Therapeutic effect and apoptosis mechanism of lung-tonifying and expectorant decoction on lung cancer rats with Qi deficiency and blood stasis
Yuan Feng, Ying Zhou, Ying Jiang, Rui Liu, Jian-Zhe Li, You-Ke Xie, Xue-Mei Li,Fang Dai
Ruikang Hospital Affiliated to Guangxi University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Nanning 530011, Guangxi Province, China
Therapeutic effect and apoptosis mechanism of lung-tonifying and expectorant decoction on lung cancer rats with Qi deficiency and blood stasis
Yuan Feng1*, Ying Zhou2, Ying Jiang3, Rui Liu1, Jian-Zhe Li4, You-Ke Xie5, Xue-Mei Li5,Fang Dai6
Ruikang Hospital Affiliated to Guangxi University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Nanning 530011, Guangxi Province, China
ARTICLE INFO
Article history:
in revised form 20 September 2015
Accepted 15 October 2015
Available online 20 November 2015
Lung cancer
Qi deficiency and blood stasis
Lung-tonifying and expectorant
decoction
Apoptosis
Objective: To explore the effect and specific mechanism of lung-tonifying and expectorant decoction on lung cancer rats with Qi deficiency and blood stasis, and aim to provide a new idea on treating the disease with traditional Chinese medicine based on syndrome differentiation. Methods: A total of 60 C57BL/6J male rats were included in the study. The model of Qi deficiency and blood stasis was established in 60 rats by using multiple-factor stimulation. About 10 rats were randomly taken to verify whether the model establishment was successful and the rest of 50 rats were divided into 5 groups with 10 rats each: blank control group, cisplatin group, low dose group, medium dose group and high dose group. The blank control group was treated with normal saline, and cisplatin group was treated with cisplatin while the other three groups were treated with lung-tonifying and expectorant decoction at different doses. The volume change in transplanted tumor, tumor inhibition rate, apoptosis rate, and expression of Bcl-2, Bax, cleaved caspase-3 and cleaved caspase-9 in 5 groups were compared. Results: The rapidest growth rate of transplanted tumor volume was observed in blank control group and the slowest in cisplatin group. The growth rate was gradually decreased with the increasing dose of lung-tonifying and expectorant decoction, and the difference in growth of tumor volume among groups was statistically significant (P<0.05). The cisplatin group showed the highest tumor inhibition rate, with dose-dependent increase (P<0.05). The apoptosis rate in low dose group was higher than blank control group but lower than high dose group (P<0.05). The apoptosis rate in medium dose group was significantly higher than blank control group (P<0.05). The apoptosis rate in high dose group was significantly higher than control group (P<0.05). The positive expression rates of Bcl-2 and Bax in all groups showed statistically significant difference (P<0.05), while expression of cleaved caspase-3 and cleaved caspase-9 in 5 groups was significantly different, with dose-dependent increase (P<0.05). Conclusions: The lung-tonifying and expectorant decoction inhibits the proliferation of tumor cells by inducing and activating the cell apoptosis in treatment of lung cancer with Qi deficiency and blood stasis, probably with good clinical therapeutic effect.
Document heading doi: 10.1016/j.apjtm.2015.10.003
1. Introduction
Lung cancer is a kind of malignant tumor with the highest morbidity and mortality in the world; based on the statistical datafrom Worth Health Organization, the morbidity of lung cancer tops the list and accounts for 12.6% of newly discovered cancer patients and 17.8% of patients who are died of cancer[1]. In recent years,the morbidity of lung cancer in China has been increased year by year, with data showing that it increases at the rate of 11% annually;many scholars predict that by 2025, the newly increased lung cancer patients would probably reach 1 million and 900 thousand would die of lung cancer, and China would become the kingdom of lung cancer in the world[2]. By far, the etiology and pathogenesisof lung cancer still remains unclear and many studies report that it may be closely related to smoking, air and environmental pollution,occupational exposure, genetic and individual factors, etc. The major treatments for lung cancer are surgery, radiotherapy, chemotherapy and molecular targeting treatment, which all achieve certain degree of efficacy but fail to meet the patients' expectations and a deeper research is required. Researchers claimed that the basic principles for lung cancer treatment, ‘individualized treatment, chemotherapy by stage, local-whole balance, survival rate-survival quality balance,cost-effect balance, Chinese-western balance, constant verification',carried considerably guiding significance in clinical treatment[3].
