Analysis of Satisfaction with Business Cost in Shanghai Using Structural Equation Modeling Approach
GUO Yan(郭彦),SUN M ing-gui(孙明贵)
Glorious Sun School of Business&Management,Donghua University,Shanghai200051,China
Analysis of Satisfaction with Business Cost in Shanghai Using Structural Equation Modeling Approach
GUO Yan(郭彦)*,SUN M ing-gui(孙明贵)
Glorious Sun School of Business&Management,Donghua University,Shanghai200051,China
Tracing the origins of business cost,to define the satisfaction assessment factors on the business cost in Shanghaiwas investigated in this paper.Arguing that these effects:a single low cost is not only the criterion determ ining satisfaction.Other im portant factors,such as enterprise internal cognitive attitude,stability of the external environment,the quality of perceptions of government services can affect satisfaction.within structural equation modeling(SEM)approach,six sets of hypotheses are drawn up and tested with a samp le of 338 enterprises using questionnaires.Additionally,the analyses of findings introduce the crucial importance of these features in the assessment of satisfaction with business cost in Shanghai.Finally,the results show that internal cognitive has a positive im pact on satisfaction.Stability of the external environment has a significant relationship with the effectiveness of government services.Stability of the external environmeat and the effectiveness of government servises have a positive effect on satisfaction.
business cost;structural equation modeling(SEM); satisfaction
Introduction
The studying of business cost originated from“Fortune”,world's best business city ranking in the mid-1990s.It is commonly used in a comparative study on business environment applications.According to describing a cost,investor immediately makes a corresponding decision into investment.A number of research institutions and internationally renowned consulting companies also have carried out business cost of the investigation and investment environment,such as CEBR (Centre for Economics Business Research(1999)),JETRO (Japan External Trade Organization(1995)),Nikkei PC (2000),Arthur Andersen(2002),KPMG(2002),M inistry of Industry surveys of Australia(2002),MMK Consulting firm of Canada and Andy Holloway(2004).However,there is no professional organization in China.
About the elements of the business costs in Shanghai,scholars have different divisions.Fu et al.[1]made a comparative study on business cost majorly considered labor costs,property acquisition costs,communications costs (including transportation),utilities expenses and adm inistrative costs in Shanghai,Beijing,etc.Fu and Sheng[2]made up elaborated explicit costs(such as labor,land),the hidden costs (such as policy,transportation,government services)on the Shanghai and neighboring cities.An and Li[3]compared with business cost of Nanjing,Wuxi,Kunshan,Ningbo,Shanghai,including transaction costs(human factors,land,water and electricity prices,government operational efficiency,development of market mechanisms,etc.)and other costs (social security situation,etc.).Enterprise Investigation Team in Zhejiang Province[4]conducted a survey in which they compared with Jiangsu,Zhejiang,Guangdong,Fujian Provinces and Shanghai on satisfaction with business costs of land and real estate,infrastructure,market economy,supporting industries,labor quality,legalenvironment.Sun and Chen[5]demonstrated that constitute of business cost was hard costs(the factors of production(labor,land,etc.))and soft costs(by law,government policy,etc.)with the empirical data in Xi'an,Beijing,Shanghai,and Shenzhen.Wang et al.[6]considered cost of doing business in Shanghai and trends of structural changes in the status of factor costs(labor,land,energy and capital costs),operating costs (transportation,consulting,etc.),the system costs (governmentapprovaland control index,etc.)and other costs. Su and Sun[7]analyzed business cost structure in Jiangsu,Zhejiang Provinces and Shanghai and got the impact on industrial transfer path by the factor cost ratio(commercial facilities and land costs,labor costs)and transaction cost(the efficiency of government operations,market-oriented,cost infrastructure,research and development capabilities). Currently,the definition of the cost of doing business does not determ ine in academ ic,so the elements are classified according to their research needs.
In general,researches on the cost of doing business are built on empirical analysis and investigation reports according to Enterprise Survey Team in 2003 making business cost assessment report in Shanghai,Jiangsu,Zhejiang,Fujian,Shandong,Guangdong Provinces.Satisfaction survey results show that:foreign investor satisfied the social credit environment and legal environment in Zhejiang,but satisfaction and efficiency of service levels of government in the last ranking was scoring in Shandong Province[8].Enterprise Investigation Team in Zhejiang Province[4]surveyed more than 100 companies and the results showed that investor in medium-sized privately-owned and foreign manufacturers tended to choose Hangzhou,Ningbo and Wenzhou,Jiaxing,Taiwan(5 Cities). According to the survey by Quzhou City Enterprise Survey Team[9],when compared cost of doing business for entrepreneurs satisfaction in Quzhou's enterprise with those of Jinhua,Lishui,Wenzhou and Shangrao Cities,analyses survey showed that Quzhou's satisfaction survey was in middle level in the five cities.ShanghaiWaigaoqiao Free Trade Zone Investment Environment Survey Report,noting Waigaoqiao government departments backward management and service awareness is weak,so thatenterprises cannotget timely changing policy Trade Zone,China's labor cost advantage is insufficient to cover product quality and service issues[10].Although these studies have provided a useful mapping of business cost research,the performance implications of this strategy for the development enterprise remain under-explored in Shanghai.
Shanghai,an internationalmetropolis,has been one of the highest levels of profitability in amajor city with the cost-benefit analysis perspective.The satisfaction with costof doing business in Shanghai will directly affect the economic development ofShanghai.In 2002,Jiang Y R,Vice Mayor of Shanghai,3rd Economist Roundtable opening meeting speech in Shanghai on February 28,said Shanghai would strive to reduce the cost of doing business for investors[11].Since then scholars setoff on a wave of studies on business cost in Shanghai.Facing with labor costs,land and real estate prices continue to rise,a lot of foreign capital inflow into surrounding cities phenomenon such as the topic Shanghai project focuses on controlling business costs and industrial development in Shanghai[11].“173 planning”has opened to interpretation to cut business costs,promoting connotation of manufacturing in Shanghai. Nowadays,the establishment of free trade zone in Shanghai is still considered on reducing business costs,seeking a new way of development in Shanghai and enhancing the competitiveness in Shanghai.In recent,along with manpower,land,raw materials,energy and rents rose sharply and the appreciation of the RMB,as well as a series of policy changes,business enterprises is facing unprecedented comprehensive business cost impact,especially rising cost of doing business in Shanghai. Business enterprises will be the way to properly treat the cost[12].To this end,we surveyed business costs satisfaction in Shanghai.
