利用功能叶片钾含量作为水稻钾营养诊断指标的可行性研究
薛欣欣, 李岚涛, 鲁剑巍, 李小坤, 任 涛, 丛日环, 周 鹂
(华中农业大学资源与环境学院, 农业部长江中下游耕地保育重点实验室, 武汉 430070)
利用功能叶片钾含量作为水稻钾营养诊断指标的可行性研究
薛欣欣, 李岚涛, 鲁剑巍*, 李小坤, 任 涛, 丛日环, 周 鹂
(华中农业大学资源与环境学院, 农业部长江中下游耕地保育重点实验室, 武汉 430070)

水稻; 功能叶; 钾素营养; 诊断指标
作物化学分析诊断是一种传统且最为常用的营养诊断方法,与土壤诊断、无损诊断等方法相比,能够更直观、精确地反映作物营养状况,并且在较长一段时间内仍将是作物营养诊断的主要手段[1-2]。有学者指出作物出现缺乏症状时的养分含量较稳定,受养分来源的影响较小,因此作物化学分析诊断具有普遍意义[3]。

本研究在前人成果的基础上,选择了水稻主茎从上往下的第二功能叶作为全生育期钾素营养的诊断部位。一方面考虑到该叶位的叶片样品采集方便,对水稻植株损伤较小;另一方面则考虑到该叶位的叶片以全展开叶的状态存在于整个生育期。本研究在田间试验的基础上,探讨利用水稻功能叶片作为水稻钾素营养诊断指标的可行性,旨在为水稻钾肥的合理施用提供科学依据。
1 材料与方法
1.1 试验设计
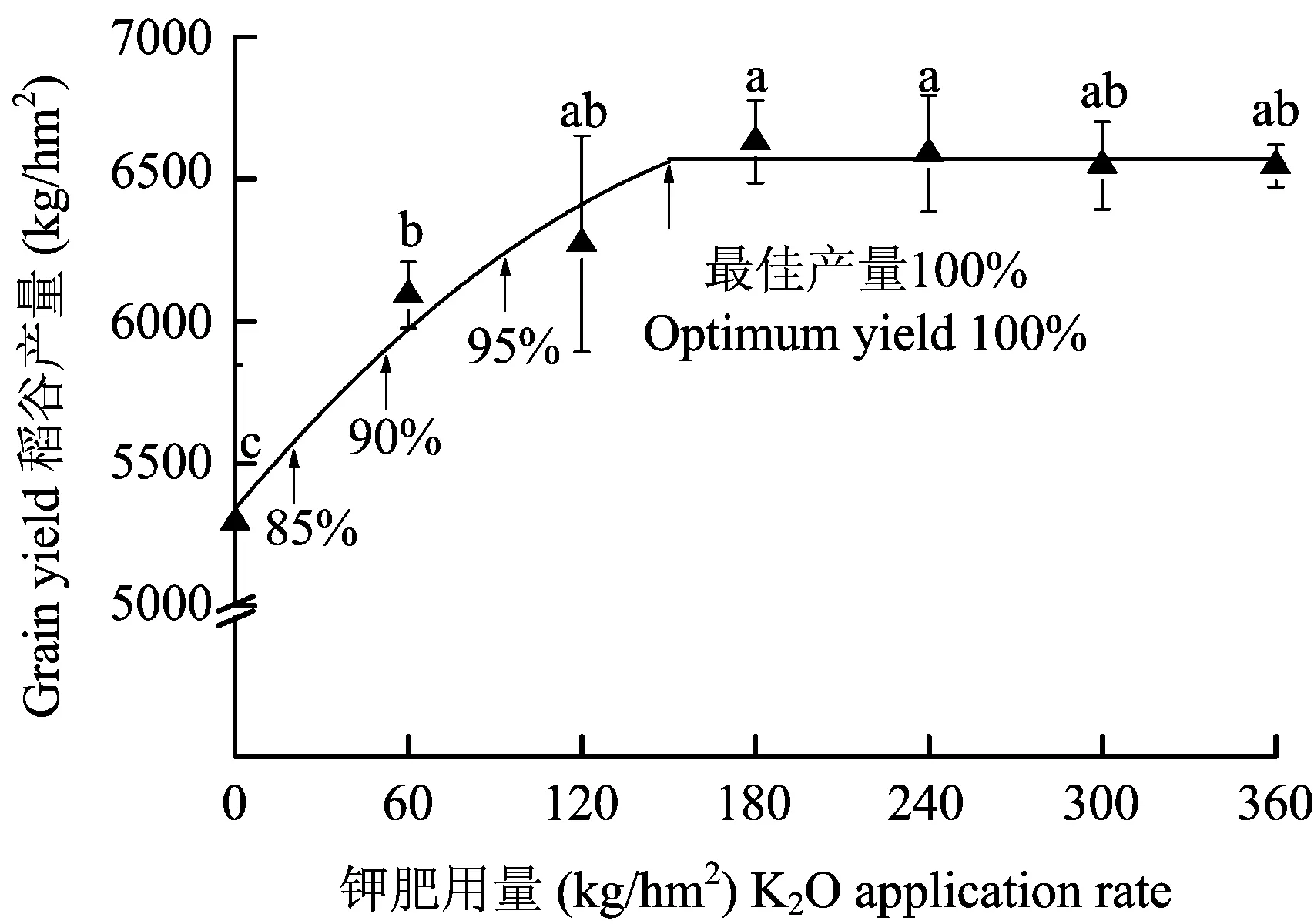
田间试验于2012年5月至9月在湖北省蕲春县向桥乡进行。供试水稻品种为两优6326,土壤为花岗片麻岩母质发育的砂壤性水稻土。土壤基础理化性状: pH 5.0,有机质含量36.1 g/kg,全氮2.0 g/kg,速效磷2.1 mg/kg,速效钾36.0 mg/kg,缓效钾114.2 mg/kg。试验设K2O 0、60、120、180、240、300和360 kg/hm27个钾肥处理,分别用K0、K60、K120、K180、K240、K300和K360表示。为避免生育期间追施钾肥对水稻植株钾含量变化曲线的影响,因此钾肥作基肥一次性施入;氮肥按N 180 kg/hm2分3次施用,分别为基肥50%、分蘖肥25%和穗肥25%;磷肥按P2O590 kg/hm2作基肥一次性施入。水稻种植采用大田育秧、移栽的方式,秧田肥料用量按N 57 kg/hm2,P2O526 kg/hm2和K2O 30 kg/hm2施用;移栽密度为25.5×104/hm2,单株/穴,秧苗生长良好。试验采用随机区组排列,小区面积4 m×7.5 m,3次重复。其他栽培管理措施同常规大田。
1.2 样品采集及分析
第二功能叶的采集 于水稻分蘖初期(移栽后10 d)、分蘖盛期(移栽后20 d)、有效分蘖临界期(移栽后31天)、拔节期(移栽后44 d)、孕穗期(移栽后58 d)、齐穗期(移栽后68 d)分别在各小区采集代表性植株6株,将主茎从上到下的第二功能叶进行收集,105℃杀青30min,70℃烘干至恒重,记录各时期的干重,磨碎、过筛后测钾。成熟期取未采样的1/2小区进行测产,单打单收记录各小区稻谷产量。
植物样品钾含量用1 mol/L的HCl振荡浸提2 h,过滤、稀释、火焰光度计测定[19]。
1.3 相关计算公式及方法
1)二次加平台(quadratic plus plateau)钾肥肥效模型[20]:
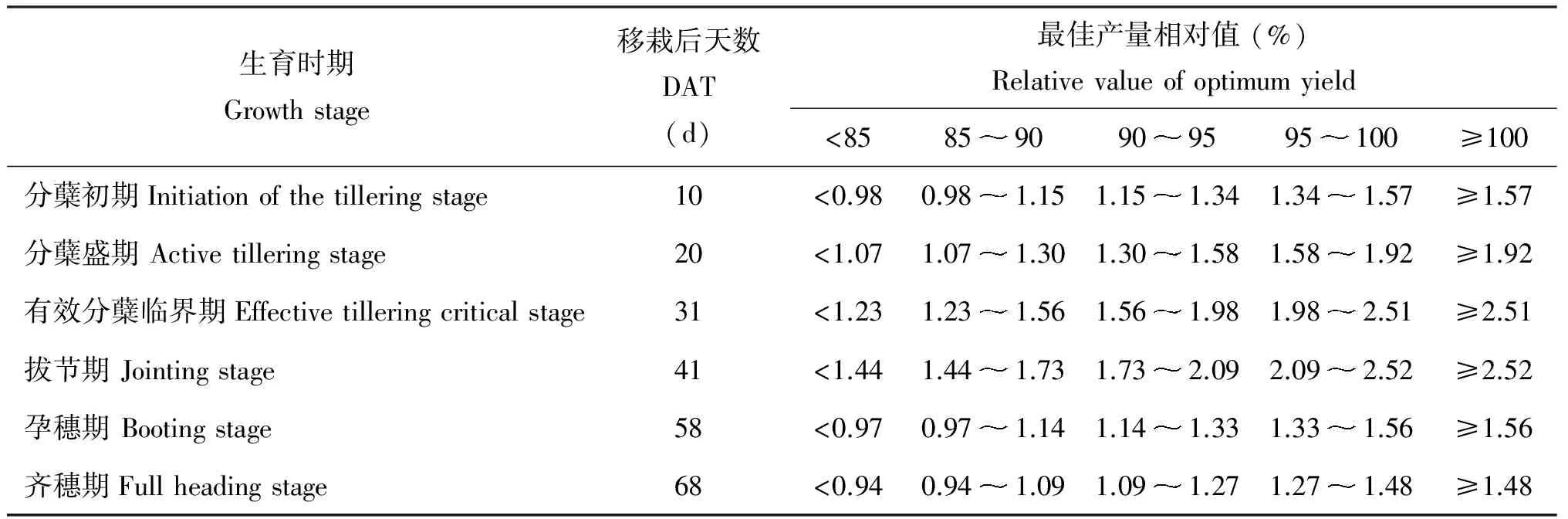
y=a+bx+cx2(x y=p(x≥m) 式中:y为稻谷产量(kg/hm2),x为钾肥用量(K2O kg/hm2),a为截距,b为直线回归系数,c为二次回归系数,m为二次型曲线与平台的交点,p为平台产量(kg/hm2)。 2)钾含量诊断指标的建立方法(图1): 首先拟合施钾量和稻谷产量的肥效方程,按最佳产量的100%、95%、90%、85%等进行分级;拟合第二功能叶钾含量与产量的回归方程;将各级临界产量值代入回归方程中求出对应的第二功能叶钾含量临界值,最终建立钾素营养诊断指标。 图1 功能叶钾含量诊断指标建立方法Fig.1 Method of establishing the diagnosis index of the functional leaf potassium content 1.4 数据处理 数据分析和绘图运用Microsoft Excel、Origin 8.0、SPSS 17.0和SAS统计软件进行。 2.1 钾肥用量对稻谷产量的影响 图2 钾肥用量对水稻产量的影响及钾肥肥效模型Fig.2 Effect of potassium application rates on the grain yield and the potassium fertilizer efficiency model[注(Note): 图中不同字母表示施肥处理间差异达到5%显著水平 Different letters indicate significant at 5% level between treatments.] 