鼻咽癌中miR-BARTs的研究进展
潘林江,叶志华,黄素宁,陈 罡
(广西医科大学第一附属医院a.放疗科; b.病理科,广西 南宁530021)
鼻咽癌中miR-BARTs的研究进展
潘林江a,叶志华b,黄素宁a,陈 罡b
(广西医科大学第一附属医院a.放疗科; b.病理科,广西 南宁530021)
微小RNA(miRNAs)是一类具有调控功能的内源性非编码单链小分子RNA,长约18~24个核苷酸,与鼻咽癌(nasopharyngeal carcinoma,NPC)的发生发展、诊断以及预后、转归有关。BamH1 A右向转录(BamH1 A rightward transcripts,BARTs)是EB病毒(EBV)中一组经转录后选择性多剪接的基因产物,存在于EBV所有潜伏状态的miRNA,共22种(miR-BART1—22),并表达于NPC等EBV感染相关的恶性肿瘤。阐明miR-BARTs在NPC的作用机制对指导临床治疗有重要意义。
鼻咽癌; BamH1 A; 右向转录; EB病毒; 基因调控
鼻咽癌(nasopharyngeal carcinoma,NPC)是我国南方地区和东南亚最常见的恶性肿瘤之一。在我国NPC总发病率为3.61/10万,粗死亡率为1.99/10万,且复发转移率较高,严重危害人类健康;NPC的发生与遗传易感性、环境因素和EB病毒(EBV)感染有关[1]。微小RNA(microRNA,miRNA)是一类具有调控功能的非编码蛋白质的单链小分子RNA,能调控病毒基因和宿主细胞基因。EBV是首个被发现能够编码miRNA的人类病毒[2]。有研究[3]发现,EBV编码的BamH1 A 右向转录(BamH1 A rightward transcripts,BARTs)在鼻咽癌的发生发展中起调控作用。本文就NPC中miR-BARTs的基因调控机制作一综述。
1 EBV与NPC
EBV在NPC的发生发展中起重要作用。一方面,EBV本身可通过表达潜伏膜蛋白-1(latent membrane protein-1,LMP-1)影响细胞周期使NPC细胞永生化;另一方面,LMP-1的表达使细胞骨架相关蛋白Ezrin上调,从而引起NPC CNE1细胞侵袭和转移能力增强。另外,EBV本身亦可通过改变宿主细胞结构使染色体高度浓缩,可能有利于病毒的复制[4]。EBV链的缺失能改变LMP-1序列,从而引起CD4+T细胞抗原决定簇的缺失[5],可能引起EBV源性的肿瘤细胞免疫逃逸,导致EBV的潜伏感染,致瘤性增强。
2 miR-BARTs简介
BARTs最初是在研究C15 NPC异种移植瘤的cDNA文库中被发现,其广泛存在于EBV感染的NPC患者中。目前miR-BARTs共22种(miR-BART1—22),是一类长度约18~24个核苷酸,具有调控功能的非编码蛋白质的单链小分子RNA,可存在于EBV的所有潜伏状态[6]。有研究[7]发现,miR-BARTs通过降解靶mRNA或抑制其转录后翻译发挥对病毒自身基因和宿主细胞基因的表达,促进肿瘤细胞的生长和抑制肿瘤细胞凋亡。miR-BARTs可通过下调EBV基因表达从而使肿瘤获得免疫逃逸并潜伏生长[8-9]。miR-BARTs也可通过调控EBV基因以及宿主细胞基因的表达,在NPC的发生发展中发挥作用。
3 miR-BARTs在NPC中的调节机制
3.1 miR-BARTs在调节EBV基因表达中的作用
miR-BART2-5p与Bam H1 A片段左向的第5个阅读框编码(Bam H1 A fragment containing the fifth left open reading from frame(BALF5)转录产物高度互补结合,通过裂解结合区域,最终下调BALF5的表达[10]。BALF5作为EBV-DNA聚合酶基因编码病毒DNA复制所需重要蛋白BALF5蛋白,提示BALF5的表达降低从而导致病毒数量减少,可能有利于EBV进入潜伏状态,使NPC躲避宿主的免疫攻击,从而导致NPC的发生发展。
