一种提高风洞天平灵敏度的测量方法
王惠伦, 解亚军, 姜亚军
(1. 西北工业大学 航空学院, 西安 710072; 2. 西北工业大学 陕西省光信息技术重点实验室, 西安 710072)
一种提高风洞天平灵敏度的测量方法
王惠伦1, 解亚军1, 姜亚军2
(1. 西北工业大学 航空学院, 西安 710072; 2. 西北工业大学 陕西省光信息技术重点实验室, 西安 710072)
传统应变测量方法在小量程气动力测量方面存在灵敏度不高的问题。针对此现象,从单分量入手,设计以位移测量法为基础的悬臂梁天平。以3台悬臂梁天平为例:1台传统应变天平,2台不同槽深的新型位移天平,分别进行静态校准试验及有限元仿真。将光纤应变计应用于1mm槽深位移天平,进行准度计算;将光纤、电阻2种应变计同时粘贴在传统应变天平及2mm槽深位移天平,进行2种应变计及2种测量方法的性能对比。由试验结果可知:试验中1mm槽深位移天平准度为0.02%;2mm槽深位移天平位移法测量灵敏度相比传统测量方法提高3倍;2mm槽深位移天平灵敏度为1mm槽深天平的1.57倍,但准度有所下降。本研究为小量程气动载荷的测量提供新思路。
位移法;单分量天平;光纤应变计;灵敏度;小量程气动力
0 引 言
风洞天平是测力试验中重要的测量装置,用于测量作用在模型上空气动力载荷的大小、方向和作用点[1]。随着风洞测力试验技术需求的提高,风洞天平正朝着小型化、高灵敏度、高精准度的方向发展,因此灵敏度是影响天平质量的重要因素之一。尤其是在小量程气动力测量方面,传统应变测量方法存在灵敏度不高的问题。传统应变测量方法是将电阻应变计粘贴在天平相应元件处,用以将被测模型受力或力矩产生的应变值转换为电阻变化量,电阻应变计通过组成惠斯顿电桥将电阻变化量转换为电信号输出。