2014年诺贝尔物理学奖专题(高亮度蓝色发光二极管)
照亮世界的“新”光
罗毅,汪莱
(清华大学电子工程系,北京 100084)
高亮度GaN基蓝光与白光LED的研究和进展
刘坚斌,李培咸,郝跃
热点追踪
2014年诺贝尔物理学奖专题(高亮度蓝色发光二极管)
·编者按·
2014年10月7日,瑞典皇家科学院将2014年诺贝尔物理学奖联合授予日本名古屋大学的赤崎勇、天野浩以及美国加州大学圣巴巴拉分校的中村修二,以表彰他们在发明一种新型高效节能光源方面的贡献,即蓝色发光二极管(LED).在颁奖词中,诺贝尔奖委员会写道:“白炽灯照亮20世纪,而LED灯将照亮21世纪”.
20世纪60年代,LED所用的材料是GaAsP,发红光(λp=650 nm),在驱动电流为20 mA时,光通量很小,相应的发光效率约0.1 Im/W.70年代中期,引入元素In和N,使LED产生绿光(λp=555 nm)、黄光(λp=590 nm)和橙光(λp=610 nm),光效也提高到l Im/W.到80年代年代初,出现的LED光源,使得红色LED的光效达到10 Im/W.对于一般照明而言,人们更需要白色的光源,实现蓝光LED成为关键. 1973年,日本松下电器公司东京研究所的赤崎勇最早开始了蓝光LED的基础性开发,1978年,他决定尝试用MOVPE方法来制备高质量GaN材料.他的学生天野浩经过一千多次的试验,偶然发现选用氮化铝(AlN)做缓冲层并适当降低温度可以外延出较高质量的GaN膜,首次研制出高质量的氮化镓材料.此外,P型GaN是实现蓝光LED的另一个关键技术,1989年,赤崎勇与天野浩利用电子辐照实现GaN材料的p型掺杂.之后,中村修二用简单易行、低成本的氮气氛热退火方法代替难于产业化生产的低能电子束辐照,发展了实用化的p型GaN制备技术.
赤崎勇、天野浩、中村修二的研究使人们进入一场前所未有的光源革命,使更高效、更便宜、更智能的照明设备被开发成为可能.LED作为绿色节能光源的代表,发光效率可达80%~90%,耗电量不到白炽灯的十分之一.LED照明还具有使用寿命长、响应速度快、体积小、重量轻、安全性能高等多重优势.蓝光LED技术的出现只是短短20年前的事情,但它带来了白光照明,为整个人类社会创造了福祉.正如诺贝尔委员会主席皮尔·德尔辛教授所说:“蓝光LED出现的最重要意义,便是使得白光可以被顺利造出来,带来明亮、节能的白色光源.这个发明,可谓点亮了全世界的新型光源,它与传统光源相比有更加持久高效节能等优势”.
目前,美国GE、荷兰PHILIPS、德国OSRAM等世界三大照明公司的LED产值己占公司产值的25%以上.预计到2020年,LED元件、LED灯具的发光效率将分别达235 Im/W、166 Im/W,LED照明应用领域会进一步扩大,LED照明产值将占50%以上,成为主流照明光源.我国在上海、大连、南昌、厦门、深圳、扬州和石家庄建立了7个国家级半导体照明工业产业化基地,长三角、珠三角、闽三角以及北方地区成为四大半导体照明产业聚集区域,LED将在普通照明、背景照明和超越照明等应用领域快速成长.
本专题得到了于彤军教授(北京大学物理学院、北京大学宽禁带半导体研究中心)的大力支持.
·热点数据排行·
截至2015年1月14日,中国知网(CNKI)和Web of Science(WOS)的数据报告显示,有关蓝色发光二极管研究的期刊文献分别为176与1628条,本刊将相关数据按照:研究机构发文数、作者发文数、期刊发文数、被引用频次进行排行,结果如下.

研究机构发文数量排名(CNKI)

研究机构发文数量排名(WOS)
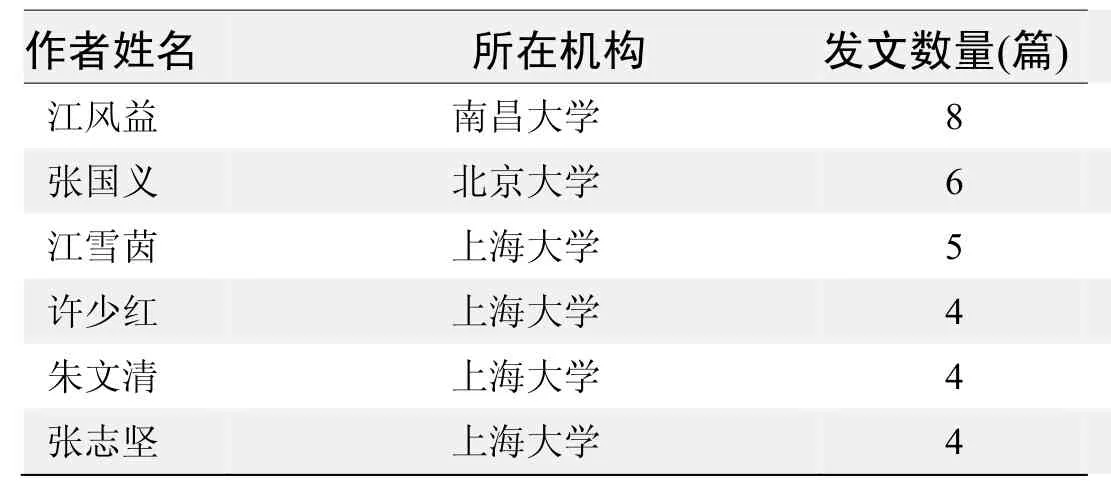
作者发文数量排名(CNKI)
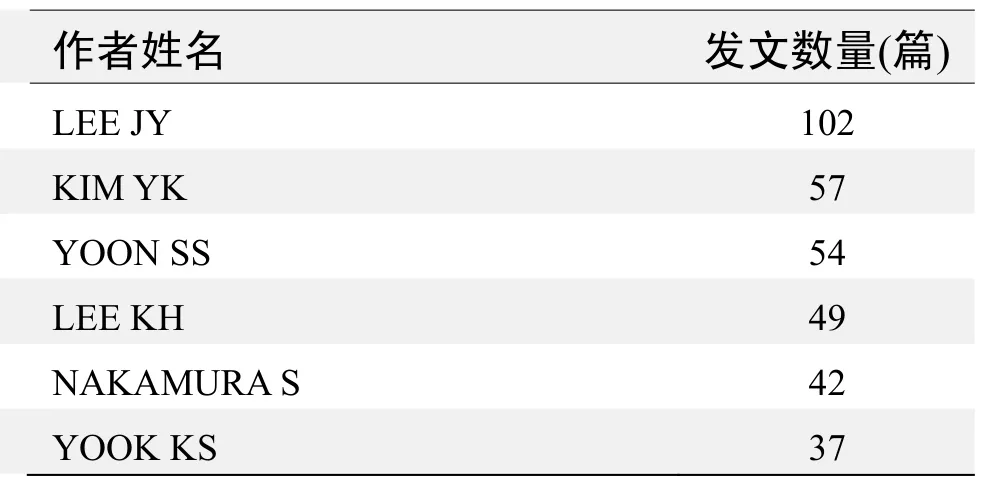
作者发文数量排名(WOS)
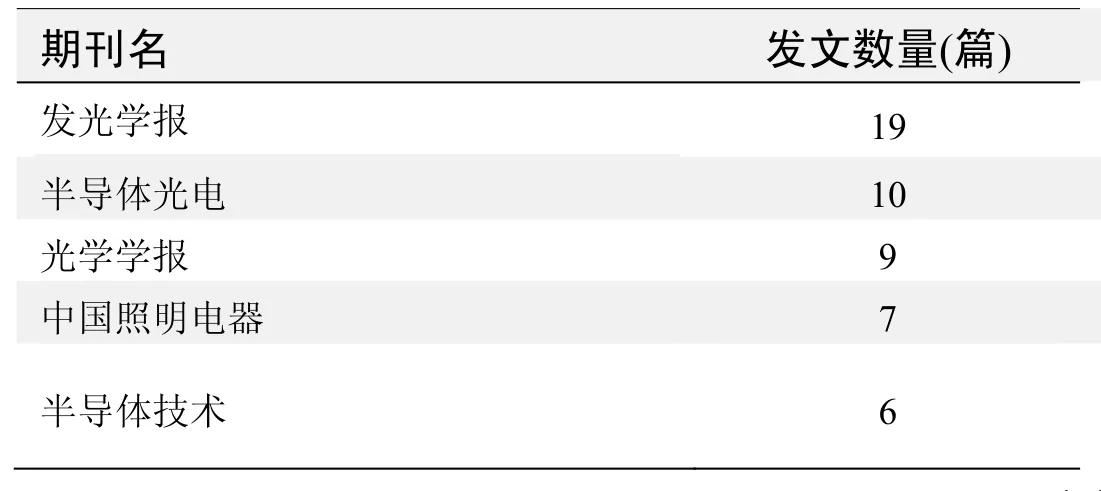
期刊发文数量排名(CNKI)
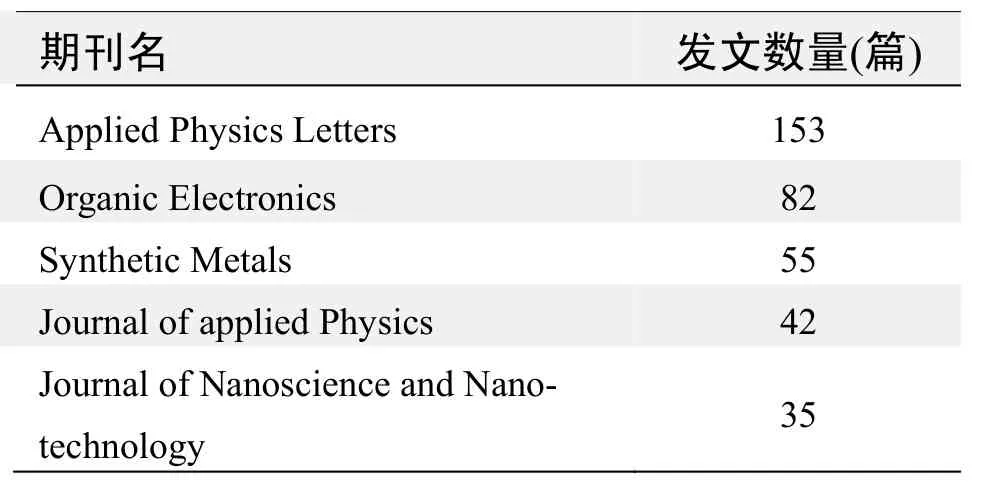
期刊发文数量排名(WOS)
根据中国知网(CNKI)数据报告,有关蓝色发光二极管研究的高被引论文排行结果如下.