miR-BARTs与EBV基因的3′UTRs结合可下调LMP1[6]和潜伏膜蛋白2A(latent membrane protein,LMP2A)[11]的表达,其信号通路尚不明确,目前可调节LMP表达的miR-BARTs见表1。LMP1是肿瘤坏死因子受体家族的一个功能同源体,具有瘤基因功能的蛋白质[12],可促进癌细胞生长增殖,促进NPC的侵袭和转移等,而其高表达可以抑制肿瘤细胞生长[13]。LMP2A在EBV潜伏感染及转化细胞过程中发挥重要作用,EBV潜伏感染的B细胞中均检测到LMP2A的表达,LMP2A具有潜在的T细胞激活表位,能介导宿主杀伤性T细胞作用的发挥[14]。因此可认为miR-BARTs通过上调LMP1和LMP2A表达可抑制EBV致癌性。
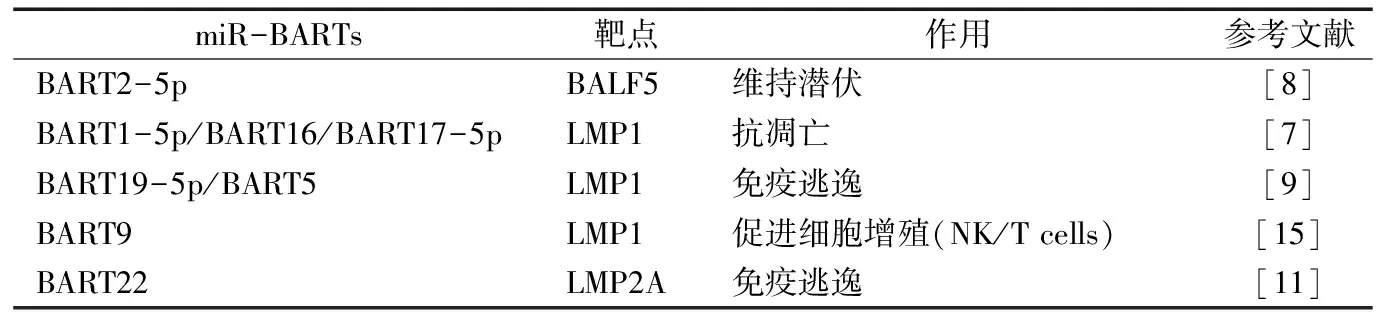
表1 miR-BARTs调节EBV基因的靶点及作用
3.2 miR-BARTs在调节其他基因表达中的作用
miR-BARTs可通过调节细胞周期相关基因的表达,影响细胞增殖和凋亡正常的相关信号通路,从而抑制细胞凋亡和诱导肿瘤免疫逃逸。p53正向凋亡调控因子(p53-up regulated modulator of apoptosis,PUMA),为首个被报道的miR-BARTs靶点[16]。PUMA属于Bcl2家族中BH3-only的一种促凋亡蛋白,通过调节线粒体中细胞色素C的释放启动凋亡[17]。miR-BART5通过与PUMA基因的3′UTR结合,在转录后水平负向地调节PUMA的表达,从而抑制NPC细胞的凋亡。有研究[16]证实,凋亡药物的敏感性在缺少miR-BART5或PUMA异常表达的EBV阳性NPC细胞系中明显增强。BH3-only蛋白Bim是miR-BART1簇的作用靶点,miR-BART1簇必须共同联合作用,才能发挥调节作用,阻断PUMA介导的细胞凋亡[18]。
Lin等[19]发现miR-BART20-5p可通过与靶mRNA的3′UTR结合下调转录因子TBX21的表达。通过抑制TBX21的活性可间接抑制p53在NK/T淋巴瘤细胞株中的作用,提示miR-BART20-5p可以阻断p53依赖的细胞凋亡,但是miR-BART20-5p在上皮癌中低表达。EBV miR-BART2-5p可以下调MICB基因而促使肿瘤细胞免疫逃逸;MICB为NK细胞的配体,表达于细胞表面,其表达下调可能是肿瘤细胞逃脱NK细胞攻击的原因[20]。固有免疫相关基因importin7(IPO7)是潜在的[21-22],IPO7基因可通过编码重要的受体蛋白,运输转录因子进入细胞核[23],提示可能通过调节固有免疫使肿瘤细胞获得免疫逃逸。
另外,miR-BARTs可以广泛下调一些Wnt抑制分子,使肿瘤发生率增高,如WIF1、APC、NLK[24]。miR-BART3-5p通过下调肿瘤抑制基因DICE1的表达,促进NPC发生发展[25]。另有研究[26]发现,miR-BART6-5p可以抑制人Dicer的表达。Dicer是合成miRNA所需的一种重要的酶,提示miR-BART6-5p可抑制miRNA表达,并通过减少抑制相关的miRNA合成,从而可能促进NPC肿瘤生长,见表2。
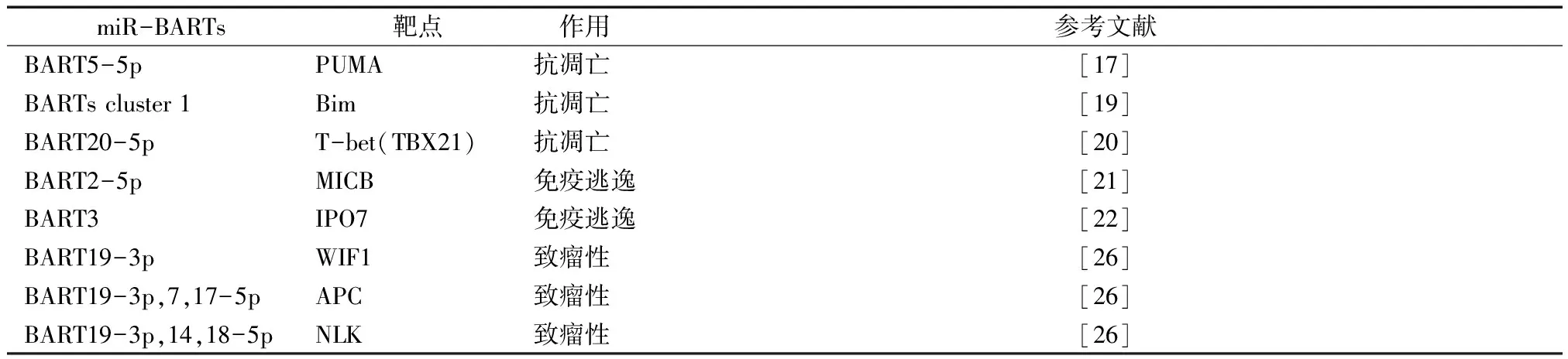

表2 miR-BARTs调节宿主细胞的靶点及作用
4 总结与展望
近些年来,随着miRNA-BARTs及其靶基因和相关信号通路的研究不断深入,miRNA-BARTs在NPC发生发展、侵袭和转移中的作用得以揭示。miRNA-BARTs能精确地调节自身的基因表达,形成有利于自身繁衍和潜伏的调节机制;通过下调宿主细胞的mRNA表达,达到有效的感染致病力。但miRNA-BARTs在NPC中的作用途径和调控机制还有待阐明。miRNA-BARTs以及它们的作用靶点与NPC的关系及其具体的调控机制有待进一步研究证实,miRNA-BARTs的研究将为NPC的预防、早期诊断和治疗提供新的靶点,为广大NPC患者带来福音。
[1] Xu Z J,Zheng R S,Zhang S W,et al.Nasopharyngeal carcinoma incidence and mortality in China in 2009[J].Chin J Cancer,2013,32(8):453-460.
