击常常能有效地击破量子保密通信系统的安全性.比如说“大脉冲攻击”法,由于光学器件总会有一定反射能力.窃听者因此向光路中发射高亮度激光.对于某些量子保密通信系统的实现方案,被反射回来的光会被系统中的极化或相位调制器调制,这样,攻击者就得到了发射方信号态的极化或相位信息,而不会引入额外的干扰,也就不会被发现.再如“高能破坏攻击”使用高亮度激光击毁衰减器,破坏了弱相干光源,随后就可以使用“分束器攻击”或者“分离光子数攻击”窃取密钥.主动攻击法还有“伪装态攻击”、“相位再映射攻击”等.而侧信道攻击法是指量子通信系统可能存在泄漏密钥信息的侧信道.侧信道攻击最出名的就是分离光子数攻击,此外,最近提出的针对有记忆的装置无关QKD系统的攻击就利用了经典协商信道的侧信道泄漏.
3量子通信的基本方法
3.1实用化点对点量子通信
该方法要求随机改变相干态脉冲强度而测出单光子计数率[13~16].以此为输入参数提炼出最终码.采用该法所得最终码,其安全性与用理想单光子源所获最终码等价.对于弱相干态光源所发射的脉冲,有一部分是多光子脉冲,一部分是单光子脉冲.诱骗态方法的主要功能是测算在接受端Bob的探测结果(初始码)中,有多少起源于发射端(Alice端)光源的单光子脉冲,多少起源于发射端的多光子脉冲.基于这个至关重要的参数,就可以提炼出安全的最终码,其安全性等同于只采用了由发射端单光子脉冲产生的那部分初始码而抛弃了多光子脉冲产生的那部分初始码.在安全性方面最后的效果就等同于使用了理想单光子源.
2003年,美国西北大学黄元瑛博士提出了在量子密码理论实用化上具有革命性的Decoy-State思想[13]用以解决光子数分离攻击.可是黄的结果尚不能立即实用于现有真实系统,清华大学王向斌教授于2005年的理论研究[14]表明,采用三强度随机切换的诱骗信号量子密码方案可以准确侦察出任何窃听行为,包括所谓的光子数分离攻击,并可立即实用于现有真实系统,其中包含通道噪声,大损耗等.三强度诱骗信号方法可以让合法用户计算出至关重要的参量:多光子脉冲份额的上限值.有此上限值,结合前人理论结果,便可以获得绝对安全的最终码.由该理论给出的关键计算公式,诱骗态方法具有了立即的实用价值(见图4).这也使得量子密钥分发有可能成为整个量子信息领域最先走入社会实用的分支.
诱骗态方法的首个实验由清华大学和中国科技大学等单位的联合团队完成[28],这也成为历史上首次超过100 km的安全量子密钥分发.同一时期的实验还有美国橡树岭国家实验室与美国国家标准局团队的合作实验[29]、维也纳大学等单位的实验[30]等.此后,中国科技大学结合光开关技术,把诱骗态方法用于量子网络,先后实现了3节点与5节点的量子网络安全通信[4].迄今为止,基于诱骗态方法的量子密钥分发已经至少获得世界主要研究机构近20个公开发表的在不同条件下的实验证实.尽管诱骗态方法未必就是唯一方法[31;32],由于其安全性和实用性,事实上,诱骗态方法已经成为当前量子密码走向实际应用的最重要方法.近年来,中国科学家们致力于参与这一主战场的研究,在实验与理论方面取得国际领先的广泛成果.自清华—中科大联合团队2007年在国际上率先利用诱骗态手段实现了绝对安全距离超过一百公里的量子密钥分发[28]以来,中国科技大学潘建伟小组又于2010年率先实现绝对安全距离达200 km的量子密钥分发[3],为目前国际上绝对安全量子密钥分发最远距离.他们还采用光开关技术,于2008年10月初完成了诱骗态量子密钥分发的“光量子电话网”[4](此前国内外其他小组的量子密码网络的实验因为没有采用诱骗态方法而不安全).清华大学王向斌小组则通过系统化的理论研究已经证明即便光源强度有较大涨落诱骗态方法依然有效,给出了相关安全成码的计算公式[7;33~38].
3.2量子网络通信
辅以光开关技术后,诱骗态方法还可用以实现量子通信网络.由于没有量子存储器,这种网络的量子密钥分发距离不能超越点对点的量子密钥分发距离.然而,网络上的任何两个用户可以通过光开.关切换实现量子密钥分发.我国在2009年实现了3节点的链状量子通信网络[4],为世界上首个基于诱骗态方案的量子语音通信网络系统,实现了实时网络通话和三方对讲功能,演示了无条件安全的量子通信的可实用化.此成果很快被美国《Science》杂志以“量子电话”为题进行了报道,亦被欧洲物理学会《物理世界》以“中国诞生量子网络”为题做了专题报道..随后,又实现了5 COQC网络以及Tokyo QKD network不同,这两个量子通信网络是基于诱骗态方案的成熟技术,追求并逐步实现满足信息论定义下严格安全性要求的实用性,而不是欧洲、美国和日本同行所做的多种技术的混合展示.我国此类小规模的演示性网络还有多节点的城域量子政务网.
3.2.13 节点量子电话网
2008年10月,中国科学技术大学潘建伟组在合肥建成了一个基于可信中继方式的3节点量子电话网.采用相位编码的诱骗态BB84方案.网络结构如图5示.
图5中实线为光纤量子信道,虚线为经典信道USTC和Binhu以及USTC和Xinglin之间各建成了一套诱骗态QKD.USTC的节点同时充当了可信中继的角色.原则上,另两个节点也可以充当可信中继,进一步扩展网络.
两条链路的量子信道光纤长度都在20 km左右,最终成码率均大于15 kbps,如表1所示.这个指标可以满足基于“One Time Pad”的保密电话需求.
该网络在国际上第一个实现了实时量子加密电话应用的网络,时间上和SECOQC基本同步,性能指标也基本上相同.该网络的建成是量子通信一次最生动的应用展示,使我国量子通信的应用水平一下子步入国际前列,在世界上激起了很大的反响.
3.2.25 节点量子电话网
2009年8月,中国科学技术大学潘建伟小组在合肥建成了一个星型5节点全通量子电话网络.网络结构示意如图6.
图6中所示1#光纤长10.047 km,2#光纤长8.447 km,3#光纤长9.904 km,4#光纤长8.417 km,5#光纤长60 km,如表2所示.
该网络节点最短通信距离约为17 km.各节点安全成码率如表3所示.
从表3中可见,该网络在通信距离为20 km时,安全成码率最低,仍可达120 kbps.因此该网络可实现基于“One time pad”的安全保密电话功能.