We explore the satisfaction of cost of doing business in Shanghai is divided into two core objective studies:enterprise and government.Firstly,business background and concept to which we refer above is sketched in the introduction.Secondly,we develop and test six sets of hypotheses using a sample of 338 enterprises,and extend this research by presentingmathematical statistics in structural equation modeling(SEM)method to verify the hypotheses in section 1.Thirdly,we prove that internal cognitive has a positive impact on satisfaction.Stability of the external environment has a positive relationship with the effectiveness of government services,and they have a positive effect on satisfaction in section 2.Finally,we conclude a general discussion and directions for further research in section 3.
1 Roadm ap and Research Methods
1.1 Research methods
SEM is a new statistical method in the m id-70s of last century,Sweden statisticians,sociologists Karl Gustav Jöreskog psychometric first proposed the concept[13].In 1980s the method spread into China,it was extensively used in economics,sociology,management,psychology and other fields.Multivariate data analysis as an important tool can solve a number of reasons,because the real problem of the relationship betweenmultiple results cannot be directly observed or latent variables.Structural model is actually a sense of the regressionmodel.Its main work is not only to make sure the model is appropriate,but also becomes a method of values between latent variables corresponding regression path coefficients estimated[14].We develop and test six proposed hypotheses,through SEM analysis verified observation covariance between variables,using statistical tools to test the potential relationship between the variables assumed to be reasonable.
1.2 Hypothesis of study
Business decision-makers concerned about not only price satisfaction butalso quantifiable business costs.We can consider that decision-makers within the enterprise cognitive approach,the stability of the external environment and the quality of government services perceived to constitute the overall awareness of the costof doing business in Shanghaisatisfaction. Therefore,we propose six assumptions(Table 1),combined with structural equation model of mathematical statistics as an analysis tool to verify,described in Table 1.Six hypothetical relationships are established.
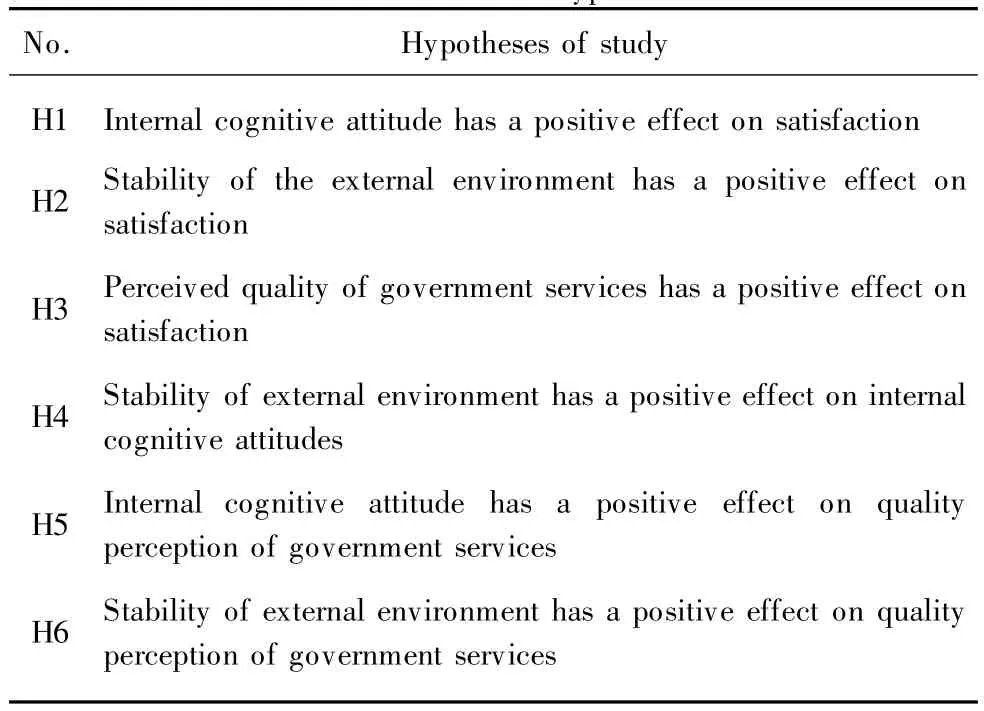
Table 1 Research hypotheses
1.3 Project of the study
Based on assumptions of research and there are two principal part objects:enterprise and government.We designed the satisfaction survey analysis for the three categories of 29 indicators to construct themodel of Shanghaibusiness costs and build the mutual relationship each other on satisfaction model (Fig.1).The relationships between the indicators can be clear,and we discuss these relationships inmore detail in section 2.