目前常用增加天平灵敏度方法有:(1) 工程计算中对天平元件进行优化设计,如网格法、正交实验设计法、投影梯度法、二次函数逼近法等[2];(2) 有限元分析法,对天平进行有限元仿真,以找出最佳测量位置;(3) 测量电路采用惠斯顿全桥电路,以增大信号的输出。
本文提出一种新型测量方法:位移测量法,通过结构上的改进,提高风洞天平的灵敏度。从单分量天平入手,在悬臂梁上下表面测量应变位置开槽,放大了施加相同载荷时悬臂梁产生的形变。将光纤应变计纵向粘贴在槽口两端,用于感受被测模型受力或力矩时槽口位移的改变量,并将其转换为光纤应变计波长的变化量,达到测量气动力的目的,如图1所示,其中虚线为受力产生形变,w为槽口尺寸,w为变形后槽口位移量,相应应变值计算见公式(1)。
(1)
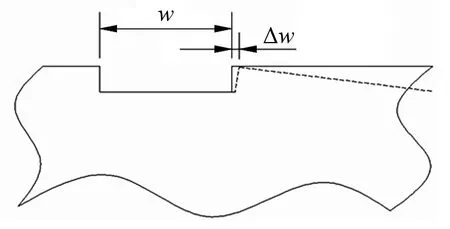
图1 位移测量示意图
文中以应变测量法为基础的天平称为应变天平,以位移测量法为基础的天平称为位移天平。通过对比光纤、电阻2种应变计在应变天平与位移天平中的应用,探讨传统应变天平与位移天平的灵敏度性能。
1 位移天平系统
位移天平系统由位移天平、光纤应变计、光信号解调系统组成。
1.1 位移天平设计
位移天平包括固定端、天平主体、上下槽口,如图2所示。
(1) 通过有限元软件Abaqus[10-13]仿真,天平固定端尺寸对应变计粘贴处产生应变的影响不大,故由试验台尺寸确定:长120mm,宽90mm,高22mm。
(2) 位移天平法向力设计载荷为400N,通过工程计算[3]得到天平主体尺寸:长200mm、宽14mm、高20mm。