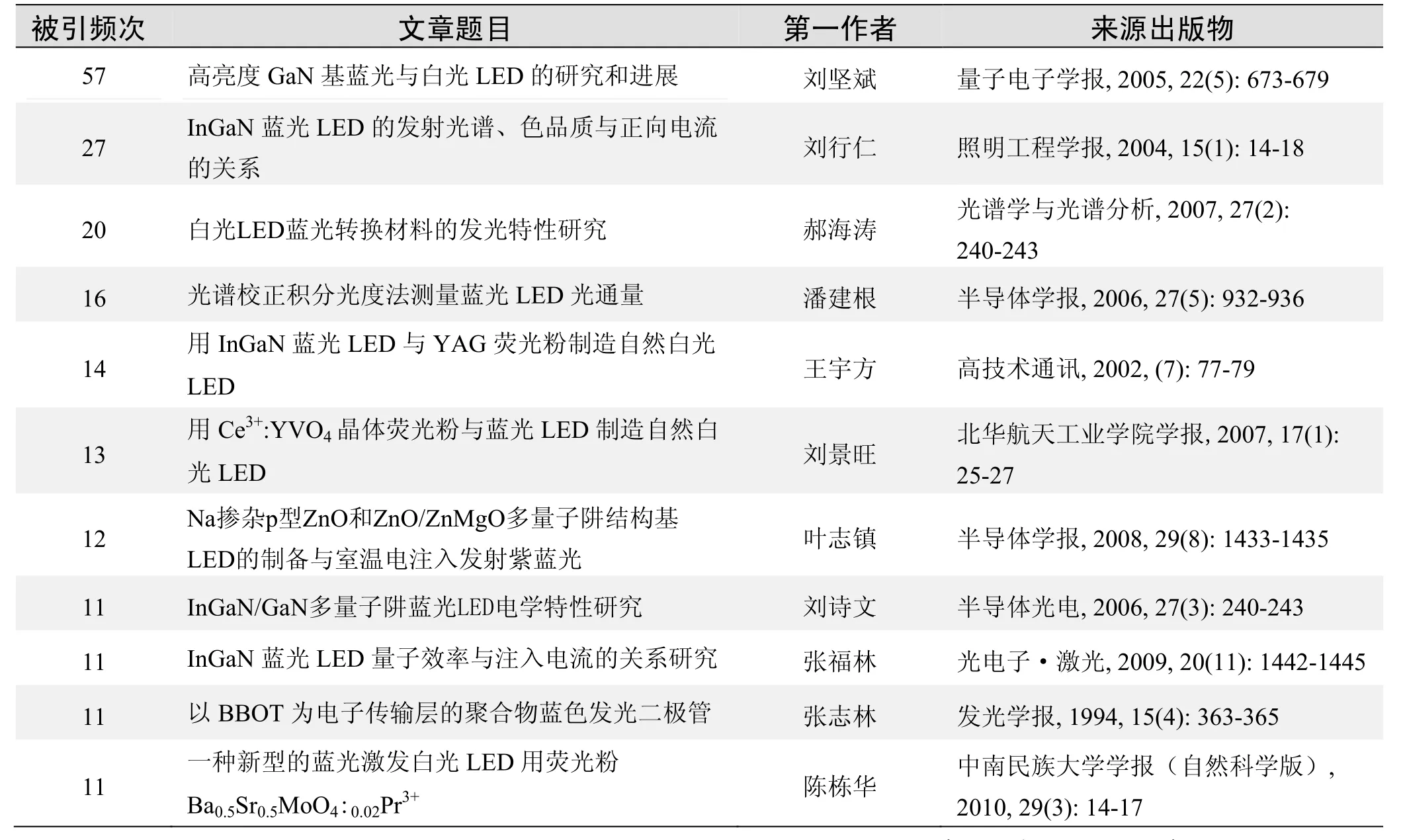
国内数据库高被引论文排行
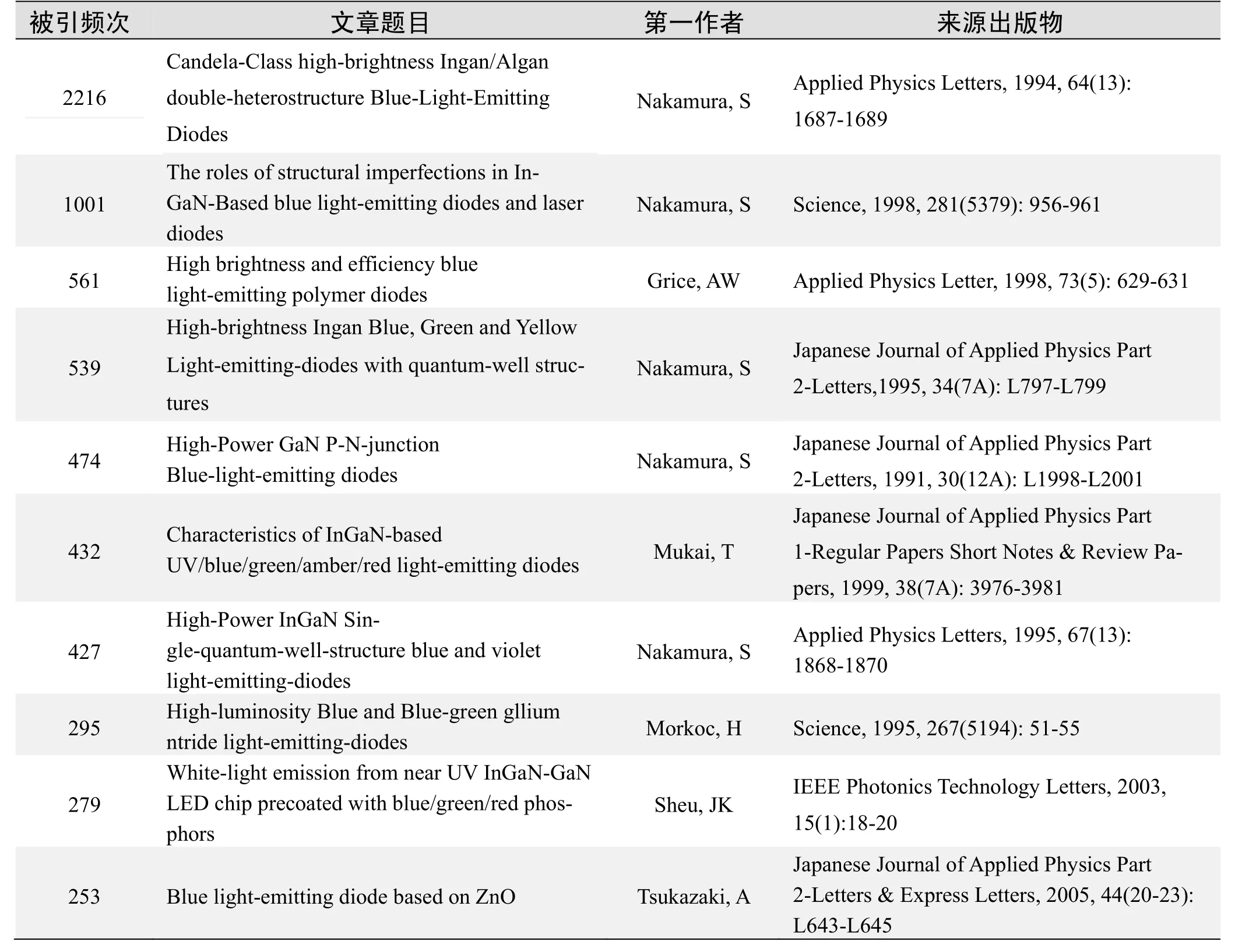
根据Web of Science统计数据,有关蓝色发光二极管研究的高被引论文排行结果如下.