2.2 钾肥用量对第二功能叶钾含量的影响 图3 水稻第二功能叶钾含量的变化特征Fig.3 Temporal variations of the K contents of the 2nd functional leaves of rice at different growth stages under different K application rates[注(Note): IT—分蘖初期Initiation of the tillering stage; AT—分蘖盛期Active tillering stage; ET—有效分蘖临界期Effective tillering critical stage; J—拔节期Jointing stage; B—孕穗期Booting stage; F—齐穗期Full heading stage.] 2.3 第二功能叶钾含量与稻谷产量和钾肥用量的相关性分析 第二功能叶钾含量与稻谷产量和钾肥用量相关分析结果(表1)表明,第二功能叶钾含量与稻谷产量的关系适合用对数方程拟合,各时期的相关系数均达极显著水平(P<0.01);钾肥用量和第二功能叶钾含量的关系则适合用一元二次方程拟合,除分蘖盛期显著相关外(P<0.05),其余各时期均达极显著相关(P<0.01)。由此可以看出,第二功能叶钾含量可以准确地预测稻谷产量水平和反映钾肥施用水平,适合作水稻钾营养的诊断部位。 表1 第二功能叶钾含量与稻谷产量和钾肥用量的相关系数(R2) 注(Note): * 和** 分别表示相关系数达5%和1%显著水平 Indicate the correlation coefficients are significant at the 5% and 1% levels, respectively. DAT—Days after the transplanting. 图4 第二功能叶钾含量和稻谷产量的关系Fig.4 Relationship between the potassium contents of the 2nd functional leaves and the grain yields of rice at different stages[注(Note): IT—分蘖初期Initiation of the tillering stage; AT—分蘖盛期Active tillering stage; ET—有效分蘖临界期Effective tillering critical stage; J—拔节期Jointing stage; B—孕穗期Booting stage; F—齐穗期Full heading stage. * 和** 分别表示相关系数达5%和1%显著水平Indicate the correlation coefficients are significant at the 5% and 1% levels, respectively. DAT—Days after the transplanting.] 生育时期Growthstage移栽后天数DAT(d)最佳产量相对值(%)Relativevalueofoptimumyield<858590909595100≥100分蘖初期Initiationofthetilleringstage10<0.980.981.151.151.341.341.57≥1.57分蘖盛期Activetilleringstage20<1.071.071.301.301.581.581.92≥1.92有效分蘖临界期Effectivetilleringcriticalstage31<1.231.231.561.561.981.982.51≥2.51拔节期Jointingstage41<1.441.441.731.732.092.092.52≥2.52孕穗期Bootingstage58<0.970.971.141.141.331.331.56≥1.56齐穗期Fullheadingstage68<0.940.941.091.091.271.271.48≥1.48 注(Note): DAT—Days after the transplanting. 2.4 第二功能叶钾含量作为钾营养诊断指标的建立 由产量结果可知,本研究所设置的钾肥梯度为水稻钾素诊断提供了可行性(图2)。回归分析结果表明,第二功能叶钾含量和产量适合用对数方程拟合(图4)。根据图1所示的植株钾含量诊断指标建立方法,经计算得到第二功能叶钾含量分级指标(表2)。