关节镜下纽扣钢板固定术治疗不稳定锁骨远端骨折
陈建海 党育 付中国 姜保国
·论著·
关节镜下纽扣钢板固定术治疗不稳定锁骨远端骨折
陈建海 党育 付中国 姜保国
目的 探讨关节镜下纽扣钢板固定术治疗不稳定锁骨远端骨折的临床疗效。方法 回顾性分析17例不稳定锁骨远端骨折经关节镜下纽扣钢板固定术后临床结果。通过Constant评分,简明肩关节功能测试(simple shoulder text,SST),VAS疼痛评分对患者在最后一次随访时的肩关节功能进行评价。结果 本组患者共17例,男性10例,女性7例。平均年龄42.6岁(27~68岁)。按照Robinson骨折分型,均为3B型。 17例患者均获得随访,平均随访时间50个月(42~66个月)。16例患者骨折愈合,平均愈合时间3.2个月,1例骨折不愈合。术中发现合并关节内损伤 2例, SLAP损伤1例, Bankart损伤1例,术中分别予以修复。患者术后Constant评分患侧平均93.1分(72~100分),健侧98.3分(90~100分)。SST患侧平均10.7分(8~12分),健侧11.6分(9~12分)。VAS评分患侧平均1.9分(0~4分),健侧1.7分(0~5分)。结论 关节镜下纽扣钢板固定术具有临床效果良好,创伤小,可同时处理关节内合并损伤,喙锁弹性固定,不需要再次手术等优点。可以作为锁骨远端骨折治疗的一个选择。
锁骨骨折;关节镜;肩;微创
锁骨远端骨折占锁骨骨折的12%~15%[1]。锁骨远端骨折合并喙锁韧带断裂常常表现为不稳定性骨折,保守治疗出现骨折不愈合的机率高达21%[2]。尽管有部分骨折不愈合的患者临床症状轻微[2],但会影响肩关节的功能。因此,多数医师建议对不稳定锁骨远端骨折进行手术治疗[3-5]。手术治疗可以获得高达98%的骨折愈合率[6]。锁骨远端骨折的特点是既有骨折,又有韧带损伤,临床上治疗方法多种多样,常报道的内固定方法包括克氏针、张力带、喙锁螺钉、锚钉、锁骨钩板、解剖钢板以及缝线固定等。金属内植物在骨折愈合后常常需要再次手术取出。各种治疗方法优、缺点并存,目前尚无统一的治疗方法。
关节镜下纽扣钢板固定治疗锁骨远端骨折是一种比较新的微创治疗方法,其技术来源于治疗肩锁关节脱位的关节镜下纽扣钢板固定术[7]。我们回顾性分析关节镜下纽扣钢板固定术治疗锁骨远端骨折的临床效果,探讨此技术的潜在优、缺点。
资 料 与 方 法
一、一般资料
收集2010年9月至2012年12月在我科接受手术治疗的21例不稳定锁骨远端骨折患者,其中17例符合纳入标准,男性10例,女性7例,平均年龄42.6岁,按照Robinson锁骨骨折分型[8]均为3B型骨折。纳入标准:(1)诊断为不稳定锁骨远端骨折;(2)接受关节镜下纽扣钢板固定治疗术。排除标准:(1)诊断为不稳定锁骨远端骨折,但没有进行关节镜下纽扣钢板固定手术,包括切开复位锁骨钩钢板固定、解剖锁定钢板固定、切开纽扣钢板固定;(2) 陈旧性锁骨远端骨折。