国外数据库高被引论文排行
照亮世界的“新”光*
罗毅,汪莱
(清华大学电子工程系,北京 100084)
1实至名归的世纪发明
2014年10月7日,举世瞩目的新一届诺贝尔物理学奖揭晓,三位来自日本的科学家赤崎勇(图1(a))、天野浩(图1(b))和中村修二(图1(c),中村获奖的工作在日本完成,之后加入了美国籍)因发明高亮度蓝光发光二极管(light-emitting diode,LED)而分享了这一荣誉.这一结果被许多业内人士看成实至名归,但也有一些人觉得出乎意料.在人们的印象中,诺贝尔物理学奖应该是颁发给在物理上有重大发现或重要创新的科学家,而蓝光LED中的物理看上去似乎并没有那么“新奇”.事实上,诺贝尔物理学奖历史上也多次颁发给“技术发明”类的成果,例如1986年德国和瑞士的科学家因为研制出第一台电子显微镜和扫描隧道显微镜而获奖,又如2009年两位来自美国贝尔实验室的科学家博伊尔和史密斯因为发明了目前在数字成像领域已被广泛使用的电荷耦合器件(CCD)而获奖.因此,只要是对人类社会具有重大贡献的发明,即使其中的物理概念看上去不那么新奇,也依然会受到世界的认可.不要忘了,诺贝尔本人就是一位发明家.

那么,蓝光LED为什么会显得如此重要呢?官方的获奖理由中提到“for the invention of efficient blue light-emitting diodes which has enabled bright and energysaving white light sources”即基于蓝光LED可以获得高亮度且节能的白光光源.可以说,正是蓝光LED的发明,使得人类的照明历史发生了一次革命性的变化.1879年,爱迪生点燃了第一盏具有广泛实用价值的白炽灯,在相当长的一段时间内白炽灯都是人类主要的电光源.二战以后,低压荧光灯——日光灯又作为新的照明灯具被广泛使用.人类在上世纪初就发现了半导体中的电致发光现象,60年代初,基于GaAs半导体晶体首次实现了红外光LED,后来又很快制作出红光LED和绿光LED.如果能够制作出蓝光LED,就可以利用红绿蓝三基色实现全彩显示和白光照明.蓝光在三基色中最为重要,因为它波长最短,光子能量最高.利用荧光转换材料,可以很方便地把蓝光转变为波长更长的可见光,从而也能实现白光.然而,蓝光LED的研究进展并不顺利.直到上世纪90年代,第一支商业化的蓝光LED才被中村修二研制成功.基于类似技术,后续又实现了高亮度绿光LED和蓝紫光激光器.从此以后,在世界范围内掀起了蓝光LED的研发热潮,其性能也不断提升.利用蓝光LED芯片加黄色荧光粉的方法可以制作出简单、高效的白光光源.目前,白光LED的光效最高已超过300 Im/W,远远高于白炽灯的10~15 Im/W和日光灯的70~80 Im/W.采用高效的LED光源代替传统光源的意义是巨大的.首先,照明用电占整个社会用电量的比例为15%左右,因此,节省照明用电意味着大量节省能源.其次,用电量的减少意味着因发电产生的污染气体排放也会降低.以我国2013年的数据测算,如果照明用电节省50%,相当于每年节省4个三峡大坝的发电量,减少标准煤的消耗量1.28亿吨,减少二氧化碳排放量约4000万吨.此外,LED作为半导体光源,其可靠性要远高于传统的真空光源,因此更换成本也变得更低.目前,LED灯具已经大规模应用于户外照明,如路灯、隧道灯等,并逐渐开始向室内照明渗透.另一方面,LED已经几乎完全替代了传统的冷阴极荧光,成为液晶显示中不可或缺的背照明光源.由于LED体积小的特点,使得手机、平板电脑等新兴移动数码设备可以做得十分轻薄,满足了人们对高品质生活的需求.可以说,今天蓝光LED已经到处使用,并业已深刻地改变了人们的生活,基于蓝光LED的半导体照明技术契合了当今社会对“节能减排”的紧迫需求,当之无愧地成为人类照明历史上里程碑式的革命.如果说白炽灯照亮了20世纪,那么LED将照亮21世纪,而这一切距离蓝光LED被发明,仅仅过去了20年.也许正因为如此,诺贝尔奖才授予了蓝光LED的发明人而不是LED的发明人吧.
2蓝光LED=“一根筋”的工匠精神+运气
虽然现在蓝光LED已经在我们日常生活中随处可见,如手机摄像头旁的闪光灯就是蓝光芯片和黄色荧光粉组成的,但是在上世纪80年代时,却被全世界公认为技术难题,甚至被认为是20世纪不可能完成的任务之一.赤崎勇、天野浩和中村修二这3位科学家正是在那个时候勇敢地选择了这一课题并最终获得了成功.
1907年,英国马可尼电子公司的英国工程师Henry Joseph Round最早发现了半导体中的电致发光现象.我们知道,孤立原子外围存在分立的电子能级,电子从高能级往低能级跃迁,能量可以以光子的形式释放出来.半导体可以看成是一种内部原子周期性排列的晶体.原子组成晶体后,原来分立的能级扩展成了分立的能带,电子也可以从高能带(导带)往低能带(价带)跃迁,并以光子的形式将多余的能量释放出来.光子能量和这两个能带之间的能量差(禁带宽度)相当,因此发光波长和半导体材料密切相关.1961年,美国德州仪器公司的Bob Biard和GaryPittman基于GaAs材料制作了最早的红外LED.但是由于所发的红外光不可见,红外LED被主要用于传感和一些光电设备中.1962年,美国通用电气公司一名34岁的普通研究人员Nick Holonyak基于GaAsP半导体制作了红光LED[1],随即LED被广泛地用于电路板的通电指示,简单的数码显示等.1968年,美国贝尔实验室的Logan等人利用在GaP中掺入N的技术,实现了绿光LED[2],但是出于原理上的限制,发光不强,也只能用于指示、电话按键的背光等.在红光和绿光LED突破之后,人们很自然地想到了基于新材料去实现蓝光LED.
从禁带宽度上考虑,比较合适的蓝光LED材料有三类,一类是SiC材料,属于IV-IV族半导体,一类是ZnSe基材料,属于II-VI族半导体,另外一类是GaN基材料,也就是最后成功的材料,属于III-V族半导体.一般地,要实现高效的LED,需要半导体材料满足以下一些要求:(1)直接带隙材料,即导带底和价带顶在动量空间中的位置一致;(2)晶体质量高,材料中缺陷尽可能少;(3)容易进行n型和p型掺杂,形成p-n结;(4)可以通过改变化合物半导体的组分来实现不同的禁带宽度,形成异质结.用这4条要求衡量,SiC在晶体质量和掺杂方面的问题都不大,事实上最早商品化的蓝光LED就是基于SiC的p-n结器件;然而由于SiC是间接带隙材料,从物理原理上就限制了其发光效率不可能高,所以人们很自然地把注意力转向了直接带隙的ZnSe基和GaN基材料.ZnSe基材料和GaN基材料面临的共同问题都是p型掺杂难以获得;此外,GaN的合成还十分困难,生长得到的材料具有很高的线缺陷(位错)密度(>1010cm-2),而ZnSe的晶体质量相对要好得多(位错密度<103cm-2).按照传统半导体物理的认识,GaN这么高的位错密度不可能发强光.因此,当时世界上研究蓝光LED的科学家中,选择ZnSe的超过了10000人,而选择GaN的不到10人.
2.1名古屋师生关键突破
赤崎勇是一名GaN材料的坚定支持者.上世纪70年代时他就职于松下电器产业东京研究所,在完成了红、绿光LED的研发后,他决定将蓝光LED作为毕生的事业.也许正是这种在工业界的经历使得他考虑问题的方式与众不同.他认为,和ZnSe相比,GaN材料的物理和化学性质要稳定得多,一旦解决材料质量问题,未来的实用性会更强.1981年,他转到名古屋大学当一名教授,并选择金属有机物化学气相沉积(MOCVD)技术开始了GaN薄膜材料的外延生长.所谓的“外延”生长是指在厚层晶体材料(衬底)的表面进行薄膜(外延层)的“共格”生长,即外延层和衬底最好是同一种材料或晶格常数(原子间距)相近的材料.例如,在GaAs衬底上外延生长GaAs薄膜.遗憾的是,在自然界人们找不到GaN的块状晶体,人工合成也很困难,自然就没有GaN同质衬底可供使用.经过比较,赤崎勇选择了晶体结构和GaN接近但是晶格常数失配达13%的蓝宝石作为衬底材料进行GaN的异质外延.异质外延的缺点是显而易见的,由于晶格失配,GaN外延层和蓝宝石衬底之间存在失配应力,应力的释放会导致GaN内部产生大量缺陷.这样的材料无法应用于器件.