该网络第一次实现了任意节点间实时互联互通的网络控制功能,对于量子通信网络组网技术的成熟具有重要意义.
3.3量子纠缠与量子通信
作为量子信息处理上最重要的资源之一,量子纠缠在量子保密通信上的应用价值主要有两个方面:一是直接基于纠缠分发可以实现共享量子密钥,二是基于量子中继的远程量子通信的基础.传统的量子纠缠态是指一种两光子态的线性叠加态.
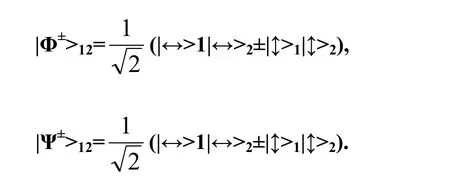
由于两个光子可以位于空间不同地点,纠缠光子对可以形成不同地域的非经典关联.这种关联性可以直接用于共享密钥.借助于不同地点预先共享纠缠光子对,可以实现量子态隐形传输.这也是基于量子中继的远程量子通信的基础技术.量子纠缠对还可用于一类容错量子保密通信中[38].
3.3.1量子纠缠分发
所有基于纠缠的量子通信任务都需要通信双方预先共享量子纠缠态(见图7).因此,纠缠光子对分发技术是一切后续目标的基础.光子对在偏振空间的纠缠态由于检测方式简单和各种其他的易操作性,这种纠缠光子对具有特别重要的应用前景.近年来,这方面的实验研究十分活跃.维也纳小组于2003年完成了600 m距离的自由空间偏振纠缠分发[7].后来有其他欧美小组在光纤中实现了1 km的量子纠缠分发.我国科学家于2006年完成了13 km距离的自由空间偏振纠缠分发[8].其纠缠源来自基于BBO晶体的II型参量下转换.在经过滤波片后每秒约产出10000个纠缠对,波长为702.2 nm,后光路采用了大型望远镜系统进行接收探测.此实验结果一个标志性的意义在于首次证实光子纠缠对分发距离可以超过与大气层等效衰减的距离.这对尚在论证中的以卫星为中转站的洲际量子密钥分发的可行性无疑有着重要启示[39].除了自由空间外,纠缠光子对分发也在光纤中也成功实现了[40~44].现今实用中的偏振纠缠对主要依靠下转换方法产生.这是一种概率性纠缠源.研究表明,高品质确定性纠缠源是有可能的[45].
3.3.2量子态隐形传输
量子态隐形传输就是把量子信息从一个光子上转移到远处另外一个光子上而不必传输光子本身.实现这一任务需要空间两处预先共享纠缠光子对,在实施隐形态传输时还需在一个端点进行Bell测量,之后依据此测量结果对另一个端点的偏振光子进行适当操作.
首个量子态隐形传输于1997年底在奥地利Zeilinger小组完成[6].这项工作由Bouwmeester以及中国学者潘建伟等人基于下转换光子对以及分光镜的集体测量技术完成.这项工作引起了全世界的广泛关注,也使得全世界对量子信息的研究热潮空前高涨.之后,世界各国科学家对这一问题进行了更加广泛和深入的研究.其中,中国学者们在世界各地都取得了多项领先实验成果.他们于2003年首次在室内实现了基本四光子的量子态隐形传输试验[46],使得量子态隐形传输能应用在更加广泛的量子通信和量子计算中.2004年,在首次实现五光子纠缠的基础上,又实现了一种更新颖的量子态隐形传输,即终端开放的量子态隐形传输[47],为后继分布式量子信息处理做出了贡献.2006年,首次实现了两光子复合系统的量子态隐形传输[48].此前,所有的量子态隐形传输实验都只能传输单个粒子的量子态,而实现复合系统量子态隐形传输一直是个巨大的实验难题.2010年,中国学者们在中国本土更实现了举世瞩目跨越长城的16 km距离的量子态隐形传输[49].到2012年,中国科学家们在青海湖地区已经实现了百公里量级的量子态隐形传输和量子密钥分发[50],这也是迄今为止真正量子纠缠分发的最远距离.同1997年首个实验的厘米量级相比,其进展在10多年前是根本不敢想象的.这一成果将对远距离量子通信的实现产生深远影响.
量子态隐形传输技术可直接用于纠缠转换.纠缠转换是量子中继的基本操作单元,是可以用来克服远距离量子通信中的光子数损耗的最终手段[51].
如图8所示,通过对光束4和2的Bell测量,在空间分离的光束1和3,形成纠缠光子对.1998年,潘建伟等人首次实现了量子纠缠交换,使得没有经过任何相互作用的两个光子产生了量子纠缠[50;52].我们如果基于现有的远距离自由空间的量子传输技术,实现同等距离量级的纠缠转换,这将成为量子中继的重要基础.
3.3.3量子纠缠纯化
纠缠是量子通信中的基本资源.然而,在纠缠分发过程中,由于通道噪声,远距离的共享纠缠光子对质量会有下降,从而影响量子通信任务的实现.纠缠对提纯理论结论是,只要初始共享的纠缠对噪声低于一定水平,就可以提炼出较少对的纯纠缠对,对纯纠缠对在两端进行同一基矢测量即可获得绝对安全的密码.最初的量子纠缠纯化方案需要用到受控非门,但精确的受控非门无法用现有技术实现.2001年,潘建伟等提出了无需受控非门的纠缠纯化理论方案[9],使得以现有技术实现纠缠纯化成为可能.2003年,他们利用该方案成功实现了对任意纠缠态的纠缠纯化[10](图9),《Nature》杂志以封面论文的形式发表了该研究成果.
3.4量子中继与远程量子通信及远程量子网络通信
目前采用诱骗态方法的最远实验距离是200 km.尽管随着检测技术的提高,该距离还会进一步提高,但是,由于成码率随着距离呈指数衰减,而单量子态信号又不能在中途放大,因此,基于经典相干态光源的诱骗态方法很难直接完成全球化量子通信任务.
远程量子通信的最终实现将依赖于量子中继[17;18].其基本思想是:在空间建立许多站点.以量子纠缠分发技术先在各相邻站点间建立共享纠缠对,以量子存储技术将纠缠对储存.采用远距离自由空间传输技术实现量子纠缠转换,即增长量子纠缠对的空间分隔距离.如果预先将纠缠对布置在各相邻站点,纠缠转换操作后便可实现次近邻站点间的共享纠缠.继续操作下去,原则上可以实现在很远的两个站点间建立共享纠缠.即实现远距离量子通信.