若以最佳产量的95%为临界值标准,当第二功能叶钾含量在分蘖初期、分蘖盛期、有效分蘖临界期、拔节期、孕穗期和齐穗期分别低于1.34%、1.58%、1.98%、2.09%、1.33%和1.27%时,则需要追施钾肥以避免水稻植株因缺钾而导致减产。 3.1 第二功能叶钾含量的变化及差异 3.2 第二功能叶作为钾素诊断指标的可行性分析 水稻从分蘖期到齐穗期对钾素的需求占整个生育期的80%以上[23-24],掌握该阶段的水稻钾素营养状况对作物正常生长及产量形成具有重要的意义。本文研究发现各生育期的第二功能叶钾含量与产量和施钾量相关关系极显著;从取样原则上来讲,第二功能叶存在于整个生育期,而且该叶位叶片容易获取并对作物的损坏程度小。综上所述,以水稻主茎第二功能叶作为分蘖期到齐穗期的营养诊断部位是可行的。施用效果显著为钾营养诊断提供了可靠的保证。陈新平等[25]认为,在对肥效模型进行评价时,应该从模型的拟合程度和推荐施肥量的节省程度两方面综合考虑。本研究用二次加平台模型进行拟合的程度远高于其他模型,而且节省钾肥;通过肥效方程以及第二功能叶钾含量的回归方程,建立了营养诊断指标,既节约钾资源,又保证较高的经济产出。 本研究阐明了以功能叶片钾含量作为钾营养诊断指标的可行性,初步建立了该试验条件下各生育期水稻植株钾营养诊断指标;然而该研究结果是否受种植品种、种植时期及气候环境等诸多因素的影响,仍需进行深入研究。 3)第二功能叶钾含量作为植株钾营养诊断指标的操作性较强,且能够精准地预测稻谷产量水平。若以95%为产量临界值标准,在该试验条件下,当第二功能叶钾含量在分蘖初期、分蘖盛期、有效分蘖临界期、拔节期、孕穗期和齐穗期分别低于1.34%、1.58%、1.98%、2.09%、1.33%和1.27%时,则水稻植株处于钾素缺乏水平,需要补充钾肥以维持正常的钾素需求。 [1] 江立庚, 曹卫星, 姜东, 等. 水稻叶氮量等生理参数的叶位分布特点及其与氮素营养诊断的关系[J]. 作物学报, 2004, 30(8): 745- 750. Jiang L G, Cao W X, Jiang Detal. Distribution of leaf nitrogen, amino acids and chlorophyll in leaves of different positions and relationship with nitrogen nutrition diagnosis in rice[J]. Acta Agronomica Sinica, 2004, 30(8): 745-750. [2] Yue S, Meng Q, Zhao Retal. Critical nitrogen dilution curve for optimizing nitrogen management of winter wheat production in the north China plain[J]. Agronomy Journal, 2012, 104(2): 523-529. [3] 李延, 马居米·让德迪优, 秦遂初. 缺镁对水稻生理代谢的影响及诊断指标研究[J]. 浙江农业大学学报, 1995, 21(3): 279-283. Li Y, Macumi J D D, Qin S C. Studies on diagnosis of Mg-deficiency and physiological metabolism of rice grown under Mg-deficiency conditions[J]. Journal of Zhejiang Agricultural University, 1995, 21(3): 279-283. [4] 郭彬, 林义成, 丁能飞, 等. 水稻氮素及钾素叶位分布特点及诊断叶位研究[J]. 浙江农业学报, 2009, 21(3): 299-302. Guo B, Lin Y C, Ding N Fetal. Distribution of nitrogen and potassium in different leaf positions and relationship with nitrogen and potassium diagnosis in rice (Oryzasativa)[J]. Acta Agriculturae Zhejiangensis, 2009, 21(3): 299-302. [5] 陈智慧, 王火焰, 周健民, 等. 不同钾素水平对水稻不同部位含钾量的影响[J]. 土壤, 2013, 45(3): 489-494. Chen Z H, Wang H Y, Zhou J Metal. Dynamic changes of rice K content influenced by different soil K levels[J]. Soils, 2013, 45(3): 489-494. [6] 朱维和, 温应和, 谢茂和. 