胶北地体早前寒武纪重大岩浆事件、陆壳增生及演化*
刘建辉 刘福来 丁正江 刘平华 王舫
LIU JianHui1,LIU FuLai1,DING ZhengJiang2,LIU PingHua1 and WANG Fang1
1. 中国地质科学院地质研究所,北京 100037
2. 山东省第三地质矿产勘查院,烟台 264000
1. Institute of Geology,Chinese Academy of Geological Sciences,Beijing 100037,China
2. Exploration Institute of Geology and Mineral Resources,Yantai 264000,China
2015-02-06 收稿,2015-05-13 改回.
1 引言
大陆地壳的起源及增生机制是早前寒武纪地质研究的重要科学课题之一。位于华北克拉通东南缘的胶北地体(图1a),是华北克拉通早前寒武纪古老地体的典型代表,涉及到太古宙陆壳的增生机制及形成过程,以及古元古代胶-辽-吉带的构造演化等早前寒武纪重要科学问题,成为华北克拉通早前寒武纪地学研究的热点地区。花岗质岩类作为早前寒武纪地壳最主要的岩石组成,是记录地壳增生及构造演化最主要的物质载体,通过对其形成时代、成因及其可能经历的构造-变质热事件的研究,能为我们正确理解早期陆壳的增生机制及构造演化提供重要的依据。研究显示,大陆地壳的增生主要发生在太古宙(Taylor and McLennan,1995;Hawkesworth and Kemp,2006a,b;Rollinson,2007;Cawood et al.,2013),而富钠质的TTGs(英云闪长岩-奥长花岗岩-花岗闪长岩)组合是现今太古宙陆壳最主要的组成物质(Barker,1979;Jahn et al.,1981;Martin et al.,2005),代表着太古宙陆壳的增生,其成因研究是揭示和理解太古宙陆壳增生与演化的关键(Taylor and McLennan,1997;Condie,2005)。TTGs形成于含水玄武质岩石在石榴角闪岩相或榴辉岩相的部分熔融已被地球化学及实验岩石学研究所证实(Barker,1979;Condie,1986;Martin,1987,1999;Rapp et al.,1991,2003;Rapp and Watson,1995;Rollinson,1997;Foley et al.,2002;Xiong,2006);然而,有关TTGs 形成的构造背景一直存在板块和非板块模式之争,存在多种不同的构造成因模式(Martin,1999;Smithies,2000;Smithies and Champion,2000;Foley et al.,2002;Martin et al.,2005;Condie,2005;Hawkesworth et al.,2010;Adam et al.,2012)。已有的调查研究显示,胶北地体内主要存在中太古宙~2.9Ga、新太古宙~2.7Ga 及~2.5Ga 多期TTGs,以及古元古代构造前ca.2.2~2.0Ga 及构造后~1.8Ga 等多期早前寒武纪花岗质岩浆事件。最近的研究显示,古元古代多期花岗质岩石主要形成于板块内部太古宙陆壳的重熔(Liu et al.,2014a)。与全球其它主要太古宙陆壳一样,TTGs 是胶北太古宙陆壳最主要的组成物质,对于其成因模式,存在俯冲洋壳的部分熔融(Jahn et al.,2008)或加厚下地壳的部分熔融(Wu et al.,2014a;Xie et al.,2014)两种解释。因此,如何理解胶北不同期次TTGs 的形成过程,对于正确理解胶北太古宙陆壳的形成机制具有重要的意义。
最近几年,针对胶北地体内早前寒武纪重要岩浆事件的代表性岩石组合开展了大量的同位素年代学、岩石地球化学、Nd 同位素及锆石Hf 同位素特征的分析研究(Tang et al.,2007;Jahn et al.,2008;Zhou et al.,2008a;刘建辉等,2011,2012,2014;刘平华等,2013;Liu et al.,2013a,b,c,2014a,b;Wang et al.,2014;Wu et al.,2014a,b;Xie et al.,2014;Zhang et al.,2014;Shan et al.,2015),厘定出胶北地体内以TTGs 片麻岩为代表的多期早前寒武纪重大岩浆事件,晚太古代(~2.5Ga)及古元古代(~1.86Ga)的两期变质事件,以及太古宙地壳增生及再造过程,并可能存在古老(>3.55Ga)陆壳物质的再循环(Liu et al.,2014a)等重要研究进展。本文拟通过总结前人的这些研究成果,旨在使该区早前寒武纪重大岩浆事件的性质,陆壳增生机制及演化获得更好的理解。
2 地质背景
胶北地体是指位于郯庐断裂以东,五莲-烟台断裂以北的地区,在大地构造上位于华北克拉通的东缘,胶-辽-吉构造带的西南端,紧邻苏鲁超高压带(图1a)。该地体主要由太古宙花岗质(TTG)片麻岩、变质基性-超基性岩及表壳岩,古元古代花岗岩类及变质基性岩,古元古代高级变质的粉子山群及荆山群,低级变质的芝罘群,以及新元古代低级变质的蓬莱群等寒武纪变质-变形基底,中生代花岗岩类及中-新生代沉积地层组成(图1b)(山东省地质矿产局,1991;卢良兆等,1996;唐俊等,2004;周喜文等,2004;Jahn et al.,2008;Zhou et al.,2008a,b;李旭平等,2001;Liu et al.,2013a,b,c)。
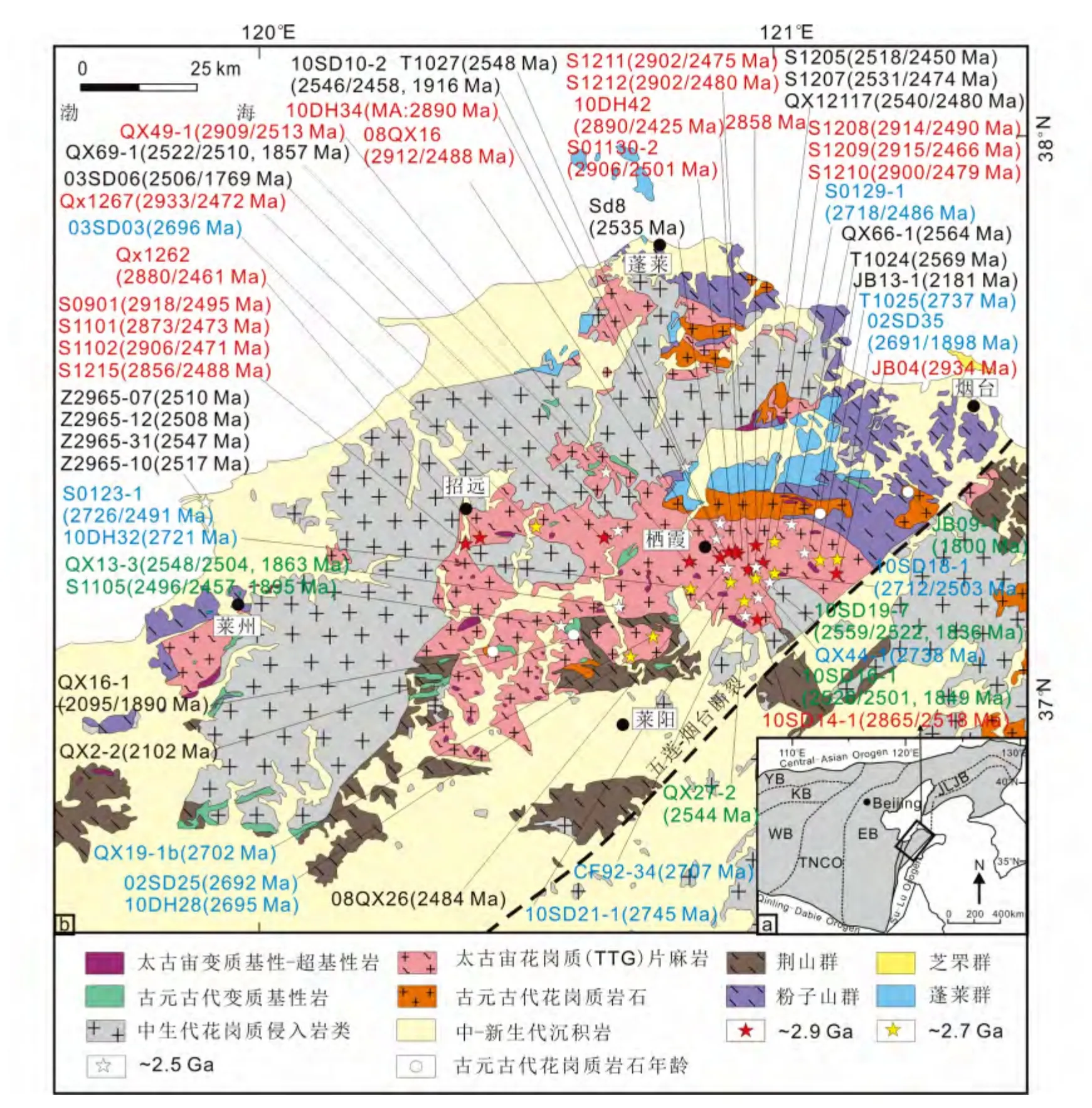
图1 华北克拉通构造单元划分(a,据Zhao et al.,2005 修改)及胶北地区地质简图(据山东省地质矿产局,1991;Zhou et al.,2008a,Liu et al.,2013a 修改)与锆石U-Pb 年龄的样品分布(b)YB-阴山地块;KB-孔兹岩带;WB-西部块体;TNCO-中部造山带;EB-东部块体;JLJB-胶-辽-吉带. 年龄据Tang et al. ,2007;Jahn et al. ,2008;Zhou et al. ,2008a;刘建辉等,2011;刘平华等,2013;Liu et al. ,2013a,2014a;Wang et al. ,2014;Wu et al. ,2014b;Xie et al. ,2014;Shan et al. ,2015,以及作者未发表数据Fig.1 Tectonic subdivisions of the North China Craton (a,modified after Zhao et al.,2005),simplified geological map of the Jiaobei Terrane (modified after BGMRS,1991;Zhou et al.,2008a;Liu et al.,2013a)and distribution of the samples with zircon U-Pb ages (b)YB-Yinshan Block;KB-Khondalite Belt;WB-Western Block;TNCO-Trans-North China Orogen;EB-Eastern Block;JLJB-Jiao-Liao-Ji Belt. Ages after Tang et al.,2007;Jahn et al.,2008;Zhou et al.,2008a;Liu et al. ,2011;Liu et al. ,2013;Liu et al. ,2013a,2014a;Wang et al. ,2014;Wu et al. ,2014b;Xie et al. ,2014;Shan et al. ,2015,and unpublished data
太古宙花岗质(TTG)片麻岩在栖霞附近呈穹窿状大面积出露,主要包括~2.9Ga、~2.7Ga 及~2.5Ga 三期岩浆事件,它们主要源自3.4 ~2.7Ga 新生地壳的重熔或再造,并伴有少量老地壳的加入(Liu et al.,2013a;Wang et al.,2014;Wu et al.,2014b;Xie et al.,2014;Shan et al.,2015),并经历了~1.86Ga 和~2.5Ga 两期变质热事件(Jahn et al.,2008;Zhou et al.,2008a;刘建辉等,2011;Liu et al.,2013a);这些片麻岩普遍遭受强烈剪切变形作用,定向构造发育,常形成条纹和条带状构造,内部流柔褶皱发育(刘建辉等,2011)。在TTG 片麻岩内部,斜长角闪片麻岩、黑云母变粒岩、黑云斜长片麻岩及变质基性-超基性岩呈大小不等的透镜体或不规则脉状体产出,同样显示遭受强烈剪切变形,深熔混合岩化作用强烈(刘建辉等,2011;刘平华等,2011a,b,2012)。古元古代花岗岩类出露面积较小,呈零星分布,根据其侵位时间及变形作用,可划分为构造前变形花岗质片麻岩类及构造后末变形的花岗岩类,它们可与辽-吉地区的古元古代花岗岩类对比,源自板内陆壳物质的重熔(Liu et al.,2014a)。胶北地体内古元古代孔兹岩系(包括粉子山群、荆山群)不整合于TTG 片麻岩之上,其具有3.34 ~2.20Ga 的碎屑锆石U-Pb 年龄(Wan et al.,2006)。这些组成胶北地体早前寒武纪变质基底的岩石,经历了高角闪岩相-麻粒岩相变质作用,具有顺时针P-T 演化路径(刘文军等,1998;周喜文等,2004;刘平华等,2010,2013;王舫等,2010;Tam et al.,2011,2012a,b,c;Liu et al.,2013c,2015),并伴随普遍的深熔作用(Liu et al.,2014b)。变质锆石U-Pb 年代学研究表明,其变质作用的时间约为1.95 ~1.85Ga(Zhou et al.,2008b;Tam et al.,2011,2012a,b;刘福来等,2012;Liu et al.,2013c),其中高压麻粒岩相峰期变质时间约在1.90 ~1.85Ga 之间(刘平华等,2011a,b;Liu et al.,2013c)。芝罘群主要分布在芝罘岛,碎屑锆石U-Pb 年代学分析结果显示其沉积时代应晚于约1.8Ga(Liu et al.,2013b)。新元古代蓬莱群是一套绿片岩相-低角闪岩相的浅变质岩系(山东地质矿产局,1991;Zhou et al.,2008a),目前,对于其形成的构造背景、沉积时间及属性仍有争议(Li et al.,2007;Zhou et al.,2008a;初航等,2011)。