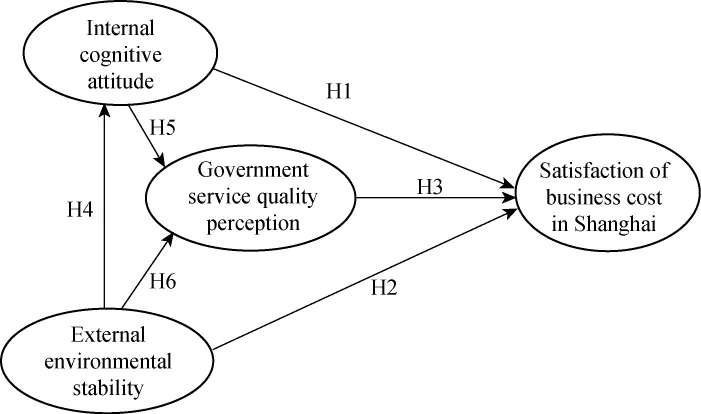
Fig.1 Satisfaction ofmodel of business cost in Shanghai
1.4 Structural equation variable system s and indicator variables
There are 29 satisfactory indicators of three categories survey,which are as follows:Internal costs(rental prices,housing prices,land transaction prices,the price of labor,water prices,electric prices,social security costs,health insurance costs,logistics costs,infrastructure,communication costs,taxes,and various administrative fees),corporate the external environment(market economic order,the production environment,the quality of labor,legal environment,social credit,and e-commerce environment),government services costs(efficiency of government,the administrative exam ination and approval procedures,quality of service and attitude of staff professional quality,professional staff ethics,transparency in government affairs,law enforcement policies,the stability and continuity of policies and regulations,and policy planning guide and role).
It is important to emphasize that before filling in questions regarding the business cost types,respondents were mentioned above.We have selected one to one(face to face) questionnaire way to control the quality and authenticity of thesurveymethod,in order tomake research resultsmore valuable. Data were analyzed and tested using SEM to examine the relationship between various factors and satisfaction,and calculated data using AMOS21.0 and SPSS19.0 statistical software.In this study,likert5 point scale[15]means that the minimum level 1 and 5 represents the highest level,ranging from 1(strongly disagree)to 5(strongly agree).The averaged responses to these items formed a composite index of extensive evaluations for analysis.Our goal is to promote intercomparison study of diverse values scale.The survey work is carried out in Shanghai,taking into account the cost of doing business in Shanghai research data fruitful in recent years. Numerous scholars have contributed with comparative data.For this reason,in the construction of model variables system,according to research presented above,we assume that combines elements of business costs in Shanghai with independence and operability principles.We design the survey system with four latent variables and 29 variables observed variables,as shown in Table 2.
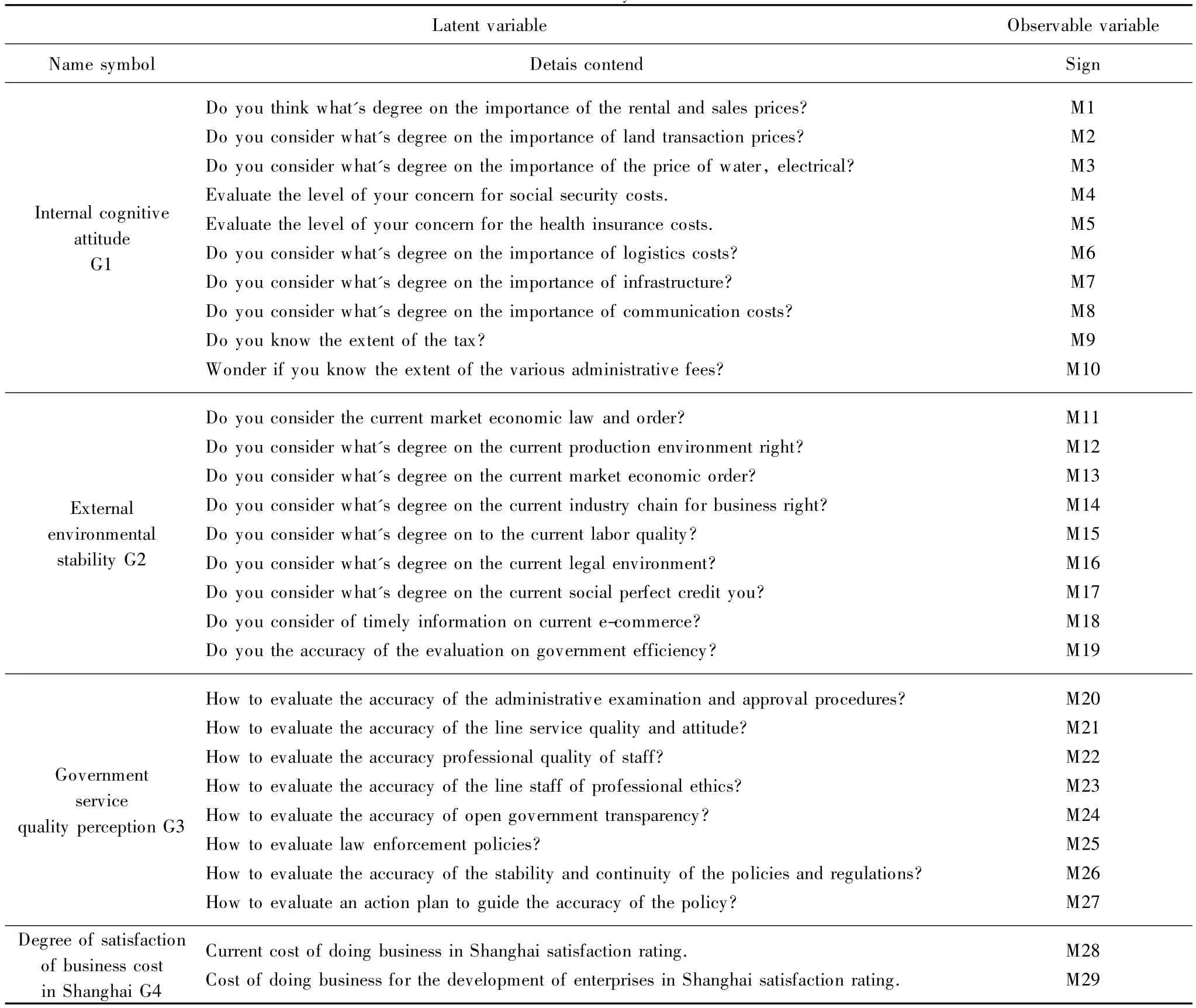
Table 2 Variable system of SEM
1.5 Data collection
A survey consisted of a sample of 300 enterprises was conducted in Shanghai.a survey of the costof doing business in Shanghai was made.In this study,we use a questionnaire survey of leaders and decision-makers and relevant department's responsible person with the site visits,interviews,mail,send E-mail,etc.A total of 602 questionnairesweremailed along with pre-addressed postage paid envelops and a cover letter explaining the purpose of the study.This procedure yielded 338 usable questionnaires and resulted in a response rate of 56. 33%.In the course of the investigation,sending questionnaire surveys were analyzed using targeted,of which 300 valid questionnaires at last.As Nunnally proposed that the number of survey sample is 10 times the amount of significant variables[16],the number of valid sample article(300>290)is in line with the sample multiple logistic(ML)method prescribed.