GaN晶体质量的关键突破发生在1985年.当时还是赤崎勇博士生的天野浩,在蓝宝石衬底上先生长一层AlN缓冲层(900~1000℃),再将温度升高(950~1060℃)生长GaN[3].由于缓冲层释放了GaN和蓝宝石之间的失配应力,这种“两步法”生长技术使得GaN的晶体质量显著改善,满足了器件制作的基本要求.这一发现的过程也相当具有戏剧性.当时天野浩使用的MOCVD设备是自己搭建的,有一天当他做实验时突然发现加热装置有一些问题,温度没有升到平时那么高,无法生长GaN,于是他灵光一现地决定先通入Al源生长AlN试一试,过了一会温度又升了上去,他又通入Ga源生长GaN.这样反而得到表面光滑且没有裂纹的GaN晶体,比以往的结果都要好.当然,这一偶然发现是建立在长期坚持不懈实验的基础上.那段时间,天野浩除了过年休息几天外,几乎每天都进行生长材料的实验,已经积累了1500多次生长的经验.
在获得高质量GaN晶体薄膜后,名古屋的这对师生开始瞄准下一个目标——LED器件.LED从本质上说是一个二极管,二极管的核心结构是半导体p-n结.p-n结是由n型半导体(内部含有大量自由电子)和p型半导体(内部含有大量带正电的自由载流子——空穴)组成的界面.一般而言,非故意掺杂的半导体更接近绝缘体,为了让半导体导电,需要在其中适当地掺入一些杂质,根据杂质原子的种类可以使半导体材料内部含有大量的自由电子或大量的空穴.对GaN而言,n型掺杂比较容易实现,但p型掺杂却十分困难.在GaN中经常使用的p型掺杂剂是Zn或者Mg,但是掺入这些杂质后,GaN往往仍体现高阻特性,这意味着p型掺杂剂并没有被激活.到了80年代末期,临近博士毕业的天野浩去一个研究所进行为期一个月的实习,在进行样品的阴极荧光测试时发现,被低能电子束辐照过的掺Zn的GaN样品具有更高的发光强度,这一发现让他感到惊喜.他认为这是由于低能电子束使得GaN发生了变化.但是,当他测量其电学特性时,发现并没有任何变化.他又对掺Mg的GaN进行了同样的电子束辐照实验,结果成功地获得了p-GaN[4].在这一关键突破的基础上,他和赤崎勇在1989年顺理成章地实现了当时世界上第一支GaN基p-n结LED.尽管亮度还很低,但是这让从事氮化物蓝光LED研究的人员看到了曙光.
值得指出的是,同一时期赤崎勇和天野浩也开展过InGaN材料的外延生长.InGaN材料属于GaN基材料系的三元化合物.GaN的禁带宽度较宽(3.4 eV),发光波长较短,通过增加In的组分比例可以调节InGaN的发光波长到更长的蓝光波段,人眼会更加敏感.另一方面,当时人们已经知道,采用双异质结结构可以获得更高的发光效率.双异质结也被称为“三明治”结构,在此结构中,载流子会被两边禁带宽度较宽的势垒材料限制在中间禁带宽度较窄的势阱材料中,从而具有更高的载流子浓度和发光效率.基于这两点,理论上采用InGaN/GaN双异质结结构会制作出更亮的蓝光LED.1986年,赤崎勇和天野浩制作出了In含量仅百分之几的InGaN单晶,但受限于生长工艺无法添加更多的In,他们放弃了进一步的努力.1989年,日本NTT公司的松冈隆志通过降低生长温度,提高氨气流量,以及改用氮气作为载气的方法,获得了In组分为44%的InGaN单晶,这一方法也成为后来InGaN材料生长的标准工艺.1992年,赤崎勇和天野浩在未使用InGaN单晶的情况下,将p型AlGaN和n型AlGaN作为双势垒,将Zn和Si共掺的GaN作为势阱,从而形成双异质结,制作出了比以往的p-n结型更亮的蓝光LED,外量子效率为1.5%.
2.2小公司的工程师震惊世界
赤崎勇和天野浩的工作,解决了材料制备的关键问题,为研制GaN基LED及其它器件奠定了重要基础.中村修二正是受到他们工作的启发并加以改进,才最终实现了具有商业价值的高亮度蓝光LED.中村在1989年才开始介入蓝光LED的研发工作,他当时是日本德岛一所小化工厂——日亚化学的技术开发人员,已经在日亚工作了十年.在这十年里,他承担并完成了Ga金属提纯,GaP晶体的合成,GaAs晶体的合成,GaAlAs的液相外延等多项研发任务.由于研究经费的限制,他几乎全凭一己之力,从搭建设备开始,经过2至3年的努力,每每都能成功完成研发任务.但是由于竞争对手太多,且日亚的生产规模较小,缺少直接检测制备样品质量的设备,他研发的这些产品很难在市场上为公司挣得利润.因此,当中村提出要向蓝光LED发起挑战并获得了日亚高层的支持后,他决定选择一条看上去竞争没那么激烈的技术路线,这自然就是基于GaN材料的技术.
1988年3月,中村修二去美国佛罗里达大学学习MOCVD技术.一年后回到日本,他开始搭建生长GaN材料的MOCVD设备.他改进了传统的MOCVD反应室设计,使其更适合GaN材料的生长.GaN材料的生长温度比传统半导体要高很多,一般在1000℃以上.在高温下,衬底表面的气体会自发向上扩散,造成外延表面的氮分压不够,GaN容易分解.中村发明了一种双束流反应室结构[5],即一路为水平气流携带化学反应的前驱物进入反应室,另外一路为垂直的气流从反应室自上而下进入.这一设计的优点在于,垂直气流在外表面提供较高的氮分压,从而抑制了已淀积的GaN的分解.
随后,中村修二又改进了赤崎勇和天野浩发明的在蓝宝石衬底上异质外延GaN的“两步法”工艺.他采用低温GaN缓冲层(500℃左右)替代了AlN缓冲层,并对GaN缓冲层的厚度等条件进行了优化.结果获得了晶体质量更高的GaN材料,其背景载流子浓度比当时名古屋大学报道的数据还要低一个量级[5].这一基于低温GaN缓冲层的“两步法”工艺后来成为工业界生长GaN基LED的标准工艺.中村也面临GaN的p型掺杂问题.他首先模仿了赤崎勇和天野浩发明的低能电子束辐照方法来获得p-GaN,发现在电子束辐照过程中,如果在样品下面加热则可以获得更好的结果;他进而确认,仅仅依靠加热而不采用电子束照射样品,也可以获得p-GaN.最终,他发明了更加简单实用且效果更好的在氮气中退火的方法来实现p-GaN[6].后来的研究表明,p-GaN中的Mg会被MOCVD外延过程中引入的H钝化,形成Mg-H络合物.无论是低能电子辐照还是热退火,都是通过借助外部能量破坏Mg-H键而激活Mg杂质的.现在,热退火激活p-GaN的方法也已成为工业界制作蓝光LED的标准工艺.
1991年3月,中村修二试制出了GaN基p-n结LED,由于中心波长在紫外光范围,所以人眼看上去仍然感觉较暗,但是寿命超过了1000个小时.与此同时,美国3M公司采用ZnSe实现了蓝光激光器,学术杂志争相报道,甚至预言蓝光属于II-VI族半导体,GaN希望渺茫.中村此时心情很压抑,但是当他得知ZnSe激光器的寿命只有秒量级时又重新振作了精神.为了获得更亮的发光,他将下一个目标锁定为InGaN/GaN双异质结LED.然而,此时日亚的社长却执意要求中村尽快将p-n结LED产业化,以便早日占领市场收回投资.中村在劝说社长无果后,只能独自偷偷进行InGaN薄膜的研究.只花了几个月时间,1992年9月InGaN/GaN双异质结LED终于研究成功.至此,中村的研究成果已经超过了当时所有的竞争者,稳居世界领先地位.但是他仍不满足,他又通过往InGaN中掺入杂质形成发光中心来进一步提高发光波长.最终经过优化,中村修二实现了亮度达到1 cd的蓝光LED,日亚于1993年10月成功将其商品化,这比当时市售的SiC蓝光LED亮了整整100倍.这一事件震惊了整个世界.后来,中村又陆续发明了高亮度的绿光LED(In组分更多的InGaN发光)和蓝紫光激光器,也使日亚化学一跃成为LED领域的世界巨头.