Lung cancer belongs to the category of ‘lung block, rushing respiration, breath with cough, lung cough, lung distension' in the theory of traditional Chinese medicine. Lung is a delicate organ,susceptible to invasion of harmful substance which would cause disorder in lung, stasis in Qi and blood, obstruction in veins and arteries, coexistence of toxin and blood stasis, and the lump would be formed as time passes. Spleen is the organ producing phlegm while lung is the one reserving phlegm. If the transportation and transformation of spleen fail, the essence of water and food cannot be transported and transformed so that the damp can be easily gathered,and phlegm is produced and remains in lung. The clinical symptoms for patients at early stage are mild and both lung and spleen are hurt. As the condition progresses, Qi-stagnation and blood stasis would occur, phlegm would be produced, heat-transmission would develop after long-time stasis, and fluids would be consumed; deficiency syndrome is more common. A number of doctors believe that the morbidity of lung cancer is closely related to Qi deficiency as well as invasion of harmful substance, and meanwhile the weakness of body is the internal cause of viscera imbalance while the invasion of harmful substance is the external cause. It is believed that the basic principles of “differentiating symptoms and disease, strengthening the Qi while eliminating the pathogenic factors, concentrating in local and whole, regulating yin-yang balance” in treatment can not only effectively kill and inhibit lung cancer cells, and control the condition, but also can regulate the body, improve the immunologic function and further improve the overall therapeutic effect. Researchers in one study analyzed 108 cases of advanced non-small cell lung cancer and found out that about 60.2% of patients were Qideficiency and blood-stasis syndrome and thus, supplementing Qi and activating blood circulation, dissipating phlegm and resolving masses were the major way for treatment[4]. The present study takes lung cancer rats with Qi deficiency and blood stasis as objects, to preliminarily explore the molecule mechanism of cell apoptosis in treating lung cancer with Qi deficiency and blood stasis by using lung-tonifying and expectorant decoction at different concentrations and to provide new ideas and reference base for future clinical treatment.
2. Materials and methods
2.1. Experimental materials
2.1.1. Animal
C57BL/6J male rats free from specific pathogen, weighed 20-22 g, were purchased from Animal Experiment Center of School of Medicine, Wuhan University, with Catalog No. 00015614, and were raised at room temperature.
2.1.2. Equipments and instruments
The Lewis lung cancer cell line was purchased from Shanghai Cell Institutes, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences. The Forma vertical ultra-low temperature refrigerator was purchased from Thermo company. Ⅸ51 inverted microscope was purchased from OLYMPUS, Japan. CO2constant temperature incubator was purchased from Thermo company. Microscopic image acquisition system was purchased from OLYMPUS, Japan (Ⅸ71 + cryogenic camera). Biological safety cabinet was purchased from Thermo company. Low speed desktop centrifuge (TDZ5-WS) was purchased from Wuhan Face Trade Limited Company. Electro thermal and thermostatic water tank was purchased from Wuhan Ideal Scientific Equipment Co., LTD. Minipump was purchased from Qilinbeier Company (GL-802B). Precision electronic balance was purchased from Precisa, Switzerland (ES8200C 10 mg-8 000 g). Image analysis software used in the study was Image-Pro Plus5.0.
2.1.3. Medicines and chemical reagents
The 10% fetal calf serum (NQBB import original), dulbecco's modified eagle medium, trypsin (0.25% pancreatin and 0.02% ethylene diamine tetraacetic acid, biological reagent), and sterile Hanks buffer solution were from Wuhan Jieyangsheng Science and Technology Ltd. The components of lung-tonifying and expectorant decoction were: Codonopsis pilosula 20 g, Astragalus membranaceus 15 g, unprocessed rehmannia 15 g, aster 10 g, Ligusticum wallichii 10 g, red peony root 12 g, Salvia miltiorrhizae 10 g, radix peucedani 10 g, almond 10 g, Curcuma zedoaria 10 g, rhizoma sparganii 10 g,Sculellaria barbata 10 g, Oldenlandia diffusa 15 g, carapax trionycis 10 g and liquorice 6 g. Cisplatin injection was from Hospira Australia Pty Ltd., with Catalog No. H20090521 (50 mL: 50 mg).