3 太古宙-古元古代重要岩浆事件
3.1 中太古宙岩浆事件
TTGs 片麻岩是胶北地体内现今揭露的最主要的中太古宙岩石,代表胶北地体中太古宙重要的岩浆活动及陆壳增生作用。这些TTGs 片麻岩主要呈灰色条带状或片麻状构造产出,变形作用及变质深熔作用明显(图2a),内部常分布有透镜体状或不规则基性残留体(图2b)。它们在野外产出特征及矿物成分上与晚太古宙侵入的TTG 片麻岩相似,在野外很难区分出不同期次形成的TTGs 片麻岩。最近,随着锆石SHRIMP 及LA-ICP-MS U-Pb 测年在胶北地体内的不断开展,大量的中太古宙TTGs 片麻岩被揭露(图1b),它们的岩浆锆石年龄较为统一,主要集在~2.9Ga(John et al.,2008;Liu et al.,2013a;Wang et al.,2014;Wu et al.,2014b;Xie et al.,2014 及未发表数据,表1),指示胶北地体在中太古宙(~2.9Ga)显著的岩浆活动及陆壳增生作用。而且这些中太古宙TTGs 片麻岩普遍记录了~2.5Ga 的变质作用(表1)。
3.2 新太古宙岩浆事件
胶北地体内除了出露有大量中太古宙TTGs 片麻岩外,还分布有大面积的以TTGs 片麻岩为代表的新太古宙花岗质片麻岩。这些花岗质片麻岩在侵位时代上可以划分为新太古宙早期及新太古宙末两期。其中新太古宙早期主要包括花岗闪长质片麻岩(图2c)、英云闪长质片麻岩及少量二长(钾长)花岗质片麻岩,这些岩石变质变形及深熔作用明显,局部有后期钾质花岗岩的注入(图2d)。锆石U-Pb 测年显示,它们的岩浆锆石U-Pb 年龄较为统一,分布在2691 ~2745Ma 之间(Faure et al.,2003;Tang et al.,2007;Jahn et al.,2008;Liu et al.,2013a;Wu et al.,2014b;表1),指示新太古宙早期约~2.7Ga 陆壳形成事件,同时伴有部分早期陆壳的重熔,形成少量的二长花岗质片麻岩。
新太古宙末除了TTGs 片麻岩以外(图2e),还包括花岗岩及条带状二长花岗片麻岩(图2f,g)。这些岩石同样普遍遭受了强烈的变质深熔作用及变形作用,常形成条纹和条带状构造,内部流柔褶皱发育(图2e,g)。这些晚太古宙花岗质片麻岩内部常产出有与强变形方向平行、断续分布的基性麻粒岩透镜体、脉体或岩墙(图2e,f)。这些基性麻粒岩的原岩时代约为~2.5Ga(Liu et al.,2013c),与新太古宙末花岗质片麻岩的侵位时代大致相当。大量的锆石U-Pb 测年结果显示,它们的岩浆锆石U-Pb 年龄统一分布在2500 ~2569Ma 之间(Faure et al.,2003;Jahn et al.,2008;Zhou et al.,2008a;Liu et al.,2013a;Wang et al.,2014;Wu et al.,2014b;Shan et al.,2015;表1),指示新太古宙末约~2.5Ga的花岗质岩浆事件,并伴随有准同期的变质作用。
3.3 古元古代岩浆事件
古元古代花岗质岩石在胶北地体内零星出露,分布面积不大(图1b)。结合胶北约19.5 ~18.5Ga 古元古代碰撞构造事件(Tam et al.,2011,2012a,b;Liu et al.,2013c),以及这些花岗质岩石野外地质产出特征及岩相学特征,被划分为碰撞构造事件前形成的经历了变质变形作用的构造前花岗质片麻岩及碰撞构造事件后没经历变质变形的构造后花岗岩(Liu et al.,2014a)。主要岩性包括变形的含角闪石/黑云母二长花岗质片麻岩(图2h,i)及未变形的含黑云母正长(二长)花岗岩(图2j),在岩性上具有A 型花岗岩的特征。变形的古元古代花岗质片麻岩在TTGs 片麻岩中呈侵入岩体产出,内部分布有古元古代超基性岩脉,与古元古代变质地层粉子山群及荆山群呈不整合接触(Liu et al.,2014a)。它们侵入的时间在ca.2.2 ~2.0Ga 之间,并记录了古元古代~1.86Ga 变质作用(刘建辉等,2011;Liu et al.,2014a)。代表胶北地体内发生在古元古代ca.1.95 ~1.85Ga 碰撞构造事件之前ca.2.2 ~2.0Ga 的陆内花岗质岩浆活动(Liu et al.,2014a)。未变形的古元古代黑云母正长花岗岩与古元古代变质地层荆山群及粉子山群呈侵入关系(Liu et al.,2014a)。最近的研究显示,它们发生岩浆侵位的时间为~1.8Ga,代表胶北地体内古元古代碰撞构造事件后~1.8Ga 陆内花岗质岩浆活动(Liu et al.,2014a)。
4 太古宙花岗质岩石地球化学特征
本文总结了胶北具有精确锆石U-Pb 年龄的太古宙不同期次TTGs 片麻岩及花岗片麻岩的地球化学数据,旨在查明胶北太古宙不同期次TTGs 片麻岩及花岗片麻岩的岩石地球化学、微量元素地球化学特征。本文讨论的地球化学数据来自Tang et al.,2007;Jahn et al.,2008;Wu et al.,2014a;Xie et al.,2014;以及作者未发表数据。
4.1 主量元素地球化学特征

图2 胶北地体太古宙-古元古代花岗质岩石野外照片Fig.2 Photographs of Archean-Paleoproterozoic granitoid rocks
胶北不同期次太古宙花岗质岩石的主量元素如图3 所示,SiO2含量在60.67% ~77.49% 之间,Al2O3含量在11.66% ~17.19%之间,FeOT含量在0.70% ~6.74%之间,MgO 在0.13% ~2.5%之间,CaO 在0.54% ~6.29%之间,Na2O 在1.68% ~6.95%之间,K2O 在0.49% ~5.15%之间,以及较低的TiO2和P2O5含量,分别在0.02% ~0.86%和0.01% ~0.19% 之间。除了Na2O 与SiO2无明显相关性,K2O 与SiO2具有弱的正相关外,而其它主量元素含量与SiO2表现为明显的负相关(图3)。在An-Ab-Or 三角分类图解上(图4a),大部分样品落在英云闪长岩、花岗闪长岩及奥长花岗岩区,它们绝大部分具有高的Al2O3含量(>15%),属高铝型TTG 岩石(Barker and Arth,1976;Martin et al.,2005),在SiO2-K2O 协变图解上(图3,Rickwood,1989),落在中钾或低钾区,Na2O/K2O 比值大于1(图4b)。少量~2.5Ga样品落在花岗岩区(图4a),具有较低的Al2O3含量(图3)及
较高的K2O 含量,Na2O/K2O 比值小于1(图4b),落在高钾钙碱性系列区。此外,这些岩石的Mg#指数在13 ~52 之间,除了6 个~2.5Ga 花岗岩样品及2 个~2.9Ga 高硅奥长花岗岩样品具有极低的Mg#指数外(图4c),其它样品均与全球典型太古宙TTGs 样品的Mg#指数一致(Condie,2005;Martin et al.,2005)。并与SiO2含量显示出弱的负相关性(图4c)。
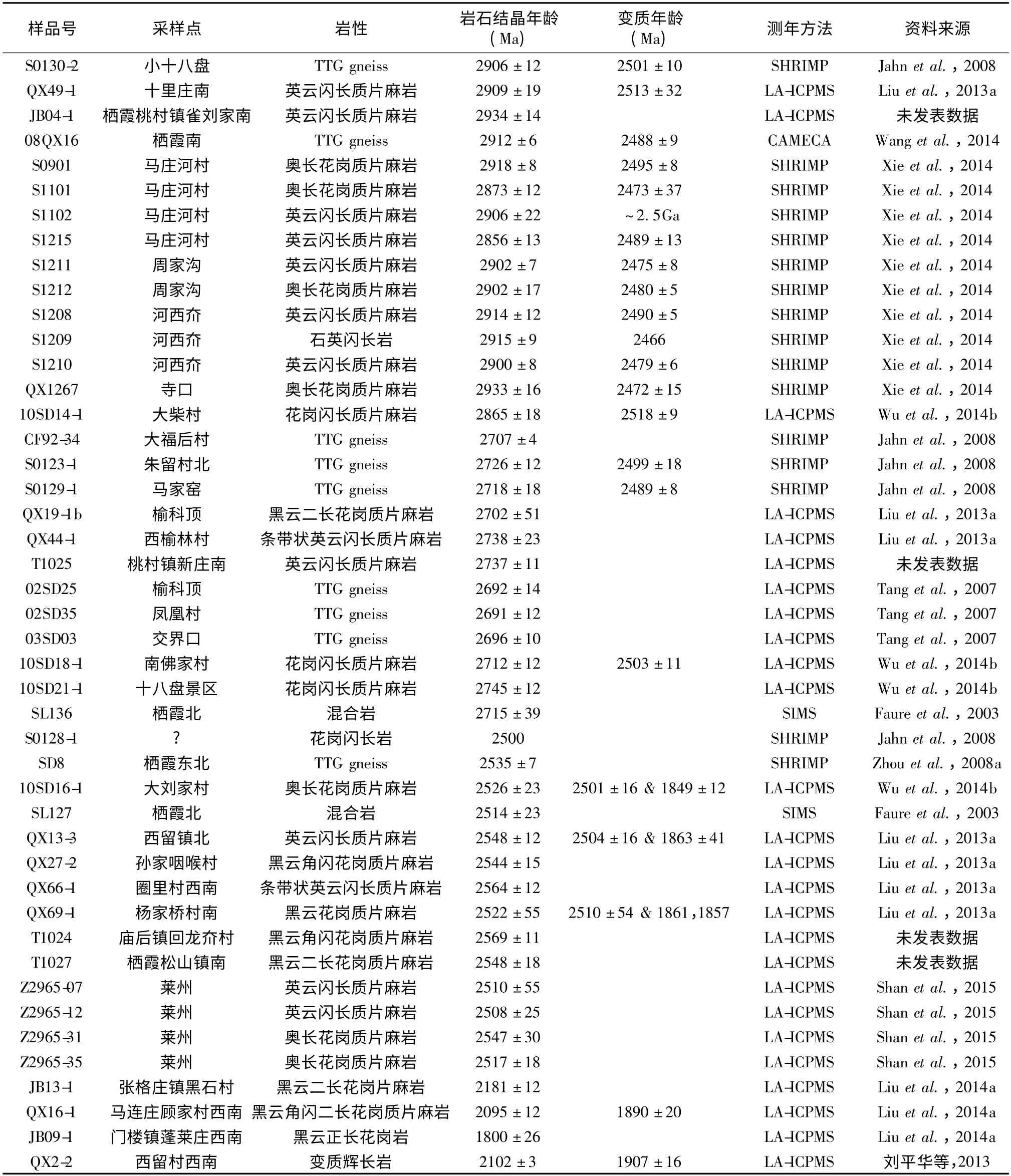
表1 胶北早前寒武纪主要岩浆事件代表性岩石样品的锆石U-Pb 年龄统计表Table 1 Summary of zircon U-Pb ages of representative samples of the Early precambrian major magmatic events in the Jiaobei terrane
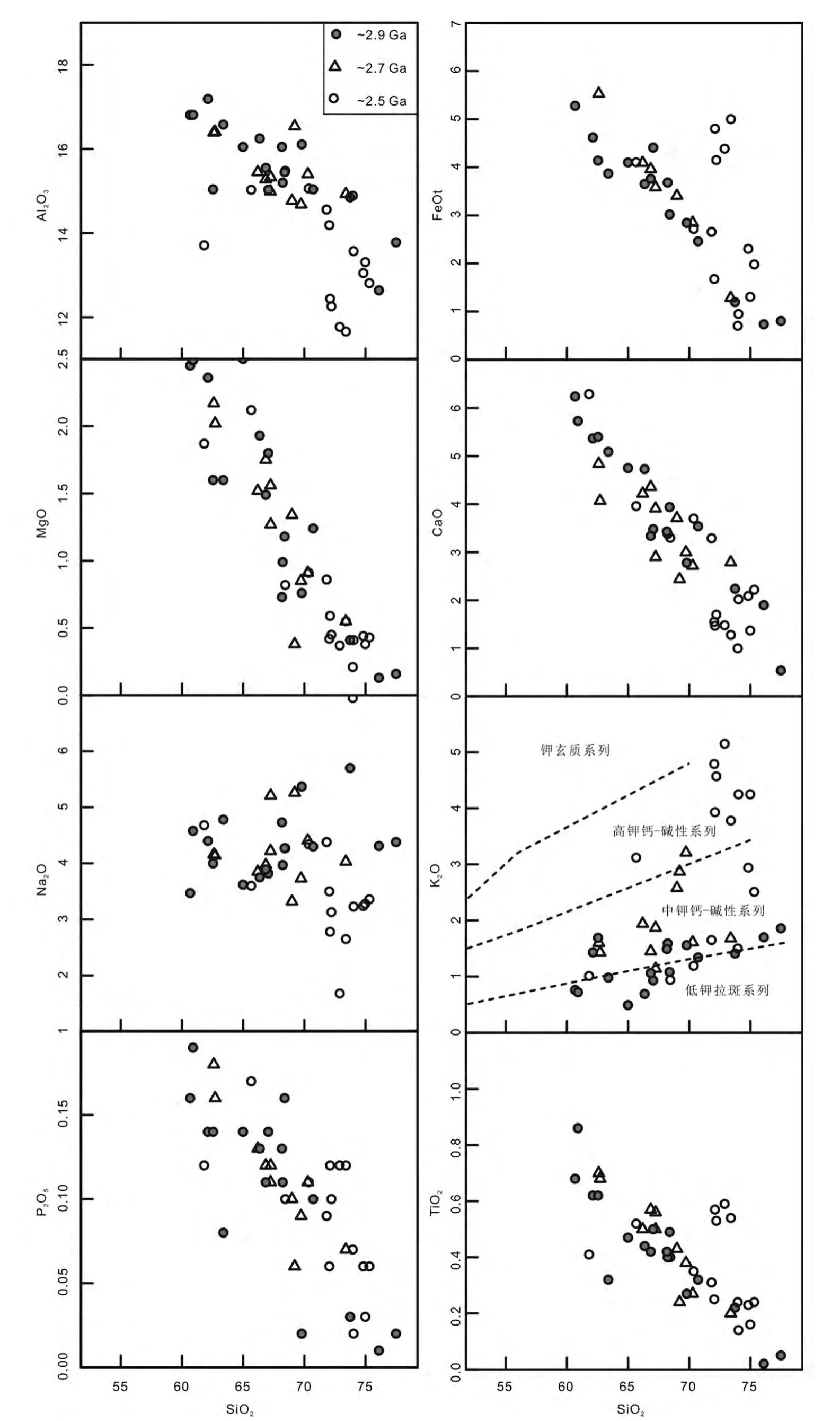
图3 胶北地体太古宙花岗质岩类选择的主量元素Harker 变量图解Fig.3 Harker compositional variation diagrams showing selected major elements variations for Archean granitoid gneisses from the Jiaobei terrane

图4 胶北地体太古宙花岗质岩类的An-Ab-Or 三角分类图解(a,底图据Barker,1979)、SiO2-Na2O/K2O 图(b)和SiO2-Mg#图(c)Fig.4 Feldspar An-Ab-Or classification diagram (a,after Barker,1979),SiO2-Na2O/K2O diagram (b)and SiO2-Mg# diagram(c)

图5 胶北太古宙花岗质岩石地球化学分类图(底图据Frost et al.,2001)Fig.5 Geochemical classification diagrams of Archean granitoid rocks from the Jiaobei terrane (after Frost et al.,2001)
在SiO2-FeOT/(FeOT+MgO)分类图上,除几个~2.5Ga花岗质岩石样品外,均分布在镁质系列区域(图5a)。在SiO2-(K2O +Na2O-CaO)分类图上,所有样品均落在钙性到钙-碱性系列区域(图5b)。在A/CNK-A/NK 图解上,胶北太古宙花岗质岩石的铝饱和指数A/CNK 主要集中在0.9 ~1.1之间,主要分布在偏铝质至弱过铝质区域(图5c)。
4.2 微量元素地球化学特征
胶北地体太古宙不同期次的花岗质岩石的稀土及微量元素配分曲线如图6 所示。在稀土元素球粒陨石标准化配分曲线图上(图6a,c,e),所有样品轻重稀土元素分馏明显,配分曲线均表现为明显的右倾型模式,轻稀土富集,重稀土亏损。数据统计显示,(La/Yb)N比值变化大,在3.42 ~108.4 范围内变化。太古宙~2.9Ga、~2.7Ga 及~2.5Ga TTG 片麻岩无明显铕异常(图6a);但晚太古宙~2.5Ga 花岗片麻岩显示出明显的弱负铕异常(图6c,e)。