可以看到,赤崎勇和天野浩为蓝光LED做出了先驱性贡献,解决了GaN异质外延和p型掺杂的问题,而中村修二在他们工作的基础上进行了改良和创新,并最终获得了成功.虽然中村只是一个小企业的普通研发人员,但是他发明高亮度蓝光LED,距离他开始着手这项工作只用了短短四年时间.应该说,他在日亚公司前十年的研发经历,使他对材料生长设备的搭建和生长工艺掌握得很熟练,对基本的材料和器件物理理解得也很深刻,这为他在蓝光LED上的成功奠定了基础.3位日本科学家充分发扬了日本人的“工匠精神”,认准的事情“一根筋”地做到底,不从众、不惧困难,终于受到了幸运女神的垂青.
值得一提的是,尽管目前异质外延的蓝光LED的内量子效率最高已经超过90%,但是GaN材料中的位错密度仍然在108 cm-2量级.为什么蓝光LED的发光效率对位错不敏感?这一原因至今仍存在一些争议.或许这也是赤崎勇、天野浩和中村修二3人的幸运之处吧.如果GaN真的和传统半导体一样,那么今天历史的发展将是另外一番模样.但是历史没有如果,由于GaN材料的快速发展和市场做出的选择,II-VI族半导体发光器件的研究也逐渐黯淡下来,越来越少的人再去关心II-VI族半导体材料究竟还能不能实现实用化的蓝、绿光器件了.
3世界为之鼓舞
在日亚成功实现了蓝绿光LED的商品化后,世界范围内均掀起了GaN基LED的研究和产业化热潮.全彩色大尺寸户外显示屏、白光LED灯具等一大批新产品应运而生.由此也带动了LED产业发展和宽禁带半导体材料研究两股热潮.
3.1带动产业发展
由于LED在手机、平板电脑、笔记本电脑、显示器、液晶电视等消费类电子产品以及照明灯具上的广泛应用,世界范围内迅速发展形成了从设备、原材料,到材料外延、芯片,再到封装、应用的LED长产业链.数以千万计的就业机会被创造出来,而每年的市场规模可达几千亿美元.我国从“十五”期间开始了相关产业的部署,发展到今天,已经成为世界上最大的LED封装产业国.半导体照明材料也已经被我国纳入战略性新兴产业.一批优秀的民族企业也得益于产业发展而站到了世界的舞台上.
3.2促进学科发展
在LED产业发展的同时,一批相关的学科也找到了新的增长点.针对GaN基LED材料的研究,使得以GaN、SiC为代表的宽禁带半导体材料进入了科学工作者的视野,材料学、物理学和电子学的内容因此得到了丰富和发展.宽禁带半导体和传统的Si、GaAs/InP基半导体相比,禁带更宽,对应光波长更短,除了可以制作蓝绿光发光器件,还有可能在紫外波段替代传统的真空光源和真空探测器.此外,宽禁带半导体更接近绝缘体,它们的物理化学性质稳定,适合大功率和高温工作,在实现大功率电子器件方面优势明显.有学者预测,继LED之后,电子器件将是宽禁带半导体的下一个热点应用.基于LED的半导体照明技术也给照明这一传统学科注入了新的活力.由于LED芯片尺寸小,单位面积的光通量高,使得基于LED的照明灯具需要对光学系统进行精心的设计,以满足照明舒适度的要求.同时,经过光学系统设计后的LED灯具,在照度均匀度和光能利用率方面也比传统灯具更具优势.基于非成像光学的光学曲面构建已经成为LED照明应用中不可或缺的技术.此外,LED的光谱(较窄的蓝光峰和较宽的黄光峰)和太阳光以及传统的照明光源都不一样,随着LED大规模应用,LED光谱对人眼和生物的影响也开始受到重视,色度学、光度学和生物学可以碰撞出新的交叉学科.未来,LED照明向智能照明方向发展已经成为许多业内人士的共识.可以想象,自动感知人体情绪的色温调整、无线光通信、显示与照明一体化等叠加在LED照明上的新功能今后都有可能出现在我们的生活中.
·高被引论文摘要·
被引频次:58
高亮度GaN基蓝光与白光LED的研究和进展
刘坚斌,李培咸,郝跃
GaN基蓝光LED高亮度化对传统照明光源带来了很大冲击.简述了GaN材料和GaN基蓝光LED器件结构的发展,阐述了为了改善LED性能的一些新措施、LED在照明光源上的应用优势,给出了白光LED的常用制备方法以及最新的研究成果.最后,提出了需要着重解决的问题.
光电子学;半导体材料;GaN;蓝光LED;白光LED
来源出版物:量子电子学报, 2005, 22(5): 673-679联系邮箱:刘坚斌,lightingbug@sohu.com
被引频次:27
InGaN蓝光LED的发射光谱、色品质与正向电流的关系
刘行仁,郭光华,林秀华
摘要:测量了InGaN蓝色发光二极管(LED)在不同正向电流If驱动下的发射光谱、色品坐标、光通量、光效等性质的变化.探讨了它们与If的依赖关系.结果表明,发射光谱和峰值波长λp随电流IF从5 mA~20 mA增加,发生蓝移,当IF大于25 mA直到50 mA后,λp又逐渐红移,光谱的半高宽(FWHM)和色坐标x和y值也发生变化,光通量呈亚线性增加,而光效下降.解析随If增加,影响蓝光LED性能的因素是多方面的.此外,还发现EL光谱中有弱的紫外光辐射.
关键词:蓝色LED;InGaN;发射光谱;色品质
来源出版物:照明工程学报, 2004, 15(1): 14-18
被引频次:20
白光LED蓝光转换材料的发光特性研究
郝海涛,周禾丰,梁建,等
摘要:用稀土氧化物作为原料,通过高能球磨与反应烧结的方法,在1300℃合成了高纯度的铈激活和铈、钆共激活的钇铝石榴石蓝光转换材料,采用X射线衍射分析了产物的晶体结构,采用发射光谱和激发光谱研究了基质中Ce3+的发光特性以及Gd3+对它的影响.结果表明,产物为立方晶系的钇铝石榴石晶体,可以被蓝光有效激发,通过调整掺杂离子的摩尔浓度,荧光粉的发射波长可覆盖530~560 nm的黄绿光范围.利用荧光粉转换法制备了白光LED(light emitting diode,发光二极管),在工作电流为20 mA、工作电压为3.5 V的条件下,所制备的白光LED色坐标x=0.310,y=0.323,光效26.131 m·W-1,显色指数81.8,色温6605 K.
关键词:钇铝石榴石;激发光谱;发射光谱;白光LED
来源出版物:光谱学与光谱分析, 2007, 27(2): 240-243联系邮箱:许并社,xubs@public. ty.sx.cn
被引频次:16
光谱校正积分光度法测量蓝光LED光通量
潘建根,沈海平,冯华君
摘要:介绍了一种光谱校正积分光度法及其在蓝光LED光通量测量中的应用,对测量中的各种不确定因素作了理论分析,并与单纯的分光光度法和积分光度法的不确定度作了比较,证明该方法可实现极高的测量精度.这对于LED的品质评价具有重要意义.
关键词:LED;光度;光通量;测量;不确定度
来源出版物:半导体学报, 2006, 27(5): 932-936联系邮箱:沈海平,hainiushen@163.com
被引频次:14
用InGaN蓝光LED与YAG荧光粉制造自然白光LED
王宇方,杨志坚,丁晓民,等
摘要:报导了用国内自行研制的InGaN/GaN蓝光发光二极管(LED)与钇铝石榴石(YAG)荧光粉结合而得的白光发光二极管(W-LED).在室温,正向电压3.5 V,正向电流20 mA时,W-LED轴向亮度为1 cd,CIE色坐标为(0.31,0.38),接近纯白色(0.33,0.33).
关键词:白光;LED;YAG荧光粉
来源出版物:高技术通讯, 2002,(7): 77-79
被引频次:13
用Ce3+:YVO4晶体荧光粉与蓝光LED制造自然白光LED
刘景旺
摘要:本文报导了通过结合自行制备的掺铈钒酸钇晶体(Ce3+:YVO4)荧光粉与InGaN/GaN蓝光发光二极管(LED)结合而得的白光发光二极管(W-LED).在室温、正向电压3.5 V、正向电流20 mA时W-LED的CIE色坐标为(0.32,0.37),接近纯白色(0.33,0.33).
关键词:白光;LED;Ce3+:YVO4荧光粉
来源出版物:北华航天工业学院学报,2007, 17(1): 25-27
被引频次:12
Na掺杂p型ZnO和ZnO/ZnMgO多量子阱结构基LED的制备与室温电注入发射紫蓝光
叶志镇,林时胜,何海平,等
摘要:在硅单晶上,采用了环境友好的ZnO/Zn0.9Mg0.1O多层量子阱结构作为有源层,Na作为p型掺杂元素,制备了ZnO发光二极管(LED).该LED在室温电注入条件下,实现了较强的紫蓝发光,且有效控制了缺陷发光.这项工作将为ZnO LED走向应用起到重要的推进作用.