1.6 Samp le analyses
Finally,this procedure yielded 300 useable questionnaires. The sample consists of300 companies in Shanghai,including 50 industrialmanufacturing enterprises,accounting for 16.67%; 46 commercial enterprises,accounting for 15.33%;42 financial companies,accounting for 14%;36 real estate enterprises,accounting for 12%;36 logistics advertising companies,accounting for 12%;48 trade enterprises,accounting for 16%;30 cosmetics companies,accounting for 10%;the Group's headquarters,accounting for 6,2%;and other companies(consulting services),accounting for 6,2%.
From the business perspective of capital sources,including 196 Chinese enterprises,accounting for 65.33%,56 foreign-owned enterprises,accounting for18.67%and 39 joint ventures (13%),9 cooperative Joint Venture(CJV)(3%)(see Table 3).
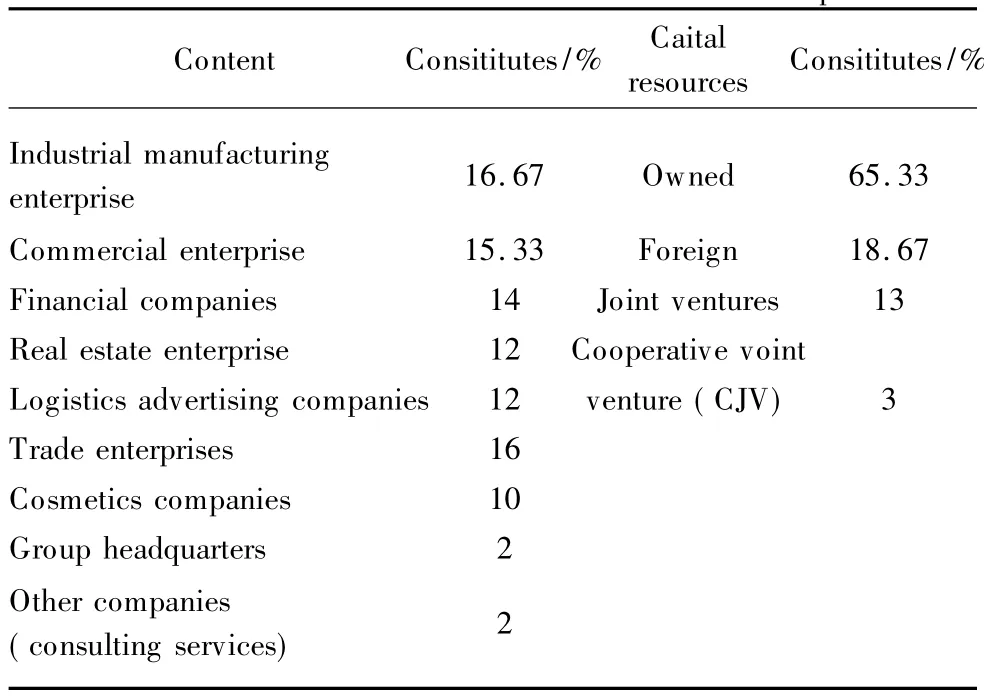
Table 3 Statistical Characteristics table of the sample
2 Analyses and Results
2.1 Reliability testing
The reliability was evaluated and the results indicated the consistency coefficient(Cronbach's Alpha)values for testing the data in academ ia.According to Nunnally's[16]viewpoints,Cronbach's Alpha coefficients are closer to 1,the highest reliability,but certainly cannotbe1,so repeatedly inmeasuring a problem.Hair et al.pointed out that the internal consistency coefficient greater than 0.7(Cronbach's Alpha>0.7) indicated higher scale reliability[17].However,in the exploratory study,the internal consistency coefficient can be lower than 0.7,but should be greater than 0.6.In this study,using SPSS19.0 for each setof variable consistency test(results presented in Table4)in each variable,Cronbach's Alpha values were greater than 0.6,indicating that the reliability of the scale was acceptable.

Table 4 Reliability test
2.2 Validation ofmeasures
A combination of SPSS19 and AMOS21 software packages was used to carry out all the data analyses.This study first examined the univariate skewness and kurtosis of the variables and we found that the figureswere acceptable.Next,this study performed the Kaiser-Meyer-Olkin(KMO)and Bartletter's test because both methods were w idely used in previous studies to ensure that the data have inherent sufficient correlations to perform exploratory factor analysis(EFA)[18].To understand the factor structure and the measurement quality,a principal component analysis was concluded content validity.Content validity wasmainly considered the degree of correlation between the measurement of the content and information collection,which reflecting the reality of the degree scale applications.We use factor analysis to test the content validity,the KMO (Kaiser-Meyer-Olkin)statistic 0.842,greater than 0.7 (Bagozzi and Yi gave the standard KMO:KMO>0.9 represents Good,0.8<KMO<0.9 represents Good,0.7<KMO<0.8 represents Average,0.6<KMO<0.7 represents not suitable,KMO<0.5 represents not suitable[19]),and Bartlett test of sphericity significant factor analysis test is fitting to meet prerequisite factor analysis.In a subsequent factor analysis,using the varimax rotations,extracted four factors,the variance contribution rate of 66.67%,among 4 main factors was 60.23%,63.35%,52%and 66.67%.In survey research,the factor variance contribution rate can reach 60% (generally more than 50%of the common factors can be removed)[18].