(3) 结合有限元仿真、光纤栅区长度、光纤预拉伸及光纤测量范围要求,槽口尺寸设计为长10mm,宽14mm,深1mm、2mm。
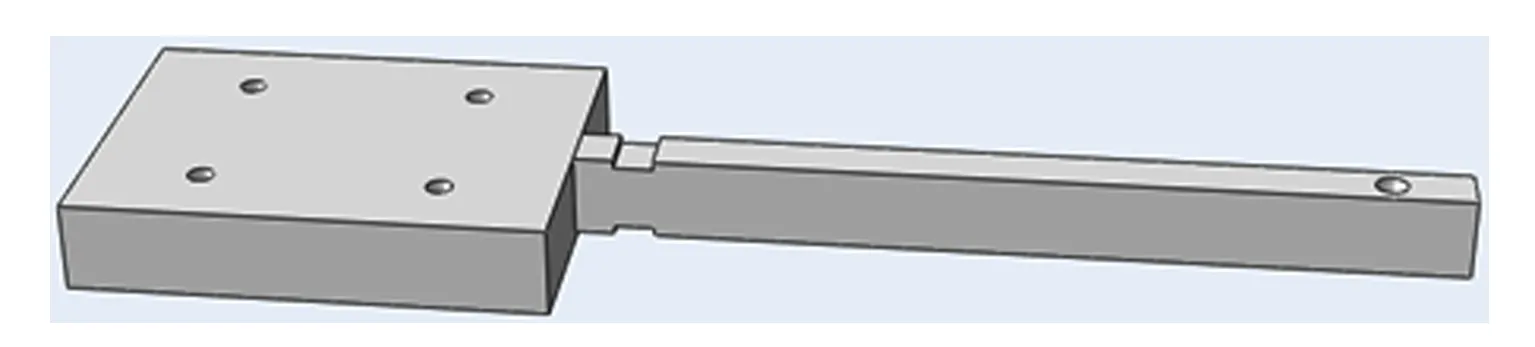
图2 新型单分量位移天平
1.2 光纤应变计
试验中选用光纤布拉格光栅(FBG)传感器作为应变计,其中用于传感作用的栅区长度为10mm,两端用于传光的尾纤各1m,如图3所示,栅区两端分别纵向粘贴在上下槽口处。当宽谱光经过光栅时,满足布拉格公式条件的波长的光都能被部分或全部反射。布拉格公式与光栅有效折射率和光栅周期有关,通过拉伸或压缩光纤光栅,可以改变光纤光栅的周期和有效折射率,从而改变光纤光栅反射波长,达到传感的目的[4-9]。
静校试验中,光纤应变计波长变化量与所加载荷成正比。上表面光纤应变计测量拉应变,波长变化量为正,下表面光纤应变计测量压应变,波长变化量为负,故应变计粘贴时要进行预拉伸,以保证压应变的测量。一般来说,光纤光栅波长变化量与应变之间存在比例关系:1pm的波长变化量对应于1.2με。
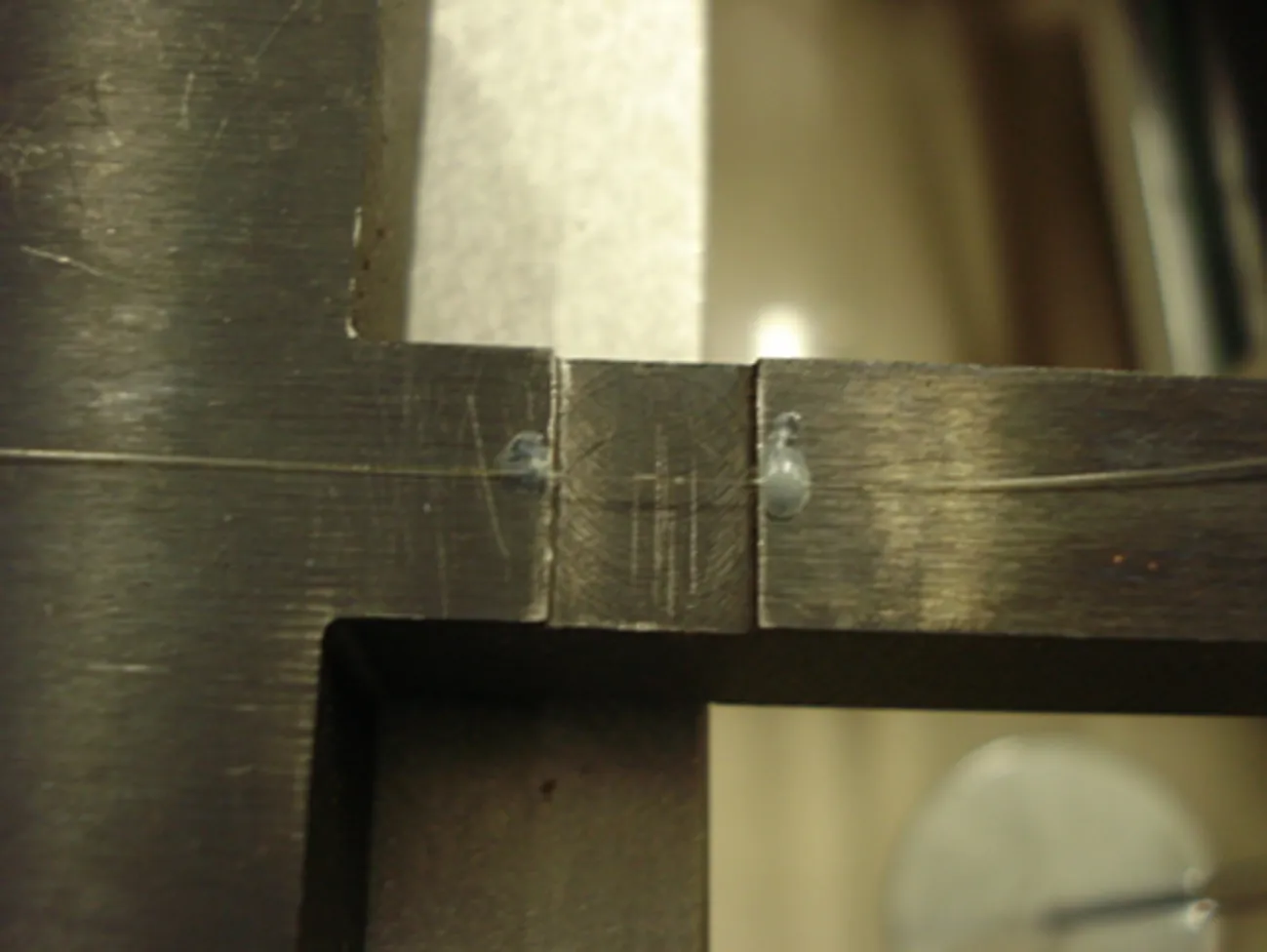
图3 光纤应变计粘贴图
1.3 光信号解调系统
试验中解调系统选用SM130光纤光栅动态解调仪,内置激光光源,可以同时实现4个通道的实时信号采集,并可通过计算机相关界面编程对各通道数据进行叠加计算。
2 天平静校试验及有限元分析
试验选取3种天平:(1) 1#应变天平:天平主体不开槽,粘贴光纤、电阻应变计;(2) 1#位移天平:天平主体开槽1mm,粘贴光纤应变计;(3) 2#位移天平:天平主体开槽2mm,粘贴光纤、电阻应变计。