[2] Pfeffer S,Zavolan M,Grasser F A,et al.Identification of virus-encoded microRNAs[J].Science,2004,304(5671):734-736.
[3] Lo A K,Dawson C W,Jin D Y,et al.The pathological roles of BART miRNAs in nasopharyngeal carcinoma[J].J Pathol,2012,227(4):392-403.
[4] 冯海燕,黄光武.EB病毒与鼻咽癌发生发展关系的研究进展[J].中华肿瘤防治杂志,2008,15(22):1753-1755.
[5] Tang Y L,Lu J H,Cao L,et al.Genetic variations of EBV LMP1 from nasopharyngeal carcinoma biopsies:potential loss of T cell epitopes[J].Braz J Med Biol Res,2008,41(2):110-116.
[6] Dai R,Ahmed S A.MicroRNA:a new paradigm for understanding immunoregulation,inflammation,and autoimmune disease[J].Transl Res,2011,157(4):163-179.
[7] Rigoutsos I.New tricks for animal microRNAS:targeting of amino acid coding regions at conserved and nonconservedsites[J].Cancer Res,2009,69(8):3245-3248.
[8] Yoshizaki T,Kondo S,Wakisaka N,et al.Pathogenic role of Epstein-Barr virus latent membrane protein-1 in the development of nasopharyngeal carcinoma[J].Cancer Lett,2013,337(1):1-7.
[9] Riley K J,Rabinowitz G S,Yario T A,et al.EBV and human microRNAs co-target oncogenic and apoptotic viral and human genes during latency[J].EMBO J,2012,31(9):2207-2221.
[10] Barth S,Pfuhl T,Mamiani A,et al.Epstein-Barr virus-encoded microRNA miR-BART2 down-regulates the viral DNA polymerase BALF5[J].Nucleic Acids Res,2008,36(2):666-675.
[11] Lung R W,Tong J H,Sung Y,et al.Modulation of LMP2A expression by a newly identified Epstein-Barr Virus-Encoded MicroRNA miR-BART22[J].Neoplasia,2009,11(11):1174-1184.
[12] Xu Y,Shi Y,Yuan Q,et al.Epstein-Barr Virus encoded LMP1 regulates cyclin D1 promoter activity by nuclear EGFR and STAT3 in CNE1 cells[J].J Exp Clin Cancer Res,2013,32:90.