关键词:LED;Na掺杂;p型ZnO;ZnO/ZnMgO多量子阱
来源出版物:半导体学报, 2008, 29(8): 1433-1435联系邮箱:叶志镇,yezz@cmsce.zju.edu.cn
被引频次:11
InGaN/GaN多量子阱蓝光LED电学特性研究
刘诗文,郭霞,艾伟伟,等
摘要:对不同温度(120~363 K)下InGaN/GaN多量子阱(MQW)结构蓝光发光二极管(LED)的电学特性进行了测试与深入的研究.发现对数坐标下I-V特性曲线斜率随温度变化不大.分别用载流子扩散-复合模型和隧道复合模型对其进行计算,发现室温下其理想因子远大于2,并且随着温度的下降而升高;而隧穿能量参数随温度变化不大.这说明传统的扩散-复合载流子输运模型不再适用于InGaN/GaN MQW蓝光LED.分析指出由于晶格失配以及生长工艺的制约,外延层中具有较高的缺陷密度和界面能级密度,导致其主要输运机制为载流子的隧穿.
关键词:氮化镓;蓝光发光二极管;理想因子
来源出版物:半导体光电, 2006, 27(3): 240-243联系邮箱:刘诗文,liushiwen@emails.bjut.edu.cn
被引频次:11
InGaN蓝光LED量子效率与注入电流的关系研究
张福林,林旭,廖欣,等
摘要:研究了InGaN蓝光LED量子效率随注入电流的变化关系,当注入电流还未达到额定电流时,LED量子效率就随着注入电流增加而快速降低.通过Matlab计算出在俄歇复合的无辐射复合机制下量子效率与注入电流的理论关系式.与实验值的拟合结果显示,大电流注入下,LED的效率衰落同时由俄歇复合及其产生的热电子从发光有源区泄露引起.由蓝光LED这一效率-电流特性,提出了增强InGaN蓝光LED效率的途径.
关键词:InGaN LED;量子效率;非辐射复合;俄歇复合;大功率LED驱动
来源出版物:光电子·激光, 2009, 20(11): 1442-1445联系邮箱:张福林,fulin05@163.com
被引频次:11
以BBOT为电子传输层的聚合物蓝色发光二极管
张志林,蒋雪茵,许少鸿,等
摘要:我们以PVCZ作为空穴传导层,BBOT为电子传导层,制成了双层结构的发光二极管.亮度和效率都大大超过单层器件.发射为蓝光,亮度达680 cd/m2,称此器件为I型二极管.为了提高BBOT的稳定性,我们进一步制成一种改进型双层结构二极管.其稳定性虽有所提高,但提高不大约一倍左右.可是其蓝光亮度却有很大提高,达1700 cd/m2,我们称此器件为II型二极管.
关键词:电子传输层;发光二极管;BBOT;电致发光;流明效率;热蒸发;透明电极;发光效率
来源出版物:发光学报, 1994, 15(4): 363-365
被引频次:11
一种新型的蓝光激发白光LED用荧光粉Ba0.5Sr0.5MoO4:0.02Pr3+
陈栋华,李秋霞,黄佳平
摘要:为寻找应用于白光LED的红色荧光粉,采用固相法成功地合成了Ba0.5Sr0.5MoO4:0.02Pr3+x(0.005≤x≤0.04)红光荧光粉,并对样品分别进行了X射线衍射分析、透射电镜测试和荧光光谱的测定.通过表征可知,该荧光粉可被400~500 nm蓝光范围有效激发,掺杂Pr3+并未显著影响样品的晶体结构,最佳掺杂x为0.02.同时讨论了温度和基质对晶体结构以及发光性能的影响.
关键词:发光;固相法;发光二极管;荧光粉
来源出版物:中南民族大学学报(自然科学版), 2010, 29(3): 14-17联系邮箱:陈栋华,chendh46@hotmail.com
被引频次:2216
来源出版物:Applied Physics Letters, 1994, 64(13): 1687-1689
被引频次:1001
The roles of structural imperfections in InGaN-Based blue light-emitting diodes and laser diodes
Nakamura, S
Abstract: High-efficiency light-emitting diodes emitting amber, green, blue, and ultraviolet light have been obtained through the use of an InGaN active layer instead of a GaN active layer. The localized energy states caused by In composition fluctuation in the InGaN active layer are related to the high efficiency of the InGaN-based emitting devices. The blue and green InCaN quantum-well structure light-emitting diodes with luminous efficiencies of 5 and 30 lumens per watt, respectively, can be made despite the large number of threading dislocations(1×108to 1×1012cm-2). Epitaxially laterally overgrown GaN on sapphire reduces the number of threading dislocations originating from the interface of the GaN epilayer with the sapphire substrate; InGaN multi-quantum-well structure laser diodes formed on the GaN layer above the SiO2mask area can have a lifetime of more than 10,000 hours. Dislocations increase the threshold current density of the laser diodes.
Keywords: Grown GaN films; gallium nitride; buffer Layer; hydrogenation; superlattices; luminescence; sapphire; Mg
来源出版物:Science, 1998, 281(5379): 956-961联系邮箱:Nakamura, S; shuji@nichia.co.jp
被引频次:561
High brightness and efficiency blue light-emitting polymer diodes
Grice, AW; Bradley, DDC; Bernius, MT; et al.
Abstract: Efficient blue electroluminescence, peaked at 436 nm, is demonstrated from polymer light-emitting diodes operating at high brightness. A dioctyl-substituted polyfluorene was used as the emissive layer in combination with a polymeric triphenyldiamine hole transport layer. The luminance reaches 600 cd/m2at a current density of 150 mA/cm2for a bias voltage of 20 V, corresponding to an efficiency of 0.25 cd/A and a luminosity of 0.04 Im/W. These values are optimized at a critical emissive layer thickness.
Keywords: electroluminescence
来源出版物:Applied Physics Letter, 1998, 73(5): 629-631联系邮箱:Grice, AW; D.Bradley@Sheffield.ac.uk
被引频次:539
High-brightness Ingan Blue, Green and Yellow Light-emitting-diodes with quantum-well structures
Nakamura, S; Senoh, N; Iwasa, N; et al.
Abstract: High-brightness blue, green and yellow light-emitting diodes(LEDs)with quantum well structures based on III-V nitrides weregrown by metalorganic chemical vapor deposition on sapphire substrates. The typical green LEDs had a peak wavelength of 525 nm and full width at half-maximum(PWHM)of 45 nm. The output power, the external quantum efficiency and the luminous intensity of green LEDs at a forward current of 20 mA were 1 mW, 2.1% and 4 cd, respectively. The luminous intensity of green LEDs(4 cd)was about 40 times higher than that of conventional green GaP LEDs(0.1 cd). Typical yellow LEDs had a peak wavelength of 590 nm and FWHM of 90 nm. The output power of yellow LEDs was 0.5 mW at 20 mA. When the emission wavelength of III-V nitride LEDs with quantum well structures increased from the region of blue to yellow, the output power decreased dramatically.
Keywords: InGaN; AlGAN; quantum well structure; Blue LED; Green FED; Yellow LED
来源出版物:Japanese Journal of Applied Physics Part 2-Letters,1995, 34(7A): L797-L799
被引频次:474
High-Power GaN p-n-junction Blue-light-emitting diodes
Nakamura, S; Mukai, T; Senoh, M
Abstract: High-power p-n junction blue-light-emitting diodes(LEDs)were fabricated using GaN films grown with GaN buffer layers. The external quantum efficiency was as high as 0.18%. Output power was almost 10 times higher than that of conventional 8-mcd SiC blue LEDs. The forward voltage was as low as 4V at a forward Current of 20 mA. This forward voltage is the lowest ever reported for GaN LEDs. The peak wavelength and the full width at half-maximum(FWHM)of GaN LEDs were 430 nm and 55 nm, respectively.
Keywords: GaN; buffer layer; P-N junction LED; output power; external quantum efficiency; forward voltage
来源出版物:Japanese Journal of Applied Physics Part 2-Letters, 1991, 30(12A): L1998-L2001
被引频次:432
Characteristics of InGaN-based UV/blue/green/amber/red light-emitting diodes
Mukai, T; Yamada, M; Nakamura, S
Abstract: Highly efficient light-emitting diodes(LEDs)emitting ultraviolet(UV); blue, green, amber and red light have been obtained through the use of InGaN active layers instead of GaN active layers. Red LEDs with an emission wavelength of 675 nm, whose emission energy was almost equal to the band-gap energy of InN, were fabricated. The dependence of the emission wavelength of the red LED on the current(blue shift)is dominated by both the band-tilling effect of the Idealized energy states and the screening effect of the piezoelectric held. In the red LEDs, a phase separation of the InGaN layer was clearly observed in the emission spectra, in which blue and red emission peaks appeared. In terms of the temperature dependence of the LEDs, InGaN LEDs are superior to the conventional red and amber LEDs due to a large band offset between the active and cladding layers. The localized energy states caused by In composition fluctuation in the InGaN active layer contribute to the high efficiency of the InGaN-based emitting devices, in spite of the large number of threading dislocations and a large effect of the piezoelectric field. The blue and green InGaN-based LEDs had the highest external quantum efficiencies of 18% and 20% at low currents of 0.6 mA and 0.1 mA, respectively.