2.1 1#位移天平静校试验及有限元分析
1#位移天平的静校是通过光纤解调仪得到波长变化量,进而得到载荷与应变的关系式。
有限元仿真中,天平材料为45#钢,物理参数为弹性模量E=209GPa,泊松比μ=0.3。采用四面体网格划分,整体网格为5mm,局部网格为3.5mm。在不同载荷作用下,根据节点位移来得到槽口位移量,节点位移云图如图4所示,由公式(1)得到相应应变值,其中w取10mm。计算应变值与试验结果对比如表1所示。
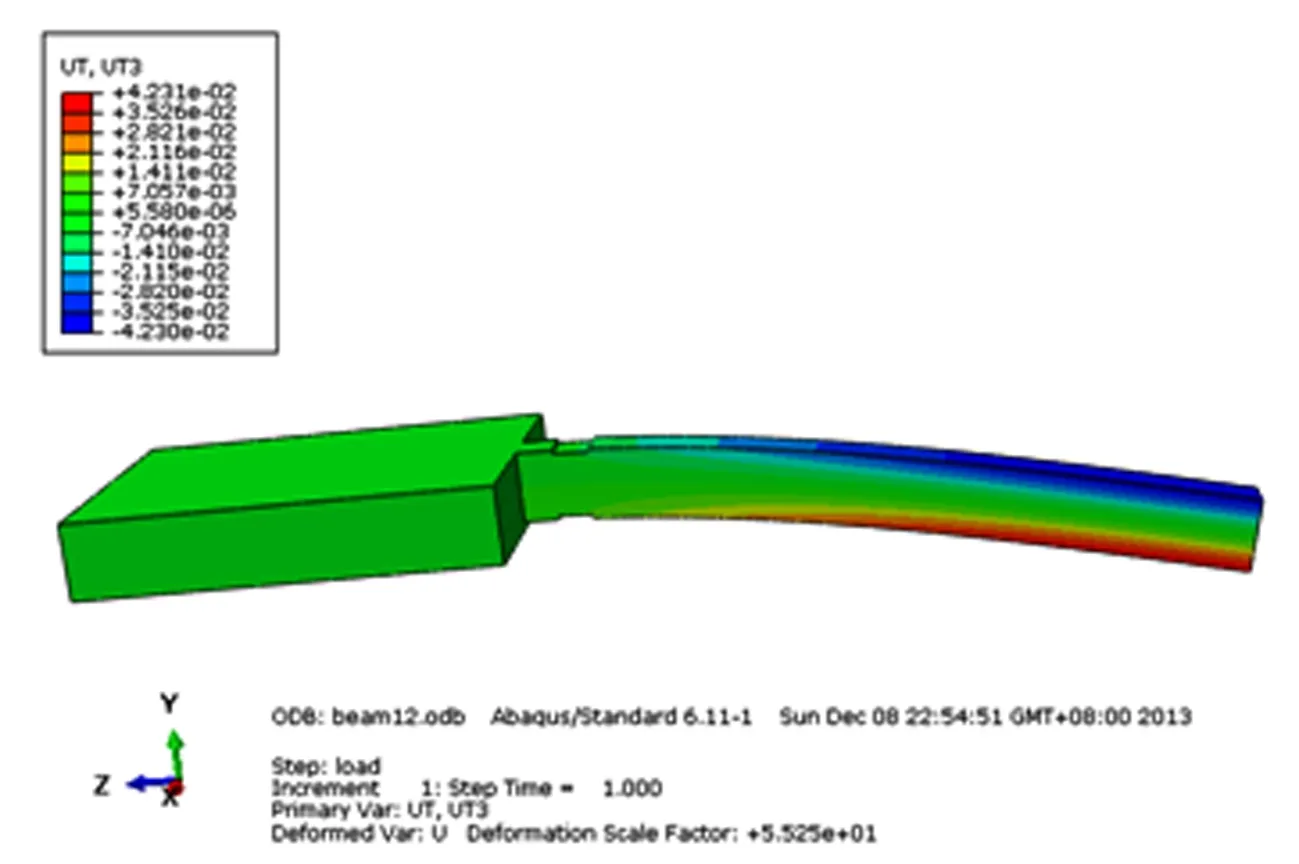
图4 节点位移云图
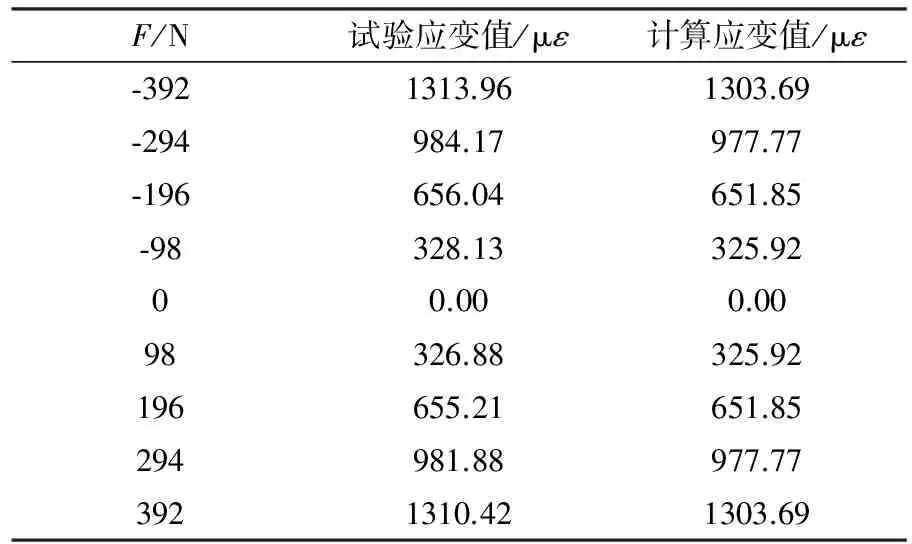
F/N试验应变值/με计算应变值/με⁃3921313.961303.69⁃294984.17977.77⁃196656.04651.85⁃98328.13325.9200.000.0098326.88325.92196655.21651.85294981.88977.773921310.421303.69
从表1可以看出,有限元仿真与试验结果基本一致,试验数据可靠,有限元网格划分及计算结果可用。施加载荷时应变线性度好,输出信号大。仿真计算中固定端的位移及转角均设置为0,处于理想状态,故施加正负法向载荷引起的应变值完全对称。试验中,施加正负法向载荷,得到的应变值对称性较好,但有所差异,可能由于天平上下两面不完全对称引起的,一侧存在用于天平走线及安装的2mm台阶,在试验中引起一定差异;另外试验过程中外界不确定因素存在一定影响。静校准度为0.02%,满足国军标先进指标。
2.2 2种测量方法灵敏度对比试验