量子中继与经典中继(俗称“可信中继”)在安全性上是完全不一样的.可信中继是通过中继把形成的密码“接力”下去.它要求所有中继站都是安全的.在通信双方跨越的中继站中只要有一个不安全,则通信内容完全不安全.而量子中继(图10)的中继站只转换纠缠却看不到密码.即便所有中继站都不安全,两个通信终端间形成的密钥及以此为基础的通信仍然绝对安全.
如前文所述,实现量子中继的几项基本技术组件,量子纠缠分发,量子纠缠转换已经获得10 km量级的实现,这已经具备建立具有实际价值的量子中继站的要求.要实现有意义的量子中继,还需要能对量子纠缠态存储.这项要求具有巨大挑战性,实际上是量子中继的最关键技术.2007年,潘建伟小组提出了具有存储功能并且对信道长度抖动不敏感、误码率低的高效率量子中继器的理论方案[53];在此基础上,2008年,该小组利用冷原子气体在国际上首次实现了具有存储和读出功能的量子中继器[54],建立了由300 m光纤连接的两个冷原子系综之间的量子纠缠.这种冷原子系综之间的量子纠缠可以被读出并转化为光子纠缠,以进行进一步的传输和量子操作.《Nature》杂志发布了题为“量子推动”的新闻稿,称赞该工作“扫除了量子通信中的一大绊脚石”,并在网页上发布了题为“量子密码可以走远了”的报道.同年底,该成果入选欧洲物理学会评选的“The best of 2008”.2009年,清华大学小组提出了改进的方案[55],使得容错量子中继操作甚至无需校验光.
3.5自由空间量子通信
自由空间量子通信是解决光子数信道损耗问题的另一有效途径.研究表明,利用低轨卫星和自由空间纠缠光子分发,通过“量子信号从地面上发射并穿透大气层——卫星接收到量子信号并按需要将其转发到另一特定卫星——量子信号从该特定卫星上再次穿透大气层到达地球某个角落的指定接收地点”的方法(图11),很有希望实现更远距离乃至全球化的量子通信.由于量子信号的携带者光子在外层空间传播时几乎没有损耗,如果能够在技术上实现纠缠光子在穿透整个大气层后仍然存活并保持其纠缠特性,人们就可以在卫星的帮助下实现全球化的量子通信.2005年的13 km自由空间量子纠缠和量子密钥分发[8],和2010年的16 km远距离自由空间量子态隐形传输实验[49],2013年实现的基于浮空平台,利用了多项自动跟踪扫描对准技术的量子密钥分发实验[50]以及之前的量子纠缠实验[56;57]为星地量子通信打下了重要基础.
4关键技术
现有的量子保密通信的物理实现方式大多基于单光子水平的弱相干光和纠缠光通信.主要硬件技术包括弱相干光源和纠缠光源,传输与检测.在软体方面还包括最终码提炼(编码)技术.衡量系统先进性的主要指标是产生安全最终码的成码能力.系统每秒生成安全最终码正比于系统重复率与每脉冲成码率.而每脉冲成码率除了受到误码率和损耗率的影响外,还取决于提炼(编码)软体技术.可以从提高光源编码质量,通道传输,以及同步检测,探测器效率等方面来降低误码率.此外,对于无存储量子通信网络,以光开关为代表的弱光传输路径的有效控制也是关键技术之一.
基于量子中继器的未来远程量子网络的技术基础包括光存储和两光子态的联合测量.目前这两项技术都已经在实验室中获得实现[6;10;46;54].然而,量子关键器件的研发,对量子通信网络实用化至关重要.其中,单光子探测系统是处于核心地位的量子关键器件,其参数指标直接制约着量子通信系统的性能,其性能提升对于量子通信系统起着基础性的作用,目前较为前沿的有高速诱骗态光源技术、基于周期极化铌酸锂波导的上转换探测器技术、高速近红外单光子探测技术等.
5总结与展望
经典保密通信的安全性未获数学证明.借助量子特性可以实现严格数学证明的安全通信.虽然以弱相干态为源的现有系统[20;23~27]对其所报告的密钥分发距离并不安全,但我们仍然有其他办法用现有技术实现绝对安全的量子密码系统,例如诱骗态方法[28~30]、纠缠对分发方法[8]等.就未来而言,理想单光子源或纠缠源技术的发展将会大大提高量子密码系统的效率与实用性能.有了量子纠缠方法,提炼、转换和存储为技术基础的量子中继技术将会最终实现任意远距离的安全量子通信及通信网络.由于篇幅有限,本文中有关量子通信的实现部分,仅选择了部分基于线性光学的方法.本文未涉及连续变量的量子通信[58~60],例如连续变量量子纠缠[61~65]、连续变量量子隐型态传输[66~70]、连续变量量子密钥分发等重要内容[71~80];也未包含在量子通信上有重要潜在应用价的量子存储[81~83]、指示单光子源诱骗态方法[84;85]等内容.
·高被引论文摘要·
被引频次:69
量子信息研究进展
李传锋,郭光灿
量子信息论是经典信息论与量子力学相结合的新兴交叉学科.本文综述了量子信息领域的研究进展.即包括了为人们所熟知的量子通信与量子计算领域,也包括了刚刚兴起的但却有巨大潜力的量子对策论等领域.本文以介绍量子信息论的基本理论框架为主,同时也介绍了量子信息领域的实验研究进展.
量子信息;量子通信;量子计算;量子对策论
来源出版物:物理学进展,2000,20(4): 407-431
被引频次:53
量子通信与量子计算
苏晓琴,郭光灿
摘要:量子信息学是物理学目前研究的热门领域.它主要包括量子通信和量子计算.文章简要介绍了量子通信和量子计算的理论框架,包括量子纠缠、量子不可克隆定理、量子密钥分配、量子隐形传态、量子并行计算、Shor以及Grover的量子算法,并介绍该领域的研究进展.
关键词:量子信息;量子通信;量子计算;量子纠缠;量子隐形传态;量子密码
来源出版物:量子电子学报,2004,21(6): 706-718
被引频次:51
量子信息引论
郭光灿
摘要:文章在简述量子信息的发展背景之后,介绍了量子纠缠、量子计算、量子密码、量子因特网、量子克隆、量子对策论等方面的内容,既阐述了相关的基本概念,也论及最新的研究进展.
关键词:量子信息;量子通信;量子计算;量子对策论
来源出版物:物理,2001,30(5): 286-293
被引频次:39
量子纯态的纠缠度
石名俊,杜江峰,朱栋培
摘要:纠缠态在量子计算和量子通讯中起着重要作用.考虑了量子纯态在时间反演变换下的行为以及相应的密度矩阵在Hilbert-Schmidt空间中的表示,并由此对纠缠度给出较为直观的几何解释.