水稻植株体内钾素的分布[J]. 土壤通报, 1982, (2): 53-58. Zhu W H, Wen Y H, Xie M H. Distribution of potassium in rice plants[J]. Chinese Journal of Soil Science, 1982, (2): 53-58. [7] 王强盛, 丁艳锋, 王绍华. 水稻分蘖期钾素营养诊断研究[A]. 中国作物学会. 中国作物学会栽培专业委员会换届暨学术研讨会论文集[C]. 北京: 中国作物学会, 2007. Wang Q S, Ding Y F, Wang S H. Nutrition diagnosis of potassium at tillering stage of rice [A]. The Crop Science Society of China, Chinese Crop Cultivation of Professional Committee of the transition and academic symposium proceedings [C]. Beijing: The Crop Science Society of China, 2007. [8] 李刚华, 丁艳峰, 薛利红, 王绍华. 利用叶绿素计(SPAD-502)诊断水稻氮素营养和推荐追肥的研究进展[J]. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2005, 11(3): 412-416. Li G H, Ding Y F, Xue L H, Wang S H. Research progress on diagnosis of nitrogen nutrition and fertilization recommendation for rice by use chlorophyll meter[J]. Plant Nutrition and Fertilizer Science, 2005, 11(3): 412-416. [9] Wallihan E F, Moomaw J C. Selection of index leaf for studying the critical concentration of nitrogen in rice plants[J]. Agronomy Journal, 1967, 59(5): 473-474. [10] Peng S, Garcia F V, Laza R Cetal. Increased N-use efficiency using a chlorophyll meter on high-yielding irrigated rice[J]. Field Crops Research, 1996, 47(2): 243-252. [11] Lin F F, Qiu L F, Deng J Setal. Investigation of SPAD meter-based indices for estimating rice nitrogen status[J]. Computers and Electronics in Agriculture, 2010, 71(1): 60-65. [12] Raveh E. Citrus leaf nutrient status: A critical evaluation of guidelines for optimal yield in Israel[J]. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Soil Science, 2013, 176(3): 420-428 [13] 李刚华, 薛利红, 尤娟, 等. 水稻氮素和叶绿素SPAD叶位分布特点及氮素诊断的叶位选择[J]. 中国农业科学, 2007, 40(6): 1127-1134. Li G H, Xue L H, You Jetal. Spatial distribution of leaf N content and SPAD value and determination of the suitable leaf for N diagnosis in rice[J]. Scienica Agricultura Sinica, 2007, 40(6): 1127-1134. [14] 危常州, 张福锁, 朱和明, 等. 新疆棉花氮营养诊断及追肥推荐研究[J]. 