2.2. Establishment of lung cancer models with Qi deficiency and blood stasis
A total of 60 cleaning C57BL/6J male rats weighed 20-22 g, with age of 5 wk, were included in the study and raised in animal room with constant temperature and humidity. Food and water were autoclaved.
The 60 rats were made into models of Qi deficiency and blood stasis by using multiple-factor stimulation according to[5]. The performance and symptoms of rats were observed. About 6 wk after the modelingoperation, 10 rats were randomly taken out to verify whether the model establishment was successful, by determining the blood rheology of eyeball blood.
2.3. Grouping and administration
The Lewis lung cancer cell line at logarithmic phase was taken to digest, centrifuge, count and resuspend to make a suspension at the concentration of 1.0×107/mL. About 0.2 mL of suspension was inoculated to the right axilla of rats subcutaneously, after which the rest 50 rats were divided into 5 groups with 10 in each. The blank control group was treated with normal saline and raised normally,while cisplatin group was treated with intraperitoneal injection of cisplatin 1 mg/kg per day For the other three groups, the effective constituents in lung-tonifying and expectorant decoction were extracted through decocting method; and low dose group, medium dose group and high dose group were divided according to the 5, 10,20 times human equivalent dose. For low dose group, 0.7 g/kg lungtonifying and expectorant decoction was given per day, and 1.4 g/kg for medium dose group per day while 2.8 g/kg for high dose group per day. The dosage was 0.5 mL for each rat once a day. The rats in experiment group were raised by giving a gavage of isopyknic normal saline and cisplatin group was given daily intraperitoneal injection of cisplatin at the dose of 1 mg/kg.
2.4. Indexes observation
The general condition and mental state of rats were observed every 3 d, and the size of tumor was measured with vernier caliper. According to the formula V = ab2/2, the volume of tumor was calculated (a is the shortest diameter of tumor, b is the longest diameter), and the tumor growth curve was drawn. About 3 wk after continuous medication, the animals were sacrificed and the tumors without subsidiary tissue were taken for measurement of weight. The tumor weight index and tumor inhibition rate were calculated by using the following formula respectively: tumor weight index = weight of tumor/weight of body; tumor inhibition rate = (1-average weight of tumor in experiment group/average weight of tumor in control group)×100.00%. The tumor apoptosis index was determined by using terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase (TdT)-mediated dUTP nick-end labeling method[6], and expression of Bcl-2, Bax,cleaved caspase-3 and cleaved caspase-9 in apoptosis pathway was determined by using western blot[7].
Interpretation of results: when positive signal was located in the karyon and the color varied from light yellow to brown along with the levels of apoptosis, the criterion for apoptotic cells assessment were: (1) single and scattered distribution; (2) no inflammatory response all around; (3) apoptotic nuclei seen with karyorrhexis,concentrated chromatin adhesion or pyknosis. If no apoptosis was seen in positive cells, but they showed single distribution and dramatically different stain intensity, they can be identified as apoptotic cells. The apoptotic index was calculated in the view of 2 000 cells at high magnification of 10×40.
2.5. Statistical analysis
The data were input to SPSS18.0 software for processing. The measurement data were expressed as mean±SD. t test was performed for the comparison between groups and intra-group comparison. The enumeration data were expressed as percentage and X2was performed. Results with P<0.05 were considered to be statistically significantly different.
3. Results
3.1. Effect of lung-tonifying and expectorant decoction on tumor volume in Lewis lung cancer rats
During the 3-week continuous medication, no rats were dead in all groups. The highest growth rate of volume was observed in blank control group while the lowest in cisplatin group. The growth rate of tumor in experiment group was decreased along with the increased dose of lung-tonifying and expectorant decoction and the difference in volume growth in all groups at different time was statistically significant (P<0.05) (Table 1).

Table 1 Change of tumor volume in Lewis lung cancer rats (mean±SD, mm3).
3.2. Effect of lung-tonifying and expectorant decoction on tumor inhibition rate in Lewis lung cancer rats
The heaviest tumor was observed in blank control group while the lightest in cisplatin group, showing a decreasing trend with the increased dose of lung-tonifying and expectorant decoction (P <0.05). The tumor weight index was the highest in blank control group while the lowest in cisplatin group, showing a decreasing trend with the increased dose of lung-tonifying and expectorant decoction (P< 0.05). The highest tumor inhibition rate was observed in cisplatin group, with the dose-dependent increasing trend (P<0.05) (Table 2).