关键词:纯态;纠缠度;密度矩阵;量子通讯;反演变换;纠缠态;混合态 定域性;纠缠程度;量子态
来源出版物:物理学报,2000,49(5): 825-829
被引频次:36
一种量子局域网方案及其性能分析
朱畅华,裴昌幸,马怀新,于晓飞
摘要:提出了一种基于纠缠交换和经典交换的量子局域网方案.采用载波侦听多址/碰撞检测协议实现多址,由经典交换机传送建立和释放信道等控制消息,通过纠缠交换建立收发端光子的纠缠,基于量子隐形传态的原理传递量子信息.对该量子局域网进行性能分析,结果表明系统传输量子信息的吞吐率随着通信双方成功建立纠缠的概率、发端成功进行Bell态测量的概率和接收端成功检测到发送量子比特的概率增大而显著增加.
关键词:量子通信;局域网;纠缠交换;载波侦听多址/碰撞检测
来源出版物:西安电子科技大学学报(自然科学版),2006,33(6): 839-843
被引频次:28
量子安全直接通信
龙桂鲁,王川,李岩松,邓富国
摘要:量子通信利用量子力学原理进行信息传输和处理,具有高安全、高容量等优点.量子安全直接通信在量子信道中直接传输秘密信息,是一种新式的量子通信模式.自2000年提出以来,量子安全直接通信得到了迅速的发展.该文综述量子安全直接通信的基本原理,描述几个典型的量子安全直接通信协议.最后介绍量子安全直接通信的最新发展动态,展望量子安全直接通信的未来.
关键词:量子安全直接通信;量子通信;两步方案;量子一次便笺方案;网络通信;QSDC
来源出版物:中国科学:物理学 力学 天文学,2011,41(4): 332-342
被引频次:28
二能级原子与相干态腔场相互作用过程中的纠缠交换
赖振讲,杨志勇,白晋涛,等
摘要:用量子信息学的观点,分析了发生在一个多个原子和腔场组成的系统中最大纠缠态在原子和多模类奇-偶相干态光场之间相互转移的物理过程,该系统中原子和腔场之间由依赖于强度耦合的Jaynes-Cummings模型描述.结果发现:通过控制原子与腔场相互作用的时间,并对原子的状态进行测量,原子的最大纠缠态可以转换为类奇-偶相干态光场的最大纠缠态,反之,纠缠的多模类奇-偶相干态光场也可以转换为原子的最大纠缠态.
关键词:量子信息;腔量子电动力学;连续变量纠缠态;纠缠交换和传递
来源出版物:物理学报,2004,53(11): 3733-3738
被引频次:28
量子通信
薛鹏,郭光灿
摘要:量子通信是经典通信和量子力学相结合的一门新兴交叉学科.文章综述了量子通信领域的研究进展,既包括人们所熟知的量子隐形传态、密集编码和量子密码学,也包括刚刚兴起但却有巨大潜力的量子通信复杂度和远程量子通信等领域.文章介绍了量子通信的基本理论框架,同时也涉及了这个领域最新的实验研究的进展.
关键词:量子通信;量子隐形传态;量子密集编码;量子密码术;量子通信复杂度;远程量子通信
来源出版物:物理,2002,31(6): 385-391
被引频次:22
基于纠缠的选择自动重传量子同步通信协议
周南润,宾阳,王立军
摘要:分析经典选择重传自动请求重传(automatic repeat-request,ARQ)协议之后,利用量子力学中纠缠态的非定域关联性,提出了数据链路层的选择重传ARQ量子同步通信协议.该协议把链路分为准备阶段和发送阶段.在线路准备阶段完成EPR(Einstein-Podolsky-Rosen)关联对的分发,建立量子信道;在发送阶段完成数据帧和量子确认帧的传送.从吞吐量和信道利用率等方面比较分析了几种常见的数据链路层通信协议的性能.研究表明,该协议可以有效地提高数据链路层的最大吞吐量和信道利用率,改善选择重传ARQ协议的性能,在受时间瓶颈限制的通信中有着重要的应用价值.
关键词:量子通信;量子纠缠;选择自动重传协议;同步通信
来源出版物:物理学报,2010,59(4): 2193-2199
被引频次:20
利用三粒子纠缠态建立量子隐形传态网络的探讨
周小清,邬云文
摘要:利用W态纠缠源可以产生三纠缠粒子,用这些相互纠缠的粒子作为量子信道,再辅以经典信道传送Bell基联合测量信息和von Neumann测量信息,便可实现量子隐形传态网络.基于上述思想,研究了三纠缠粒子量子隐形传态网络的物理基础,得到了基于三粒子W态下隐形传态的幺正变换矩阵,设计了一个基于三纠缠粒子的量子隐形传态网络,给出了一个基于该网络的通信方案.网络中的各站点按所述方法便可实现任意站点间的量子通信.
关键词:量子通信;量子隐形传态;W态
来源出版物:物理学报,2007,56(4): 1881-1887
被引频次:2406
Experimental quantum teleportation
Bouwmeester; Pan,JW; Mattle,K; et al.
Abstract: 参见本期“经典文献推荐”栏目.
被引频次:1669
Unconditional quantum teleportation
Furusawa,A; Sorensen,JL; Braunstein,SL; et al.
Abstract: 参见本期“经典文献推荐”栏目.
被引频次:958
Teleportation of continuous quantum variables
Braunstein,SL; Kimble,HJ
Abstract: 参见本期“经典文献推荐”栏目.
被引频次:505
Deterministic quantum teleportation with atoms
Riebe,M; Haffner,H; Roos,CF; et al.
Abstract: 参见本期“经典文献推荐”栏目.
被引频次:479
Deterministic quantum teleportation of atomic qubits
Barrett,MD; Chiaverini,J; Schaetz,T; et al.
Abstract: Quantum teleportation(1)provides a means to transport quantum information efficiently from one location to another,without the physical transfer of the associated quantum-information carrier. This is achieved by using the non-local correlations of previously distributed,entangled quantum bits(qubits). Teleportation is expected to play an integral role in quantum communication(2)and quantum computation(3). Previous experimental demonstrations have been implemented with optical systems that used both discrete and continuous variables(4-9),and with liquid-state nuclear magnetic resonance(10). Here we report unconditional teleportation(5)of massive particle qubits using atomic(Be-9(+))ions confined in a segmented ion trap,which aids individual qubit addressing. We achieve an average fidelity of 78 percent,which exceeds the fidelity of any protocol that does not use entanglement(11). This demonstration is also important because it incorporates most of the techniques necessary for scalable quantum information processing in an ion-trap system(12,13).