在原始地幔标准化微量元素蛛网图上(图6b,d,f),大部分TTG 片麻岩富集Ba、K、Rb 及Sr 等大离子亲石元素,亏陨Nb、Ta 及Ti 等高场强元素(图6b,d,f)。数据统计显示,除了2 个~2.9Ga 高硅奥长花岗岩样品具有较低的Sr 含量外,其它大部分太古宙TTG 片麻岩具有较高的Sr 含量,在209 ×10-6~604 ×10-6之间(图7a),此外,~2.5Ga 花岗片麻岩具有较低的Sr 含量(图7a),在微量元素蛛网图上显示明显的Sr 亏陨(图6f)。Y 含量在0.56 ×10-6~45.9 ×10-6之间,其中太古宙TTG 片麻岩Y 含量相对较低,~2.5Ga 花岗片麻岩Y 含量相对较高(图7b),Sr/Y 比值变化范围大,在2.20 ~511 之间。太古宙TTG 片麻岩及花岗片麻岩均具有较低的Cr 及Ni 含量,分别在1.93×10-6~83.8×10-6及0.72×10-6~45×10-6之间(图7c,d)。太古宙TTG 片麻岩的Sr、Y、Cr 及Ni 含量与SiO2含量显示弱的负相关性(图7)。
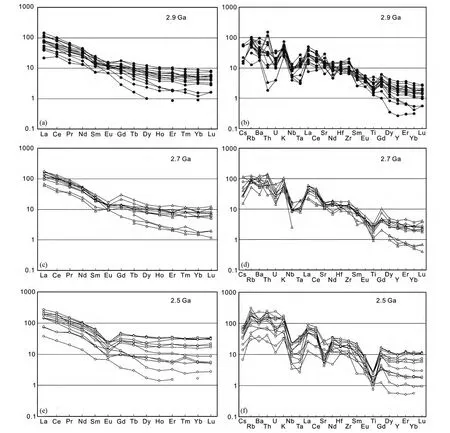
图6 胶北地体太古宙不同期次花岗质岩石球粒陨石标准化稀土模式图(a、c、e)及原始地幔标准化微量元素蛛网图(b、d、f)(标准化值据Sun and McDonough,1989)Fig.6 Chondrite-normalized REE patterns (a,c,e)and primitive mantle-normalized trace element spider diagrams (b,d,f)for Archean granitoid rocks from Jiaobei terrane (normalization values after Sun and McDonough,1989)
5 锆石Hf 同位素特征
锆石Hf 同位素被证明是一种示踪岩浆源区、岩石成因及约束地壳演化极佳的方法(Kinny and Maas,2003;吴福元等,2007)。为了能够更好的理解胶北早前寒武纪重要岩浆事件的性质、地壳增生及演化过程,本文对胶北地体早前寒武纪不同期次的TTG 片麻岩及花岗质片麻岩的锆石Hf 同位素开展了系统的统计,统计数据主要来自Liu et al.,2013a,2014a;Wang et al.,2014;Wu et al.,2014b;Xie et al.,2014;Zhang et al.,2014 及作者未发表数据。
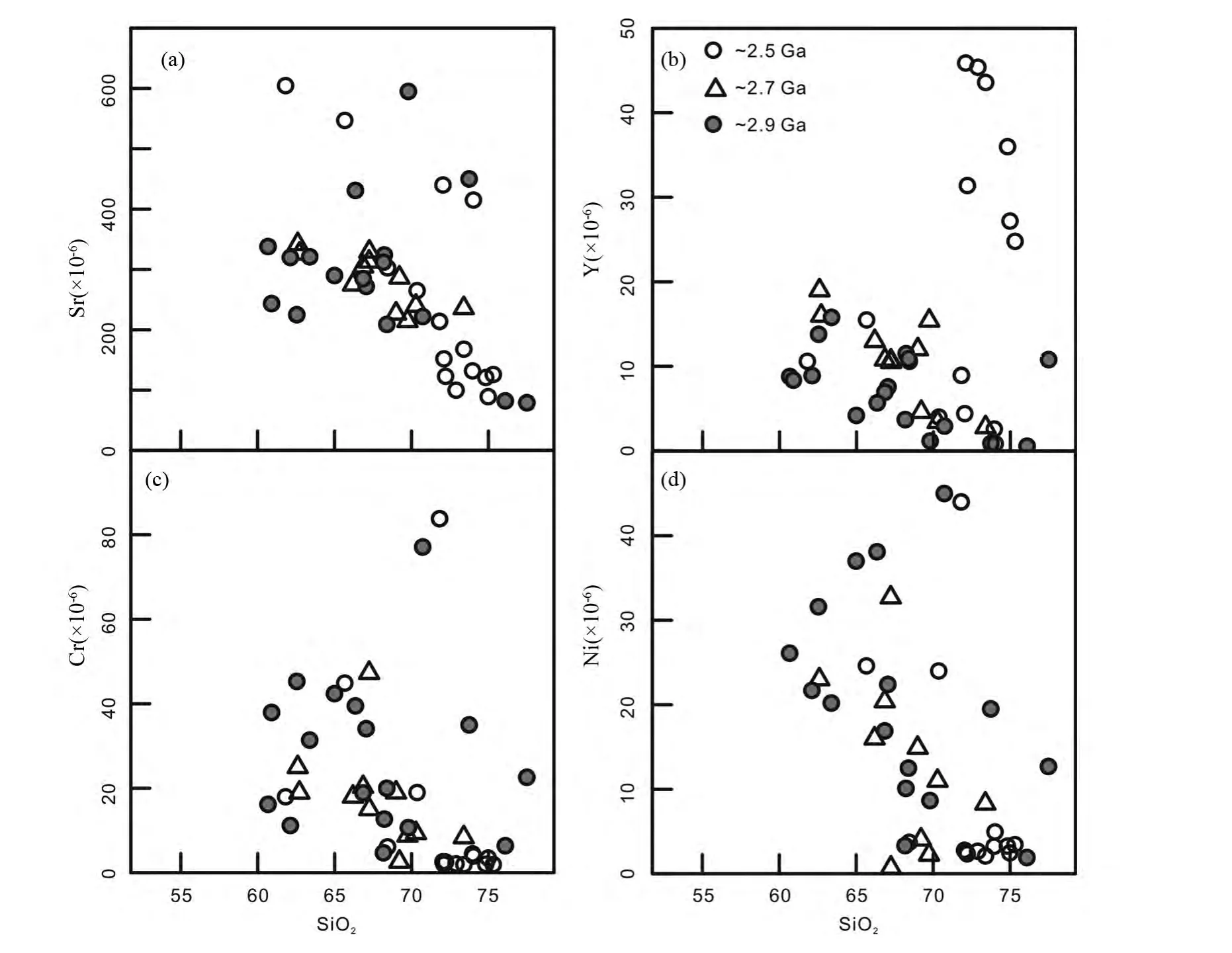
图7 胶北太古宙花岗质岩石选择性微量元素Harker 成分变化图解Fig.7 Harker compositional variation diagrams showing selected trace elements Sr,Y,Cr and Ni variations for the Archean granitoids from the Jiaobei terrane
胶北太古宙不同期次花岗质岩石及古元古代不同期次花岗质岩石的锆石Hf 同位素数据统计结果如图8 所示。来自165 个~2.9GaTTG 片麻岩锆石Hf 同位素分析数据显示,除了两个分析锆石的εHf(t)为负值外,其余所有锆石具有正的εHf(t)值(图8a),两阶段Hf 模式年龄主要分布在ca.3.3~2.9Ga 之间(图8b)。247 个~2.7Ga TTG 片麻岩或花岗片麻岩锆石Hf 同位素分析数据显示,绝大部分具有正的εHf(t)值(图8c),两阶段Hf 模式年龄跟~2.9Ga TTG 片麻岩类似,主要分布3.3 ~2.9Ga 之间,少量具有弱的负εHf(t)值和更老的模式年龄(图8c,d)。326 个~2.5Ga TTG 片麻岩或花岗片麻岩锆石Hf 同位素分析数据显示,大部分锆石具有正的εHf(t)值,两阶段Hf 模式年龄主要分布在ca.2.9~2.7Ga 之间,少部分锆石具有负的εHf(t)值,以及更老的两阶段Hf 模式年龄(图8e,f)。而相对有限数量的古元古代花岗质岩石的锆石Hf 同位素分析数据显示,它们大部分具有负的εHf(t)值,少量具有正的εHf(t)值,两阶段Hf 模式年龄分布较广,主要分布在ca.3.2 ~2.3Ga 之间(图8g,h)。
6 讨论及结论
6.1 岩石成因
6.1.1 太古宙TTG 片麻岩及花岗片麻岩
实验岩石学及地球化学研究表明,TTGs 形成于含水玄武质岩石在石榴角闪岩相或榴辉岩相的部分熔融(Barker,1979;Condie,1986;Martin,1987,1999;Rapp et al.,1991,2003;Rapp and Watson,1995;Rollinson,1997;Foley et al.,2002;Xiong,2006)。但对于TTGs 形成的构造环境却存在多种不同的模式,主要存在三种构造模式:(1)加厚下地壳或大洋高原地壳的部分熔融(Smithies,2000;Smithies and Champion,2002;Condie,2005);(2)俯冲洋壳(板片)的部分熔融(Martin,1999;Martin et al.,2005;Foley et al.,2002;Rapp et al.,2003);(3)加厚大洋弧地壳的部分熔融(Hawkesworth et al.,2010;Adam et al.,2012;Polat,2012)。
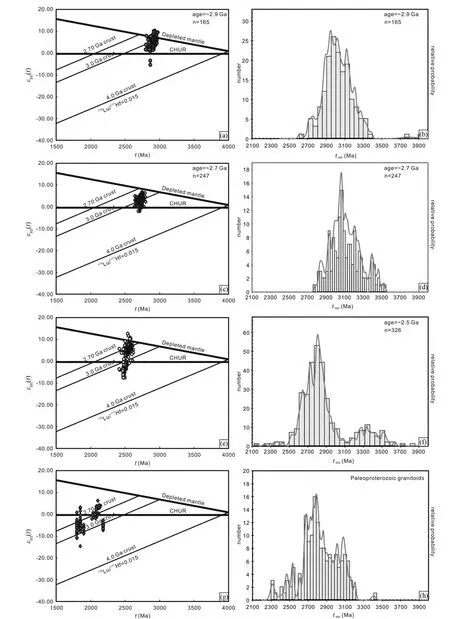
图8 胶北地体太古宙及古元古代花岗质岩石锆石Hf 同位素成分(a、c、e、g)锆石U-Pb 年龄对εHf(t)值及变化;(b、d、f、h)锆石Hf 模式年龄直方柱状图Fig.8 Zircon Hf isotopic composition of the Archean and Paleoproterozoic granitoid rocks from the Jiaobei terrane(a,c,e,g)zircon U-Pb ages-εHf(t)variations;(b,d,f,h)histograms of the zircon Hf model ages
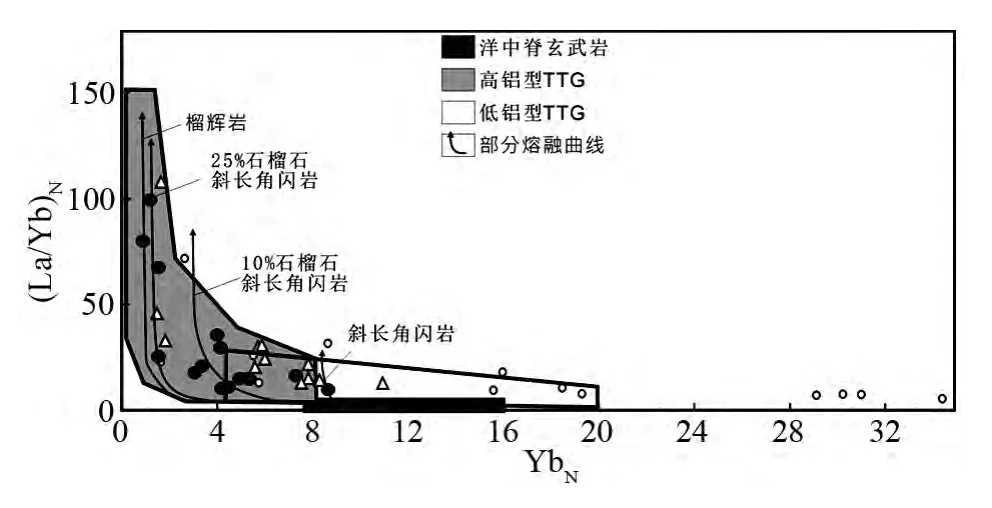
图9 胶北太古宙花岗质岩石球粒陨石标准化YbN-(La/Yb)N 图解(据Drummond and Defant,1990)Fig.9 Chondrite-normalized YbN-(La/Yb)N diagram of Archean granitoid rocks from the Jiaobei terrane (after Drummond and Defant,1990)
胶北太古宙不同期次的TTG 片麻岩主要为镁质(图5a),准铝质至弱过铝质(图5c),低钾-中钾钙碱性系列(图3、图5b),具有高的Na2O 及Al2O3含量(图3),属高铝TTGs。在稀土元素球粒陨石标准化配分曲线上,它们富集轻稀土,亏损重稀土,配分曲线均表现为明显的右倾型模式,显示强烈的轻重稀土分异,无明显的Eu 异常(图6a,c,e)。在原始地幔标准化蛛网模式图上表现为富集Ba、K、Rb 及Sr等大离子亲石元素,亏损Nb,Ta 及Ti 等高场强元素(图6b,d,f)。这些地球化学特征指示源区无斜长石的残留,石榴石及角闪石是主要的残留相。胶北TTG 岩石在球粒陨石标准化的YbN-(La/Yb)N部分熔融图解上,主要分布在石榴石-斜长角闪岩及榴辉岩为残留相的太古宙高铝TTGs 区域内(图9)。结合TTGs 成因的实验岩石学及地球化学研究,表明胶北地体太古宙TTGs 起源于基性玄武质岩石在石榴石和角闪石为主要残留相的部分熔融。尽管太古宙TTGs 与高硅埃达克质岩石在地球化学具有很大的相似性,具有弧型岩浆岩的特征(Martin,1999;Martin et al.,2005),但同时太古宙高硅TTG 岩石具有较低的Mg#指数,相对较低Sr、Cr 及Ni 含量,与埃达质岩石在地球化学上并不完全可以对比(Smithies,2000;Kamber et al.,2002;Condie,2005)。而且只要有合适的源区岩石,在合适的条件下,可以在不同的构造背景下形成具有类似地球化学特征的岩石。胶北TTG 片麻岩具有较低的Mg#指数,相对较低的Sr、Cr 及Ni 含量,这可能难以用俯冲板片交代橄榄质地幔的部分熔融的成因模式来理解(Condie,2005)。加上,胶北不同期次TTG 片麻岩相互重叠分布,并没有呈带状分布,因此,加厚地壳的部分熔融应更适合于胶北TTG 片麻岩的成因模式。
岩浆锆石的U-Pb 年龄代表岩石形成的时间,而锆石的Hf 模式年龄主要代表地壳物质从地幔出来的时间。根据胶北太古宙不同期次TTG 片麻岩的锆石Hf 同位素数据结果(图8a-f),~2.9Ga TTG 片麻岩主要源自ca.3.3 ~2.9Ga 新生地壳的重熔(再造);~2.7Ga TTG 片麻岩同~2.9Ga TTG片麻岩具有类似的源区,同样主要源自3.3 ~2.9Ga 新生地壳的重熔(再造);~2.5Ga TTG 片麻岩则具有更年轻的源区,主要源自ca.2.9 ~2.7Ga 新生地壳的重熔。结合胶北太古宙不同期次TTG 片麻岩的地球化学特征及空间分布,胶北TTG 片麻岩可能形成于加厚新生地壳的部分熔融。
胶北太古宙分布的少量花岗片麻岩,它们相对于TTG 片麻岩,具有高的K2O 含量,K2O/Na2O 大于1,属高钾系列。并具有明显的负Eu 异常,低的Sr 含量,负的εHf(t)值,以及比准同期TTG 片麻岩更老的锆石Hf 模式年龄,而且它们主要呈小岩体或岩脉产出。这些表明,它们可能是在准同期TTG 岩浆形成侵位过程导致先期存在的老陆壳的重熔而成。
6.1.2 古元古代花岗质岩石