二、手术方法
手术均在全麻下进行。患者取沙滩椅体位(图1),头部偏向健侧。标画肩关节镜体表标记,进行常规患肩及上肢消毒。关节镜从后方通道进入关节腔,直视下建立前方位于肩袖间隙的工作通道(图2)。进行关节内常规检查,尤其注意检查有无盂唇和肩袖结构损伤。如果术中发现关节内损伤即刻给予处理。直视下建立前外侧经冈上肌腱前部的关节镜第二观察通道(图3),通过交换棒将关节镜转移到第二观察通道(图4)。沿肩胛下肌上缘向内显露喙突下表面(图5),探钩确定喙突的内外侧边缘。C型臂机透视确定喙突在锁骨表面的垂直投影位置,即锥形韧带止点位置,切开皮肤2 cm,显露锁骨上表面。将前交叉韧带导向器放置在喙突下表面中央位置,经锁骨向喙突打入导针,透视确认导针位置无误(图6),经导针使用4.5 mm空心钻钻孔(图7),引入摆渡钢丝,取出导向器(图8)。取2枚四孔纽扣钢板,去除袢,用2枚5号爱惜康缝线按照图9所示进行钢板连接。将纽扣钢板通过摆渡钢丝穿过锁骨和喙突,1枚位于喙突下,另1枚位于锁骨表面。复位骨折,如果骨折端有软组织崁入,可以使用探钩进行松解(图10)。维持骨折复位,收紧缝线进行打结固定。再次透视确认骨折复位(图11),关节镜检查喙突下钢板完全贴附喙突下表面(图12)。常规关闭切口。

图1 患者位于沙滩椅体位,头向健侧倾斜
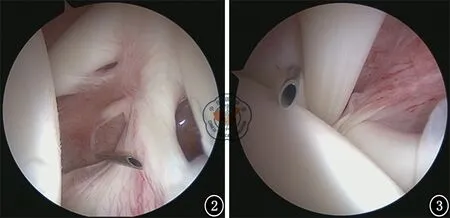
图2 关节镜常规自后方通道插入关节腔,建立前方肩袖间隙工作通道 图3 建立长头肌腱后缘的关节镜第二观察通道
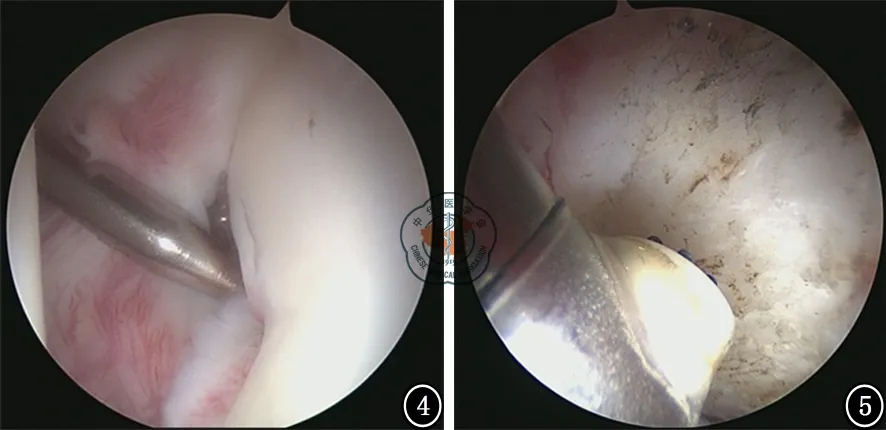
图4 插入交换棒,经交换棒将关节镜转到此通道,以观察喙突下间隙 图5 使用射频刀显露喙突下表面,确定喙突内、外侧边缘
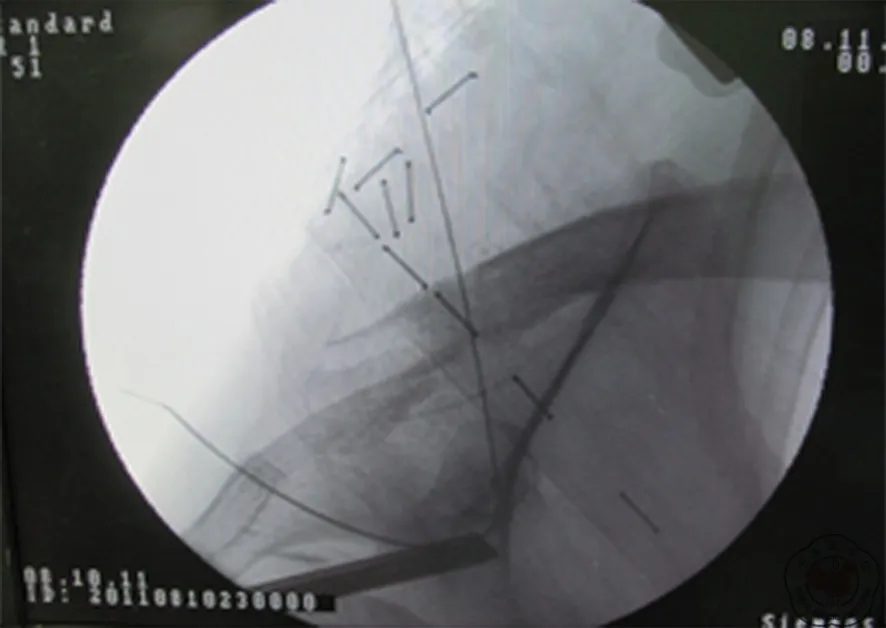
图8 经空心钻引入摆渡钢丝,取出导向器
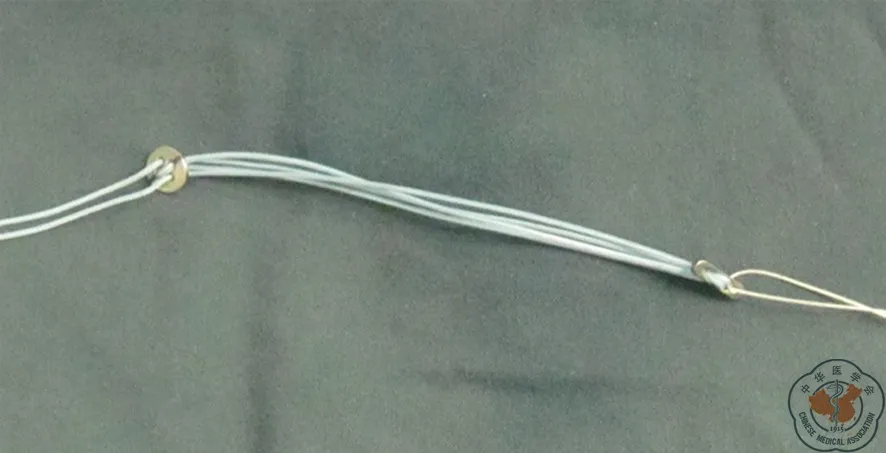
图9 用于喙锁固定的Tightrope内植物,部分病例使用此内植物,其余病例将2枚纽扣钢板通过2根5号爱惜康缝线按照Tightrope 缝线连接方法进行组装

图10 使用探钩协助骨折复位
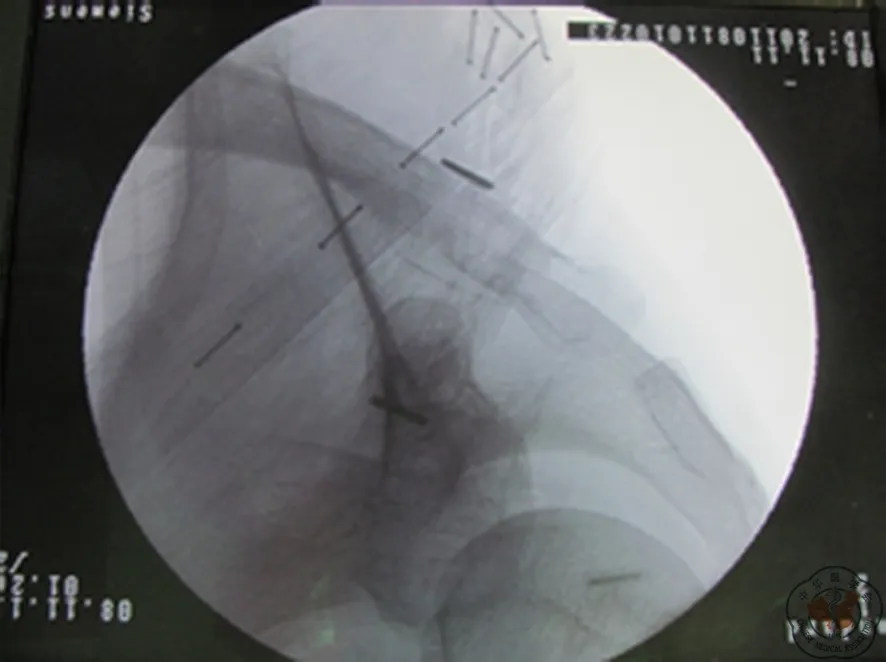
图11 骨折复位,缝线打结固定完毕,术中透视像
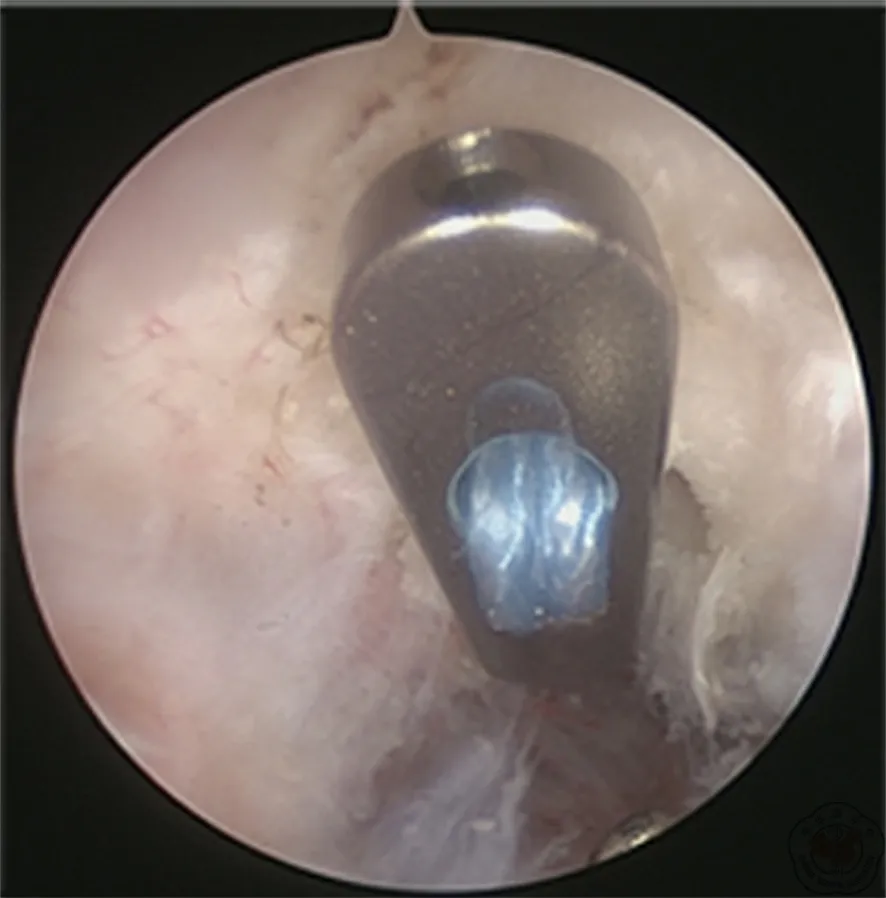
图12 关节镜检查喙突下钢板完全贴服喙突下表面
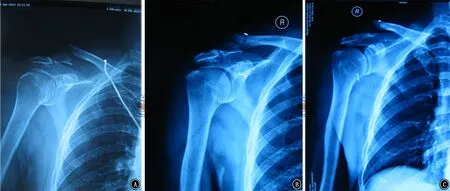
图13 关节镜下纽扣钢板内固定术前(A)、术后 1周(B)和术后4个月(C)X线片
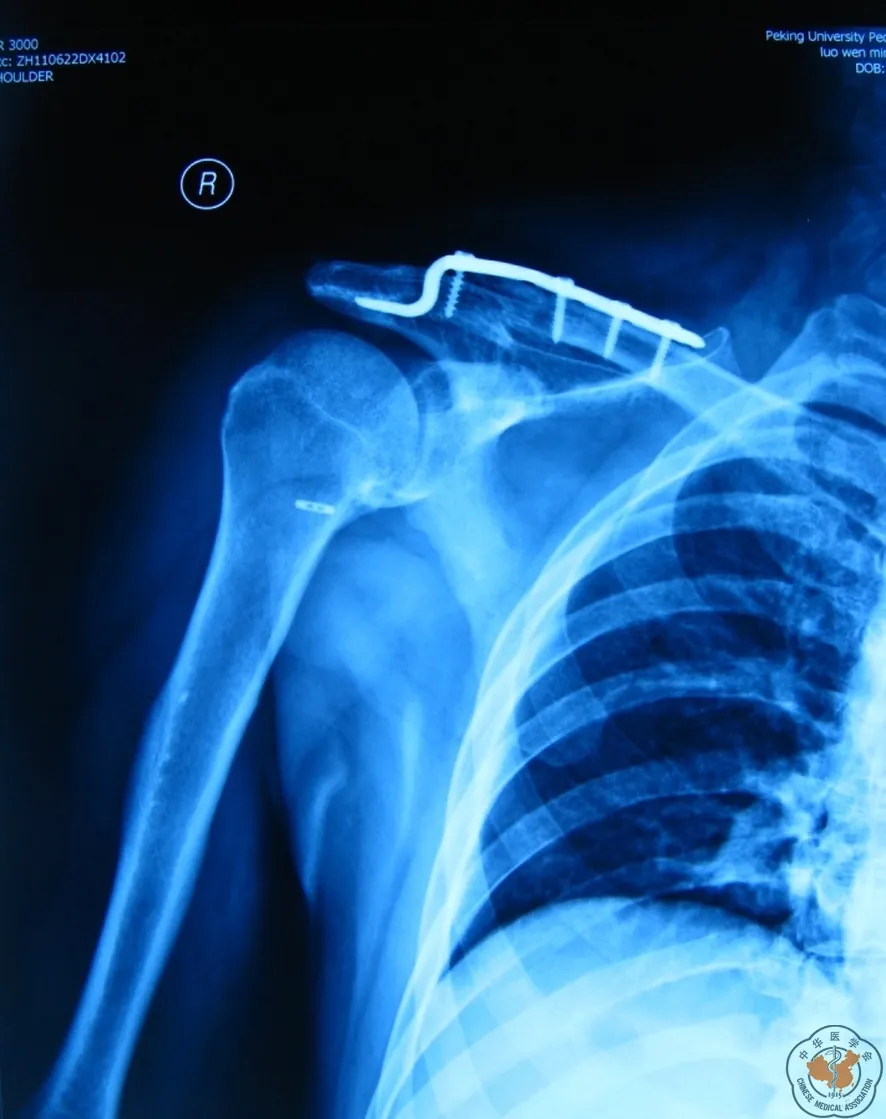