Keywords: podolsky-rosen channels; trapped ions; state; information; operations
来源出版物:Nature,2004,429(6993): 737-739联系邮箱:Wineland,DJ; djw@boulder.nist.gov
被引频次:390
Quantum teleportation using three-particle entanglement
Karlsson,A; Bourennane,M
Abstract: We investigate the “teleportation” of a quantum state using three-particle entanglement to either one of two receivers in such a way that,generally,either one of the two,but only one,ran fully reconstruct the quantum state conditioned on the measurement outcome of the other. We furthermore delineate the similarities between this process and a quantum nondemolition measurement.
Keywords: theorem; cannot; logic; state
来源出版物:Physical Review A,1998,58(6): 4394-4400联系邮箱:Karlsson,A; andkar@ele.kth.se
被引频次:368
Complete quantum teleportation using nuclear magnetic resonance
Nielsen,MA; Knill,E; Laflamme,R; et al.
Abstract: Quantum-mechanical systems have information processing capabilities(1,2)that are not possible with classical devices,One example is quantum teleportation(3),in which the quantum state of a system is transported from one location to another without moving through the intervening space. But although partial implementations(4,5)of quantum teleportation over macroscopic distances have beenachieved using optical systems,the final stage of the teleportation procedure-which allows the complete recovery of the original state-was omitted. Here we report an experimental implementation of full quantum teleportation over interatomic distances using liquid-state nuclear magnetic resonance. We achieve teleportation of the quantum state of a carbon nucleus to a hydrogen nucleus in molecules of trichloroethylene,by exploiting natural phase decoherence of the carbon nuclei. Such a teleportation scheme may be used as a subroutine in larger quantum computations,or for quantum communication.
Keywords: entanglement; state; computation; channels
来源出版物:Nature,1998,396(6706): 52-55
被引频次:312
Quantum teleportation of a polarization state with a complete Bell state measurement
Kim,YH; Kulik,SP; Shih,Y
Abstract: We report a quantum teleportation experiment in which nonlinear interactions an used for the Bell state measurements. The experimental results demonstrate the working principle of irreversibly teleporting an unknown arbitrary polarization state from one system to another distant system by disassembling into and then later reconstructing from purely classical information and nonclassical EPR correlations. The distinct feature of this experiment is that all four Bell states can be distinguished in the Bell state measurement. Teleportation of a polarization state can thus occur with certainty in principle.
来源出版物:Physical Review Letters,2001,86(7): 1370-1373
被引频次:280
Multipartite entanglement for continuous variables: A quantum teleportation network
van Loock,P; Braunstein,SL
Abstract: We show that one single-mode squeezed state distributed among N parties using linear optics suffices to produce a truly N-partite entangled state for any nonzero squeezing and arbitrarily many parties. From this N-partite entangled state,via quadrature measurements of N-2 modes,bipartite entanglement between any two of the N parties can be “distilled”,which enables quantum teleportation with an experimentally determinable fidelity better than could be achieved in any classical scheme.
来源出版物:Physical Review Letters,2000,84(15): 3482-3485
被引频次:224
Quantum teleportation between light and matter
Sherson,Jacob F; Krauter,Hanna; Olsson,Rasmus K; et al.
Abstract: Quantum teleportation(1)is an important ingredient in distributed quantum networks(2),and can also serve as an elementary operation in quantum computers(3). Teleportation was first demonstrated as a transfer of a quantum state of light onto another light beam(4-6); later developments used optical relays(7)and demonstrated entanglement swapping for continuous variables(8). The teleportation of a quantum state between two single material particles(trapped ions)has now also been achieved(9,10). Here we demonstrate teleportation between objects of a different nature-light and matter,which respectively represent ‘flying’ and ‘stationary’ media. A quantum state encoded in a light pulse is teleported onto a macroscopic object(an atomic ensemble containing 10(12)caesium atoms). Deterministic teleportation is achieved for sets of coherent states with mean photon number(n)up to a few hundred. The fidelities are 0.58+/-0.02 for n=20 and 0.60+/-0.02 for n=55-higher than any classical state transfer can possibly achieve(11). Besides being of fundamental interest,teleportation using a macroscopic atomic ensemble is relevant for the practical implementation of a quantum repeater(2). An important factor for the implementation of quantum networks is the teleportation distance between transmitter and receiver; this is 0.5 metres in the present experiment. As our experiment uses propagating light to achieve the entanglement of light and atoms required for teleportation,the present approach should be scalable to longer distances.
Keywords: podolsky-rosen channels; single photons; state; operations; storage
来源出版物:Nature,2006,443(7111): 557-560联系邮箱:Polzik,ES; polzik@nbi.dk
·推荐论文摘要·
全光纤量子通信系统中的高速偏振控制方案
李申,马海强,吴令安,等
摘要:偏振控制在光通信中是至关重要的技术,关系着通信系统的稳定性和误码率.本文提出一种基于双向Sagnac环工作方式的全光纤高速偏振控制方案,通过调节环中一个光纤电光相位调制器的相位差而精确控制光场偏振方向,并且实现了单个端口输出各种偏振态,无需后续耦合操作.相位控制精度为10-3rad,最大消光比可达30 dB,工作速率可达2 GHz.由于本方案的精度、调制速度和稳定性都很高,并采用了器件简单、成本低廉的全光纤光路,易于集成,在量子保密通信等光通信领域中有很好的应用前景.
关键词:光纤偏振控制器;Sagnac环;量子通信
来源出版物:物理学报,2013,62(8): 084214联系邮箱:吴令安,wula@aphy.iphy.ac.cn
量子关联简介
周涛,龙桂鲁,傅双双,等
摘要:量子纠缠作为一种非局域的关联,是一种重要的资源而被广泛应用于量子信息处理.然而,最近的研究结果发现,可分态中也可以存在非经典的关联,量子纠缠只是量子关联的一部分;非纠缠的量子关联在一些量子通信和量子计算任务中扮演着重要的角色.文章简要综述了量子关联的基本概念,描述了几种常见的量子关联度量,并介绍了量子关联在量子信息处理中的作用以及一些最新动态.
关键词:量子纠缠;量子关联;量子失协;量子信息处理
来源出版物:物理,2013,42(8): 544-551联系邮箱:龙桂鲁,gllong@tsinghua.edu.cn
基于不同介质间量子密钥分发的研究
周飞,雍海林,李东东,等
摘要:文章主要解决了偏振编码的光子在不同介质间进行量子密钥分发的问题,定量地分析了光子不同分量的不同透过率引起的误码率问题,并实际分析了空气-水介质间量子密钥分发引起的误码率.进一步给出了可以消除这种非理想BB84协议的单光子补偿方案,以及可以采用更加鲁棒、实用性的抗界面非幺正噪声的双光子编码方案,从而为未来实现全地域广域量子通信迈出了重要的一步.