胶北古元古代花岗质岩石主要包括变形的角闪黑云二长花岗质片麻岩和黑云二长花岗质片麻岩及未变形的黑云母正长(二长)花岗岩,前者大约形成于2.0 ~2.2Ga,后者大约形成于1.8Ga,它们在矿物成分上主要包括石英、钾长石及斜长石,以及少量的黑云母或角闪石,显示出富钾,具有A型花岗岩的特征(Liu et al.,2014a)。锆石Hf 同位素分析显示,它们大部分具有负的εHf(t)值,以及老的Hf 模式年龄,显示与胶北TTG 岩石具有相同的地壳演化趋势(Liu et al.,2014a,图8b,c),暗示它们主要源自太古宙陆壳的重熔。此外,伴随古元古代2.2 ~2.0Ga 花岗质岩浆活动,存在大量的镁铁质岩体或岩墙的侵位(刘平华等,2013),在辽-吉地区分布有大量类似的2.2 ~2.0Ga 花岗质岩,这些花岗质岩石可能代表胶-辽-吉带在2.2 ~2.0Ga 时期伸展构造背景下陆壳的重熔。而1.8Ga 花岗质岩浆活动则可能代表胶-辽-吉带在1.95 ~1.85Ga 碰撞造山作用后的伸展构造背景下的陆壳重熔。
6.2 陆壳增生及演化
显生宙大陆地壳主要通过沿俯冲带构造加积作用及新生岩浆岩的侵位而增生(Sengor et al.,1993)。然而,目前对于太古宙陆壳的增生机制仍没获得统一的认识(Foley et al.,2002;Rapp et al.,2003;Hawkesworth et al.,2010)。研究显示,太古宙是全球陆壳形成的主要时期(Taylor and McLennan, 1995; Hawkesworth and Kemp, 2006a, b;Rollinson,2007;Cawood et al.,2013),而TTGs 是现今保留的太古宙陆壳最主要的组成物质,因此,TTG 岩石的形成过程代表着陆壳的形成过程。
胶北地体主要存在~2.9Ga、2.7Ga 及2.5Ga 三期TTG片麻岩,代表胶北地体太古宙三期重要的陆壳增生事件,它们的锆石Hf 模式主要分布在ca.3.4 ~2.7Ga 之间,代表胶北新生基性地壳的主要形成阶段。此外,需要注意的是,尽管没发现更老的陆壳,但并不代表曾经不存在更老的陆壳,而是可能被剥蚀掉而不复存在,并且大量的研究已经证实,胶北或华北克拉通存在太古宙早期古老陆壳物质及其再循环(Liu et al.,1992,2008;Song et al.,1996;Wang et al.,1998;靳克等,2003;Zheng et al.,2004;简平等;2005;Wu et al.,2005,2008;Gao et al.,2006;Wang et al.,2007;Zhou et al.,2007;Diwu et al.,2013;刘建辉等,2014)。胶北古元古代花岗质岩浆活动主要代表在伸展环境陆壳物质的重熔作用。因此,通过对胶北地体内早前寒武纪重大岩浆事件的性质及成因研究,总结出胶北地体早前寒武纪>2.9Ga、~2.9Ga、~2.7Ga,~2.5Ga、ca.2.2 ~2.0Ga、1.95 ~1.85Ga及~1.8Ga 等多个陆壳增生及演化阶段(图10)。
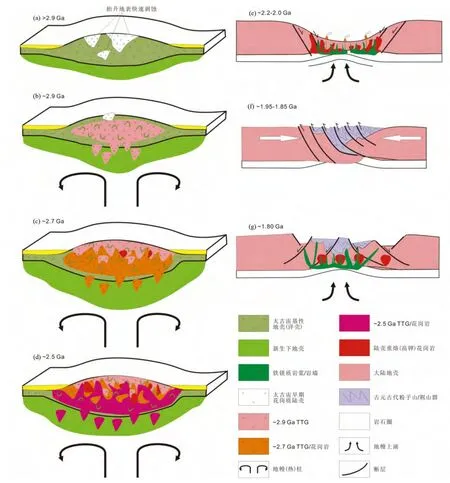
图10 胶北早前寒武纪陆壳增生及演化示意图Fig.10 Schematic diagram showing various stages in growth and evolution of the Early Precambrian continental crust in the Jiaobei terrane
(1)>2.9Ga:主要为基性地壳(洋壳)的增生,同时可能存在一些早期的规模有限的花岗质陆壳,由于相对于基性地壳较小的密度,使早期形成的花岗质岩浆通过底辟作用快速上升,剥露地表,遭受快速剥蚀,导致太古宙早期的花岗质陆壳难以保留下来(图10a)。
(2)~2.9Ga:在加厚的下地壳,主要为ca.3.3 ~2.9Ga新生的基性地壳,由于地幔(热)柱上涌,发生部分熔融,形成~2.9Ga TTGs,代表胶北~2.9Ga 陆壳增生(图10b)。
(3)~2.7Ga:在加厚的下地壳,主要为ca.3.3 ~2.9Ga新生的基性地壳,由于地幔(热)柱上涌,发生部分熔融,形成~2.7Ga TTGs,代表胶北~2.7Ga 陆壳增生,~2.7GaTTGs 岩浆作用过程中,同时伴随有老陆壳的熔融,形成小规模的陆壳重熔型(高钾)花岗岩(图10c)。
(4)~2.5Ga:在加厚的下地壳,主要为ca.2.9 ~2.7Ga新生的基性地壳,由于地幔(热)柱上涌,发生部分熔融,形成~2.5Ga TTGs,代表胶北~2.5Ga 陆壳增生,~2.5Ga TTGs岩浆作用过程中,同时伴随有老陆壳的熔融,形成小规模的陆壳重熔型(高钾)花岗岩(图10d)。
(5)~2.2 ~2.0Ga:由于地幔物质的上涌,使太古宙形成的陆壳发生伸展减薄,形成裂谷,太古宙陆壳发生重熔,形成古元古代ca.2.2 ~2.0Ga 花岗质岩石,同时存在大量铁镁质岩墙/脉的侵位,以及双峰式火山活动(图10e)。
(6)~1.95 ~1.85Ga:在该时期,胶北经历了强烈的挤压碰撞构造作用,古元古代早期(ca.2.2 ~2.0Ga)形成的裂谷发生挤压闭合,并导致卷入挤压作用的早前寒武纪物质发生高压麻粒岩相变质(图10f)。
(7)~1.8Ga:地幔物质上涌,陆壳伸展减薄,陆壳物质重熔,形成~1.8Ga 花岗岩(图10f)。
致谢 感谢两位论文评审人审阅全文,并提出宝贵的修改意见。
Adam J,Rushmer T,O’Neil J and Francis D. 2012. Hadean greenstones from the Nuvvuagittuq fold belt and the origin of the Earth’s early continental crust. Geology,40(4):363 -366
Barker F and Arth JG. 1976. Generation of trondhjemitic-tonalitic liquids and Archean bimodal trondhjemite-basalt suites. Geology,4(10):596 -600
Barker F. 1979. Trondhjemite:Definition,environment and hypotheses of origin. In:Barker F (ed.). Trondhjemites,Dacites and Related Rocks. Amsterdam:Elsevier,1 -12
Bureau of Geology and Mineral Resources of Shandong Province(BGMRS). 1991. Regional Geology of Shandong Province.Beijing:Geological Publishing House,6 -524 (in Chinese)
Cawood PA,Hawkesworth CJ and Dhuime B. 2013. The continental record and the generation of continental crust. Geol. Soc. Am.Bull.,125(1 -2):14 -32
Condie KC. 1986. Origin and early growth rate of continents.Precambrian Research,32(4):261 -278
Condie KC. 2005. TTGs and adakites:Are they both slab melts?Lithos,80(1 -4):33 -44
Chu H,Lu SN,Wang HC,Xiang ZQ and Liu H. 2011. U-Pb age spectrum of detrital zircons from the Fuzikuang Formation,Penglai Group in Changdao,Shandong Province. Acta Petrologica Sinica,27(4):1017 -1028 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Diwu CR,Sun Y,Wilde SA,Wang HL,Dong ZC,Zhang H and Wang Q. 2013. New evidence for ~4.45Ga terrestrial crust from zircon xenocrysts in Ordovician ignimbrite in the North Qinling Orogenic Belt,China. Gondwan Research,23(4):1484 -1490
Drummond MS and Defant MJ. 1990. A Model for trondhjemite-tonalitedacite genesis and crustal growth via slab melting:Archean to modern comparison. Journal of Geophysical Research,95(B13):21503 -21521
Faure M,Lin W,Monié P,Le Breton N,Poussineau S,Panis D and Deloule E. 2003. Exhumation tectonics of the ultrahigh-pressure metamorphic rocks in the Qinling orogen in East China:New petrological-structural-radiometric insights from the Shandong Peninsula. Tectonics,22(3):1018 -1040
Foley SF,Tiepolo M and Vannucci R. 2002. Growth of early continental crust controlled by melting of amphibolite in subduction zones.Nature,417(6891):637 -640
Frost BR,Arculus RJ,Barnes CG,Collins WJ,Ellis DJ and Frost CD.2001. A geochemical classification for granitic rocks. Journal of Petrology,42(11):2033 -2048