中国农业科学, 2002, 35(12): 1500-1505. Wei C Z, Zhang F S, Zhu H Metal. Study on cotton nitrogen diagnosis and top dressing recommendation in North Xinjiang[J]. Scienica Agricultura Sinica, 2002, 35(12): 1500-1505. [15] Bates T E. Factors affecting critical nutrient concentrations in plants and their evaluation: a review[J]. Soil Science, 1971, 112(2): 116-130. [16] 张晓海, 苏贤申, 廖德智. 烤烟钾素营养快速诊断研究[A]. 马阳. 全国学术年会农业分会场论文专集[C]. 北京: 中国农学通报期社, 2004. Zhang X H, Su X S, Liao D Z. Studies of diagnose on potassium nutrition of flue-cure tobacco [A]. Ma Y. The national conference on agriculture [C]. Beijing: Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin Press, 2004. [17] Raber D. Fertilization recommendations for citrus orchards in seasonal recommendations for citrus orchards[M]. Israel: Extension Service, Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Development, State of Israel, 2011. 28-37. [18] 马忠玉, 吴永常. 我国水稻品种遗传改进在增产中的贡献分析[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2000, 14(2): 112-114. Ma Z Y, Wu Y C. Contribution of rice genetic improvement to yield increase in China[J]. Chinese Journal of Rice Science, 2000, 14(2): 112-114. [19] 夏颖, 姜存仓, 王晓丽, 等. 嫁接对不同棉花基因型钾效率的影响[J]. 中国生态农业学报, 2012, 20(1): 34-39. Xia Y, Jiang C C, Wang X Letal. Effects of grafting on potassium use efficiency of different cotton genotypes[J]. Chinese Journal of Eco-Agriculture, 2012, 20(1): 34-39. [20] 贾良良, 陈新平, 张福锁, 等. 北京市冬小麦氮肥适宜用量评价方法的研究[J]. 中国农业大学学报, 2001, 6(3): 67-73. Jia L L, Chen X P, Zhang F Setal. Study of optimum N supplying rate in winter-wheat of Beijing area[J]. Journal of China Agricultural University, 2001, 6(3): 67-73. [21] 谢少平. 高等植物钾离子吸收的调节[J]. 植物生理学通讯, 1989, (4): 1-7. Xie S P. Regulation of potassium absorption in higher plants[J]. Plant Physiology Communications, 1989, (4): 1-7. [22] 陆景陵. 植物营养学[M]. 北京: 中国农业大学出版社, 2003. Lu J L. Plant nutrition[M]. Beijing: Chinese Agricultural University Press. 2003. [23] 潘圣刚, 翟晶, 曹凑贵, 等. 氮肥运筹对水稻养分吸收特性及稻米品质的影响[J]. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2010, 16(3): 522-527. Pan S G, Zhai J, Cao C Getal. Effects of nitrogen management practices on nutrition uptake and grain qualities of rice[J]. Plant Nutrition and Fertilizer Science, 2010, 16(3): 522-527. [24] 李云春. 几种不同类型水稻养分吸收特性及施肥效果研究[D]. 武汉: 华中农业大学硕士学位论文, 2012. Li Y C. Study on nutrients absorption characteristics and NPK fertilization effects of several different types of rice[D]. Wuhan: Ms Thesis of Huazhong Agriculture University, 2012. [25] 陈新平, 周金池, 王兴仁, 等. 小麦-玉米轮作制中氮肥效应模型的选择-经济和环境效益分析[J]. 土壤学报, 2000, 37(3): 346-354. Chen X P, Zhou J C, Wang X Retal. Economic and environmental evaluation on models for describing crop yield response to nitrogen fertilizers at winter-wheat and summer-corn rotation system[J]. Acta Pedologica Sinica, 2000, 37(3): 346-354. Feasibility study of using potassium content of functional leaves of rice as potassium diagnostic index XUE Xin-xin, LI Lan-tao, LU Jian-wei*, LI Xiao-kun, REN Tao, CONG Ri-huan, ZHOU Li (CollegeofResourcesandEnvironment,HuazhongAgriculturalUniversity/KeyLaboratoryofArableLandConservationofMiddleandLowerReachesofYangtzeRiver,MinistryofAgriculture,Wuhan430070,China) 【Objectives】 Plant tissue is widely used for the diagnose of plant nutrient status. The second functional leaf from the top of rice is easy sampled, with negligible injury to rice growth, and will not absciss during the whole growth stages. The feasibility of using the potassium content in the 2nd functional leaf as rice nutrition diagnosis method was studied. 【Methods】 A field experiment was conducted with different K2O application rates of 0, 60, 120, 180, 240, 300 and 360 kg/ha. The potassium contents in the 2nd functional leaf were tested at different growth periods and the grain yields were weighed. Regression analysis was performed to evaluate the relationship between the potassium contents in the 2nd functional leaf and the grain yields and K application rates. 