关键词:量子密钥分发;不同介质;菲涅耳公式;误码率
来源出版物:物理学报,2014,63(14): 140303联系邮箱:彭承志,pcz@ustc.edu.cn
基于对称W态和身份认证的安全量子通信协议
刘超,耿焕同,刘文杰
摘要:由于W态纠缠的强鲁棒性,它被认为是更适用于量子信息处理和量子安全通信的信息载体.针对4粒子W态或3粒子非对称W态量子直接通信效率低下或物理实现困难等缺陷,利用3粒子对称W态和量子身份认证机制,提出了一种新的确定型安全量子通信协议.该协议由认证码生成、量子态准备、量子态分发、安全检测与身份认证和消息通信五阶段组成,通信双方只需进行两粒子Bell基、单粒子Z基或X基测量,通信效率也有所提高,即1个3粒子W态传输1经典比特信息.安全分析证明该协议能有效抵抗各类窃听者Eve攻击和伪装攻击,具有较好的安全特性.
关键词:量子密码;量子通信;确定型安全直接通信;对称W态;身份认证
来源出版物:计算机应用,2014,34(2): 438-441联系邮箱:耿焕同,htgeng@nuist.edu.cn
基于四粒子GHZ态的可控量子双向隐形传态及安全性
胡钰安,叶志清
摘要:提出一个基于四粒子GHZ纠缠态实现未知单粒子态的可控量子双向传态方案.通信双方Alice和Bob以及控制方事先密享两对四粒子GHZ纠缠态以构建量子信道,根据纠缠粒子的不同分发方式,以及测量时所选择的不同测量基,可以分别实现三方和四方参与的可控量子双向传态.通信开始后,Alice和Bob分别对自己拥有的部分粒子作量子投影测量,若控制方同意双方通信,则对自己拥有的粒子作测量并通过经典信道公布测量结果.通信双方根据控制方公布的测量结果对各自的某个粒子作相应的幺正变换,即可在己方的粒子上重建对方待传的量子态.由于第三方Charlie以及第四方Dennis的加入,整个双向传态的安全性大为提高.
关键词:量子通信;可控量子隐形传态;GHZ纠缠态;Bell基测量;安全性
来源出版物:光子学报,2014,43(8): 0827001联系邮箱:叶志清,yezhiqing2008@163.com
中尺度沙尘暴对量子卫星通信信道的影响及性能仿真
聂敏,尚鹏钢,杨光,等
摘要:中尺度沙尘暴是美国内华达州、我国北部及中东国家等地沙尘天气的常见形式.为了研究中尺度沙尘暴对量子卫星通信信道的影响,首先分析了沙尘暴的物理特性,根据中尺度沙尘暴的扩散模型,提出了中尺度沙尘特性与量子纠缠度的关系;然后仿真了沙尘特性对量子卫星信道参数的影响.结果表明,如果沙尘扩散时间为12 h,中尺度沙尘粒子半径分别为1和25 μm,则量子卫星信道的纠缠度依次为0.6和0.4,信道的利用率分别为0.9和0.8,信道容量分别为0.95和0.8.由此可见,量子信道的各种参数与沙尘暴的特性密切相关.因此,为了提高量子卫星通信的可靠性,应根据沙尘灾变程度,自适应调整卫星信道的各种参数.
关键词:量子通信;中尺度沙尘暴;量子纠缠
来源出版物:物理学报,2014,63(24): 240303联系邮箱:尚鹏钢,shang_penggang@163.com
基于稳定子码的在噪声信道的量子安全直接通信方案研究
安辉耀,于涛,刘敦伟,等
摘要:量子安全直接通信是继量子密钥分配后,量子通信领域又一重要的研究领域,它要求通信双方在预先不需要建立共享密钥的情况下就可以实现消息的保密传输.不同于属于非确定通信的量子密钥分配,量子直接通信受信道噪声的影响更大,需要更好的检错纠错能力.本文根据稳定子码纠错理论和GHZ三态纠缠粒子的特性提出了一套基于稳定子码理论的量子直接通信方案,使其在保持无条件安全性的基础上可以对单量子的相位和比特错误进行纠错检错,大大降低了信道的整个通信过程的量子比特错误率.
关键词:量子直接通信;稳定子码;噪声信道
来源出版物:量子光学学报,2014,20(3): 187-191联系邮箱:于涛,tayu@pku.edu.cn
量子稳定子码的码字纠缠
陈小余
摘要:量子计算和量子通信是量子信息科学的两个重要组成部分.量子算法通常用到实系数等权重纯态,其中重要的一类是图态,图态的纠缠已经得到系统的研究.量子通信中不可避免地要用量子纠错码,其中最广泛使用的是与图态紧密相关的量子稳定子码,可以看作是由图态与经典编码两个要素构成的.本文将论证量子编码复杂度与量子码字纠缠的关系.为研究量子码字的纠缠,将证明几何测度、对数鲁棒纠缠和相对熵纠缠等纠缠测度对于量子稳定子码字而言是相等的,纠缠的上下界可由量子编码的生成元确定.用经典编码可以构造一类量子码,称为CSS码.其中最常用的是对偶包含法.对于CSS对偶包含码的码字,证明它的纠缠等于其经典生成元的个数.本文给出Gottesman码以及相关码的纠缠公式,还发展了迭代算法用来数值计算纠缠量.
关键词:量子编码;多组分纠缠;量子测量
来源出版物:中国科学:物理学 力学 天文学,2015,45(3): 030001联系邮箱:陈小余,xychen@zjgsu.edu.cn
Deterministic quantum teleportation with feed-forward in a solid state system
Steffen,L; Salathe,Y; Oppliger,M; et al.
Abstract: Engineered macroscopic quantum systems based on superconducting electronic circuits are attractive for experimentally exploring diverse questions in quantum information science(1-3). At the current state of the art,quantum bits(qubits)are fabricated,initialized,controlled,read out and coupled to each other in simple circuits. This enables the realization of basic logic gates(4),the creation of complex entangled states(5,6)and the demonstration of algorithms(7)or error correction(8). Using different variants of low-noise parametric amplifiers(9),dispersive quantum non-demolition single-shot readout of single-qubit states with high fidelity has enabled continuous(10)and discrete(11)feedback control of single qubits. Here we realize full deterministic quantum teleportation with feed-forward in a chip-based superconducting circuit architecture(12-14). We use a set of two parametric amplifiers for both joint two-qubit and individual qubit single-shot readout,combined with flexible real-time digital electronics. Our device uses a crossed quantum bustechnology that allows us to create complex networks with arbitrary connecting topology in a planar architecture. The deterministic teleportation process succeeds with order unit probability for any input state,as we prepare maximally entangled two-qubit states as a resource and distinguish all Bell states in a single two-qubit measurement with high efficiency and high fidelity. We teleport quantum states between two macroscopic systems separated by 6 mm at a rate of 104s-1,exceeding other reported implementations. The low transmission loss of superconducting waveguides is likely to enable the range of this and other schemes to be extended to significantly larger distances,enabling tests of non-locality and the realization of elements for quantum communication at microwave frequencies. The demonstrated feed-forward may also find application in error correction schemes.