Gao LZ,Zhao T,Wan YS,Zhao X,Ma YS and Yang SZ. 2006. Report on 3. 4Ga SHRIMP zircon age from the Yuntaishan Geopark in Jiaozuo,Henan Province. Acta Geologica Sinica,80(1):52 -57
Hawkesworth CJ and Kemp AIS. 2006a. Evolution of the continental crust. Nature,443(7113):811 -817
Hawkesworth CJ and Kemp AIS. 2006b. Using hafnium and oxygen isotopes in zircons to unravel the record of crustal evolution.Chemical Geology,226(3 -4):144 -162
Hawkesworth CJ,Dhuime B,Pietranik AB,Cawood PA,Kemp AIS and Storey CD. 2010. The generation and evolution of the continental crust. Journal of the Geological Society,167(2):229 -248
Jahn BM,Gikson AY,Peucat JJ and Hickman AH. 1981. REE geochemistry and isotopic data of Archean silicic volcanics and grantoids from the Pillbara Block,Western Australia:Implications for the early crustal evolution. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta,45(9):1633 -1652
Jahn BM,Liu DY,Wan YS,Song B and Wu JS. 2008. Archean crustal evolution of the Jiaodong Peninsula,China,as revealed by zircon SHRIMP geochronology,elemental and Nd-isotope geochemistry.Am. J. Sci.,308(3):232 -269
Jian P,Zhang Q,Liu DY,Jin WJ,Jia XQ and Qian Q. 2005. SHRIMP dating and geological significance of Late Achaean high-Mg diorite(sanukite)and hornblende-granite at Guyang of Inner Mongolia.Acta Petrologica Sinica,21 (1):151 - 157 (in Chinese with English abstract)Jin K,Xu WL,Wang QH,Gao S and Liu XC. 2003. Formation time and sources of the Huaiguang“Migmatitic granodiorite”in Bengbu,Anhui Province: Evidence from SHRIMP zircon U-Pb geochronology. Acta Geoscientia Sinica,24(4):331 - 335(in Chinese with English abstract)
Kamber BS,Ewart A,Collerson KD,Bruce MC and McDonald GD.2002. Fluid-mobile trace element constraints on the role of slab melting and implications for Archean crustal growth models.Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology,144(1):38 -56
Kinny PD and Maas R. 2003. Lu-Hf and Sm-Nd isotope systems in zircon. Reviews in Mineralogy and Geochemistry,53(1):327 -341 Li XH,Chen FK,Guo JH,Li QL,Xie LW and Siebel W. 2007. South China provenance of the lower-grade Penglai Group north of the Sulu UHP orogenic belt,eastern China:Evidence from detrital zircon ages and Nd-Hf isotopic composition. Geochemical Journal,41(1):29-45
Li XP,Guo JH,Zhao GC,Li HK and Song ZJ. 2011. Formation of the Paleoproterozoic calc-silicate and high-pressure mafic granulite in the Jiaobei terrane,eastern Shandong,China. Acta Petrologica Sinica,27(4):961 -968(in Chinese with English abstract)
Liu DY,Nutman AP,Compston W,Wu JS and Shen QH. 1992.Remnants of ~3800Ma crust in the Chinese part of the Sino-Korean Craton. Geology,20(4):339 -342
Liu DY,Wilde SA,Wan YS,Wu JS,Zhou HY,Dong CY and Yin XY.2008. New U-Pb and Hf isotopic data confirm Anshan as the oldest preserved segment of the North China Craton. Am. J. Sci.,308(3):200 -231
Liu FL,Liu PH,Ding ZJ,Liu JH,Yang H and Hu WH. 2012. Genetic mechanism of granitic leucosome within high-pressure granulite from the Early Precambrian metamorphic basement of Shandong Peninsula,SE North China Craton. Acta Petrologica Sinica,28(9):2686 -2696 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Liu FL,Liu PH,Wang F,Liu JF,Meng E,Cai J and Shi JR. 2014b.U-Pb dating of zircons from granitic leucosomes in migmatites of the Jiaobei Terrane,southwestern Jiao-Liao-Ji Belt,North China Craton:Constraints on the timing and nature of partial melting. Precambrian Research,245:80 -99
Liu JH,Liu FL,Liu PH,Wang F and Ding ZJ. 2011. Polyphase magmatic and metamorphic events from Early Precambrian metamorphic basement in Jiaobei area:Evidences from the zircon UPb dating of TTG and granitic gneisses. Acta Petrologica Sinica,27(4):943 -960 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Liu JH,Liu FL,Ding ZJ,Liu PH,Wang F and You JJ. 2012. The zircon Hf isotope characteristics of ~2. 5Ga magmatic event,and implication for the crustal evolution in the Jiaobei terrane,China.Acta Petrologica Sinica,28(9):2697 - 2704 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Liu JH,Liu FL,Ding ZJ,Liu CH,Yang H,Liu PH,Wang F and Meng E. 2013a. The growth,reworking and metamorphism of Early Precambrian crust in the Jiaobei terrane,the North China Craton:Constraints from U-Th-Pb and Lu-Hf isotopic systematics,and REE concentrations of zircon from Archean granitoid gneisses.Precambrian Research,224:287 -303