[13] Zhao Y,Pang T Y,Wang Y,et al.LMP1 stimulates the transcription of eIF4E to promote the proliferation,migration and invasion of human nasopharyngeal carcinoma[J].FEBS J,2014,281(13):3004-3018.
[14] Mao Y,Zhang D W,Zhu H,et al.LMP1 and LMP2A are potential prognostic markers of extranodal NK/T-cell lymphoma,nasal type(ENKTL)[J].Diagn Pathol,2012,7:178.
[15] Ramakrishnan R,Donahue H,Garcia D,et al.Epstein-Barr virus BART9 miRNA modulates LMP1 levels and affects growth rate of nasal NK T cell lymphomas[J].PLoS One,2011,6(11):e27271.
[16] Choy E Y,Siu K L,Kok K H,et al.An Epstein-Barr virus-encoded miroRNA targets PUMA to promote host cell survival[J].J Exp Med,2008,205(11):2551-2560.
[17] Cazanave S C,Wang X,Zhou H,et al.Degradation of Keap1 activates BH3-only proteins Bim and PUMA during hepatocyte lipoapoptosis[J].Cell Death Differ,2014,21(8):1303-1312.
[18] Marquitz A R,Mathur A,Nam C S,et al.The Epstein-Barr virus BART microRNAs target the pro-apoptotic protein Bim[J].Virology,2011,412(2):392-400.
[19] Lin T C,Liu T Y,Hsu S M,et al.Epstein-Barr virus-encoded miR-BART20-5p inhibits T-bet translation with secondary suppression of p53 in invasive nasal NK/T-cell lymphoma[J].Am J Pathol,2013,182(5):1865-1875.
[20] Nachmani D,Stern Ginossar N,Sarid R A.Diverse herpesvirus MicroRNAs target the stress-induced immune ligand MICB to escape recognition by natural killer cells[J].Cell Host Microbe,2009,5(4):376-385.
[21] Dölken L,Malterer G,Erhard F,et al.Systematic analysis of viral and cellular microRNA targets in cells latently infected with human gamma-herpesviruses by RISC immunoprecipitationassay[J].Cell Host Microbe,2010,7(4):324-334.
[22] Vereide D T,Seto E,Chiu Y F,et al.Epstein-Barr virus maintains lymphomas via its miRNAs[J].Oncogene,2014,33(10):1258-1264.
[23] Yang I V,Wade C M,Kang H M,et al.Identification of novel genes that mediate innate immunity using inbred mice[J].Genetics,2009,183(4):1535-1544.
[24] Wong A M,Kong K L,Tsang J W,et al.Profiling of Epstein-Barr virus-encoded microRNAs in nasopharyngeal carcinoma reveals potential biomarkers and oncomirs[J].Cancer,2012,118(3):698-710.
[25] Lei T,Yuen K S,Xu R,et al.Targeting of DICE1 tumor suppressor by Epstein-Barr virus-encoded miR-BART3* microRNA in nasopharyngeal carcinoma[J].Int J Cancer,2013,133(1):79-87.
[26] Iizasa H,Wulff B E,Alla N R,et al.Editing of Epstein-Barr virus-encoded BART6 microRNAs controls their dicer targeting and consequently affects viral latency[J].J Biol Chem,2010,285(43):33358-33370.
(责任编辑:钟荣梅)
Research Progress in miR-BARTs in Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma
PAN Lin-jianga,YE Zhi-huab,HUANG Su-ninga,CHEN Gangb
(a.DepartmentofRadiotherapy; b.DepartmentofPathology,theFirstAffiliatedHospitalofGuangxiMedicalUniversity,Nanning530021,China)
MicroRNAs(miRNAs) are a class of endogenous small non-coding single-stranded 18-24 nucleotide RNAs that play important roles in gene regulation.It has been reported that miRNAs play a vital role in the occurrence,development,diagnosis and prognosis of nasopharyngeal carcinoma(NPC).BamH1-A rightward transcripts(BARTs),including 22 viral miRNAs,are located in long alternative spliced Epstein-Barr virus(EBV) transcripts and expressed in EBV-associated malignant tumors.It is of great clinical significance to illuminate the mechanism of action of miR-BARTs in NPC.
nasopharyngeal carcinoma; BamH1 A; rightward transcript; EB virus; gene regulation
2014-10-10
潘林江(1966—),男,学士,副教授,主要从事肿瘤放疗的基础及临床研究。
陈罡,教授,E-mail:chen_gang_triones@163.com。
R739.63
A
1009-8194(2015)05-0096-03
10.13764/j.cnki.lcsy.2015.05.037