Keywords: InGaN; GaN; LEDs; blue; green; amber; SQW; ELOG; dislocations
来源出版物:Japanese Journal of Applied Physics Part 1-Regular Papers Short Notes & Review Papers, 1999, 38(7A): 3976-3981
被引频次:427
High-Power InGaN Single-quantum-well-structure blue and violet light-emitting-diodes
Nakamura, S; Senoh, M; Iwasa, N; et al.
Abstract: High-power blue and violet light-emitting diodes(LEDs)based on III-V nitrides were grown by metalorganic chemical vapor deposition on sapphire substrates. As an active layer, the InGaN single-quantum-well-structure was used. The violet LEDs produced 5.6 mW at 20 mA, with a sharp peak of light output at 405 nm, and exhibited an external quantum efficiency of 9.2%. The blue LEDs produced 4.8 mW at 20 mA and sharply peaked at 450 nm, corresponding to an external quantum efficiency of 8.7%, These values of the output power and the quantum efficiencies are the highest ever reported for violet and blue LEDs.
Keywords: GaN
来源出版物:Applied Physics Letters, 1995, 67(13): 1868-1870
被引频次:295
High-luminosity Blue and Blue-green gllium ntride light-emitting-diodes
Morkoc, H ; Mohammad, SN
Abstract: Compact and efficient sources of blue tight for full color display applications and lighting eluded and tantalized researchers for many years. Semiconductor light sources are attractive owing to their reliability and amenability to mass manufacture. However, large band gaps are required to achieve blue color. A class of compound semiconductors formed by metal nitrides, GaN and its allied compounds Al-GaN and InGaN, exhibits properties well suited for not only blue and blue-green emitters, but also for ultraviolet emitters and detectors. What thwarted engineers and scientists from fabricating useful devices from these materials in the past was the poor quality of material andlack of p-type doping. Both of these obstacles have recently been overcome to the point where high-luminosity blue and blue-green light-emitting diodes are now available in the marketplace.
Keywords: GaN chemical vapor-deposition; molecular-beam epitaxy; GaN; growth; GaAs; semiconductors
来源出版物:Science, 1995, 267(5194): 51-55
被引频次:279
White-light emission from near UV InGaN-GaN LED chip precoated with blue/green/red phosphors
Sheu, JK; Chang, SJ; Kuo, CH; et al.
Abstract: Phosphor-converted light-emitting diodes(LEDs)were fabricated by precoating blue/green/red phosphors onto near ultraviolate(n-UV)LED chips prior to package into LED lamps. With a 20-mA injection current, it was found that the color temperature T-c was around 5900 K and the color-rendering index R-a was around 75 for the "n-UV+blue/green/red" white LED lamps. It was also found that no changes in color temperature T-c and color-rendering index R-a could be observed when we increased the injection from 20 to 60 mA. These results indicate that such "n-UV+blue/green/red" white LEDs are much more optically stable than the conventional "blue+yellow" LEDs.
Keywords: color-rendering index; color temperature; GaN; phosphor; white-light light-emitting diode(LED)
来源出版物:IEEE Photonics Technology Letters, 2003, 15(1): 18-20
被引频次:253
Blue light-emitting diode based on ZnO
Tsukazaki, A; Kubota, M; Ohtomo, A; et al.
Abstract: A near-band-edge bluish electroluminescence(EL)band centered at around 440 nm was observed from ZnO p-i-n homojunction diodes through a semi-transparent electrode deposited on the p-type ZnO top layer. The EL peak energy coincided with the photoluminescence peak energy of an equivalent p-type ZnO layer, indicating that the electron injection from the n-type layer to the p-type layer dominates the current, giving rise to the radiative recombination in the p-type layer. The imbalance in charge injection is considered to originate from the lower majority carrier concentration in the p-type layer, which is one or two orders of magnitude lower than that in the n-type one. The current-voltage characteristics showed the presence of series resistance of several hundreds ohms, corresponding to the current spread resistance within the bottom n-type ZnO. The employment of conducting ZnO substrates may solve the latter problem.
Keywords: ZnO; light-emitting diode; thin film; pulsed laser deposition; self-absorption
来源出版物:Japanese Journal of Applied Physics Part 2-Letters & Express Letters, 2005, 44(20-23): L643-L645
联系邮箱:kaswasaki, M; kawasaki@imr.tohoku.ac.jp
·推荐论文摘要·
基于纳米压印技术制作的线偏振蓝光LED
李万永,韩彦军,罗毅
摘要:提出一种准确计算LED偏振度(PR)的方法,并采用纳米压印技术制作了线偏振蓝光LED.方法考虑了LED朗伯型发光,计算整个半平面入射光透过光栅的TM模在TE和TM模中所占百分比.详细分析了光栅材料、光栅周期、占空比和光栅高度等对PR的影响.结果表明,当Al金属光栅周期为150 nm、占空比为0.5和光栅高为120 nm时,PR几乎为1;利用纳米压印技术结合感应耦合等离子刻蚀技术,制作了铝金属光栅.实际测试结果表明,将蓝光LED的偏振消光比(PER)由1.0∶1.0大幅度提高为2.2∶1.0.
关键词:线偏振LED;Al金属光栅;偏振度(PR);偏振消光比(PER);纳米压印
来源出版物:光电子激光, 2013, 24(6): 1042-1047联系邮箱:韩彦军,yjhan@mail.tsinghua.edu.cn
Effect of Stepwise Doping on Lifetime and Efficiency of Blue and White Phosphorescent Organic Light Emitting Diodes
Lee, Song Eu; Lee, Ho Won; Lee, Seok Jae; et al.
Abstract: We investigated a light emission mechanism of blue phosphorescent organic light emitting diodes(PHOLEDs), using a stepwise doping profile of 2, 8, and 14 wt.% within the emitting layer(EML). We fabricated several blue PHOLEDs with phosphorescent blue emitter iridium(III)bis[(4,6-difluorophenyl)-pyridinato-N,C-2]picolinate doped in N,N'-dicarbazolyl-3,5-benzene as a p-type host material. A blue PHOLED with the highest doping concentration as part of the EML close to an electron transporting layer showed a maximum luminous efficiency of 20.74 cd/A, and a maximum external quantum efficiency of 10.52%. This can be explained by effective electron injection through a highly doped EML side. Additionally, a white OLED based on the doping profile was fabricated with two thin red EMLs within a blue EML maintaining a thickness of 30 nm for the entire EML.
Keywords: Blue Phosphorescent Organic Light Emitting Diodes; Stepwise Doping Structure; Charge Trapping Effect
来源出版物:Journal of Nanoscience and Nanotechnology, 2015, 15(2): 1456-1459
Substituent effects in twisted dibenzotetracene derivatives: Blue emitting materials for organic light-emitting diodes
Xiao, Jinchong; Liu, Zhenying; Zhang, Xuemin; et al.
Abstract: A series of dibenzotetracene derivatives containing different substituents at the 11-, 12-positions have been successfully synthesized and characterized. Single crystal X-ray analysis indicates that the new molecules have a twisted structure, which can effectively decrease the intermolecular aggregation in the solid-state. The effect of both substitueut and packing on the corresponding physical properties was also investigated. In addition, organic light-emitting diodes doped with 11,12-difluoro-9,14-diphenyl-dibenzo [de,qr]tetracene into the emitter 9,9'-(1,3-phenylene)bis-9H-carbazole were fabricated and exhibit good performance.
Keywords: Synthesis; Single crystal; Twisted structure; Optoelectronic property; Acene; Organic light-emitting diodes
来源出版物:Dyes and Pigments, 2015, 112: 176-182联系邮箱:Xiao, JC,jcxiaoiccas@gmail.com; jwzhao2011@sinano.ac.cn
Carrier Transport Improvement in Blue InGaN Light-Emitting Diodes Via Reduced Polarization Using a Band-Engineered Electron Blocking Layer
Sun, Pei; Dang, Suihu; Li, Tianbao; et al.
Abstract: This study numerically investigates the effect of using a new electron blocking layer(EBL)for blue InGaN light-emitting diodes(LEDs)to improve hole injection efficiency and electron confinement. Simulation results suggest that the carrier transportation behavior of the EBL can be appropriately modified by adept control of the graded AlGaN layer. Furthermore, when compared with the conventional LED structure, the redesigned LED with graded AlGaN layer shows a slight improvement in forward voltage and a significant enhancement in light output power. The redesigned LED can achieve an exceptional increment of 106.6% in light output power at 100 mA when compared with conventional LED. The observed improvement in the photoelectric performance of blue LEDs is primarily due to the reduced polarization effect at the last-barrier/EBL interface, as a result of the graded Al composition in EBL.
Keywords: Electron blocking layer(EBL); light-emitting diodes(LEDs); polarization effect
来源出版物:Journal of display technology, 2014, 10(12): 1101-1105联系邮箱:Li, Tianbao; litianbao@tyut.edu.cn
New Bipolar Host Materials for Realizing Blue Phosphorescent Organic Light-Emitting Diodes with High Efficiency at 1000 cd/m2
Cho, Min Ju; Kim, Sun Jae; Yoon, Seung Hee; et al.