图14 钩板翻修术后
三、术后处理
肩关节护具悬吊患肩4周。术后4周进行肩关节被动上举、外旋活动;术后第2个月进行强化的关节牵拉练习,主动辅助的肩关节上举、内外旋活动。术后2个月后,骨折初步愈合,局部无压痛后开始肩关节主动活动,肩袖及肩胛带肌肉力量和耐力练习,逐步恢复日常活动。
四、术后随访
术后每个月复查一次,拍摄X线片,检查骨折愈合情况,直至骨折骨性愈合。末次随访通过肩关节Constant评分、简明肩关节评分(simple shoulder text,SST),VAS疼痛评分,肩关节活动范围检查等对患者进行评价。
结 果
17例患者均获得随访,平均随访时间50个月(42~66个月)。16例患者骨折愈合,平均愈合时间3.2个月,1例骨折不愈合。术中发现合并关节内损伤2例, SLAP损伤1例, Bankart损伤1例,术中分别给予修复。
患者术后Constant评分患侧平均93.1分(72~100分),健侧98.3分(90~100分)。SST患侧平均10.7分(8~12分),健侧11.6分(9~12分)。VAS评分患侧平均1.9分(0~4分),健侧1.7分(0~5分)。
1例骨折不愈合患者,男性,初次手术时年龄50岁,酒后骑电动车摔伤右肩,骨折分型为锁骨远端3B型,既往糖尿病史,血糖控制不佳。入院后行关节镜下纽扣钢板内固定术(图13),术后进行常规制动和康复锻炼。术后复查内固定失效,骨折移位,观察至术后4个月,骨折不愈合,局部压痛,肩关节功能明显受限。患者再次入院,将内植物取出,髂骨取骨植骨,锁骨钩钢板内固定术(图14)。第二次手术后3个月骨折愈合,12个月后取出锁骨钩钢板,患者肩关节功能基本恢复正常,Constant评分91分,SST评分11分,VAS评分1分。
讨 论
锁骨是连接上肢与躯干的唯一骨性结构,上肢通过肩锁关节和喙锁韧带牢固与锁骨连接,喙锁韧带又分为锥形韧带和斜方韧带。不稳定的锁骨远端骨折最主要特点是喙突与近端锁骨连接结构破坏,主要表现为喙锁韧带断裂。因此,对于不稳定的锁骨远端骨折的治疗,既要考虑骨折因素,同时要重视喙锁韧带损伤的处理。
Robinson等[2]对不稳定的锁骨远端骨折保守治疗结果进行分析研究,共101例患者进行保守治疗,14%因为无法耐受持续的疼痛而接受手术治疗,骨折不愈合率高达21%。Neer[3]提出对不稳定锁骨远端骨折进行手术治疗以避免骨折不愈合的发生。有关锁骨远端骨折手术治疗方法种类很多,包括克氏针张力带固定[9]、锚钉固定[10]、锁骨钩钢板固定[11-12]、锁骨远端解剖钢板固定[13]、纽扣钢板固定[14-15]、钢板结合韧带重建[16]、Bosworth螺钉固定等[17]。手术后并发症如克氏针移位、锚钉缝线断裂、锁骨钩肩峰下刺激症状、螺钉断裂、锁骨应力性骨折等,金属内植物常常需要二次手术取出。随着关节镜技术的发展,关节镜下喙锁固定手术获得了较多的开展[7,14-15],关节镜手术的优势在于微创,重建喙锁稳定性,不需要二次手术取出内植物,同时处理关节内合并损伤等。