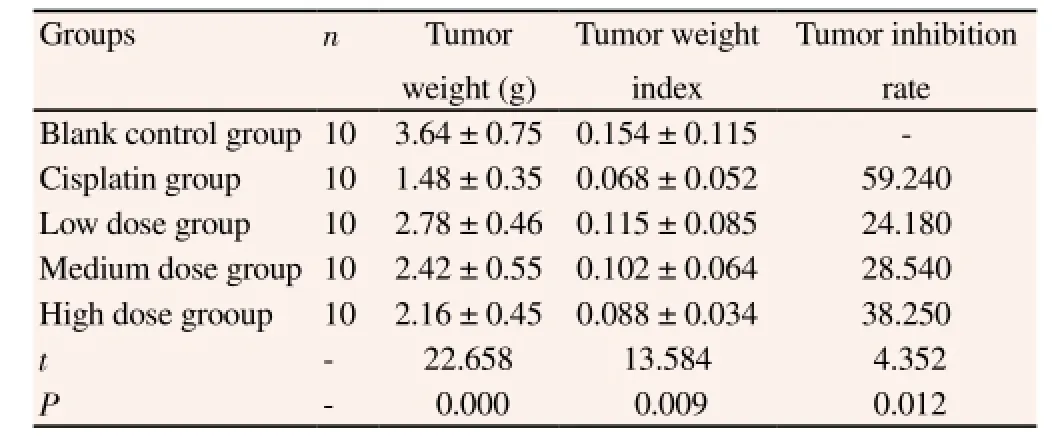
Table 2 Index related to tumor in Lewis lung cancer rats (mean±SD).
3.3. Comparison of apoptosis rate of tumor cells and protein expressions
The cell apoptosis rate in low dose group was higher than that in blank control group but lower than that in cisplatin group, with statistically significant difference (P<0.05). The apoptosis rate in medium dose rate was significantly higher than that in blank control group (P<0.05), but there was no statistically significant difference,compared with cisplatin group (P>0.05). The apoptosis rate in high dose group was significantly higher than in control group (P<0.05). The difference of positive expression rate of Bcl-2 and Bax in all groups was statistically significant (P<0.05), and the difference in expression of cleaved caspase-3 and cleaved caspase-9 in all groups was also statistically significant (P<0.05), with dose-dependent trend(P<0.05) (Table 3).
4. Discussion
Traditional Chinese medicine plays an effective role in treating lung cancer by directly killing the tumor cells, inhibiting the angiogenesis of tumor, regulating the organism's immunologic function, reversing the multidrug resistance of tumor, inducing the apoptosis of tumor cells, affecting the expression of oncogene,improving the microcirculation and hemorheology, and influencing the proliferation cycle of tumor cells, etc. However, there is no consolidated standard criterion in traditional Chinese medicine for the differentiation and classification, which are mostly clinically done based on experience. In the traditional Chinese medicine, it is held that lung cancer is a kind of disease intermingled with both deficiency and excess, and that the deficiency of Qi and yin is the internal pathological basis while deficiency, phlegm, stasis and toxin occur throughout the whole pathogenetic process, which are also the necessary condition for the morbidity of lung cancer. The treatment should be dependent on the patient's clinical manifestation and therapeutic principles should be formulated according to the differentiation and classification of symptoms and signs; clinically,treatments often start from phlegm stagnation, spleen and lung,benefiting Qi and activating blood circulation, and deficiency of yang[8]. The present study aims to further explore the specific molecule mechanism of cell apoptosis in clinical efficacy of lung cancer treatment, from the perspective of effect of lung-tonifying and expectorant decoction on lung cancer, with reference of many domestic reports and years' clinical experience.