【Results】 The grain yields are significantly different under different K application rates. A quadratic plus plateau model well descriped the significant relationship between K application rates and the grain yield, satisfies the requirement of potassium status diagnosis. The potassium contents of the 2nd functional leaves was increased significantly with the increase of the K application rates. The K contants of the 2nd functional leaves was in range of 0.85%-2.72% from the beginning of the tillering stage to the full heading stage and reach the highest values at the jointing stage. The correlation analysis shows that the potassium content of the 2nd functional leaves were significantly correlated with the grain yield and potassium application rates (P<0.05). The yields are classified as five ranks, i.e., <85%, 85%-90%, 90%-95%, 95%-100% and >100% of the maximum yield. The corresponding K contents of the 2nd functional leaves were calculated according to the regression equation. When the 95% of optimal yield was set as the critical yield, the calculated K contents were 1.34%, 1.58%, 1.98%, 2.09%, 1.33% and 1.27% at initial tillering, active tillering, effective tillering, jointing, booting and full heading stages, respectively.【Conclusions】 The potassium content of the 2nd functional leaves are significantly related to the K2O application rates and yields, so, is suitable to be used as the potassium status diagnosis index at the different rice development periods. If the 95% of optimum yield is set as the critical yield level, rice would be found potassium deficiency when the 2nd functional leaf contents are below 1.34%, 1.58%, 1.98%, 2.09%, 1.33% and 1.27% at the tillering stage, active tillering stage, effective tillering critical stage, jointing stage, booting stage and full heading stage, respectively. rice; functional leaf; potassium status; diagnostic index 2014-01-02 接受日期: 2014-05-04 公益性行业(农业)科研专项 (201203013);中央高校基本科研业务费专项(2013PY113);长江学者和创新团队发展计划项目(IRT1247)资助。 薛欣欣(1986—), 男, 陕西咸阳人, 博士研究生, 主要研究作物养分管理方面的研究。E-mail: xuexinxin.2010@webmail.hzau.edu.cn * 通信作者 Tel: 027-61379276, E-mail: lunm@mail.hzau.edu.cn S158.3; S511.01 A 1008-505X(2015)02-0492-08
2 结果与分析





3 讨论



4 结论