关节镜下纽扣钢板固定术治疗不稳定锁骨远端骨折,其手术设计理念在于通过重建喙锁稳定性,将不稳定锁骨远端骨折转变成稳定的锁骨远端骨折。手术仅通过纽扣钢板固定喙突与锁骨近端骨折块,对于锁骨远近端骨折块没有进行固定。随访结果显示绝大部分患者获得了与健侧相同的功能水平,说明手术设计理念得到了实现。Pujol等[18]在2008年报道了4例关节镜下双纽扣钢板固定不稳定锁骨远端骨折病例,4例均获得骨性愈合,患者术后功能恢复良好。Baumgarten[15]同年报道1例关节镜下使用Tightrope纽扣钢板系统治疗不稳定锁骨远端骨折,骨折在术后3个月愈合,患者没有功能障碍。Loriaut等[19]2015年5月报道21例锁骨远端骨折患者接受关节镜下纽扣钢板固定治疗的结果,81%的患者恢复伤前工作,Constant评分平均94分,VAS疼痛评分平均0.5分,有1例骨折发生不愈合。本研究的病例数量和结果与Loriaut的研究结果相当。Loriaut提出可以将此手术方式作为治疗不稳定锁骨远端骨折的首选方式。考虑到关节镜手术的学习曲线较长,我们建议此手术应在关节镜技术成熟的医院开展。
大多数的创伤骨科医师熟悉切开复位、锁骨钩钢板内固定术,这是一项广泛使用的技术,手术效果可靠,但缺点也很显著,如术后较长时间的肩关节疼痛、钢板内侧锁骨应力性骨折、二次取出内固定等。Lin等[20]对40例锁骨远端骨折或肩锁关节脱位经锁骨钩钢板治疗的患者进行临床随访,通过体格检查、X线片和动静态B超进行临床评估,结果发现15例(37.5%)患者有肩峰下撞击综合征,其中6例伴有肩袖损伤,这15例患者的肩关节功能明显低于无撞击综合征的患者,钩板导致的肩峰下骨磨损发生在20例(50%)患者中。Lin等认为锁骨钩板发生肩峰下撞击的几率较高,只有取出内植物才能解决问题,建议在骨折和/或韧带愈合后尽早取出内植物。Flinkkilä等[21]对比了Tightrope纽扣钢板系统(21例)和锁骨钩钢板(19例)治疗锁骨远端骨折的临床效果,结果每组各有1例骨折不愈合,Constant评分Tightrope组平均93分,锁骨钩钢板组89分;DASH评分Tightrope组平均6分,锁骨钩钢板组11分。提示关节镜下纽扣钢板固定可以获得与锁骨钩钢板相似的临床结果,但避免了锁骨钩钢板的诸多缺点。
Pauly等[22]前瞻性分析肩锁关节脱位并发关节内损伤的发生率,分析了125例肩锁关节脱位患者,其中Rockwood Ⅲ型6例,Ⅴ型119例。关节镜检查发现合并关节内病变38例(30.4%),确定与外伤有关的损伤9例(7.2%),退变性损伤确定与外伤无关的18例(14.4%),无法确定是否与外伤有关的11例(8.8%)。肩锁关节脱位与锁骨远端骨折有着类似的创伤机制,在本研究中也发现2例合并关节内损伤,术中一并予以处理,这也是关节镜治疗锁骨远端骨折的一个优势,开放手术不能发现关节内损伤。