Rat-derived and human-derived lung cancer cell lines are usually used to establish the models of Qi deficiency and blood stasis and they are often implanted to back side of axilla. In the present study,Lewis lung cancer cell line was taken and C57BL/6J male rats were chosen to avoid the immunoreaction and rejection reaction caused by the implantation of human lung cancer cell line A549. By choosing C57BL/6J male rats, it can provide the most similar microcirculation to the one from which tumor cells of lung cancer derives, maintain the original biological characteristics of tumor cells, and more precisely predict the therapeutic effect of lung-tonifying and expectorant decoction on lung cancer treatment. Results showed the rapidest growth rate of tumor volume in blank control group and the slowest in cisplatin group; it also showed that the growth rate was gradually decreased with the increased dose of lung-tonifying and expectorant decoction while the tumor inhibition rate increased with the dose-dependent trend (P<0.05). In addition, the results of tumor apoptosis index determined by terminal deoxynucleotidyltransferase-mediated dUTP nick-end labeling method showed that the application of lung-tonifying and expectorant decoction can significantly increase the cell apoptosis rate, with dose-dependent trend, suggesting that lung-tonifying and expectorant decoction can treat lung cancer by activating the apoptosis system, and retarding the proliferation and growth of lung cancer cells so that the therapeutic effect of cisplatin can be achieved. However, in the present study, the lung-tonifying and expectorant decoction was not combined to use with cisplatin. Thus, the combination of lungtonifying and expectorant decoction and cisplatin may need further research to explore the new ideas and methods to clinically treat lung cancer and to further clinically improve the therapeutic effect.

Table 3 Comparison in cell apoptosis rate and expressions of apoptotic factors (mean±SD)
Many clinical researches confirm that the incidence of tumor is not simply caused by infinite multiplication of cells and one more important principle is the blocked apoptotic pathway and lost apoptosis function[9]. Cell apoptosis, also called programmed cell death, is a process that cells commit to suicide actively and die,induced by signals inside and outside the cells. The occurrence and development of cell apoptosis can be divided into initial period,effective period, and degradation period. After the integration of apoptosis signals inside and outside the cells, the signaling protein in cytoplasm would transmit the signals to the performer of apoptosis of certain tissue, namely, caspase, and the activated caspase would further degrade the specific substrate and lead to cell apoptosis finally.
B cell lymphoma/leukemia-2 gene (Bcl-2 gene) is a kind of the earliest known protooncogene and the major modulator in signal transduction of cell apoptosis, with the function to inhibit the cell apoptosis[10]. At the present, at least 15 kinds of homologous proteins of it are known and can be divided into former apoptosis protein and inhibitor of apoptosis protein, according to their structure and function. The inhibitor of apoptosis protein, Bcl-2, can directly integrated with mitochondria and induce the release of cytochrome C. Bcl-x1 can integrate with caspase-9 binding protein and activate the caspase-9. Caspase-9 binding protein can inhibit the activation of caspase-3. The former apoptosis protein Bax can directly integrate with mitochondrial membrane to form transmembrane channel for mitochondria and accelerate the release of cytochrome C. Apoptosis protein Bid can be hydrolyzed by caspase-8, and its hydrolysis product, carboxyl terminal fragment, can trigger mitochondria to release cytochrome C. The nature of genetic expression of Bcl-2 family is determined by the nature of cells' receiving signal stimulus. The activation of inhibitor of apoptosis protein is induced by cytokines while the expression of former apoptosis protein is activated by DNA damage transduced by P53 protein. The regulation of protein levels is the reflection of Bcl-2 proteins' function of regulating function and the phosphorylation of apoptosis protein Bid can relieve its inhibitory function on inhibitor of apoptosis protein Bcl-x1[11]. Bcl-2 gene mainly locates in the upstream of caspase-3 and indirectly inhibits the activation of caspase-3 through factors in the downstream so as to inhibit the cell apoptosis. Researchers believed that Bcl-2 was the important inhibitory apoptotic gene,whose overexpression can inhibit the cell apoptosis by prolonging the duration of tumor cells and inhibiting the release of cytochrome C, Smac and apoptosis-inducing factors from mitochondria by altering the permeability of mitochondria so as to inhibit the integration of cytochrome C and Apaf-1, indirectly inhibit the Procaspase-3 in the upstream and inhibit the cleaved-caspase-3[12]. In another study, it was believed that Bcl-2 prolonged the life span of cells and increased the number of cells by inhibiting cell apoptosis to hinder or delay the normal cell differentiation, and thus increased the opportunity of genovariation which contributed to the occurrence of tumor[13]. In another study, adenovirus Bax gene was used to transfect human lung cancer cell line and the activation as well as apoptosis of caspase and the inhibition of cell proliferation, which can inhibit the growth of tumor and up-regulate the expression of Bax and induce apoptosis were observed[14].