Liu JH,Liu FL,Ding ZJ,Yang H,Liu CH,Liu PH,Xiao LL,Zhao L and Geng JZ. 2013b. U-Pb dating and Hf isotope study of detrital zircons from the Zhifu Group,Jiaobei Terrane,North China Craton:Provenance and implications for Precambrian crustal growth and recycling. Precambrian Research,235:230 -250
Liu JH,Liu FL,Ding ZJ,Liu PH,Guo CL and Wang F. 2014a.Geochronology, petrogenesis and tectonic implications of Paleoproterozoic granitoid rocks in the Jiaobei Terrane,North China Craton. Precambrian Research,255(Part 2):685 -698
Liu JH,Liu FL,Ding ZJ,Liu PH and Wang F. 2014. U-Pb dating and Hf isotope study of Early Archean zircons from the Jiaobei Terrane,North China Craton:Evidence for growth and recycling of ancient continental crust. Acta Petrologica Sinica,30(10):2941 -2950(in Chinese with English abstract)
Liu PH,Liu FL,Wang F and Liu JH. 2010. Genetic mineralogy and metamorphic evolution of mafic high-pressure (HP)granulites from the Shandong Peninsula,China. Acta Petrologica Sinica,26(7):2039 -2056 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Liu PH,Liu FL,Wang F and Liu JH. 2011a. In-situ U-Pb dating of zircons from high-pressure granulites in Shandong Peninsula,eastern China and its geological significance. Earth Science Frontiers,18(2):33 -54 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Liu PH,Liu FL,Wang F and Liu JH. 2011b. Genetic characteristcs of the ultramafic rocks from the Early Precambrian high-grade metamorphic basement in Shandong Peninsula, China. Acta Petrologica Sinica,27(4):922 - 942 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Liu PH,Liu FL,Wang F,Liu JH,Yang H and Shi JR. 2012.Geochemical characteristics and genesis of the high-pressure mafic granulite in the Jiaobei high-grade metamorphic basement. Acta Petrologica Sinica,28(9):2705 -2720 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Liu PH,Liu FL,Liu CH,Wang F,Liu JH,Yang H,Cai J and Shi JR.2013c. Petrogenesis,P-T-t path,and tectonic significance of highpressure mafic granulites from the Jiaobei terrane,North China Craton. Precambrian Research,233:237 -258
Liu PH,Liu FL,Wang F,Liu JH and Cai J. 2013. Petrological and geochronological preliminary study of the Xiliu ~2.1Ga meta-gabbro from the Jiaobei terrane,the southern segment of the Jiao-Liao-Ji Belt in the North China Craton. Acta Petrologica Sinica,29(7):2731 -2390 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Liu SJ,Jahn BM,Wan YS,Xie HQ,Wang SJ,Xie SW,Dong CY,Ma MZ and Liu DY. 2015. Neoarchean to Paleoproterozoic highpressure mafic granulite from the Jiaodong Terrain,North China Craton: Petrology, zircon age determination and geological implications. Gondwana Research,28(2):493 -508
Liu WJ,Zhai MG and Li YG. 1998. Metamorphism of the high-pressure basic granulite in Laixi,eastern Shandong,China. Acta Petrologica Sinica,14(4):449 -459 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Lu LZ,Xu XC and Liu FL. 1996. Early Precambrian Khondalites in North China. Changchun:Changchun Press,219 - 230 (in Chinese)
Martin H. 1987. Petrogenesis of Archaean trondhjemites,tonalites,and granodiorites from Eastern Finland: Major and trace element geochemistry. Journal of Petrology,28(5):921 -953
Martin H. 1999. Adakitic magmas:Modern analogues of Archaean granitoids. Lithos,46(3):411 -429
Martin H,Smithies RH,Rapp R,Moyen JF and Champion D. 2005. An overview of adakite,tonalite-trondhjemite-granodiorite (TTG),and sanukitoid: Relationships and some implications for crustal evolution. Lithos,79(1 -2):1 -24
Polat A. 2012. Growth of Archean continental crust in oceanic island arcs. Geology,40(4):383 -384
Rapp RP,Watson EB and Miller CF. 1991. Partial melting of amphibolite/eclogite and the origin of Archean trondhjemites and tonalites. Precambrian Research,51(1 -4):1 -25
Rapp RP and Watson EB. 1995. Dehydration melting of metabasalt at 8~32kbar:Implications for continental growth and crust-mantle recycling. J. Petrol.,36(4):891 -931
Rapp RP,Shimizu N and Norman MD. 2003. Growth of early continental crust by partial melting of eclogite. Nature,425(6958):605 -608 Rickwood PC. 1989. Boundary lines within petrologic diagrams which use oxides of major and minor elements. Lithos,22(4):247 -263
Rollinson H. 1997. Eclogite xenoliths in West African kimberlites as residues from Archaean granitoid crust formation. Nature,389(6647):173 -176