In order to test the construct validity AMOS21.0“bootstrap”was used in the way corrective estimated Biascorrected Percentile Method.The results of Bias-corrected percentile method(see Table 5),all normalized correlation coefficients were not contained an interval,and therefore the validity of all facets represented a difference.
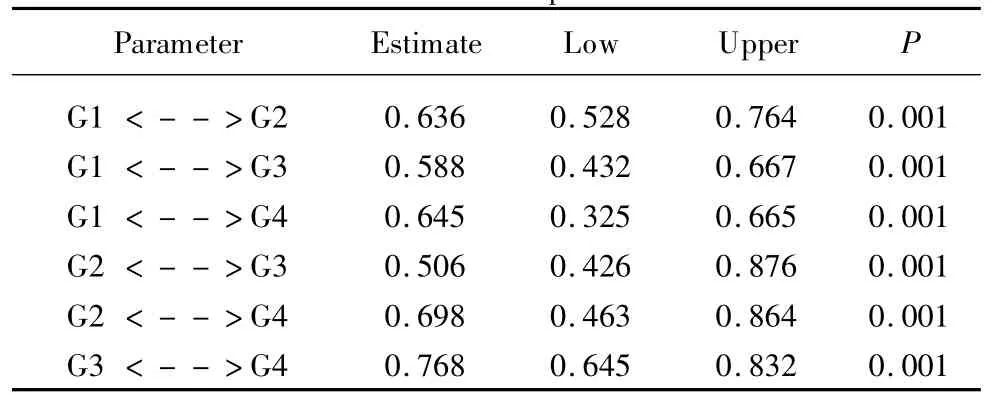
Table 5 Bias-corrected percentilemethod
Note:Double arrow(“<-->”)means that the increase of the relative path will at least reduce the residuals of themodel between two variablesmeasurable variables chi-square value
2.3 Hypothese testing and model to determ ine
Through reliability and validity testing,it shows that the reliability and validity of an indicator system of this study are strong enough to support our study.And then wewill dealwith latent variables(in Table 2)and themeasured variables into the structure in accordance with the hypothesis equation(Model 1),using AMOS21.0 in parameter estimation,and model path coefficient estimates and assumptions test as shown in Table 6. Itmentioned that H1,H2,H5(both<0.5)significantly affected satisfaction of business cost.
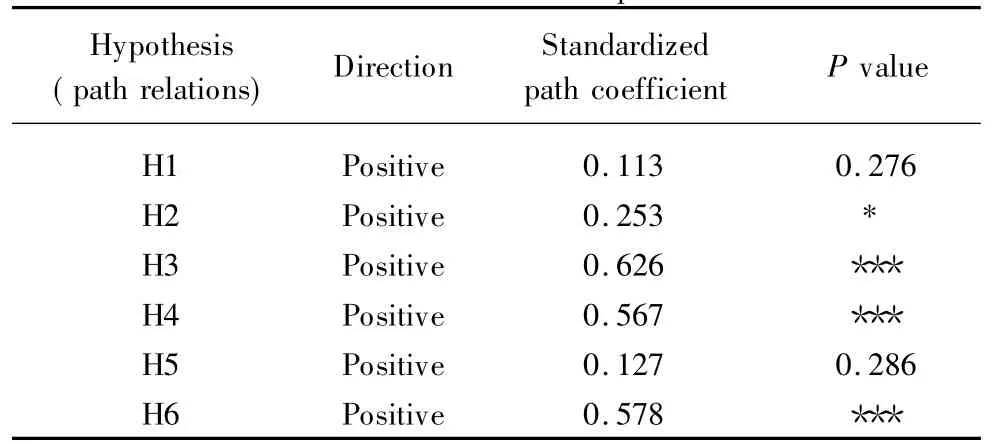
Table 6 Estimate of themodel path coefficient
Note:“*”indicates significance at the 0.5 level,“***”indicates significance at the0.01 level
We will deal with all indicator amounts by means of definition of relevant variables,measurementof formulamodel,establishment of structural formula model and fixed load method.After the preliminary analyses,structural equation modeling with maximum likelihood estimation was used to model test above.Bagozzi and Yi[19]hold that ideal value of SMC should be above 0.5.SMC value of most indicators are above 0.5 on average.Therefore,indicators in this study are suitable to be used as measurement indicators for latent variables.We delete non-significance at the0.1 path confidence level to make an amend;as model 2,add attitude to internal cognitive to satisfaction path,other paths remain unchanged as model3;add internal cognitive attitude to perceived quality of government services path on model 2;other paths remainunchanged,asmodel4.Themodel links control variables to the satisfaction of business cost.
This study examined the model 4-factorstructure by performing one factor EFA on the average scores of each modle1,model2,model3—order construct[20].Table 7 fit coefficients of each model,combined with comprehensive coefficient ratio chi-square values,such as freedom of the Comprehensive Comparison Model 1,Model 2,Model 3,and Model4 fitting results.Finally,we obtained fitting results of model 1 preferably(the final research models).In the specification of the structural model,the residuals of the mediatormay covey[21].