Cysteinylaspartate-specific protease (caspase), is a sort of zymogen,which has no active structure in the normal circumstances and can be activated into a group of enzymes with protein solubility when induced by apoptosis signal. When cell apoptosis happens, caspase is generally activated and thus believed as the final pathway for apoptosis. By far, caspase family has got 14 members altogether,among which caspase-1 and caspase-3 are studied the most. Caspase family is the key part in the process of cell apoptosis, whose activation and abnormal expression can both lead to apoptosis, and hence, it is called death protease that regulates cell apoptosis by interacting with many protein factors[15]. Caspase regulates the cell apoptosis through the interaction with cytochrome C, death receptor,anti-apoptotic factors, apoptotic factors, and apoptosis-inhibited factors, etc. A lot of researches affirm that the factor triggering the apoptosis in the most cases, is finally related to the signaling pathway mediated by caspase-3 that is closely related to the occurrence and development of tumor. Generally, caspase-3 exists in the cytoplasm as 23 ku Pro-caspase-3, and when cells are activated and cleaved under the apoptosis signal, cleaved-caspase-3 is formed. In many researches, it is verified that caspase-3 expression in kinds of tumor cells is decreased[16], and it was reported that caspase-3 expression in mucous epithelium of normal bronchia, atypical hyperplasia, lung cancer, and metastatic carcinoma of lymph node were gradually decreased and believed that the underexpression of caspase-3 may be closely related to the occurrence and development of tumor[17]. Researchers in another study cultured human lung carcinoma, squamous carcinoma, undifferentiated carcinoma, and bronchoalveolar carcinoma in paclitaxel and found that the apoptotic cells increased from 22% to 69%, and meanwhile the activity of caspase-3 increased, suggesting that paclitaxel can induce the apoptosis of human lung cancer cells and is closely related to activityof caspase-3[18]. It was reported in another study that the abnormal activity of caspase-3 in non-small cell lung cancer may be related to the defect in the process in which activated caspase-3 in cytoplasm transferred to karyon[19].
In conclusion, lung-tonifying and expectorant decoction may carry good clinically therapeutic effect in the treatment for lung cancer with Qi deficiency and blood stasis, by inducing and activating the cell apoptosis to inhibit the proliferation of tumor cells. However,further polycentric clinical experiments with large sample should be required so as to confirm the effectiveness and security.
Conflict of interest statement
We declare that we have no conflict of interest.
[1] Dresler C. The changing epidemic of lung cancer and occupational and environmental risk factors. Thorac Surg Clin 2013; 23(2): 113-122.
[2] Shu QJ, Li P, Wang BB, Zhu GM. Mechanism on inhibition of Lewis lung carcinoma in mice with Dahuang Zhechong pills. Chin Arch Tradit Chin Med 2011; 29(8): 1807-1811.
[3] Cai XC, Zhou HL, Qin J, Luo MC, Deng GH. The study of inhibition rate on Lewis lung carcinoma mice with Salvia chinensis Benth. Polysaccharide injection. Asia Pac Trad Med 2015; 11(1): 14-15.
[4] Li P, Shu QJ. Effect and mechanism of Dahuangchong pills on angiogenesis of rats with Lewis lung cancer. Chin Arch Trad Chin Med 2015; 3(1): 175-178.
[5] Yang MH, Zang YS, Li B. Mechanism of lung cancer angiogenesis:recent advance. Acad J Second Milit Med Univ 2013; 34(4): 434-439.
[6] Tan BB, Li Y, Han J, Fan LQ, Zhao Q, Song ZC, et al. Relationship of cyclooxygenase-2 and multidrug resistance associated factors to chemosensitivities in gastrointestinal carcinomas. J Sichuan Univ (Med Sci Edit) 2010; 41(1): 128-131.
[7] Qi X, Xu XG, Jiang YC. Apoptosis induced by sorbitol due to the increase of CK2 inhibitor. Chin J Gerontol 2014; doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-9202.2014.21.093.