Rollinson H. 2007. Early Earth Systems:A Geochemical Approach.Oxford:Blackwell Publishing
Sengor AMC,Natal` in BA and Burtman VS. 1993. Evolution of the Altaid tectonic collage and Palaeozoic crustal growth in Eurasia.Nature,364:299 -307
Shan HX,Zhai MG,Wang F,Zhou YY,Santosh M,Zhu XY,Zhang HF and Wang W. 2015. Zircon U-Pb ages,geochemistry,and Nd-Hf isotopes of the TTG gneisses from the Jiaobei terrane:Implications for Neoarchean crustal evolution in the North China Craton.Precambrian Research,98:61 -74
Smithies RH. 2000. The Archaean tonalite-trondhjemite-granodiorite(TTG)series is not an analogue of Cenozoic adakite. Earth Planet.Sci. Lett.,182(1):115 -125
Smithies RH and Champion DC. 2002. The Archaean high-Mg diorite suite:Links to tonalite-trondhjemite-granodiorite magmatism and implications for Early Archaean crustal growth. J. Petrol.,41(12):1653 -1671
Song B,Nutman AP,Liu DY and Wu JS. 1996. 3800 to 2500Ma crustal evolution in the Anshan area of Liaoning Province,northeastern China. Precambrian Research,78(1 -3):79 -94
Sun SS and McDonough WF. 1989. Chemical and isotopic systematics of oceanic basalts:Implications for mantle composition and processes.In:Saunders AD and Norry MJ (eds.). Magmatism in the Ocean Basins. Geological Society,London,Special Publications,42(1):313 -345
Tam PY,Zhao GC,Liu FL,Zhou XW,Sun M and Li SZ. 2011. Timing of metamorphism in the Paleoproterozoic Jiao-Liao-Ji Belt:New SHRIMP U-Pb zircon dating of granulites,gneisses and marbles of the Jiaobei massif in the North China Craton. Gondwana Research,19(1):150 -162
Tam PY,Zhao GC,Zhou XW,Sun M,Guo JH,Li SZ,Yin CQ,Wu ML and He YH. 2012a. Metamorphic P-T path and implications of high-pressure pelitic granulites from the Jiaobei massif in the Jiao-Liao-Ji Belt,North China Craton. Gondwana Research,22(1):104-117
Tam PY,Zhao GC,Sun M,Li SZ,Iizuka YY,Ma GSK,Yin CQ,He YH and Wu ML. 2012b. Metamorphic P-T path and tectonic implications of medium-pressure pelitic granulites from the Jiaobei massif in the Jiao-Liao-Ji Belt,North China Craton. Precambrian Research,220 -221:177 -191
Tam PY,Zhao GC,Sun M,Li SZ,Wu ML and Yin CQ. 2012c.Petrology and metamorphic PT path of high-pressure mafic granulites from the Jiaobei massif in the Jiao-Liao-Ji Belt,North China Craton.Lithos,155:94 -109
Tang J,Zheng YF,Wu YB,Zha XP and Zhou JB. 2004. Zircon U-Pb ages and oxygen isotopes of metamorphic rocks in the western part of the Shandong Peninsula. Acta Petrologica Sinica,20(5):1063 -1086 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Tang J,Zheng YF,Wu YB,Gong B and Liu XM. 2007. Geochronology and geochemistry of metamorphic rocks in the Jiaobei terrane:Constraints on its tectonic affinity in the Sulu orogen. Precambrian Research,152(1 -2):48 -82
Taylor SR and McLennan SM. 1995. The geochemical evolution of the continental crust. Reviews of Geophysics,33(2):241 -265
Taylor SR and McLennan SM. 1997. The origin and evolution of the Earth’s continental crust. Journal of Australian Geology &Geophysics,17(1):55 -62
Wan YS,Song B,Liu DY,Wilde SA,Wu JS,Shi YR,Yin XY and Zhou HY. 2006. SHRIMP U-Pb zircon geochronology of Palaeoproterozoic metasedimentary rocks in the North China Craton:Evidence for a major Late Palaeoproterozoic tectonothermal event.Precambrian Research,149(3 -4):249 -271
Wang F,Liu FL,Liu PH and Liu JH. 2010. Metamorphic evolution of Early Precambrian khondalite series in North Shandong Province.Acta Petrologica Sincia,26(7):2057 - 2072 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Wang HL,Chen L,Sun Y,Liu XM,Xu XY,Chen JL,Zhang H and Diwu CR. 2007. ~4. 1Ga xenocrystal zircon from Ordovician volcanic rocks in western part of North Qinling orogenic belt.Chinese Science Bulletin,52(21):3002 -3010
Wang LG,Qiu YM,McNaughton NJ,Groves DI,Luo ZK,Huang JZ,Miao LC and Liu YK. 1998. Constraints on crustal evolution and gold metallogeny in the northwestern Jiaodong Peninsula,China,from SHRIMP U-Pb zircon studies of granitoids. Ore Geology Reviews,13(1 -5):275 -291
Wang W,Zhai MG,Li TS,Santosh M,Zhao L and Wang HZ. 2014.Archean-Paleoproterozoic crustal evolution in the eastern North China Craton:Zircon U-Th-Pb and Lu-Hf evidence from the Jiaobei terrane. Precambrian Research,241:146 -160
Wu FY,Yang JH,Liu XM,Li TS,Xie LW and Yang YH. 2005. Hf isotopes of the 3. 8Ga zircons in eastern Hebei Province,China:Implications for early crustal evolution of the North China Craton.Chinese Science Bulletin,50(21):2473 -2480