Oh等[23]系统分析21项研究的425例锁骨远端不稳定骨折病例,结果发现不稳定锁骨远端骨折手术治疗的不愈合率为1.6%。本研究也有1例锁骨远端骨折不愈合病例,此病例发生骨折不愈合的主要原因是术中骨折复位不良,骨折端反常活动增加,最终将纽扣钢板之间的缝线磨断,导致内固定失效。反思这例病例,我们认识到进行喙锁固定只是重建了喙锁垂直方向的稳定性,不稳定骨折在骨折区域软组织(斜方肌与三角肌腱膜)损伤要重于稳定性骨折,由于骨折在水平方向还是存在不稳定,因此单纯喙锁固定并不能将不稳定骨折完全转变成稳定性骨折,提示我们应该改良固定方式,即增加锁骨骨折块间水平方向的固定。
结论:不稳定型锁骨远端骨折多数需要手术治疗,目前尚无统一的治疗方法。关节镜辅助下的纽扣钢板固定术是近年逐渐开展的一种新术式,具有微创,可同时处理关节内合并损伤,喙锁弹性固定,不需要再次手术等优点。这一术式临床效果良好,但技术要求较高,可以作为锁骨远端骨折治疗的一个选择。
[1] Heppenstall RB.Fractures and dislocations of the distal clavicle[J].Orthop Clin North Am, 1975,6(2):477-486.
[2] Robinson CM, Cairns DA. Primary nonoperative treatment of displaced lateral fractures of the clavicle[J]. J Bone Joint Surg Am, 2004, 86(4): 778-782.
[3] Neer CS. Fractures of the distal third of the clavicle[J]. Clin Orthop,1968,(58): 43-50.
[4] Jou IM, Chiang EP, Lin CJ, et al. Treatment of unstable distal clavicle fractures with Knowles pin[J]. J Shoulder Elbow Surg,2011,20 (3): 414-419.
[5] Meda PV, Machani B, Sinopidis C, et al. Clavicular hook plate for lateral end fractures: a prospective study[J]. Injury,2006,37 (3): 277-283.
[6] Stegeman SA, Nacak H, Huvenaars KH, et al. Surgical treatment of Neer type-II fractures of the distal clavicle: a meta-analysis[J]. Acta Orthop, 2013, 84(2): 184-190.