为了对2种测量方法进行比较,在1#应变天平和2#位移天平上分别同时粘贴光纤、电阻2种应变计,如图5所示,其中电阻应变计的供桥电压为10V,输出的电压信号采用安捷伦数字万用表测量。
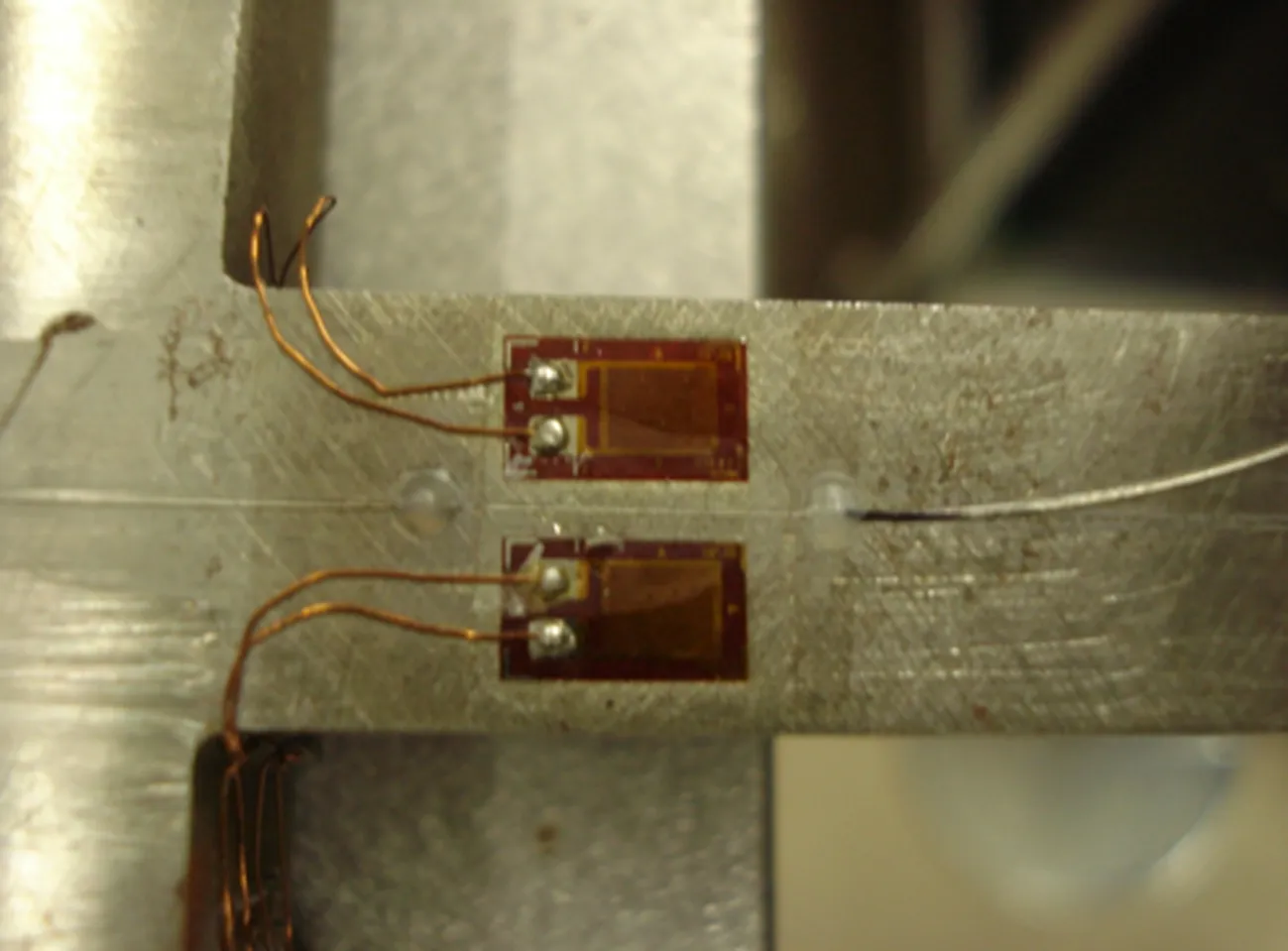
(a) 传统应变天平(1#应变天平)
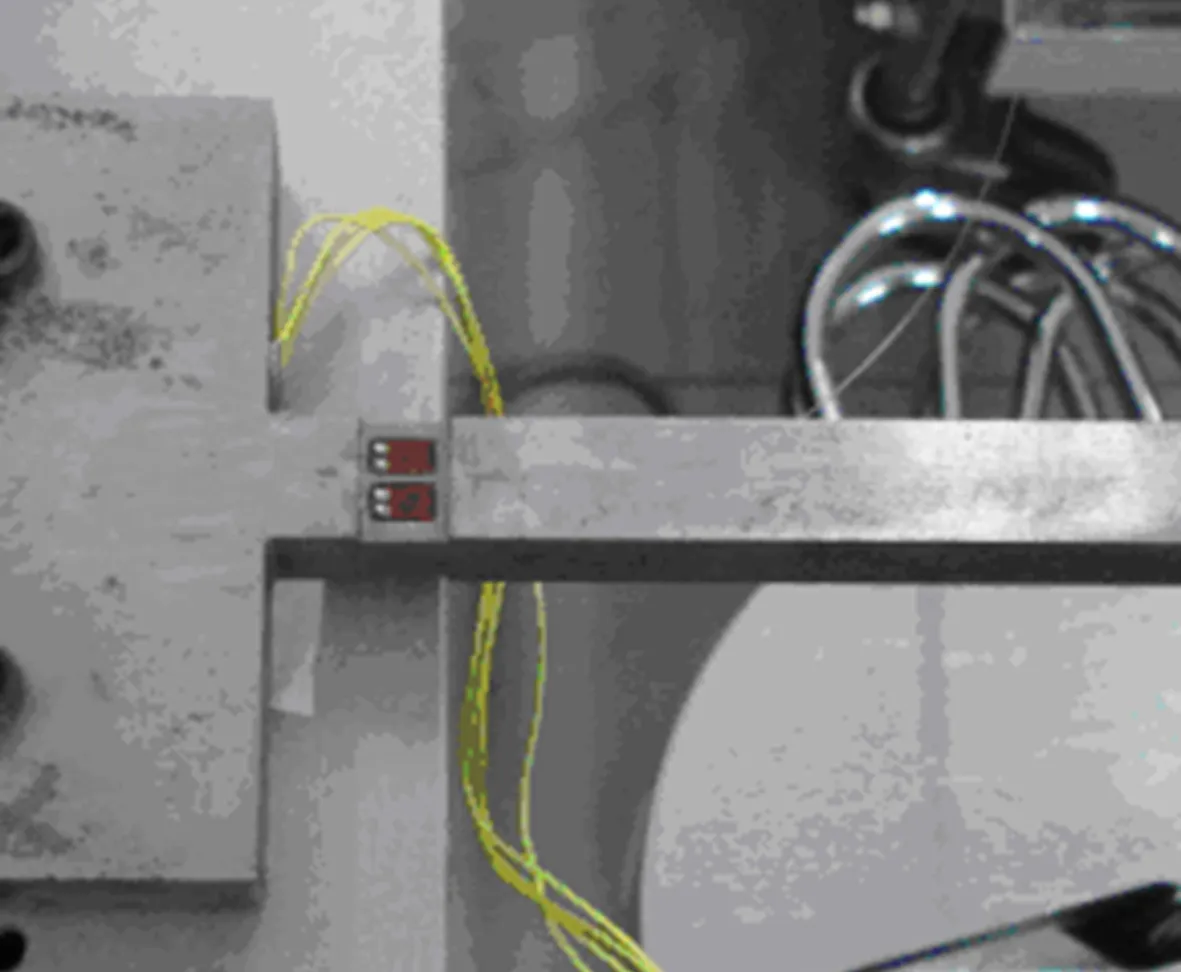
(b) 开槽2mm位移天平(2#位移天平)
2#位移天平试验数据如表2、图6所示,可以看出光纤应变计和电阻应变计的输出与载荷之间均存在良好的线性关系。本文利用每单位力产生的微应变来衡量其灵敏度的高低。试验中电阻应变计组全桥,输出灵敏度指悬臂梁受载荷变形后每一侧应变计输出的信号,则单侧光纤应变计与单侧电阻应变计性能相比如下:
(1) 传统天平中,电阻应变计输出为1.57με/N,光纤应变计输出为1.49με/N,两者量值相当。
(2) 2#位移天平中,电阻应变计输出为1.61με/N,光纤应变计输出为2.63με/N,为电阻输出1.64倍,说明基于位移测量方法的新型天平灵敏度更高。
试验中,光纤应变计采用上下信号叠加方法计算天平公式,进一步增大信号输出值,在此种计算方法下2#位移天平输出为5.26με/N,为电阻应变计输出的3.27倍。
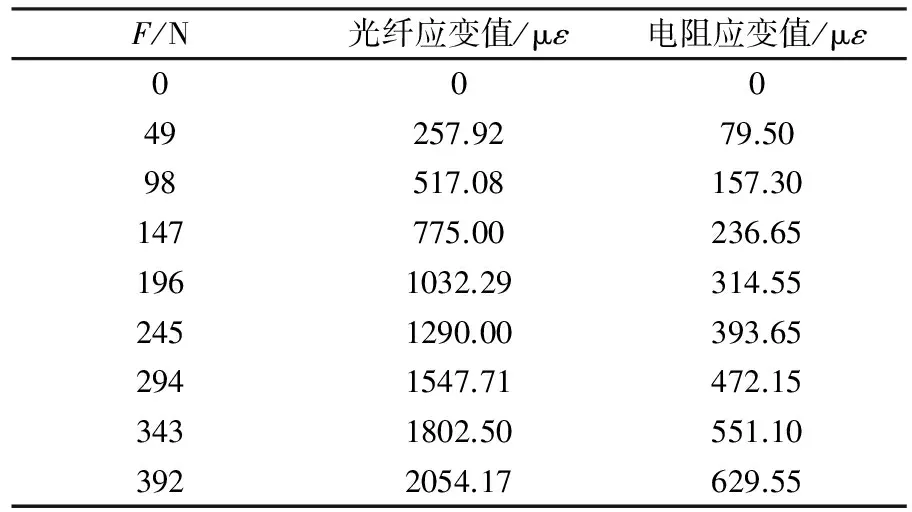
表2 2#位移天平试验结果
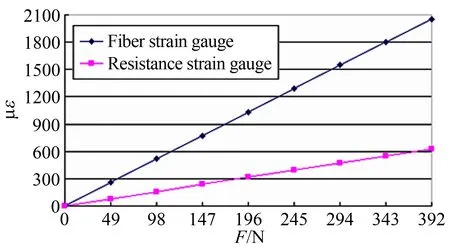
图6 2#位移天平两种应变计试验结果
2.3 槽深对灵敏度影响
为探究开槽深度对灵敏度的影响,将1#位移天平与2#位移天平结果进行对比,如表3、图7所示。