Wu FY,Li XH,Zheng YF and Gao S. 2007. Lu-Hf isotopic systematics and their applications in petrology. Acta Petrologica Sinica,23(2):185 -220 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Wu FY,Zhang YB,Yang JH,Xie LW and Yang YH. 2008. Zircon UPb and Hf isotopic constraints on the Early Archean crustal evolution in Anshan of the North China Craton. Precambrian Research,167(3-4):339 -362
Wu ML,Zhao GC,Sun M and Li SZ. 2014a. A synthesis of geochemistry and Sm-Nd isotopes of Archean granitoid gneisses in the Jiaodong Terrane:Constraints on petrogenesis andtectonic evolution of the Eastern Block,North China Craton. Precambrian Research,255:885 -899
Wu ML,Zhao GC,Sun M,Li SZ,Bao Z,Tam PY,Eizenhöefer PR and He YH. 2014b. Zircon U-Pb geochronology and Hf isotopes ofmajor lithologies from the Jiaodong Terrane:Implications for the crustal evolution of the Eastern Block of the North China Craton. Lithos,190 -191:71 -84
Xie SW,Xie HQ,Wang SJ,Kroner A,Liu SJ,Zhou HY,Ma MZ,Dong CY,Liu DY and Wan YS. 2014. Ca. 2. 9Ga granitoid magmatism in eastern Shandong,North China Craton:Zircon dating,Hf-in-zircon isotopic analysis and whole-rock geochemistry.Precambrian Research,255:538 -562
Xiong XL. 2006. Trace element evidence for growth of early continental crust by melting of rutile-bearing hydrous eclogite. Geology,34(11):945 -948
Zhang SB,Tang J and Zheng YF. 2014. Contrasting Lu-Hf isotopes in zircon from Precambrian metamorphic rocks in the Jiaodong Peninsula:Constraints on the tectonic suture between North China and South China. Precambrian Research,245:29 -50
Zhao GC,Sun M,Wilde SA and Li SZ. 2005. Late Archean to Paleoproterozoic evolution of the North China Craton:Key issues revisited. Precambrian Research,136(2):177 -202
Zheng JP,Griffin WL,O’Reilly SY,Lu FX,Wang CY,Zhang M,Wang FZ and Li HM. 2004. 3.6Ga lower crust in central China:New evidence on the assembly of the North China Craton. Geology,32(3):229 -232
Zhou HY,Liu DY,Wan YS,Wilde SA and Wu JS. 2007. 3. 3Ga magmatic events in the Anshan area:New SHRIMP age and geochemical constraints. Acta Petrologica et Mineralogica,26(2):123 -129
Zhou JB,Wilde SA,Zhao GC,Zheng CQ,Jin W,Zhang XZ and Cheng H. 2008a. SHRIMP U-Pb zircon dating of the Neoproterozoic Penglai Group and Archean gneisses from the Jiaobei Terrane,North China,and their tectonic implications. Precambrian Research,160(3 -4):323 -340
Zhou XW,Wei CJ,Geng YS and Zhang LF. 2004. Discovery and implications of the high-pressure pelitic granulite from the Jiaobei massif. Chinese Science Bulletin,49(18):1942 -1948
Zhou XW,Zhao GC,Wei CJ,Geng YS and Sun M. 2008b. EPMA UTh-Pb monazite and SHRIMP U-Pb zircon geochronology of highpressure pelitic granulites in the Jiaobei massif of the North China Craton. American Journal of Science,308(3):328 -350
附中文参考文献
初航,陆松年,王惠初,相振群,刘欢. 2011. 山东长岛地区蓬莱群辅子夼组碎屑锆石年年龄谱研究. 岩石学报,27(4):1017-1028
简平,张旗,刘敦一,金维浚,贾秀勤,钱青. 2005. 内蒙古固阳晚太古代赞岐岩(sanukite)-角闪花岗岩的SHRIMP 定年及其意义.岩石学报,21(1):151 -157
靳克,许文良,王清海,高山,刘晓春. 2003. 蚌埠淮光“混合花岗闪长岩的形成时代及源区:锆石SHRIMP U-Pb 地质年代学证据.地球学报,24(4):331 -335
李旭平,郭敬辉,赵国春,李洪奎,宋召军. 2011. 胶北地块早元古代钙硅酸盐岩与高压基性麻粒岩成因及地质意义. 岩石学报,27(4):961 -968
刘福来,刘平华,丁正江,刘建辉,杨红,胡伟华. 2012. 山东半岛高压麻粒岩中花岗质浅色脉体的成因. 岩石学报,28(9):2686-2696
刘建辉,刘福来,刘平华,王舫,丁正江. 2011. 胶北早前寒武纪变质基底多期岩浆-变质热事件:来自TTG 片麻岩和花岗质片麻岩中锆石U-Pb 定年的证据. 岩石学报,27(4):943 -960
刘建辉,刘福来,丁正江,刘平华,王舫,游君君. 2012. 胶北~2.5Ga岩浆热事件的锆石Hf 同位素特征及其对地壳演化的指示意义. 岩石学报,28(9):2697 -2704
刘建辉,刘福来,丁正江,刘平华,王舫. 2014. 胶北太古宙早期锆石U-Pb 定年及Hf 同位素研究:华北克拉通古老陆壳增生及再循环的证据. 岩石学报,30(10):2941 -2950
刘平华,刘福来,王舫,刘建辉. 2010. 山东半岛基性高压麻粒岩的成因矿物学及变质演化. 岩石学报,26(7):2039 -2056
刘平华,刘福来,王舫,刘建辉. 2011a. 山东半岛高压麻粒岩中锆石的U-Pb 定年及其地质意义. 地学前缘,18(2):33 -54
刘平华,刘福来,王舫,刘建辉. 2011b. 山东半岛早前寒武纪高级变质基底中超镁铁质岩的成因. 岩石学报,27(4):922 -942
刘平华,刘福来,王舫,刘建辉,杨红,施建荣. 2012. 胶北高级变质基底中高压基性麻粒岩的地球化学特征及其成因. 岩石学报,28(9):2705 -2720
刘平华,刘福来,王舫,刘建辉,蔡佳. 2013. 胶北西留古元古代~2.1Ga变辉长岩岩石学与年代学初步研究. 岩石学报,29(7):2371 -2390
刘文军,翟明国,李永刚. 1998. 胶东莱西地区基性高压麻粒岩的变质作用. 岩石学报,14(4):449 -459
卢良兆,徐学纯,刘福来. 1996. 中国北方早前寒武纪孔兹岩系. 长春:长春出版社,219 -230
山东省地质矿产局. 1991. 山东省区域地质志. 北京:地质出版社,6 -524
唐俊,郑永飞,吴元保,查向平,周建波. 2004. 胶东地块西部变质岩锆石U-Pb 定年和氧同位素研究. 岩石学报,20(5):1063-1086
王舫,刘福来,刘平华,刘建辉. 2010. 胶北地区早前寒武纪孔兹岩系的变质演化. 岩石学报,26(7):2057 -2072
吴福元,李献华,郑永飞,高山. 2007. Lu-Hf 同位素体系及其岩石学应用. 岩石学报,23(2):185 -220
周喜文,魏春景,耿元生,张立飞. 2004. 胶北栖霞地区泥质高压麻粒岩的发现及其地质意义. 科学通报,49(14):1424 -1430