[7] Salzmann GM, Walz L, Buchmann S, et al. Arthroscopically assisted 2-bundle anatomical reduction of acute acromioclavicular joint separations[J]. Am J Sports Med, 2010, 38(6): 1179-1187.
[8] Robinson CM. Fractures of the clavicle in the adult. Epidemiology and classification[J]. J Bone Joint Surg Br, 1998 ,80(3):476-484.
[9] Kona J, Bosse MJ, Staeheli JW, et al. Type II distal clavicle fractures: a retrospective review of surgical treatment[J]. J Orthop Trauma, 1990, 4(2): 115-120.
[10] Bezer M, Aydin N, Guven O. The treatment of distal clavicle fractures with coracoclavicular ligament disruption: a report of 10 cases[J]. J Orthop Trauma, 2005, 19(8): 524-528.
[11] Klein SM, Badman BL, Keating CJ, et al. Results of surgical treatment for unstable distal clavicular fractures[J]. J Shoulder Elbow Surg, 2010, 19(7): 1049-1055.
[12] Hsu TL, Hsu SK, Chen HM, et al. Comparison of hook plate and tension band wire in the treatment of distal clavicle fractures[J]. Orthopedics, 2010, 33(12): 879.
[13] Lee SK, Lee JW, Song DG, et al. Precontoured locking plate fixation for displaced lateral clavicle fractures[J]. Orthopedics, 2013, 36(6): 801-807.