Keywords: superconducting circuits; qubits; entanglement; computation; information
来源出版物:Nature,2013,500(7462): 319-322联系邮箱:Steffen,L; lsteffen@phys.ethz.ch
Deterministic quantum teleportation between distant atomic objects
Krauter,H ; Salart,D; Muschik,CA; et al.
Abstract: Quantum teleportation is a key ingredient in quantum networks(1,2)and one of the building blocks for quantum computation(3,4). Teleportation between distant material objects using light as the quantum-information carrier has been a particularly exciting goal. Here we propose and demonstrate the deterministic continuous-variable teleportation between distant material objects. The objects are macroscopic atomic ensembles at room temperature. Entanglement required for teleportation is distributed by light propagating from one ensemble to the other. We demonstrate that the experimental fidelity of the quantum teleportation is higher than that achievable by any classical process. Furthermore,we demonstrate the benefits of deterministic teleportation by teleporting a sequence of spin states evolving in time from one distant object onto another. The teleportation protocol is applicable to other important systems,such as mechanical oscillators coupled to light or cold spin ensembles coupled to microwaves.
Keywords: light; qubits; communication; operations; ensembles; matter
来源出版物:Nature Physics,2013,9(7): 400-404联系邮箱:Polzik,ES; polzik@nbi.dk
Deterministic quantum teleportation of photonic quantum bits by a hybrid technique
Takeda,Shuntaro; Mizuta,Takahiro; Fuwa,Maria; et al.
Abstract: Quantum teleportation(1)allows for the transfer of arbitrary unknown quantum states from a sender to a spatially distant receiver,provided that the two parties share an entangled state and can communicate classically. It is the essence of many sophisticated protocols for quantum communication and computation(2-5). Photons are an optimal choice for carrying information in the form of 'flying qubits',but the teleportation of photonic quantum bits(6-11)(qubits)has been limited by experimental inefficiencies and restrictions. Main disadvantages include the fundamentally probabilistic nature of linear-optics Bell measurements(12),as well as the need either to destroy the teleported qubit or attenuate the input qubit when the detectors do not resolve photon numbers(13). Here we experimentally realize fully deterministic quantum teleportation of photonic qubits without post-selection. The key step is to make use of a hybrid technique involving continuous-variable teleportation(14-16)of a discrete-variable,photonic qubit. When the receiver’s feedforward gain is optimally tuned,the continuous-variable teleporter acts as a pure loss channel(17,18),and the input dual-rail-encoded qubit,based on a single photon,represents a quantum error detection code against photon loss(19)and hence remains completely intact for most teleportation events. This allows for a faithful qubit transfer even with imperfect continuous-variable entangled states: for four qubits the overall transfer fidelities range from 0.79 to 0.82 and all of them exceed the classical limit of teleportation. Furthermore,even for a relatively low level of the entanglement,qubits are teleported much more efficiently than in previous experiments,albeit post-selectively(taking into account only the qubit subspaces),and with a fidelity comparable to the previously reported values.
Keywords: podolsky-rosen channels; experimental realization; state; computation; operations; qubits
来源出版物:Nature,2013,500(7462): 315-318联系邮箱:Furusawa,A; akiraf@ap.t.u-tokyo.ac.jp
Unconditional quantum teleportation between distant solid-state quantum bits
Pfaff,W; Hensen,BJ; Bernien,H; et al.
Abstract: Realizing robust quantum information transfer between long-lived qubit registers is a key challenge for quantum information science and technology. Here we demonstrate unconditional teleportation of arbitrary quantum states between diamond spin qubits separated by 3 meters. We prepare the teleporter through photon-mediated heralded entanglement between two distant electron spins and subsequently encode the source qubit in a single nuclear spin. By realizing a fully deterministic Bell-state measurement combined with real-time feed-forward,quantum teleportation is achieved upon each attempt with an average state fidelity exceeding the classical limit. These results establish diamond spin qubits as a prime candidate for the realization of quantum networks for quantum communication and network-based quantum computing.
Keywords: spin; qubits; information; register; diamond
来源出版物:Science,2014,345(6196): 532-535联系邮箱:Hanson,R; r.hanson@tudelft.nl
Relativistic Quantum Teleportation with Superconducting Circuits
Friis,N; Lee,AR; Truong,K; et al.
Abstract: We study the effects of relativistic motion on quantum teleportation and propose a realizable experiment where our results can be tested. We compute bounds on the optimal fidelity of teleportation when one of the observers undergoes nonuniform motion for a finite time. The upper bound to the optimal fidelity is degraded due to the observer’s motion. However,we discuss how this degradation can be corrected. These effects are observable for experimental parameters that are within reach of cutting-edge superconducting technology.
来源出版物:Physical Review Letters,2013,110(11)文献号: 113602
Near-deterministic quantum teleportation and resource-efficient quantum computation using linear optics and hybrid qubits
Lee,Seung-Woo; Jeong,Hyunseok
Abstract: We propose a scheme to realize deterministic quantum teleportation using linear optics and hybrid qubits. It enables one to efficiently perform teleportation and universal linear-optical gate operations in a simple and near-deterministic manner using all-optical hybrid entanglement as off-line resources. Our analysis shows that our approach outperforms previous ones when considering both the resource requirements and fault-tolerance limits.
来源出版物:Physical Review A,2013,87(2)文献号: 022326联系邮箱:Jeong,Hyunseok; h.jeong37@gmail.com
Quantum teleportation from a propagating photon to a solid-state spin qubit
Gao,WB; Fallahi,P; Togan,E; et al.
Abstract: A quantum interface between a propagating photon used to transmit quantum information and a long-lived qubit used for storage is of central interest in quantum information science. A method for implementing such an interface between dissimilar qubits is quantum teleportation. Here we experimentally demonstrate transfer of quantum information carried by a photon to a semiconductor spin using quantum teleportation. In our experiment,a single photon in a superposition state is generated using resonant excitation of a neutral dot. To teleport this photonic qubit,we generate an entangled spin-photon state in a second dot located 5m away and interfere the photons from the two dots in a Hong-Ou-Mandel set-up. Thanks to an unprecedented degree of photon-indistinguishability,a coincidence detection at the output of the interferometer heralds successful teleportation,which we verify by measuring the resulting spin state after prolonging its coherence time by optical spin-echo.