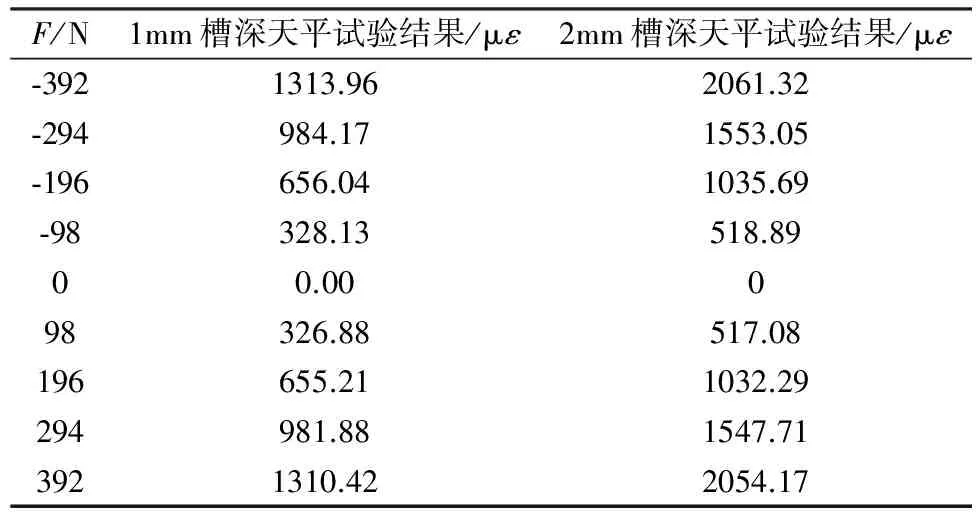
表3 不同槽深天平试验结果对比
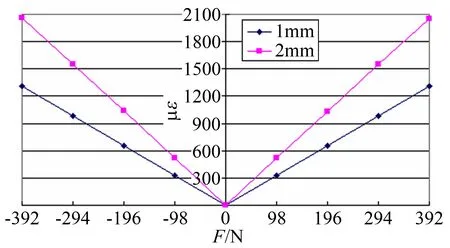
图7 不同槽深试验结果对比
从结果可知,槽深1mm位移天平灵敏度为3.34με/N,准度为0.02%,槽深2mm位移天平灵敏度为5.26με/N,为1mm槽深位移天平的1.57倍,准度为0.09%。因此增加槽口深度虽然可以提高天平灵敏度,但天平刚度下降会导致准度有所降低。
3 结 论
分析新研制的位移天平静校试验数据,可得到以下结论:
(1) 位移天平输出应变值与有限元仿真数据对比,输出结果一致,证明了位移天平的可行性。
(2) 将光纤应变计与电阻应变计同时应用于传统应变天平中,两者灵敏度相当。
(3) 位移天平输出信号大、对称性好、准度高。位移天平中光纤应变计输出灵敏度高于电阻应变计,避免在小量程气动载荷测量时信号输出小,甚至淹没在干扰信号中。
本文从单分量天平入手进行位移测量法的原理性探索,对于风洞试验中实现多分量位移天平测量仍需进一步研究。此外,还需考虑光纤引线的封装与保护等问题。综上所述,基于位移测量法的新型天平为小量程载荷测量提供了新思路。
[1] 贺德馨. 风洞天平[M]. 北京: 国防工业出版社, 2001.
He Dexin. Wind tunnel balance[M]. Beijing: National Defence Industry Press, 2001, 05
[2] 刘高计, 谌满荣, 于卫青, 等. 风洞应变天平灵敏度设计方法研究[J]. 弹箭与制导学报, 2006, 2: 94-97.
Liu Gaoji, Chen Manrong, Yu Weiqing, et al. Design methods for wind tunnen strain gauge ballance sensitivity[J]. Journal of Projectiles Rockets Missiles and Guidance, 2006, 2: 94-97.
[3] 苟文选. 材料力学[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2005.
Gou Wenxuan. Strength of materials[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2005.
[4] 邹芳, 刘丽. 光纤Bragg光栅传感器应用概述[J]. 科技广场, 2010, 6: 102-105.
Zou Fang, Liu Li. Review of application for fiber bragg grating sensors[J]. Science Mosaic, 2010, 6: 102-105.
[5] 安勇龙, 叶敦范. 光纤光栅传感器的工作原理和应用实例[J]. 仪器仪表与分析监测, 2005, 1: 5-7, 11.
An Yonglong, Ye Dunfan. The principles and applied examples of fiber bragg grating sensor[J]. Instrumentation Analysis Monitoring, 2005, 1: 5-7, 11.