Table 7 Fitting degree index
Note:GFI-goodness of fit index;AGFI-amend goodness of fit index;RMSEA-root-mean-square error of approximation;NFI-normed fit index;TLI-Tucker-Lewis index;IFI-incremental fit index;CFI-comparative fit index
To sum up,based on Amos 21.0 software we use internal sense cost of doing business,and a sense stability of the quality of the environment outside the enterprise and government services were confirmatory factor analysis.Factor coefficients from estimation results were shown in Table 5.The coefficient estimateswere not standardized load CR(critical ratio values) in the 0.01 levels significantly.Each question items were standardized load factor above 0.5,indicating that each construct single weft was verified and confirmed.The convergent validity of each measurement scale projects standardized load factor was smaller than various concepts,reflecting little correlation,indicating that there was a good discriminate validity;at the same time,themodel fit indicators criterion was shown from absolute fit indicators,GFI was greater than 0.9(see Table 7),Bagozzi and Yi[19]proposed that justifiable to evaluate fitting degree of relevant model,RMSEA is error of approximation index.When below 0.1,it indicates good fit;when below 0.05,it indicates perfect fit;the highermeasurement indicatorsare goodness of fit index,such as GFI and AGFI.The fitting degree of the model was better. Almost all these indicators in this study were close to 0.9,indicating good fitting degree;fitting from value-added indicators;NFI,CFIand IFIwere close to 1.It indicated that themodel fitwas also good from the stream lined look goodness of fit index,which also reflected the model was better[22]. Foregoing value of some fit index is to evaluate fitting degree of overallmode l and verify rigor of the structure,so that we can further determine fitting degree of internal model structure,namely individual observational variables of amodel or intrinsic quality of overall structural equation.Its parameters path is shown in Fig.2.
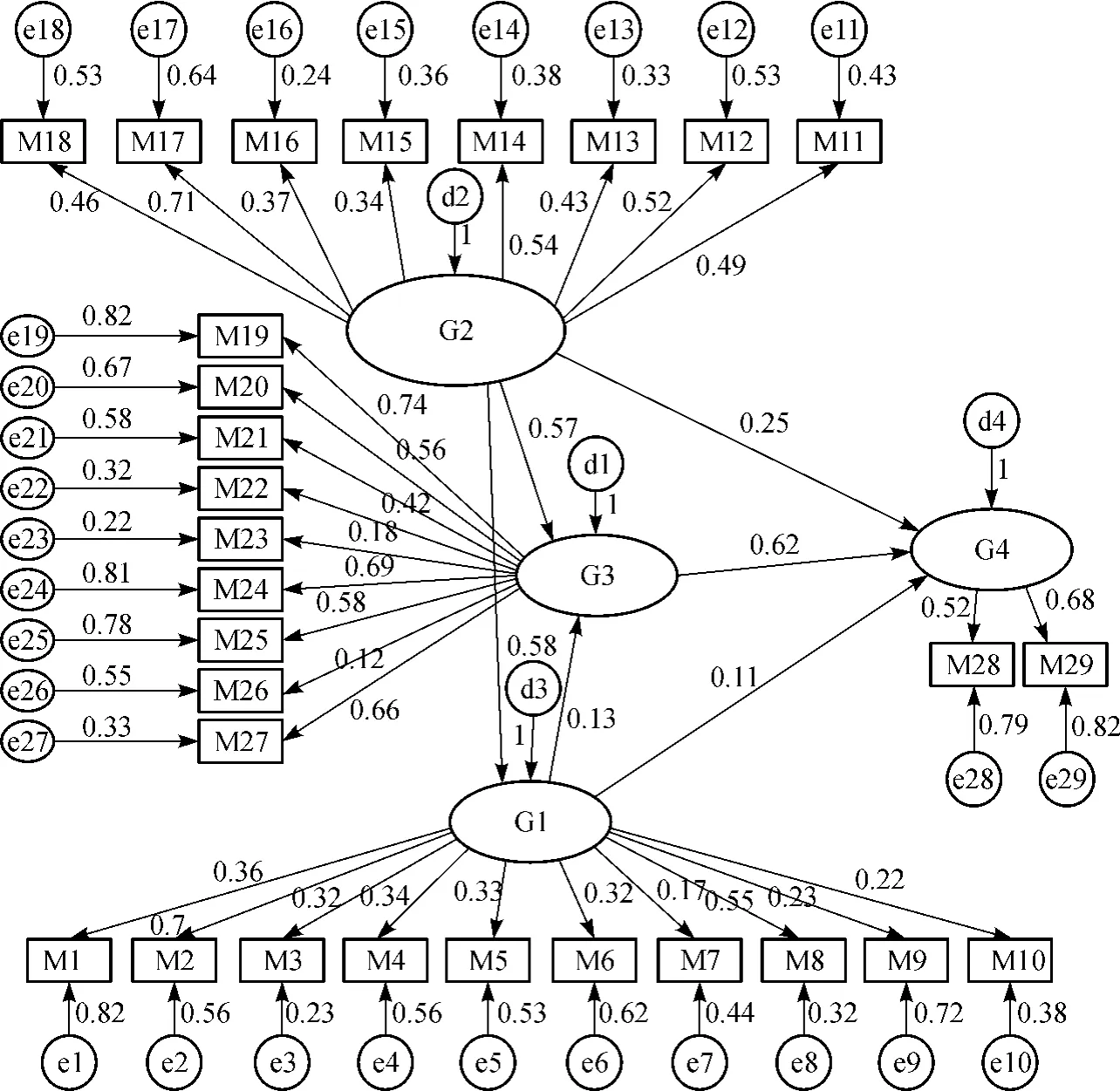
Fig.2 Outcomes ofmodel fitting
2.4 Analyses and results
By a structural equation model,we can verify the six conclusions.
(1)Quality perception of government services has a directimpact on the satisfaction of business cost in Shanghai,path coefficient of 0.62.
(2)Internal cognitive attitude also has a positive to influence on business cost satisfy the path coefficient is0.11.
(3)External environmental stability of the enterprise also has a positive effect on satisfaction,and path coefficient is 0.26;while the external environmental stability can guide internal cognitive attitude in interprise,and its path coefficient is 0.58.
(4)Internal cognitive attitude hasalso a positive impacton and a sense of government business costs.The path coefficient is 0.13.
(5)The impact of mass sense of the path coefficient exceeds 0.5.Since the coefficient shows the government services quality perception of business costs satisfaction in Shanghaihas a direct impact on the path coefficient is 0.62. And the external environmental stability enterprise can guide internal cognitive attitude,and its path coefficient of 0.58 shows that the quality perception of government service factors is relatively large.