[14] Takase K, Kono R, Yamamoto K. Arthroscopic stabilization for Neer type 2 fracture of the distal clavicle fracture[J]. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg, 2012, 132(3): 399-403.
[15] Baumgarten KM. Arthroscopic fixation of a type II-variant, unstable distal clavicle fracture[J]. Orthopedics,2008,31(12). pii: orthosupersite.com/view.asp?rID=32937.
[16] Seyhan M, Kocaoglu B, Kiyak G, et al. Anatomic locking plate and coracoclavicular stabilization with suture endo-button technique is superior in the treatment of Neer Type II distal clavicle fractures[J]. Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol, 2015, 25(5): 827-832.
[17] Yamaguchi H, Arakawa H, Kobayashi M. Results of the bosworth method for unstable fractures of the distal clavicle[J]. Int Orthop, 1998, 22(6): 366-368.
[18] Pujol N, Philippeau JM, Richou J, et al. Arthroscopic treatment of distal clavicle fractures: a technical note[J]. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc, 2008, 16(9): 884-886.
[19] Loriaut P, Moreau PE, Dallaudière B, et al. Outcome of arthroscopic treatment for displaced lateral clavicle fractures using a double button device[J]. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc, 2015, 23(5): 1429-1433.
[20] Lin HY, Wong PK, Ho WP, et al. Clavicular hook plate May induce subacromial shoulder impingement and rotator cuff lesion--dynamic sonographic evaluation[J].J Orthop Surg Res,2014,9:6.
[21] Flinkkilä T, Heikkilä A, Sirniö K, et al. TightRope versus clavicular hook plate fixation for unstable distal clavicular fractures[J]. Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol, 2015, 25(3): 465-469.
[22] Pauly S, Kraus N, Greiner S, et al. Prevalence and pattern of glenohumeral injuries among acute high-grade acromioclavicular joint instabilities[J]. J Shoulder Elbow Surg,2013,22(6):760-766.
[23] Oh JH, Kim SH, Lee JH, et al. Treatment of distal clavicle fracture: a systematic review of treatment modalities in 425 fractures[J]. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg, 2011, 131(4): 525-533.
(本文编辑:李静)
陈建海,党育,付中国,等.关节镜下纽扣钢板固定术治疗不稳定锁骨远端骨折[J/CD]. 中华肩肘外科电子杂志,2015,3(3):133-140.
Arthroscopic button plate fixation therapy for instable distal clavicular fracture
ChenJianhai,DangYu,FuZhongguo,JiangBaoguo.
DepartmentofTraumaandOrthopaedics,PekingUniversityPeople′sHospital,PekingUniversityTrafficMedicineCenter,Beijing100044,China
JiangBaoguo,Email:jiangbaoguo@vip.sina.com
Background The cases of distal clavicular fracture account for 12%-15% of all clavicular fracture cases. Distal clavicular fracture combined with coracoclavicular ligament rupture frequently behave as unstable fracture, with the opportunity for fracture non-union in conservative therapy being as high as 21%. Although partial patients with fracture nonunion show mild clinical symptoms, the symptomatic nonunion may affect the functions of shoulder joint. Therefore, most of physicians suggest operative treatment for unstable distal clavicular fracture. The operative treatment can achieve fracture union rate up to 98%. The distal clavicular fracture is characterized by fracture combined with ligament injury, and there are also diversified clinical therapies. The frequently reported internal fixation methods include kirschner wire, tension band, coraco-clavicular screw, anchor, clavicular hook plate,anatomical locking plate as well as suture fixation, etc. After fracture union, the metallic internal implants are frequently required to be taken out through operation. Different therapies have both their advantages and disadvantages. At present, there has been no unified therapy for unstable distal clavicular fracture.Arthroscopic button plate fixation therapy for unstable distal clavicular fracture is a relatively new minimally invasive treatment method, and its technology is originated from arthroscopic button plate fixation for the treatment of dislocation of acromioclavicular joint.We made retrospective analysis on the clinical effects of arthroscopic button plate fixation on distal clavicular fracture and discussed the potential advantages and disadvantages of this therapy. Method Ⅰ. General materials:Twenty-one patients with unstable distal clavicular fracture who
operative treatment in our department during the period from September 2010 to December 2012 are collected,seventeen cases of these meet inclusion criteria, namely 10 male cases and 7 female cases, with an average age of 42.6 years; according to Robinson clavicular fracture classification, all fracture cases are of type 3B fracture. Inclusion criteria: (1) Diagnosed as unstable distal clavicular fracture; (2) Received arthroscopic button plate fixation treatment. Exclusion criteria: (1) Diagnosed as unstable distal clavicular fracture, but has not received arthroscopic button plate fixation treatment, including open reduction Clavicle hook plate fixation, anatomic locking plate fixation and open button plate fixation; (2) Old distal clavicular fracture.