[8] Lv M. Clinical observation of treatment for idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis(with Qi deficiency and blood stasis) with method of benefiting Qi and activating blood. [dissertation]. Guangzhou: Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine; 2014.
[9] Li YB, Yang JM, Fang RM, Chen WQ, Lin LZ. Effect of invigorating Qi and removing phlegm on stress protein GRP78 in endoplasmic reticulum/ Bip, caspase-12 in rats with lung cancer. J Tradit Chin Med 2014; 55(11):955-958.
[10] Araz O, Demirci E, Ucar EY, Calik M, Karaman A, Durur-Subasi I, et al. Roles of Ki-67, p53, transforming growth factor-β and lysyl oxidase in the metastasis of lung cancer. Respirology 2014; 19(7): 1034-1039.
[11] Chu YJ, Jiang JG, Tan WL, Liu RF, Zhang YM, Cui YL, et al. Expression and clinical meaning of apoptosis related gene Fas/Fasl in non-small cell lung cancer. Chin J Gerontol 2014; doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-9202.2014.08.028.
[12] Chen C, Chen HB, Teng MJ, Dou YQ. Effects of Fuzheng Sanjie recipe on tumor MVD, HIF-1 and COX-2 in mice with Lewis transplantation lung cancer. World J Integr Trad West Med 2015; doi: 10.13935/j.cnki. sjzx.150412.
[13] Li YH, Lu DY, Ye XW, Chen Y. Effect of scorpion and centipede water decoction on inhibiting mouse Lewis lung carcinoma and on immune organs. Trad Chin Drug Res Clin Pharmcol 2015; 26(3): 311-314.
[14] Sun XS, Wu TT, Ran S, Tian JR, Tan TT, Ren J. Progress on activity against tumor angiogenesis of ligustrazine. Food and Drug 2013; 15(3):223-226.
[15] Sun LL, Fang RM, Zhang JT, Lin LZ. Study of Yiqi Chutan recipe in suppressing H1650 lung cancer by regulating endoplasmic reticulum stress response. J Guangzhou Univ Trad Chin Med 2014; 31(4): 573-577.
[16] Li Y. In vitro and in vivo experimental study of invigorating spleen and removing phlegm for the prevention of non-small cell lung cancer.[dissertation]. Nanning: Guangxi University of Chinese Medicine; 2014.
[17] Piotrowicz RS, Damaj BB, Hachicha M, Incardona F, Howell SB,Finlayson M. A6 peptide activates CD44 adhesive activity, induces FAK and MEK phosphorylation, and inhibits the migration and metastasis of CD44- expressing cells. Mol Cancer Ther 2011; 10(11): 2072-2082.
[18] Yae T, Tsuchihashi K, Ishimoto T, Motohara T, Yoshikawa M, Yoshida GJ, et al. Alternative splicing of CD44 mRNA by ESRP1 enhances lung colonization of metastatic cancer cell. Nat Commun 2012; doi:10.1038/ ncomms1892.
[19] Gannon HS, Jones SN. Using mouse models to explore MDM- p53 signaling in development, cell growth, and tumorigenesis. Genes Cancer 2012; 3(3-4): 209-218.
15 August 2015
Yuan Feng, M.M., Attending Physician, Ruikang Hospital Affiliated to Guangxi University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Nanning 530011,Guangxi Province, China.
Tel: 13006914616
Foundation project: It is supported by Guangxi Nature Fund, 2015.
 Asian Pacific Journal of Tropical Medicine2015年11期
Asian Pacific Journal of Tropical Medicine2015年11期
- Asian Pacific Journal of Tropical Medicine的其它文章
- Demographic, socioeconomic and environmental changes affecting circulation of neglected tropical diseases in Egypt
- Phenolic profile and biological potential of Endopleura uchi extracts
- Roots extracts of Adenophora triphylla var. japonica improve obesity in 3T3-L1 adipocytes and high-fat diet-induced obese mice
- Anti TB drug resistance in Tanga, Tanzania: a cross sectional facility base prevalence among pulmonary TB patients
- In vitro inhibitory effects of plumbagin, the promising antimalarial candidate, on human cytochrome P450 enzymes
- Vibrio spp. from Macrobrachium amazonicum prawn farming are inhibited by Moringa oleifera extracts