(6)The prerequisite level of stability in the external environment can be perceived by the internal cognitive attitude which was affected indirectly by the quality of government service satisfaction.The path coefficient is 0.75.The research shows that the quality perception of government service can greatly affect satisfaction,while a stable perception quality of government service can be filed the external environment awareness within the enterprise business costs,and indirectly affects satisfaction.Its path coefficient is 0.69.This paper verifies that the satisfaction with cost of doing business in Shanghai.Bagozzi and Yi[19]hold that ideal value of SMC should be above0.5.SMC value ofmost indicators is above0. 5 on average.Therefore,indicators are suitable to be used as measurement indicator for latent variables in this study.
2.5 Hypothesis verification results
Overall,all of hypotheses(H1,H2,H3,H4,H5,and H6)are supported.We find that internal cognitive has a positive impact on satisfaction.Stability of the external environment has a positive relationship with the effectiveness of government services,and they both have a positive effect on satisfaction(see Table 8).
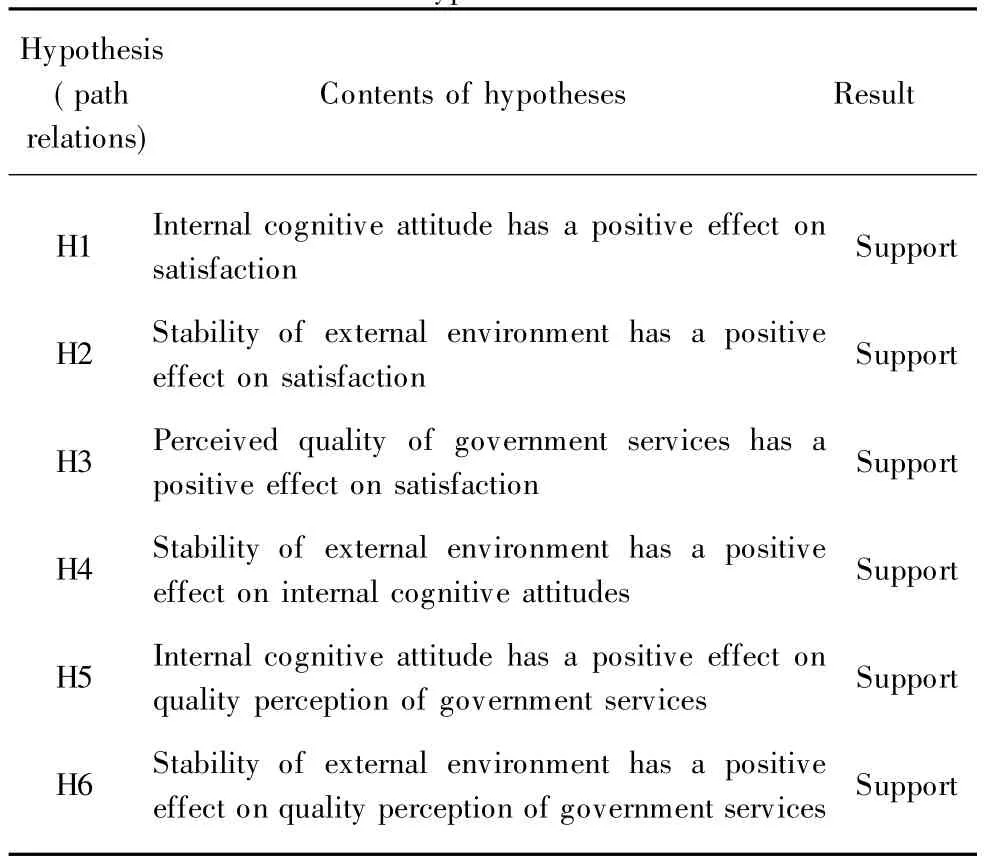
Table 8 Hypothesis verification
3 Conclusions
This study uses SEM approach to exam ine a mechanism under four components of the satisfaction with business cost model contributes to new satisfactory performance by a mediating effect of two different components of satisfaction. Survey results of 300 enterprise units indicate support for all of the hypothesized relationship.Specifically,stability of the external environment can be used as an indirect determ inant of new performance through a mediator of quality perception of government service.Thus,quality perception of government service acts as a mediator in the relationship between three satisfaction components.The mediating effects are more complex than the direct relationships of the components on satisfactory performance previously assumed.We can draw the follow ing conclusions.
Firstly,external environmental stability has a positive impact on satisfaction business cost in Shanghai.The stability of the external environment in the decision to invest in an enterprise environment,considering whether“low business cost price”,but also consider the cost of doing business is“affected by the external environment,”and“within a reasonable range,”enterprises is“acceptable.”Along with social and economic development,the cost of land,manpower,resources are irreversible rise year after year.The level of business costs has become a national or regional development.A good government policy will enhance management practices particularly in investors which are strategically poised to benefitmost from laws.
Secondly,the quality perception of government services has a positive impact on the cost of doing business in Shanghai satisfaction.On one hand,perception of the quality of government services refers to the efficiency of the government's business,adm inistrative examination and approval procedures,quality of service and attitude of staff service quality,staff professional ethics,transparency in government affairs,law enforcement policies,stability of policies and regulations and continuity planning role in guiding policy attention and awareness of the importance of business services.On the other hand,it refers to the degree to understand the quality of business-to-business services,government perception.
Thirdly,quality perception and the stability of the external environment are necessary conditions for government services to improve internalbusinessenterprises in which the cognitive costs can be reflected in any service industry.In the long run,we will only channels of communication established,in order to achieve a direct dialogue between the government and enterprises[23].We allow enterprises to understand the process of government to business cost management,understanding the uncertainty in the external environment,which can enhance the understanding of government services.Additionly by reducing the government's expectations for enterprise,enterprises hope to improve business satisfaction indirect costs.Government's ability can be operated by the city's consciousness and administrativemanagementof the external environmental factors affecting the stability and efficient government policies and transparent legal norms.It brings stability in the external environmentwhich can significantly decrease business costs thus the satisfaction of business cost increase in enterprise.