Ⅱ. Operative method:operation was performed under general anesthesia. Allow the patient to take sand beach chair posture, with head leaning to the other side. Draw shoulder joint anatomic marks under shoulder arthroscopy, and perform conventional disinfection on affected shoulder and upper limbs. The arthroscope enters the joint cavity from posterior portal; Under direct vision, establish the anterior working portal located in rotator interval. perform intra-articular routine inspection, pay particular attention to inspect whether there is structural damage to glenoid labrum and rotator cuff. If intra-articular injury is discovered during operation, immerely treat it. Under direct vision, establish the anterolateral second observation portal under arthroscope through anterior supraspinatus tendon, and transfer the arthroscope to the second observation portal through exchange rod. Along the upper edge of musculus subscapularis, inward expose the lower surface of coracoid, and use a feller to determine the madial and lateral edges of coracoid. Perform C-arm X-ray machine fluoroscopy to demine the vertical projection position of coracoid on clavicular surface, namely the conical ligament attachment position; open skin by 2 cm, and expose the clavicular upper surface. Place the anterior cruciate ligament guider on the central location of coracoid lower surface, drive guide pin into coracoid through clavicle; perform fluoroscopy to validate that the position of guide pin is corret; through guide pin, use a 4.5 mm hollow drill for drilling, introduce the shuttle wire, and take out guider. Take two 4-hole button plates, remove loop spinalium, and use two No.5 Ethicon suture to perform plate connection as shown in Figure 9. By means of shuttle wire, introduce the button plates to pass through clavicle and coracoid, place one plate under coracoid, place another plate on the surface of clavicle. Perform reduction of fracture. If there are soft tissues entrapped at the fracture end, use probe for release. Maintain fracture reduction, tighten the suture for knotting and fixation, perform fluoroscopy again to validate fracture reduction; perform arthroscopy to validate that the plate under coracoid is completely attached on the lower surface of coracoid. Conventionally close incision.Ⅲ. Postoperative treatment:Use shoulder joint protector to suspend the injured shoulder for 4 weeks. In 4 weeks post operation, allow the shoulder joint to perform passive uplifting and external rotation activities; In the 2nd month after operation, perform intensive joint traction exercise, active assisted shoulder joint uplifting as well as internal and external rotation activities; 2 months post operation, when preliminary fracture healing is realized and there is no local pressing pain, start active motion of shoulder joint, gradually recover daily activities as well as muscle strength and endurance training on rotator cuff and shoulder girdle.Ⅳ. Post-operative follow-up:After operation, perform re-examination once per month, take X-ray film, examine the fracture union situation until bony union of fracture. In the final follow-up, make evaluation on patient through shoulder joint constant scoring, simple shoulder joint test (SST), VAS pain scoring and examination on the range of shoulder joint motion.Results All 17 cases obtained follow-up, with average follow-up time of 50 months (42-66 months). 16 cases achieved fracture union, with average union time of 3.2 months; there is 1 case of nonunion. During the operation 2 cases of combined intra-articular injury, 1 case of SLAP injury and 1 case of Bankart injury are discovered and respectively repaired. Average postoperative constant score of the patients is 93.1 points (72-100 points), with health side score of 98.3 points (90-100 points). SST affected side score is 10.7 points on average (8-12 points), with health side score of 11.6 points (9-12 points). VAS average score is 1.9 points (0-4 points), with health side score of 1.7 points (0-5 points). 1 case of fracture nonunion, male, aged 50 at the time of initial operation, right shoulder is injured by falling from electric bicycle in drunk driving, fracture typing is 3B distal clavicle fracture; this patient has pervious history of diabetes, with unsatisfactory blood glucose control. After hospital admission, perform arthroscopic internal fixation with button plate, and postoperative conventional bracing and rehabilitation training; According to postoperative re-examination, internal fixation failure and fracture displacement are discovered; make observation until 4 months after operation; fracture nonunion, local pressing pain and obviously limited shoulder joint functions are discovered. After readmission of the patients, take out the internal implants, take ilium for bone grafting, perform internal fixation with clavicular hook-plate; In 3 months after the operation for the second time, fracture union is realized; 12 months later, take out clavicular hook-plate; the shoulder joint functions of the patients are basically recovered to normal level, with Constant score of 91 points, SST score of 11 points and VAS score of 1 point.Conclusion Most of unstable distal clavicular fracture cases need operative treatment, but there has been no unified therapy at present. Arthroscope-assisted button plate fixation is a new operation method which has been gradually developing in recent years, which is minimally invasive, being able to treat combined intra-articular injury at the same time, realize elastic fixation of coracoclavicular, without need for reoperation. This new operation method can realize good clinical effects, but has high technical requirements. It can be an option for treatment of distal clavicular fracture.
Arthroscopic button plate fixation;Therapy;Clavicular fracture;Distal
10.3877/cma.j.issn.2095-5790.2015.03.002
教育部创新团队(IRT1201);卫生公益性行业科研专项基金(201002014)
100044北京大学人民医院创伤骨科 北京大学交通医学中心
姜保国,Email:jiangbaoguo@vip.sina.com
2015-07-15)