[6] 侯尚林, 胡春莲, 马义元. 光纤Bragg光栅及其应用研究进展[J]. 兰州理工大学学报, 2004, 30(1): 93-96.
Hou Shanglin, Hu Chunlian, Ma Yiyuan. Optical fiber Bragg gratings and progress of their application research[J]. Journal of Lanzhou University of Technology, 2004, 30(1): 93-96.
[7] 尚丽平, 张淑清, 史锦珊. 光纤光栅传感器的现状与发展[J]. 燕山大学学报, 2001, 25(2): 139-143.
Shang Liping, Zhang Shuqing, Shi Jinshan. The development and statue quo of fiber grating sensor[J]. Journal of Yanshan University, 2001, 25(2): 139-143.
[8] Pieterse F F, van Wyk J. An experimental four-component optical fiber balance[C]. 7th International Symposium on Strain-Gauge Balances, 2006.
[9] 刘胜春, 姜德生, 郝义昶. 光纤光栅测力传感器的研究及应用[J]. 武汉理工大学学报, 2006, 30(2): 209-211.
Liu Shengchun, Jiang Desheng, Hao Yichang. Application and research of load cell based FBG sensors[J]. Journal of Wuhan University of Technology, 2006, 30(2): 209-211.
[10] 庄茁. Abaqus有限元软件6.4版入门指南[M]. 清华大学出版社.
Zhuang Zhuo. The finite element software version 6.4 entry Guide for abaqus[M]. Tsinghua University press.
[11] 石亦平. Abaqus有限元分析实例详解[M]. 机械工业出版社.
Shi YiPing. Finite element analysis of detailed examples for Abaqus[M]. Machinery Industry Press.
[12] 顾岩. 有限元分析法在风洞天平中的应用[R]. 流体力学实验与测量, 1992, 12.
Gu Yan. The application of finite element analysis in wind tunnel balance[R]. Experiments and measurements in fluid mechanics, 1992, 12.
[13] 于亚婷, 杜平安, 王振伟. 有限元法的应用现状研究[J]. 机械设计, 2005, 22(3): 6-8.
Yu Yating, Du Pingan, Wang Zhenwei. Research on the current application status of f inite element method[J]. Journal of Machine Design, 2005, 22(3): 6-8.
(编辑:李金勇)
A new method for improving the measurement sensitivity of wind tunnel balance
Wang Huilun1, Xie Yajun1, Jiang Yajun2
(1. School of Aeronautics, Northwestern Polytechnical University, Xi’an 710072, China; 2. Key Laboratory of Optical Information Technology, Northwestern Polytechnical University, Xi’an 710072, China)
The sensitivity of traditional measurement of small scope aerodynamic force is not very high. Aiming at this problem, this paper introduces a new measurement method: Displacement measurement method. It means setting two grooves at the same place as where the traditional gauges are pasted, then measuring the displacement of the grooves as it changs when the grooves are loaded to get the balance formula. Here take three kinds of single component balances as an example: One traditional strain balance and two kinds of the displacement balances with different grooves. The traditional balance and the displacement balance with 2mm grooves are pasted with two kinds of strain gauges, which are the optical fiber strain gauge and the strain gauge respectively, to compare the performance of both the gauges and the measurement methods. And an optical fiber strain gauge is used in the displacement balance with 1mm grooves to compare the different sensitivity caused by different depths of the grooves. The static calibration test and the finite element simulation are carried out, and we can draw conclusions as follows: The new measurement method can improve the sensitivity compared to the traditional methods, and the deeper the groove is, the higher the sensitivity becomes. For example, the sensitivity of the new balance with 2mm deep grooves is improved by 3 times compared to the traditional strain balance, 1.57 times compared to the 1mm deep grooves. The accuracy of the new balance with 1mm deep grooves is 0.02%, meeting the accuracy requirements. The accuracy of the balance with 2mm deep grooves is 0.09%. It thus shows that increasing the depth of the grooves would lower the accuracy, which may be caused by the decrease of the rigidity of the balance. Therefore the size of the grooves should be chosen carefully. This paper provides a new idea for small scope aerodynamic force measurement.
displacement measurement method;single component balance;optical fiber strain gauge;sensitivity;small scope aerodynamic force
1672-9897(2015)01-0083-05
10.11729/syltlx20140003
2014-01-02;
2014-02-22
WangHL,XieYJ,JiangYJ.Anewmethodforimprovingthemeasurementsensitivityofwindtunnelbalance.JournalofExperimentsinFluidMechanics, 2015, 29(1): 83-86,91. 王惠伦, 解亚军, 姜亚军. 一种提高风洞天平灵敏度的测量方法. 实验流体力学, 2015, 29(1): 83-86,91.
V211.72
A

王惠伦(1988-),女,吉林长春人,硕士研究生。研究方向:实验流体力学。通信地址:陕西省西安市碑林区友谊西路127号西北工业大学(710072)。E-mail:wanghuilun1988@163.com