Aswith any research,there are lim itations associated with the studies.Therefore,the design of this study is issued as a part of lim itations that open up opportunities for future research.Single informant bias could be amatter of concern as only senior executive managers completed the survey instrument.Future research could attempt to avoid such concerns by recruiting multiple informants such as new development managers,marketing managers or operations managers.We use cross-sectional data rather than a longitudinal study.Time and cost constraints lim ited the feasibility of suchan approach.Therefore,this study is primarily based on the subjective assessment of the key informant.The evaluation of satisfaction is inclined toward subjective biases.Forthcoming research that collects a diversity of viewpoints(e.g.,objective data)can potentially overcome.
[1]Fu JW,Jin F,Tu Q Y.Comparative Study on Business Cost of Beijing,Shanghai,Shenzhen[J].Social Sciences,2003(5): 14-18.(in Chinese)
[2]Fu Y J,Sheng J Z.Shanghai Business Cost Exploration[J]. Shanghai Economy,2003(5):14-18.(in Chinese)
[3]An LW,Li F Z.5 Cities Business Cost in Yangtze River Delta[J].ManagementWorld,2004(8):28-36.(in Chinese)
[4]Investigation Team in Zhejiang Provinces.Business Cost Geometry[J].Financial Management and Research,2004,(3):43-47.(in Chinese)
[5]Sun J,Chen K.Applied Business Costs-Relationship Software Engineer Salary of Real Estate Prices[J].Value Engineering,2005(5):94-96.(in Chinese)
[6]Wang C Y,Ju X P,Sun M G.Constitute Factors of Business Cost Analysis of Trends in Shanghai[J].East China Economic Management,2007,21(6):4-10.(in Chinese)
[7]Su Y X,Sun M G.Analysis of Business Costs in Structural and the Impact on Industry of the Transfer Path in Jiangsu,Zhejiang,Shanghai[J].Nanjing University of Finance and Economics,2011(4):15-25.(in Chinese)
[8]Zhang W,Yi N,Zhang W X.2003 Assessment Report of Shanghai,Jiangsu,Zhejiang,Fujian,Shandong,Guangdong Five Provinces and One City Business Costs[J].Zhejiang Statistics,2004(11):13-15.(in Chinese)
[9]Shao A M,Gao J D.Quzhou Corporate Business Costs Satisfaction Survey Analysis[J].Zhejiang Statistic s,2004 (10):41(in Chinese)
[10]Cui J.Shanghai Waigaoqiao Free Trade Zone Investment Environment Survey[J].China Foreign Investment,2004(2): 29-33.(in Chinese)
[11]Jiang Y R.The Government Should Strive to Reduce Business Cost Investors[N].Chinese Cities Reported,2002(3):9.(in Chinese)
[12]Zhou Z Z,Sun M G.Business Cost Impact of Changes in M igration Policy-Making Enterprises[J].Shanghai Economic Research,2010(3):82-93.(in Chinese)
[13]Jöreskog K G.Structural Analysis of Covariance and Correlation Matrices[J].Psychometrika,1978,43:443-477.
[14]Yang R H.Labor Mobility Empirical Analysis:Non-monetary Factors[J].Technical Economics and Management Research,2011(1):25-28.(in Chinese)
[15]Norman M B,Seymour S,Brian W.Asking Questions:The Definitive Guide to Questionnaires Sign—for Market Research,Political Pulls,Social and Health Questionnaires[D]. Chongqing:Chongqing University Press,2011,1(1):75-77.
[16]Nunnally JP.Sychometric Theory[M].New York:McGraw-Hill,1978:3-9.
[17]Hair JF J,Anderson R E,Tatham R L,et al.Multivariate Data Analysis[M].5th ed.Englewood Cliffs,NJ:Prentice Hall,1998.
[18]Steve W.Technology Trends for Small Business in 2014[J]. New Hampshire Business Review,2014(1):23.
[19]Bagozzi R P,Yi Y.the Evaluation of Structural Equation Models[J].Journal of the Academy of Marketing Science,1988,16 (1):74-94.
[20]Ramani G,Kumar V.Interaction Orientation and Firm Performance[J].Journal of Marketing,2008,72(1):27-45.
[21]Preacher K,Hayes A.Asymptotic a Dresampling Strategies for Assessing and Comparing Indirect Effects in Multiple Mediator Models[J].Behavior Research Methods:Instruments,&Compute rs,2008,40(3):879-891.
[22]Johannes V.Relocation of Headquarters and International Taxation[J].Journal of Public Economics,2011(95):171-172
[23]Zhou Z Z,Wang Z Z,Sun M G.Entropy Correction Method Regional Business Costs G1 Comprehensive Evaluation Model and Empirical Study[J].Yunnan University of Finance and Economics,2013,159(1):45-52.(in Chinese)
C931.2
A
1672-5220(2015)04-0688-07
date:2014-03-18
s:National Social Science Foundation of China(No.10BJL044);Doctoral Innovation Projectof Donghua University:the Central Universities Science Fundamental Research in China(No.CUSF-DH-D-2015064)
*Correspondence should be addressed to GUO Yan,E-mail:gydhu2010@163.com
 Journal of Donghua University(English Edition)2015年4期
Journal of Donghua University(English Edition)2015年4期
- Journal of Donghua University(English Edition)的其它文章
- Empirical Analysis of Binary Logistic Model for the Influencing Factors of the Chinese Urban and Rural Residents'Woolen Products Consumption—Based on Questionnaires of 513 Urban and Rural Residents in 16 Provinces
- Ontology Mapping Based on Bayesian Network
- Diurnal and Seasonal Variations in Particulate Matter at Shanghai during the Heavy Haze and Non-haze Periods
- Swept-Volume Display System Based on Cylindrical Space Projection and Curved Reflectors
- Existence of Solutions for Infinity-Point Nonlinear Fractional Boundary Value Problem at Resonance
- Human Mouth-State Recognition Based on Image Warping and Sparse Representation Combined with Homotopy