Abstract: New host molecules such as 9-(6-(9H-carbazol-9-yl)pyridin-3-yl)-6-(9H-carbazol-9-yl)-9H-pyrido[2,3-b]indole(pPCB2CZ)and 9-(6-(9H-carbazol-9-yl)pyridin-2-yl)-6-(9H-carbazol-9-yl)-9H-pyrido[2,3-b]indole(mPCB2CZ)were designed and synthesized for blue phosphorescent organic light-emitting diodes(PhOLEDs). The glass transition temperatures of two host molecules were measured higher than 120 degrees C, and the identical triplet energies were determined to be 2.92 eV for both molecules. The bis(3,5-difluoro-2-(2-pyridyl)phenyl-(2-carboxypyridyl)iridium(III)(FIrpic)-doped mPCB2CZ-based PhOLED exhibited practically useful driving voltage of 4.8 V in a simple organic three layer device configuration which has a smaller number of interfaces in conventional multilayer PhOLEDs. Also, the high quantum efficiency of 23.7% is reported at the practically useful brightness value of 1000 cd/m2.
Keywords: organic light emitting diode; phosphorescence; bipolar host; carboline; quantum efficiency
来源出版物:Acs Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2014, 6(22):19808-19815
联系邮箱:Kwon, JH; jhkwon@khu.ac.kr; dchoi8803@korea.ac.kr
Recoverable degradation of blue InGaN-based light emitting diodes submitted to 3 MeV proton irradiation
De Santi, C.; eneghini, M.; Trivellin, N.; et al.
Abstract: This paper reports on the degradation and recovery of two different series of commercially available InGaN-based blue light emitting diodes submitted to proton irradiation at 3 MeV and various fluences(10(11), 10(13), and 10(14)p(+)/cm(2)). After irradiation, we detected(i)an increase in the series resistance, in the sub-turn-on current and in the ideality factor,(ii)a spatially uniform drop of the output optical power, proportional to fluence, and(iii)a reduction of the capacitance of the devices. These results suggest that irradiation induced the generation of non-radiative recombination centers near the active region. This hypothesis is further confirmed by the results of the recovery tests carried out at low temperature(150 degrees C).
Keywords: Electrical Characteristics; GaN; Damage; LEDs; Temperature; GaAs; Mg
来源出版物:Applied Physics Letters, 2014, 105(21)联系邮箱:Meneghini, M; matteo.meneghini@dei.unipd.it
Tuning Emission Colors from Blue to Green in Polymeric Light-Emitting Diodes Fabricated using Polyfluorene Blends
Quites, Fernando, Jr.; Faria, Gregorio Couto; Germino, Jose Carlos; et al.
Abstract: The photo- and electroluminescent properties of single-layer two-component blends composed of one blue emitter polymer and one green emitter polymer were studied. The blue emitter, poly[(9,9-dioctylfluorenyl-2,7-diyl)-alt-co-(9,9-di-{5'-pentanyl}-fluorenyl-2,7-diyl)](PFOFPen), was used as the matrix, and the green emitter, poly[(9,9-dihexylfluorenyl-2,7-diyl)-alt-co-(bithiophene)](F6T2), was used as the guest. The F6T2 content in the blends varied from 0.0075 wt % to 2.4 wt %. Remarkable differences were observed between the electroluminescent(EL)and photoluminescent(PL)spectra of these blends, which indicated that the mechanism for excited-state generation in the former process had a higher efficiency in the aggregated phase than in the nonaggregated phase. Blending these two polymers gradually tuned the emission color from blue(PFOFPen and blends with <0.75 wt % F6T2)to green(F6T2 and blends with >0.75 wt % F6T2). The photophysical processes involved in both EL and PL emission are also discussed.
Keywords: electroluminescence; devices; morphology; PPV
来源出版物:Journal of Physical Chemistry A, 2014, 118(45): 10380-10390联系邮箱:Atvars, TDZ; tatvars@iqm.unicamp.br
Effect of arylamine hole-transport units on the performance of blue polyspirobifulorene light-emitting diodes
Abbaszadeh, Davood; Nicolai, Herman T.; Craciun, N. Irina; et al.
Abstract: The operation of blue light-emitting diodes based on polyspirobifluorene with a varying number of N,N,N',N' tetraaryldiamino biphenyl(TAD)hole-transport units(HTUs)is investigated. Assuming that the electron transport is not affected by the incorporation of TAD units, model calculations predict that a concentration of 5% HTU leads to an optimal efficiency for this blue-emitting polymer. However, experimentally an optimum performance is achieved for 10% TAD HTUs. Analysis of the transport and recombination shows that polymer light-emitting diodes with 5%, 7.5%, and 12.5% TAD units follow the predicted behavior. The enhanced performance of the polymer with 10% TAD originates from a decrease in the number of electron traps, which is typically a factor of three lower than the universal value found in many polymers. This reduced number of traps leads to a reduction of nonradiative recombination and exciton quenchingat the cathode.
Keywords: recombination; polyfluorene; copolymers
来源出版物:Physical Review B, 2014, 90(20): 205204
Blue Inorganic Light Emitting Diode on Flexible Polyimide Substrate Using Laser Lift-Off Process
Barange, Nilesh; Kim, Young Dong; Ko, Hyungduk; et al.
Abstract: The fabrication process for the blue GaN inorganic light emitting diode(ILED)on flexible polyimide(PI)substrate by laser lift off(LLO)method was demonstrated. The GaN epi-structure was grown on patterned sapphire wafer. GaN samples were temporary bonded with polyimide substrate by flexible silver epoxy. Separation of the whole GaN LED film from GaN/sapphire wafer was accomplished using a single KrF excimer(248 nm)laser pulse directed through the transparent sapphire wafer. Device fabrication was carried out on both rigid silicon and flexible polyimide substrate, and I-V performance for both devices was measured. The optimized LLO process for the whole GaN LED film transfer would be applicable in flexible LED applications without compromising electrical properties.
Keywords: Laser Lift Off; Inorganic Light Emitting Diode; Flexible Substrate; Blue Light Emitting Diode
来源出版物:Journal of Nanoscience and Nanotechnology, 2014, 14(11): 8237-8241
Deep blue organic light-emitting diode using non anthracene-type fused-ring spiro[benzotetraphene-fluorene]with aromatic wings
Kim, Min-Ji; Lee, Chil-Won; Gong, Myoung-Seon
Abstract: We prepared three spirobenzotetraphene-based fused-ring spiro [benzo[ij]tetraphene-7,9'-fluorene](SBTF)derivatives for use in non anthracene-type deep-blue organic light-emitting diode(OLED)hosts. 3-(2-Naphthyl)-10-naphthylspiro[benzo[ij]tetraphene-7,9'-fluorene](N-NSBTF),3-[4-(2-naphthyl)phenyl]-10-naphthylspiro[benzo[ij]tetraphene-7,9'-fluorene](NP-NSBTF),and 3-(phenyl)-10-naphthylspiro [benzo[ij] tetraphene-7,9'-fluorene](P-NSBTF)were synthesized via multi-step Suzuki coupling reactions. The optimized device structure - ITO/N,N'-bis-[4-(di-m-tolylamino)phenyl]-N,N'-diphenylbiphenyl-4,4'-diamine(DNTPD, 60 nm)/bis[N-(1-naphthyl)-N-phenyl] benzidine(NPB, 30 nm)/ NSBTF hosts: LBD(5%)(20 nm)/ aluminum tris(8-hydroxyquinoline)(Alq(3),20 nm)/LiF/Al- was characterized by its blue electroluminescence to have a current efficiency of 6.25 cd/A, a power efficiency of 5.07 lm/W, and an external quantum efficiency of 5.24% at 18.7 mA/cm2at CIE coordinates of 0.130, 0.149.
Keywords: Fluorescence; Deep blue host; Spiro[benzotetraphene-fluorene]; Color purity; Fused-ring
来源出版物:IEEE Journal of Quantum Electronics, 2014, 50(11): 911-920联系邮箱:Gong, MS; msgong@dankook.ac.kr
(责任编辑王帅帅,卫夏雯)
Candela-Class high-brightness Ingan/Algan double-heterostructure Blue-Light-Emitting Diodes
Nakamura, S; Mukai, T; Senoh, M
Candela-class high-brightness InGaN/AlGaN double-heterostructure(DH)blue-light-emitting diodes(LEDs)with the luminous intensity over 1 cd were fabricated. As an active layer, a Zn-doped InGaN layer was used for the DH LEDs. The typical output power was 1500 muW and the external quantum efficiency was as high as 2.7% at a forward current of 20 mA at room temperature. The peak wavelength and the full width at half-maximum of the electroluminescence were 450 and 70 nm, respectively. This value of luminous intensity was the highest ever reported for blue LEDs.
GaN growth; doped GaN; films; temperature; Movpe
*摘编自《物理》2014年43卷12期802~808页