Keywords: single-photon; dot spin; entanglement distribution; electron spins; atomic qubits; computation; semiconductor; information;feedforward; ensembles
来源出版物:Nature Communications,2013,4文献号: 2744联系邮箱:Imamoglu,A; imamoglu@phys.ethz.ch
Quantum teleportation of spin coherent states: beyond continuous variables teleportation
Pyrkov,Alexey N; Byrnes,Tim
Abstract: We introduce a quantum teleportation scheme that transfers a spin coherent state between two locations using entanglement. In the scheme an unknown spin coherent state lying on the equator of the Bloch sphere,such as realized in a coherent two-component Bose-Einstein condensate,is teleported onto a distant spin coherent state using only elementary operations and measurements. The scheme works in the regime beyond the standard continuous variables approximation based on the Holstein-Primakoff transformation. We analyze the error of the protocol with the number of particles N in the spin coherent state under decoherence and find that it scales favorably with N. The simplicity of the operations involved and the robustness under decoherence should make the protocol suitable under realistic experimental conditions.
Keywords: quantum teleportation; spin coherent state; Bose-Einstein condensate; quantum entanglement; macroscopic qubit
来源出版物:New Journal of Physics,2014,16文献号: 073038联系邮箱:Pyrkov,Alexey N; pyrkov@icp.ac.ru
Quantum Teleportation of Dynamics and Effective Interactions between Remote Systems
Muschik,Christine A; Hammerer,Klemens; Polzik,Eugene S; et al.
Abstract: Most protocols for quantum information processing consist of a series of quantum gates,which are applied sequentially. In contrast,interactions between matter and fields,for example,as well as measurements such as homodyne detection of light are typically continuous in time. We show how the ability to perform quantum operations continuously and deterministically can be leveraged for inducing nonlocal dynamics between two separate parties. We introduce a scheme for the engineering of an interaction between two remote systems and present a protocol that induces a dynamics in one of the parties that is controlled by the other one. Both schemes apply to continuous variable systems,run continuously in time,and are based on real-time feedback.
Keywords: atomic ensembles; light; communication; entanglement; information; operations; interface
来源出版物:Physical Review Letters,2013,111(2)文献号:020501
Quantum teleportation with nonclassical correlated states in noninertial frames
Mehri-Dehnavi,Hossein; Darabad,Robabeh Rahimi; Mohammadzadeh,Hosein; et al.
Abstract: Quantum teleportation is studied in noninertial frame,for fermionic case,when Alice and Bob share a general nonclassical correlated state. In noninertial frames,two fidelities of teleportation are given. It is found that the average fidelity of teleportation from a separable and nonclassical correlated state is increasing with the amount of nonclassical correlation of the state. However,for any particular nonclassical correlated state,the fidelity of teleportation decreases by increasing the acceleration.
Keywords: Quantum teleportation; Noninertial frames; Nonclassical correlation
来源出版物:Quantum Information Processing,2015,14(3): 1025-1034联系邮箱:Darabad,RR; rrahimid@uwaterloo.ca
Quantum teleportation of multiple degrees of freedom of a single photon
WANG Xi-lin; CAI Xin-dong; SU Zu-en; et al.
Abstract: Quantum teleportation’ provides a ‘disembodied’ way to transfer quantum states from one object to another at a distant location,assisted by previously shared entangled states and a classical communication channel. As well as being of fundamental interest,teleportation has been recognized as an important element in long-distance quantum communication’,distributed quantum networks’ and measurementbased quantum computation. There have been numerous demonstrations of teleportation in different physical systems such as photons’s,atoms’,ionsio,H,electrons’ and superconducting circuits’3. All the previous experiments were limited to the teleportation of one degree of freedom only. However,a single quantum particle can naturally possess various degrees of freedom internal and external and with coherent coupling among them. A fundamental open challenge is to teleport multiple degrees of freedom simultaneously,which is necessary to describe a quantum particle fully and,therefore,to teleport it intact. Here we demonstrate quantum teleportation of the composite quantum states of a single photon encoded in both spin and orbital angular momentum. We use photon pairs entangled in both degrees of freedom(that is,hyper-entangled)as the quantum channel for teleportation,and develop a method to project and discriminate hyper-entangled Bell states by exploiting probabilistic quantum non-demolition measurement,which can be extended to more degrees of freedom. We verify the teleportation for both spin-orbit product states and hybrid entangled states,and achieve a teleportation fidelity ranging from 0.57 to 0.68,above the classical limit. Our work is a step towards the teleportation of more complex quantum systems,and demonstrates an increase in our technical control of scalable quantum technologies.
Keywords: entanglement; state; qubits; communication; computation; operations; bits
来源出版物:Nature,2015,518(7540): 516-519联系邮箱:Lu,CY; cylu@ustc.edu.cn
Complete hyperentangled-Bell-state analysis for quantum communication
SHENG Yu-Bo; DENG Fu-guo; LONG Gui-lu
Abstract:It is impossible to unambiguously distinguish the four Bell states in polarization,resorting to linear optical elements only. Recently,the hyperentangled Bell state,the simultaneous entanglement in more than one degree of freedom,has been used to assist in the complete Bell-state analysis of the four Bell states. However,if the additional degree of freedom is qubitlike,one can only distinguish 7 from the group of 16 states. Here we present a way to distinguish the hyperentangled Bell states completely with the help of cross-Kerr nonlinearity. Also,we discuss its application in the quantum teleportation of a particle in an unknown state in two different degrees of freedom and in the entanglement swapping of hyperentangled states. These applications will increase the channel capacity of long-distance quantum communication.
Keywords: Podolsky-Rosen Channels; Entanglement; Teleportation; Cryptography; Nonlinearity; Repeaters; Photons; Theorem
来源出版物:Physical Review A,2010,82(3)文献号: 032318联系邮箱:Long,GL; gllong@tsinghua.edu.cn
编辑:卫夏雯
Teleportation of quantum states
Vaidman,L
The recent result of Bennett et al. [Phys. Rev. Lett. 70,1895(1993)] of teleportation of an unknown quantum state is obtained in the framework of nonlocal measurements proposed by Aharonov and Albert [Phys. Rev. D 21,3316(1980); 24,359(1981)]. The latter method is generalized to the teleportation of a quantum state of a system with continuous variables.
Bell-State analysis; entanglement; inequalities; information; channels; theorem
*摘编自《中国科学:信息科学》2014年44卷3期:296~311页

